Evaluation method of H2O penetration depth of drying reactor based on temperature gradient
-
摘要:
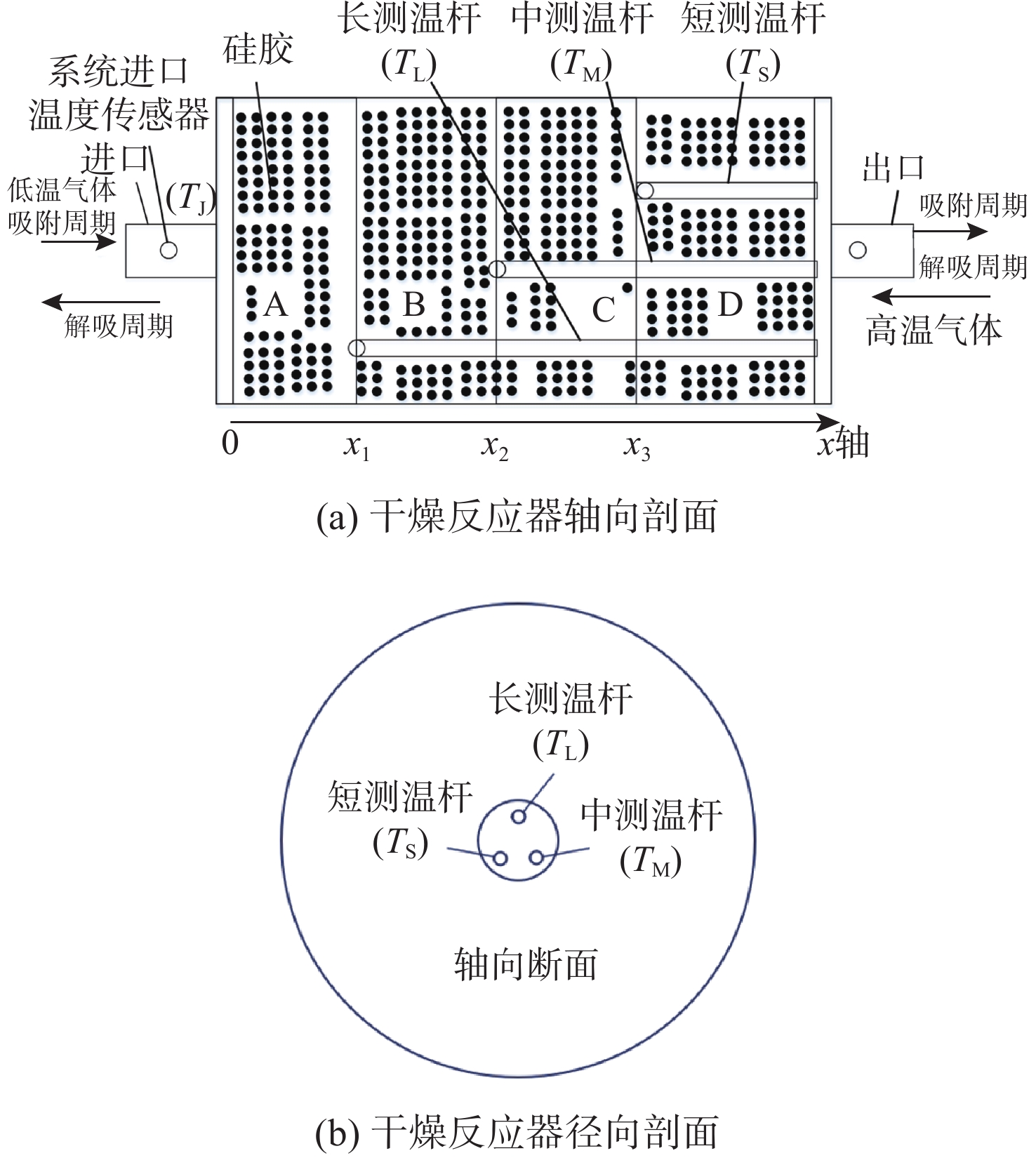
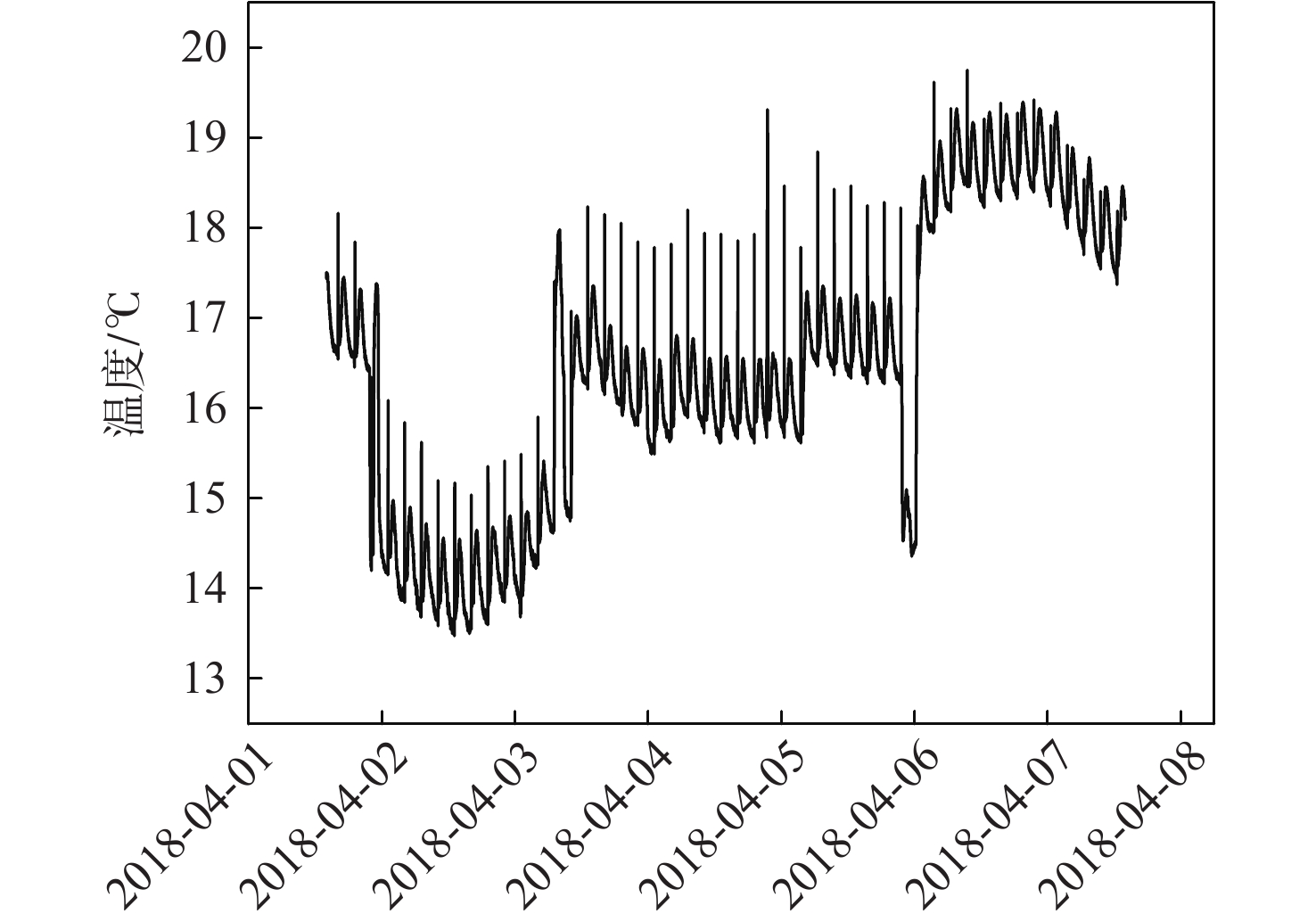
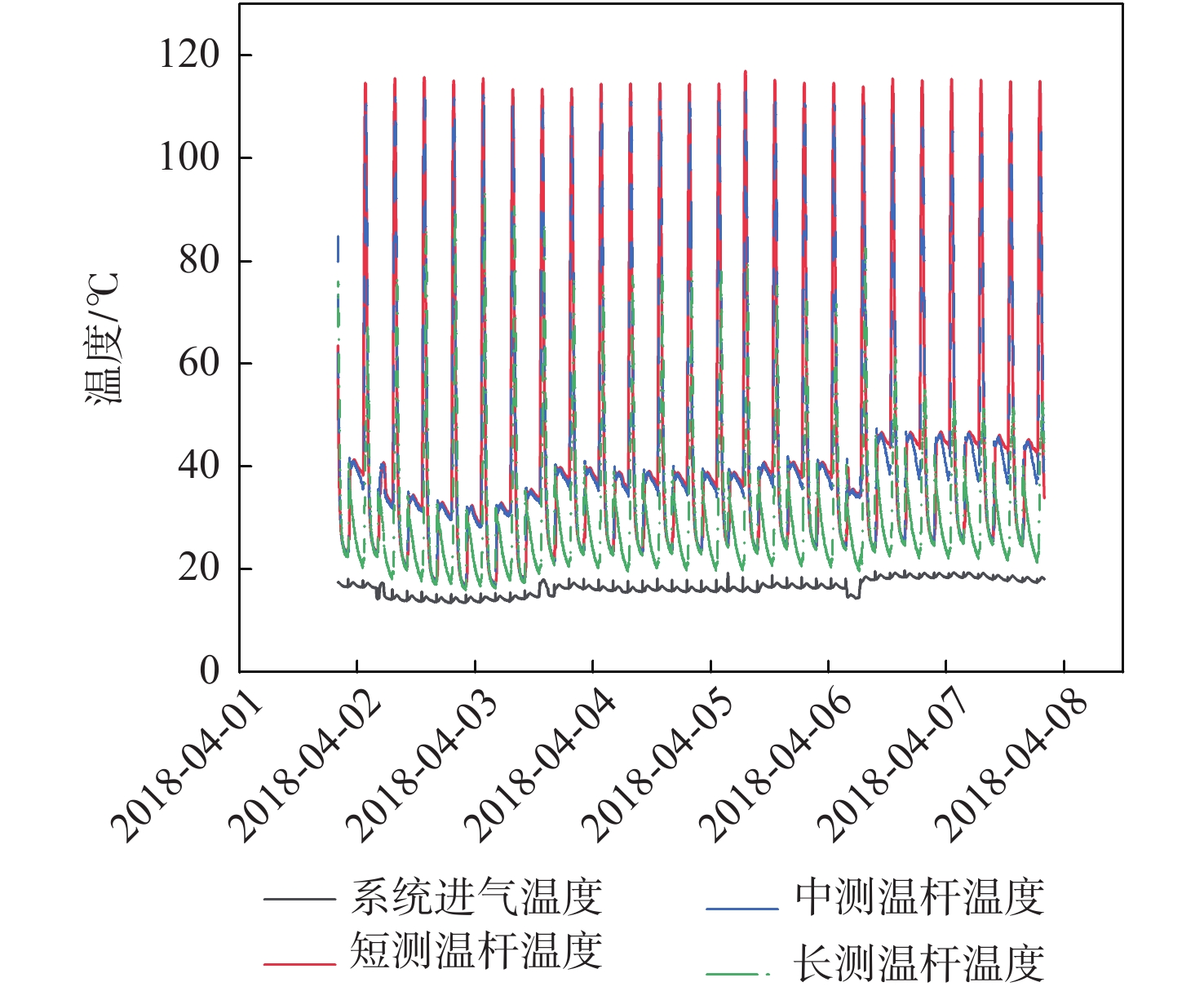
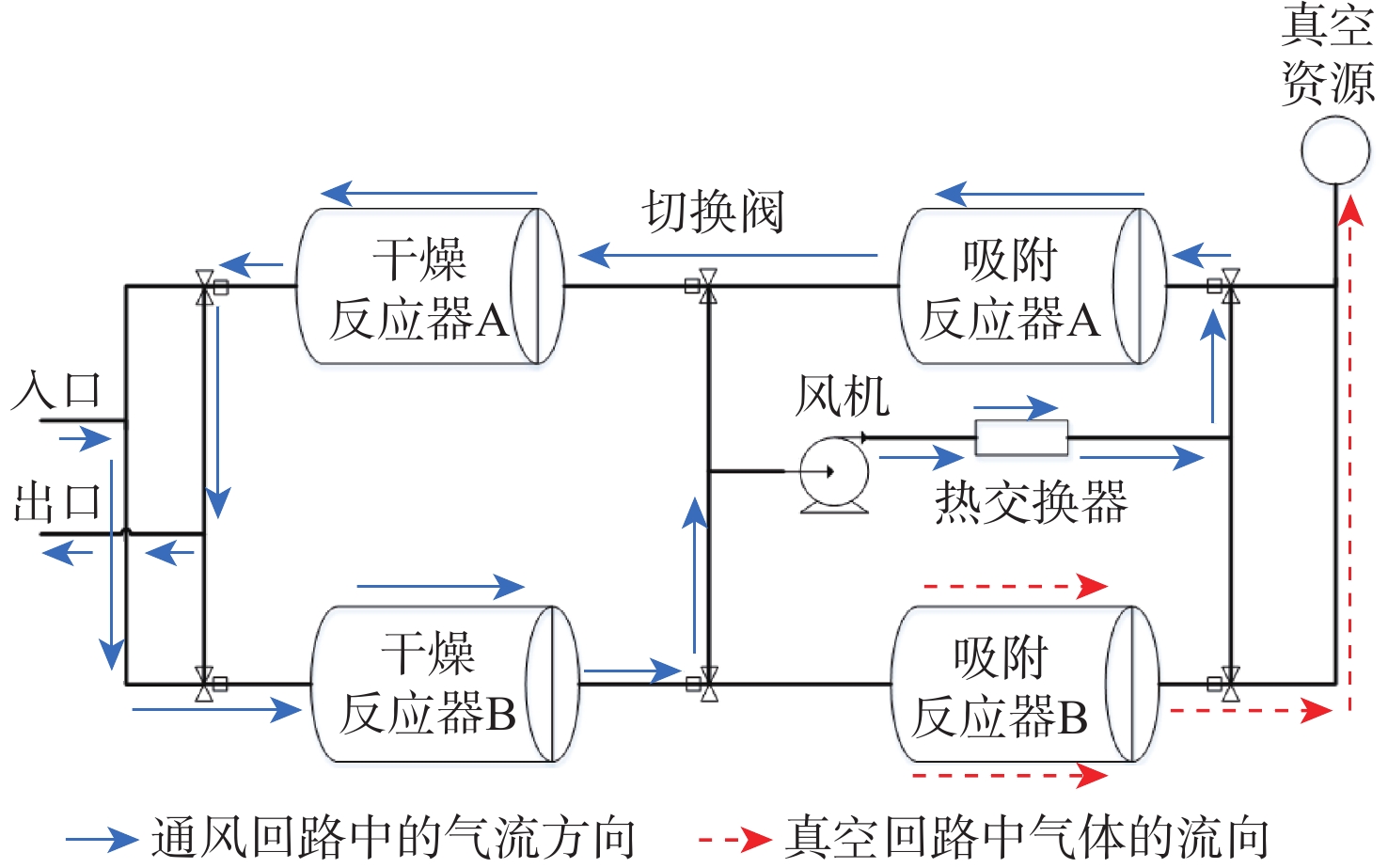
针对空间站CO2去除系统中干燥反应器对H2O穿透深度缺乏直接评估手段的问题,提出利用干燥反应器内部温度传感器的温度梯度特性来间接评估的方法;根据硅胶材料吸附H2O放热、脱附H2O吸热的物理特性,结合温度传感器在干燥反应器中的深度位置,分析了不同边界条件下温度传感器数据曲线在吸附及解吸周期内的变化特性,提出反映干燥反应器H2O穿透深度的指标集和评估方法;并对所提方法在系统的密闭舱试验中进行了验证,验证结果表明了指标集的合理性和所提方法的有效性。
Abstract:There is no direct evaluation method for the H2O penetration depth of the drying reactor in the CO2 removal system in the space station. Therefore, an indirect evaluation method based on the temperature gradient characteristics of the temperature sensor inside the drying reactor was proposed. Since silica gel has the physical characteristic of releasing heat while adsorbing H2O and absorbing heat while desorbing H2O, the variation characteristics of the temperature sensor data curve in the adsorption and desorption cycles under different boundary conditions were analyzed by considering the depth position of the temperature sensor in the drying reactor. The index set and evaluation method reflecting the H2O penetration depth of the drying reactor were proposed, and the proposed method is verified in the closed chamber test of the system, the verification results show the rationality of the index set and the effectiveness of the evaluation method.
-
Key words:
- space station /
- CO2 removal system /
- reactor /
- adsorption /
- desorption /
- water penetration depth
-
表 1 干燥周期H2O穿透深度定义(Ⅲ、Ⅳ)
Table 1. Definition of H2O penetration depth in drying cycle (Ⅲ and Ⅳ)
穿透深度 区域A 区域B 区域C 区域D III 穿透 穿透 到达,未穿透 未到达 IV 穿透 穿透 穿透 到达,是否穿透未知 表 2 吸附周期H2O穿透深度判据
Table 2. H2O penetration depth criteria in adsorption cycle
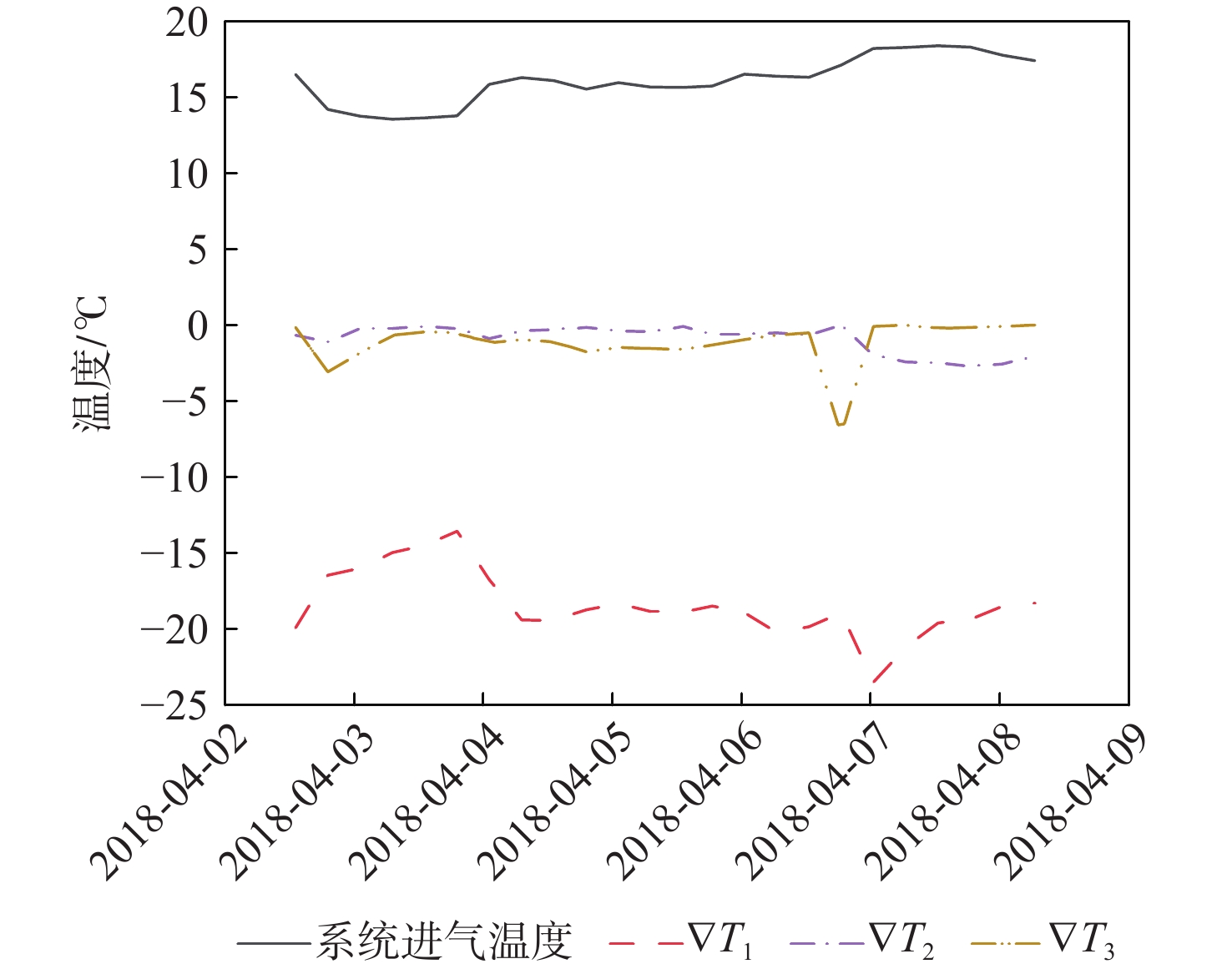
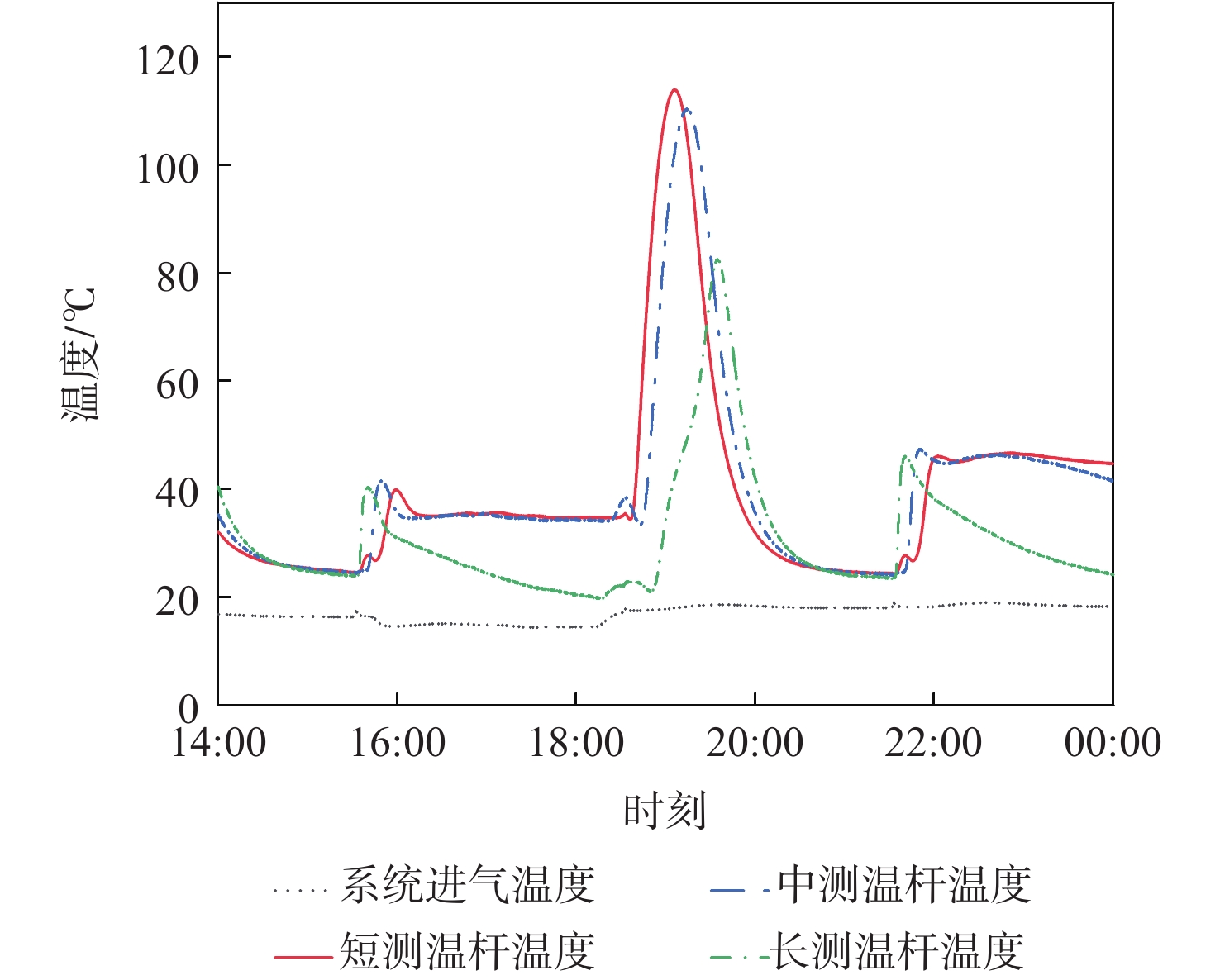
穿透深度 判据 备注 Ⅱ ∇T1<0,∇T2≥0 H2O进入但未穿透区域B Ⅲ(或以上) ∇T1<0,∇T2<0 H2O进入区域C Ⅲ ∇T1<0,∇T2<0, ∇T3=0 H2O进入但未穿透区域C Ⅳ(或级以上) ∇T1<0,∇T2<0, ∇T3<0 H2O穿透区域C进入区域D 表 3 解吸周期H2O穿透深度判据
Table 3. H2O penetration depth criteria in desorption cycle
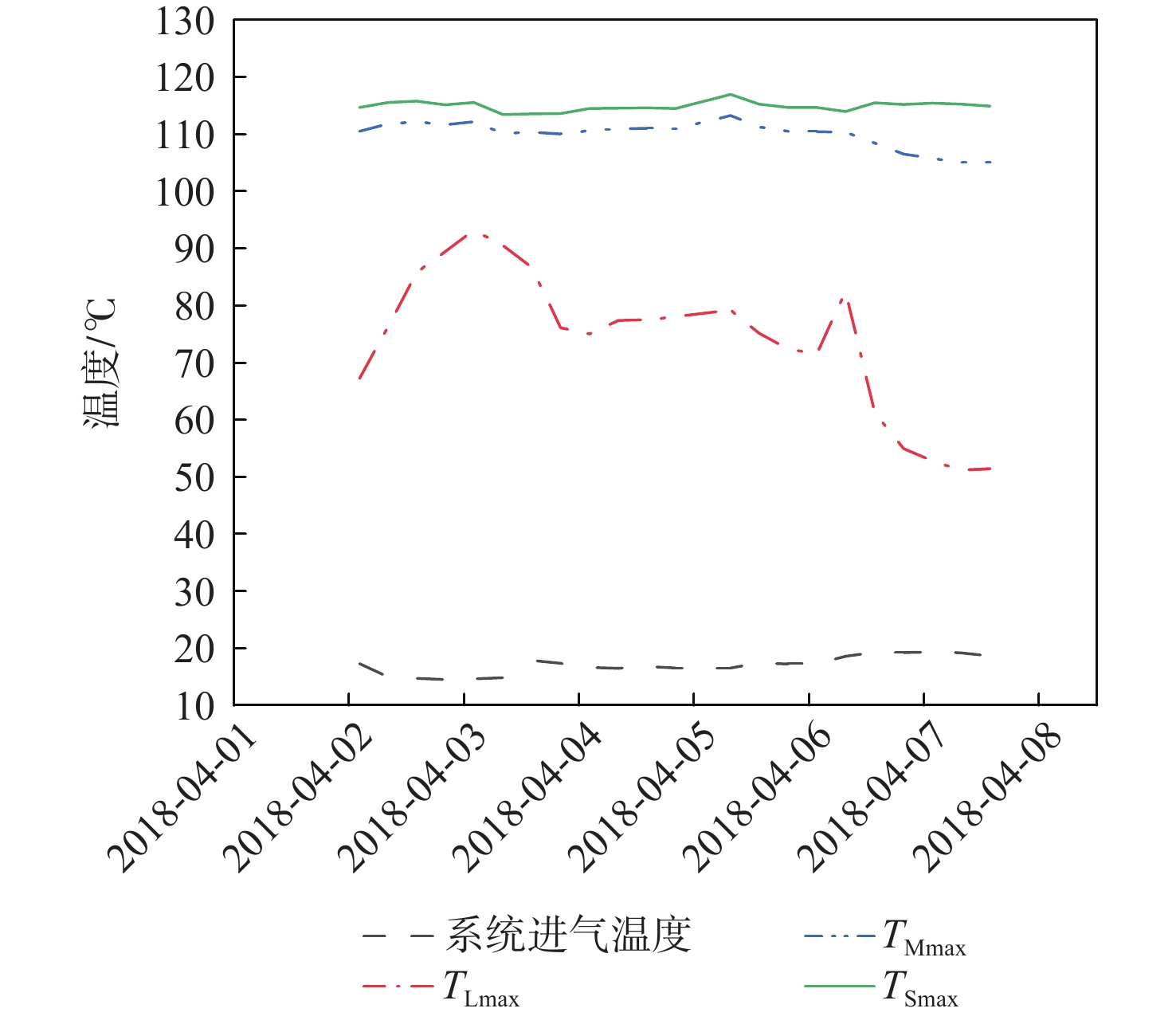
穿透深度 判据 备注 Ⅱ TLmax波动,TMmax和TSmax不变 TLmax>TLZmax,穿透深度变浅
TLmax<TLZmax,穿透深度变深Ⅲ TLmax波动,TMmax波动,TSmax不变 TMmax>TMZmax,穿透深度变浅;TMmax<TMZmax,穿透深度变深 Ⅳ(或以上) TLmax波动,TMmax波动,TSmax波动 TSmax>TSZmax,穿透深度变浅;TSmax<TSZmax,穿透深度变深 表 4 吸附及解吸周期H2O进入及穿透深度评估方法汇总
Table 4. Summary of evaluation methods for H2O entry and penetration depth in adsorption and desorption cycles
模式 进入 穿透 A B C D A B C D 吸附 √ √ √ × √ √ √ × 解吸 √ √ √ √ √ √ √ × -
[1] HUANG Y H, WANG J L, JIANG H Q, et al. Research of polymerization reactor fault diagnosis based on acoustic emission[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 221: 550-554. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.221.550 [2] ZHOU J, HUANG F N, SHEN W H, et al. Sub-period division strategies combined with multiway principle component analysis for fault diagnosis on sequence batch reactor of wastewater treatment process in paper mill[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2021, 146: 9-19. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2020.08.032 [3] LIU H R, BUVAT J C, ESTEL L, et al. Bayesian network method for fault diagnosis in a continuous tubular reactor[J]. Chemical Product and Process Modeling, 2010, 5(1): 1-9. [4] SHEIBAT-OTHMAN N, LAOUTI N, VALOUR J P, et al. Support vector machines combined to observers for fault diagnosis in chemical reactors[J]. The Canadian Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2014, 92(4): 685-695. doi: 10.1002/cjce.21881 [5] 刘敏. 人工神经网络在化学反应器故障诊断中的应用[J]. 聊城师院学报(自然科学版), 2000, 13(1): 51-54.LIU M. Fault detection in the chemical reactors using artificial neural networks[J]. Journal of Liaocheng Teachers College (Natural Science Edition), 2000, 13(1): 51-54 (in Chinese). [6] LV M B, LI Y H, GUO R. Galerkin-based extended Kalman filter with application to CO2 removal system[J]. Journal of Central South University, 2020, 27(6): 1780-1789. doi: 10.1007/s11771-020-4407-x [7] SHI L, WANG L J, WANG Z Z. The modeling and the sensor fault diagnosis of a continuous stirred tank reactor with a takagi-sugeno recurrent fuzzy neural network[J]. International Journal of Distributed Sensor Networks, 2009, 5(1): 37. doi: 10.1080/15501320802524037 [8] CMARIK G, KNOX J, HUFF T. Analysis of performance degradation of silica gels after extended use onboard the ISS[C]//Proceedings of the 48th International Conference on Environmental Systems. Albuquerque: International Conference on Environmental Systems, 2018: 1-11. [9] CMARIK G, KNOX J. Co-adsorption of carbon dioxide on zeolite 13X in the presence of preloaded water[C]//Proceedings of the 48th International Conference on Environmental Systems. Albuquerque: International Conference on Environmental Systems, 2018: 1-10. [10] 韩永强, 吴宝治, 杨润泽, 等. 分子筛CO2去除系统研究[J]. 航天医学与医学工程, 2013, 26(3): 181-184.HAN Y Q, WU B Z, YANG R Z, et al. Study on carbon dioxide removal assembly using molecular sieve technology[J]. Space Medicine & Medical Engineering, 2013, 26(3): 181-184 (in Chinese). [11] 管国锋, 赵汝溥. 化工原理[M]. 4版. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2015.GUAN G F, ZHAO R P. Principles of chemical engineering[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2015 (in Chinese). [12] SOLMUŞ İ, ANDREW S REES D, YAMALI C, et al. A two-energy equation model for dynamic heat and mass transfer in an adsorbent bed using silica gel/water pair[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2012, 55(19-20): 5275-5288. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2012.05.036 [13] ISLAM M A, PAL A, SAHA B B. Experimental study on thermophysical and porous properties of silica gels[J]. International Journal of Refrigeration, 2020, 110: 277-285. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrefrig.2019.10.027 [14] YAMAMOTO E, KATSURAYAMA K, WATANABE F, et al. Heat and mass transfer characteristics in adsorption of water vapor for silica gel packed bed adsorber[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering of Japan, 2000, 33(1): 12-18. doi: 10.1252/jcej.33.12 [15] SUN J, BESANT R W. Heat and mass transfer during silica gel-moisture interactions[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2005, 48(23-24): 4953-4962. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2005.02.043 [16] ULRICH L, RICARDO C S J, RICHARD B, et al. Fundamental thermodynamic properties of sorbents for atmospheric water capture[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 431: 134058. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.134058 [17] BERNAL V, GIRALDO L, MORENO-PIRAJÁN J C. Understanding the solid-liquid equilibria between paracetamol and activated carbon: Thermodynamic approach of the interactions adsorbent-adsorbate using equilibrium, kinetic and calorimetry data[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2021, 419: 126432. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126432 [18] 邓述波, 余刚. 环境吸附材料及应用原理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012.DENG S B, YU G. Environmental adsorption materials and their application principles[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2012 (in Chinese). [19] 周立幸, 陈淑霞, 郑禄彬. 水/硅胶吸附体系的热化学研究[J]. 物理化学学报, 1985, 1(6): 566-570. doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB19850610ZHOU L X, CHEN S X, ZHENG L B. Thermochemical study for water/silica adsorption system[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 1985, 1(6): 566-570 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB19850610 [20] 王德昌, 韩艳培, 张光, 等. 吸附制冷中硅胶吸附性能衰减特性研究[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2012, 33(2): 207-209.WANG D C, HAN Y P, ZHANG G, et al. Investigation of adsorption performance deterioration of silica gel in water adsorption refrigeration[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2012, 33(2): 207-209 (in Chinese). [21] 叶卫平. Origin9.1科技绘图及数据分析[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2019.YE W P. Origin9.1 Technology drawing and data analysis[M]. Beijing: China Machine Press, 2019 (in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: