-
摘要:
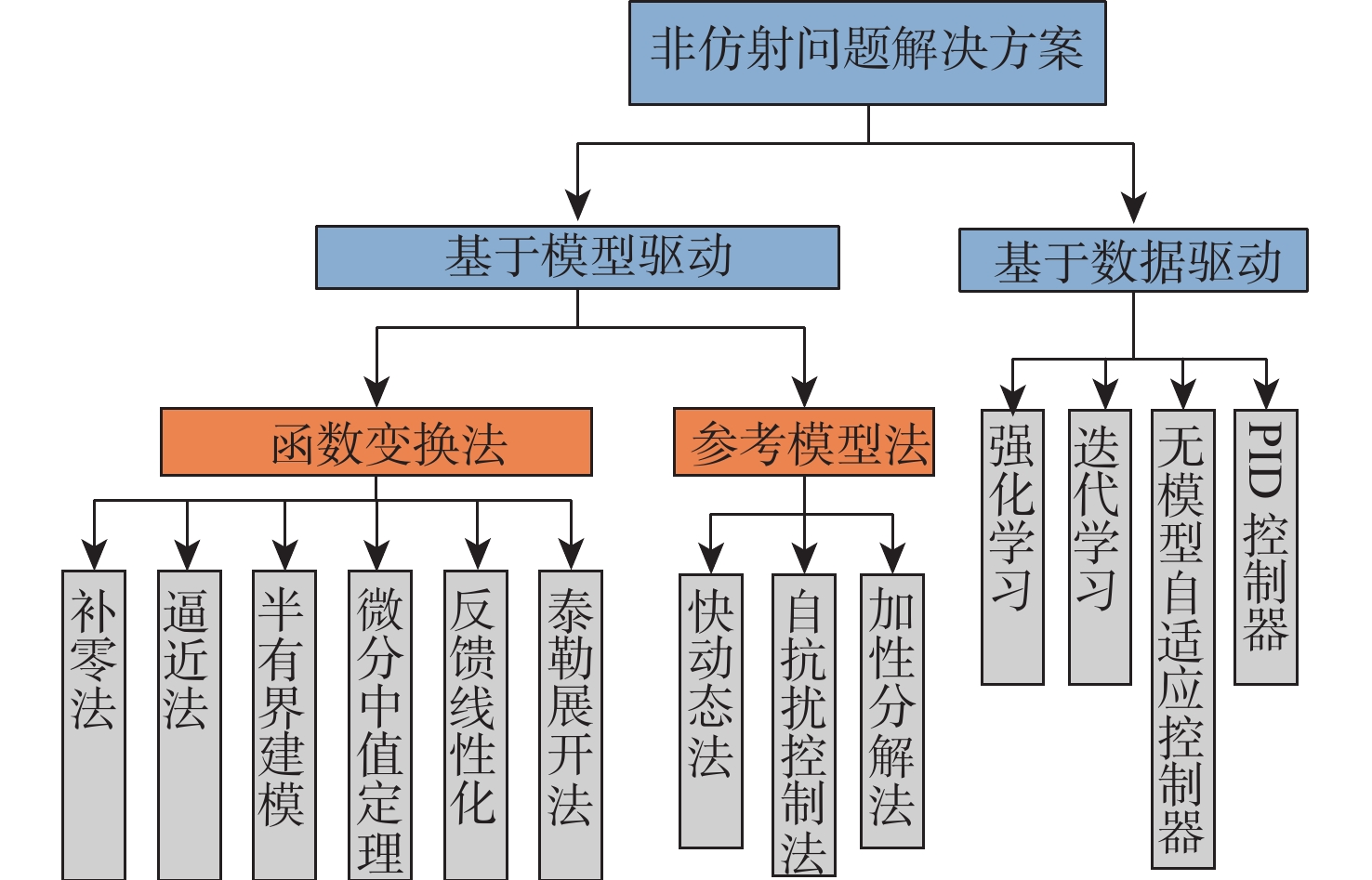
作为仿射非线性系统更一般化的描述,非仿射非线性系统所对应的实际应用更加广泛,也更贴近实际。因此,研究非仿射非线性系统的控制问题十分重要。然而,非线性系统的非仿射特性会使控制信号以非线性函数形式出现在闭环系统中,从而带来诸如控制方向未知、奇异、过零等问题。由此,解决非仿射非线性系统的控制问题面临着巨大的挑战。基于此,介绍了仿射、严格反馈和高阶系统的相关背景知识,总结和分析了解决非仿射非线性系统控制的3种解决思路,包括函数变换法、参考模型法和数据驱动法。在已有的研究成果基础上,指出非仿射非线性系统研究领域所面临的挑战和发展趋势。
Abstract:As a more general description of affine nonlinear systems, the practical applications corresponding to non-affine nonlinear systems are more comprehensive and closer to reality. Therefore, it is essential to study the control problems of non-affine nonlinear systems. However, the closed-loop system’s control signal appears as a nonlinear function due to the non-affine properties of nonlinear systems, which can lead to issues including singularity, zero-crossing, and uncertain control direction. From this point, solving control problems of non-affine nonlinear systems is a considerable challenge. This paper first introduces the relevant background knowledge of affine, strict feedback, and high-order systems, and then summarizes three solutions through literature research: function transformation method, reference model method, and data-driven method. Finally, based on existing research findings, the challenges and development trends faced in the field of non-affine nonlinear system research are proposed.
-
Key words:
- non-affine systems /
- nonlinear systems /
- strict feedback /
- data-driven /
- additive decomposition
-
表 1 6种仿射解决方案对比
Table 1. Comparison of six affine solutions
方案 适用范围 可导性约束 有界性条件 计算复杂度 泰勒展开法 +++++ +++++ +++ 反馈线性化 ++ +++++ ++++ 微分中值定理 ++ +++ +++ 半有界建模 ++ 有 ++ 逼近法 ++++ +++++ 补零法 ++++ + 注:“+”越多则相关指标越大。 -
[1] SLOTINE J J, LI W P. Applied nonlinear control[M]. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall, 1991. [2] WANG Y H, CHEN M, WU Q X, et al. Fuzzy adaptive non-affine attitude tracking control for a generic hypersonic flight vehicle[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2018, 80: 56-66. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2018.06.033 [3] XU D Z, JIANG B, SHI P. Global robust tracking control of non-affine nonlinear systems with application to yaw control of UAV helicopter[J]. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2013, 11(5): 957-965. doi: 10.1007/s12555-012-0335-3 [4] PARKER J T, SERRANI A, YURKOVICH S, et al. Control-oriented modeling of an air-breathing hypersonic vehicle[J]. Journal of Guidance Control Dynamics, 2007, 30(3): 856-869. doi: 10.2514/1.27830 [5] YU J P, SHI P, ZHAO L. Finite-time command filtered backstepping control for a class of nonlinear systems[J]. Automatica, 2018, 92: 173-180. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2018.03.033 [6] LING S, WANG H Q, LIU P X. Adaptive fuzzy dynamic surface control of flexible-joint robot systems with input saturation[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2019, 6(1): 97-107. doi: 10.1109/JAS.2019.1911330 [7] 宋永端, 宋琦. 非仿射系统的控制器设计方法综述[C]//第十三届中国控制会议. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 785-790.SONG Y D, SONG Q. Survey of the latest developments in control of non-affine systems[C]//Proceedings of the 13th Chinese Control Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 785-790(in Chinese). [8] HOVAKIMYAN N, LAVRETSKY E, SASANE A. Dynamic inversion for nonaffine-in-control systems via time-scale separation. Part I[J]. Journal of Dynamical and Control Systems, 2007, 13(4): 451-465. doi: 10.1007/s10883-007-9029-1 [9] CARDOSO G S, SCHNITMAN L. Analysis of exact linearization and aproximate feedback linearization techniques[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2011, 2011: 205939. [10] ZHANG T P, GE S S. Adaptive dynamic surface control of nonlinear systems with unknown dead zone in pure feedback form[J]. Automatica, 2008, 44(7): 1895-1903. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2007.11.025 [11] QUAN Q. Introduction to multicopter design and control[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2017. [12] 张伸. 基于干扰观测器的高超声速飞行器非线性控制方法研究 [D]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学, 2019.ZHANG S. Research on nonlinear control method of hypersonic vehicle based on disturbance observer[D]. Beijing: Beihang University, 2019(in Chinese). [13] XU L X, WANG Y L, WANG F, et al. Event-triggered active disturbance rejection trajectory tracking control for a quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2023, 449: 1-13. [14] JIANG Z P, HILL D J. A robust adaptive backstepping scheme for nonlinear systems with unmodeled dynamics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1999, 44(9): 1705-1711. doi: 10.1109/9.788536 [15] LIN W, QIAN C J. Adaptive regulation of high-order lower-triangular systems: An adding a power integrator technique[J]. Systems & Control Letters, 2000, 39(5): 353-364. [16] RUI C, REYHANOGLU M, KOLMANOVSKY I, et al. Nonsmooth stabilization of an underactuated unstable two degrees of freedom mechanical system[C]//Proceedings of the 36th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1997: 3998-4003. [17] WANG N, TAO F Z, FU Z M, et al. Adaptive fuzzy control for a class of stochastic strict feedback high-order nonlinear systems with full-state constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2022, 52(1): 205-213. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.2996635 [18] FU Z M, WANG N, SONG S Z, et al. Adaptive fuzzy finite-time tracking control of stochastic high-order nonlinear systems with a class of prescribed performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2022, 30(1): 88-96. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.3032776 [19] LIN W, QIAN C J. Adaptive control of nonlinearly parameterized systems: The smooth feedback case[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2002, 47(8): 1249-1266. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2002.800773 [20] SUN Z Y, YUN M M, LI T. A new approach to fast global finite-time stabilization of high-order nonlinear system[J]. Automatica, 2017, 81: 455-463. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2017.04.024 [21] SUN Z Y, SHAO Y, CHEN C C. Fast finite-time stability and its application in adaptive control of high-order nonlinear system[J]. Automatica, 2019, 106: 339-348. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2019.05.018 [22] POLYAKOV A. Nonlinear feedback design for fixed-time stabilization of linear control systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2012, 57(8): 2106-2110. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2011.2179869 [23] YOO S J. Low-complexity robust tracking of high-order nonlinear systems with application to underactuated mechanical dynamics[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2018, 91(3): 1627-1637. doi: 10.1007/s11071-017-3969-0 [24] LING S, WANG H Q, LIU P X. Adaptive tracking control of high-order nonlinear systems under asymmetric output constraint[J]. Automatica, 2020, 122: 109281. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2020.109281 [25] CAMERON F, SEBORG D E. A self-tuning controller with a PID structure[J]. IFAC Proceedings Volumes, 1983, 16(1): 613-622. doi: 10.1016/S1474-6670(17)62721-6 [26] LIU Y, JIANG D, YUN J T, et al. Self-tuning control of manipulator positioning based on fuzzy PID and PSO algorithm[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2021, 9: 817723. [27] FU Z L, LIU C P, RUAN S Y, et al. Design of neutrosophic self-tuning PID controller for AC permanent magnet synchronous motor based on neutrosophic theory[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 2021: 5548184. [28] CHEN C M. CiteSpace: A practical guide for mapping scientific literature[M]. New York: Nova Science Publishers, 2016. [29] FARRELL J A, POLYCARPOU M, SHARMA M, et al. Command filtered backstepping[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2009, 54(6): 1391-1395. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2009.2015562 [30] LABIOD S, GUERRA T M. Indirect adaptive fuzzy control for a class of nonaffine nonlinear systems with unknown control directions[J]. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2010, 8(4): 903-907. doi: 10.1007/s12555-010-0425-z [31] BEDROSSIAN N S. Approximate feedback linearization: the cart-pole example[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1992: 1987-1992. [32] WANG M, GE S S, HONG K S. Approximation-based adaptive tracking control of pure-feedback nonlinear systems with multiple unknown time-varying delays[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2010, 21(11): 1804-1816. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2010.2073719 [33] LIU Y H. Adaptive tracking control for a class of uncertain pure-feedback systems[J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2016, 26(5): 1143-1154. doi: 10.1002/rnc.3350 [34] HASELTALAB A, NEGENBORN R R. Adaptive control for autonomous ships with uncertain model and unknown propeller dynamics[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2019, 91: 104116. [35] RAZA A, MALIK F M, KHAN R, et al. Robust output feedback control of fixed-wing aircraft[J]. Aircraft Engineering and Aerospace Technology, 2020, 92(8): 1263-1273. [36] ZHANG S, WANG Q, YANG G, et al. Anti-disturbance backstepping control for air-breathing hypersonic vehicles based on extended state observer[J]. ISA Transactions, 2019, 92: 84-93. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2019.02.017 [37] SWAROOP D, HEDRICK J K, YIP P P, et al. Dynamic surface control for a class of nonlinear systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2000, 45(10): 1893-1899. [38] LIU Z C, DONG X M, XIE W J, et al. Adaptive fuzzy control for pure-feedback nonlinear systems with nonaffine functions being semibounded and indifferentiable[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2018, 26(2): 395-408. [39] CHEN L, WANG Q. Finite-time adaptive fuzzy command filtered control for nonlinear systems with indifferentiable non-affine functions[J]. Nonlinear Dynamics, 2020, 100(1): 493-507. doi: 10.1007/s11071-020-05536-3 [40] GE S S, ZHANG J. Neural-network control of nonaffine nonlinear system with zero dynamics by state and output feedback[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2003, 14(4): 900-918. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2003.813823 [41] LIU Y J, TONG S C, LI Y M. Adaptive neural network tracking control for a class of non-linear systems[J]. International Journal of Systems Science, 2010, 41(2): 143-158. doi: 10.1080/00207720903042947 [42] JI W Q, WANG M, QIU J B. Fuzzy-model-based output feedback controller design for discrete-time non-affine nonlinear systems via piecewise Lyapunov functions[C]//Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Information Science and Technology. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 288-293. [43] CUI Q, WANG Y J, SONG Y D. Neuroadaptive fault-tolerant control under multiple objective constraints with applications to tire production systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(8): 3391-3400. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2967150 [44] FU Y, CHAI T Y. Indirect self-tuning control using multiple models for non-affine nonlinear systems[J]. International Journal of Control, 2011, 84(6): 1031-1040. doi: 10.1080/00207179.2011.588960 [45] ZHAO S T, GAO X W. Robust adaptive control for a class of uncertain non-affine nonlinear systems using affine-type neural networks[J]. International Journal of Systems Science, 2016, 47(11): 2691-2699. doi: 10.1080/00207721.2015.1015662 [46] ZHANG H G, CUI L L, ZHANG X, et al. Data-driven robust approximate optimal tracking control for unknown general nonlinear systems using adaptive dynamic programming method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 2011, 22(12): 2226-2236. doi: 10.1109/TNN.2011.2168538 [47] GANG T T, YANG J, GAO Q, et al. A fuzzy approach to robust control of stochastic nonaffine nonlinear systems[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2012, 2012: 439805. [48] LUO S H, LEWIS F L, SONG Y D, et al. Accelerated adaptive fuzzy optimal control of three coupled fractional-order chaotic electromechanical transducers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Fuzzy Systems, 2021, 29(7): 1701-1714. doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.2984998 [49] QUAN Q, DU G X, CAI K Y. Proportional-integral stabilizing control of a class of MIMO systems subject to nonparametric uncertainties by additive-state-decomposition dynamic inversion design[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2016, 21(2): 1092-1101. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2015.2497258 [50] SONG Y D, HE L, WANG Y J. Globally exponentially stable tracking control of self-restructuring nonlinear systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(9): 4755-4765. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2951574 [51] GE S S, ZHANG J. State feedback NN control of non-affine nonlinear system with zero dynamics[C]//Proceedings of the American Control Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2003: 4530-4535. [52] LIU Y J, TONG S C, WANG W. Adaptive fuzzy output tracking control for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems[J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 2009, 160(19): 2727-2754. doi: 10.1016/j.fss.2008.12.016 [53] LAVRETSKY E, HOVAKIMYAN N. Adaptive dynamic inversion for nonaffine-in-control uncertain systems via time-scale separation. Part II[J]. Journal of Dynamical and Control Systems, 2008, 14(1): 33-41. doi: 10.1007/s10883-007-9033-5 [54] KHALIL H K. Nonlinear systems[M]. 3rd ed. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall, 2002. [55] HAN J Q. From PID to active disturbance rejection control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2009, 56(3): 900-906. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2008.2011621 [56] 金辉宇, 张瑞青, 王雷, 等. 线性自抗扰控制参数整定鲁棒性的根轨迹分析[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2018, 35(11): 1648-1653.JIN H Y, ZHANG R Q, WANG L, et al. Root locus analysis on parameter tuning robustness of linear active disturbance rejection control[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2018, 35(11): 1648-1653 (in Chinese). [57] 高志强. 自抗扰控制思想探究[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2013, 30(12): 1498-1510.GAO Z Q. On the foundation of active disturbance rejection control[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2013, 30(12): 1498-1510(in Chinese). [58] CHEN S, XUE W C, HUANG Y. On active disturbance rejection control for nonlinear systems with multiple uncertainties and nonlinear measurement[J]. International Journal of Robust and Nonlinear Control, 2020, 30(8): 3411-3435. [59] SHAO S, GAO Z. On the conditions of exponential stability in active disturbance rejection control based on singular perturbation analysis[J]. International Journal of Control, 2017, 90(10): 2085-2097. [60] ZHANG X Y, ZHANG X C, XUE W C, et al. An overview on recent progress of extended state observers for uncertain systems: Methods, theory, and applications[J]. Advanced Control for Applications, 2021, 3(2): e89. doi: 10.1002/adc2.89 [61] QUAN Q, CAI K Y. Additive decomposition and its applications to internal-model-based tracking[C]//Proceedings of the 48h IEEE Conference on Decision and Control held jointly with 28th Chinese Control Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2009: 817-822. [62] REN J R, QUAN Q, LIU C J, et al. Docking control for probe-drogue refueling: An additive-state-decomposition-based output feedback iterative learning control method[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2020, 33(3): 1016-1025. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2019.11.007 [63] REN J R, QUAN Q, ZHAO L B, et al. Two-degree-of-freedom attitude tracking control for bank-to-turn aerial vehicles: An additive-state-decomposition-based method[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2018, 77: 409-418. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2018.03.025 [64] HOU Z S, WANG Z. From model-based control to data-driven control: Survey, classification and perspective[J]. Information Sciences, 2013, 235: 3-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2012.07.014 [65] 侯忠生. 无模型自适应控制的现状与展望[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2006, 23(4): 586-592.HOU Z S. On model-free adaptive control: The state of the art and perspective[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2006, 23(4): 586-592 (in Chinese). [66] 侯忠生, 许建新. 数据驱动控制理论及方法的回顾和展望[J]. 自动化学报, 2009, 35(6): 650-667. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2009.00650HOU Z S, XU J X. On data-driven control theory: The state of the art and perspective[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2009, 35(6): 650-667 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1004.2009.00650 [67] SUTTON R S, BARTO A G. Reinforcement learning: An introduction[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2018. [68] LIU D R, XU Y C, WEI Q L, et al. Residential energy scheduling for variable weather solar energy based on adaptive dynamic programming[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2018, 5(1): 36-46. doi: 10.1109/JAS.2017.7510739 [69] NA J, HERRMANN G. Online adaptive approximate optimal tracking control with simplified dual approximation structure for continuous-time unknown nonlinear systems[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2014, 1(4): 412-422. doi: 10.1109/JAS.2014.7004668 [70] MURRAY J J, COX C J, LENDARIS G G, et al. Adaptive dynamic programming[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews), 2002, 32(2): 140-153. doi: 10.1109/TSMCC.2002.801727 [71] WANG Q, GONG L G, DONG C Y, et al. Morphing aircraft control based on switched nonlinear systems and adaptive dynamic programming[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2019, 93: 105325. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2019.105325 [72] LIN X B, YU Y, SUN C Y. Supplementary reinforcement learning controller designed for quadrotor UAVs[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 26422-26431. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2901295 [73] LIN X B, LIU J, YU Y, et al. Event-triggered reinforcement learning control for the quadrotor UAV with actuator saturation[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 415: 135-145. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.07.042 [74] 孙明轩, 黄宝健. 迭代学习控制[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 1999.SUN M X, HUANG B J. Iterative learning control[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 1999(in Chinese). [75] XU J X, TAN Y. Linear and nonlinear iterative learning control[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2003. [76] 许建新, 侯忠生. 学习控制的现状与展望[J]. 自动化学报, 2005, 31(6): 943-955.XU J X, HOU Z S. On learning control: the state of the art and perspective[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2005, 31(6): 943-955(in Chinese). [77] ASTROM K J, HAGGLUND T. PID controllers: Theory, design, and tuning[M]. Durham: Instrument Society of America, 1995. [78] ZHANG J K, GUO L. Theory and design of PID controller for nonlinear uncertain systems[J]. IEEE Control Systems Letters, 2019, 3(3): 643-648. doi: 10.1109/LCSYS.2019.2915306 [79] ZHAO C, GUO L. PID controller design for second order nonlinear uncertain systems[J]. Science China Information Sciences, 2017, 60(2): 022201. doi: 10.1007/s11432-016-0879-3 [80] HOU Z S, XIONG S S. On model-free adaptive control and its stability analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2019, 64(11): 4555-4569. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2019.2894586 [81] 侯忠生. 非参数模型及其自适应控制理论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1999.HOU Z S. Nonparametric model and its adaptive control theory[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1999(in Chinese). [82] HUI Y, CHI R H, HUANG B, et al. Observer-based sampled-data model-free adaptive control for continuous-time nonlinear nonaffine systems with input rate constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 51(12): 7813-7822. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2020.2982491 [83] LIN N, CHI R H, HUANG B, et al. Event-triggered nonlinear iterative learning control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(11): 5118-5128. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3027000 [84] CHI R H, LI H Y, SHEN D, et al. Enhanced P-type control: Indirect adaptive learning from set-point updates[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(3): 1600-1613. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2022.3154347 [85] LI X D, LI P. Stability of time-delay systems with impulsive control involving stabilizing delays[J]. Automatica, 2021, 124: 109336. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2020.109336 [86] DEGRAVE J, FELICI F, BUCHLI J, et al. Magnetic control of Tokamak plasmas through deep reinforcement learning[J]. Nature, 2022, 602: 414-419. doi: 10.1038/s41586-021-04301-9 [87] CHEN L, QUAN Q. Reinforcement learning for non-affine nonlinear non-minimum phase system tracking under additive-state-decomposition-based control framework[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 12th Data Driven Control and Learning Systems Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023. 期刊类型引用(3)
1. 贾静焕,骆晨,孙志华,詹中伟,赵明亮. 航空发动机典型连接件腐蚀仿真分析. 中国腐蚀与防护学报. 2024(04): 979-986 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 吴正江,李开伟,毛旭耀,张润林,伍健,侯健,宋卿源,张迪. 新型平衡舵阴极保护设计与保护效果评价. 装备环境工程. 2024(06): 111-118 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 王育鑫,吴波,戴乐阳,胡科峰,吴建华,杨阳,闫福磊,张贤慧. 低合金钢在模拟海洋低温环境下的电偶腐蚀研究. 中国腐蚀与防护学报. 2022(06): 894-902 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(2)
-







 下载:
下载:
 百度学术
百度学术

