-
摘要:
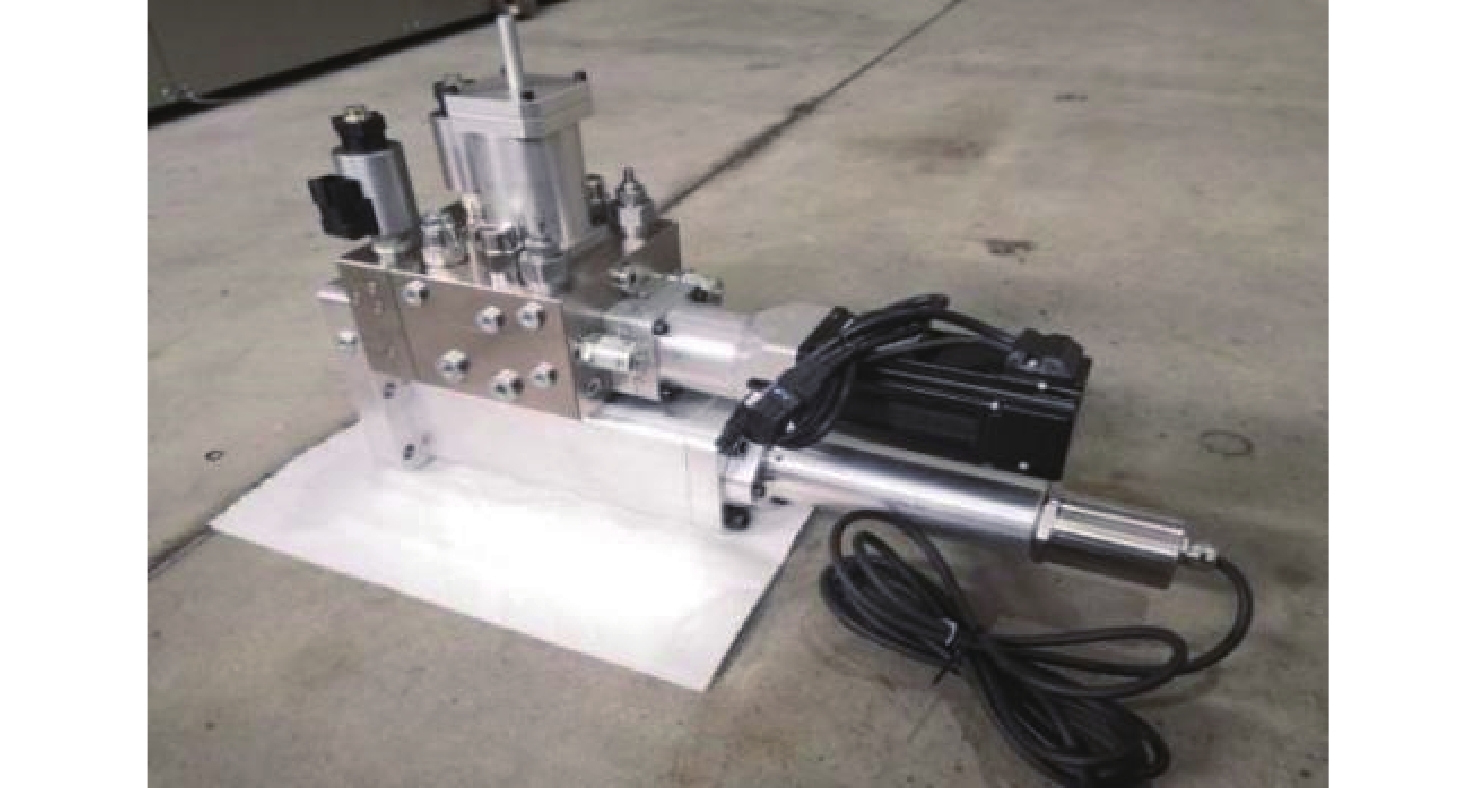
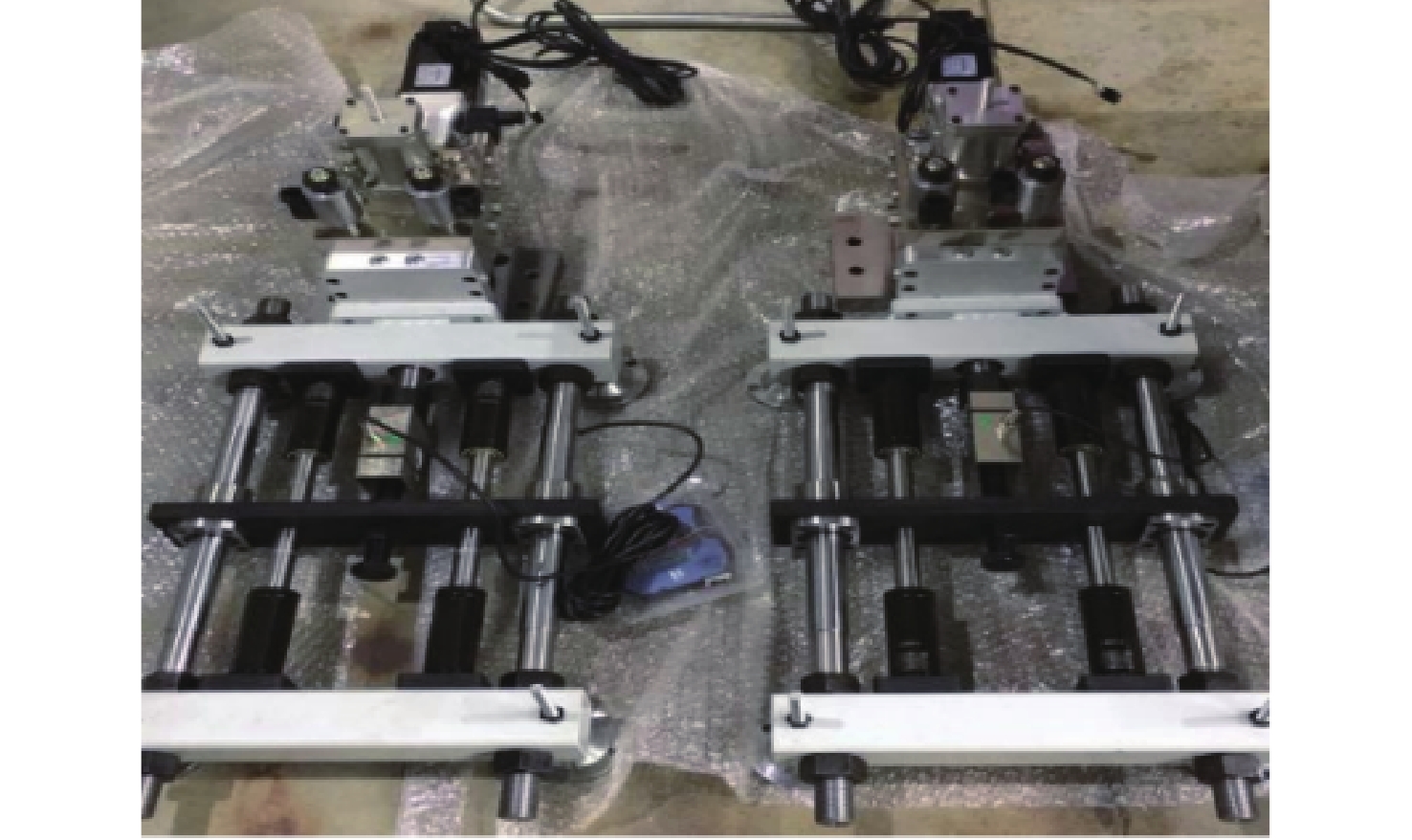
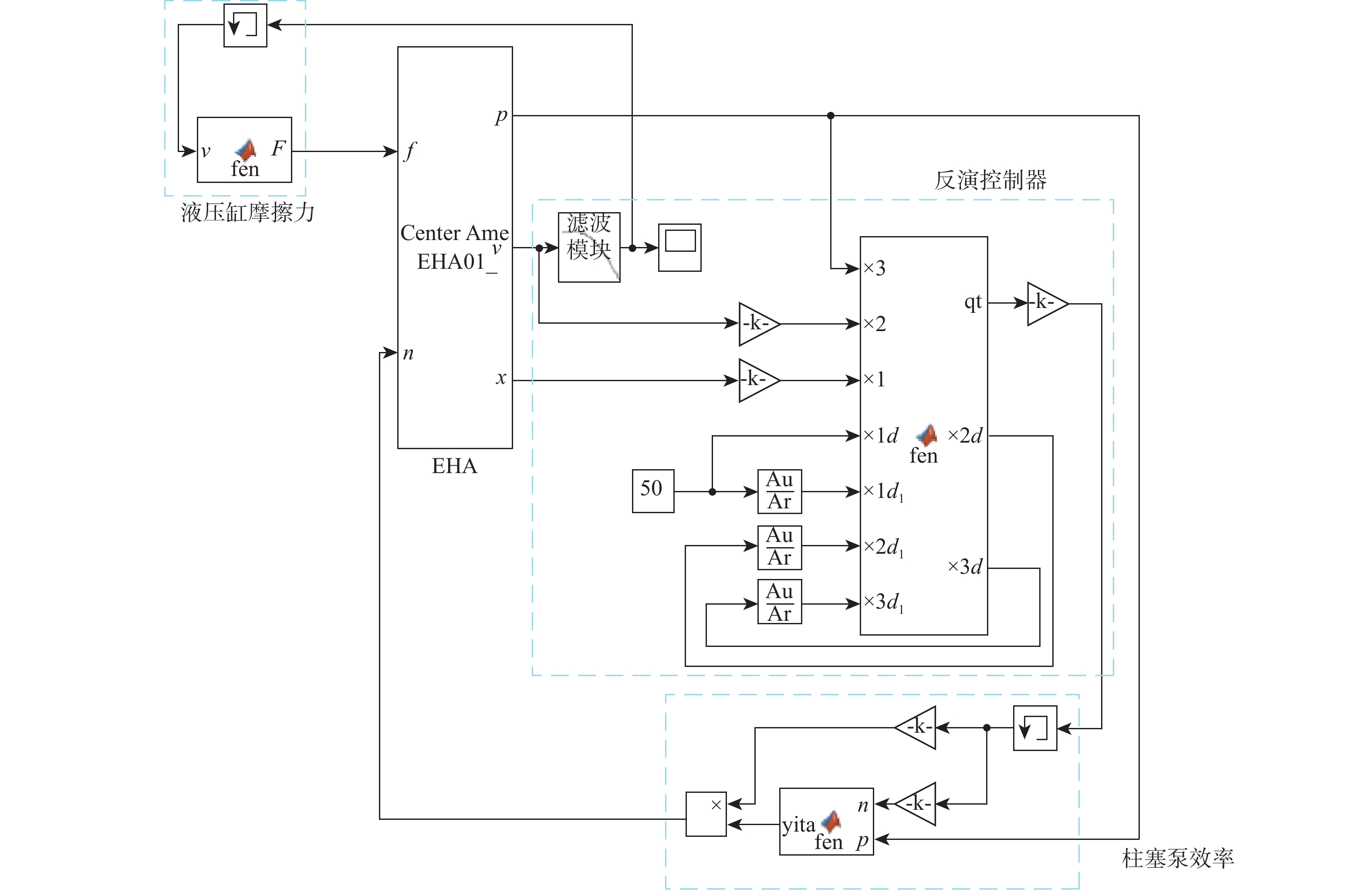
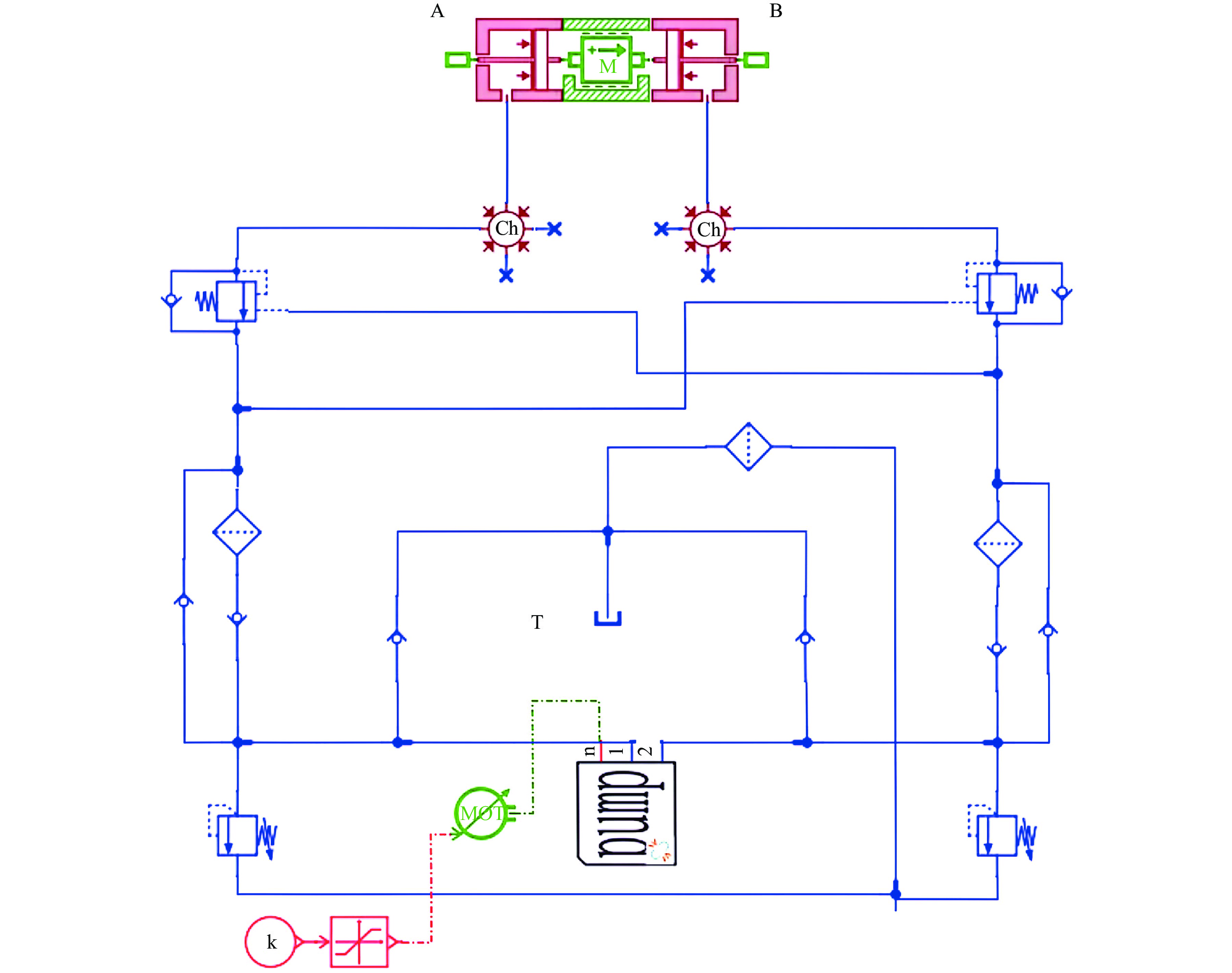
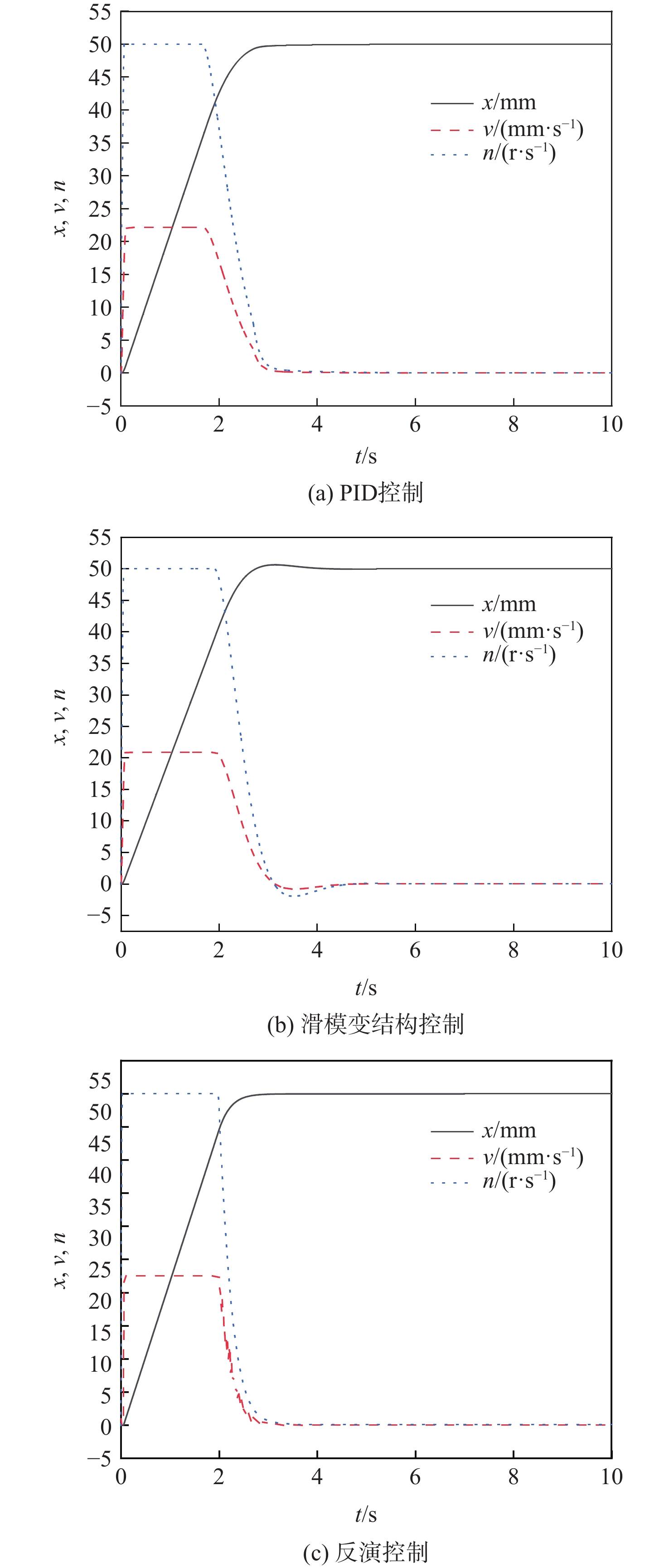
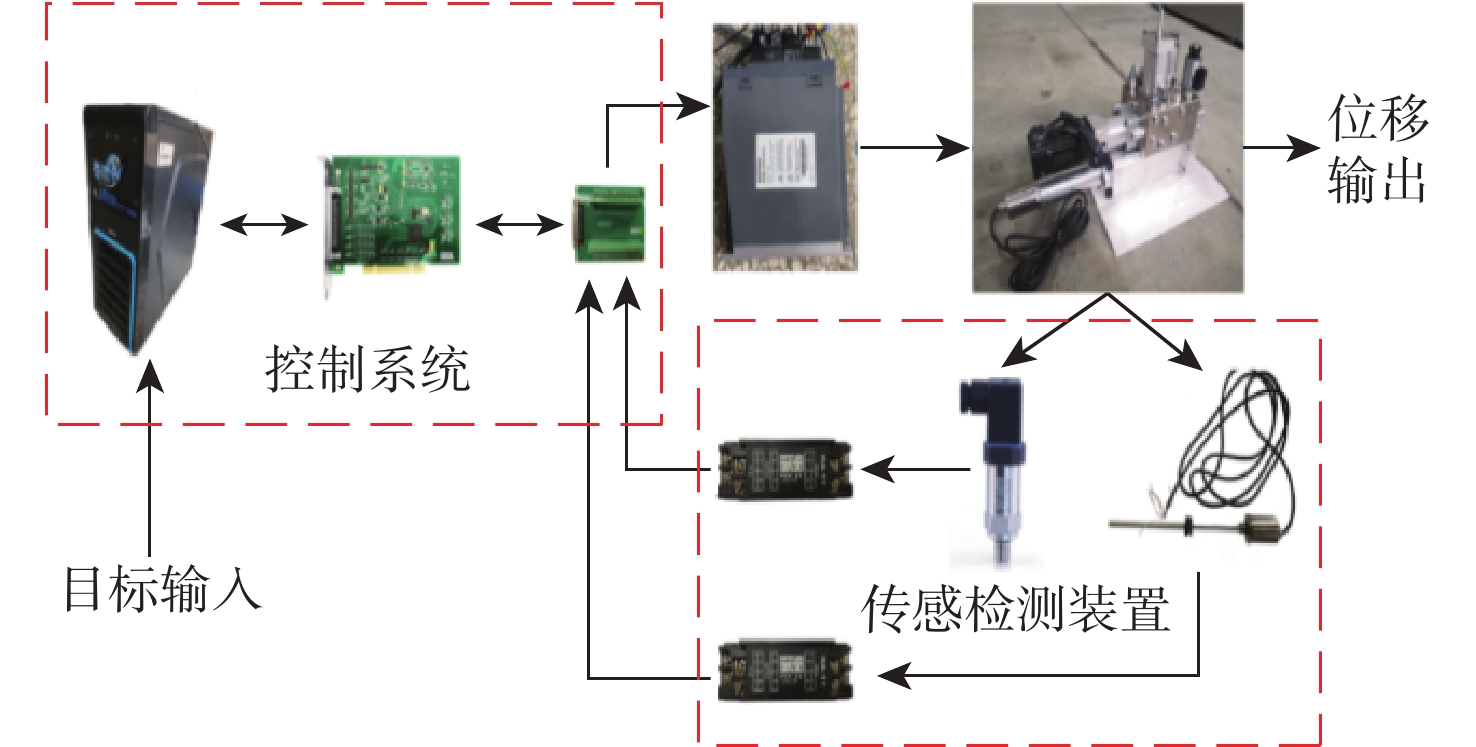
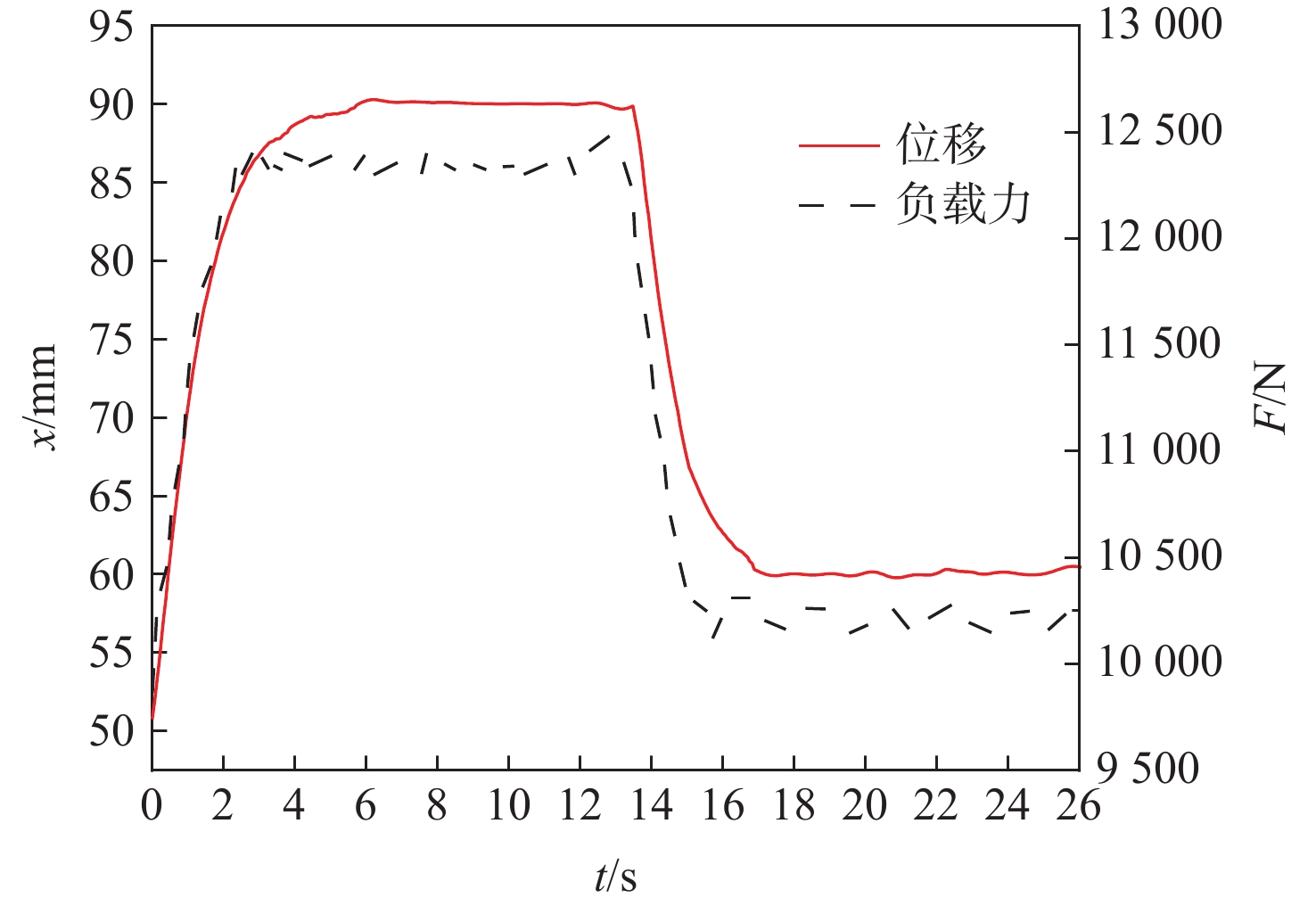
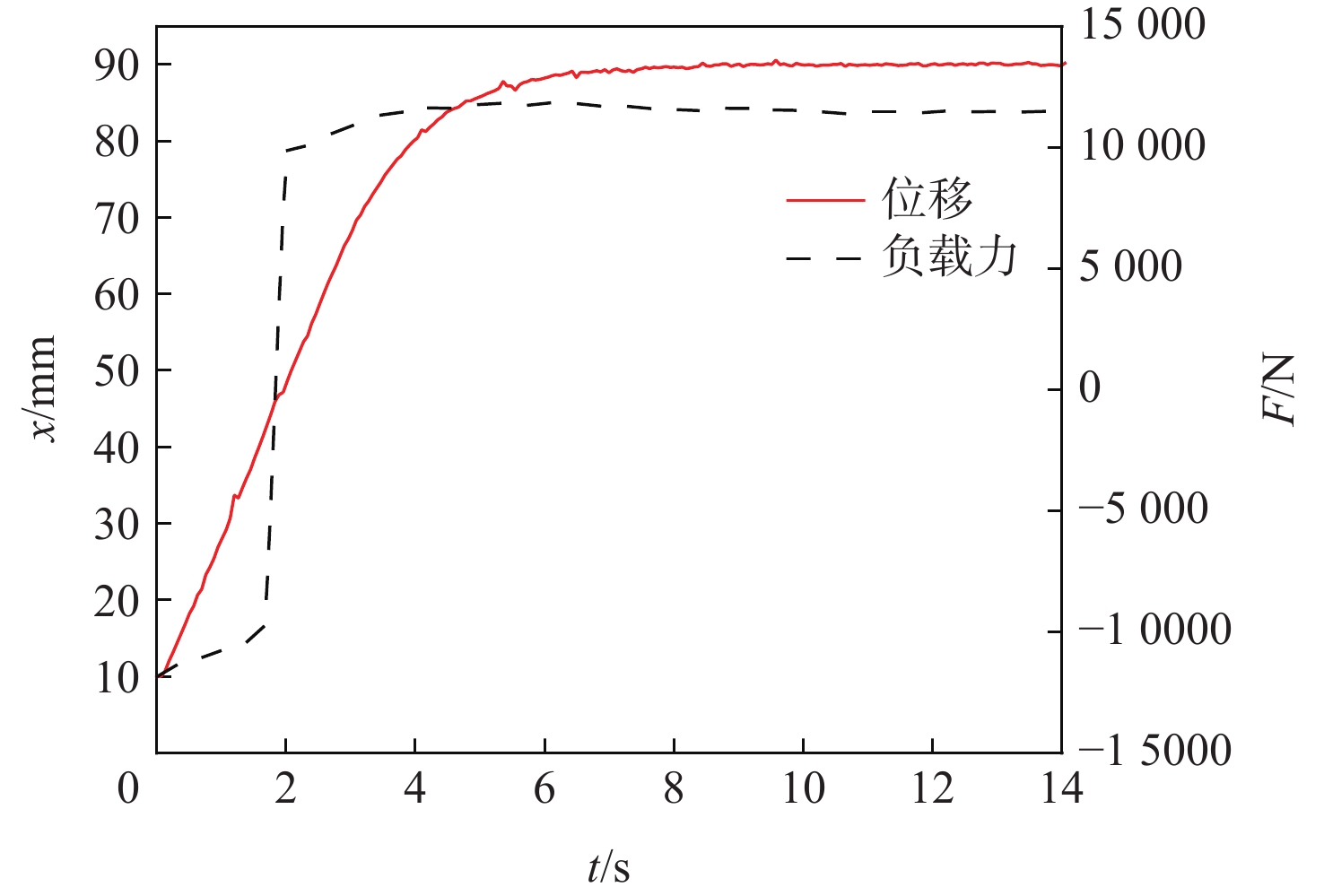
为提高钢轨打磨车打磨钢轨的平顺性及稳定性,提出以电动静液作动器(EHA)代替传统液压作动系统作为钢轨打磨车的专用执行器,考虑柱塞泵的总效率波动和液压缸动静摩擦差异大2个非线性因素,建立非线性数学模型;建立EHA的MATLAB、AMESim联合仿真模型,对PID控制、滑模变结构控制、反演控制进行控制策略对比研究,仿真分析验证反演控制在响应快速性及稳定性方面具有良好的表现。搭建四象限平台对EHA进行反演控制负载试验,结果表明:其位移控制精度达0.21 mm,具有较好的控制性能。
Abstract:In order to improve the smoothness and stability of rail grinding by the rail grinding vehicle, an electric hydrostatic actuator (EHA) was proposed to replace the traditional hydraulic system as the special actuator of the rail grinding vehicle. By considering the nonlinear factors including the total efficiency fluctuation of the plunger pump and the large difference between the dynamic and static friction of the hydraulic cylinder, a nonlinear mathematical model was established. The MATLAB and AMESim joint simulation model of EHA was established, and the control strategies of PID control, sliding mode variable structure control, and backstepping control were compared. The simulation analysis verified that the backstepping control had good performance in response speed and stability. The four quadrant platform was built to carry out the backstepping control load test of EHA. The results show that its displacement control accuracy reaches 0.21 mm, indicating good control performance.
-
表 1 EHA设计指标
Table 1. Design indexes of EHA
行程/mm 负载力/KN 速度/(mm·s−1) 位移全尺寸精度/% 100 ≤10 ≥20 ≤0.77 表 2 摩擦模型相关参数
Table 2. Relevant parameters of friction model
σ0/(N⋅m) σ1/(N⋅m⋅s−1) σ2/(N⋅m⋅s−1) vs/(N⋅m⋅s−1) fc/kN fs/kN 2.1×107 0.1 150 0.1 142 12 表 3 EHA仿真参数
Table 3. Simulation parameters of EHA
参数 数值 油缸有效行程/mm 100 油缸直径/mm 63 活塞杆直径/mm 35 泵额定转速/(r·min−1) 3000 泵排量/(ml·r−1) 1 溢流压力/MPa 8 转子惯量/(kg⋅m2) 2.7×10−5 线电阻/Ω 5.5 线电感/H 9.6×10−3 反电势常数/(V⋅m⋅r−1) 3.2×10−2 表 4 不同控制策略仿真数据
Table 4. Simulation data of different control strategies
控制策略 上升时间/s 控制精度/mm 最大超调量占比/% PID控制 4.97 0.037 0.08 滑模变结构控制 2.74 0.642 1.28 反演控制 3.56 0.035 0.07 表 5 反演控制试验数据
Table 5. Backstepping control test data
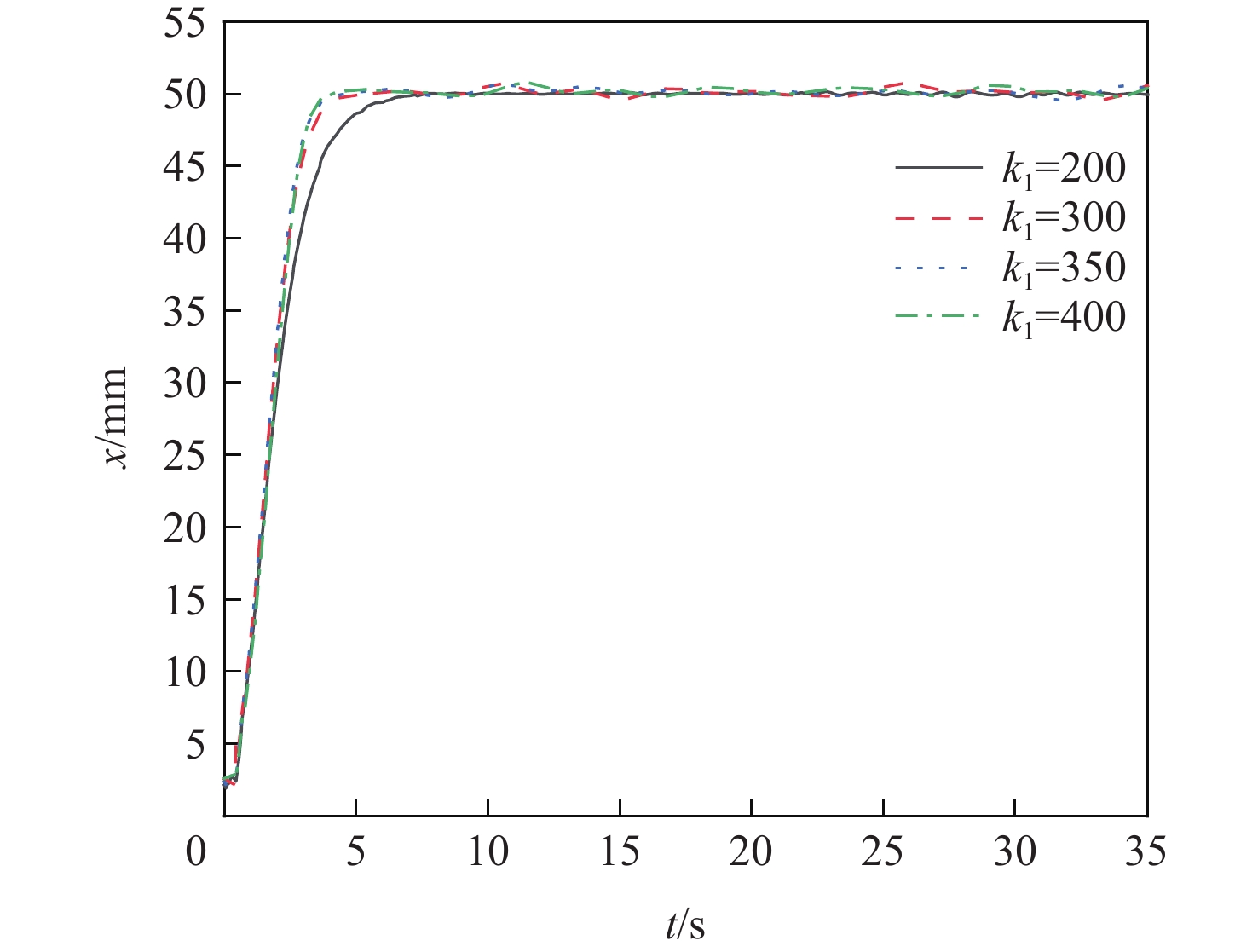
反演代表参数 上升时间/s 控制精度/mm 最大超调量占比/% k1=200 8.49 0.09 0.18 k1=300 5.54 0.72 1.43 k1=350 4.62 0.65 1.31 k1=400 4.12 0.77 1.54 -
[1] 铁道技术监督编辑部. 新时代交通强国铁路先行规划纲要[J]. 铁道技术监督, 2020, 48(9): 1-6. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9178.2020.09.001Editorial Department of Railway Quality Control. Outline of powerful nation railway advance planning in the new era[J]. Railway Quality Control, 2020, 48(9): 1-6 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9178.2020.09.001 [2] SCHOCH W. Rail grinding strategies for achieving optimum results: An inventory[J]. Rail Engineering International, 2008, 37(1): 4-6. [3] 李军. 钢轨打磨技术及其应用[J]. 铁路采购与物流, 2017, 12(3): 59-60. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7121.2017.03.015LI J. Rail grinding technology and its application[J]. Railway Purchasing and Logistics, 2017, 12(3): 59-60 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7121.2017.03.015 [4] SATOH Y, IWAFUCHI K. Effect of rail grinding on rolling contact fatigue in railway rail used in conventional line in Japan[J]. Wear, 2008, 265(9-10): 1342-1348. doi: 10.1016/j.wear.2008.02.036 [5] SROBA P, RONEY M. Rail grinding best practices[C]//Proceedings of the Annual Conference of the American Railway Engineering and Maintenance of Way Association. Chicago: IL, 2003: 1-41. [6] KALOUSEK J, SROBA P, MAGEL E. Shuswap subdivision rail samples metallographic examination of high and low rails from sharp curves[R]. Washington, D. C. : NRC, 2000. [7] 熊志林, 陶建峰, 张峰榕, 等. 采用状态估计的泵控非对称液压缸模型预测控制[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2017, 51(4): 109-115.XIONG Z L, TAO J F, ZHANG F R, et al. A model predictive control strategy of pump-controlled asymmetric cylinders using state estimation[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2017, 51(4): 109-115 (in Chinese). [8] 纪铁铃, 齐海涛, 滕雅婷. 基于AMESim和MATLAB联合仿真的EHA滑模变结构控制分析[J]. 液压与气动, 2016(3): 19-24. doi: 10.11832/j.issn.1000-4858.2016.03.004JI T L, QI H T, TENG Y T. Analysis of sliding-mode control for EHA based on AMESim and MATLAB co-simulation[J]. Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics, 2016(3): 19-24 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11832/j.issn.1000-4858.2016.03.004 [9] 付永领, 王利剑, 齐海涛, 等. 基于DSP和CPLD的电动静液作动器双余度控制器设计[J]. 测控技术, 2010, 29(1): 39-43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8829.2010.01.013FU Y L, WANG L J, QI H T, et al. Design of dual-redundancy control system for electro-hydrostatic actuator based on DSP and CPLD[J]. Measurement & Control Technology, 2010, 29(1): 39-43 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8829.2010.01.013 [10] 张星晴, 段富海. 基于遗传算法的EHA调速系统设计与优化[J]. 计算机仿真, 2014, 31(8): 32-36. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2014.08.008ZHANG X Q, DUAN F H. Design and optimization of EHA speed control system based on genetic algorithm[J]. Computer Simulation, 2014, 31(8): 32-36 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2014.08.008 [11] KOKOTOVIC P, ARCAK M. Constructive nonlinear control: Progress in the 90's[C]//Proceedings of the IFAC. Beijing: IFAC , 1999, 32(2): 49-77. [12] 冯娜娜. 钢轨打磨设备及运用[M]. 成都: 西南交通大学出版社, 2017: 6-8.FENG N N. Rail grinding equipment and its application[M]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University Press, 2017: 6-8 (in Chinese). [13] 舒志兵. 交流伺服运动控制系统[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2006: 20-33.SHU Z B. AC servo motion control system[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2006: 20-33 (in Chinese). [14] 王春行. 液压控制系统[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2011: 60-65.WANG C X. Hydraulic control system[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2011: 60-65(in Chinese). [15] 付永领, 李祝锋, 祁晓野, 等. 轴向柱塞式电液泵能量转化效率研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2014, 50(14): 204-212. doi: 10.3901/JME.2014.14.204FU Y L, LI Z F, QI X Y, et al. Research on the energy conversion efficiency of axial piston electro-hydraulic pump[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 50(14): 204-212 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3901/JME.2014.14.204 [16] 王林鸿, 吴波, 杜润生, 等. 液压缸运动的非线性动态特征[J]. 机械工程学报, 2007, 43(12): 12-19. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6686.2007.12.003WANG L H, WU B, DU R S, et al. Nonlinear dynamic characteristics of moving hydraulic cylinder[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2007, 43(12): 12-19 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0577-6686.2007.12.003 [17] CANUDAS DE WIT C, OLSSON H, ASTROM K J, et al. A new model for control of systems with friction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1995, 40(3): 419-425. doi: 10.1109/9.376053 [18] ZHOU Z, ZHENG X D, WANG Q, et al. Modeling and simulation of point contact multibody system dynamics based on the 2D LuGre friction model[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2021, 158: 104244. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2021.104244 [19] 邹怀静, 王海波, 王鑫, 等. 高功率密度微型斜盘式柱塞泵虚拟样机仿真分析[J]. 机床与液压, 2022, 50(10): 148-153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2022.10.028ZOU H J, WANG H B, WANG X, et al. Virtual prototype simulation analysis of high power density miniature axial piston pump[J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2022, 50(10): 148-153 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2022.10.028 [20] 何建海, 张建霞. 基于AMESim及MATLAB/Simulink联合仿真的风帆转角复合控制[J]. 机床与液压, 2022, 50(4): 140-145. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2022.04.027HE J H, ZHANG J X. Compound control of the sail angle based on AMESim-MATLAB/simulink co-simulation[J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2022, 50(4): 140-145 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2022.04.027 [21] BUTT K, COSTA G K, SEPEHRI N. Optimization-driven controller design for a high-performance electro-hydrostatic asymmetric actuator operating in all quadrants[J]. Journal of Dynamic Systems, Measurement, and Control, 2021, 143(9): 094503. doi: 10.1115/1.4050722 [22] ZOU H J, WANG H B, WANG X, et al. Research on electro-hydrostatic actuator for large scale operation and maintenance equipment of railway line[C]//Proceedings of the ICRT. Reston: American Society of Civil Engineers, 2022: 503-514. [23] 王鑫, 王海波, 邹怀静. 非对称液压缸EHA专用流量匹配阀的设计与分析[J]. 机床与液压, 2022, 50(6): 65-70. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2022.06.011WANG X, WANG H B, ZOU H J. Design and analysis of EHA special flow matching valve for asymmetric hydraulic cylinder[J]. Machine Tool & Hydraulics, 2022, 50(6): 65-70 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3881.2022.06.011 -







 下载:
下载: