Time-varying frequency identification of space solar power station based on variable forgetting factor
-
摘要:
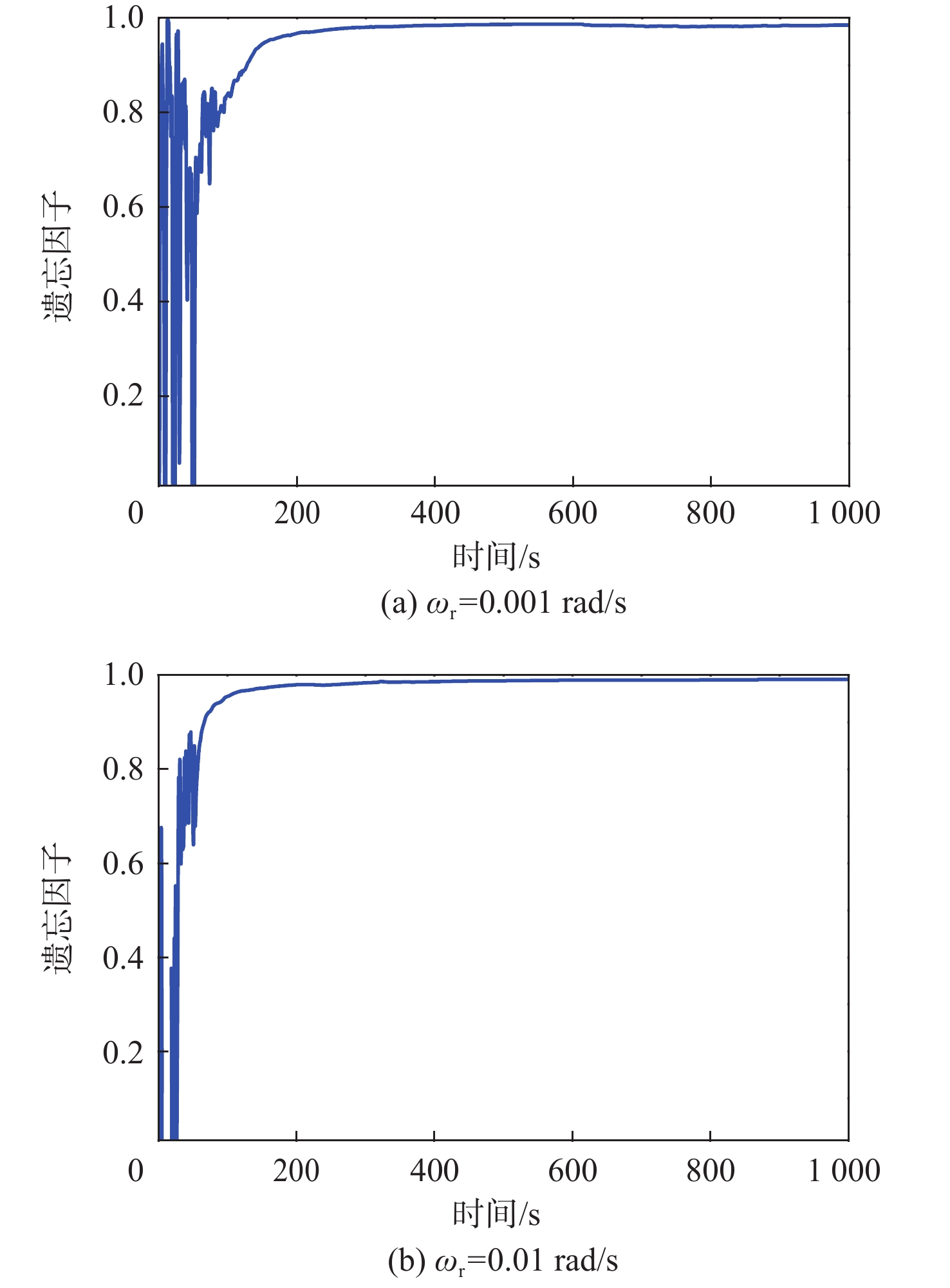
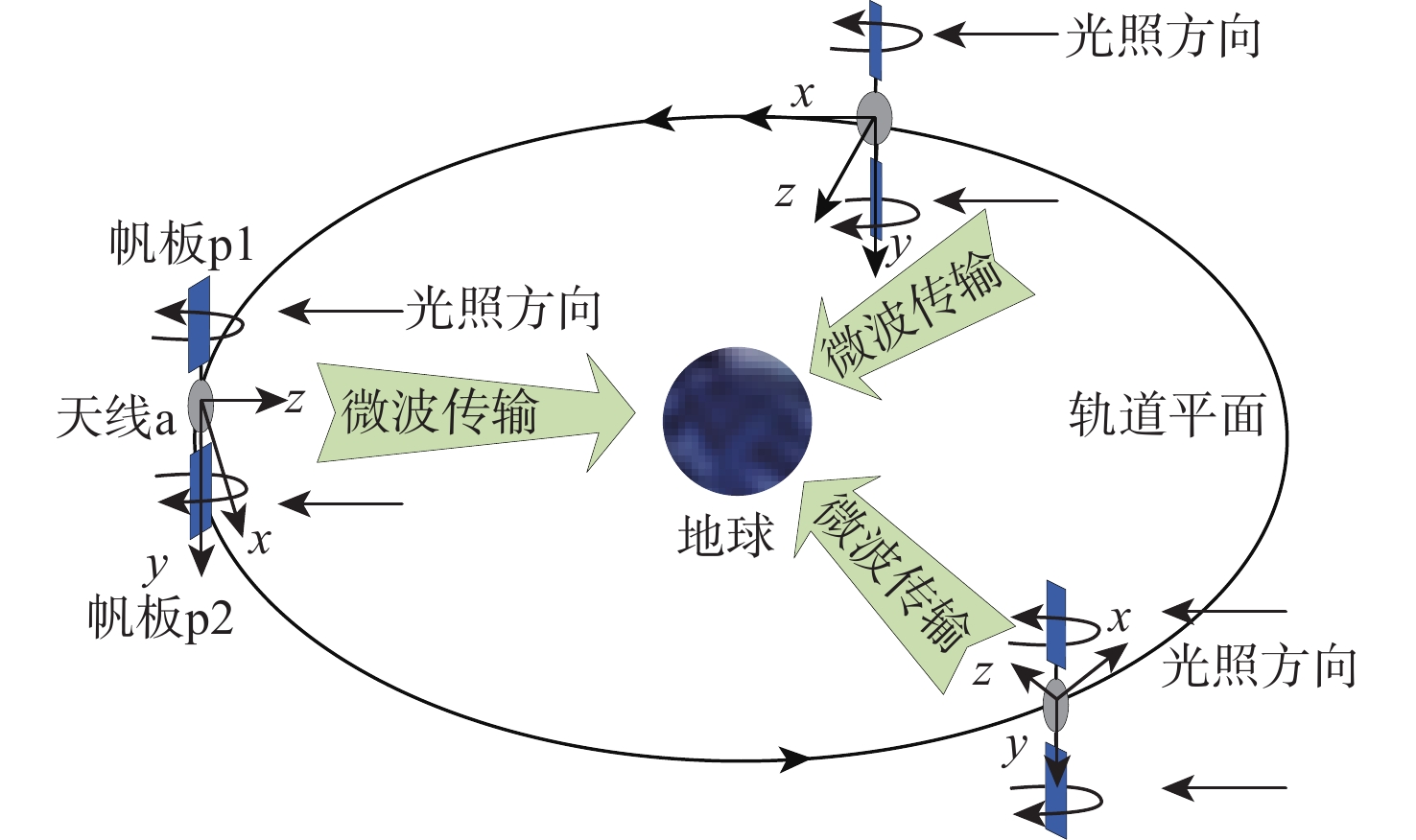
考虑空间太阳能电站(SSPS)在轨运行时帆板旋转所导致的系统变构型特征,提出一种变遗忘因子广义子空间跟踪器(VFF-GYAST)递推辨识方法,在轨辨识该时变动力学系统的模态频率参数,以提高GYAST方法对于这类时变系统的跟踪能力。基于模态综合技术和子结构方法,建立多旋转关节构型SSPS(MJ-SSPS)的时变姿态-振动耦合动力学方程;根据投影子空间理论,通过计算系统均方差来确定递推过程中的时变遗忘因子,以提高GYAST方法的跟踪性能并辨识得到系统的时变伪模态频率参数。数值仿真结果表明:所提方法能够有效地识别该大型柔性系统的时变频率参数。与传统的递推子空间方法相比,所提方法具有较高的抗噪声干扰能力,在低量测信噪比时所提方法对于频率辨识结果的相对误差的平均值小于5%,且对时变系统的跟踪性能优于基于固定遗忘因子的原始方法。
Abstract:By considering changes in the structural configuration caused by the rotation of the solar panel in the space solar power station (SSPS) during in-orbit operation, a variable forgetting factor generalized yet another subspace tracker (VFF-GYAST) method was proposed to identify the modal frequency parameters of the time-varying dynamic system in orbit. As a result, the tracking ability of the original GYAST method for the time-varying system was improved. First, the time-varying attitude-vibration coupling dynamic equation of the multirotary-joint SSPS (MJ-SSPS) was established based on modal synthesis technology and the substructure method. Based on the projection subspace theory, the time-varying forgetting factor in the recursive procedure was determined by computing the system’s mean square error, and thus the tracking performance of the original GYAST method was increased, and the time-varying pseudo modal frequency parameters of the system were identified. The computation results of numerical simulation show that the proposed method can effectively identify the time-varying frequency parameters of the large flexible system. Compared with the conventional recursive subspace method, the proposed method has higher noise-immunity ability. When the measured signal-to-noise-ratio is low, the average value of the relative error of the frequency identification results for the proposed method is still smaller than 5%. In addition, the tracking performance of the proposed method for the time-varying system is better than that of the original method with a fixed forgetting factor.
-
表 1 模型的几何和质量属性
Table 1. Geometric and mass properties of model
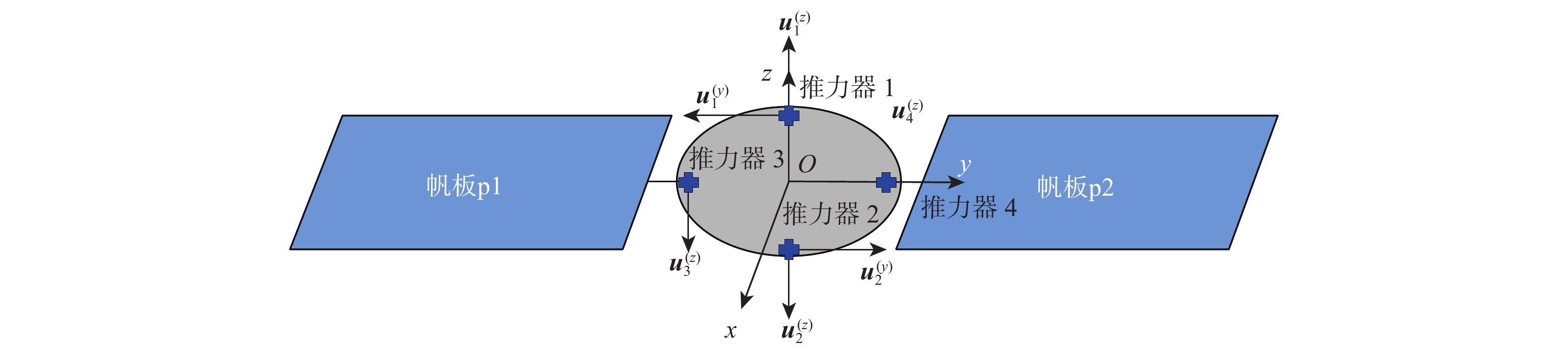
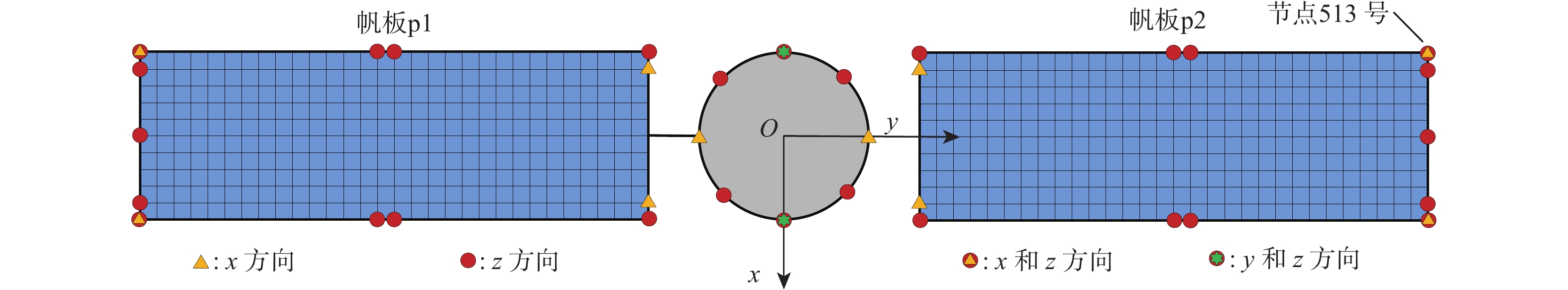
帆板p1和p2的面积/m2 微波天线a的半径/m 微波天线的质量${m_{\text{a}}}$/kg 帆板p1和p2的质量${m_{{\text{p}}1}}$与${m_{{\text{p2}}}}$/kg 帆板转动速度${\omega _{\text{r}}}$/(rad·s−1) 3000 ×1000 500 4×106 3×106 0.001 表 2 MJ-SSPS中每个部件的前10阶模态频率
Table 2. The first 10 order modal frequencies of each component in MJ-SSPS
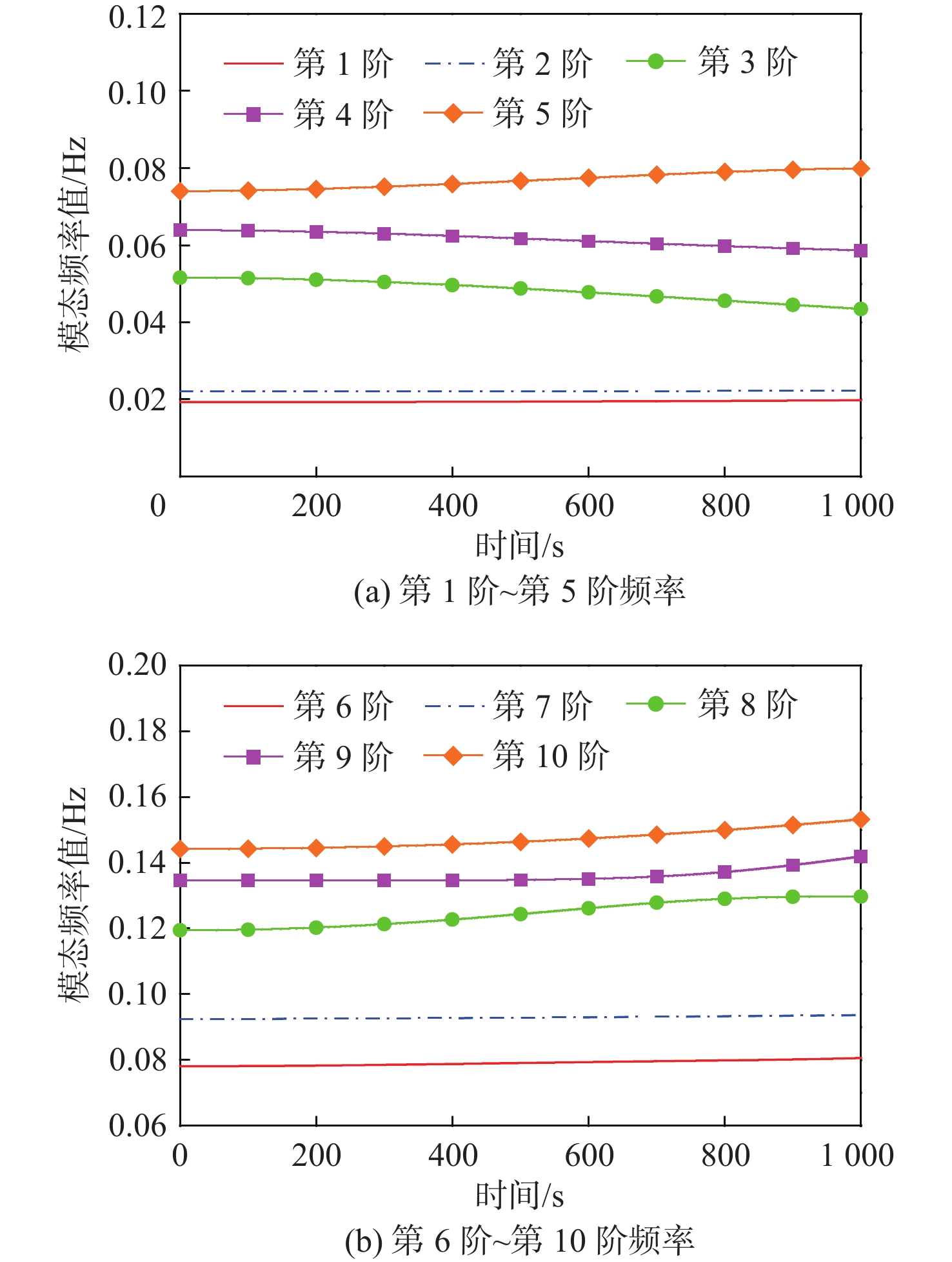
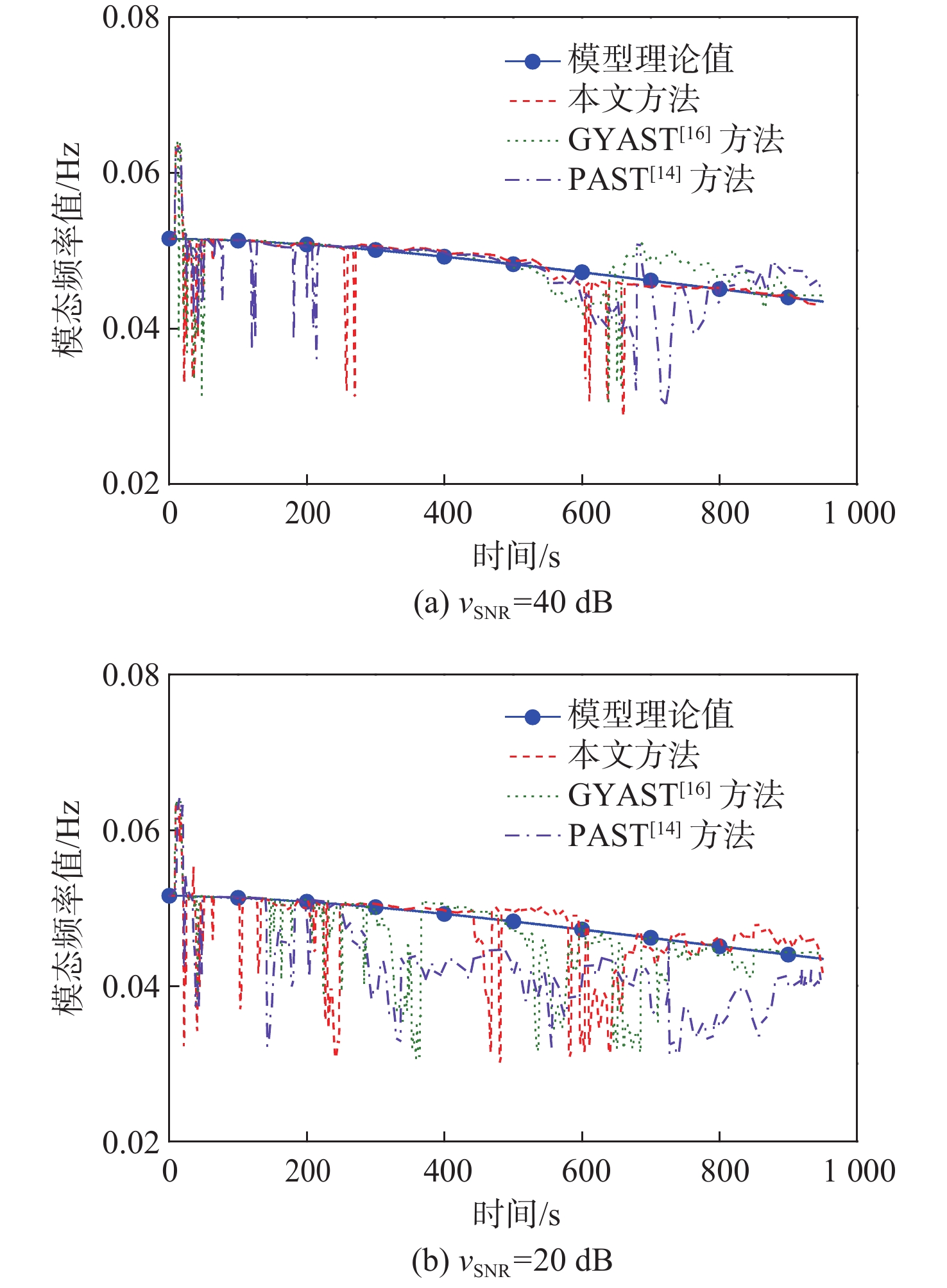
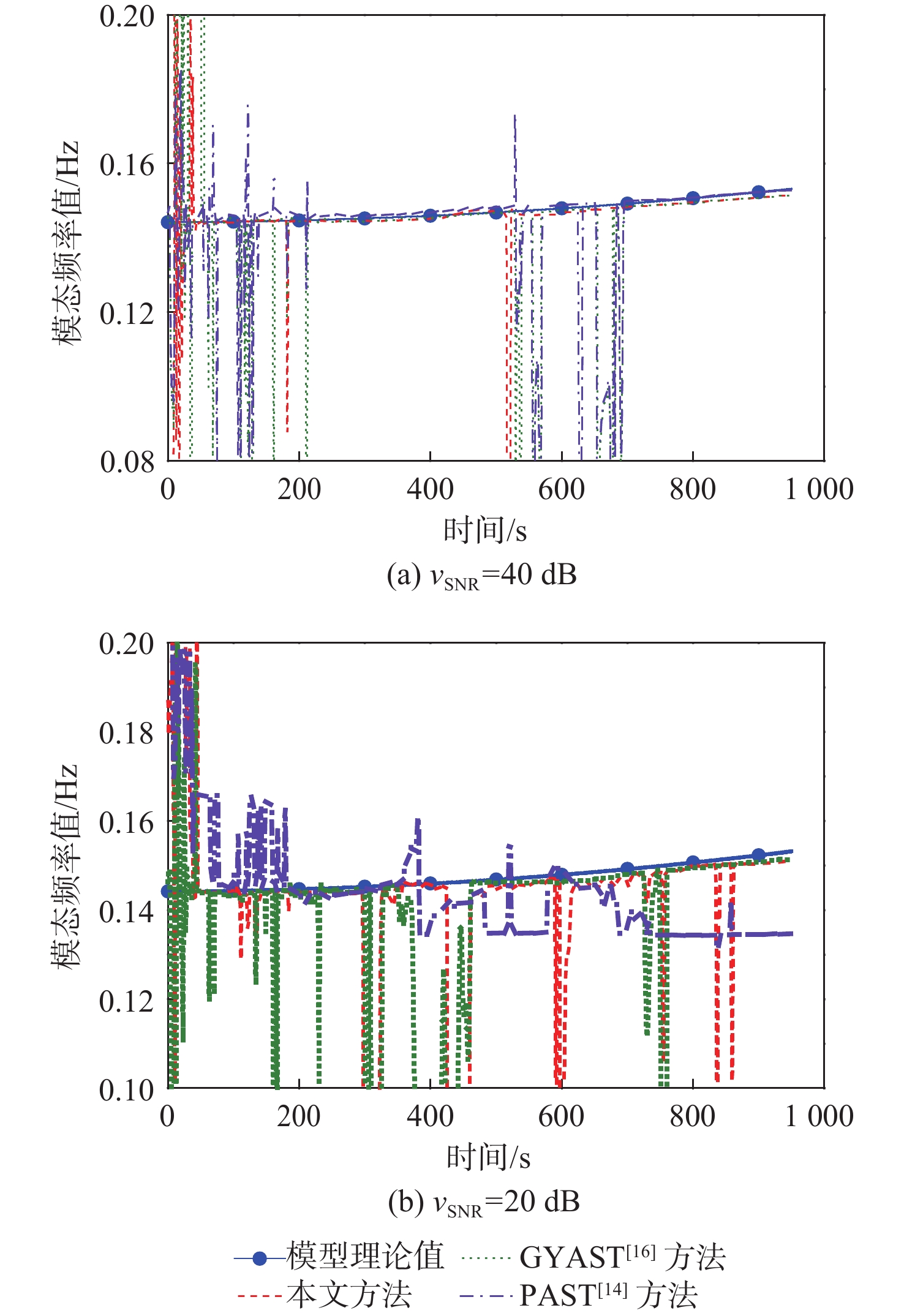
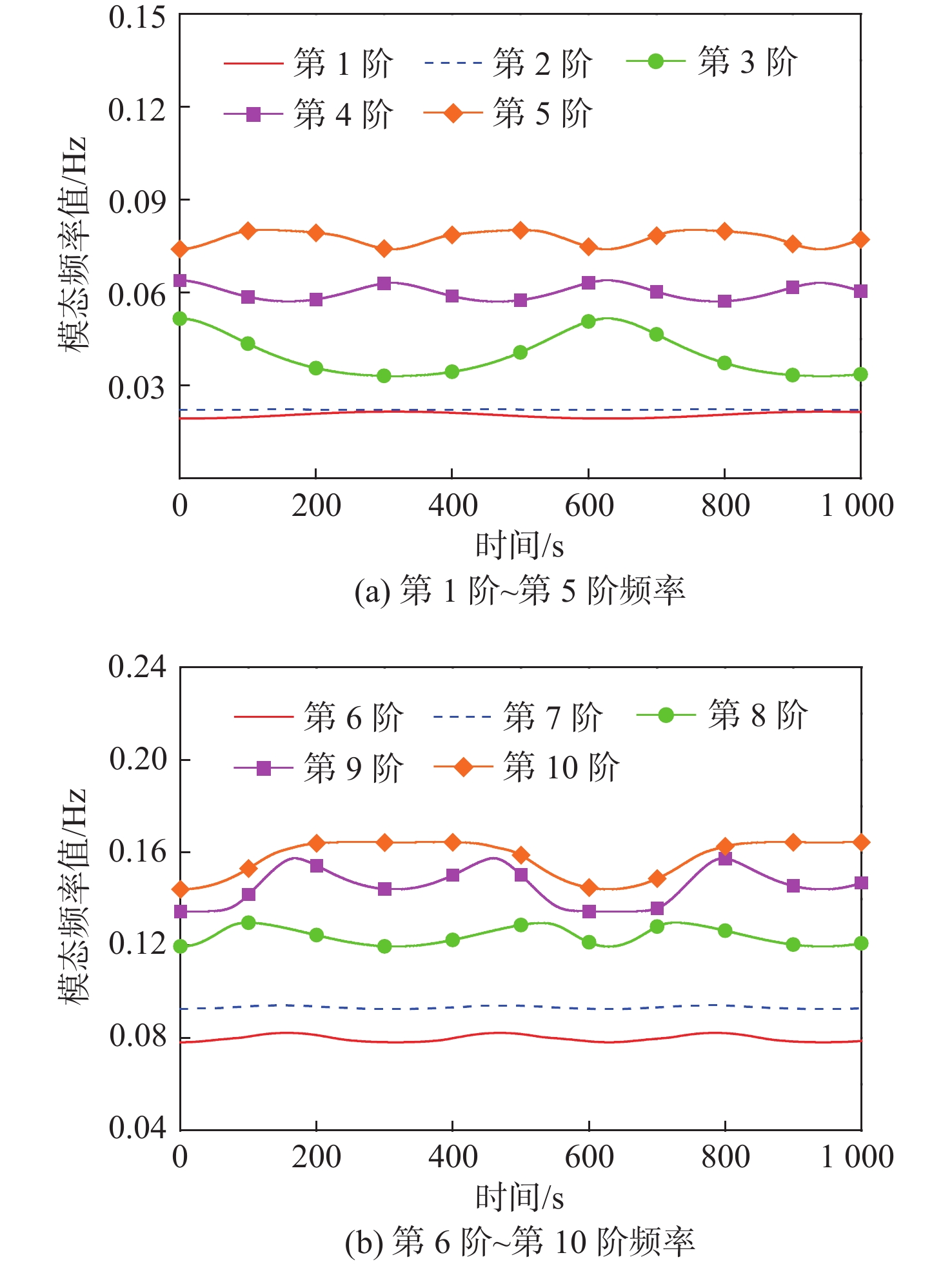
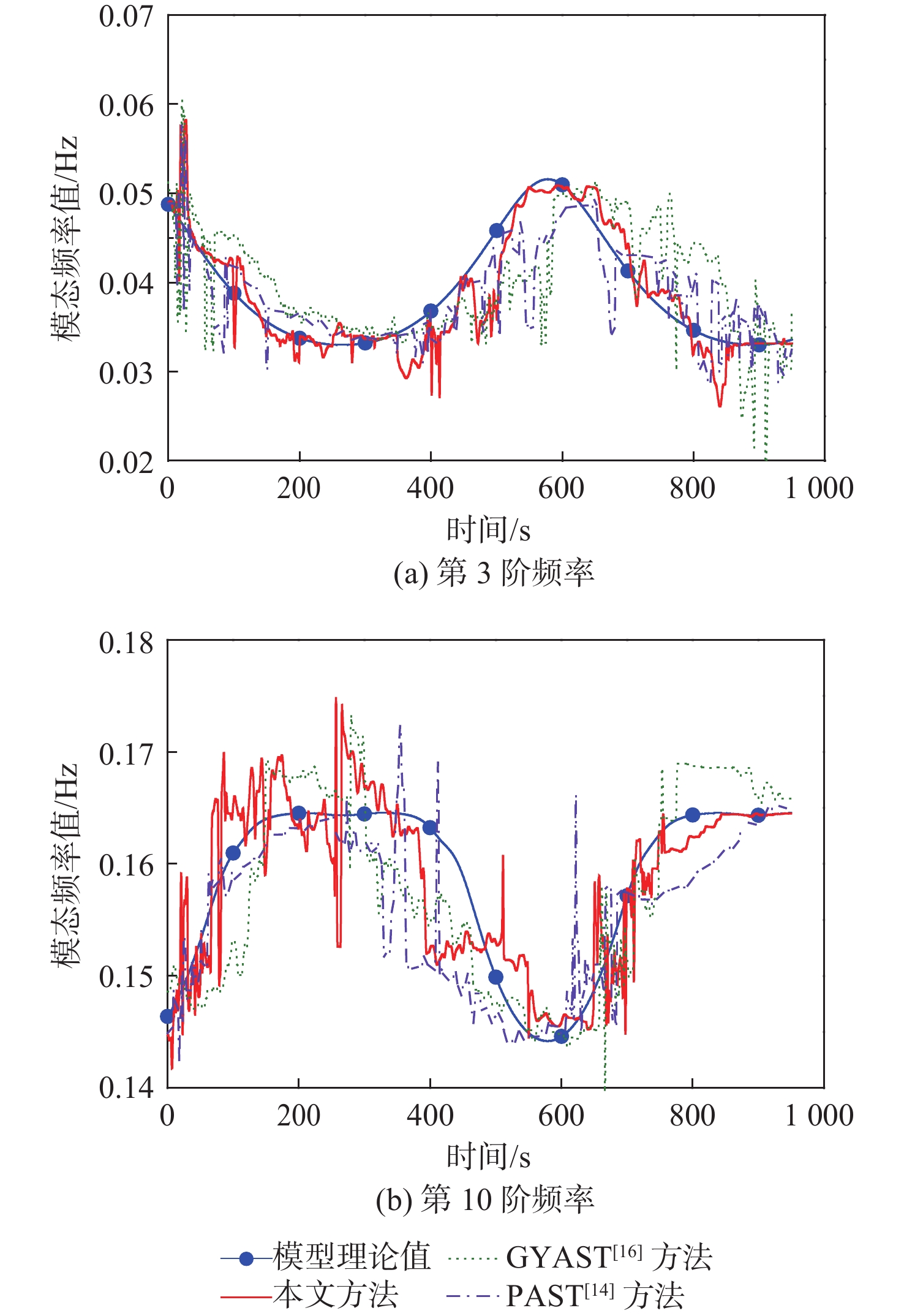
频率阶次 模态频率/Hz 微波天线a 太阳能帆板p1和p2 1 0.0510 0.0223 2 0.0942 0.0789 3 0.1643 0.1320 4 0.1930 0.1463 5 0.2614 0.4135 6 0.3611 0.4142 7 0.3612 0.7385 8 0.3676 0.7973 9 0.4069 0.9237 10 0.4631 0.9967 表 3 ${{\boldsymbol{v}}_{{\bf{SNR}}}}$为40 dB时,前10阶模态频率的相对误差
Table 3. Relative errors of the first 10 order modal frequencies in ${{\boldsymbol{v}}_{{\bf{SNR}}}}$= 40 dB
表 4 ${{\boldsymbol{v}}_{{\bf{SNR}}}}$为20 dB时,前10阶模态频率的相对误差
Table 4. Relative errors of the first 10 order modal frequencies in ${{\boldsymbol{v}}_{{\bf{SNR}}}}$= 20 dB
表 5 ωr=0.01 rad/s时,前10阶模态频率的相对误差
Table 5. Relative errors of the first 10 order modal frequencies in ωr= 0.01 rad/s
-
[1] 李丽芳, 郭朋真, 刘荣强. 一种空间超大型可展开柔性聚光器[J]. 航空学报, 2018, 39(S1): 722187.LI L F, GUO P Z, LIU R Q. Space super-large deployable flexible condenser[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2018, 39(S1): 722187 (in Chinese). [2] FAN G H, DUAN B Y, ZHANG Y Q, et al. Full-spectrum selective thin film based photonic cooler for solar cells of space solar power station[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2021, 180: 196-204. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2020.12.035 [3] WANG B C, NI Z Y, FANG B. Vibration control of space solar power station in complex environments using giant magnetostrictive actuator[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2021, 182: 119-130. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2021.02.008 [4] 邵阳, 武建文, 陈明轩, 等. 空间太阳能发电站拓扑架构及能量管理控制策略[J]. 宇航学报, 2020, 41(9): 1228-1238. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2020.09.014SHAO Y, WU J W, CHEN M X, et al. Topology architecture and energy management control strategy of space solar power station[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2020, 41(9): 1228-1238 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2020.09.014 [5] 靳其宝, 黄进, 李慧贤. 空间对称聚光太阳能系统在地球轨道的运动姿态规划研究[J]. 太阳能学报, 2021, 42(2): 464-470.JIN Q B, HUANG J, LI H X. Study of motion attitude planning of solar concentration system with spatial symmetry in space power station on geo[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2021, 42(2): 464-470 (in Chinese). [6] WEI Y, LI Q J, XU F N. Orbit-attitude-vibration coupled dynamics of tethered solar power satellite[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2021, 67(1): 393-400. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2020.09.036 [7] 刘玉亮, 邬树楠, 张开明, 等. 重力姿轨耦合效应引起的太阳能电站轨道共振[J]. 航空学报, 2018, 39(12): 222194. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2018.22194LIU Y L, WU S N, ZHANG K M, et al. Resonance in the orbital motion of solar power station due to gravitational orbit-attitude coupling[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2018, 39(12): 222194 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2018.22194 [8] 李庆军, 邓子辰, 王艳, 等. 空间太阳能电站的准对日定向姿态[J]. 宇航学报, 2019, 40(1): 29-40. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2019.01.004LI Q J, DENG Z C, WANG Y, et al. Quasi-Sun-pointing oriented attitude for solar power satellites[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2019, 40(1): 29-40 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2019.01.004 [9] YANG C, HOU X B. Iterative two-layer thermal design strategy for step sandwich antenna of space solar power satellite using modified constrained multi-objective optimization[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2021, 118: 106987. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2021.106987 [10] 吴跃民, 刘志全, 任守志. 基于遥测电流的太阳翼在轨振动参数辨识方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2018, 39(10): 1081-1088. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2018.10.003WU Y M, LIU Z Q, REN S Z. Identification method of vibration characteristics for in-orbit solar wing based on telemetry current[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2018, 39(10): 1081-1088 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2018.10.003 [11] TANG G A, CHEN B F, ZHANG M Y, et al. On-orbit modal identification for vibration suppression of flexible aerospace structure using reaction wheel actuator[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2020, 107: 106250. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.106250 [12] 倪智宇, 刘金国, 吴志刚. 一种改进的航天器时变模态参数递推辨识方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2018, 39(10): 1097-1106. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2018.10.005NI Z Y, LIU J G, WU Z G. An improved recursive identification method for time-varying modal parameters of spacecraft[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2018, 39(10): 1097-1106 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2018.10.005 [13] 岳振江, 刘莉, 余磊, 等. 结合离线知识的时变结构模态参数在线辨识[J]. 航空学报, 2019, 40(8): 222931. doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2019.22931YUE Z J, LIU L, YU L, et al. Online identification of time-varying structural modal parameters combined with offline knowledge[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2019, 40(8): 222931 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7527/S1000-6893.2019.22931 [14] YANG B. Projection approximation subspace tracking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1995, 43(1): 95-107. doi: 10.1109/78.365290 [15] WENG J H, LOH C H. Recursive subspace identification for on-line tracking of structural modal parameter[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2011, 25(8): 2923-2937. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2011.05.013 [16] ARJOMANDI-LARI M, KARIMI M. Generalized YAST algorithm for signal subspace tracking[J]. Signal Processing, 2015, 117: 82-95. doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2015.04.025 [17] CHAN S C, LIN J Q, SUN X, et al. A new variable forgetting factor-based bias-compensation algorithm for recursive identification of time-varying multi-input single-output systems with measurement noise[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(7): 4555-4568. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2019.2947121 [18] ZHU K, YU C P, WAN Y M. Recursive least squares identification with variable-direction forgetting via oblique projection decomposition[J]. IEEE/CAA Journal of Automatica Sinica, 2022, 9(3): 547-555. doi: 10.1109/JAS.2021.1004362 [19] LEUNG S H, SO C F. Gradient-based variable forgetting factor RLS algorithm in time-varying environments[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2005, 53(8): 3141-3150. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2005.851110 [20] 黄金峰, 张合新, 胡友涛, 等. 基于有限记忆变遗忘因子的子空间辨识算法[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2012, 29(7): 893-898.HUANG J F, ZHANG H X, HU Y T, et al. Subspace identification algorithm based on finite-memory variable forgetting factor[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2012, 29(7): 893-898 (in Chinese). [21] DAI B L, GONG J, LI C M, et al. Iterative learning control realized using an iteration-varying forgetting factor based on optimal gains[J]. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 2021, 43(10): 2334-2344. doi: 10.1177/0142331221996507 [22] 曲广吉. 航天器动力学工程[M]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社, 2000: 180-183.QU G J. Spacecraft dynamics engineering[M]. Beijing: China Science and Technology Press, 2000: 180-183 (in Chinese). [23] 邱吉宝, 张正平, 向树红, 等. 结构动力学及其在航天工程中的应用[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2015: 481-483.QIU J B, ZHANG Z P, XIANG S H, et al. Structural dynamics and its applications in space engineering[M]. Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China Press, 2015: 481-483(in Chinese). [24] 倪智宇, 刘金国, 畅晨光. 基于子空间方法的柔性空间机械臂未知末端载荷质量参数辨识[J]. 机械工程学报, 2018, 54(14): 132-140.NI Z Y, LIU J G, CHANG C G. Identification of unknown endpoint payload mass parameter of flexible space manipulator based on subspace method[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 54(14): 132-140 (in Chinese). [25] LIN J Q, WU H C, CHAN S C. A new regularized recursive dynamic factor analysis with variable forgetting factor and subspace dimension for wireless sensor networks with missing data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70: 9509713. -







 下载:
下载: