Adaptive layered fusion algorithm for infrared and visible video based on possibility theory
-
摘要:
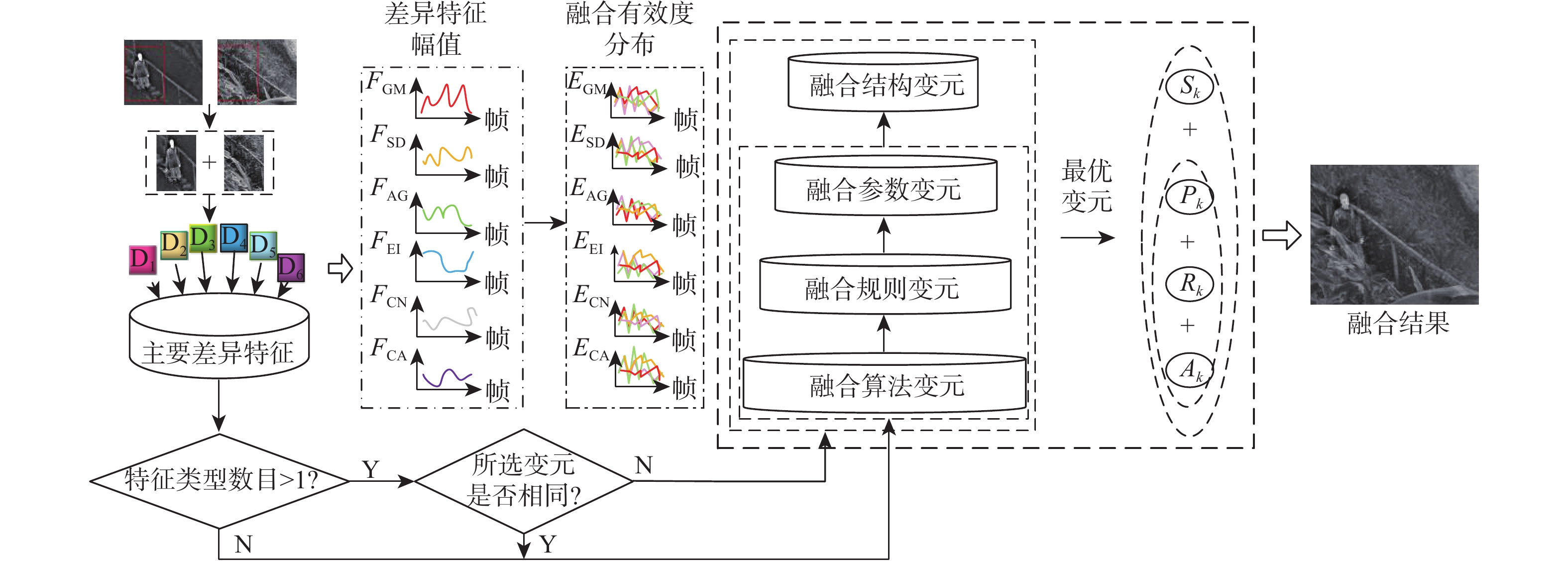
针对目前红外与可见光视频融合模型无法根据视频间差异特征动态调整融合策略,造成融合效果差甚至失效等问题,提出了一种基于可能性理论的红外与可见光视频的自适应分层融合算法。计算视频序列每帧中感兴趣区域的各类差异特征的幅值大小,得到每帧对应的主要差异特征;搭建分层融合框架,并确定各层变元,基于余弦相似性计算不同变元对各差异特征的融合有效度,利用可能性理论构造相应的融合有效度分布;逐层分析不同变元对各类差异特征的融合效果,选择出每层的最优变元;通过变元间的优化组合实现红外与可见光视频的自适应分层融合。实验结果表明:所提算法在保留红外典型目标和可见光结构细节等方面取得了显著的融合效果,并且在定量分析和定性评价上明显优于单一融合算法。
Abstract:The current infrared and visible video fusion model cannot dynamically adjust the fusion strategy according to the difference between videos, resulting in poor fusion effect or even failure. To address this issue,an adaptive layered fusion algorithm for infrared and visible video based on possibility theory was proposed. First, the magnitudes of various difference features of the region of interest in each frame of the video sequence were calculated, and the main difference features corresponding to each frame were obtained. Secondly, a layered fusion framework was built to determine the variables of each layer. The fusion effectiveness of different variables for each difference feature was calculated based on cosine similarity, and the possibility theory was used to construct the corresponding fusion effectiveness distribution.Then, the fusion effect of different variables for various difference features was analyzed layer by layer, and the optimal variable of each layer was selected. Finally, the adaptive layered fusion of infrared and visible video was realized through the optimal combination of variables. The experimental results show that the method in this paper has achieved remarkable fusion results in preserving typical infrared targets and visible structural details, and it is superior to other single fusion methods in quantitative analysis and qualitative evaluation.
-
Key words:
- image processing /
- video fusion /
- adaptive layered fusion /
- possibility theory /
- infrared video
-
表 1 部分帧差异特征的归一化结果
Table 1. Normalized difference features of someframes
差异特征 视频序列 第1帧 第12帧 第50帧 第105帧 第185帧 第200帧 GM 0.5801 0.2426 0.4845 1.0000 0.3197 0 SD 0.3231 0.1945 0.2304 0.0066 1.0000 0.4437 AG 0.2097 0.0403 0.1344 0 1.0000 0.4429 EI 0.5950 0.3563 0.2882 0.2663 1.0000 0.5973 CN 0.5165 0.2431 0.3735 0 0.5683 0.4481 CA 0.3851 0 0.4701 0.5629 0.6641 0.2062 表 2 各帧对应的最优融合算法变元
Table 2. Optimal fusion algorithm variables corresponding to each frame
视频序列 融合算法 第1帧 DTCWT 第12帧 DTCWT 第50帧 DTCWT 第105帧 SWT 第185帧 WPT/LP/CVT 第200帧 NSCT 表 3 各帧对应的最优融合规则变元
Table 3. Optimal fusion rule variables corresponding to each frame
视频序列 低频 高频 第1帧 SWA WE 第12帧 SWA AMC 第50帧 SWA WE 第105帧 SWA MC 第185帧 SWA WG 第200帧 MC AMC 表 4 各帧对应的最优融合参数变元
Table 4. Optimal fusion parameter variables corresponding to each frame
视频序列 滤波器 分解层数 第1层 其他层 第1帧 near_sym_a qshift_06 2 第12帧 near_sym_a qshift_06 3 第50帧 antomini qshift_a 4 第105帧 legall qshift_a 1 第185帧 near_sym_a qshift_06 3 第200帧 near_sym_a qshift_06 1 表 5 BEPMS数据集各评价指标结果
Table 5. Results of each evaluation index in BEPMS dataset
融合算法 QAB/F Q0 Qw Qe MI VIFF RCF CVT 0.3435 0.5474 0.7050 0.1527 1.4282 0.3462 14.4333 NSST 0.4405 0.5615 0.8100 0.2257 1.4231 0.4349 14.5350 NSCT 0.4510 0.5498 0.8016 0.2179 1.3907 0.5112 13.9504 WPT 0.3024 0.4560 0.6397 0.1078 1.1565 0.2576 14.0764 SWT 0.4333 0.5473 0.7853 0.2178 1.3348 0.3855 13.5462 LP 0.4472 0.5521 0.8035 0.2064 1.4680 0.4772 14.2224 DTCWT 0.4113 0.5712 0.7847 0.2052 1.3244 0.3878 13.6647 本文算法 0.4524 0.5737 0.8032 0.2259 1.4773 0.5220 14.4733 表 6 OTCBVS数据集各评价指标结果
Table 6. Results of each evaluation index in OTCBVS dataset
融合算法 QAB/F Q0 Qw Qe MI VIFF RCF CVT 0.4381 0.4931 0.6658 0.2307 2.0139 0.2706 27.4243 NSST 0.4762 0.4879 0.7230 0.2662 2.2226 0.3422 27.4073 NSCT 0.4004 0.4571 0.6399 0.2390 2.2304 0.1942 18.5130 WPT 0.2911 0.3960 0.5024 0.1518 1.8994 0.1319 18.8553 SWT 0.3043 0.4578 0.5569 0.1988 2.1979 0.1876 19.4402 LP 0.3689 0.4601 0.6235 0.2350 2.0329 0.2009 18.4434 DTCWT 0.3362 0.4283 0.5968 0.2231 1.8850 0.1558 27.0096 本文算法 0.4743 0.4893 0.7240 0.2730 2.2318 0.3494 27.5925 -
[1] 赵志刚, 王鑫, 彭廷海, 等. 国外中长波双波段红外成像技术的发展及应用[J]. 红外技术, 2020, 42(4): 312-319. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.7101502294ZHAO Z G, WANG X, PENG T H, et al. Status quo and application of middle and long wave dual-band infrared imaging technologies in occident[J]. Infrared Technology, 2020, 42(4): 312-319(in Chinese). doi: 10.3724/SP.J.7101502294 [2] MA J Y, MA Y, LI C. Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: A survey[J]. Information Fusion, 2019, 45: 153-178. [3] DUJ, LI W S, XIAO B, et al. Union Laplacian pyramid with multiple features for medical image fusion[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 194: 326-339. [4] 唐超影, 浦世亮, 叶鹏钊, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的低照度可见光与近红外图像融合[J]. 光学学报, 2020, 40(16): 1610001.TANG C Y, PU S L, YE P Z, et al. Fusion of low-illuminance visible and near-infrared images based on convolutional neural networks[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2020, 40(16): 1610001(in Chinese). [5] LI H F, WANG Y T, YANG Z, et al. Discriminative dictionary learning-based multiple component decomposition for detail-preserving noisy image fusion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2020, 69(4): 1082-1102. [6] 王文卿, 马笑, 刘涵. 基于联合低秩稀疏分解的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 信号处理, 2021, 37(9): 1770-1780.WANG W Q, MA X, LIU H. Infrared and visible image fusion via joint low-rank and sparse decomposition[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2021, 37(9): 1770-1780(in Chinese). [7] HU H M, WU J W, LI B, et al. An adaptive fusion algorithm for visible and infrared videos based on entropy and the cumulative distribution of gray levels[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2017, 19(12): 2706-2719. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2017.2711422 [8] ZHANG Q, WANG Y B, LEVINE M D, et al. Multisensor video fusion based on higher order singular value decomposition[J]. Information Fusion, 2015, 24: 54-71. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2014.09.008 [9] ZHANG Q, WANG L, MA Z K, et al. A novel video fusion framework using surfacelet transform[J]. Optics Communications, 2012, 285(13-14): 3032-3041. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2012.02.064 [10] 郭小铭, 吉琳娜, 杨风暴. 基于可能性信息质量合成的双模态红外图像融合算法选取[J]. 光子学报, 2021, 50(3): 0310003.GUO X M, JI L N, YANG F B. Dual-mode infrared image fusion algorithm selection based on possibility information quality synthesis[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2021, 50(3): 0310003(in Chinese). [11] JI L N, YANG F B, GUO X M. Set-valued mapping cloud model and its application for fusion algorithm selection of dual mode infrared images[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9: 54338-54349. [12] 杨风暴. 红外偏振与光强图像的拟态融合原理和模型研究[J]. 中北大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 38(1): 1-8.YANG F B. Research on theory and model of mimic fusion between infrared polarization and intensity images[J]. Journal of North University of China (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 38(1): 1-8(in Chinese). [13] 张雷, 杨风暴, 吉琳娜. 差异特征指数测度的红外偏振与光强图像多算法融合[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2018, 43(2): 49-54.ZHANG L, YANG F B, JI L N. Multi algorithm fusion of infrared polarization and intensity image based on difference feature exponential measure[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2018, 43(2): 49-54(in Chinese). [14] JI L N, YANG F B, GUO X M. Image fusion algorithm selection based on fusion validity distribution combination of difference features[J]. Electronics, 2021, 10(15): 1752. doi: 10.3390/electronics10151752 [15] 杨风暴, 吉琳娜, 王肖霞. 可能性理论及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019: 41-45.YANG F B, JI L N, WANG X X. Possibility theory and application[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019: 41-45(in Chinese). [16] LI S T, YANG B, HU J W. Performance comparison of different multi-resolution transforms for image fusion[J]. Information Fusion, 2011, 12(2): 74-84. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2010.03.002 [17] HAN Y, CAI Y Z, CAO Y, et al. A new image fusion performance metric based on visual information fidelity[J]. Information Fusion, 2013, 14(2): 127-135. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2011.08.002 -







 下载:
下载: