-
摘要:
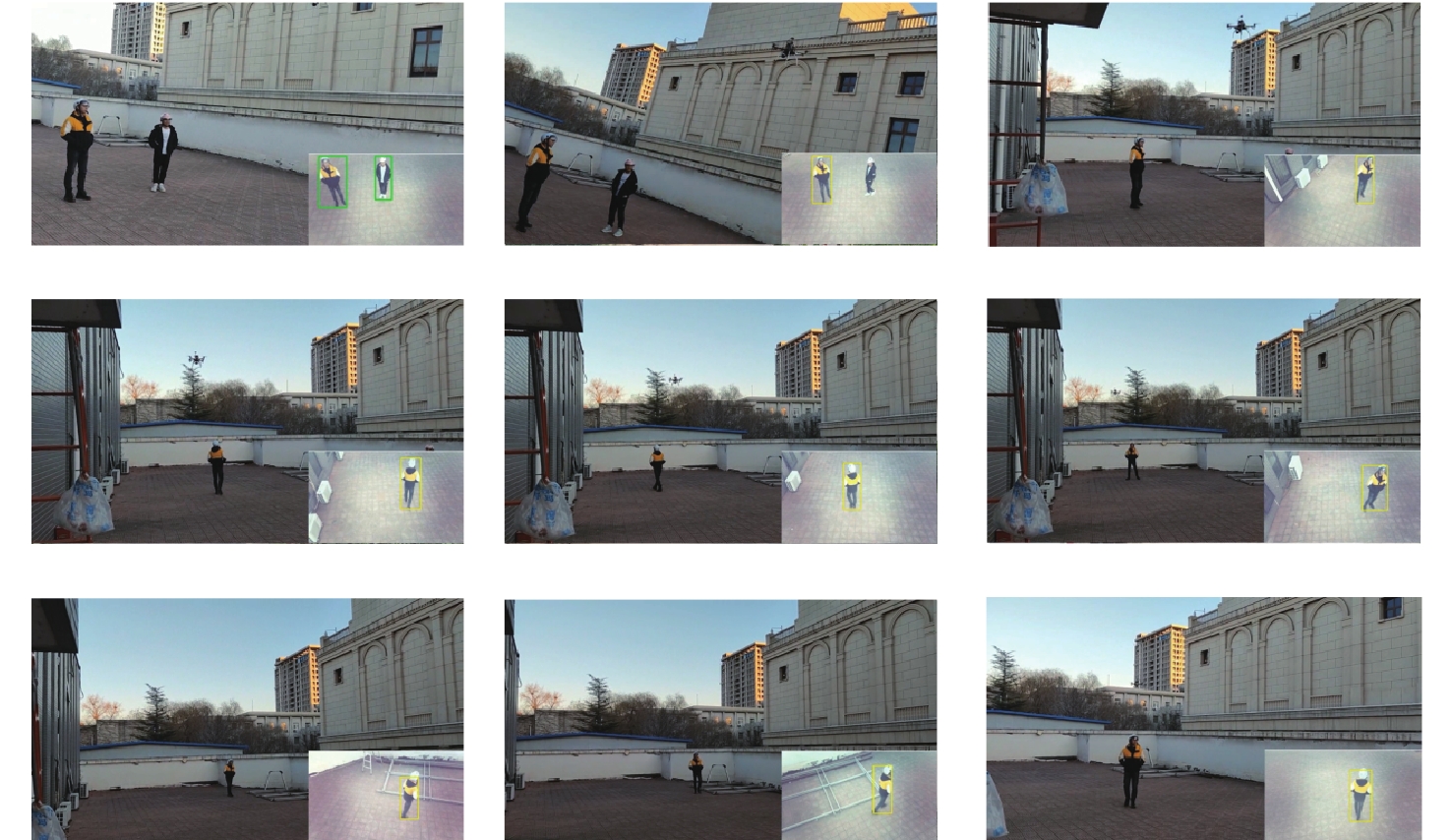
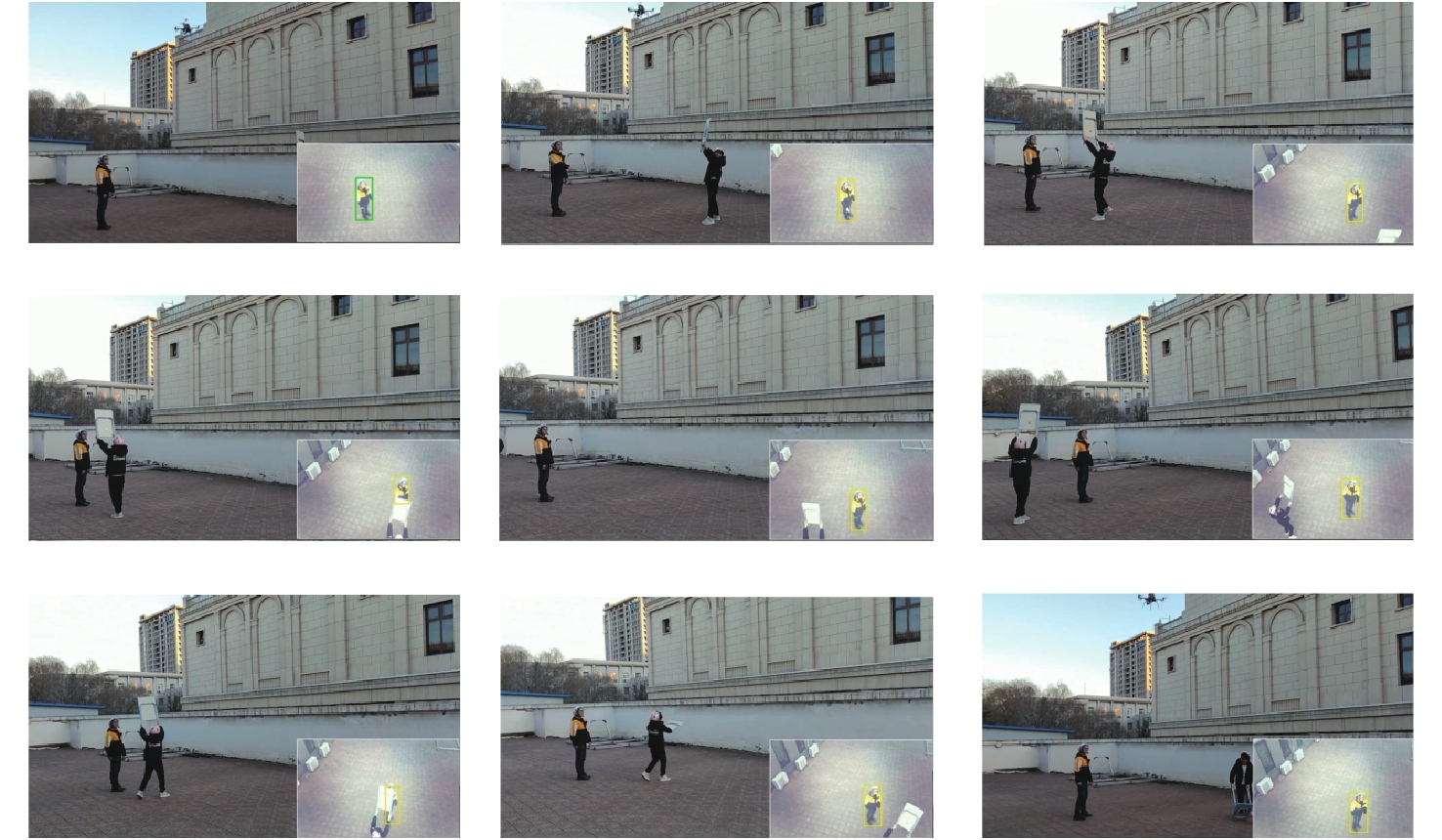
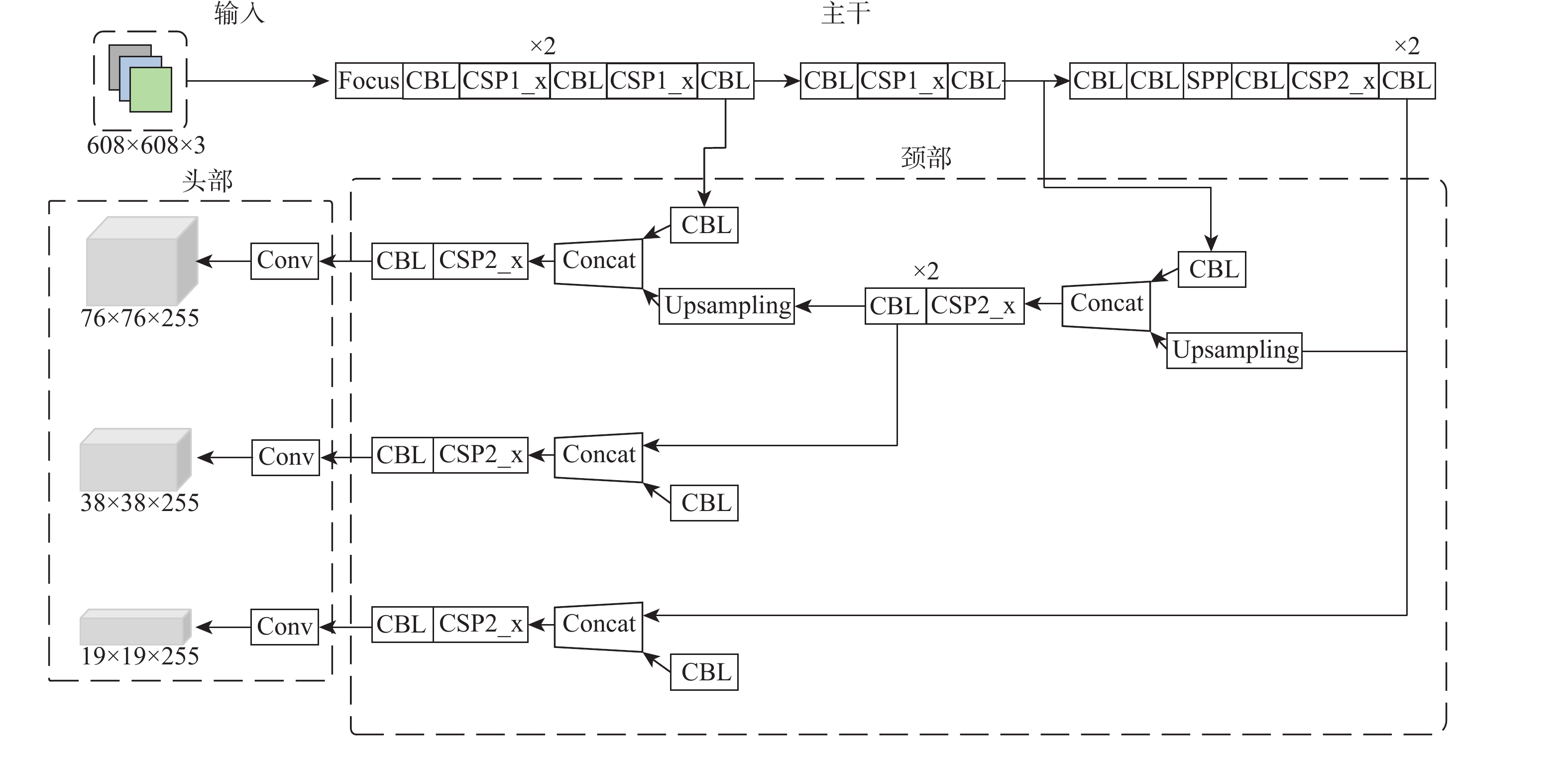
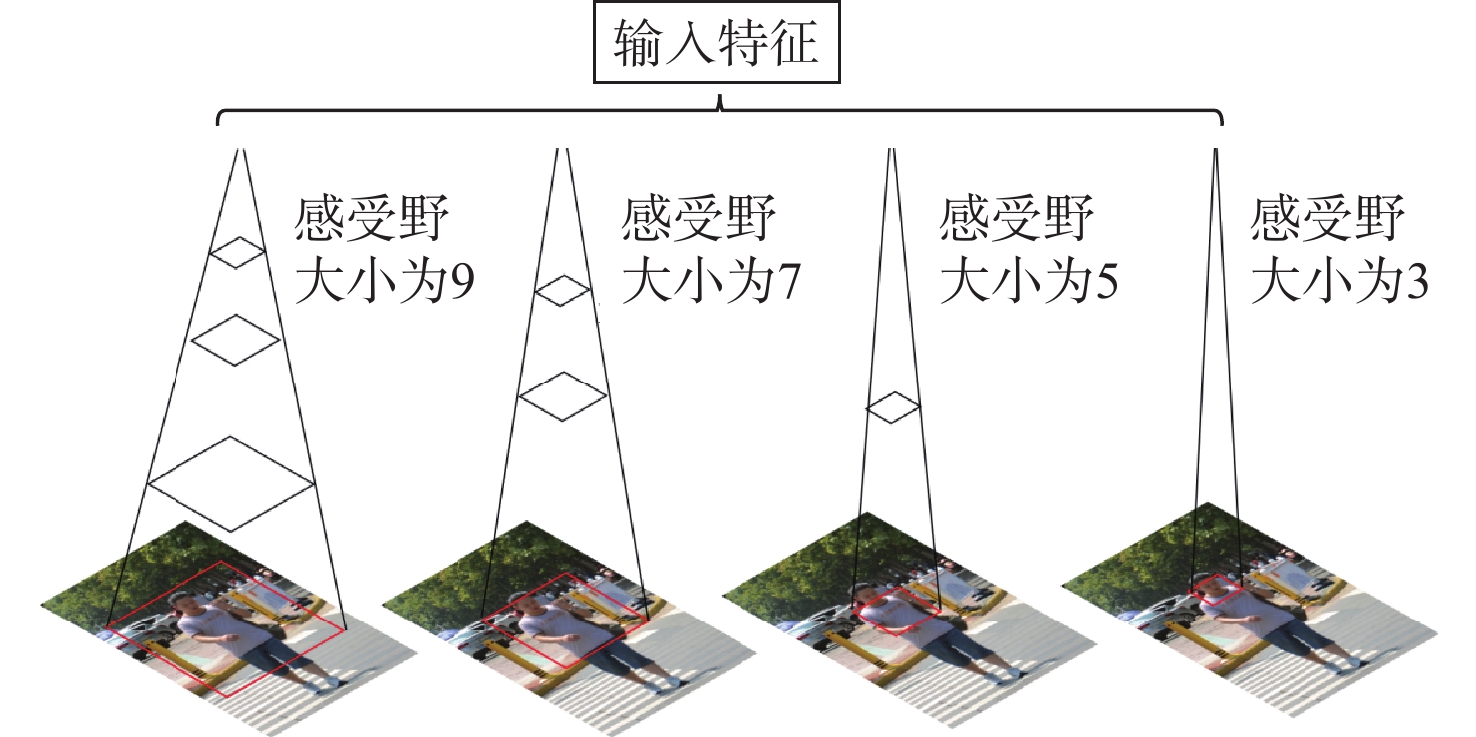
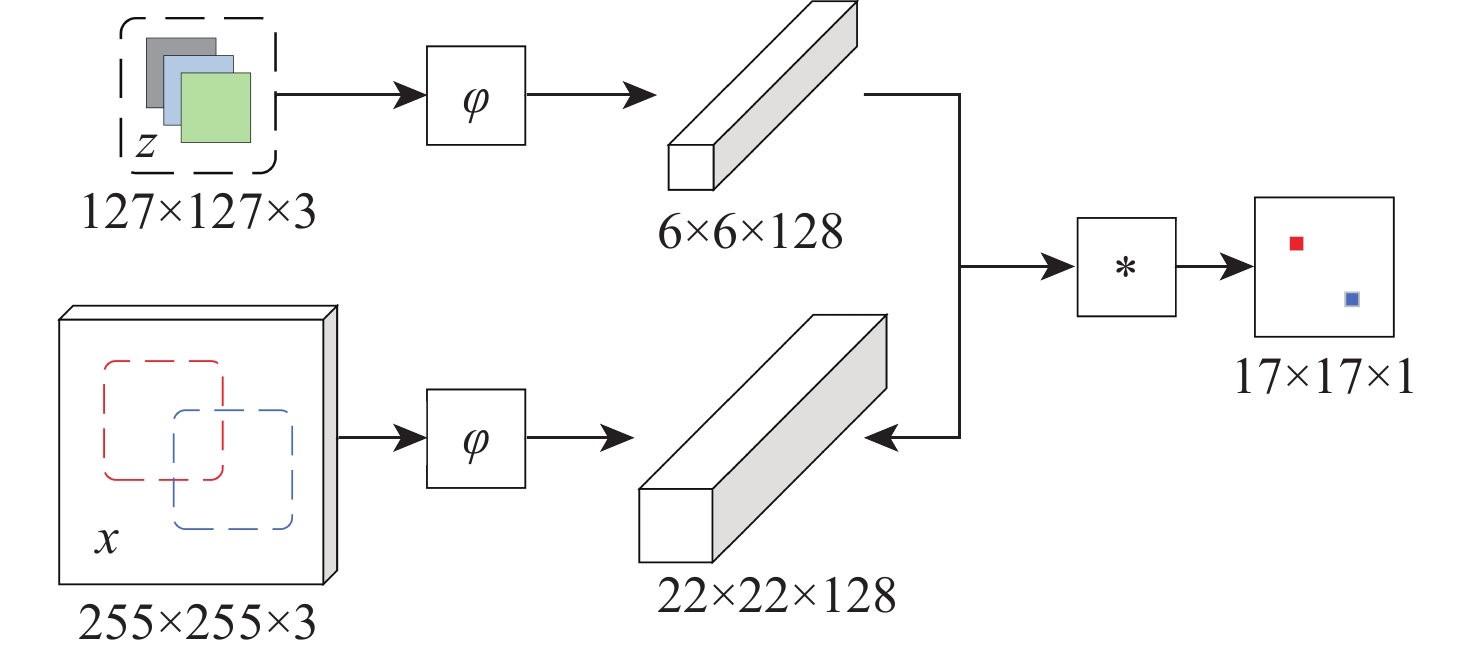
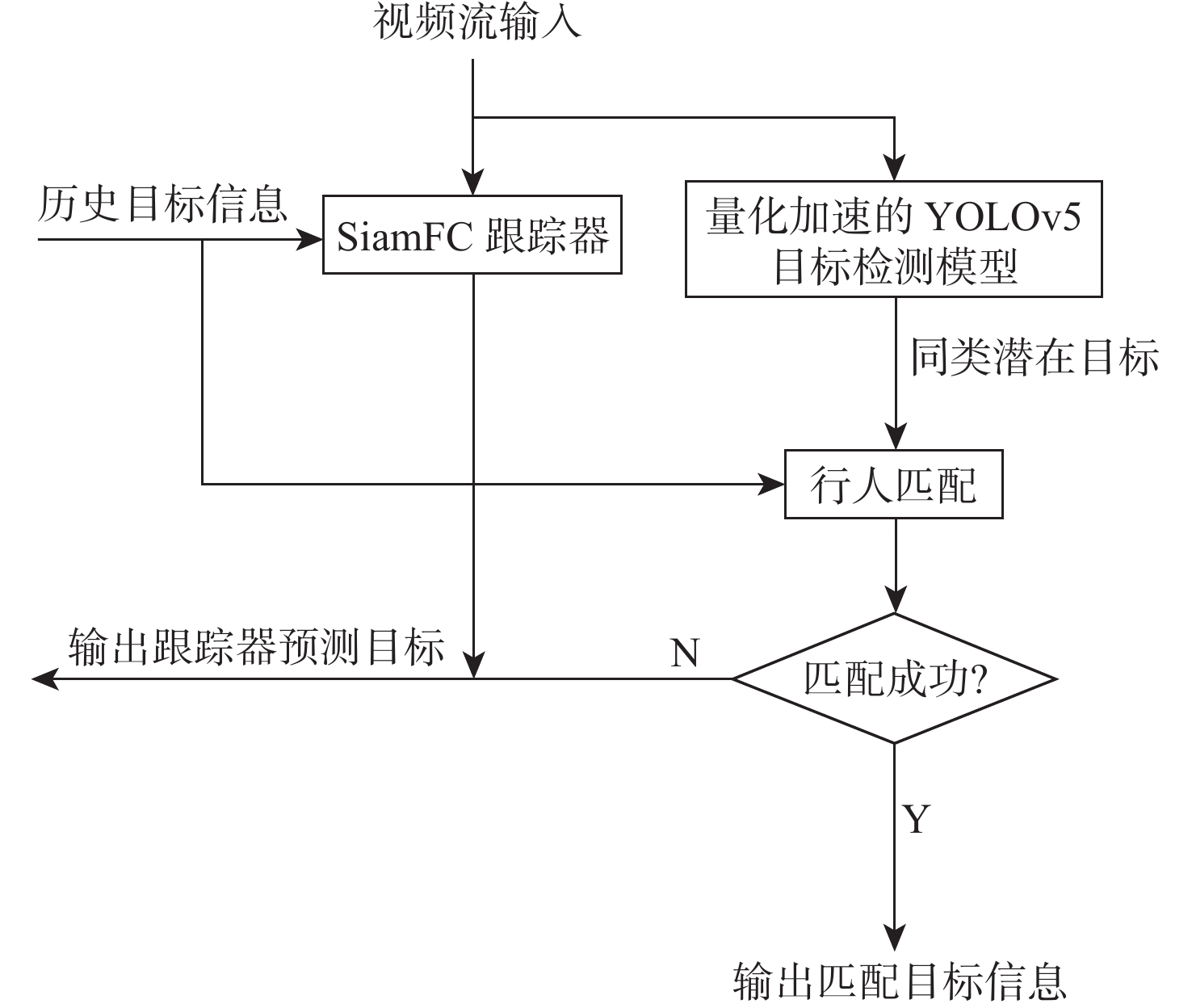
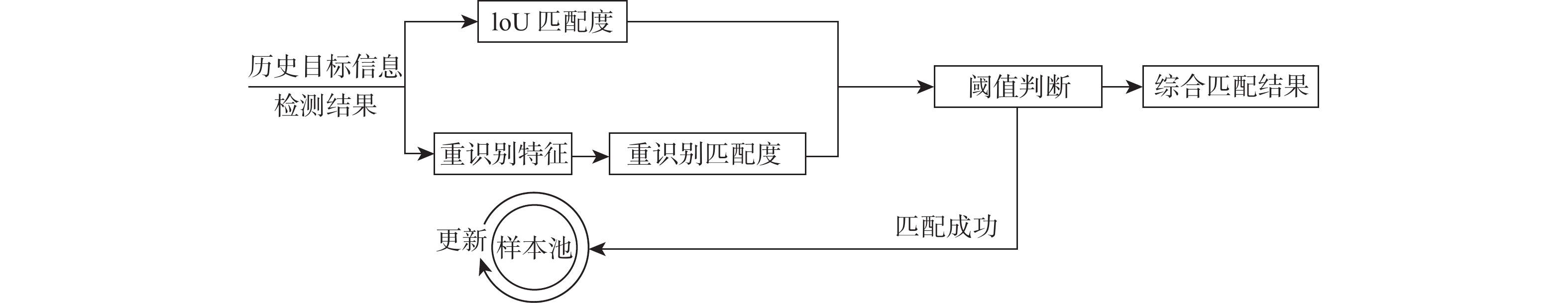
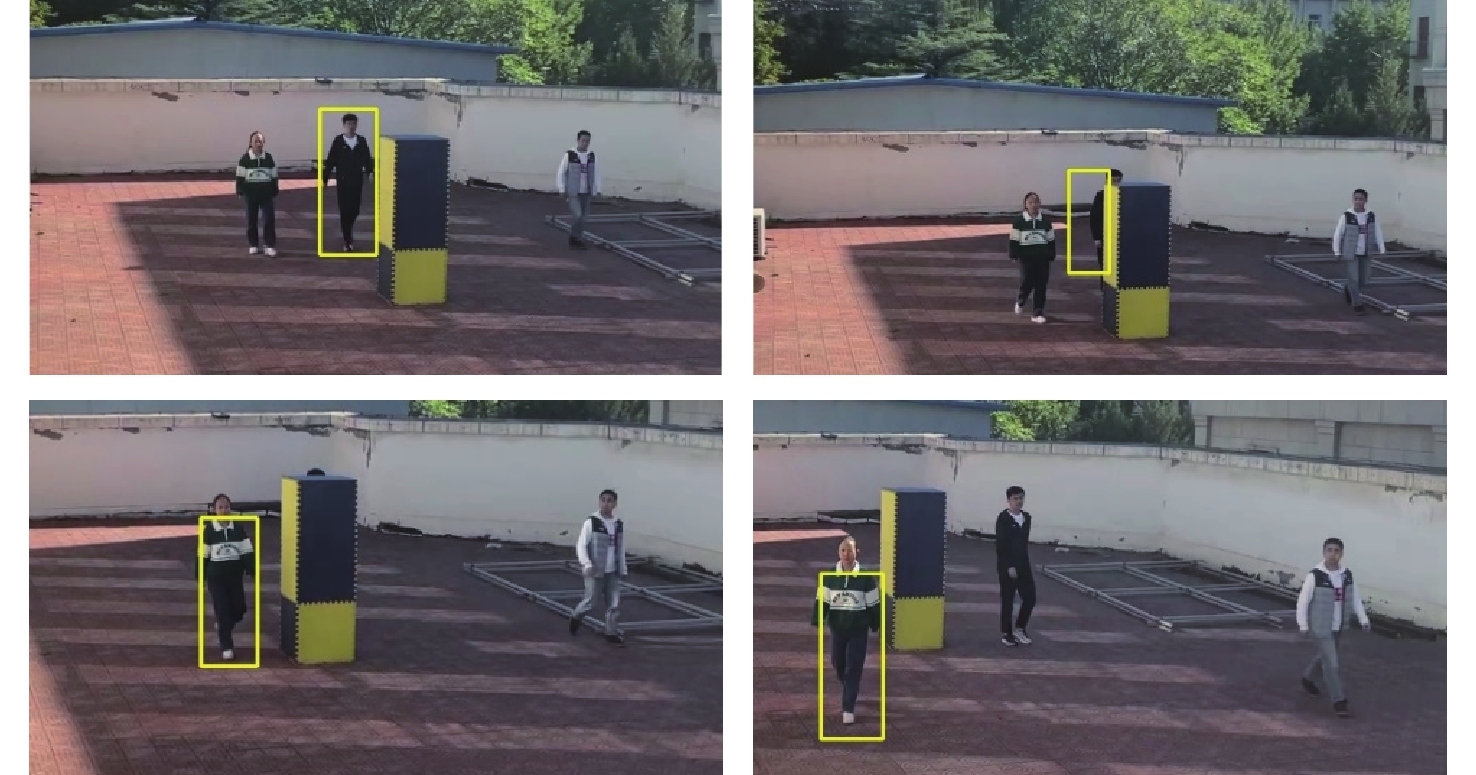
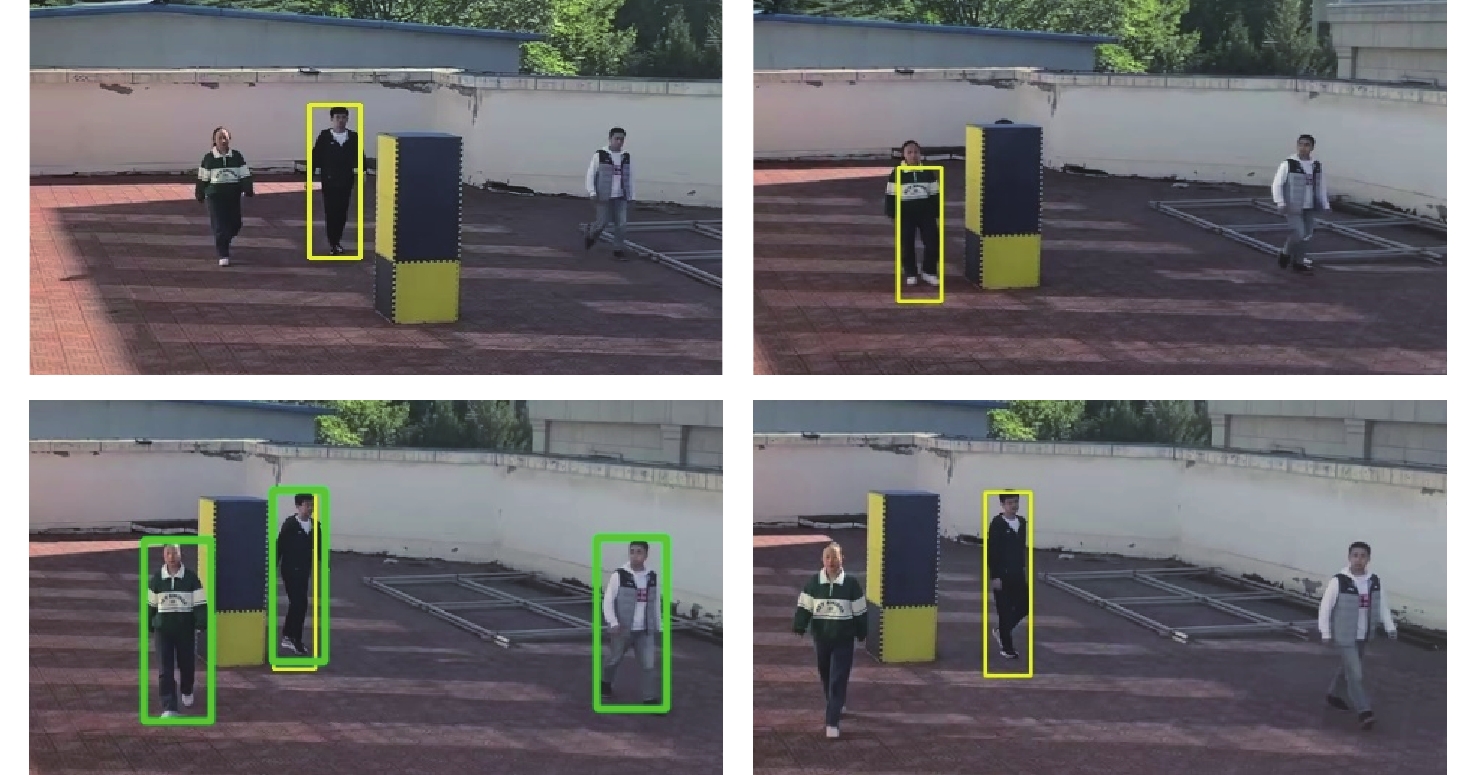
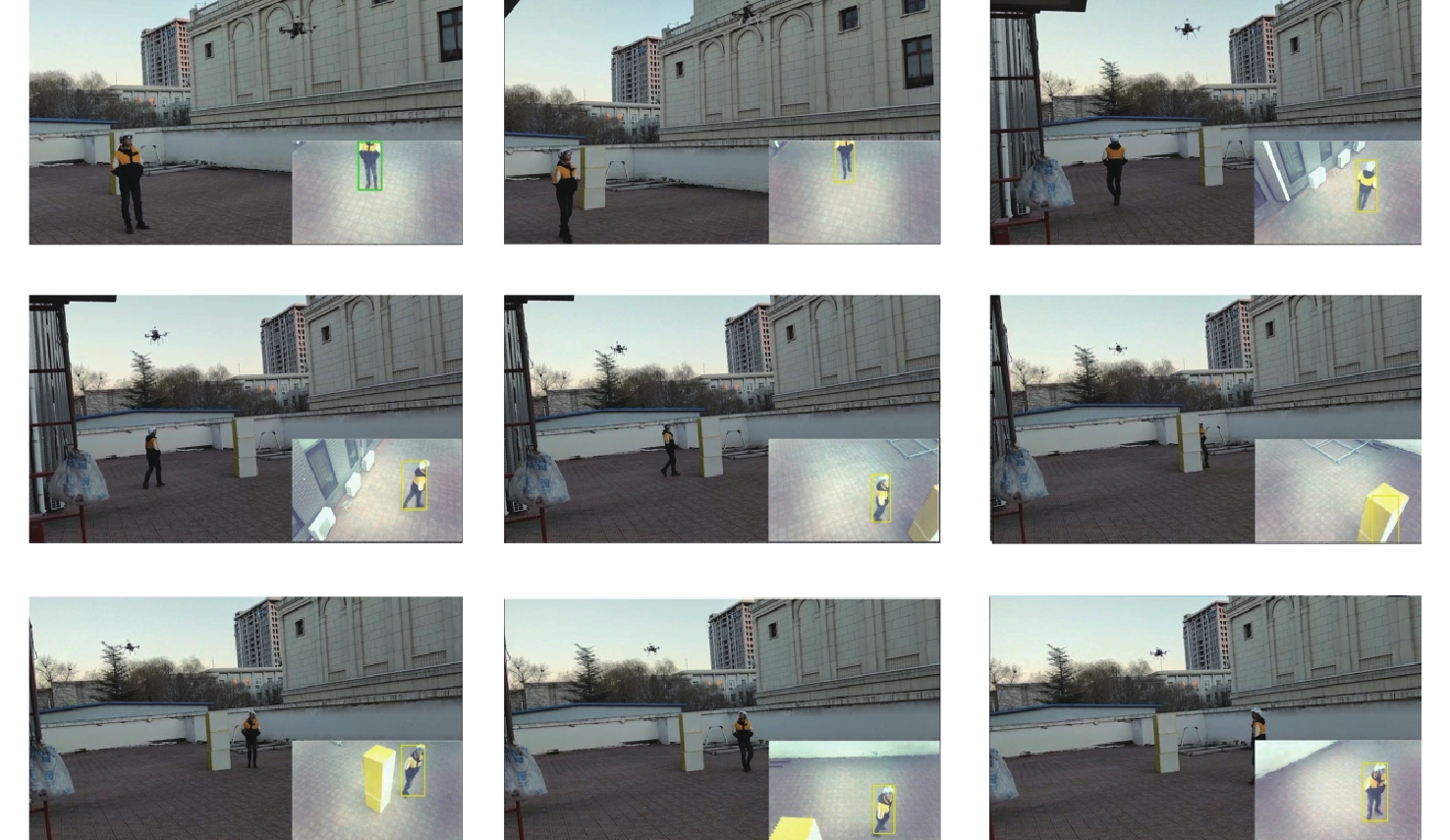
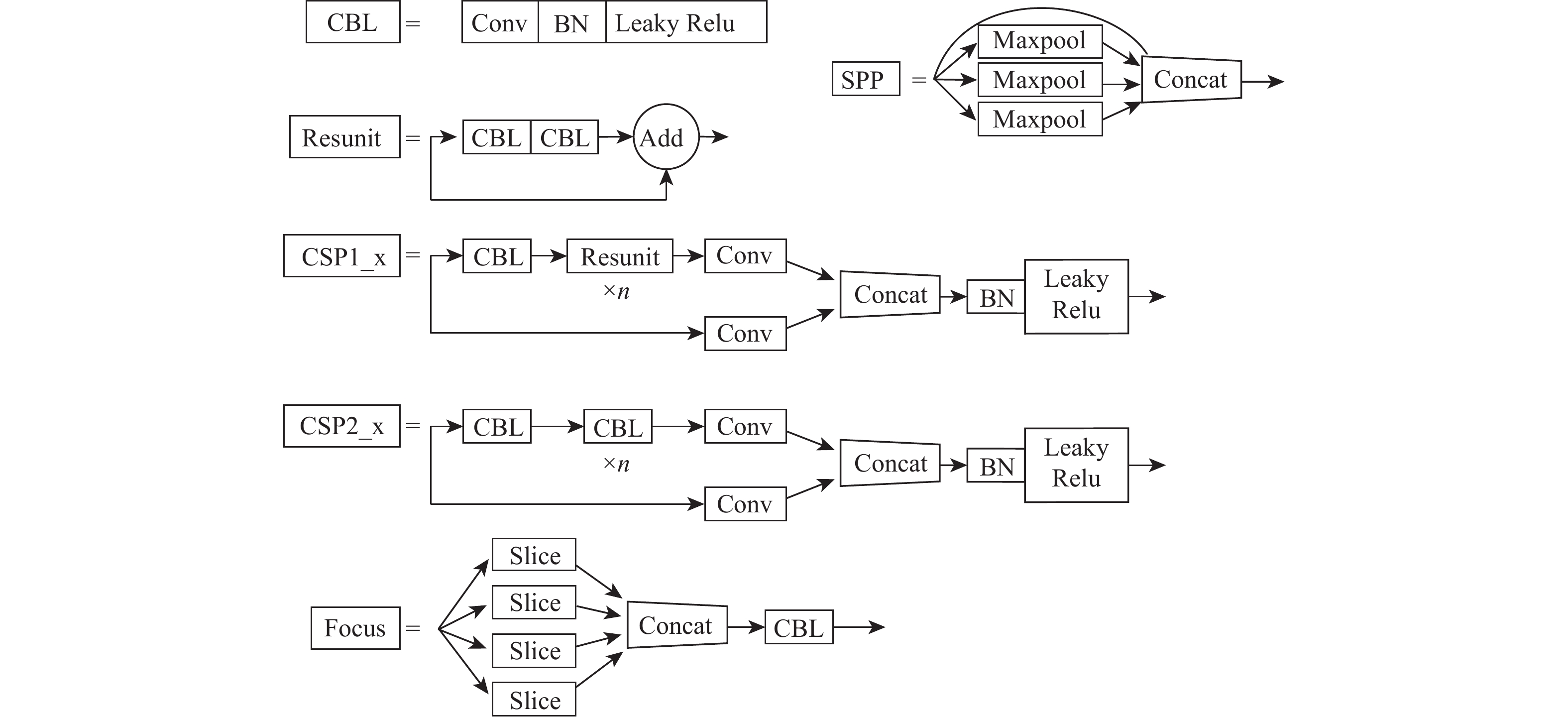
将智能检测跟踪算法与无人机(UAV)的灵活性相结合是UAV应用的研究热点。针对UAV的视角及运动导致目标滑移和遮挡的问题,提出一种基于检测和重识别的UAV行人跟踪算法。对训练好的YOLOv5进行TensorRT加速,解决UAV计算资源有限的问题;以量化加速的目标检测算法与重识别算法为基础,构建行人跟踪算法框架;设计判定行人匹配度,完成行人匹配系统设计。仿真试验表明:训练后的YOLOv5和OSNet具备一定的精度,采用TensorRT加速后的YOLOv5网络在保证精度的情况下,帧率有了近50%的提升。飞行试验表明:所提算法在行人穿插及障碍物遮挡的情况下,可以实现对目标的稳定跟踪,具备一定的实用性和有效性。
Abstract:Combining intelligent detection and tracking algorithms with the flexibility of unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) is a hot research topic for UAV applications. A UAV pedestrian tracking algorithm based on detection and re-identification was proposed for solving the problems of target slippage and occlusion due to the UAV’s viewpoint and motion. Firstly, TensorRT acceleration of trained YOLOv5 was performed to solve the problem of limited UAV computational resources; secondly, a pedestrian tracking algorithm framework was constructed based on a target detection algorithm and a re-identification algorithm with quantization acceleration; finally, the pedestrian matching degree was designed and determined to complete the pedestrian matching system design. Simulation experiments show that the trained YOLOv5 and OSNet have certain accuracy, and the YOLOv5 network with TensorRT acceleration has nearly 50% improvement in frame rate with guaranteed accuracy. The flight test shows that the proposed algorithm can achieve stable tracking of the target under the situation of pedestrian intersection and obstacle occlusion, and it has certain practicality and effectiveness.
-
表 1 PC端目标检测算法测试结果
Table 1. Test results of target detection algorithm on PC
检测模型 正确率 召回率 AP@0.5 YOLOv3 0.514 0.383 0.391 YOLOv5-n 0.413 0.297 0.284 YOLOv5-s 0.568 0.373 0.402 表 2 TensorRT在Jetson Xavier NX模块上的测试结果
Table 2. Test results of TensorRT on Jetson Xavier NX module
深度学习
框架功率/W 在线CPU
个数Jetson clock AP@0.5 帧率/
(帧·S−1)Pytorch 15 2 开启 0.402 24.8 TensorRT 15 2 开启 0.401 37.4 表 3 PC端re-id算法测试结果
Table 3. Test results of re-id algorithm on PC
重识别算法 mAP Rank1 Rank5 Rank10 DenseNet 0.643 0.847 0.943 0.963 OSNet 0.670 0.864 0.946 0.965 -
[1] 葛向然. 无人机在情报领域应用前景[J]. 电子世界, 2019(19): 98-99.GE X R. Application prospect of UAV in intelligence field[J]. Electronics World, 2019(19): 98-99 (in Chinese). [2] SONKA M, HLAVAC V, BOYLE R. 图像处理、分析与机器视觉[M] . 3版. 艾海舟,苏延超,兴军亮,等. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2011.SONKA M, HLAVAC V, BOYLE R. Image processing, analysis, and machine vision[M]. 3rd ed. AI H Z, SU Y C, Xing J L, et al, translated. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2011(in Chinese). [3] BEAUCHEMIN S S, BARRON J L. The computation of optical flow[J]. ACM Computing Surveys, 1995, 27(3): 433-466. doi: 10.1145/212094.212141 [4] HERRERO-JARABA E, ORRITE-URUÑUELA C, SENAR J. Detected motion classification with a double-background and a neighborhood-based difference[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2006, 24(12): 2079-2092. [5] CUCCHIARA R, GRANA C, PICCARDI M, et al. Detecting moving objects, ghosts, and shadows in video streams[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2003, 25(10): 1337-1342. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2003.1233909 [6] BRAGANETO U, GOUTSIAS J. Object-based image analysis using multiscale connectivity[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2005, 27(6): 892-907. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2005.124 [7] REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R, et al. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 779-788. [8] REDMON J, FARHADI A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 6517-6525. [9] REDMON J, FARHADI A. YOLOv3: An incremental improvement[EB/OL]. (2018-04-08)[2022-08-01]. [10] LIU W, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D, et al. SSD: Single shot MultiBox detector[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 21-37. [11] ZHANG N, DONAHUE J, GIRSHICK R, et al. Part-based R-CNNs for fine-grained category detection[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2014: 834-849. [12] GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1440-1448. [13] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(9):1904-1916. [14] REN S Q, HE K M, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1137-1149. [15] BOLME D S, BEVERIDGE J R, DRAPER B A, et al. Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 2544-2550. [16] HENRIQUES J F, CASEIRO R, MARTINS P, et al. Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels[C]//Pro.ceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2012: 702-715. [17] HENRIQUES J F, CASEIRO R, MARTINS P, et al. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37(3): 583-596. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2345390 [18] DANELLJAN M, KHAN F S, FELSBERG M, et al. Adaptive color attributes for real-time visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 1090-1097. [19] MA C, HUANG J B, YANG X K, et al. Hierarchical convolutional features for visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 3074-3082. [20] NAM H, HAN B. Learning multi-domain convolutional neural networks for visual tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 4293-4302. [21] NAM H, BAEK M, HAN B. Modeling and propagating CNNs in a tree structure for visual tracking[EB/OL]. (2016-08-25)[2022-08-01]. [22] HELD D, THRUN S, SAVARESE S. Learning to track at 100 FPS with deep regression networks[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 749-765. [23] BERTINETTO L, VALMADRE J, HENRIQUES J F, et al. Fully-convolutional Siamese networks for object tracking[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 850-865. [24] GUO Q, FENG W, ZHOU C, et al. Learning dynamic Siamese network for visual object tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1781-1789. [25] LI B, YAN J J, WU W, et al. High performance visual tracking with Siamese region proposal network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 8971-8980. [26] QIAN X L, FU Y W, JIANG Y G, et al. Multi-scale deep learning architectures for person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 5409-5418. [27] ZHOU K Y, YANG Y X, CAVALLARO A, et al. Omni-scale feature learning for person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 3701-3711. [28] SUN Y F, ZHENG L, YANG Y, et al. Beyond part models: Person retrieval with refined part pooling and a strong convolutional baseline[C]//Proceedings of the Europwan Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 501–518. [29] SU C, LI J N, ZHANG S L, et al. Pose-driven deep convolutional model for person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 3980-3989. [30] FANG P F, JI P, PETERSSON L, et al. Set augmented triplet loss for video person re-identification[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 464-473. [31] SUN Y F, CHENG C M, ZHANG Y H, et al. Circle loss: A unified perspective of pair similarity optimization[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 6397-6406. [32] ZHU P F, WEN L Y, DU D W, et al. Detection and tracking meet drones challenge[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2022, 44(11): 7380-7399. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2021.3119563 [33] ZHENG L, SHEN L Y, TIAN L, et al. Scalable person re-identification: A benchmark[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1116-1124. -







 下载:
下载: