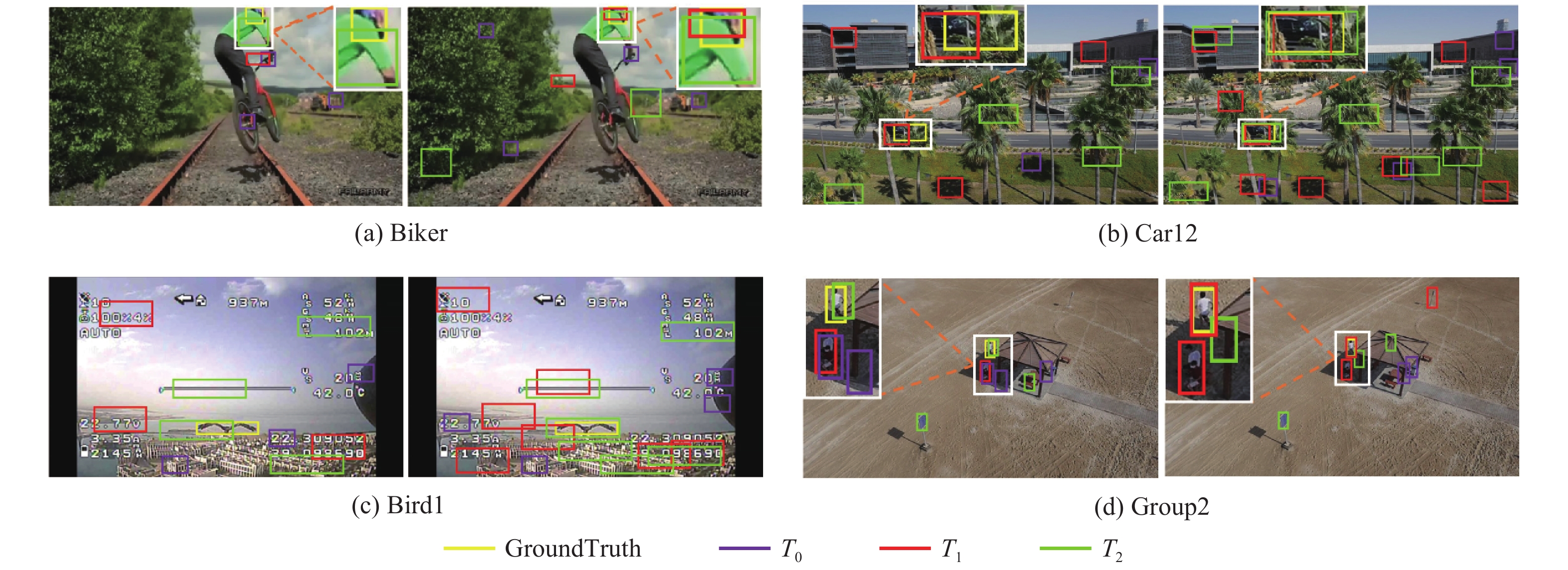
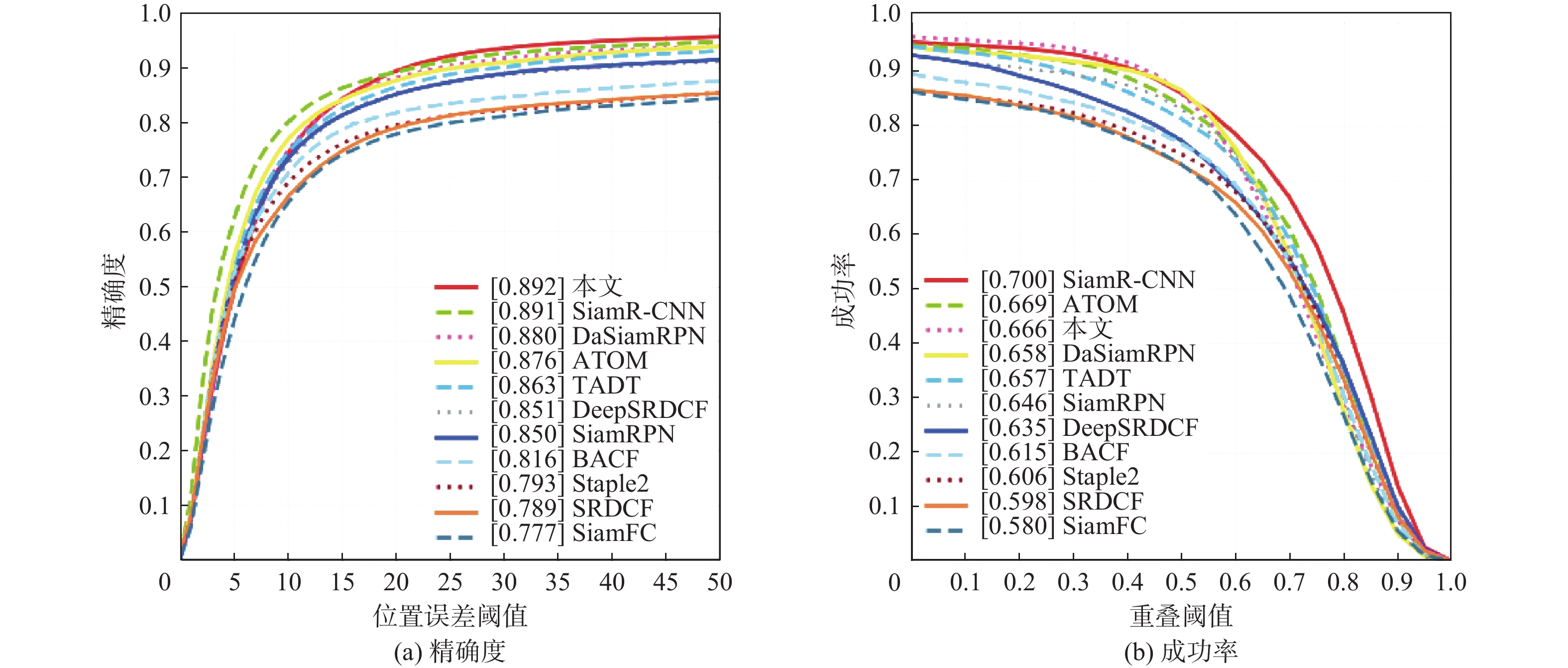
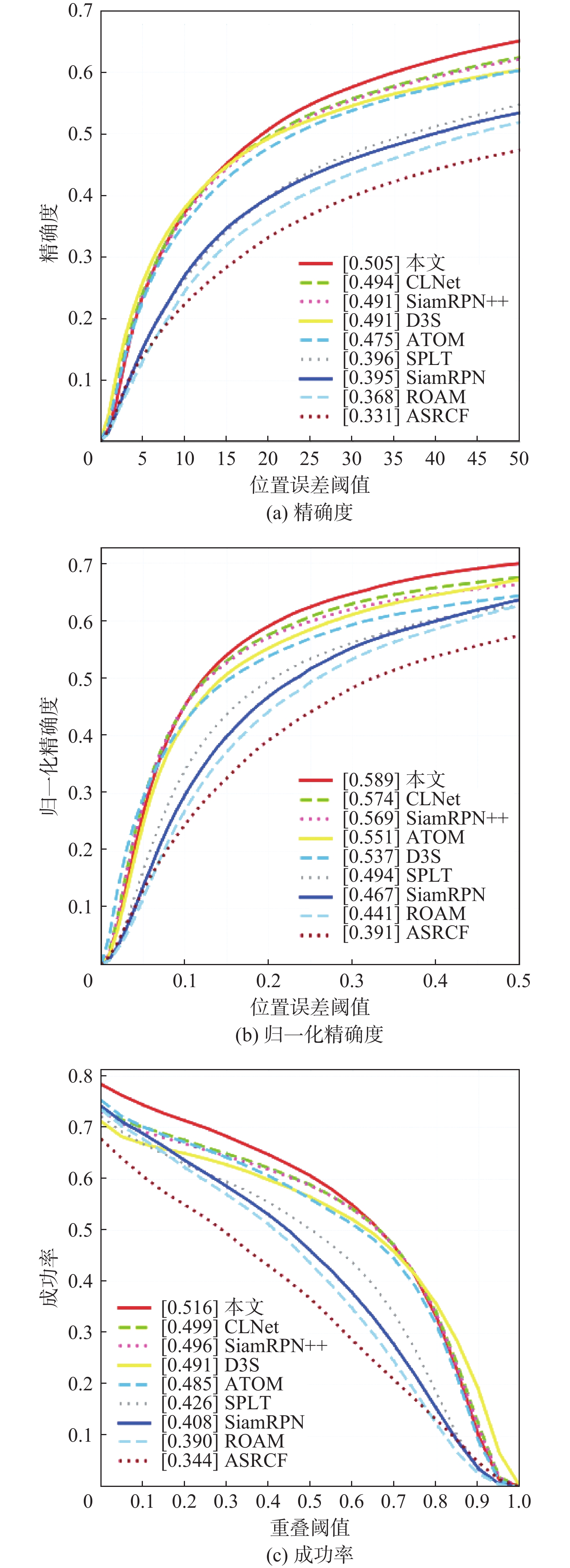
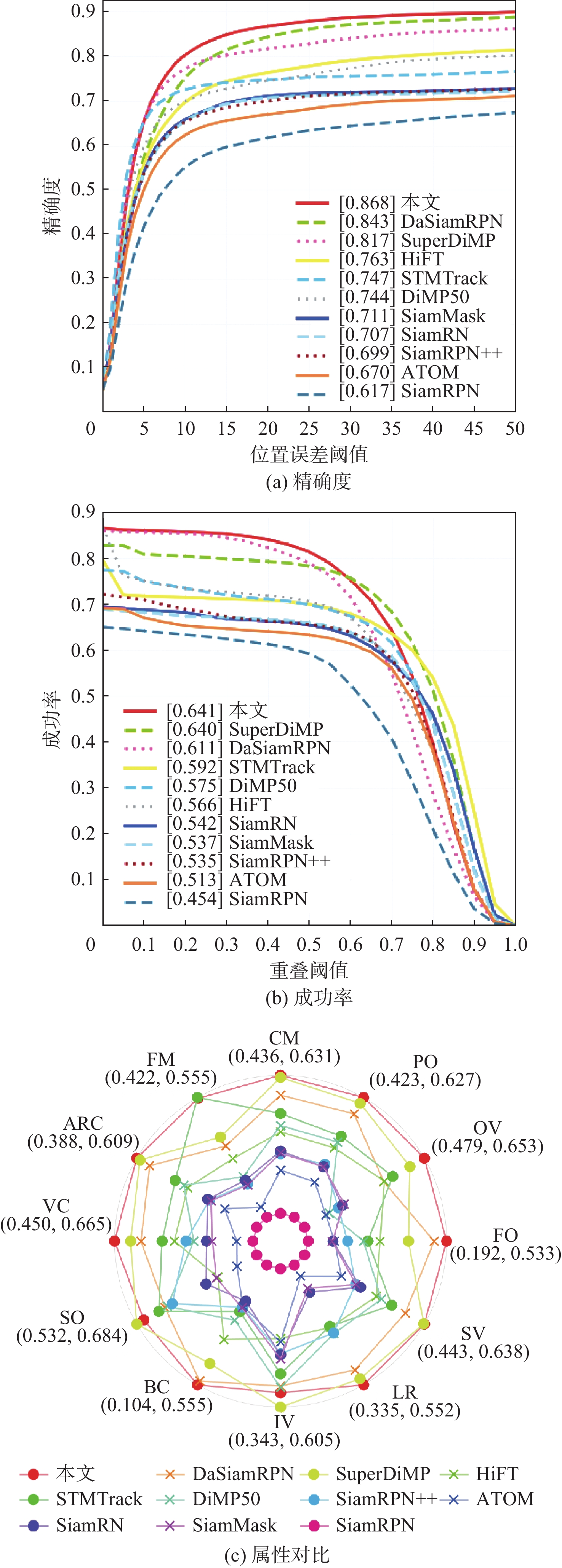
-
摘要:
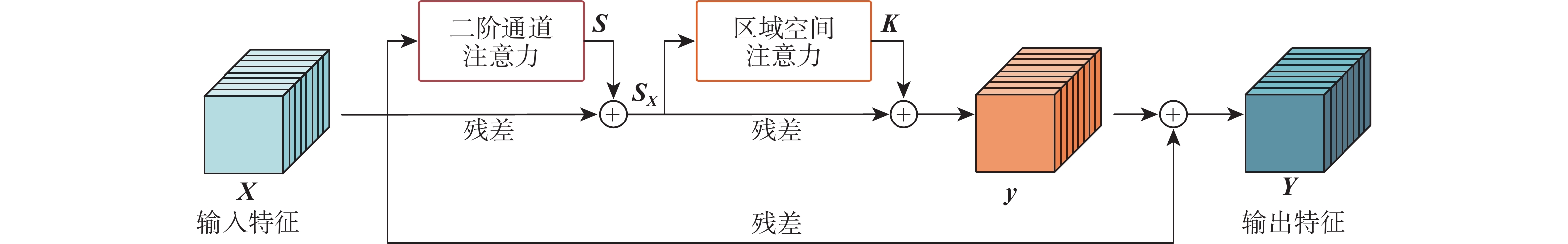
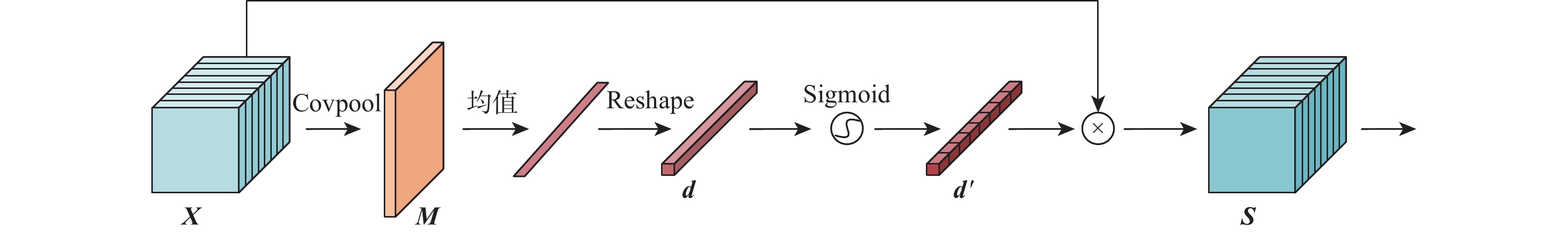
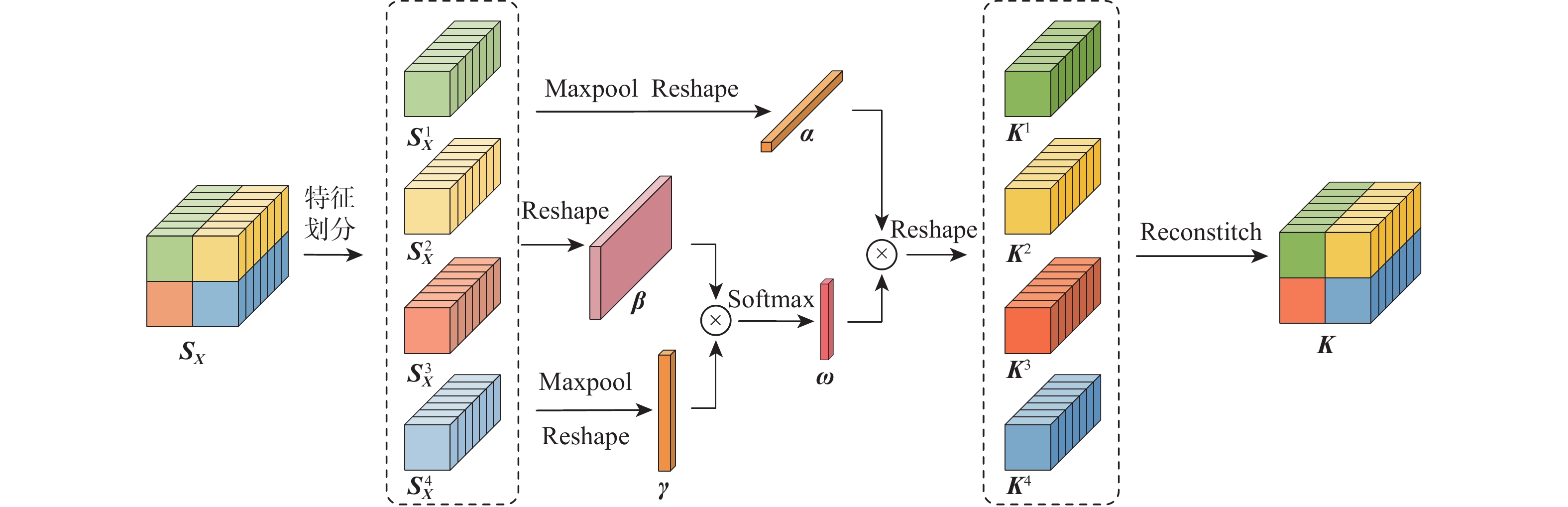
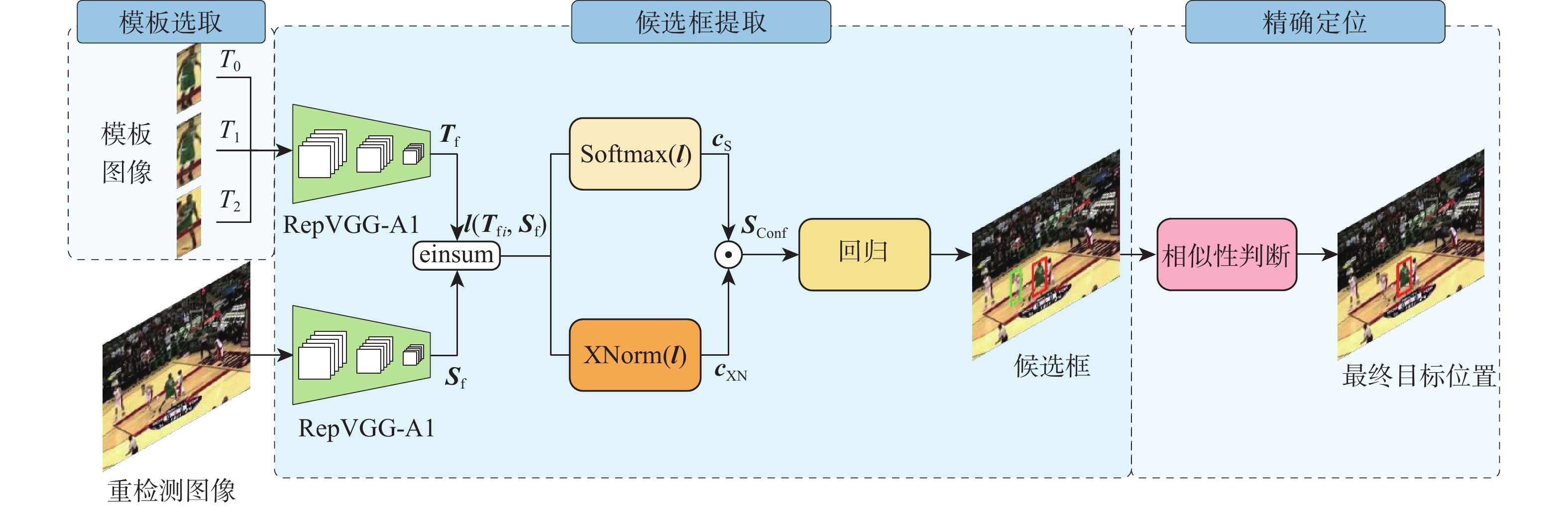
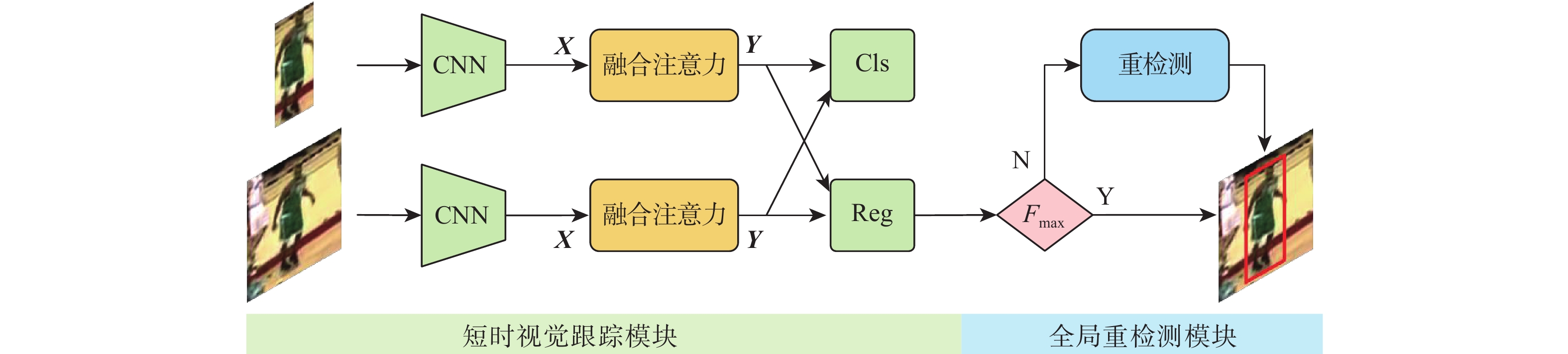
在目标尺寸变化、遮挡和出视场等复杂长时视觉跟踪环境下,现有基于深度学习的视觉跟踪算法很难对目标进行实时准确的跟踪。针对该问题,提出一种快速的长时视觉跟踪算法,该算法由一个快速短时视觉跟踪算法和一个快速全局重检测模块组成。在基准算法SiamRPN中加入二阶通道与区域空间融合的注意力模块作为短时视觉跟踪算法,在保证快速性的同时,提高算法的短时视觉跟踪精确度和成功率;为使改进后的短时视觉跟踪算法具有快速的长时视觉跟踪能力,在算法中加入提出的基于模板匹配的全局重检测模块,该模块使用轻量级网络和快速的相似度判断方法,加快重检测速率。在OTB100、LaSOT、UAV20L、VOT2018-LT、VOT2020-LT 等5个数据集上进行测试,实验结果表明,所提算法在长时视觉跟踪中具有优越的跟踪性能,平均速度达104帧/s。
Abstract:Current deep learning-based visual tracking algorithms have difficulty tracking the target accurately in real-time in complex long-term monitoring environments including target size change, occlusion, and out-of-view. To solve this problem, a fast long-term visual tracking algorithm is proposed, which consists of a fast short-term tracking algorithm and a fast global re-detection module. First, as a short-term tracking algorithm, the attention module of second-order channel and region spatial fusion is added to the base algorithm SiamRPN. Then, in order to make the improved short-term tracking algorithm have a fast long-term tracking ability, the global re-detection module based on template matching proposed in this paper is added to the algorithm, which uses a lightweight network and fast similarity judgment method to speed up the re-detection rate. The proposed algorithm is tested on five datasets (OTB100, LaSOT, UAV20L, VOT2018-LT, and VOT2020-LT). With an average tracking speed of 104 frames per second, the experimental findings demonstrate the algorithm's outstanding long-term tracking performance.
-
表 1 OTB100数据集上残差连接对跟踪性能的影响
Table 1. Effect of residual joining on tracking performance on OTB100 dataset
算法 精确度 成功率 SiamRPN 0.851 0.637 SiamRPN+融合注意力模块−残差 0.876 0.653 SiamRPN+融合注意力模块 0.888 0.665 表 2 OTB100数据集上特征划分区域对跟踪性能的影响
Table 2. Effect of feature division on tracking performance on OTB100 dataset
算法 精确度 成功率 SiamRPN 0.851 0.637 SiamRPN+传统空间注意力 0.857 0.641 SiamRPN+区域空间注意力 0.866 0.649 表 3 VOT2020-LT数据集上不同阈值的判定精确度
Table 3. Determination accuracy of different thresholds on VOT2020-LT dataset
阈值 精确度 0.91 0.660 0.93 0.665 0.95 0.673 0.97 0.676 0.99 0.687 表 4 VOT2020-LT数据集上不同网络对不同属性图像的平均处理时长
Table 4. Average processing time of pictures with different attributes by different networks on VOT2020-LT dataset
s 网络 目标较为清晰 背景复杂 小目标 目标模糊 ResNet50 2.88 6.23 5.91 8.25 VGG16 4.65 8.14 8.02 12.13 GhostNet 1.89 2.51 2.15 2.52 EfficientNet 1.78 2.913 3.16 RepVGG-A1 1.80 2.86 2.33 3.62 表 5 不同网络下重检测模块的复杂度和参数量
Table 5. Complexity and parameter quantity of re-detection module under different networks
网络 复杂度/109 FLOPs 参数量 Re(ResNet50) 4.1 30.53×106 Re(VGG16) 20.5 143.35×106 Re(GhostNet) 0.426 12.3×106 Re(EfficientNet) 2.1 16×106 Re(RepVGG-A1) 2.6 17.78×106 注: FLOPs指浮点运算数。 表 6 在SiamRPN中加入不同网络的重检测模块在LaSOT数据集中的跟踪结果
Table 6. Tracking results of adding re-detection module using different networks in SiamRPN on LaSOT dataset
网络 精确度 归一化
精确度成功率 检测速度/
(帧·s−1)SiamRPN 0.395 0.467 0.408 142 SiamRPN + Re(ResNet50) 0.496 0.579 0.475 95 SiamRPN + Re(VGG16) 0.482 0.561 0.463 77 SiamRPN +Re(GhostNet) 0.417 0.501 0.411 123 SiamRPN +Re(EfficientNet) 0.451 0.535 0.443 115 SiamRPN+Re(RepVGG-A1) 0.480 0.559 0.466 111 表 7 消融实验结果
Table 7. Ablation experiments results
SiamRPN 融合注意力 全局重检测 精确度 归一化精确度 成功率 检测速度/(帧·s−1) √ 0.395 0.467 0.408 142 √ √ 0.424 0.507 0.439 134 √ √ 0.480 0.559 0.466 111 √ √ √ 0.505 0.589 0.516 106 表 8 VOT2018-LT数据集上的F分值比较
Table 8. Comparison of F-score comparison on VOT2018-LT dataset
算法 F分值 SLT 0.456 SiamVGG 0.459 SiamRPN 0.499 SYT 0.509 ATOM 0.510 MMLT 0.546 STMTrack 0.571 DiMP50 0.598 MBMD 0.610 SPLT 0.616 本文 0.625 表 9 VOT2020-LT数据集上的F分值比较
Table 9. Comparison of F-score comparison on VOT2020-LT dataset
算法 F分值 FuCoLoT 0.409 D3S 0.438 SiamRN 0.444 SiamRPN 0.462 ASINT 0.503 STMTrack 0.550 mbdet 0.563 DiMP50 0.567 本文 0.579 表 10 长时视觉跟踪算法平均速度对比
Table 10. Average speed comparison of long-term visual tracking algorithms
算法 平均速度/(帧·s−1) mbdet 2 MBMD 2.7 SiamR-CNN 4.7 MMLT 6.1 FuColoT 6.8 LTMU 13 RLT-DiMP 14.2 SLT 14.9 SYT 17.8 ASINT 19 SPLT 25.7 本文 104 -
[1] 李玺, 查宇飞, 张天柱, 等. 深度学习的目标跟踪算法综述[J]. 中国图象图形学报, 2019, 24(12): 2057-2080. doi: 10.11834/jig.190372LI X, ZHA Y F, ZHANG T Z, et al. Survey of visual object tracking algorithms based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Image and Graphics, 2019, 24(12): 2057-2080(in Chinese). doi: 10.11834/jig.190372 [2] 刘芳, 孙亚楠, 王洪娟, 等. 基于残差学习的自适应无人机目标跟踪算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(10): 1874-1882.LIU F, SUN Y N, WANG H J, et al. Adaptive UAV target tracking algorithm based on residual learning[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(10): 1874-1882(in Chinese). [3] 张诚, 马华东, 傅慧源. 基于时空关联图模型的视频监控目标跟踪[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2015, 41(4): 713-720.ZHANG C, MA H D, FU H Y. Object tracking in surveillance videos using spatial-temporal correlation graph model[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2015, 41(4): 713-720(in Chinese). [4] LUKEŽIČ A, ZAJC L Č, VOJÍŘ T, et al. FuCoLoT–A fully-correlational long-term tracker[C]//Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 595-611. [5] 王鑫, 侯志强, 余旺盛, 等. 基于深度稀疏学习的鲁棒视觉跟踪[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2017, 43(12): 2554-2563.WANG X, HOU Z Q, YU W S, et al. Robust visual tracking based on deep sparse learning[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017, 43(12): 2554-2563(in Chinese). [6] 蒲磊, 冯新喜, 侯志强, 等. 基于级联注意力机制的孪生网络视觉跟踪算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(12): 2302-2310.PU L, FENG X X, HOU Z Q, et al. Siamese network visual tracking algorithm based on cascaded attention mechanism[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(12): 2302-2310(in Chinese). [7] LI B, YAN J, WU W, et al. High performance visual tracking with Siamese region proposal network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 8971-8980. [8] LI B, WU W, WANG Q, et al. SiamRPN++: Evolution of Siamese visual tracking with very deep networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 4277-4286. [9] DANELLJAN M, BHAT G, KHAN F S, et al. ATOM: Accurate tracking by overlap maximization[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 4655-4664. [10] CHENG S Y, ZHONG B N, LI G R, et al. Learning to filter: Siamese relation network for robust tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 4419-4429. [11] ZHU Z, WANG Q, LI B, et al. Distractor-aware Siamese networks for visual object tracking[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 103-119. [12] ZHANG Y H, WANG D, WANG L J, et al. Learning regression and verification networks for long-term visual tracking[EB/OL]. (2018-11-19)[2022-07-01]. [13] YAN B, ZHAO H J, WANG D, et al. ‘Skimming-Perusal’ tracking: A framework for real-time and robust long-term tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 2385-2393. [14] VOIGTLAENDER P, LUITEN J, TORR P H S, et al. SiamR-CNN: Visual tracking by re-detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 6577-6587. [15] FAN H, LIN L T, YANG F, et al. LaSOT: A high-quality benchmark for large-scale single object tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 5369-5378. [16] MUELLER M, SMITH N, GHANEM B. A benchmark and simulator for UAV tracking[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 445-461. [17] LUKEŽIČ A, ZAJC L Č, VOJÍŘ T, et al. Now you see me: Evaluating performance in long-term visual tracking[EB/OL]. (2018-04-19)[2022-07-01]. [18] KRISTAN M, LEONARDIS A, MATAS J, et al. The eighth visual object tracking VOT2020 challenge results[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 547-601. [19] WU Y, LIM J, YANG M H. Online object tracking: A benchmark[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 2411-2418. [20] KRISTAN M, LEONARDIS A, MATAS J, et al. The sixth visual object tracking VOT2018 challenge results[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Berlin: Springer, 2018. [21] KALAL Z, MIKOLAJCZYK K, MATAS J. Tracking-learning-detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 34(7): 1409-1422. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2011.239 [22] ZHU G, PORIKLI F, LI H D. Beyond local search: Tracking objects everywhere with instance-specific proposals[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 943-951. [23] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84-90. [24] WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 3-19. [25] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [26] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 7132-7141. [27] LI P H, XIE J T, WANG Q L, et al. Is second-order information helpful for large-scale visual recognition?[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2089-2097. [28] LIN T Y, ROYCHOWDHURY A, MAJI S. Bilinear CNN models for fine-grained visual recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1449-1457. [29] JADERBERG M, SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A, et al. Spatial transformer networks[EB/OL]. (2016-02-04) [2022-07-01]. [30] WANG X L, GIRSHICK R, GUPTA A, et al. Non-local neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 7794-7803. [31] CHENG J, WU Y, ABDALMAGEED W, et al. QATM: Quality-aware template matching for deep learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 11553-11562. [32] HAN K, WANG Y H, TIAN Q, et al. GhostNet: More features from cheap operations[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1577-1586. [33] TAN M X, LE Q V. EfficientNet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks[EB/OL]. (2020-09-11)[2022-07-01]. [34] DING X H, ZHANG X Y, MA N N, et al. RepVGG: Making VGG-style ConvNets great again[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 13728-13737. [35] SONG J G. UFO-ViT: High performance linear vision transformer without softmax[EB/OL]. (2020-09-11) [2022-07-01]. [36] IANDOLA F N, HAN S, MOSKEWICZ M W, et al. SqueezeNet: AlexNet-level accuracy with 50x fewer parameters and <0.5 MB model size[EB/OL]. (2016-11-04) [2022-07-01]. [37] RUSSAKOVSKY O, DENG J, SU H, et al. ImageNet large scale visual recognition challenge[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2015, 115(3): 211-252. doi: 10.1007/s11263-015-0816-y [38] LIN T Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common objects in context[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2014: 740-755. [39] REAL E, SHLENS J, MAZZOCCHI S, et al. YouTube-BoundingBoxes: A large high-precision human-annotated data set for object detection in video[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 7464-7473. [40] BERTINETTO L, VALMADRE J, HENRIQUES J F, et al. Fully-convolutional Siamese networks for object tracking[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 850-865. [41] LI X, MA C, WU B Y, et al. Target-aware deep tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1369-1378. [42] DANELLJAN M, HÄGER G, KHAN F S, et al. Learning spatially regularized correlation filters for visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 4310-4318. [43] GALOOGAHI H K, FAGG A, LUCEY S. Learning background-aware correlation filters for visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1144-1152. [44] BERTINETTO L, VALMADRE J, GOLODETZ S, et al. Staple: Complementary learners for real-time tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1401-1409. [45] LUKEŽIČ A, MATAS J, KRISTAN M. D3S–A discriminative single shot segmentation tracker[C]// Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 7131-7140. [46] DONG X P, SHEN J B, SHAO L, et al. CLNet: A compact latent network for fast adjusting Siamese trackers[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 378-395. [47] YANG T Y, XU P F, HU R B, et al. ROAM: Recurrently optimizing tracking model[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 6717-6726. [48] DAI K N, WANG D, LU H C, et al. Visual tracking via adaptive spatially-regularized correlation filters[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 4665-4674. [49] CAO Z A, FU C H, YE J J, et al. HiFT: Hierarchical feature transformer for aerial tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 15457-15466. [50] FU Z H, LIU Q J, FU Z H, et al. STMTrack: Template-free visual tracking with space-time memory networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 13769-13778. [51] BHAT G, DANELLJAN M, VAN GOOL L, et al. Learning discriminative model prediction for tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 6181-6190. [52] WANG Q, ZHANG L, BERTINETTO L, et al. Fast online object tracking and segmentation: A unifying approach[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1328-1338. [53] LI Y H, ZHANG X F, CHEN D M. SiamVGG: Visual tracking using deeper Siamese networks[EB/OL]. (2022-06-04)[2022-07-01]. [54] CHOI S, LEE J, LEE Y, et al. Robust long-term object tracking via improved discriminative model prediction[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 602-617. [55] DAI K N, ZHANG Y H, WANG D, et al. High-performance long-term tracking with meta-updater[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 6297-6306. -







 下载:
下载: