-
摘要:
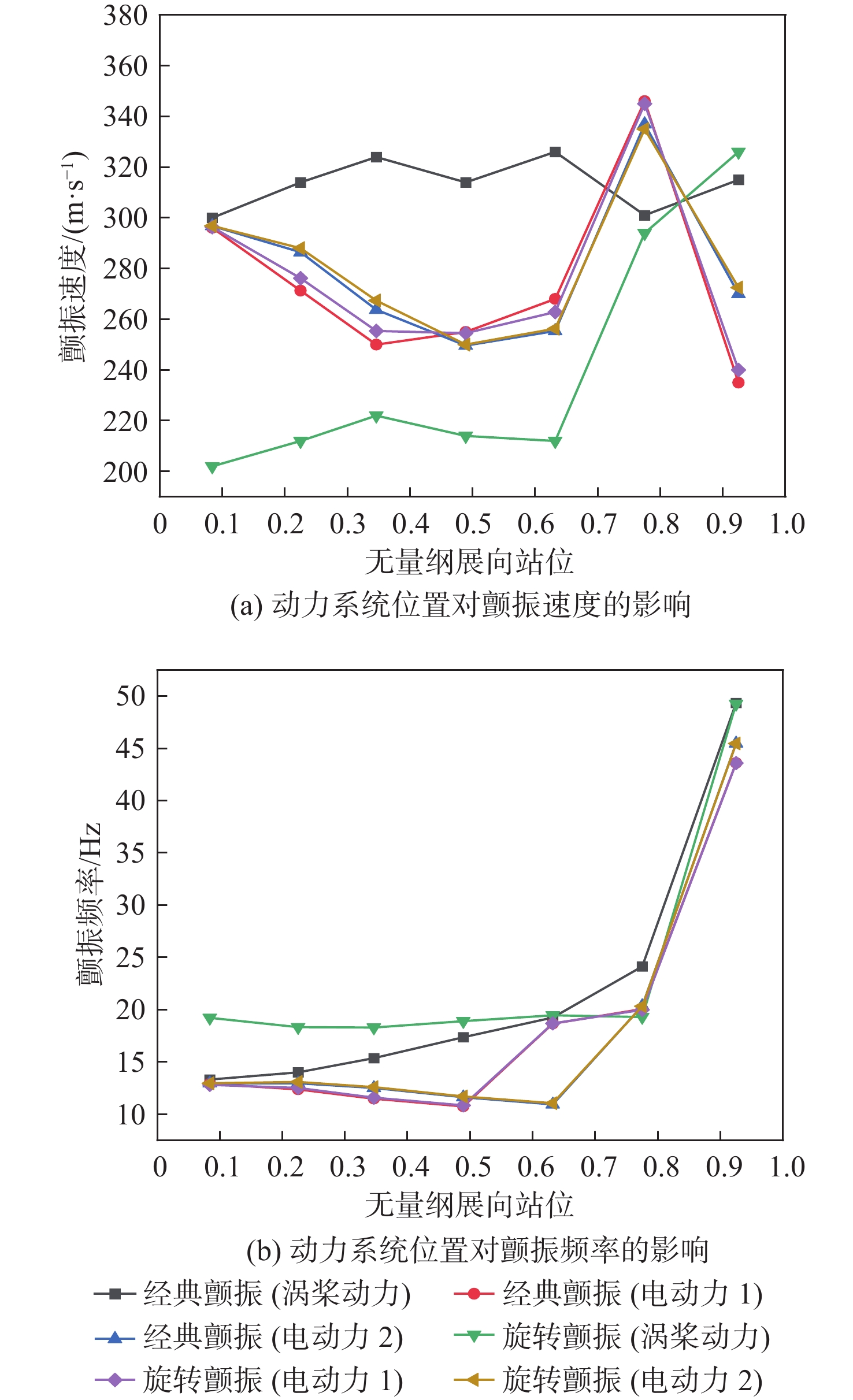
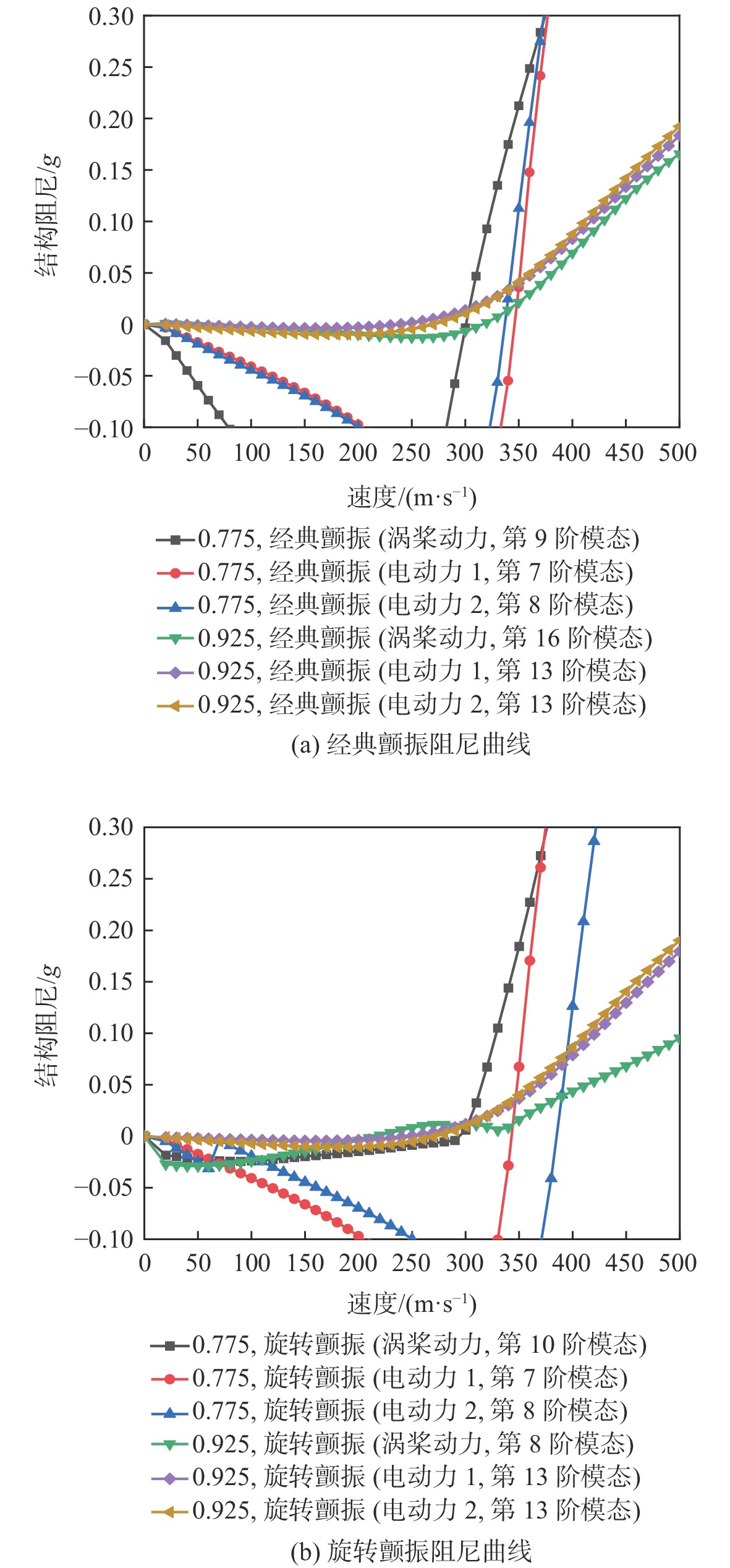
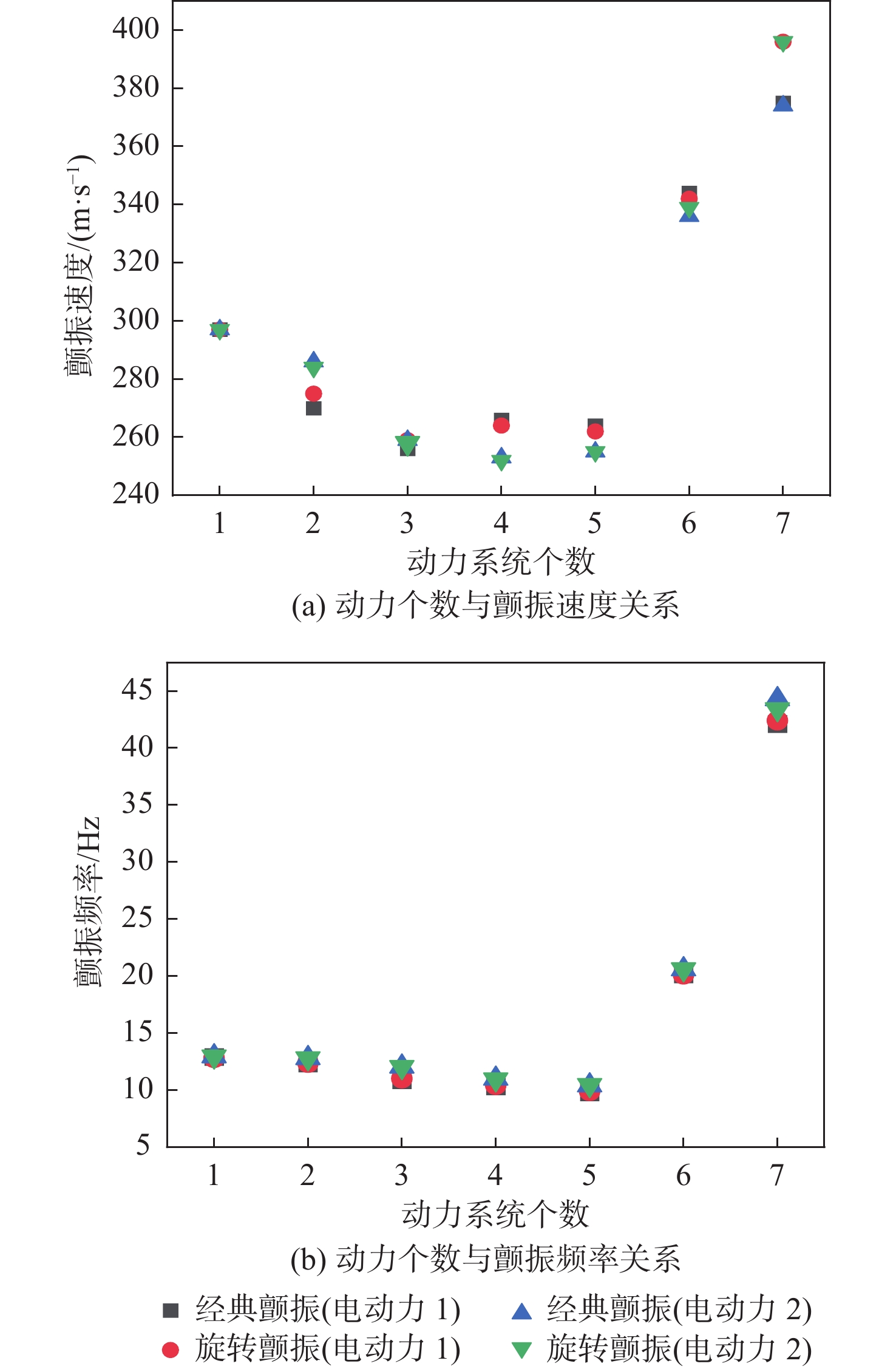
由于采用多个螺旋桨动力,旋转颤振成为分布式电推进飞机面临的重要气动弹性问题之一。基于机翼/短舱/桨耦合系统的运动关系及力作用关系,考虑机翼对螺旋桨的下洗和侧洗效应,推导出机翼、短舱和螺旋桨耦合系统的运动方程。将多套短舱/螺旋桨动力的陀螺力矩和螺旋桨非定常气动力引入机翼结构动力学模型,建立分布式电推进螺旋桨飞机颤振模型。通过对动力系统展向位置和动力系统数量的变参分析,研究分布式电推进螺旋桨飞机关键动力布局参数对旋转颤振特性的影响规律,并评估了2种典型的分布式电动螺旋桨飞机布局的颤振特性。结果表明:动力系统位于0.8倍翼展附近时,旋转颤振速度明显提高,而其他安装位置的参数不敏感。从翼根向翼梢逐渐增加动力数量的过程中,当动力个数少于5时,机翼的颤振速度对动力个数参数不敏感,而当动力个数增加至6时,机翼的经典颤振速度和旋转颤振速度均显著提高。在总刚度、总质惯量、总滑流效应和总功率等总体设计指标相当的前提下,动力系统相同分布式方案更佳,更有利于提高经典颤振速度和旋转颤振速度。
Abstract:Whirl flutter has become one of the essential aeroelastic problems faced by distributed electric propeller aircraft due to multiple propeller motors. Based on the motion and force relationship of the wing/nacelle/propeller coupling system, the downwash and sidewash effects of the wing on the propeller were considered, and the motion equation of the wing, nacelle, and propeller coupling system was derived. The gyroscopic moment of multiple sets of nacelle/propeller power and the unsteady propeller aerodynamic force were introduced into the wing structure dynamics model, and the flutter model of the distributed electric propeller aircraft was established. The influence of the critical dynamic layout parameters of the distributed electric propeller aircraft on the whirl flutter characteristics was studied through the variable parameter analysis of the spanwise position of the motor system and the number of motor systems. The flutter characteristics of two typical distributed electric propeller aircraft layouts were evaluated. The results show that when the motor system is located near 0.8 times the wingspan, the whirl flutter velocity is significantly improved, while other installation position parameters are insensitive. In the process of gradually increasing the motor quantity from the wing root to the wingtip, when the motor quantity is less than 5, the flutter speed of the wing is insensitive to the motor quantity parameter; when the motor quantity increases to 6, both the classical flutter velocity and the whirl flutter velocity of the wing are significantly improved. Under the premise that the overall design indicators such as total stiffness, total mass inertia, total slip flow effect, and total power are equivalent, the distributed scheme of the same motor system is better, which is beneficial to improving the classical flutter velocity and whirl flutter velocity.
-
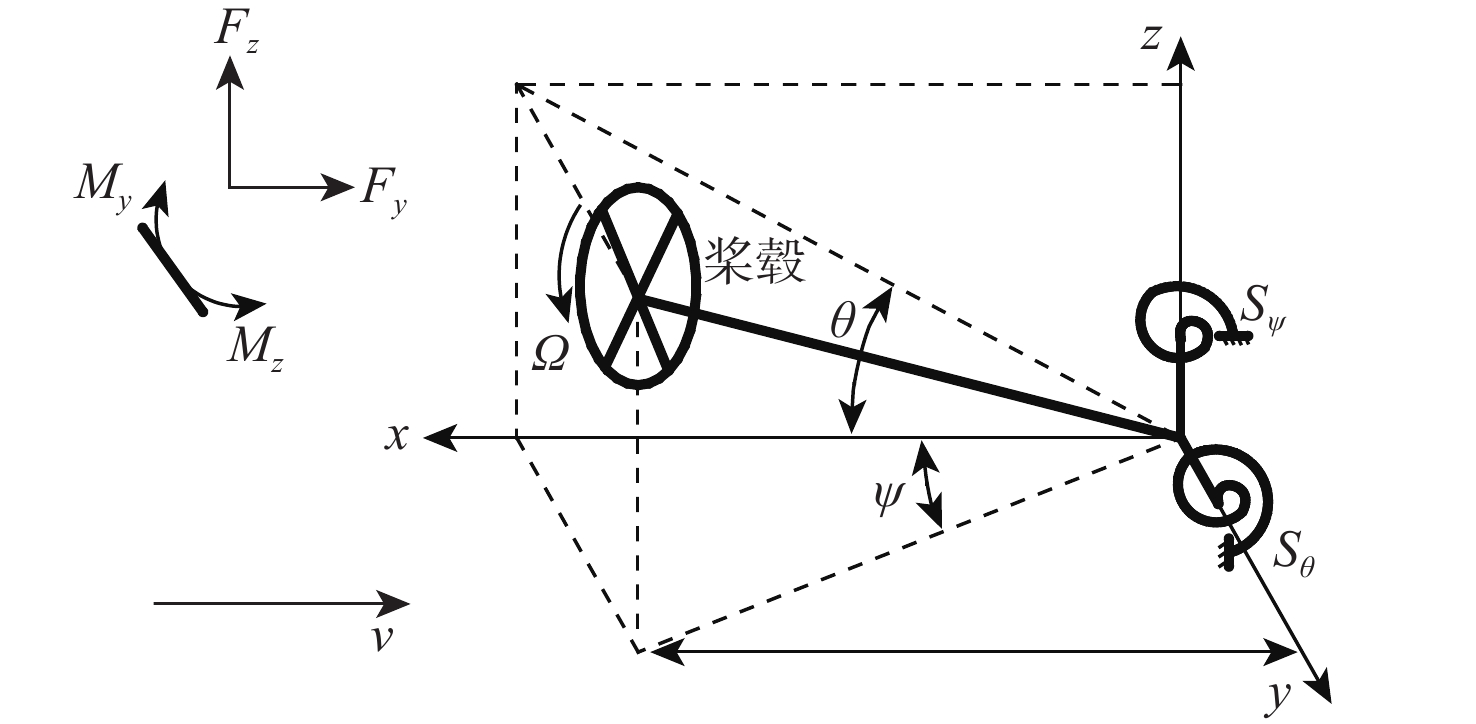
表 1 动力系统参数
Table 1. Motor system parameters
动力系统 桨盘
半径/m桨毂中心
距机翼前缘
距离/m桨叶
个数质量/kg 转动惯量/
(kg·m2)功率/
kW涡桨动力 2.21 2.64 6 260.09 99.49 3780 电动力1 0.84 0.82 6 37.14 2.05 540 电动力2 0.61 0.65 6 20 0.59 290 电动力3 1.62 1.01 6 140.03 28.84 2040 表 2 不同动力构型的颤振速度
Table 2. Flutter velocity of different dynamic configurations
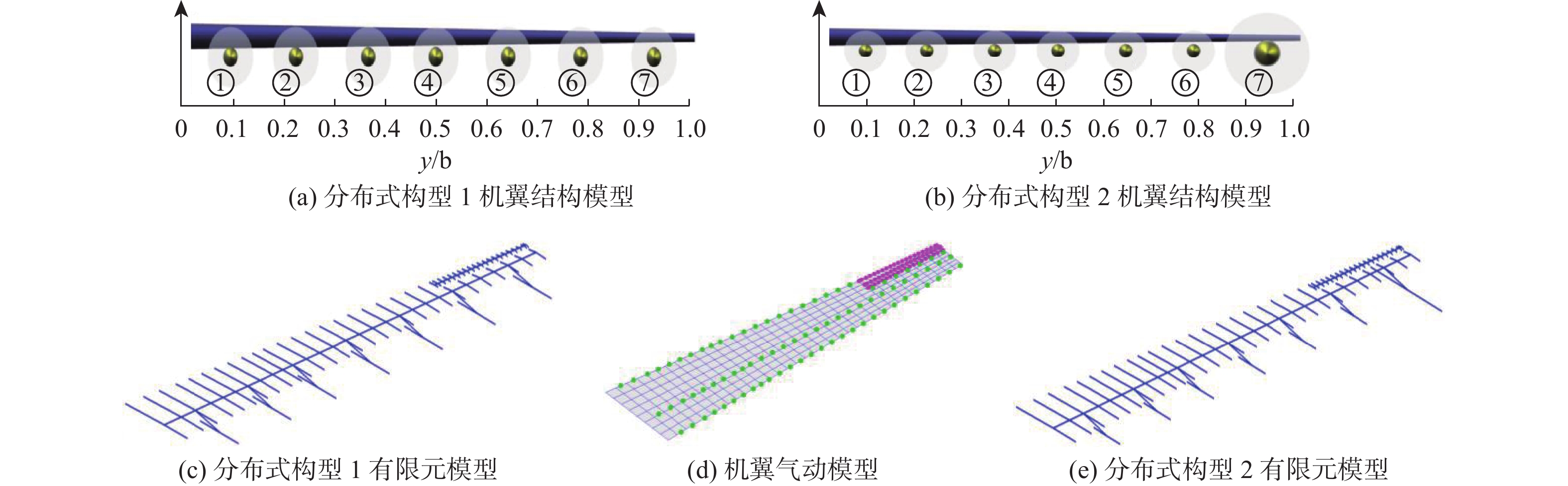
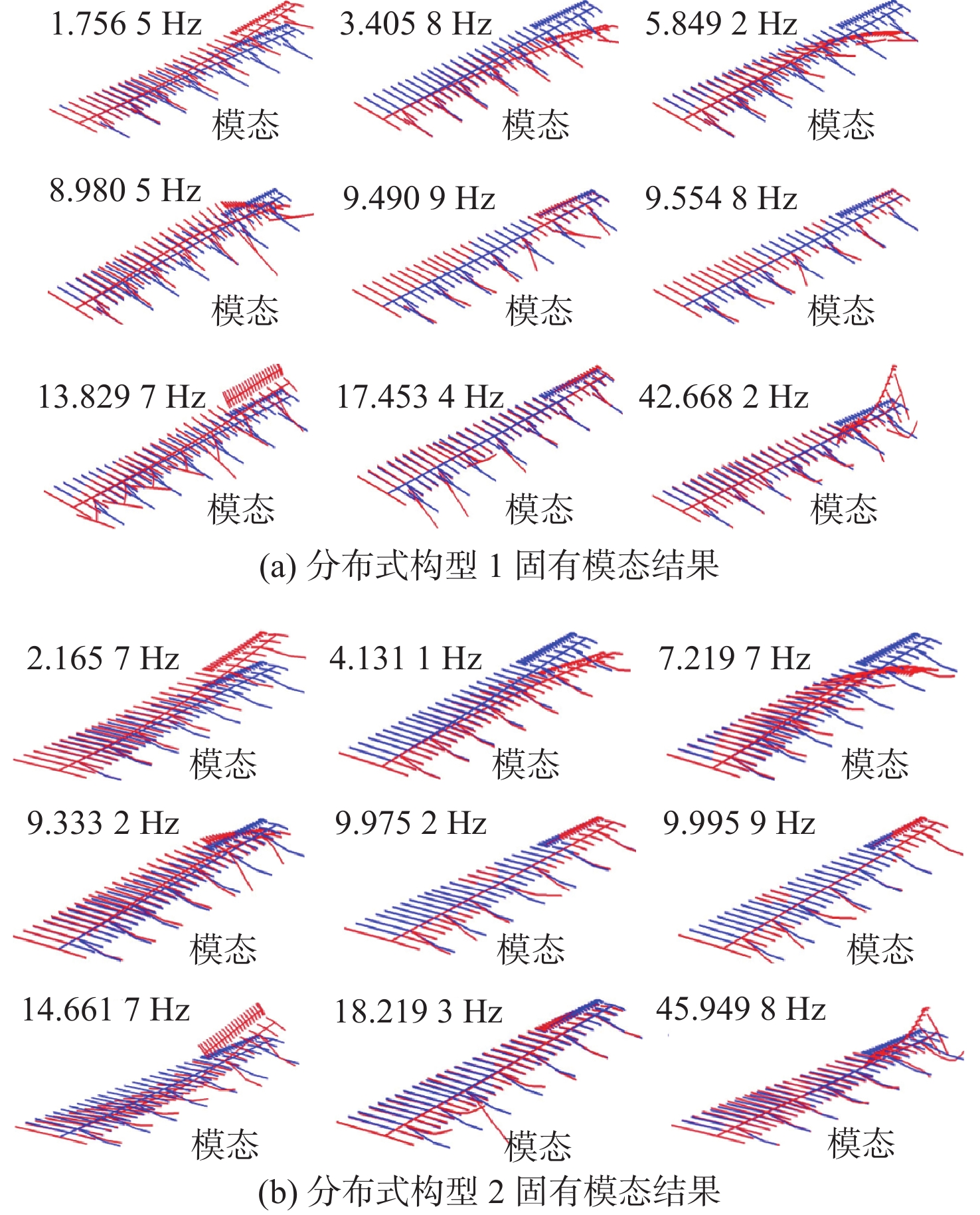
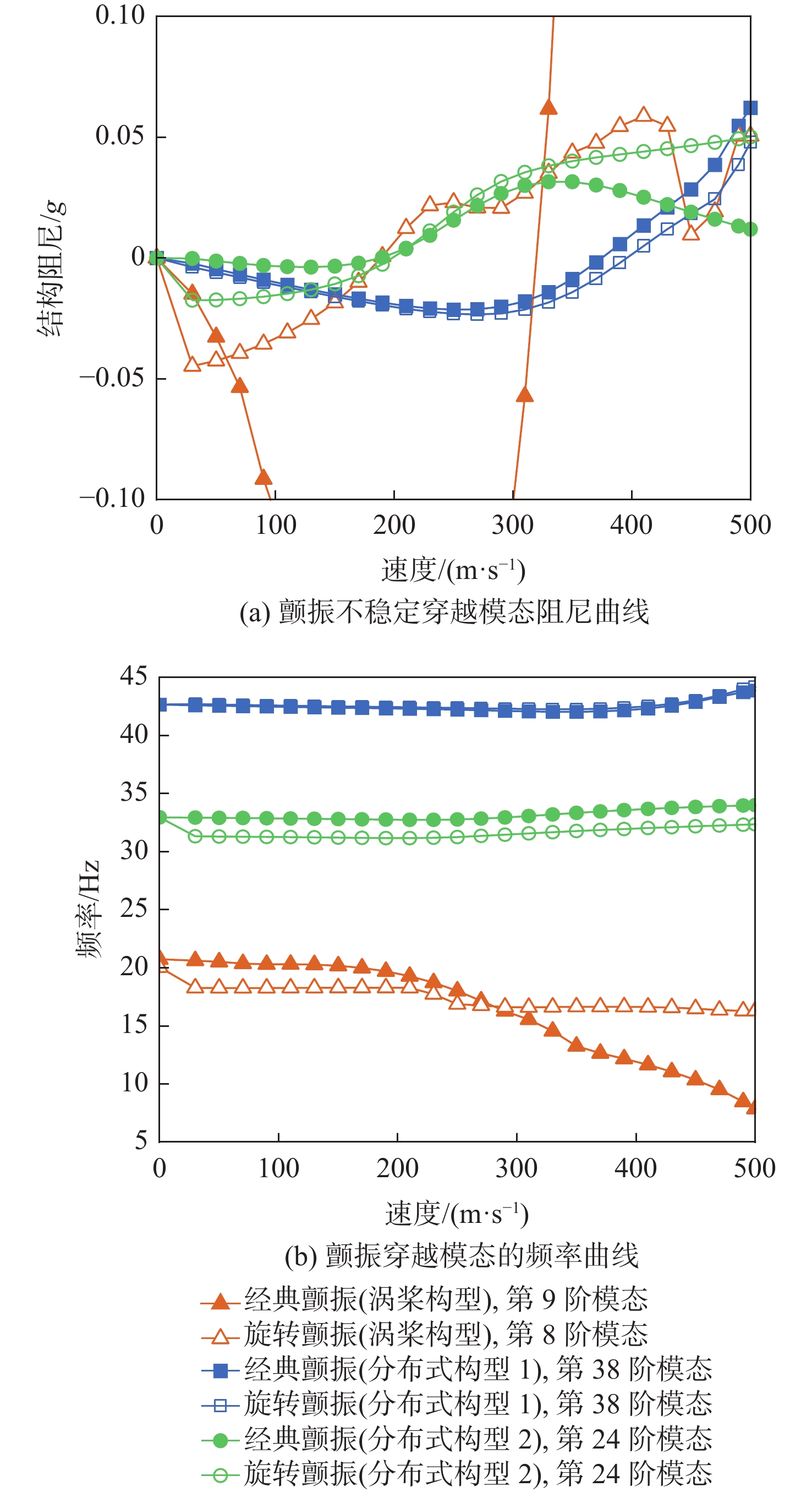
构型 经典颤振速度/(m·s−1) 旋转颤振速度/(m·s−1) 涡桨构型 320 219 分布式构型1 375 396 分布式构型2 188 198 -
[1] KIM H D, BROWN G V, FELDER J L. Distributed turboelectric propulsion for hybrid wing body aircraft[C]//Proceedings of the International Powered Lift Conference. London: Royal Aeronautical Society, 2018: 1-11. [2] 黄俊. 分布式电推进飞机设计技术综述[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(3): 624037.HUANG J. Survey on design technology of distributed electric propulsion aircraft[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(3): 624037 (in Chinese). [3] GOHARDANI A S, DOULGERIS G, SINGH R. Challenges of future aircraft propulsion: A review of distributed propulsion technology and its potential application for the all electric commercial aircraft[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2011, 47(5): 369-391. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2010.09.001 [4] GOHARDANI A S. A synergistic glance at the prospects of distributed propulsion technology and the electric aircraft concept for future unmanned air vehicles and commercial/military aviation[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2013, 57: 25-70. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2012.08.001 [5] 孔祥浩, 张卓然, 陆嘉伟, 等. 分布式电推进飞机电力系统研究综述[J]. 航空学报, 2018, 39(1): 021651.KONG X H, ZHANG Z R, LU J W, et al. Review of electric power system of distributed electric propulsion aircraft[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2018, 39(1): 021651(in Chinese). [6] KIM H D, PERRY A T, ANSELL P J. A review of distributed electric propulsion concepts for air vehicle technology[C]// Processing of the AIAA/IEEE Electric Aircraft Technologies Symposium. Reston: AIAA, 2018: 4998. [7] 中国人民解放军总装备部. 军用飞机结构强度规范第7部分:气动弹性:GJB 67.7A-2008[S]. 北京:国家军用标准-总装备部,2008: 1-8.General Armaments Department of the People's Liberation Army of China. Military aircraft structural strength specification Part 7: Aeroelasticity: GJB 67.7A-2008[S] Beijing: National Military Standard-General Armaments Department, 2008:1-8(in Chinese). [8] 中国民用航空总局运输类飞机适航标准 [M]. 北京: 中国民用航空总局, 2016: 76.Civil Aviation Administration of China. Transport category aircraft airworthiness standards[M]. Beijing: Civil Aviation Administration of China. 2016: 76(in Chinese). [9] REED W H, BLAND S R. An analytical treatment of aircraft propeller precession instability: NASA TN D-659[R]. Washington, D. C.: NASA, 1961: 6-26. [10] HOUBOLT J C, REED W H. Propeller-nacelle whirl flutter[J]. Journal of the Aerospace Sciences, 1962, 29(3): 333-346. doi: 10.2514/8.9417 [11] BLAND S R, BENNETT R M. Wind-tunnel measurement of propeller whirl-flutter speeds and static-stability derivatives and comparison with theory: NASA TN D-1807[R]. Washington, D. C.: NASA, 1963: 7-13. [12] REED W H. Review of propeller-rotor whirl flutter: NASA TR R-264[R]. Washington, D. C.: NASA, 1967:5-25. [13] RODDEN W P, ROSE T L. Propeller/nacelle whirl flutter addition to MSC/NASTRAN[C]//Proceedings of the MSC World User’s Conference. Los Angeles: MacNeal Schwendler Corp, 1989:1-29. [14] CECRDLE J. Analysis of twin turboprop aircraft whirl-flutter stability boundaries[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2012, 49(6): 1718-1725. doi: 10.2514/1.C031390 [15] 金一忱. 螺旋颤振分析[J]. 航空学报, 1993, 14(4): 210-213.JIN Y C. Whirl flutter analysis[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 1993, 14(4): 210-213 (in Chinese). [16] 刘济科, 赵令诚. 考虑弹性机翼影响的旋转颤振的动力学方程[J]. 机械强度, 1993, 15(4): 10-13.LIU J K, ZHAO L C. Dynamic equations for whirl flutter considering wing elasticity[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength, 1993, 15(4): 10-13(in Chinese). [17] 刘济科, 赵令诚. 考虑弹性机翼影响的旋转颤振方程的来解方法[J]. 机械强度, 1994, 16(2): 32-35.LIU J K, ZHAO L C. Solution method of rotating flutter equation considering the influence of elastic wing[J]. Journal of Mechanical Strength. 1994, 16(2): 32-35 (in Chinese). [18] 尧振兴, 姚一龙. 某型飞机旋转颤振特性分析[C]//第八届全国空气弹性学术交流会论文. 北京: 中国空气动力学会, 2003: 117-122(in Chinese).RAO Z X, YAO Y L. Analysis of whirl flutter characteristics of a certain aircraft[C]//Proceedings of the 8th National Aeroelasticity Academic Exchange Conference. Beijing: Chinese Aerodynamics Research Society, 2003: 117-122(in Chinese). [19] YANG Y X, HUANG G N, ZHAO D Q, et al. A New whirl flutter analysis method[C]//Processing of the 33rd AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2015, 2887. [20] 陈兆林, 杨智春, 谷迎松. 机翼对螺旋桨发动机旋转颤振的影响研究[J]. 航空学报, 2016, 37(11): 3351-3360.CHEN Z L, YANG Z C, GU Y S. Effect of wing on whirl flutter of propeller engine[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2016, 37(11): 3351-3360(in Chinese). [21] JOHNSON W. Dynamics of tilting proprotor aircraft in cruise fight: NASA TN D-7677[R]. Washington, D. C.: NASA, 1974:106-131. [22] NIXON M W. Aeroelastic response and stability of tiltrotors with elastically-coupled composite rotor blades[D]. Maryland: University of Maryland, 1993. [23] HATHAWAY E L, GANDHI F. Tiltrotor whirl flutter alleviation using actively controlled wing flaperons[J]. AIAA Journal, 2006, 44(11): 2524-2534. doi: 10.2514/1.18428 [24] 岳海龙. 倾转旋翼机倾转时旋翼/短舱/机翼耦合结构气弹响应研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2010: 23-27.YUE H L. Aeroelastic responses of coupled rotor-nacelle-wing structures of tiltrotor aircraft in conversion flight[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2010: 23-27 (in Chinese). [25] 董凌华, 杨卫东, 张呈林. 倾转旋翼/机翼耦合系统过渡状态气弹动力学试验研究[J]. 振动工程学报, 2008, 21(5): 465-470.DONG L H, YANG W D, ZHANG C L. Experiment on aeroelastic characteristics of tiltrotor aircraft in transition flight[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2008, 21(5): 465-470 (in Chinese). [26] HOOVER C B, SHEN J W, KRESHOCK A R. Propeller whirl flutter stability and its influence on X-57 aircraft design[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2018, 55(5): 2169-2175. doi: 10.2514/1.C034950 [27] HOOVER C B, SHEN J W. Parametric study of propeller whirl flutter stability with full-span model of X-57 maxwell aircraft[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2018, 55(6): 2530-2537. doi: 10.2514/1.C035081 [28] HOOVER C B, SHEN J W. Whirl flutter analysis of a free-flying electric-driven propeller aircraft[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2019, 56(2): 831-836. doi: 10.2514/1.C035263 [29] CRAVANA A, MANFREDA G, CESTINO E, et al. Aeroelastic behaviour of flexible wings carrying distributed electric propulsion systems[C]//SAE Technical Paper Series. Warrendale: SAE international, 2017, 1: 2061. -







 下载:
下载: