Rotating bending fatigue life prediction of bearing steel based on damage mechanics
-
摘要:
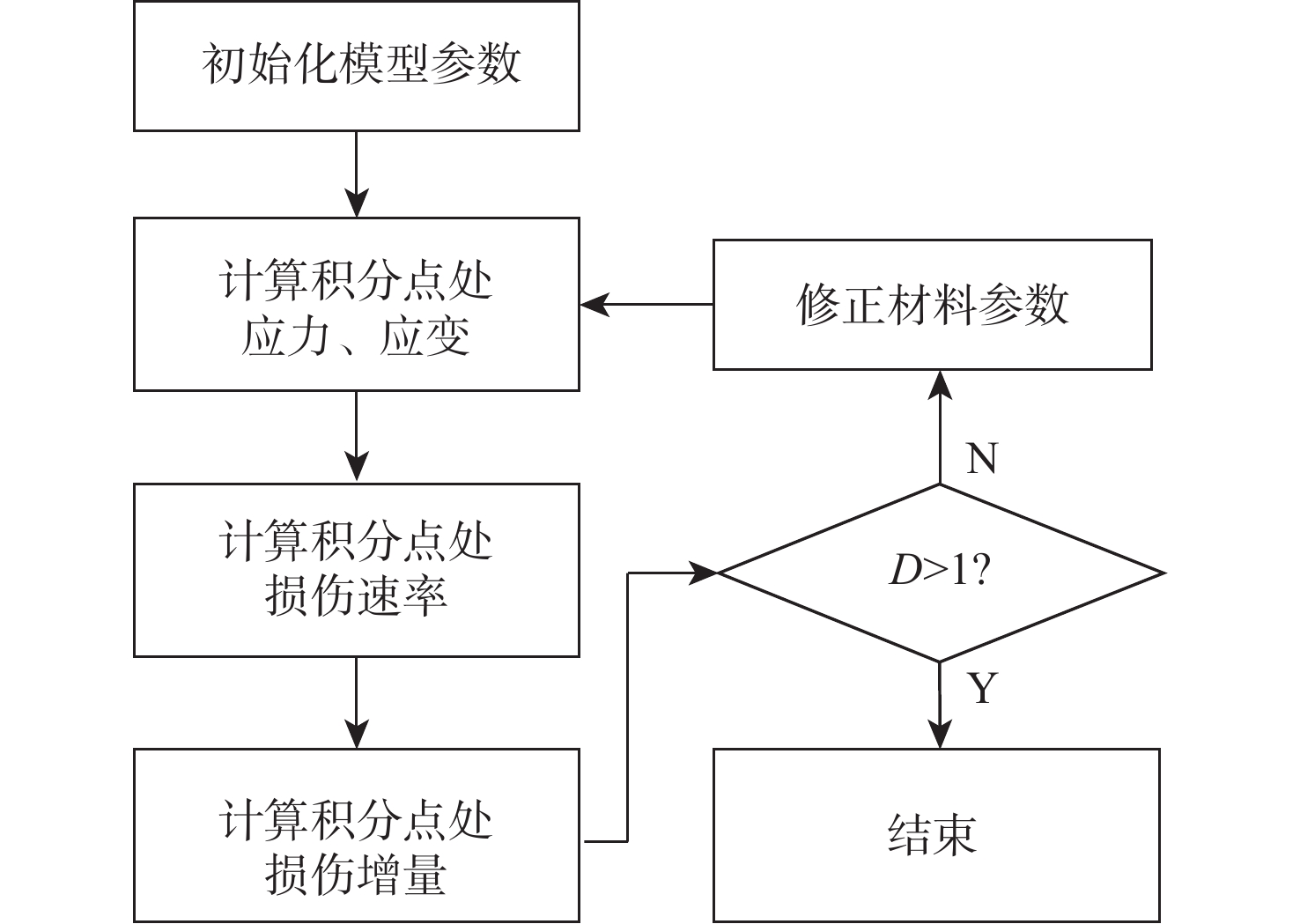
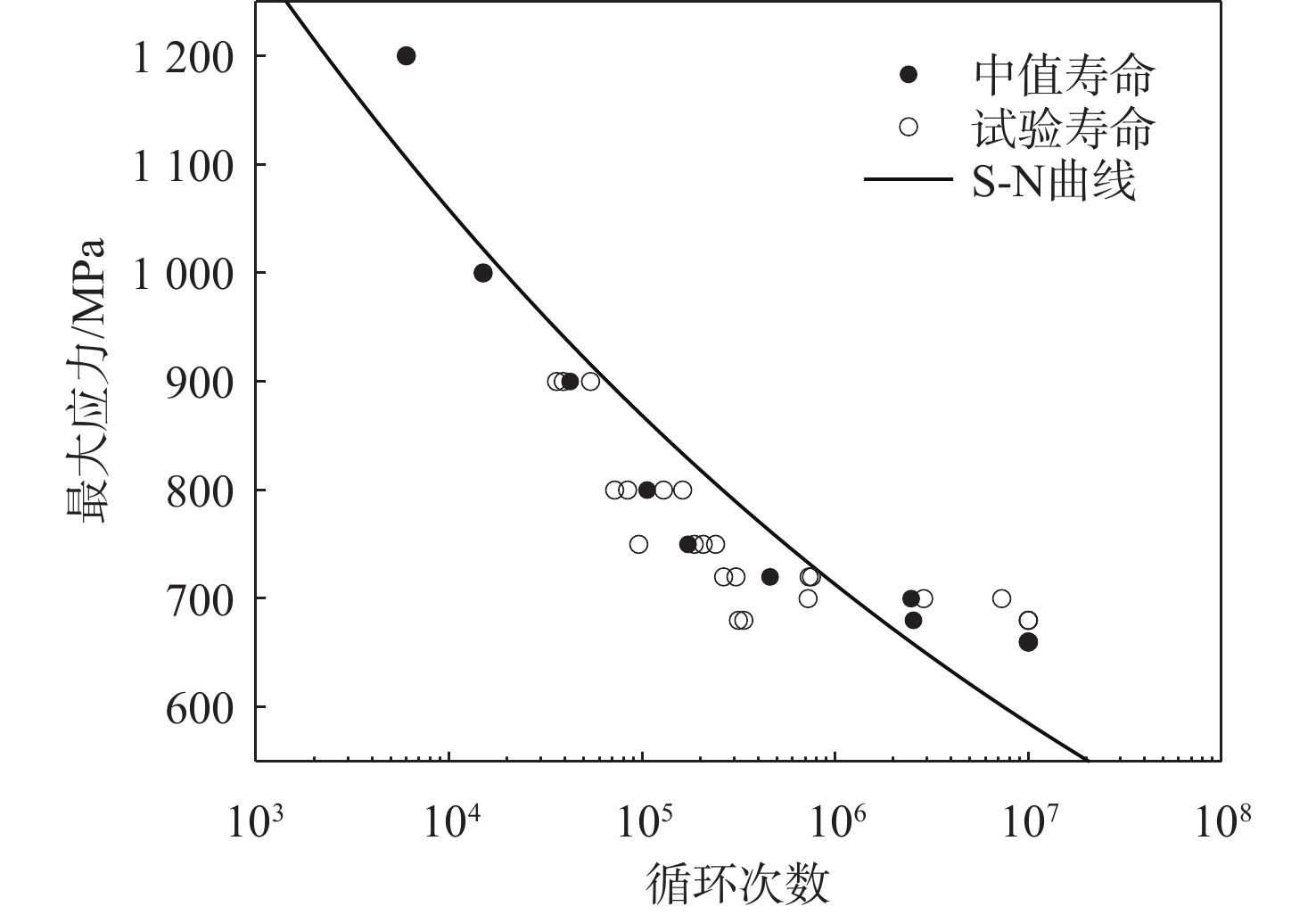
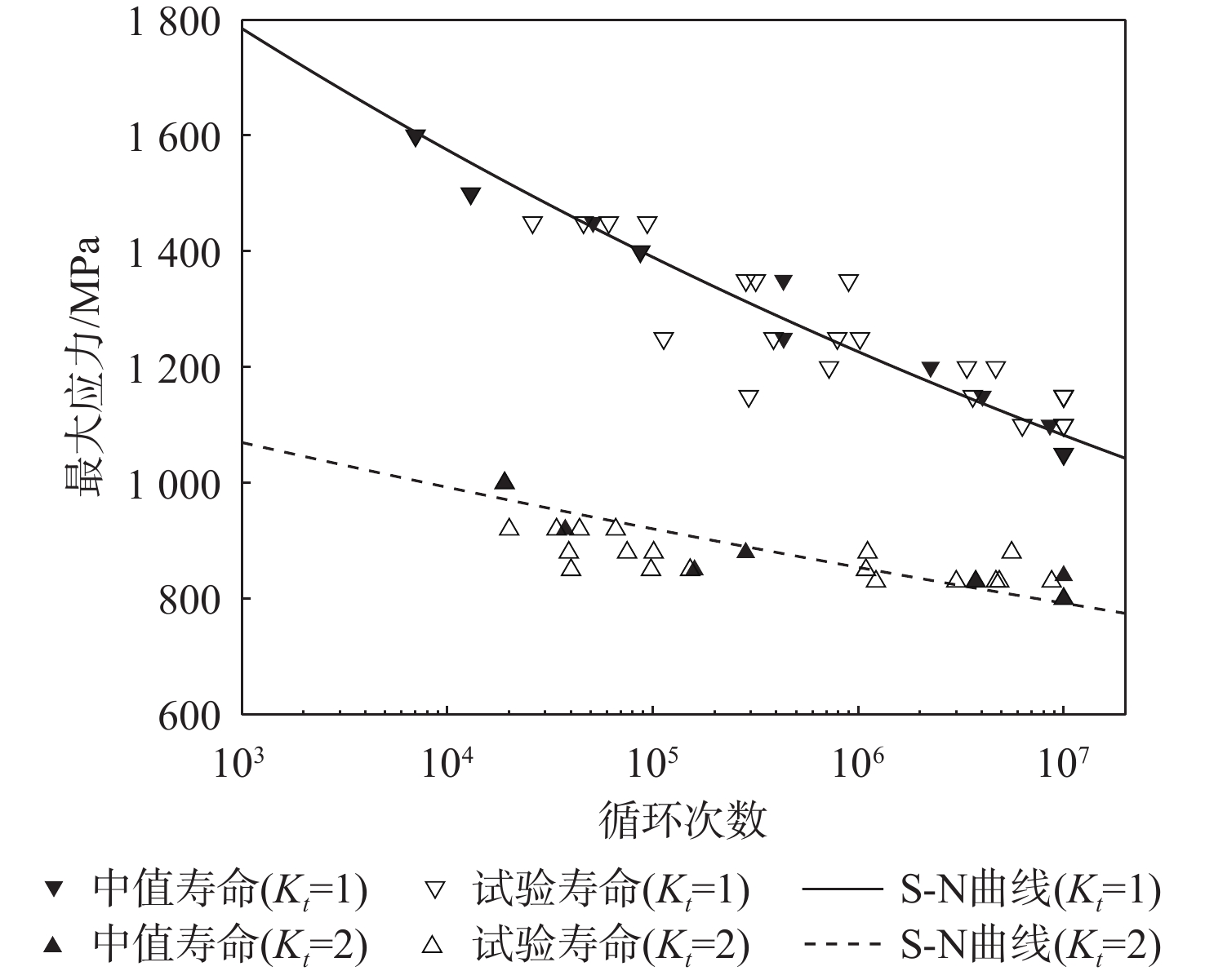
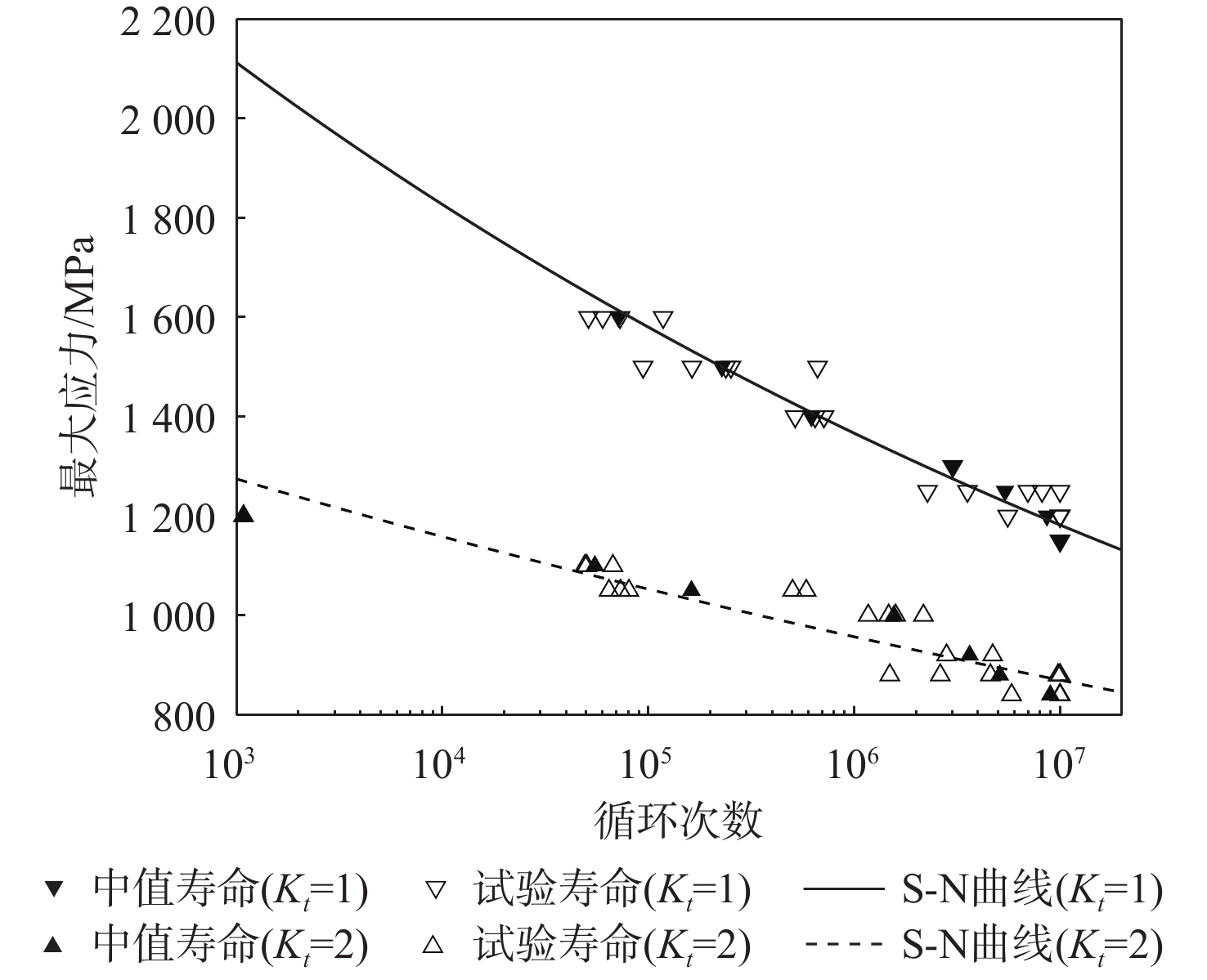
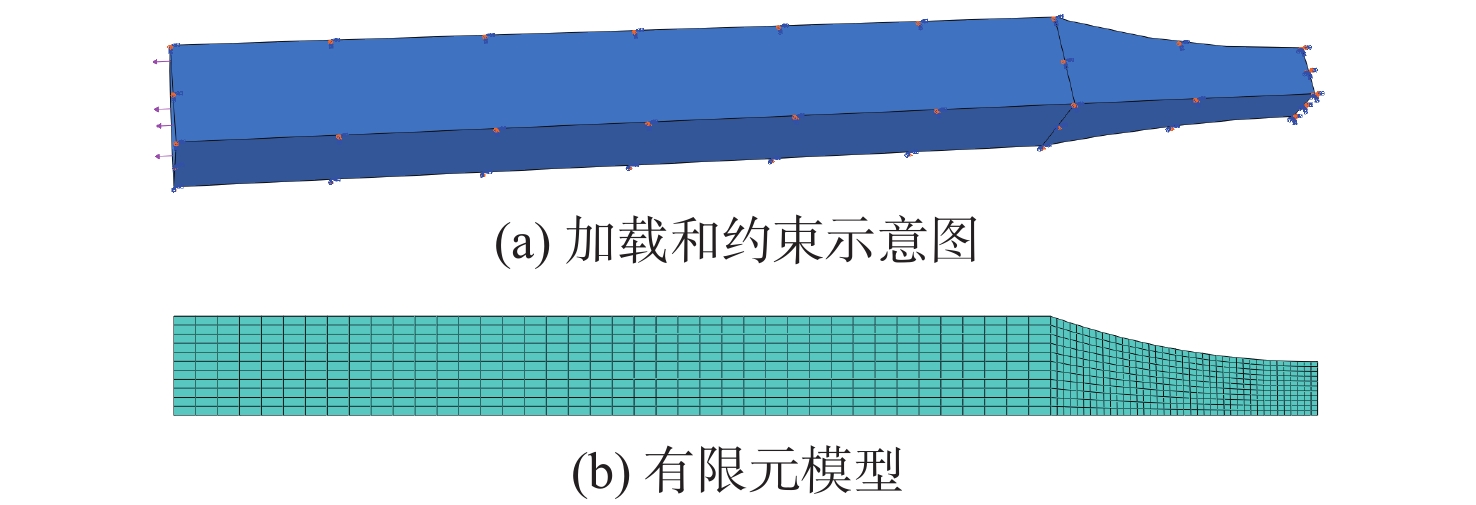
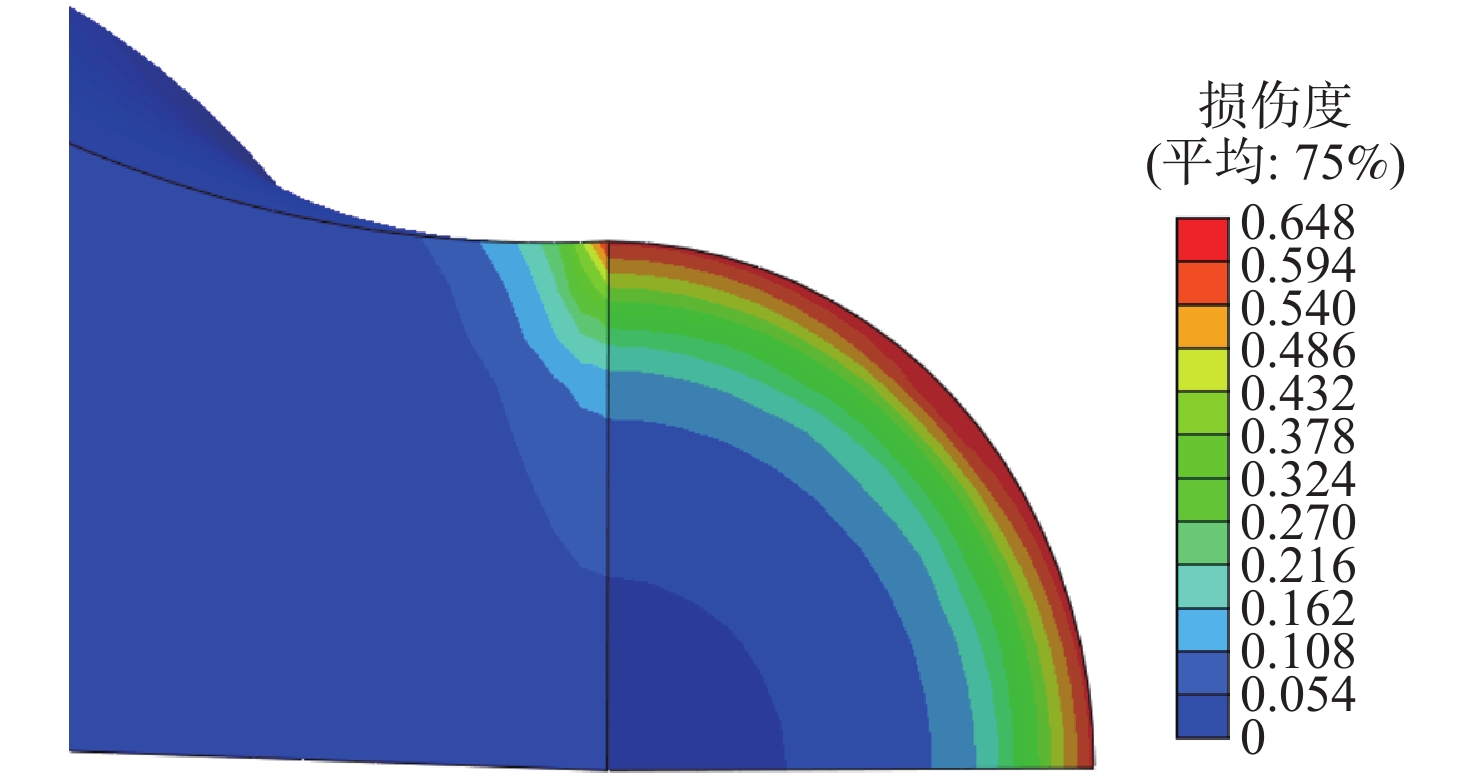
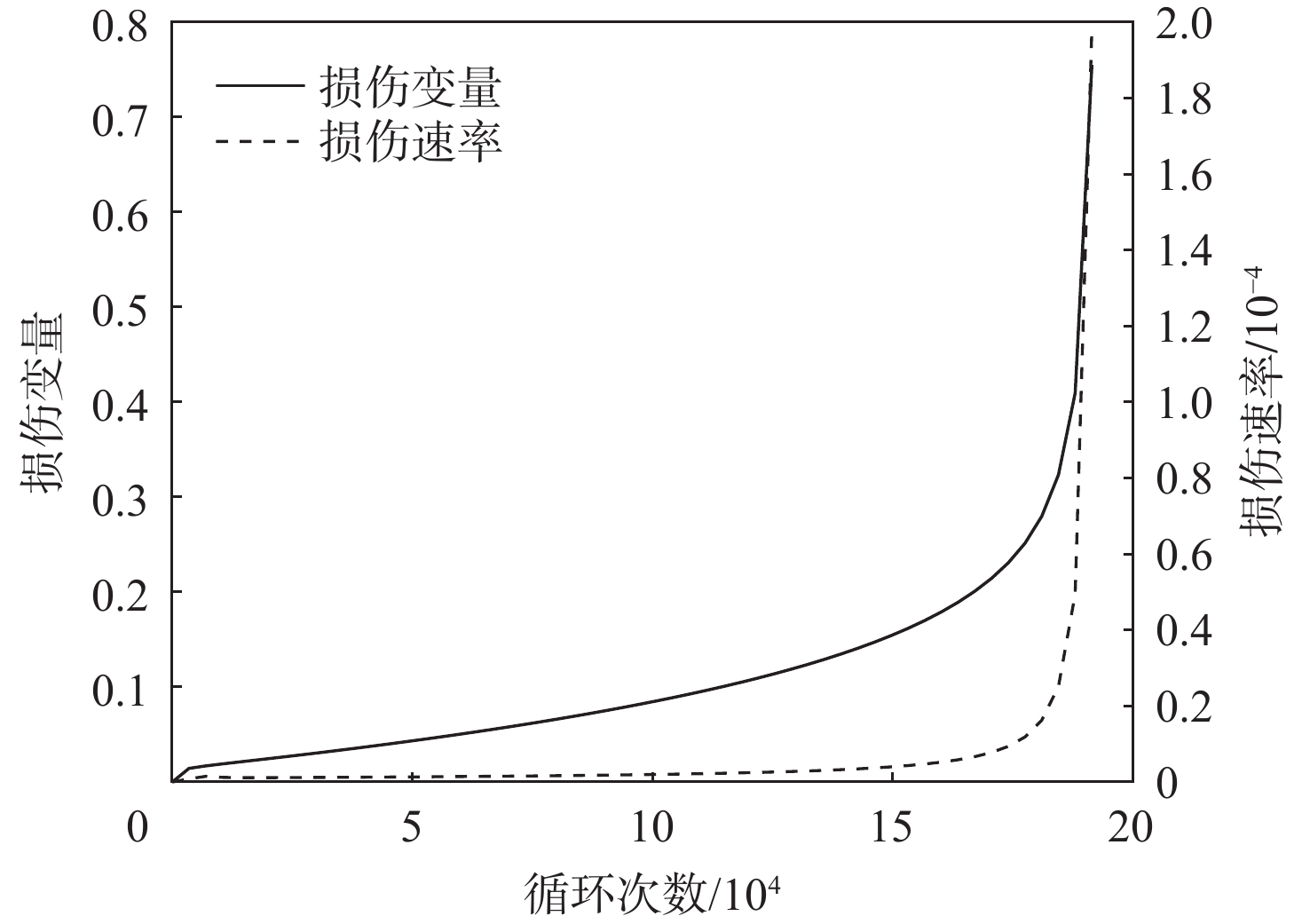
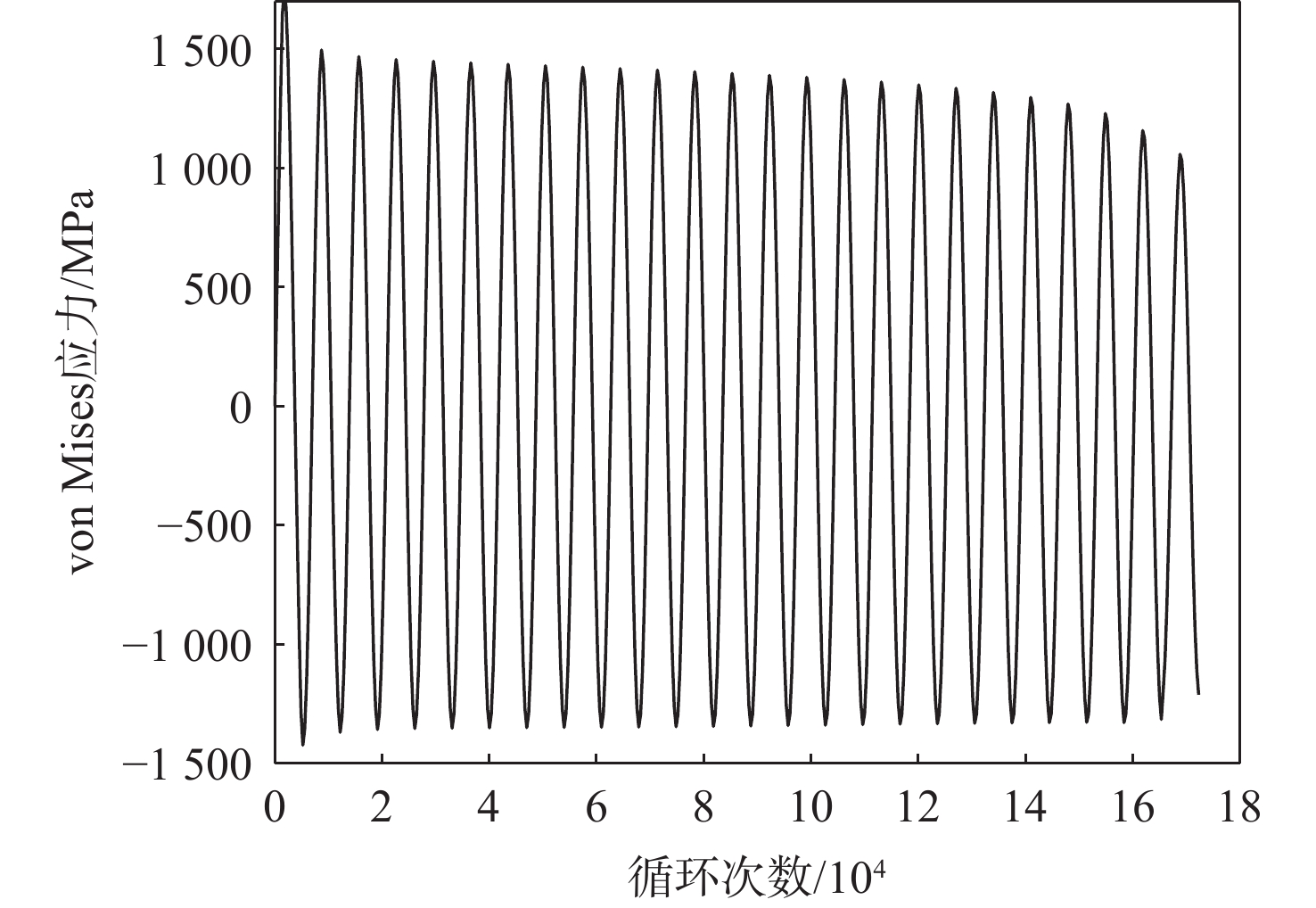
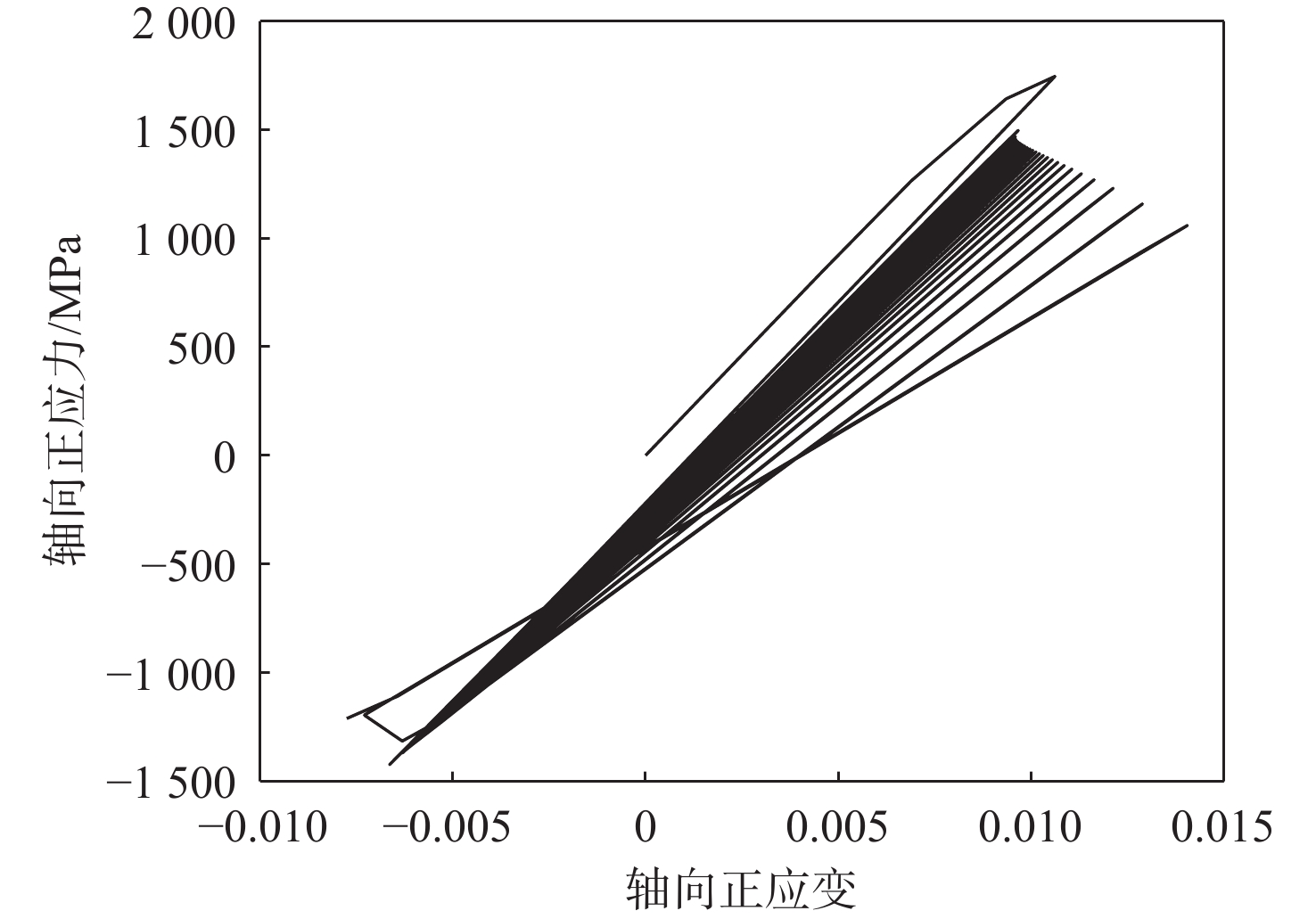
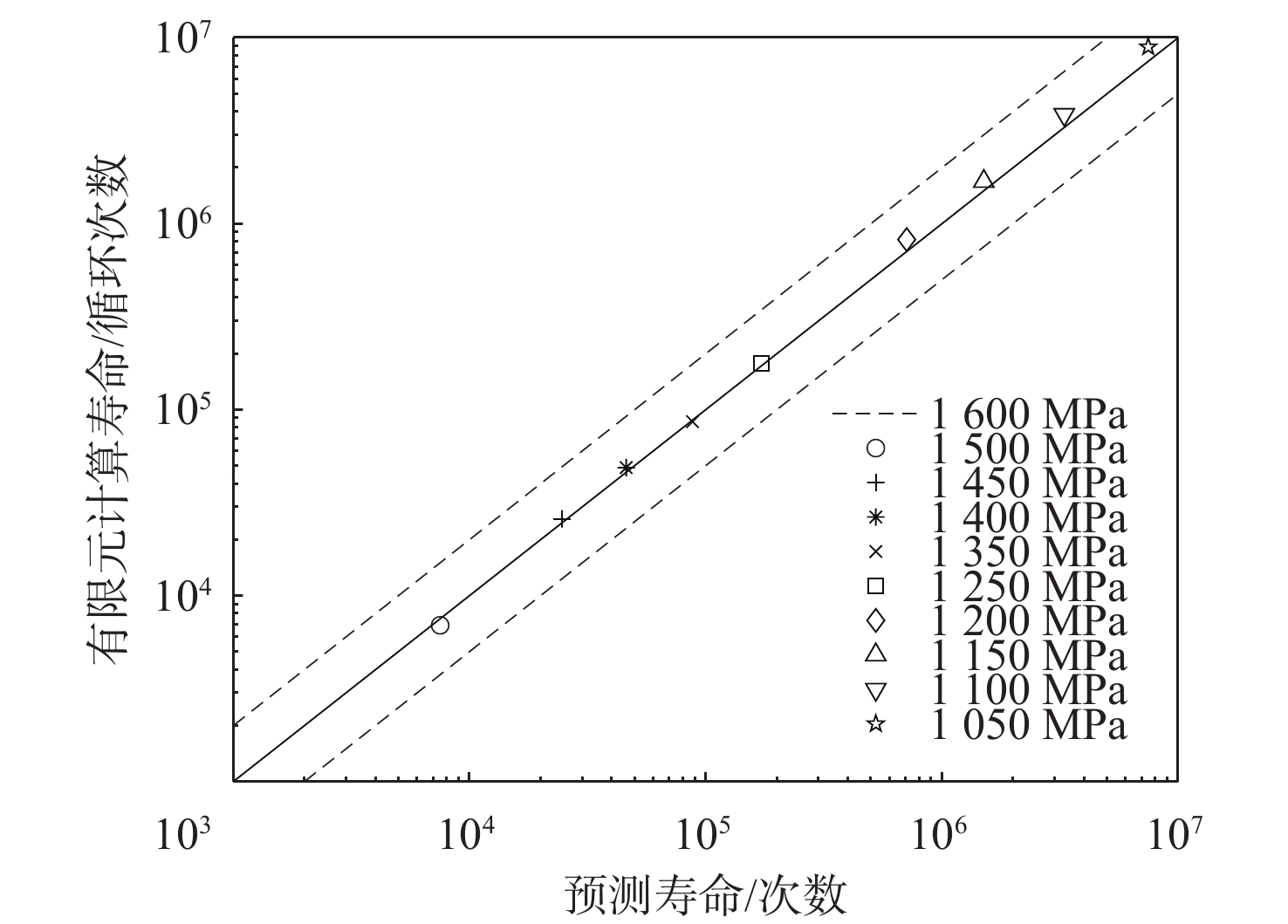
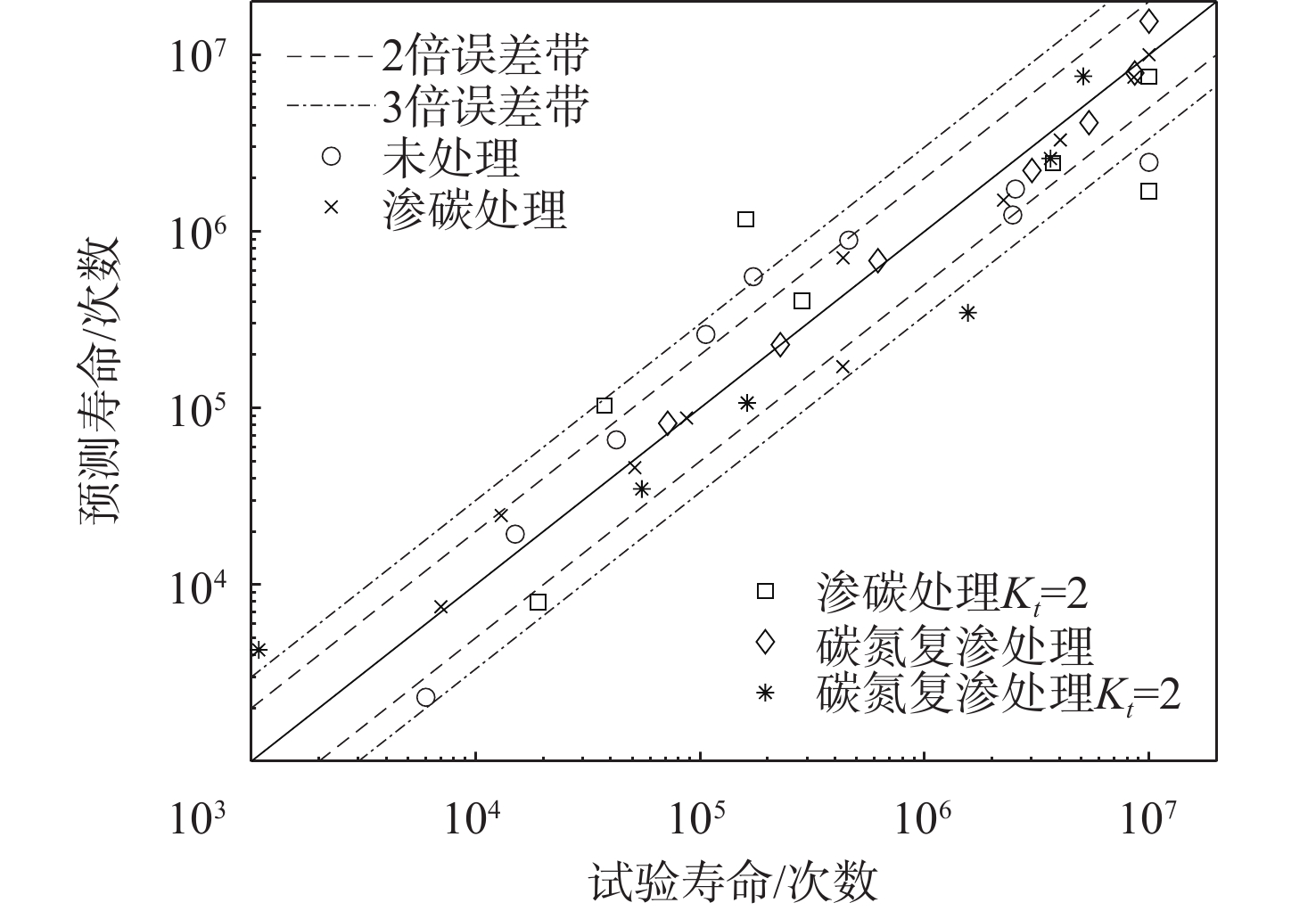
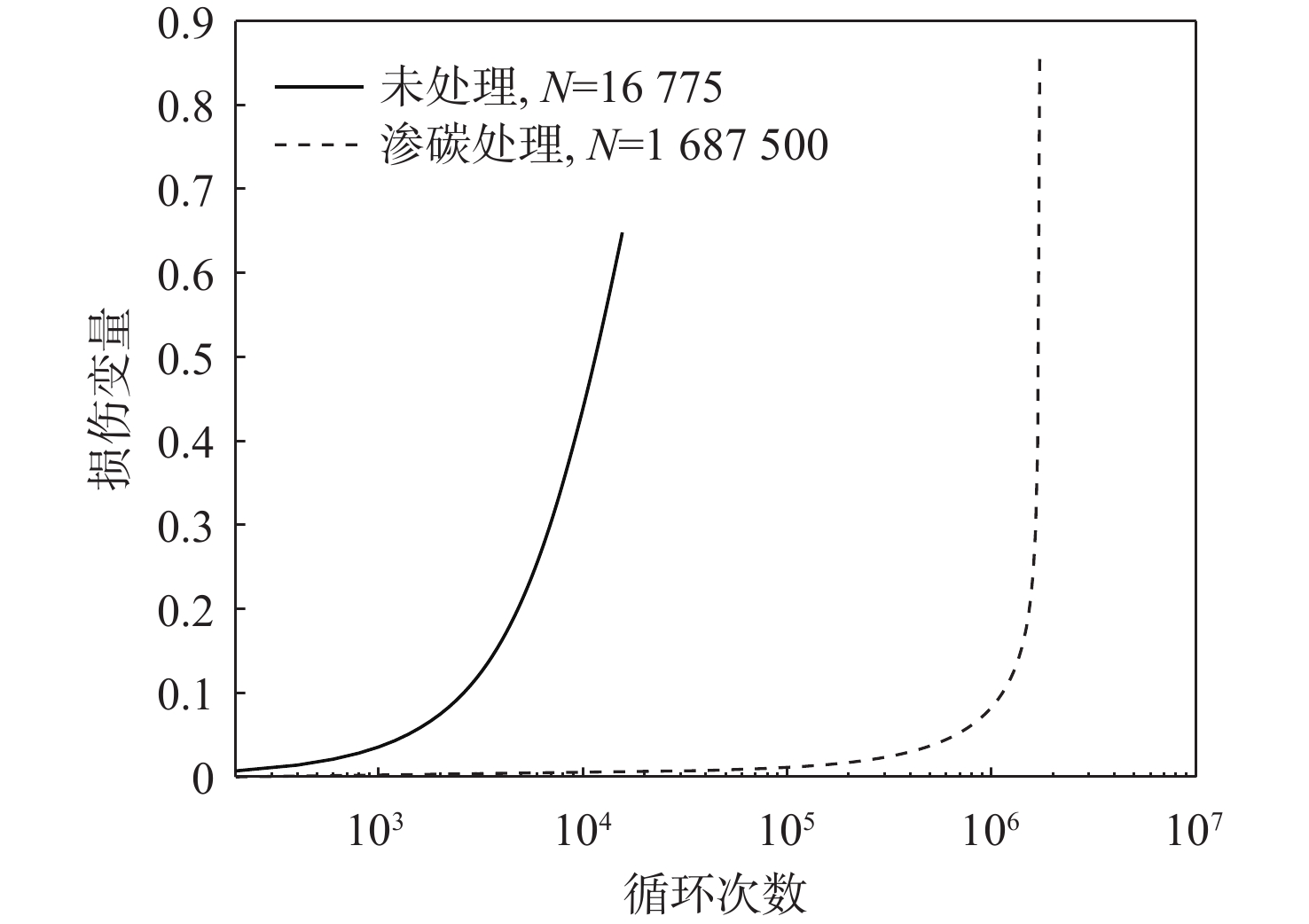
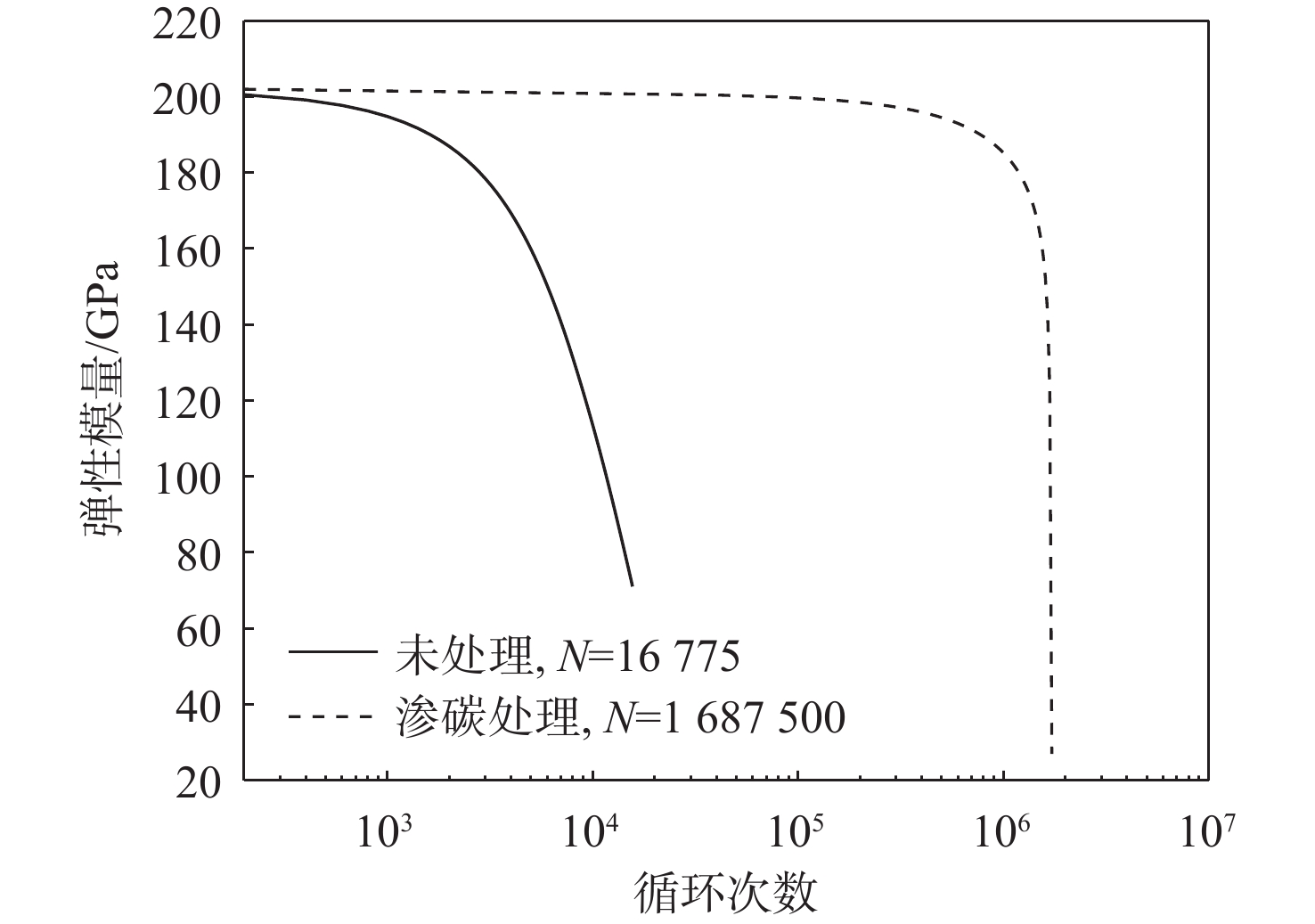
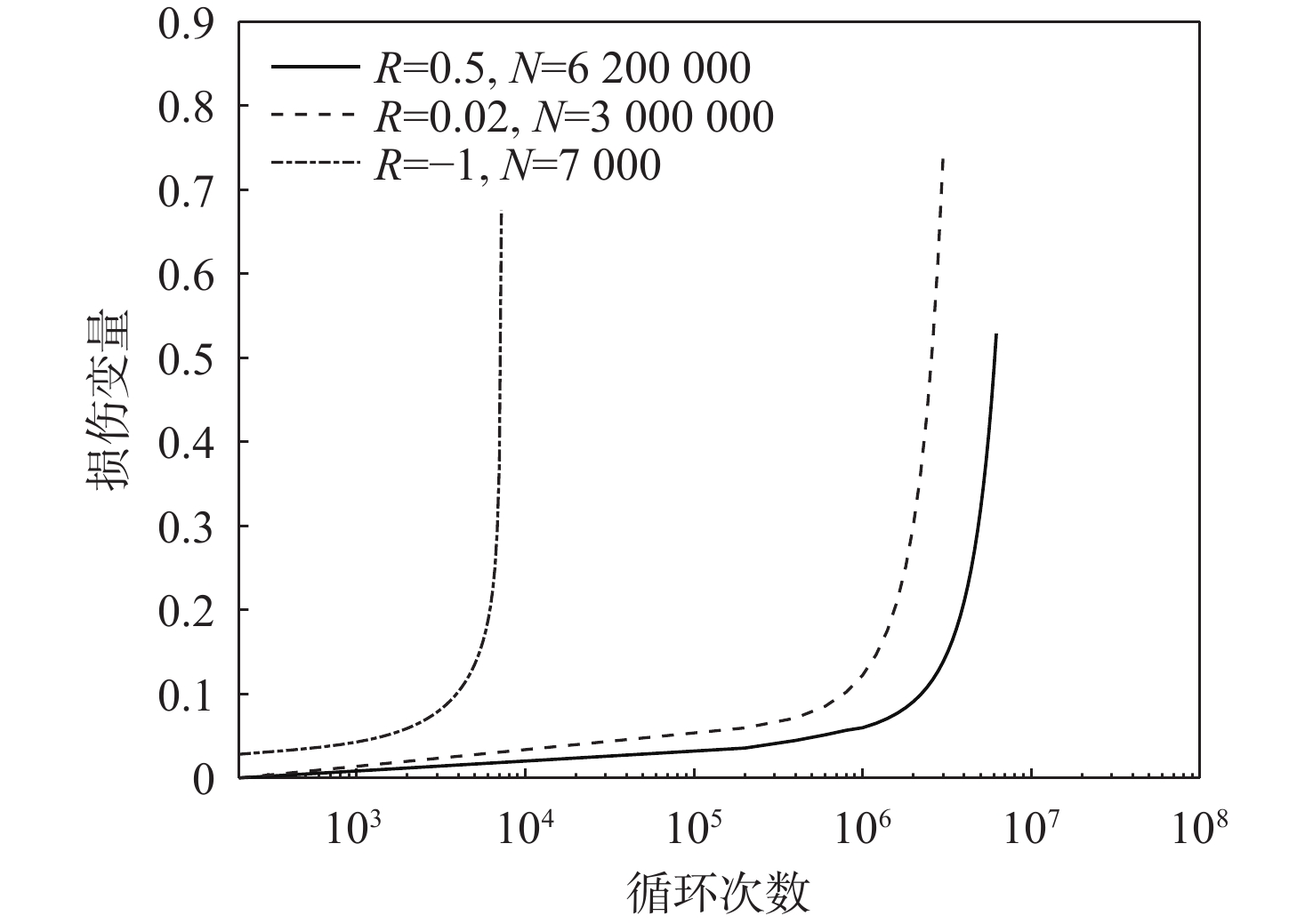
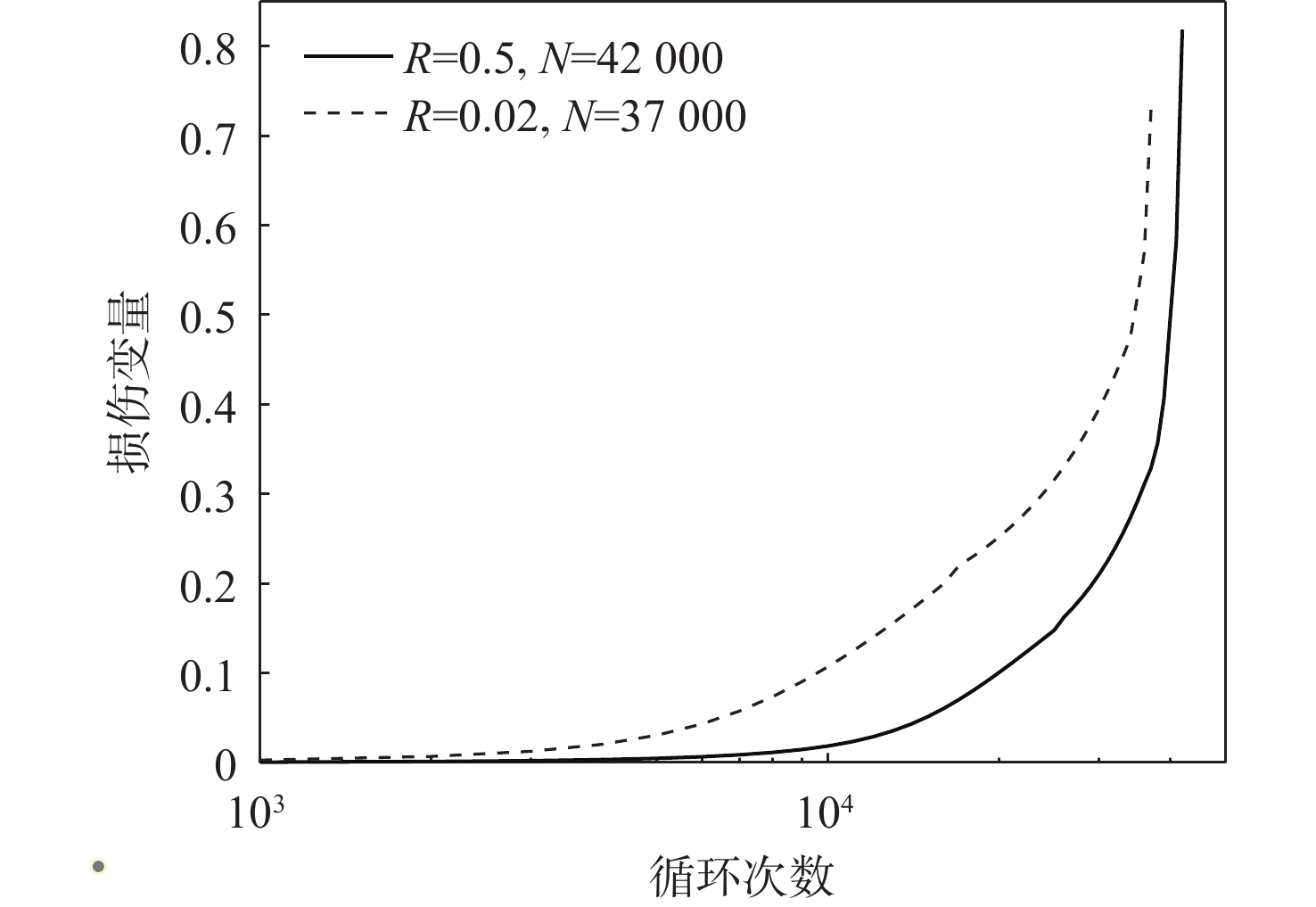
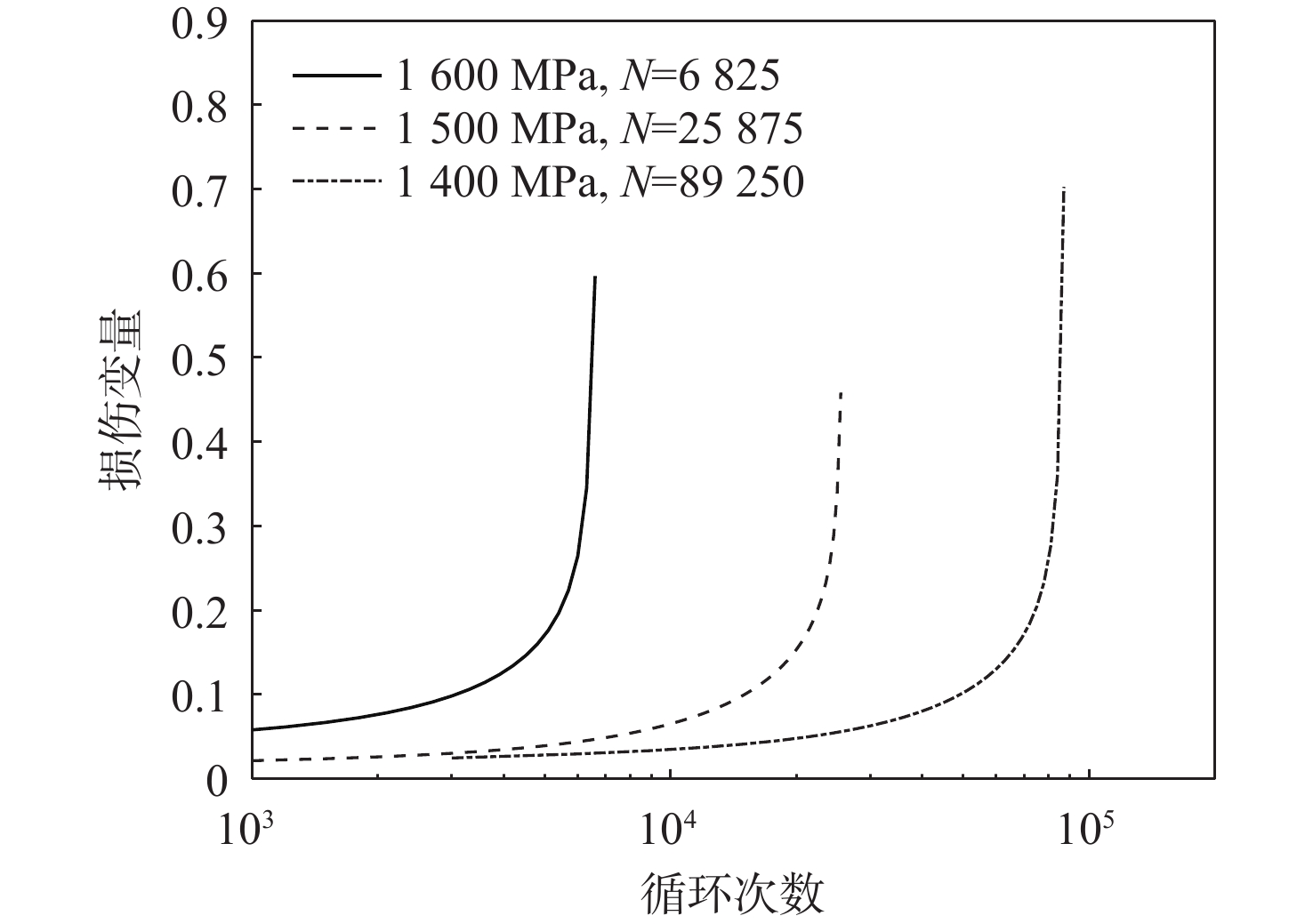
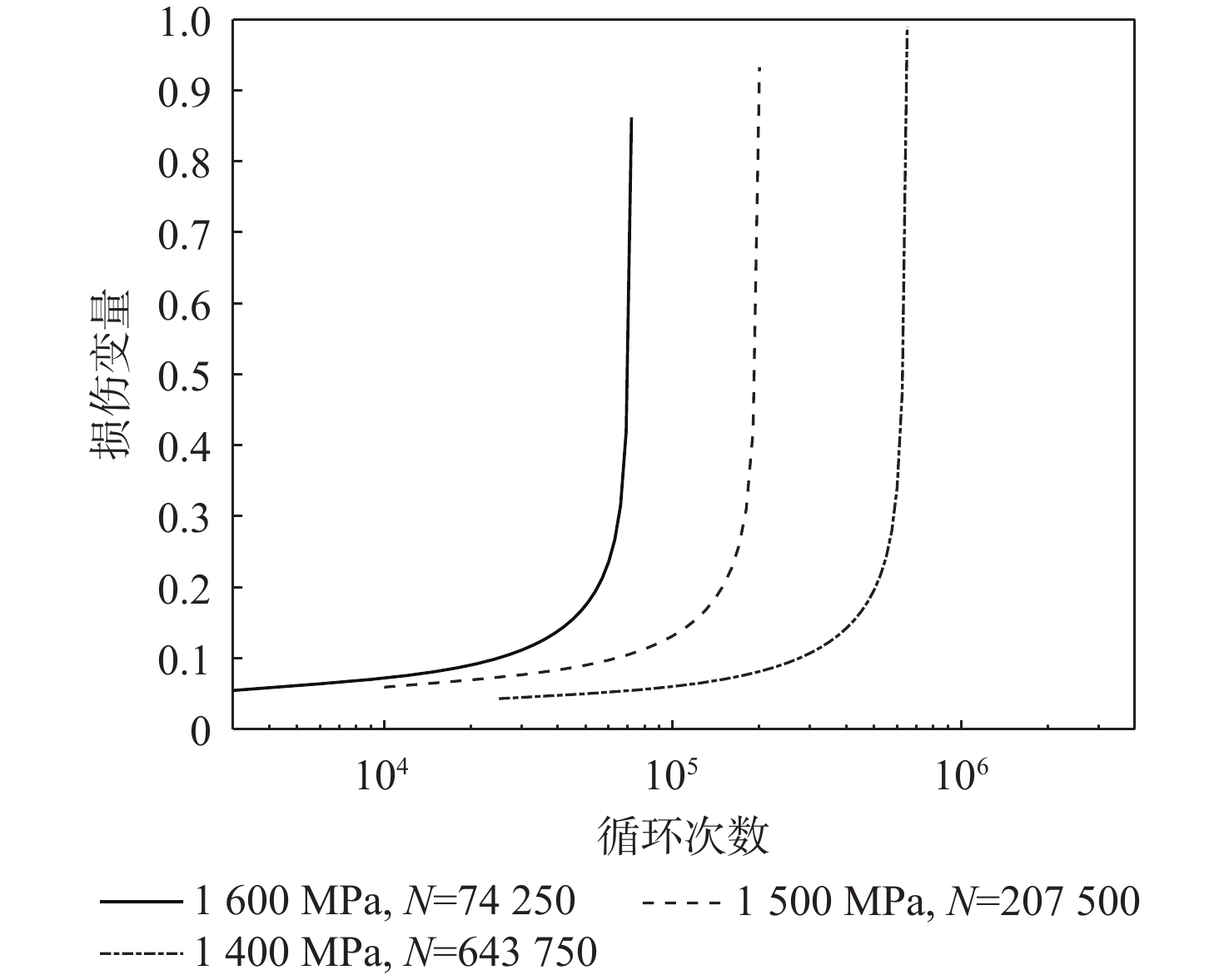
基于连续损伤力学理论,提出了考虑真空化学热处理工艺影响的疲劳损伤模型及数值计算方法,研究了M50NiL轴承钢的旋弯疲劳损伤分析及寿命预测方法。给出了本构模型、疲劳损伤演化方程和理论模型中的材料参数标定方法,基于ABAQUS平台,通过编写UMAT子程序,实现了基于硬化层影响的疲劳损伤分析的损伤力学-有限元数值计算方法;对淬火回火、渗碳及碳氮复渗2种真空化学热处理的M50NiL轴承钢,开展了旋弯疲劳试验,分析了热处理工艺对疲劳性能的影响;基于提出的疲劳损伤模型及数值计算方法,预测了M50NiL轴承钢的旋弯疲劳寿命,并与试验结果进行对比,验证了所提方法的适用性。
Abstract:This paper proposes a fatigue damage evolution model and numerical calculation method based on the theory of continuum damage mechanics, taking into account the effects of vacuum chemical heat treatment. Rotating bending fatigue damage analysis and life prediction are performed for M50NiL bearing steel. First, the constitutive model, the fatigue damage evolution equation and the material parameter calibration method in the theoretical model are presented. Second, based on the ABAQUS platform, the damage mechanics finite element numerical method for fatigue damage analysis considering the influence of the hardened layer is implemented by the UMAT subroutine. After that, the rotating bending fatigue experiments are conducted for the untreated, carburized, and carbonitrided M50NiL bearing steel, and the effect of the heat treatment process on fatigue properties is analyzed. Finally, the rotational bending fatigue life of M50NiL bearing steel is predicted using the suggested fatigue damage model and numerical approach, and the experimental findings validate the applicability of the proposed method.
-
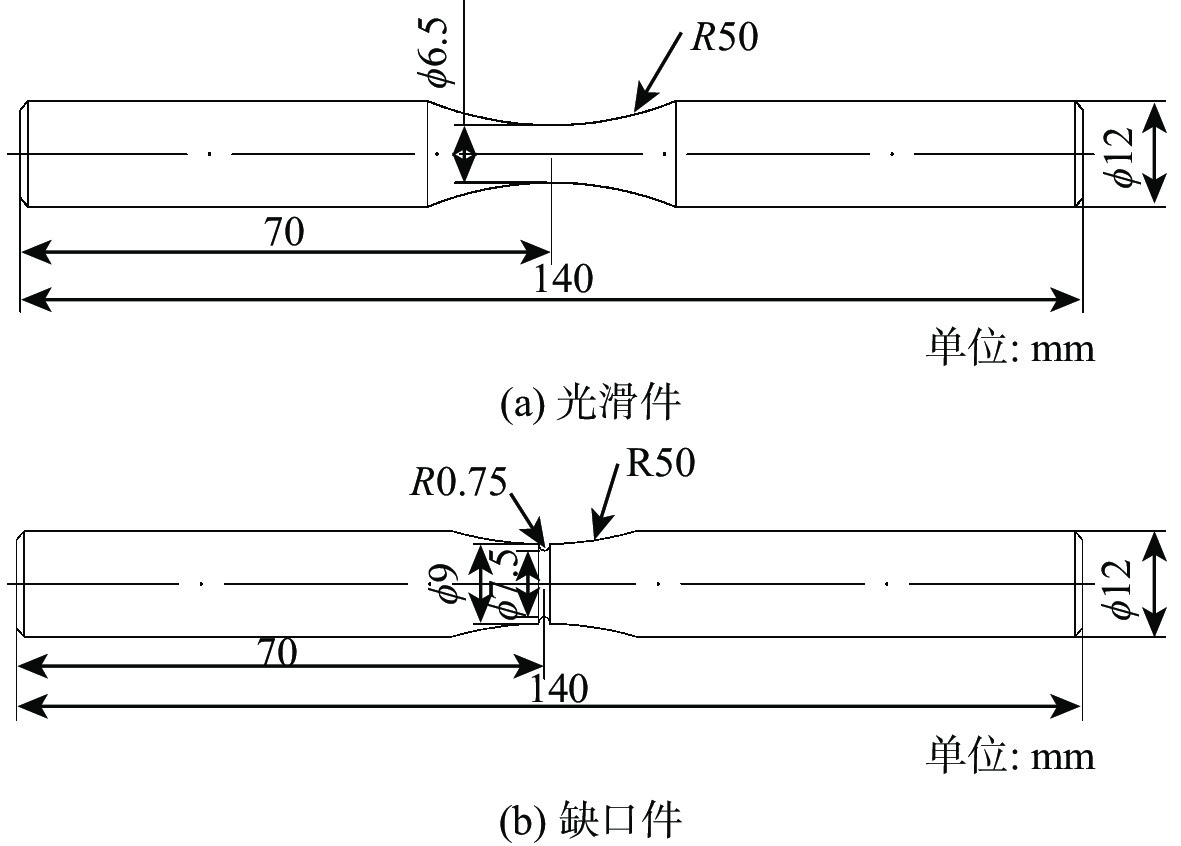
表 1 未进行表面硬化处理的M50NiL轴承钢试件的静力力学性能
Table 1. Static mechanical properties of M50NiL bearing steel specimen without surface hardening
材料 E/GPa 抗拉强度/MPa M50NiL 202 1413 表 2 渗碳和碳氮复渗的硬化层材料参数
Table 2. Material parameters of carburized and carbonitrided hardened layer
工艺 深度/mm E/GPa H/GPa Am B n 渗碳 0.4 196.71 8.60 1306.44 7317.83 0.5 0.8 198.51 8.46 1227.16 7233.58 0.5 1.2 199.78 7.45 949.23 6743.53 0.5 1.6 204.97 6.96 766.31 6781.83 0.5 2.0 203.45 6.57 675.21 6594.20 0.5 2.4 203.24 6.30 635.20 6331.17 0.5 2.8 203.05 6.15 594.34 6278.78 0.5 3.2 203.51 6.13 572.66 6287.36 0.5 3.6 203.97 6.25 611.60 6368.36 0.5 4.0 204.50 5.76 539.57 5827.44 0.5 碳氮复渗 0.4 203.92 8.38 1175.38 7296.70 0.5 0.8 199.46 7.61 947.26 7118.17 0.5 1.2 197.52 6.57 709.87 6434.09 0.5 1.6 207.77 6.13 619.92 5980.08 0.5 2.0 197.58 5.92 585.75 5948.47 0.5 2.4 200.13 5.80 571.72 5795.60 0.5 2.8 204.56 5.87 562.89 5870.99 0.5 3.2 207.28 5.87 551.67 5923.64 0.5 3.6 201.42 5.89 575.66 5848.25 0.5 4.0 201.81 5.77 564.22 5774.15 0.5 表 3 未进行表面硬化处理的M50NiL轴承钢试件的疲劳损伤材料参数
Table 3. Fatigue damage material parameters of M50NiL bearing steel specimen without surface hardening
材料 L m M50NiL 1.91×1039 11.66 表 4 渗碳和碳氮复渗表面处理的M50NiL轴承钢试件的疲劳损伤材料参数
Table 4. Fatigue damage material parameters of M50NiLbearing steel specimens carburized and carbonitrided
工艺 Kt p q s 渗碳 1 9.77×1024 1.580 2 9.77×1024 2.632 109.90 碳氮复渗 1 7.32×1017 1.360 2 7.32×1017 2.029 69.11 -
[1] 寇思源. 航空发动机主轴轴承M50NIL钢应用技术研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019.KOU S Y. Research on application technology of M50NIL steel for aviationengine spindle bearing[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [2] 王博, 杨卯生, 赵昆渝. 双真空冶炼高合金轴承钢后真空表面渗碳疲劳性能的研究[J]. 真空科学与技术学报, 2016, 36(7): 838-843.WANG B, YANG M S, ZHAO K Y. Fatigue resistance of surface-carburized Cr-co-Mo-Ni bearing steel refined by vacuum melting[J]. Chinese Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 2016, 36(7): 838-843(in Chinese). [3] 王艳江. 中碳Cr、Mo渗氮轴承钢的耐磨与疲劳性能研究[D]. 石家庄: 河北科技大学, 2017.WANG Y J. Study on wear and fatigue properties of medium carbon Cr and Mo nitriding bearing steel[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei University of Science and Technology, 2017(in Chinese). [4] WONGTIMNOI K, CHOWWANONTHAPUNYA T. Evolution of microstructure and wear resistance of carburized low carbon steel[J]. International Journal of Integrated Engineering, 2022, 14(1): 66-72. [5] WAN H Y, LU H, REN Y P, et al. Strengthening mechanisms and tensile properties of 20Cr2Mn2Mo processed by laser shock peening and vacuum carbonitriding[J]. Surface and Coatings Technology, 2022, 439: 128462. doi: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2022.128462 [6] M EURLING F. Influence of carbide and inclusion contents on the fatigue properties of high speed steels and tool steels[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2001, 23(3): 215-224. doi: 10.1016/S0142-1123(00)00087-6 [7] 史智越. GCr15轴承钢旋转弯曲疲劳性能研究[D]. 北京: 钢铁研究总院, 2019.SHI Z Y. Study on rotary bending fatigue properties of GCr15 bearing steel[D]. Beijing: Central Iron and Steel Research Institute, 2019(in Chinese). [8] PICAS I, CUADRADO N, CASELLAS D, et al. Microstructural effects on the fatigue crack nucleation in cold work tool steels[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2010, 2(1): 1777-1785. doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2010.03.191 [9] XIAO N, HUI W J, ZHANG Y J, et al. High-cycle fatigue behavior of vacuum-carburized 20Cr2Ni4 steel with different case depths[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2019, 28(6): 3413-3422. doi: 10.1007/s11665-019-04127-7 [10] 黄帅, 张国强, 王毛球, 等. 不同渗碳层深度下重载齿轮钢的疲劳性能[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2012, 24(4): 34-38.HUANG S, ZHANG G Q, WANG M Q, et al. Fatigue properties of heavy-duty gear steel with different carburized depth[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2012, 24(4): 34-38(in Chinese). [11] 孙侠生, 苏少普, 孙汉斌, 等. 国外航空疲劳研究现状及展望[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(5): 524791.SUN X S, SU S P, SUN H B, et al. Current status and prospect of overseas research on aeronautical fatigue[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(5): 524791(in Chinese). [12] 秦国华, 郭翊翔, 王华敏, 等. 飞机整体结构件的“加工变形-疲劳寿命” 多目标结构优化方法[J]. 工程力学, 2021, 38(8): 222-236.QIN G H, GUO Y X, WANG H M, et al. Multiple objective structural optimization on “machining deformation-fatigue life” of aeronautical monolithic components[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2021, 38(8): 222-236(in Chinese). [13] 武陇岗, 王瑞杰, 刘飞, 等. AZ31B/TA15异种材料电阻点焊接头的疲劳寿命预测[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2022, 43(3): 168-176.WU L G, WANG R J, LIU F, et al. Fatigue life prediction of resistance spot welded joints of AZ31B/TA15 dissimilar materials[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2022, 43(3): 168-176(in Chinese). [14] 刘俭辉, 赵贺, 冉勇, 等. 基于临界面理论的多轴等效应变疲劳寿命预估模型[J]. 中国机械工程, 2022, 33(15): 1821-1827.LIU J H, ZHAO H, RAN Y, et al. Multiaxial equivalent strain fatigue life prediction model based on critical plane theory[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 33(15): 1821-1827(in Chinese). [15] 甘磊, 吴昊, 仲政. 基于能量法的多轴疲劳寿命预测方法[J]. 固体力学学报, 2019, 40(3): 260-268.GAN L, WU H, ZHONG Z. Fatigue life prediction under multiaxial loading using energy-based models[J]. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics, 2019, 40(3): 260-268(in Chinese). [16] 游文俊, 梅威威, 王计真, 等. 考虑沙尘颗粒冲蚀损伤的航空叶片寿命预估[J]. 航空科学技术, 2022, 33(8): 68-77.YOU W J, MEI W W, WANG J Z, et al. Life prediction for the aircraft blade with sand particles erosion damage[J]. Aeronautical Science & Technology, 2022, 33(8): 68-77(in Chinese). [17] 孟莉, 杨硕, 沈泳星. 断裂相场在循环塑性与疲劳分析中的应用[J]. 固体力学学报, 2021, 42(3): 334-344.MENG L, YANG S, SHEN Y X. Phase field approach to cyclic plasticity and fatigue analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics, 2021, 42(3): 334-344(in Chinese). [18] 叶文静, 王莉华. 基于反向传播神经网络的疲劳裂纹扩展分析[J]. 力学季刊, 2021, 42(4): 752-762.YE W J, WANG L H. Fatigue crack propagation analysis based on back propagation neural network[J]. Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics, 2021, 42(4): 752-762(in Chinese). [19] SHEN F, HU W P, MENG Q C. New approach based on continuum damage mechanics with simple parameter identification to fretting fatigue life prediction[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, 2015, 36(12): 1539-1554. doi: 10.1007/s10483-015-2002-6 [20] KACHANOV L M. Rupture time under creep conditions[J]. International Journal of Fracture, 1999, 97(1): 11-18. [21] VASU K R S, VINITH Y G, UDAY S G, et al. A review on Johnson Cook material model[J]. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2022, 62: 3450-3456. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2022.04.279 [22] LEMAITRE J, CHABOCHE J L, MAJI A K. Mechanics of solid materials[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics, 1993, 119(3): 642-643. [23] XIAO Y. A continuum damage mechanics model for high cycle fatigue[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 1998, 20(7): 503-508. doi: 10.1016/S0142-1123(98)00005-X [24] SHEN F, ZHAO B, LI L, et al. Fatigue damage evolution and lifetime prediction of welded joints with the consideration of residual stresses and porosity[J]. International Journal of Fatigue, 2017, 103: 272-279. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2017.06.014 [25] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 金属材料疲劳试验旋转弯曲方法: GB/T 4337—2015[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社, 2015.China National Standardization Administration. Rotational bending method for fatigue test of metallic materials: GB/T 4337—2015[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2015(in Chinese). 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李志斌,杨卯生,曹建春,梁剑雄. M50轴承钢温度时间相关高周疲劳损伤寿命模型的研究. 钢铁研究学报. 2024(09): 1232-1244 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(0)
-







 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术

