-
摘要:
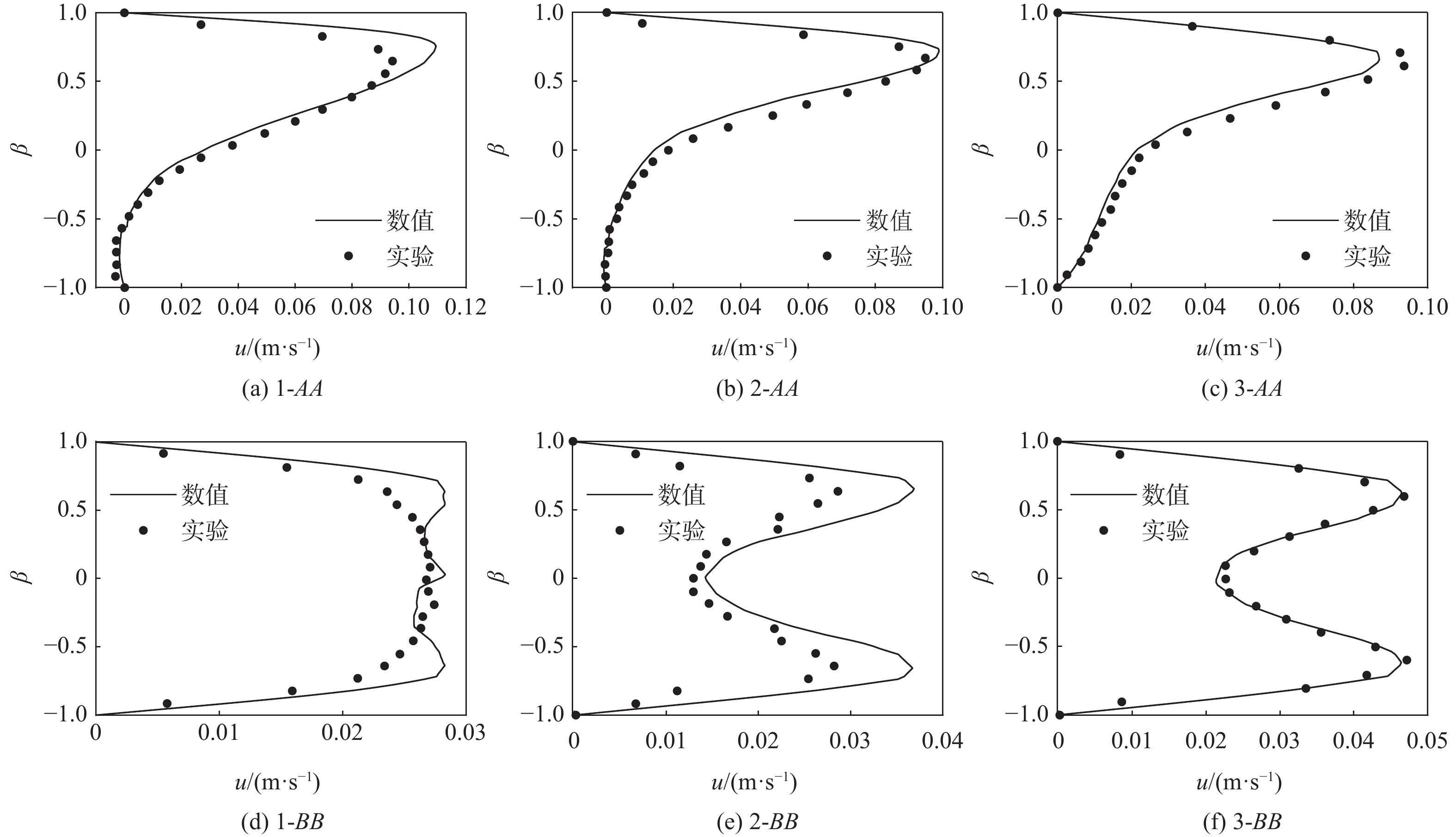
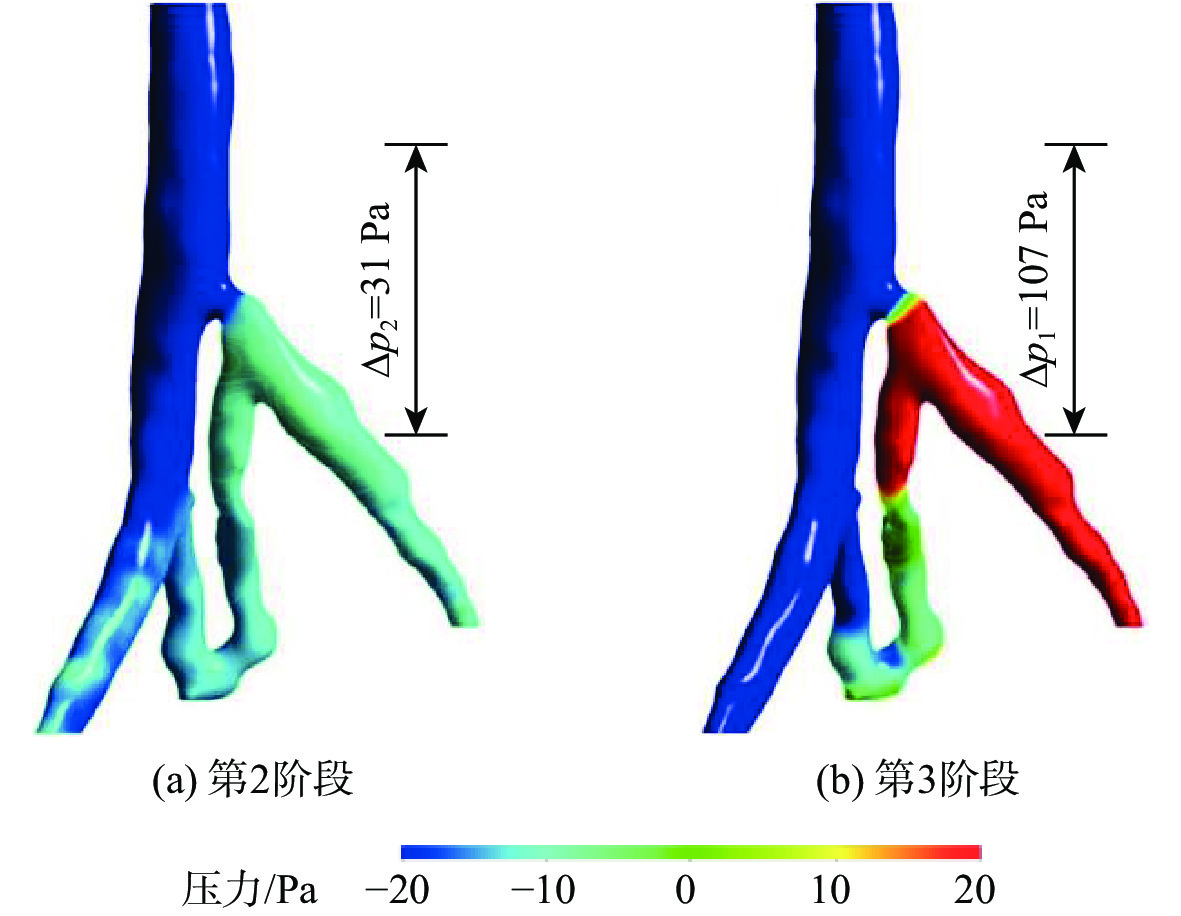
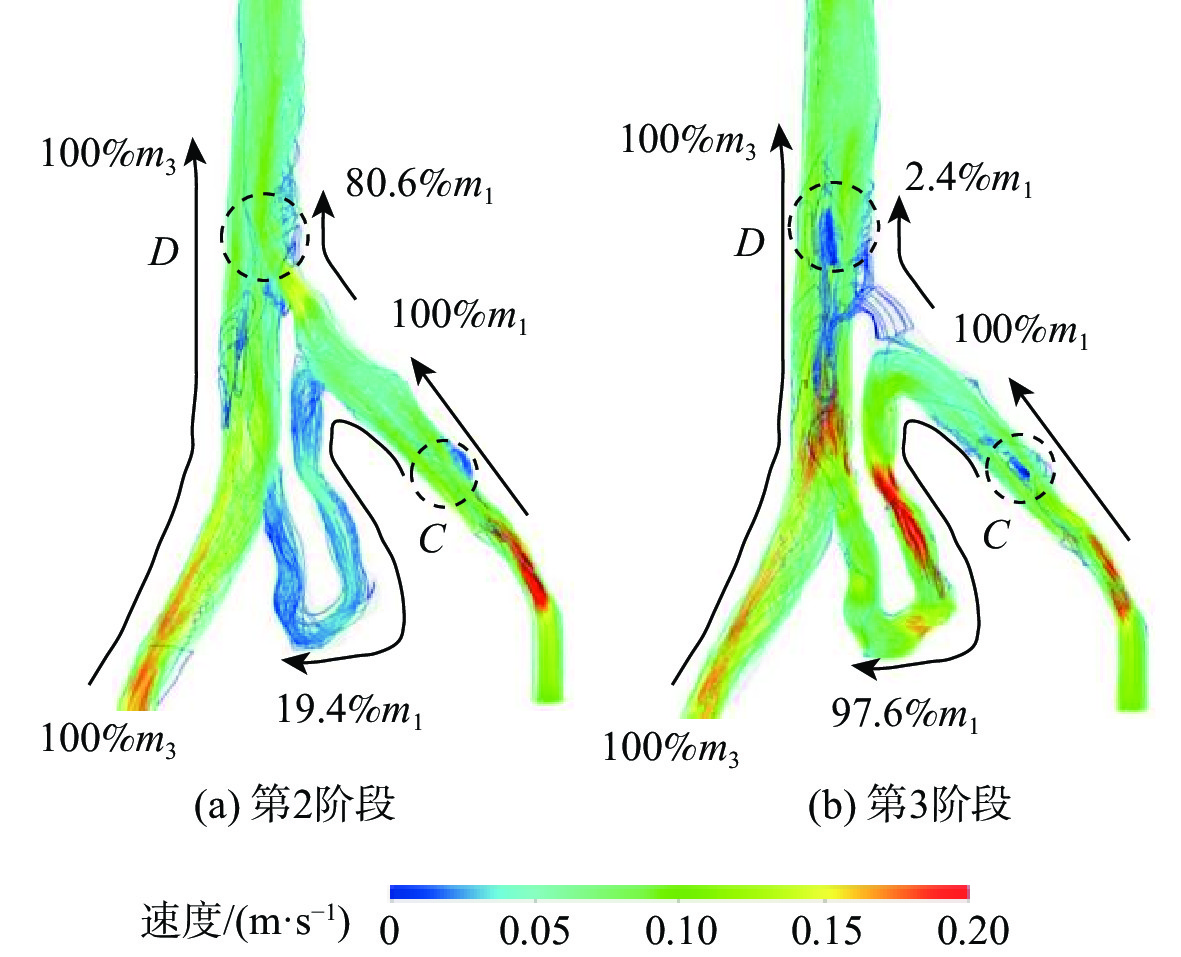
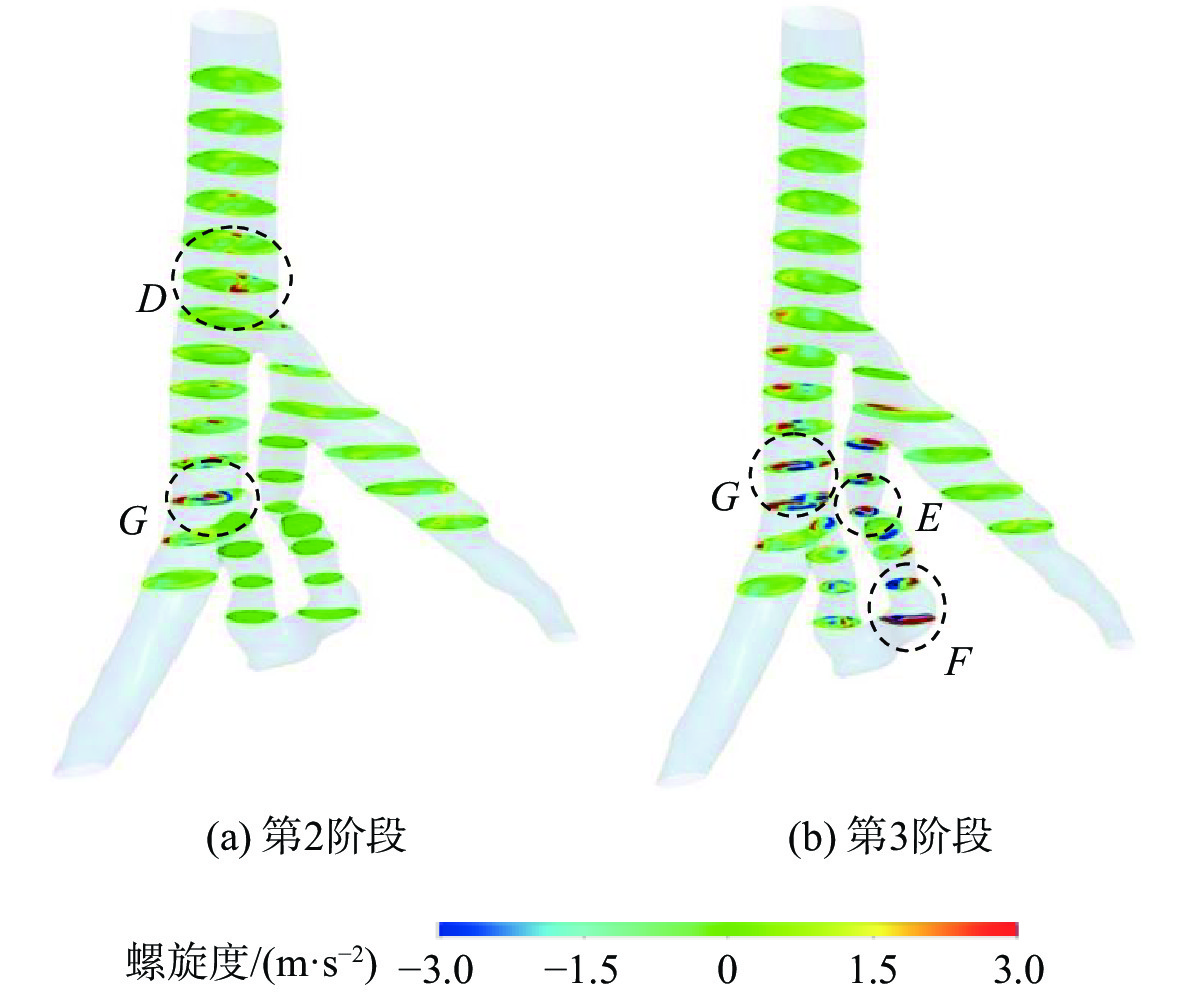
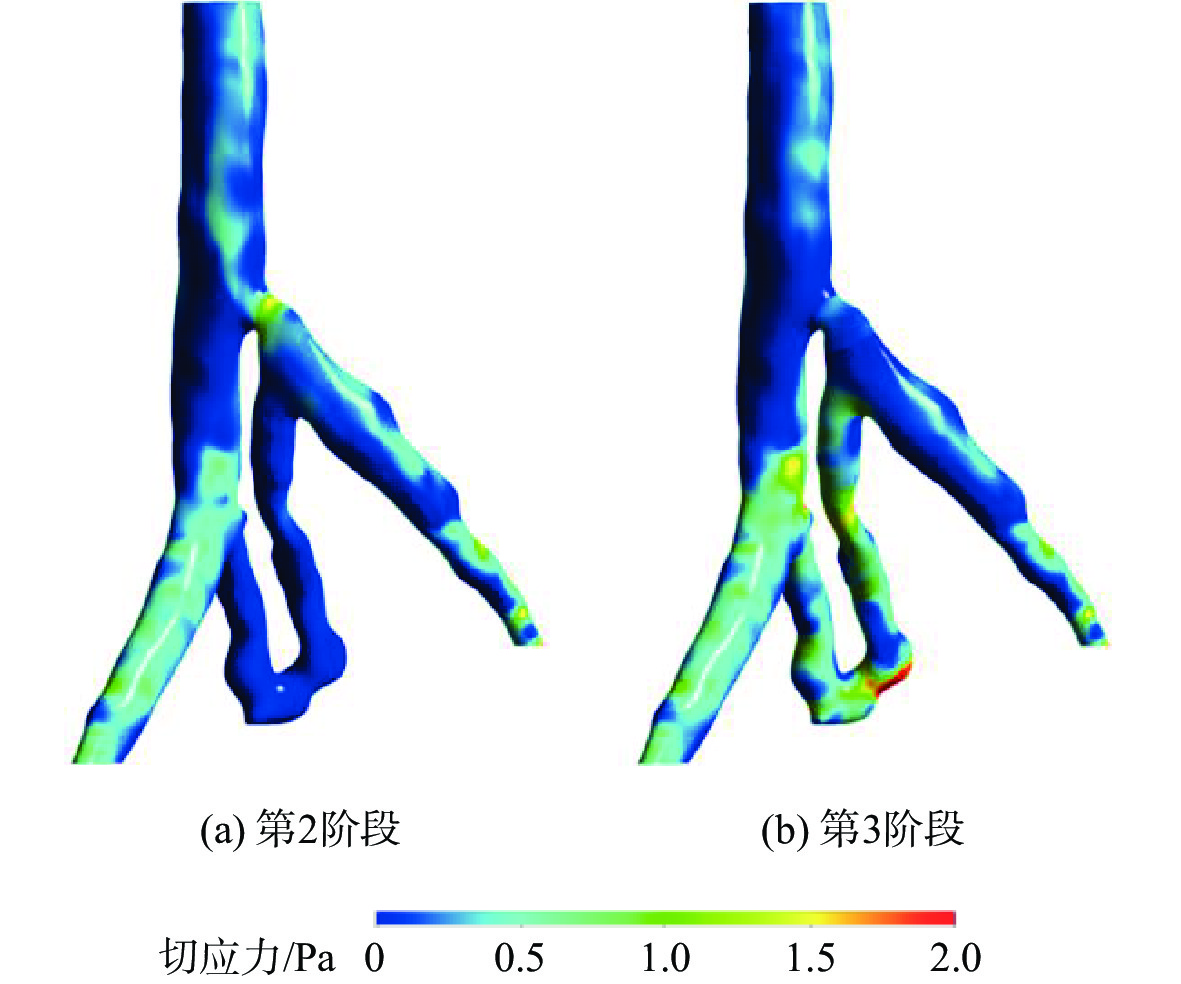
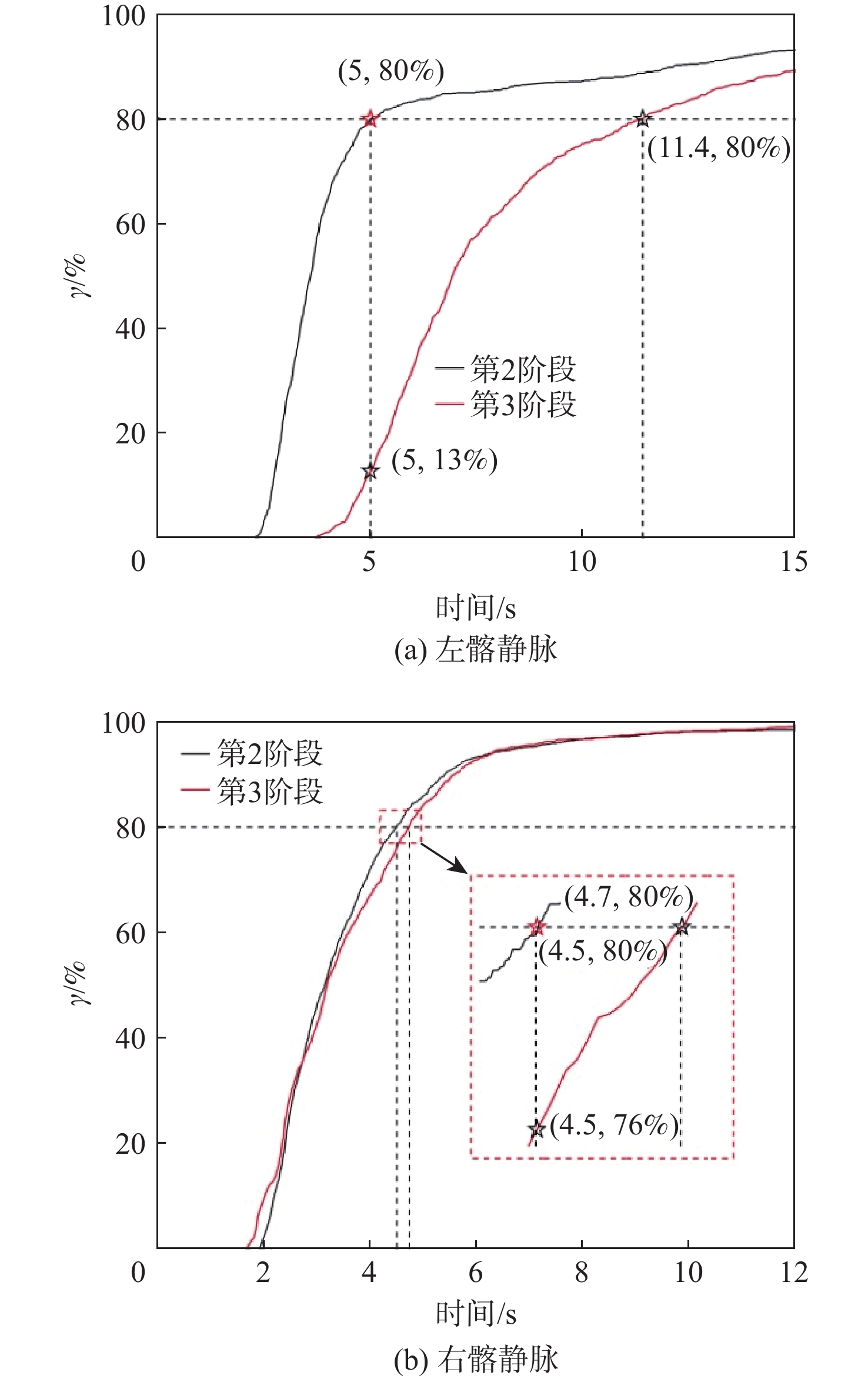
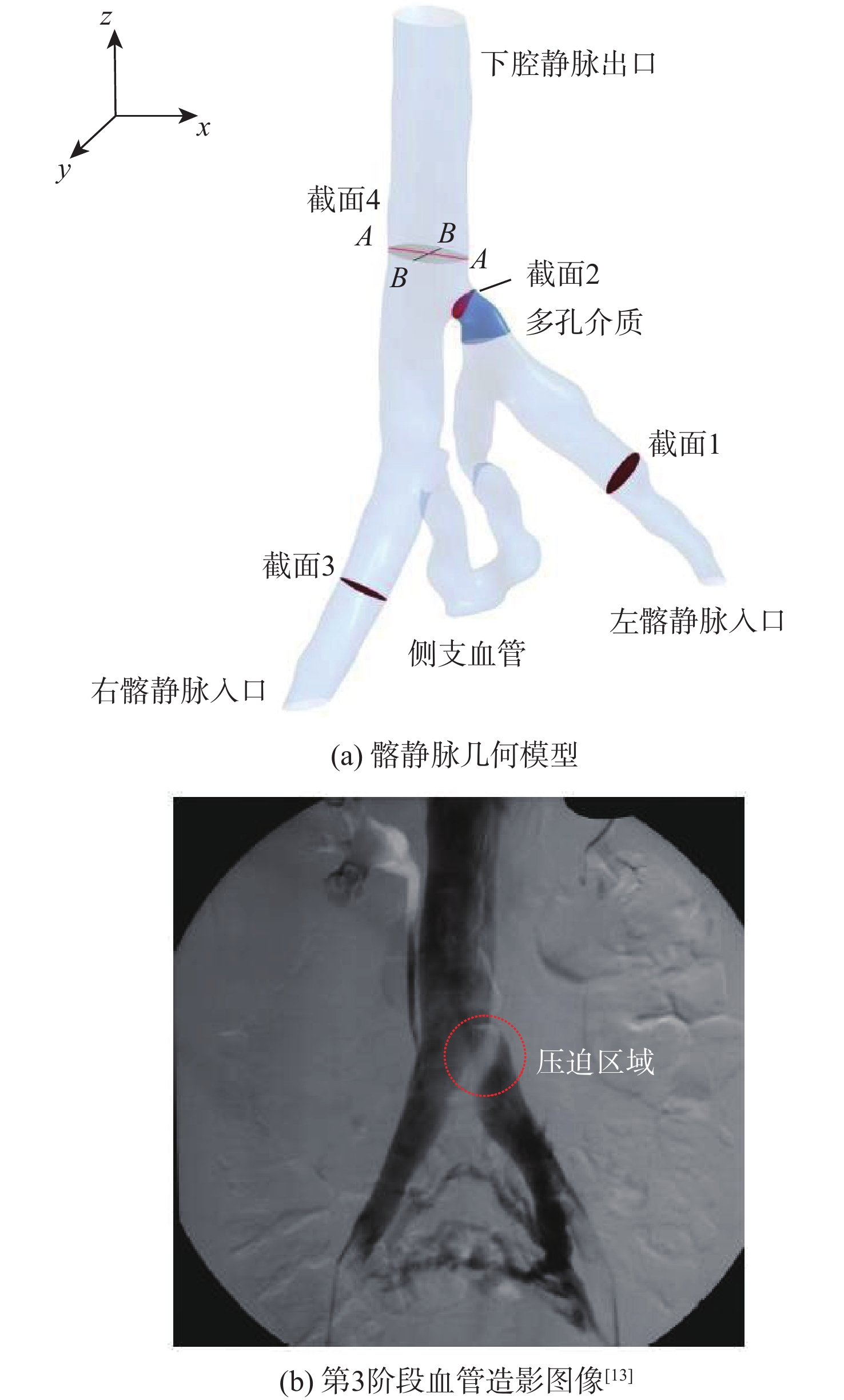
为了探究伴侧支血管的髂静脉压迫综合征出现典型症状的原因,对一典型伴侧支血管的髂静脉血流场进行了数值研究。通过调节多孔介质模型的黏性阻力系数模拟髂静脉压迫综合征发展阶段中的第二阶段和第三阶段,分析和对比了两个阶段的压力梯度、血液螺旋度和壁面切应力等血流动力学特征。研究结果表明,第三阶段的左髂静脉和下腔静脉之间的压力梯度为107 Pa,远大于第二阶段的31 Pa,但小于髂静脉压迫综合征的判断标准266 Pa。在第三阶段,侧支血管代替了左髂静脉进行回流。随着血流路径的改变,侧支血管和右髂静脉的血液螺旋度和壁面切应力远大于第二阶段。左髂静脉的长期堵塞,改变了红细胞的输运路径,延长了输运时间。尽管伴侧支血管的髂静脉压迫综合征能够进行下肢回流,患者仍呈现典型症状的原因可能是较大的压力梯度、较大的血液螺旋度、异常壁面切应力以及红细胞的输运迟滞长期的共同作用。
Abstract:To investigate the reasons for the typical symptoms of iliac vein compression syndrome with the collateral veins, a typical iliac vein blood flow field with a collateral vein was numerically studied. The viscous resistance coefficient of the porous media model was adjusted to simulate the second and third development stages of iliac vein compression syndrome. The hemodynamic characteristics in the two stages were analyzed and compared, e.g., pressure gradient, blood helicity, and wall shear stress. The results show that the pressure gradient between the left iliac vein and the inferior vena cava is 107 Pa in the third stage, which is far greater than 31 Pa in the second stage but less than the criterion of iliac vein compression syndrome, i.e., 266 Pa. In the third stage, the left iliac vein is replaced by the collateral vein to realize the venous blood flow. When the blood flow pathway changes, the blood helicity and wall shear stress in the collateral vein and right iliac vein are much greater than those in the second stage. The obstruction of the left iliac vein changes the transport pathway of the erythrocyte and prolongs the transport time. Although the venous blood flow in iliac vein compression syndrome with the collateral vein is normal, the patient still presents the typical symptoms due to the combined effort of the excessive pressure gradient, large blood helicity, abnormal wall shear stress, and transport hysteresis of erythrocytes.
-
Key words:
- iliac vein compression syndrome /
- hemodynamics /
- numerical simulation /
- porous media /
- blood helicity
-
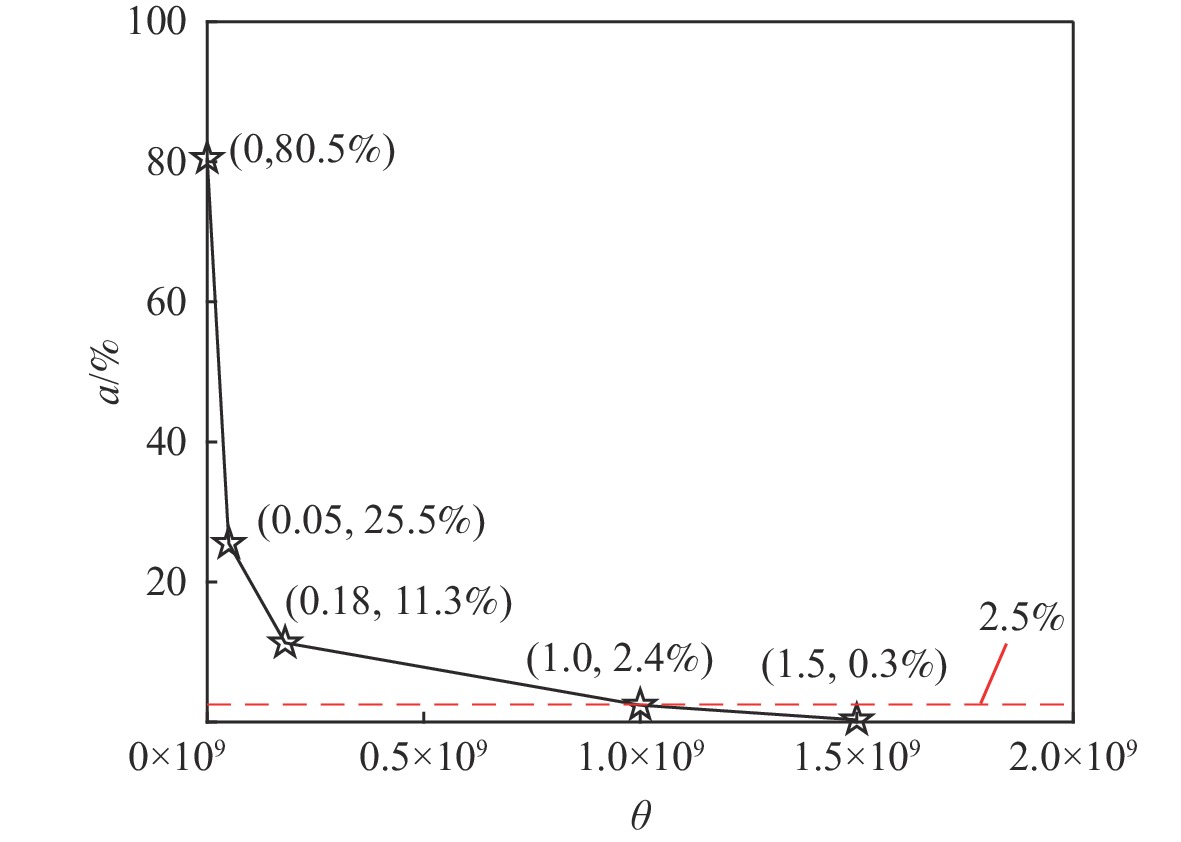
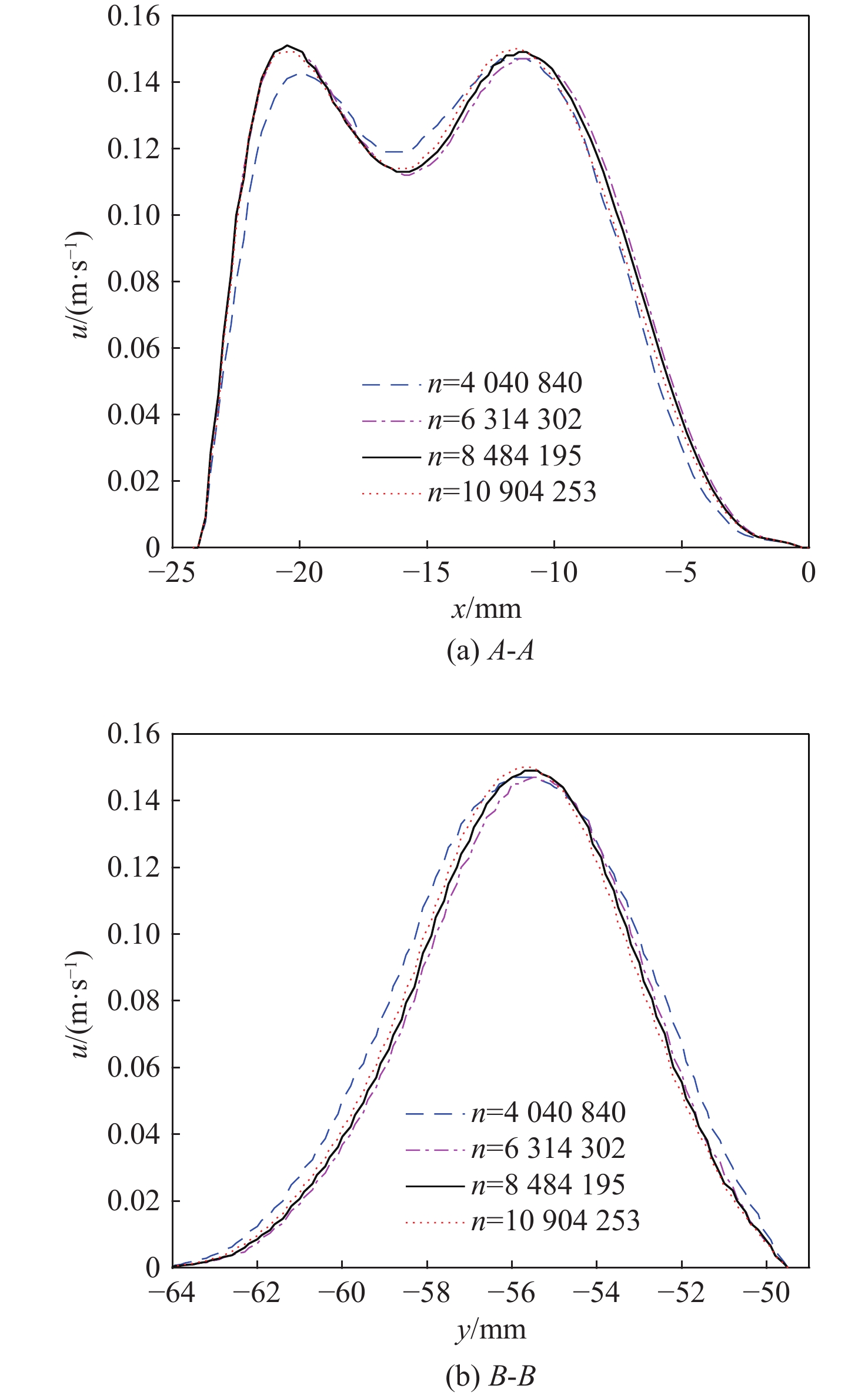
表 1 4组网格方案
Table 1. Four groups of mesh schemes
类型 网格数n 类型 网格数n Ⅰ 4 040 840 Ⅲ 8 484 195 Ⅱ 6 314 302 Ⅳ 10 904 253 -
[1] COCKETT F B, LEA THOMAS M. The iliac compression syndrome[J]. British Journal of Surgery, 2005, 52(10): 816-821. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800521028 [2] BRINEGAR K N, SHETH R A, KHADEMHOSSEINI A, et al. Iliac vein compression syndrome: clinical, imaging and pathologic findings[J]. World Journal of Radiology, 2015, 7(11): 375-381. doi: 10.4329/wjr.v7.i11.375 [3] MAY R, THURNER J. The cause of the predominantly sinistral occurrence of thrombosis of the pelvic veins[J]. Angiology, 1957, 8(5): 419-427. doi: 10.1177/000331975700800505 [4] MCMURRICH J P. The occurrence of congenital adhesions in the common iliac veins, and their relation to thrombosis of the femoral and iliac veins[J]. The American Journal of the Medical Sciences, 1908, 135(3): 342-345. doi: 10.1097/00000441-190803000-00004 [5] JOHNSSON K Å, GÖTHMAN B, NORDSTRÖM S. The iliac compression syndrome[J]. Acta Radiologica Diagnosis, 1974, 15(5): 539-545. doi: 10.1177/028418517401500508 [6] EHRICH W E, KRUMBHAAR E B. A frequent obstructive anomaly of the mouth of the left common iliac vein[J]. American Heart Journal, 1943, 26(6): 737-750. doi: 10.1016/S0002-8703(43)90285-6 [7] 王崟, 陈敬杰, 卢简言. 下肢深静脉顺行造影中侧支循环对髂静脉压迫综合征的诊断意义[J]. 中国临床医学影像杂志, 2014, 25(12): 903-905.WANG Y, CHEN J J, LU J Y. Diagnostic significance of collateral circulation for iliac vein compression syndrome in ascending venography of lower extremity[J]. Journal of China Clinic Medical Imaging, 2014, 25(12): 903-905 (in Chinese). [8] AENIS M, STANCAMPIANO A P, WAKHLOO A K, et al. Modeling of flow in a straight stented and nonstented side wall aneurysm model[J]. Journal of Biomechanical Engineering, 1997, 119(2): 206-212. doi: 10.1115/1.2796081 [9] 刘赵淼, 南斯琦, 史艺. 中等严重程度冠状动脉病变模型的血流动力学参数分析[J]. 力学学报, 2015, 47(6): 1058-1064. doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-15-085LIU Z M, NAN S Q, SHI Y. Hemodynamic parameters analysis for coronary artery stenosis of intermediate severity model[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2015, 47(6): 1058-1064 (in Chinese). doi: 10.6052/0459-1879-15-085 [10] 王庆虎, 杨少雄, 许怡隽, 等. 颈动脉分叉处血管粥样硬化斑块的体内应力分析[J]. 医用生物力学, 2019, 34(3): 268-276.WANG Q H, YANG S X, XU Y J, et al. In vivo stress analysis of an atherosclerotic plaque at carotid bifurcation[J]. Journal of Medical Biomechanics, 2019, 34(3): 268-276 (in Chinese). [11] 韩嘉玮, 胡义锋. 基于流固耦合的载瘤血管内血液流动及血管损伤分析[J]. 医用生物力学, 2019, 34(4): 372-378.HAN J W, HU Y F. Analysis of blood flow and vascular injury in aneurysm-carrying vessels based on fluid-structure interaction method[J]. Journal of Medical Biomechanics, 2019, 34(4): 372-378 (in Chinese). [12] GIJSEN F J, ALLANIC E, VAN DE VOSSE F N, et al. The influence of the non-Newtonian properties of blood on the flow in large arteries: unsteady flow in a 90 degrees curved tube[J]. Journal of Biomechanics, 1999, 32(7): 705-713. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9290(99)00014-7 [13] CAVALCANTE L P, DOS SANTOS SOUZA J E, PEREIRA R M, et al. Iliac vein compression syndrome: literature review[J]. Jornal Vascular Brasileiro, 2015, 14(1): 78-83. doi: 10.1590/1677-5449.20140027 [14] O’SULLIVAN G J, SEMBA C P, BITTNER C A, et al. Endovascular management of iliac vein compression (May-Thurner) syndrome[J]. Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology: JVIR, 2000, 11(7): 823-836. doi: 10.1016/S1051-0443(07)61796-5 [15] LIU Z J, GAO N, SHEN L G, et al. Endovascular treatment for symptomatic iliac vein compression syndrome: a prospective consecutive series of 48 patients[J]. Annals of Vascular Surgery, 2014, 28(3): 695-704. doi: 10.1016/j.avsg.2013.05.019 [16] LIU X, SUN A Q, FAN Y B, et al. Physiological significance of helical flow in the arterial system and its potential clinical applications[J]. Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 2015, 43(1): 3-15. doi: 10.1007/s10439-014-1097-2 [17] STONEBRIDGE P A, BROPHY C M. Spiral laminar flow in arteries?[J]. Lancet, 1991, 338(8779): 1360-1361. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(91)92238-W [18] CHIU T L, TANG A Y S, CHENG S W K, et al. Analysis of flow patterns on branched endografts for aortic arch aneurysms[J]. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, 2018, 13: 62-70. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2018.10.008 [19] GABBERT D D, TROTZ P, KHERADVAR A, et al. Abnormal torsion and helical flow patterns of the neo-aorta in hypoplastic left heart syndrome assessed with 4D-flow MRI[J]. Cardiovascular Diagnosis and Therapy, 2021, 11(6): 1379-1388. doi: 10.21037/cdt-20-770 [20] GARCIA J, BARKER A J, COLLINS J D, et al. Volumetric quantification of absolute local normalized helicity in patients with bicuspid aortic valve and aortic dilatation[J]. Magnetic Resonance in Medicine, 2017, 78(2): 689-701. doi: 10.1002/mrm.26387 [21] CONDEMI F, CAMPISI S, VIALLON M, et al. Fluid- and biomechanical analysis of ascending thoracic aorta aneurysm with concomitant aortic insufficiency[J]. Annals of Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 45(12): 2921-2932. [22] CHANDRAN K B, YOGANATHAN A P, RITTGERS S E. Biofluid mechanics: the human circulation [M]. 2nd ed. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 2011. [23] CHERNIACK N S, LONGOBARDO G S. Oxygen and carbon dioxide gas stores of the body[J]. Physiological Reviews, 1970, 50(2): 196-243. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.2.196 [24] JENSEN F B. Red blood cell pH, the Bohr effect, and other oxygenation-linked phenomena in blood O2 and CO2 transport[J]. Acta Physiologica Scandinavica, 2004, 182(3): 215-227. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-201X.2004.01361.x [25] SAMADY H, ESHTEHARDI P, MCDANIEL M C, et al. Coronary artery wall shear stress is associated with progression and transformation of atherosclerotic plaque and arterial remodeling in patients with coronary artery disease[J]. Circulation, 2011, 124(7): 779-788. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.021824 [26] DHAWAN S S, AVATI NANJUNDAPPA R P, BRANCH J R, et al. Shear stress and plaque development[J]. Expert Review of Cardiovascular Therapy, 2010, 8(4): 545-556. doi: 10.1586/erc.10.28 [27] ZARINS C K, GIDDENS D P, BHARADVAJ B K, et al. Carotid bifurcation atherosclerosis. Quantitative correlation of plaque localization with flow velocity profiles and wall shear stress[J]. Circulation Research, 1983, 53(4): 502-514. doi: 10.1161/01.RES.53.4.502 -







 下载:
下载: