Trajectory planning of re-entry gliding vehicle in a class of uncertain environment
-
摘要:
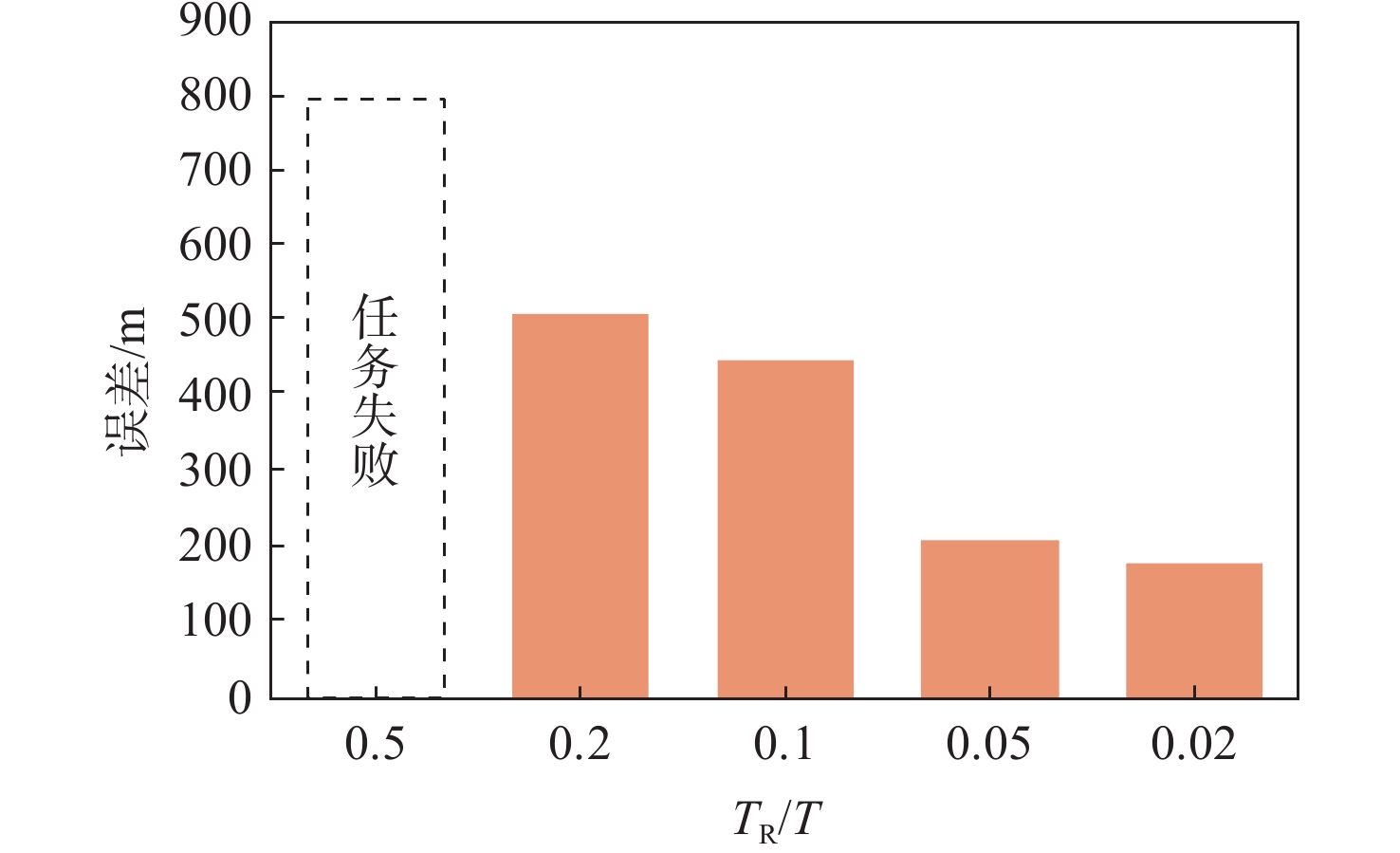
再入飞行器的飞行过程需要跨越从临近空间到地面的广大区域。在此过程中,即便是微小的建模误差和外界扰动也有可能导致飞行器偏离原先目标点或超出约束边界。为使结果更加鲁棒,对一类不确定环境下的再入飞行器轨迹规划方法进行研究,并引入了数据驱动鲁棒优化的概念以处理不确定性,提出一种数据驱动鲁棒优化轨迹规划方法。所提方法的核心思想是利用不确定参数的历史数据,动态构造不确定集合,再用鲁棒优化的方法对包含该集合的问题进行求解。所提方法相比于传统的鲁棒优化或机会约束优化有两大优势:一是无须有关不确定参数分布或范围的先验知识,也无须其符合特定形式;二是通过在线构造数据驱动的支持向量簇,令优化结果不至于过于保守。为提高计算效率,根据再入优化问题的特点进一步对所提方法进行定制。给出了所提方法数值仿真结果与传统方法对比,以说明所提方法的有效性。
Abstract:The flight process of reentry vehicles requires traversing a vast area from the near space to the ground. During this process, even minor modeling errors and external disturbances can lead to deviations from the original target point or exceed the constraint boundaries. To enhance the robustness of the results, this paper investigates a trajectory planning method for reentry vehicles under uncertain environments and introduces the concept of data-driven robust optimization to address uncertainties. A data-driven robust optimization trajectory planning approach is proposed. The core idea of the proposed method is to dynamically construct uncertainty sets using historical data of uncertain parameters and then solve the problem incorporating these sets using robust optimization techniques. Compared to traditional robust optimization or chance-constrained optimization, the proposed method offers two significant advantages: First, it does not require prior knowledge about the distribution or range of uncertain parameters, nor does it demand that they conform to a specific form. Second, by constructing data-driven support vector clusters online, the optimization results are less conservative. To improve computational efficiency, the method is further tailored according to the characteristics of reentry optimization problems. Numerical simulation results are presented and compared with traditional methods to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
-
Key words:
- reentry /
- trajectory planning /
- data-driven /
- robust optimization /
- uncertainty
-
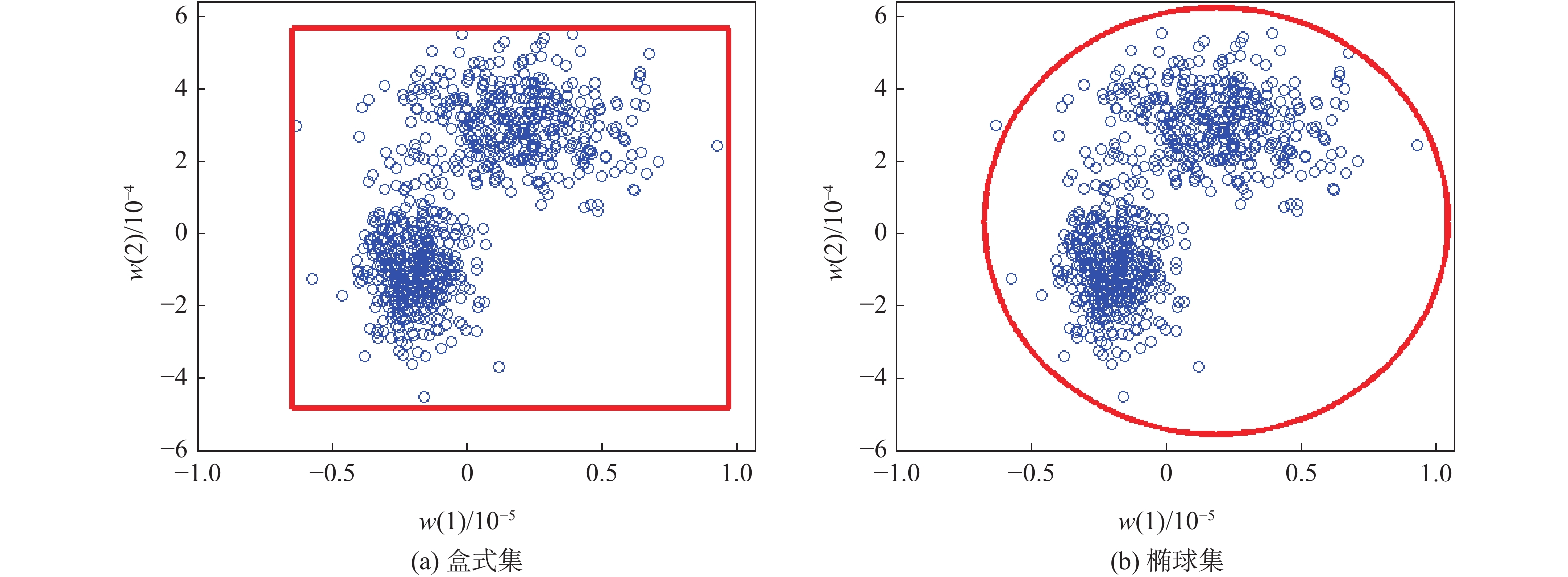
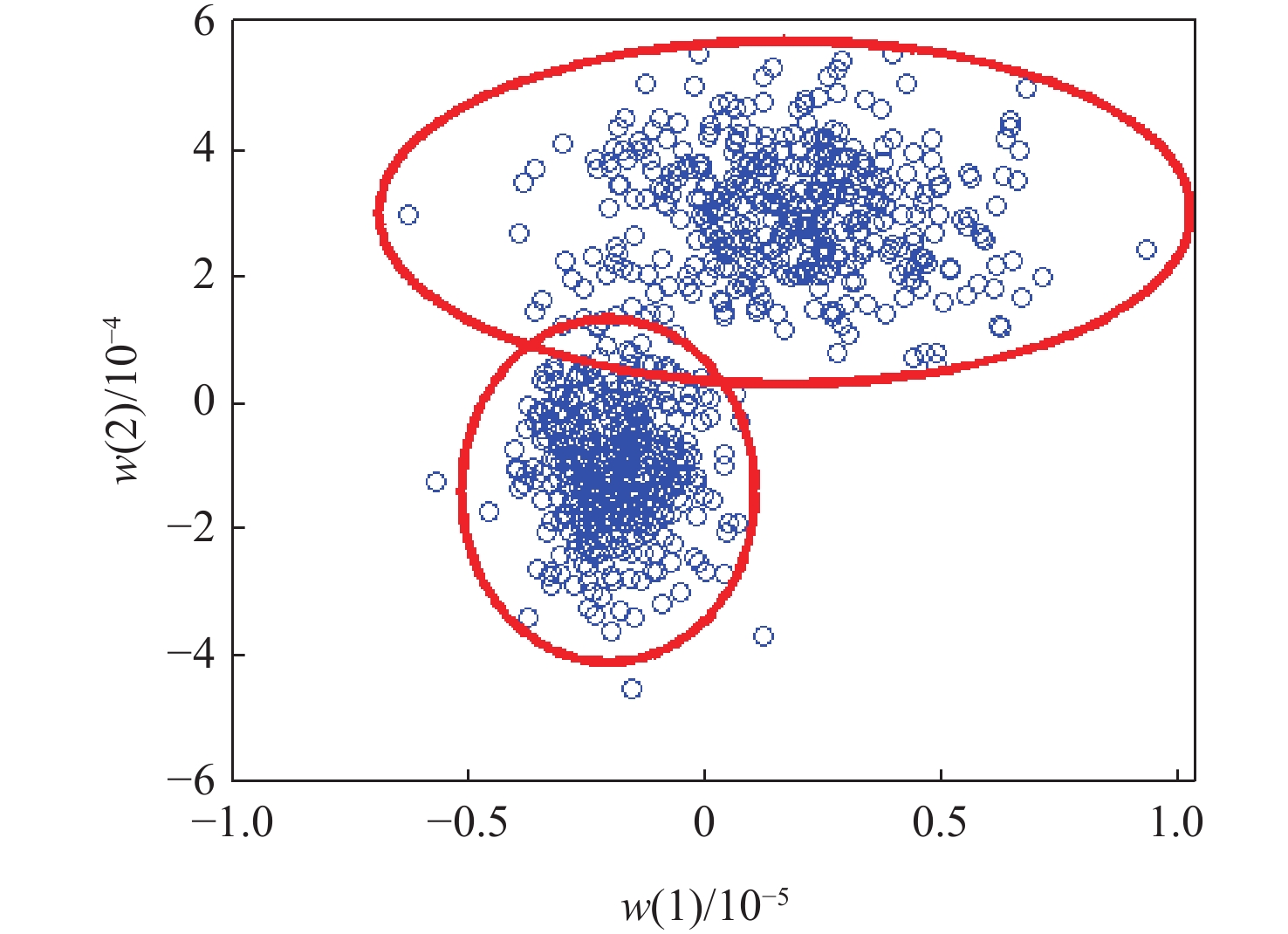
表 1 SVC中点的分类
Table 1. Classification of data points in SVC
数据点 原始问题描述 对偶问题描述 内点 ‖ψ(w(t)i′)−c‖<Rsvc2 α(t)L=0 边界点 ‖ψ(w(t)i′)−c‖=Rsvc2 0<α(t)L<1/Ni′v 外点 ‖ψ(w(t)i′)−c‖>Rsvc2 α(t)L=1/Ni′v 表 2 初末状态条件
Table 2. Initial and terminal conditions
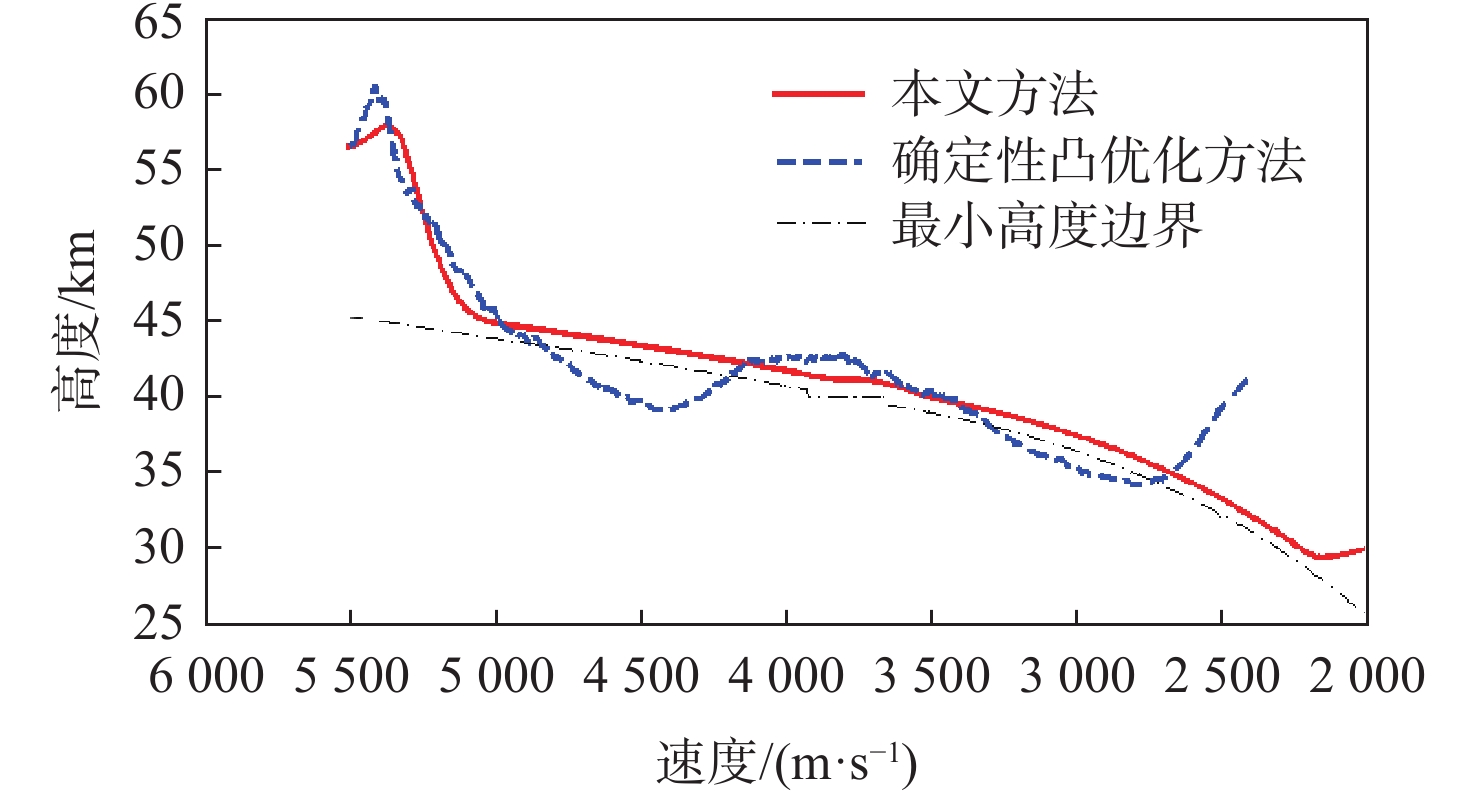
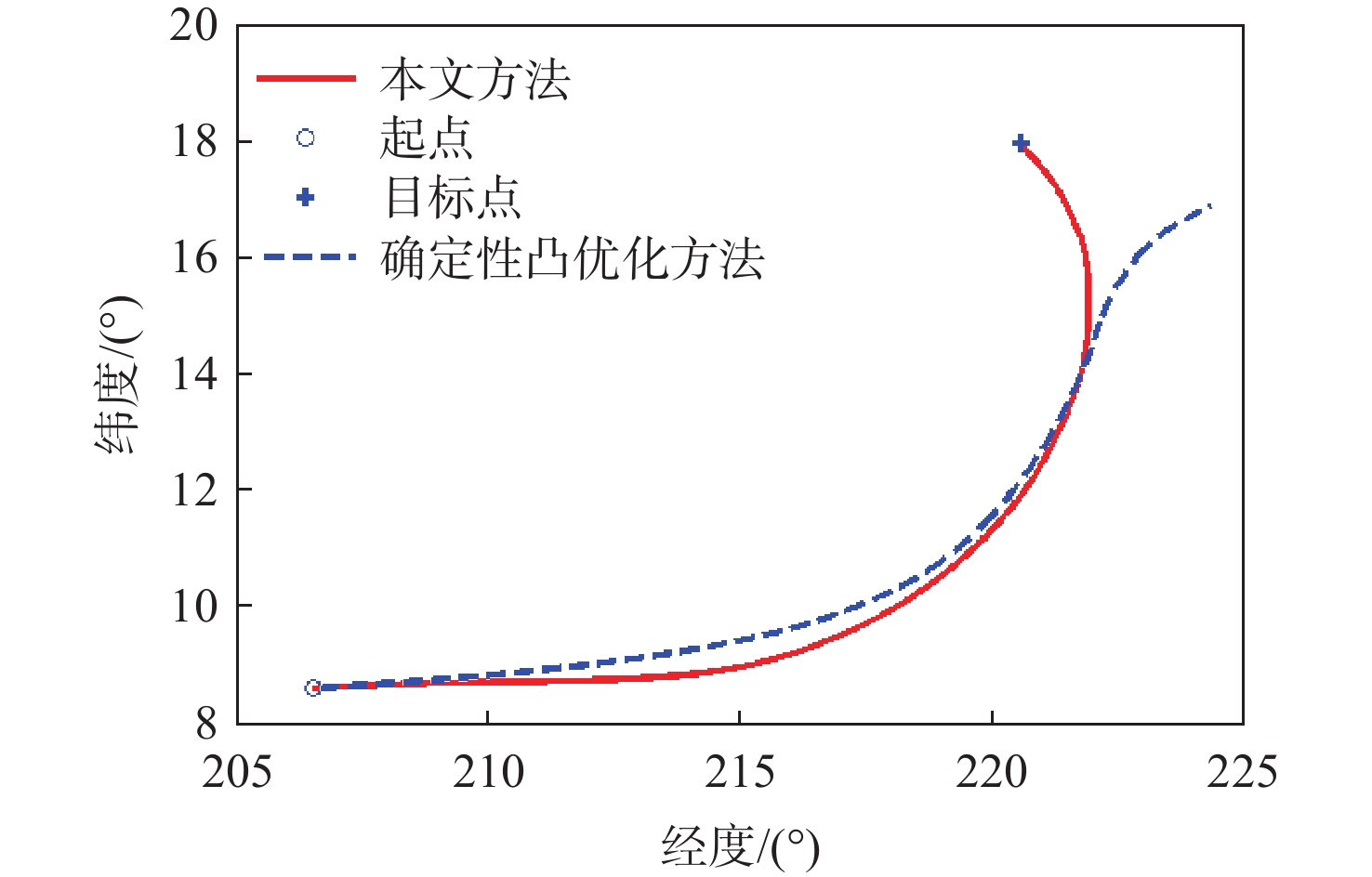
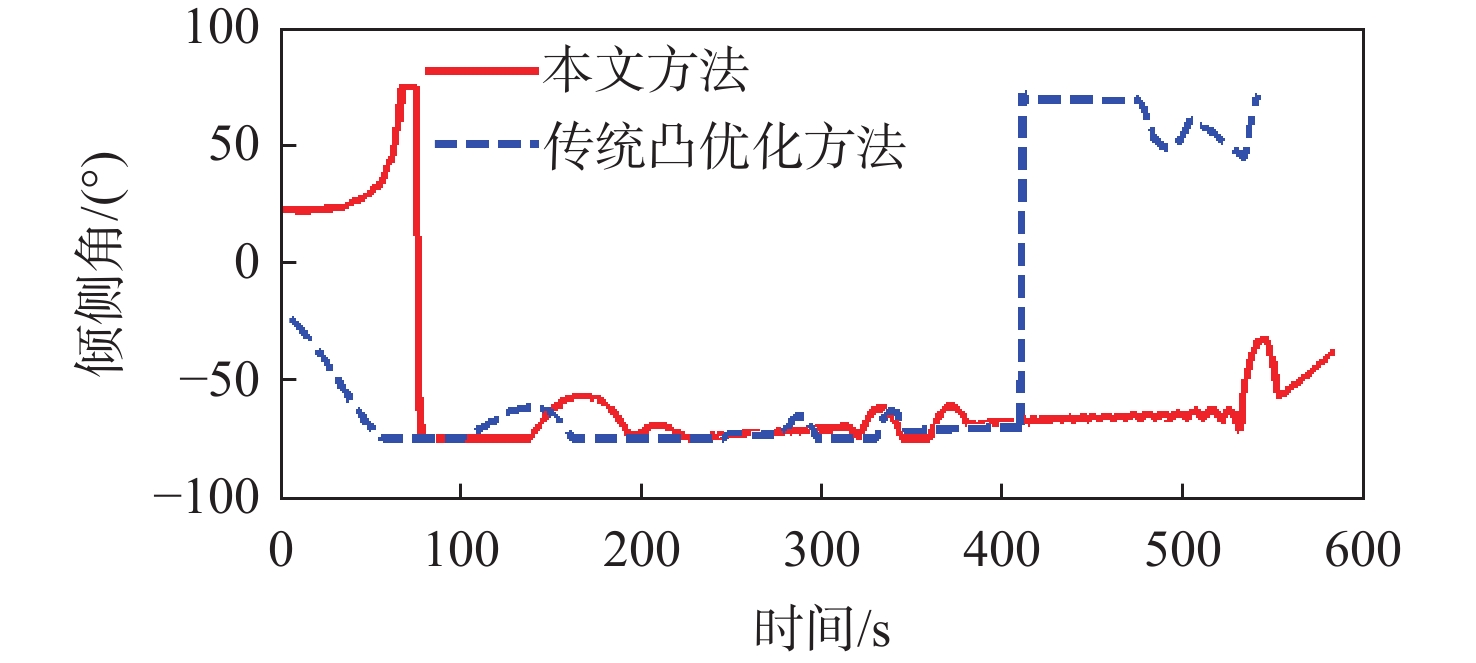
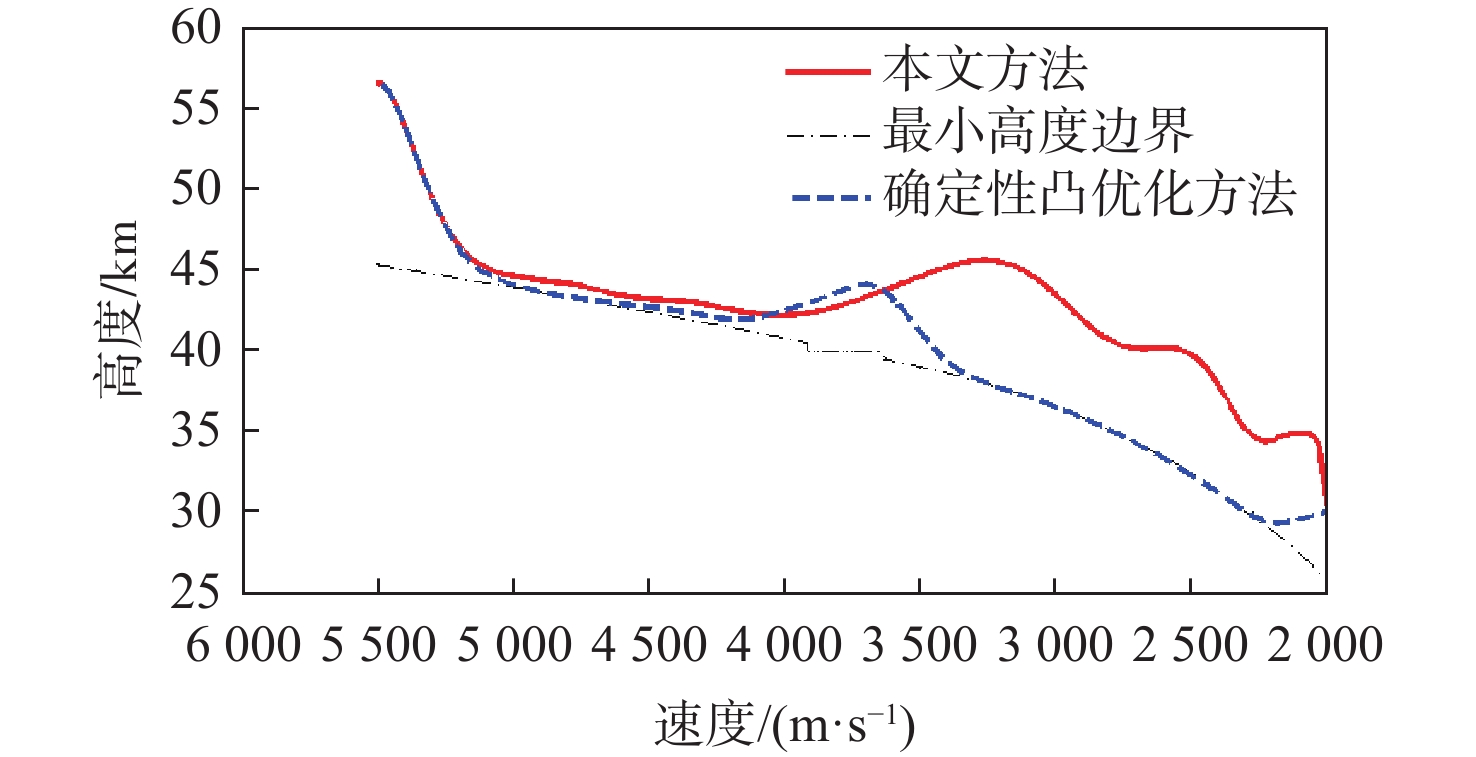
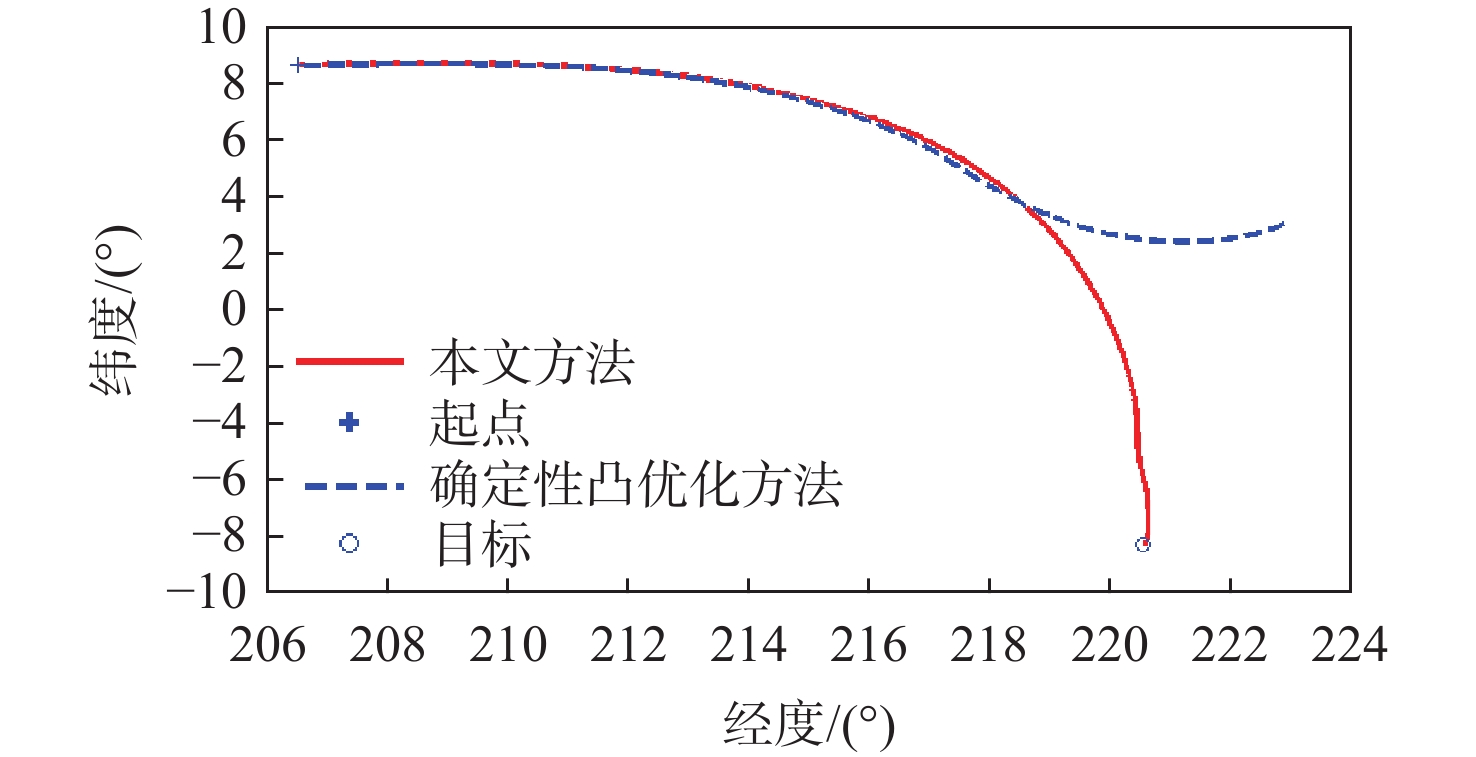
状态量 r/ km V/(m·s−1) θ/(°) ϕ/(°) γ/(°) ψ/(°) x0 85.00 6500.00 175.00 3.00 −0.50 70 xs 56.52 5500.00 206.50 8.62 0.02 86.92 xf 30.00 220.55 18 [−1,1] 表 3 计算效率对比
Table 3. Computational cost comparison
方法 CPU时间/s 确定性凸优化方法 2.5 本文方法 3.2~3.4 表 4 末状态条件(右转)
Table 4. Terminal conditions (right turn)
状态量 r/km θ/(°) φ/(°) γ/(°) xf 30.00 220.55 −8.34 [−1,1] -
[1] SMITH K M. Predictive lateral logic for numerical entry guidance algorithms[C]//Proceedings of the AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Meeting. Reston: AIAA, 2016: 1-6. [2] MAO Y F, ZHANG D L, WANG L. Reentry trajectory optimization for hypersonic vehicle based on improved Gauss pseudospectral method[J]. Soft Computing, 2017, 21(16): 4583-4592. doi: 10.1007/s00500-016-2201-3 [3] LIU X. Autonomous trajectory planning by convex optimization[D]. Ames : Iowa State University, 2013. [4] CHAI R Q, TSOURDOS A, SAVVARIS A, et al. Real-time reentry trajectory planning of hypersonic vehicles: A two-step strategy incorporating fuzzy multiobjective transcription and deep neural network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2020, 67(8): 6904-6915. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2019.2939934 [5] CHAI R Q, SAVVARIS A, TSOURDOS A, et al. Stochastic spacecraft trajectory optimization with the consideration of chance constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2020, 28(4): 1550-1559. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2019.2908938 [6] CASALINO L, MASSENI F, PASTRONE D. Deterministic and robust optimization of hybrid rocket engines for small satellite launchers[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2021, 58(6): 1893-1903. doi: 10.2514/1.A35007 [7] 刘旭, 李响, 张后军, 等. 不确定条件下采用协方差描述函数法的再入轨迹鲁棒优化[J]. 宇航学报, 2021, 42(11): 1404-1415.LIU X, LI X, ZHANG H J, et al. Robust reentry trajectory optimization under uncertainties using covariance analysis describing function technique[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2021, 42(11): 1404-1415 (in Chinese). [8] HUANG Y C, LI H Y. Reliability-based trajectory optimization using nonintrusive polynomial chaos for Mars entry mission[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2018, 61(11): 2854-2869. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2018.03.009 [9] HUANG Y C, LI H Y, DU X, et al. Mars entry trajectory robust optimization based on evidence under epistemic uncertainty[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2019, 163: 225-237. [10] BLACKMORE L, ONO M, WILLIAMS B C. Chance-constrained optimal path planning with obstacles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2011, 27(6): 1080-1094. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2011.2161160 [11] FARINA M, GIULIONI L, SCATTOLINI R. Stochastic linear model predictive control with chance constraints—A review[J]. Journal of Process Control, 2016, 44: 53-67. doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2016.03.005 [12] PAULSON J A, BUEHLER E A, BRAATZ R D, et al. Stochastic model predictive control with joint chance constraints[J]. International Journal of Control, 2020, 93(1): 126-139. doi: 10.1080/00207179.2017.1323351 [13] SHANG C, YOU F Q. A data-driven robust optimization approach to scenario-based stochastic model predictive control[J]. Journal of Process Control, 2019, 75: 24-39. doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2018.12.013 [14] ZHANG X J, MARGELLOS K, GOULART P, et al. Stochastic model predictive control using a combination of randomized and robust optimization[C]//Proceedings of the 52nd IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 7740-7745. [15] KRISHNAMOORTHY D, SUWARTADI E, FOSS B, et al. Improving scenario decomposition for multistage MPC using a sensitivity-based path-following algorithm[J]. IEEE Control Systems Letters, 2018, 2(4): 581-586. doi: 10.1109/LCSYS.2018.2845108 [16] YOU K Y, TEMPO R, XIE P. Distributed algorithms for robust convex optimization via the scenario approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(3): 880-895. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2828093 [17] SHANG C, HUANG X L, YOU F Q. Data-driven robust optimization based on kernel learning[J]. Computers & Chemical Engineering, 2017, 106: 464-479. [18] BEN-HUR A, HORN D, SIEGELMANN H T, et al. Support vector clustering[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2001, 2: 125-137. [19] HONG L J, HUANG Z Y, LAM H. Approximating data-driven joint chance-constrained programs via uncertainty set construction[C]//Proceedings of the Winter Simulation Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 389-400. [20] TEMPO R, CALAFIORE G, DABBENE F. Randomized algorithms for analysis and control of uncertain systems: With applications[M]. London: Springer London, 2013. [21] LIU X F, SHEN Z J, LU P. Entry trajectory optimization by second-order cone programming[J]. Journal of Guidance Control Dynamics, 2016, 39(2): 227-241. doi: 10.2514/1.G001210 [22] SHANG C, CHEN W H, STROOCK A D, et al. Robust model predictive control of irrigation systems with active uncertainty learning and data analytics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2020, 28(4): 1493-1504. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2019.2916753 [23] PHILLIPS T H. A common aero vehicle (CAV) model, description, and employment guide[J]. Schafer Corporation for AFRL and AFSPC, 2003: 27-28. -







 下载:
下载: