-
摘要:
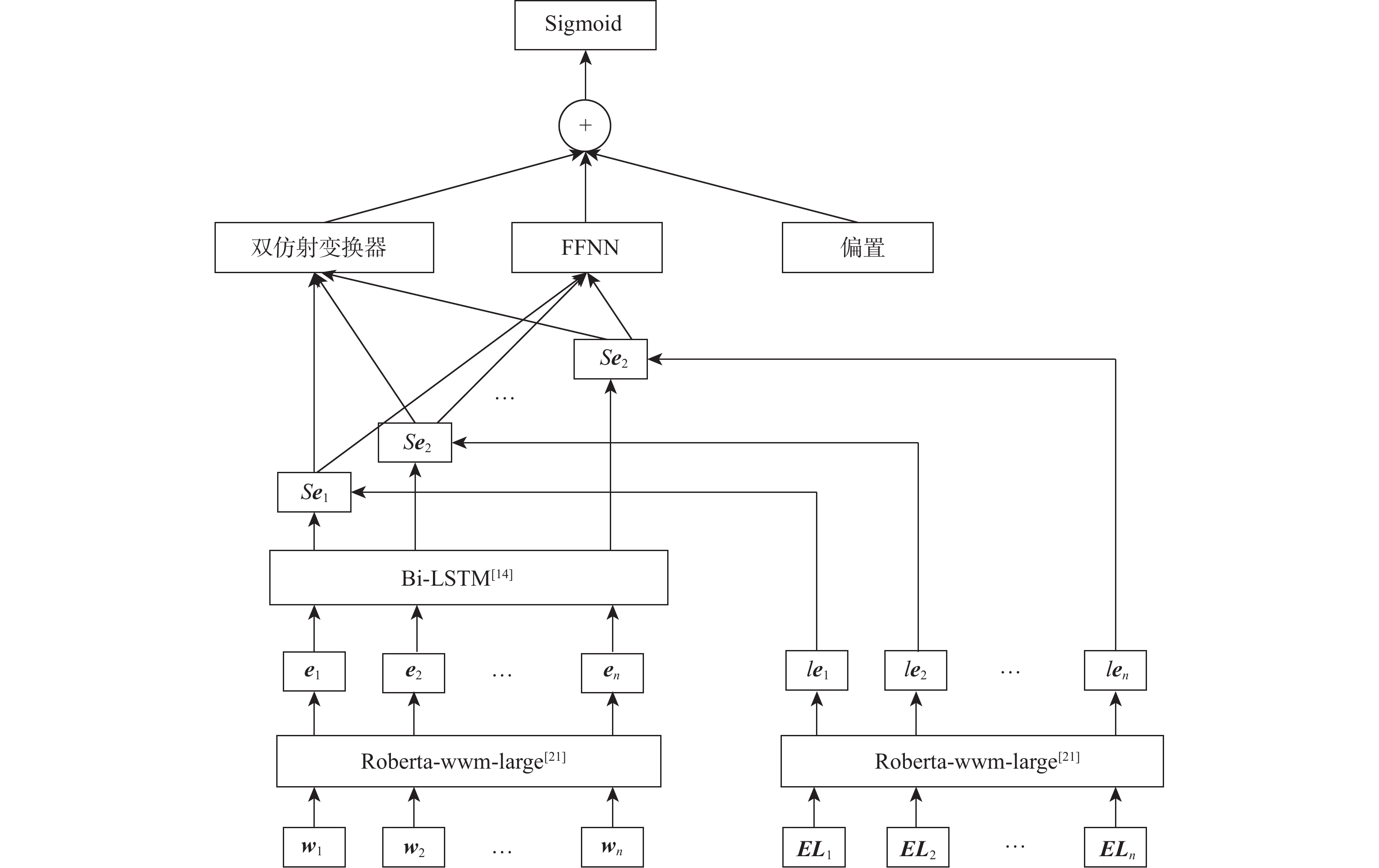
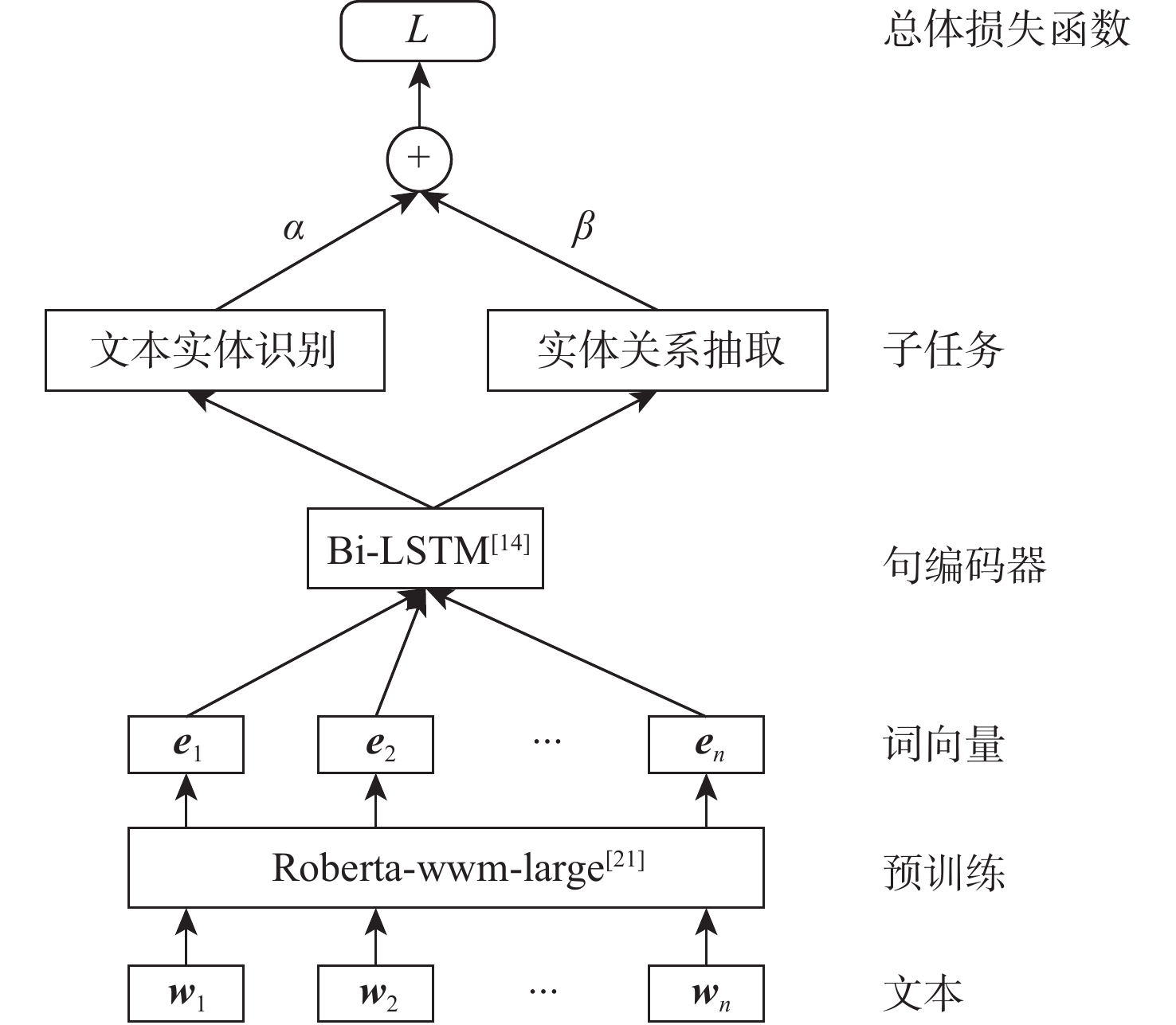
为提升电力系统故障文本在实际业务场景中的分析处理速度,提出基于预训练与多任务学习的电力故障文本信息自动抽取模型。利用预训练模型学习电力文本词语的上下文信息,挖掘词语的一阶和二阶融合特征,增强特征的表示能力,利用多任务学习框架结合命名实体识别和关系抽取2个任务的学习,实现实体识别和关系抽取的互相补充和互相促进,进而提高电力故障文本信息抽取的性能。通过对某电力网数据中心的日常业务数据进行模型验证,与其他模型相比,所提模型提高了电力故障文本实体识别和关系抽取的准确率和召回率。
Abstract:In order to improve the analysis and processing speed of power system fault text in actual business scenarios, a power fault text information extraction model based on pre-training and multi-task learning was proposed. The pre-training model was used to learn the context information of power text words. The first-order and second-order fusion features of words were mined, which enhanced the representation ability of features. The multi-task learning framework was used to combine named entity recognition and relation extraction, which realized the mutual supplement and mutual promotion of entity recognition and relationship extraction, so as to improve the performance of power fault text information extraction. The model was verified by the daily business data of a power data center. Compared with other models, the proposed model’s accuracy and recall of power fault text entity recognition and relation extraction were improved.
-
Key words:
- power fault /
- pre-training /
- multi-task learning /
- entity recognition /
- relation extraction
-
表 1 实体标签统计信息
Table 1. Entity statistics
实体类别 实体数量/个 实体占比/% 发电设备 2204 13.68 电动设备 2992 18.57 环境信息 3321 20.61 电力电缆 1046 6.49 显示设备 1543 9.575 控制器件 865 5.37 其他实体 4134 25.65 表 2 关系标签统计信息
Table 2. Relation statistics
关系类别 关系数量/个 关系占比/% 同类 2 023 21.95 原因 1757 19.06 故障 1245 13.50 从属 970 10.52 其他关系 3223 34.96 表 3 命名实体识别结果
Table 3. Results of named entity recognition
% 表 4 多命名实体识别结果
Table 4. Results of multiple named entity recognition
% 表 5 关系抽取结果
Table 5. Results of multiple relation extraction
% 表 6 多关系抽取结果
Table 6. Results of multiple relation extraction
% 表 7 消融实验结果
Table 7. Results of ablation tests
% 模型 P R 实体 关系 实体 关系 MTEIE-BERT 89.56 83.35 88.35 82.12 MTEIE-Entity 84.34 83.54 MTEIE-Relation 90.05 89.78 MTEIE 91.16 85.19 90.23 84.67 表 8 F1值混淆矩阵分析
Table 8. Confusion matrix analysis of F1
% 方法 实体识别 关系抽取 仅关系抽取 83.94 仅命名实体识别 89.91 关系抽取+命名实体识别 90.69 84.93 表 9 案例分析
Table 9. Case analysis
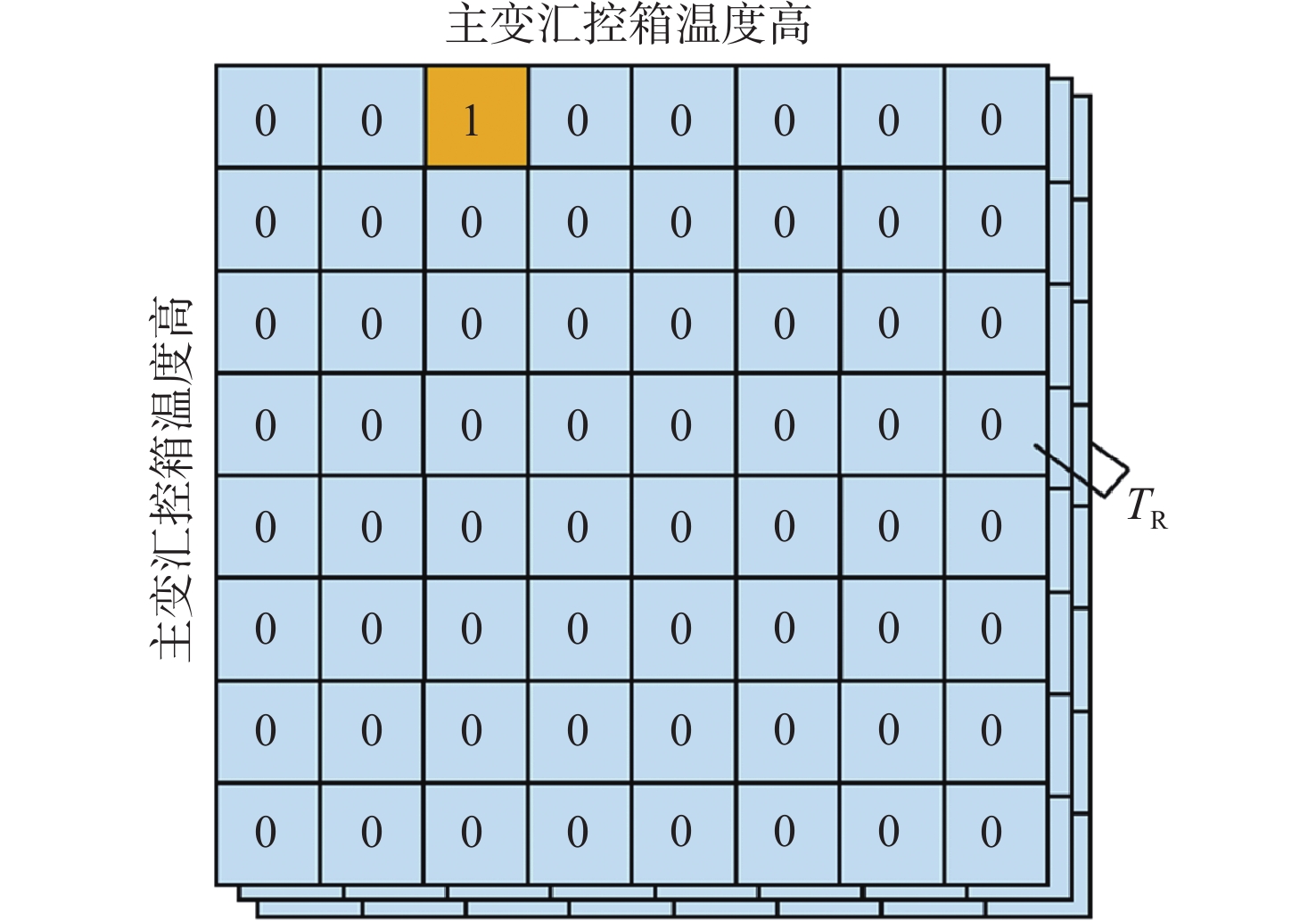
模型 案例1 案例2 原文 1号主变汇控箱内液晶显示温度与变压器本体温度差值过大,怀疑显示不准确 2号主变有载分接开关机械限位松动,导致开关出现多次滑档 Bi-LSTM+CRF+BERT {主变,汇控箱,从属关系};
{主变,温度差值,原因关系}{主变,机械限位,从属关系};
{机械限位,开关,故障关系}MTEIE {主变,汇控箱,从属关系};
{汇控箱,温度差值,故障关系};
{温度差值,显示,原因关系}{主变,机械限位,从属关系};
{机械限位,开关,原因关系} -
[1] 周念成, 廖建权, 王强钢, 等. 深度学习在智能电网中的应用现状分析与展望[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2019, 43(4): 180-191. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20180323002ZHOU N C, LIAO J Q, WANG Q G, et al. Analysis and prospect of deep learning application in smart grid[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2019, 43(4): 180-191 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7500/AEPS20180323002 [2] 李刚, 张博, 赵文清, 等. 电力设备状态评估中的数据科学问题: 挑战与展望[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2018, 42(21): 10-20. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20180331006LI G, ZHANG B, ZHAO W Q, et al. Data science issues in state evaluation of power equipment: Challenges and prospects[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2018, 42(21): 10-20 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7500/AEPS20180331006 [3] 薛禹胜, 赖业宁. 大能源思维与大数据思维的融合(一)大数据与电力大数据[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2016, 40(1): 1-8. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20151208005XUE Y S, LAI Y N. Integration of macro energy thinking and big data thinking part one big data and power big data[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2016, 40(1): 1-8 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7500/AEPS20151208005 [4] 邱剑, 王慧芳, 应高亮, 等. 文本信息挖掘技术及其在断路器全寿命状态评价中的应用[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2016, 40(6): 107-112. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20150812003QIU J, WANG H F, YING G L, et al. Text mining technique and application of lifecycle condition assessment for circuit breaker[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2016, 40(6): 107-112(in Chinese). doi: 10.7500/AEPS20150812003 [5] 邵冠宇, 王慧芳, 吴向宏, 等. 基于依存句法分析的电力设备缺陷文本信息精确辨识方法[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2020, 44(12): 178-185. doi: 10.7500/AEPS20190401001SHAO G Y, WANG H F, WU X H, et al. Precise information identification method of power equipment defect text based on dependency parsing[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2020, 44(12): 178-185 (in Chinese). doi: 10.7500/AEPS20190401001 [6] 郑伟彦, 杨勇, 卢家驹, 等. 面向配电网知识图谱的配电调度文本实体链接方法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2021, 49(4): 111-117.ZHENG W Y, YANG Y, LU J J, et al. Entity linking method of distribution dispatching texts for a distribution network knowledge graph[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2021, 49(4): 111-117 (in Chinese). [7] 余建明, 王小海, 张越, 等. 面向智能调控领域的知识图谱构建与应用[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2020, 48(3): 29-35.YU J M, WANG X H, ZHANG Y, et al. Construction and application of knowledge graph for intelligent dispatching and control[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2020, 48(3): 29-35 (in Chinese). [8] 何炎祥, 罗楚威, 胡彬尧. 基于CRF和规则相结合的地理命名实体识别方法[J]. 计算机应用与软件, 2015, 32(1): 179-185. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2015.01.046HE Y X, LUO C W, HU B Y. Geographic entity recognition method based on CRF model and rules combination[J]. Computer Applications and Software, 2015, 32(1): 179-185 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-386x.2015.01.046 [9] JACOBS P S, RAU L F. SCISOR: Extracting information from on-line news[J]. Communications of the ACM, 1990, 33(11): 88-97. doi: 10.1145/92755.92769 [10] WILLIAMS R J, ZIPSER D. A learning algorithm for continually running fully recurrent neural networks[J]. Neural Computation, 1989, 1(2): 270-280. doi: 10.1162/neco.1989.1.2.270 [11] BEKOULIS G, DELEU J, DEMEESTER T, et al. Joint entity recognition and relation extraction as a multi-head selection problem[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2018, 114: 34-45. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2018.07.032 [12] BEKOULIS G, DELEU J, DEMEESTER T, et al. Adversarial training for multi-context joint entity and relation extraction [EB/OL]. (2018-08-21) [2019-01-14]. [13] HOCHREITER S, SCHMIDHUBER J. Long short-term memory[J]. Neural Computation, 1997, 9(8): 1735-1780. doi: 10.1162/neco.1997.9.8.1735 [14] HUANG Z H, XU W, YU K. Bidirectional LSTM-CRF models for sequence tagging[EB/OL]. (2015-08-09) [2019-01-20]. [15] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J]. Communications of the ACM, 2017, 60(6): 84-90. doi: 10.1145/3065386 [16] NGUYEN T H, GRISHMAN R. Relation extraction: Perspective from convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the Workshop on Vector Space Modeling for Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2015: 39-48. [17] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: ACM, 2017: 6000-6010. [18] LI C, TIAN Y. Downstream model design of pre-trained language model for relation extraction task[EB/OL]. (2020-04-08) [2021-01-05]. [19] 佟佳弘, 武志刚, 管霖, 等. 电力调度文本的自然语言理解与解析技术及应用[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44(11): 4148-4156.TONG J H, WU Z G, GUAN L, et al. Power dispatching text analysis and application based on natural language understanding[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44(11): 4148-4156 (in Chinese). [20] 蒋晨, 王渊, 胡俊华, 等. 基于深度学习的电力实体信息识别方法[J]. 电网技术, 2021, 45(6): 2141-2149.JIANG C, WANG Y, HU J H, et al. Power entity information recognition based on deep learning[J]. Power System Technology, 2021, 45(6): 2141-2149 (in Chinese). [21] LIU Y H, OTT M, GOYAL N, et al. RoBERTa: A robustly optimized BERT pretraining approach[EB/OL]. (2019-07-26) [2021-01-06]. [22] LAFFERTY J D, MCCALLUM A, PEREIRA F C N. Conditional random fields: Probabilistic models for segmenting and labeling sequence data[C]//Proceedings of the Eighteenth International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2001: 282-289. [23] WEI M, XU Z P, HU J W. Entity relationship extraction based on Bi-LSTM and attention mechanism[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Information Systems. New York: ACM, 2021: 1-5. [24] 杨秋勇 , 彭泽武, 苏华权, 等. 基于Bi-LSTM-CRF的中文电力实体识别[J]. 信息技术, 2021, 9: 45-50.YANG Q Y, PENG Z W, SU H Q, et al. Chinese electric power entity recognition based on Bi-LSTM-CRF[J]. Information Technology, 2021, 9: 45-50 (in Chinese). [25] DOZAT T, MANNING C D. Deep biaffine attention for neural dependency parsing [EB/OL]. (2016-11-06) [2021-02-10]. [26] ZHOU W X, HUANG K, MA T Y, et al. Document-level relation extraction with adaptive thresholding and localized context pooling[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2021, 35(16): 14612-14620. [27] RAM R V S, AKILANDESWARI A, DEVI S L. Linguistic features for named entity recognition using CRFs[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Asian Language Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 158-161. [28] MA X Z, HOVY E. End-to-end sequence labeling via Bi-directional LSTM-CNNs-CRF[C]//Proceedings of the Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2016: 781-792. -







 下载:
下载: