-
摘要:
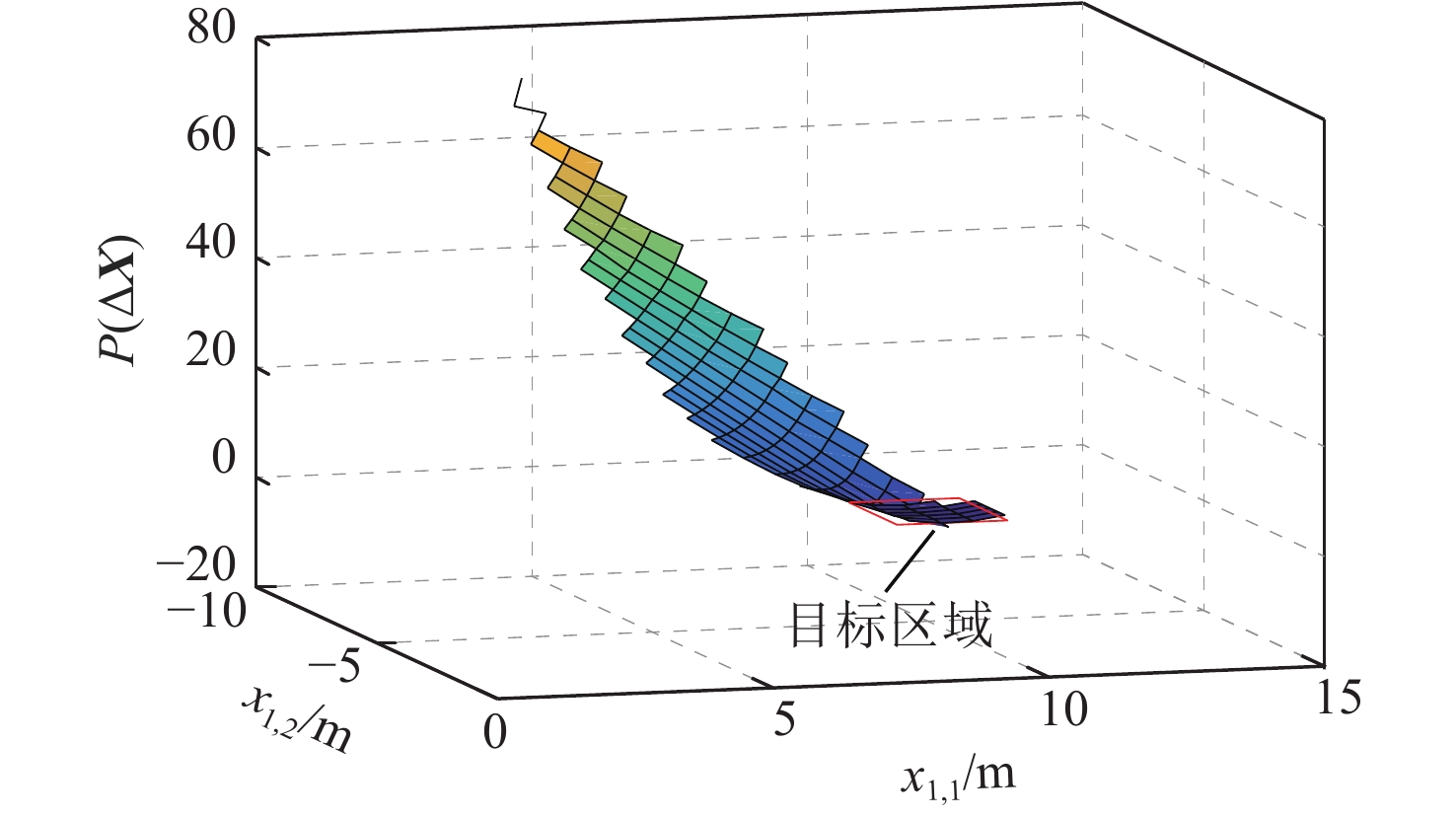
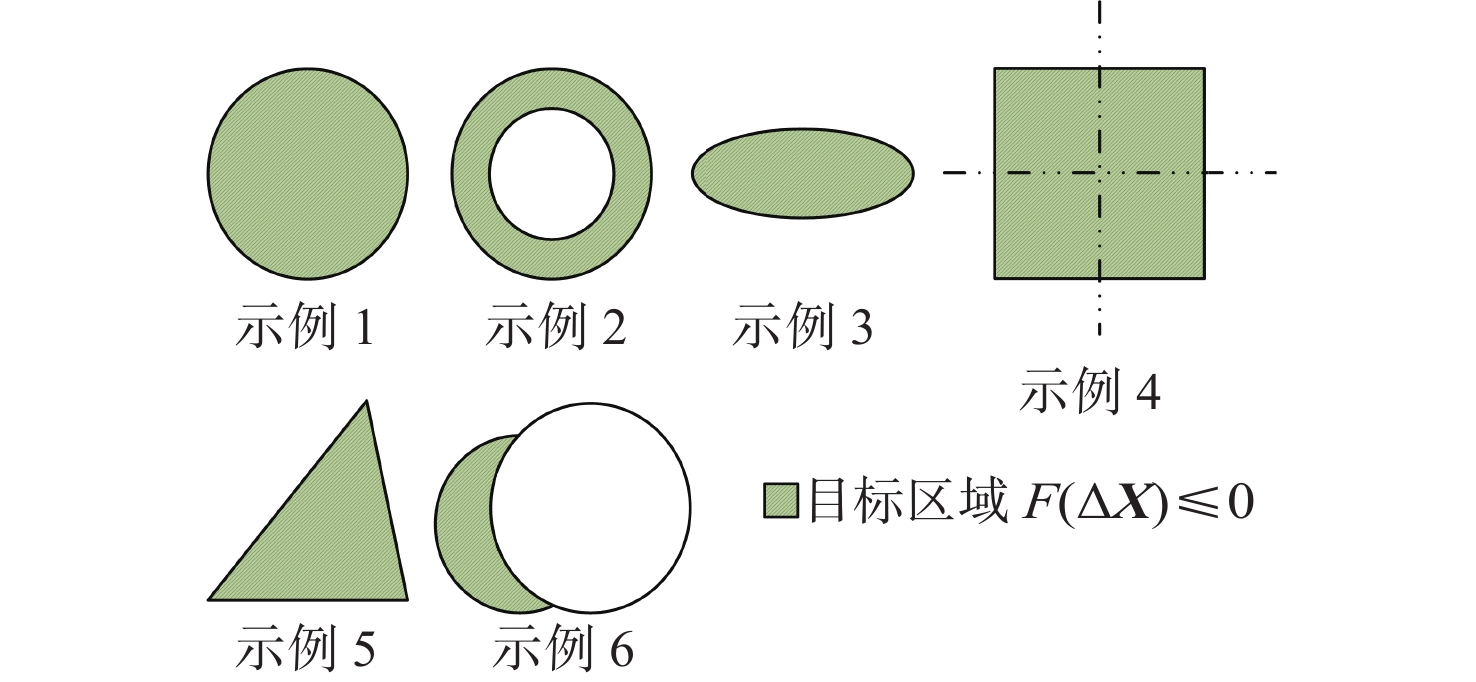
针对一类参数严格反馈型不确定非线性系统,考虑存在外界干扰的情况下,设计一种基于反推方法的自适应滑模区域到达控制器,提高系统对非匹配不确定性及未知干扰的鲁棒性。与传统的设定点控制或位置控制不同,区域到达算法的控制目标是一个以期望点为中心的目标区域。所设计控制器综合了人工势场法、自适应控制、反推技术、滑模控制和Lyapunov方法。利用人工势场法设计目标势能函数,将区域误差引入势能函数中,结合Lyapunov方法,可以实现对目标区域的到达跟踪控制。采用基于反推的区域控制思想,将高阶整体模型分解为低阶子系统,并分别设计相应的滑模面,同时在前
n -1步中结合自适应律,能够在线估计非线性系统的不确定参数项,增加所设计控制器的适用性。基于Lyapunov理论证明闭环系统的全局渐近稳定性,仿真结果表明:所设计控制器有效。Abstract:In this paper, considering the existence of external disturbances, an adaptive backstepping-based sliding mode region reaching controller is designed for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems in parametric strict-feedback form. The robustness of the system for mismatched uncertainties and unknown disturbances was recovered and strengthened. The designed controller is based on the fusion of the artificial potential field method, adaptive control, backstepping techniques, sliding mode control and the Lyapunov synthesis approach. The control target in the region reaching control technique is created as a desirable spatial region, which sets it apart from the conventional set-point control or position control. The target potential function and new Lyapunov functions are designed with the region control error in mind using the artificial potential field method in order to achieve the goal of region reaching control. The backstepping method can be used to break down large and high-order nonlinear systems into smaller, more manageable subsystems, making the suggested approach more applicable to real-world scenarios. The online estimation of the unknown parameters is obtained by the adaptive method which is combined with the first
n -1 steps of the backstepping method. The Lyapunov theorem is utilized to prove the globally asymptotic stability of the closed-loop system, and simulation results are presented to show the effectiveness of the designed controller. -
[1] KRUPA P, LIMON D, ALAMO T. Harmonic based model predictive control for set-point tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2022, 67(1): 48-62. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2020.3047579 [2] ZHANG G Q, ZHANG X K. A novel DVS guidance principle and robust adaptive path-following control for underactuated ships using low frequency gain-learning[J]. ISA Transactions, 2015, 56: 75-85. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2014.12.002 [3] YAN Z P, ZHANG M Y, ZHANG C, et al. Decentralized formation trajectory tracking control of multi-AUV system with actuator saturation[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 255: 111423. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.111423 [4] SHAO X D, HU Q L, GUO L. Adaptive spacecraft attitude tracking control with guaranteed transient performance[C]//Proceedings of the Chinese Control Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 9442-9447. [5] ZHANG H G, ZHANG X K, CAO T, et al. Active disturbance rejection control for ship path following with Euler method[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 247: 110516. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2021.110516 [6] AILON A, AROGETI S. On set-point control of a quadrotor-type helicopter with a suspended load[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Control, Automation and Robotics. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 194-199. [7] KOWALCZYK W, PRZYBYLA M, KOZLOWSKI K. Set-point control of mobile robot with obstacle detection and avoidance using navigation function-experimental verification[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2017, 85(3): 539-552. [8] ANNAMALAI A S K, SUTTON R, YANG C, et al. Robust adaptive control of an uninhabited surface vehicle[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2015, 78(2): 319-338. [9] AILON A. Simple tracking controllers for autonomous VTOL aircraft with bounded inputs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2010, 55(3): 737-743. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2010.2040493 [10] CHEAH C C, SUN Y C. Region reaching control for robots with uncertain kinematics and dynamics[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2006: 2577-2582. [11] CHEAH C C, WANG D Q. Region reaching control of robots: Theory and experiments[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2005, 974-979. [12] BOUTERAA Y, BEN ABDALLAH I, GHOMMAM J. Task-space region-reaching control for medical robot manipulator[J]. Computers & Electrical Engineering, 2018, 67: 629-645. [13] YU J W, ZHANG X H, JI J C, et al. Region-reaching control of a flexible-joint manipulator[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 2020, 142(11): 114503. doi: 10.1115/1.4047697 [14] 杨沁林, 张劲. 机械臂目标区域跟踪防撞控制[J]. 四川大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 59(3): 77-86.YANG Q L, ZHANG J. Region tracking and collision avoidance control for the manipulator[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 59(3): 77-86 (in Chinese). [15] CONTI R, FANELLI F, MELI E, et al. A free floating manipulation strategy for Autonomous Underwater Vehicles[J]. Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2017, 87: 133-146. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2016.09.018 [16] ISMAIL Z H. Region boundary-based control scheme for an underwater vehicle with an edge-based segmentation approach[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 2137-2142. [17] ISMAIL Z H, DUNNIGAN M W. Tracking control scheme for an underwater vehicle-manipulator system with single and multiple sub-regions and sub-task objectives[J]. IET Control Theory & Applications, 2011, 5(5): 721-735. [18] ISMAIL Z H, DUNNIGAN M W. A region boundary-based control scheme for an autonomous underwater vehicle[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2011, 38(17-18): 2270-2280. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2011.10.002 [19] MUKHERJEE K, KAR I N, BHATT R K P. Region tracking control of an autonomous underwater vehicle without velocity measurement[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Modelling, Identification & Control. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 213-218. [20] ISMAIL Z H, MOKHAR M B M, PUTRANTI V W E, et al. A robust dynamic region-based control scheme for an autonomous underwater vehicle[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2016, 111: 155-165. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2015.10.052 [21] CHEAH C C, WANG D Q, SUN Y C. Region-reaching control of robots[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2007, 23(6): 1260-1264. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2007.909808 [22] KHALIL H K. Nonlinear systems[M]. 2nd ed. Upper Saddle River: Prentice Hall, 1996. [23] PARK J H, JONG LEE Y. Robust visual servoing for motion control of the ball on a plate[J]. Mechatronics, 2003, 13(7): 723-738. doi: 10.1016/S0957-4158(02)00039-9 [24] JANKOVIC M, SEPULCHRE R, KOKOTOVIC P V. Constructive Lyapunov stabilization of nonlinear cascade systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1996, 41(12): 1723-1735. doi: 10.1109/9.545712 [25] WANG N, SUN J C, HAN M, et al. Adaptive approximation-based regulation control for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems without feedback linearizability[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2018, 29(8): 3747-3760. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2017.2738918 [26] ZHAO X D, WANG X Y, ZONG G D, et al. Adaptive neural tracking control for switched high-order stochastic nonlinear systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2017, 47(10): 3088-3099. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2017.2684218 [27] SUN W, SU S F, WU Y Q, et al. Adaptive fuzzy control with high-order barrier Lyapunov functions for high-order uncertain nonlinear systems with full-state constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2020, 50(8): 3424-3432. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2018.2890256 [28] MAN Y C, LIU Y G. Global adaptive stabilization and practical tracking for nonlinear systems with unknown powers[J]. Automatica, 2019, 100: 171-181. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2018.11.011 [29] YOUNG K D, UTKIN V I, OZGUNER U. A control engineer’s guide to sliding mode control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 1999, 7(3): 328-342. doi: 10.1109/87.761053 [30] ZHAO D Y, LI S Y, ZHU Q M. Output feedback terminal sliding mode control for a class of second order nonlinear systems[J]. Asian Journal of Control, 2013, 15(1): 237-247. doi: 10.1002/asjc.500 [31] 华森, 张天平, 朱秋琴, 等. 带有未知死区的机器人自适应滑模控制[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 40(S1): 102-107.HUA S, ZHANG T P, ZHU Q Q, et al. Adaptive sliding mode control of robot with unknown dead zone[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2009, 40(S1): 102-107 (in Chinese). [32] 陈志梅, 王贞艳, 张井岗. 滑模变结构控制理论及应用[M]. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2012.CHEN Z M, WANG Z Y, ZHANG J G. Sliding mode variable structure control theory and application[M]. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2012 (in Chinese). [33] KRSTIC M, KANELLAKOPOULOS I, KOKOTOVIC P V. Nonlinear design of adaptive controllers for linear systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1994, 39(4): 738-752. doi: 10.1109/9.286250 [34] KRSTIC M, KANELLAKOPOULOS I, KOKOTOVIC P V. Nonlinear and adaptive control design[M]. New York: Wiley, 1995. [35] YU J P, SHI P, ZHAO L. Finite-time command filtered backstepping control for a class of nonlinear systems[J]. Automatica, 2018, 92: 173-180. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2018.03.033 [36] 曹伟, 乔金杰, 孙明. 永磁直线电机扰动估计与补偿的位置反步控制[J]. 控制与决策, 2020, 35(6): 1409-1414.CAO W, QIAO J J, SUN M. Backstepping control of disturbance estimation and compensation for permanent magnet linear motor[J]. Control and Decision, 2020, 35(6): 1409-1414(in Chinese). [37] 王坚浩, 胡剑波. 一类非匹配不确定非线性系统的鲁棒跟踪控制[J]. 控制与决策, 2011, 26(5): 727-731.WANG J H, HU J B. Robust tracking control for a class of nonlinear systems with unmatched uncertainties[J]. Control and Decision, 2011, 26(5): 727-731(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: