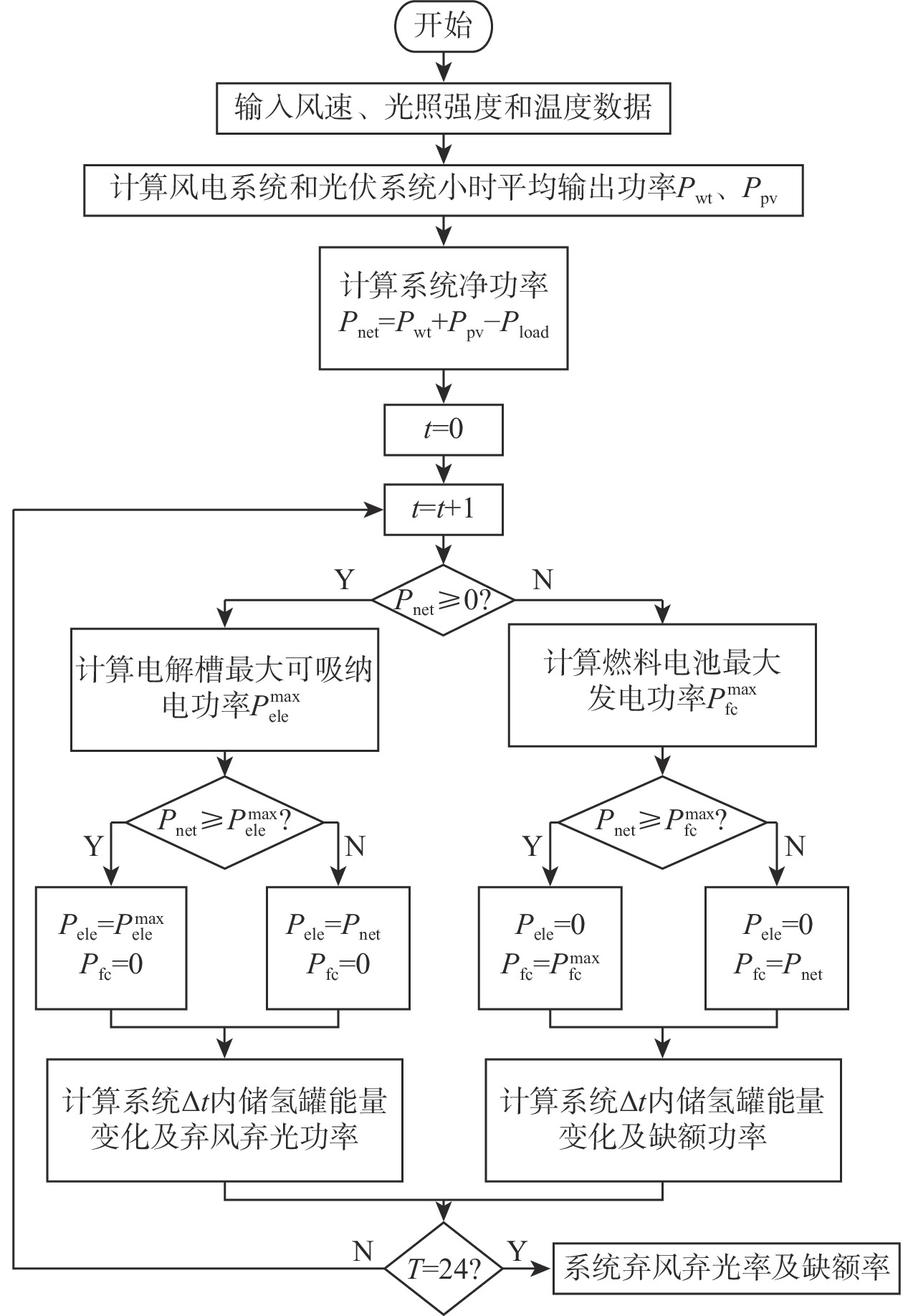
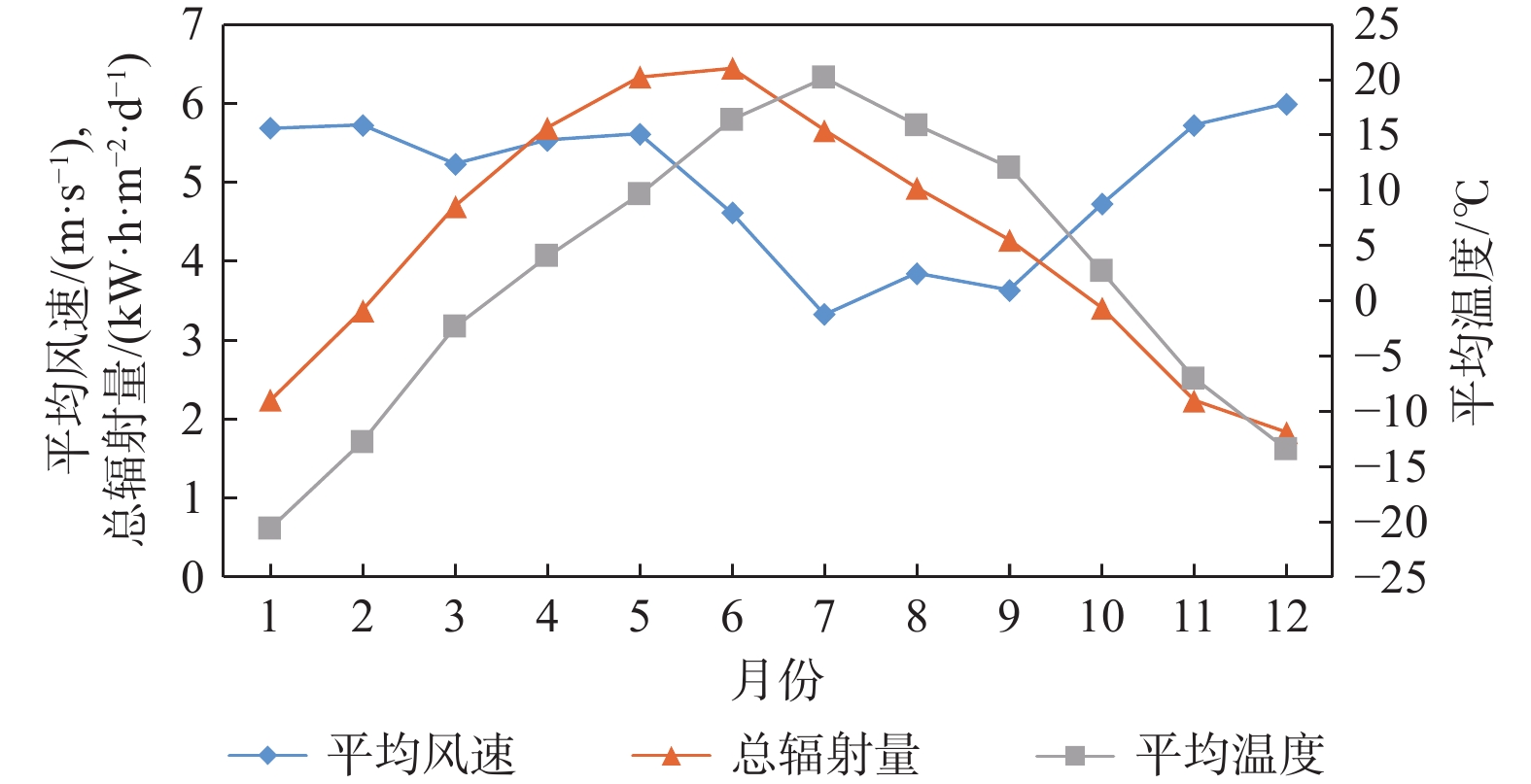
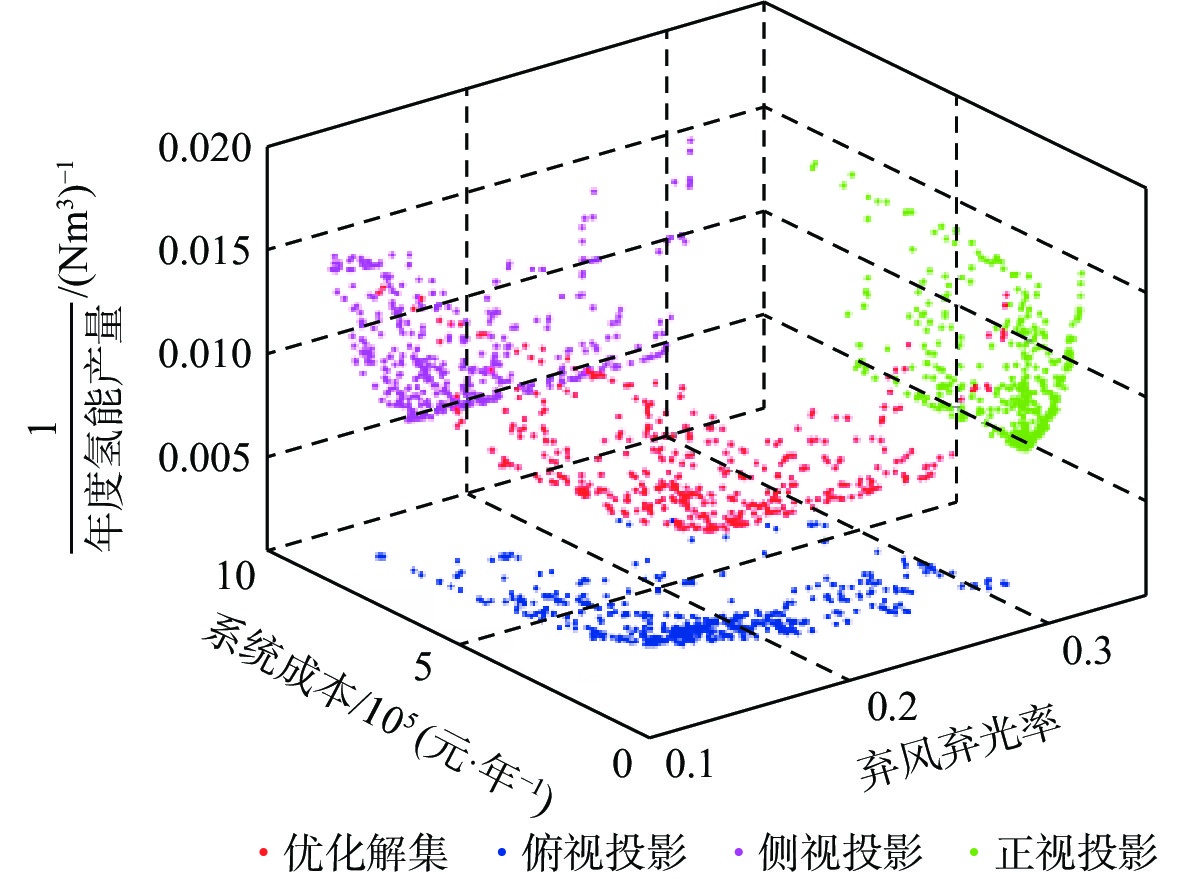
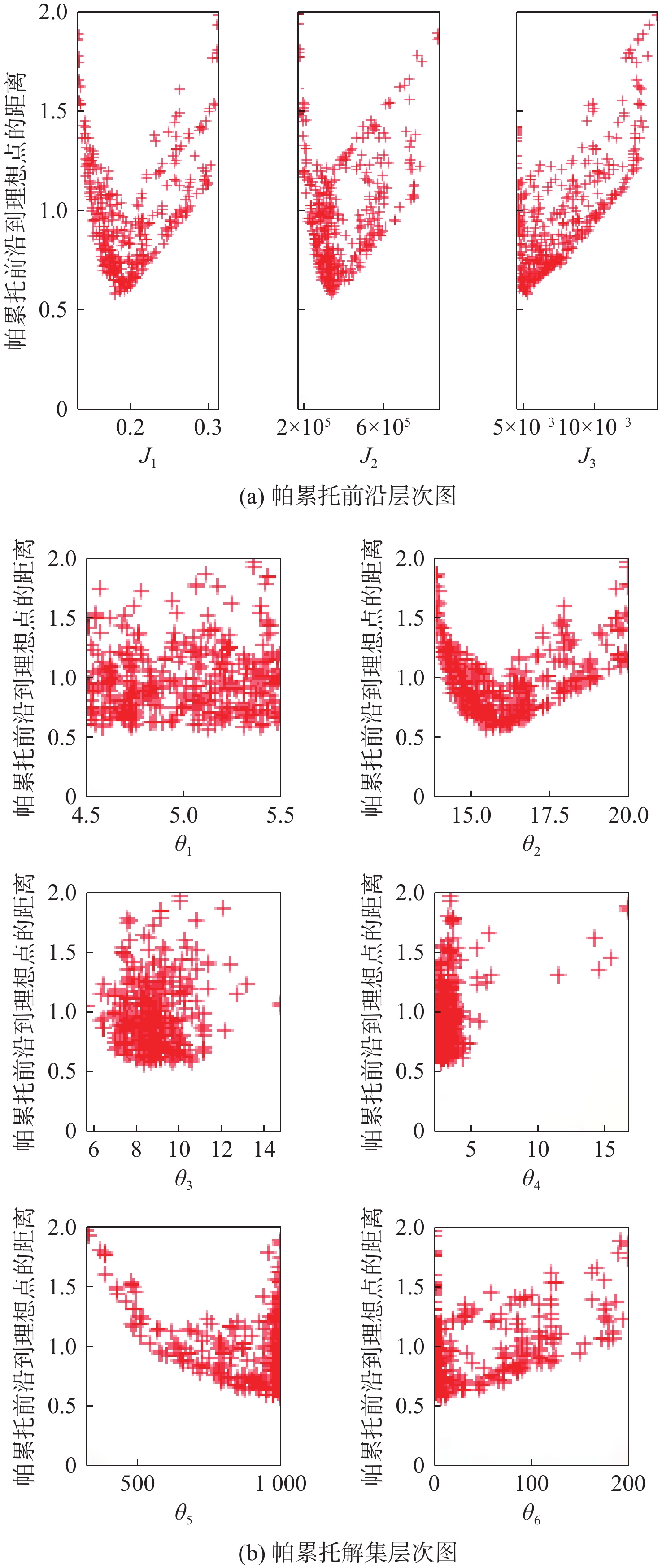
Configuration optimization of wind/photovoltaic hydrogen production system at frontier sentries
-
摘要:
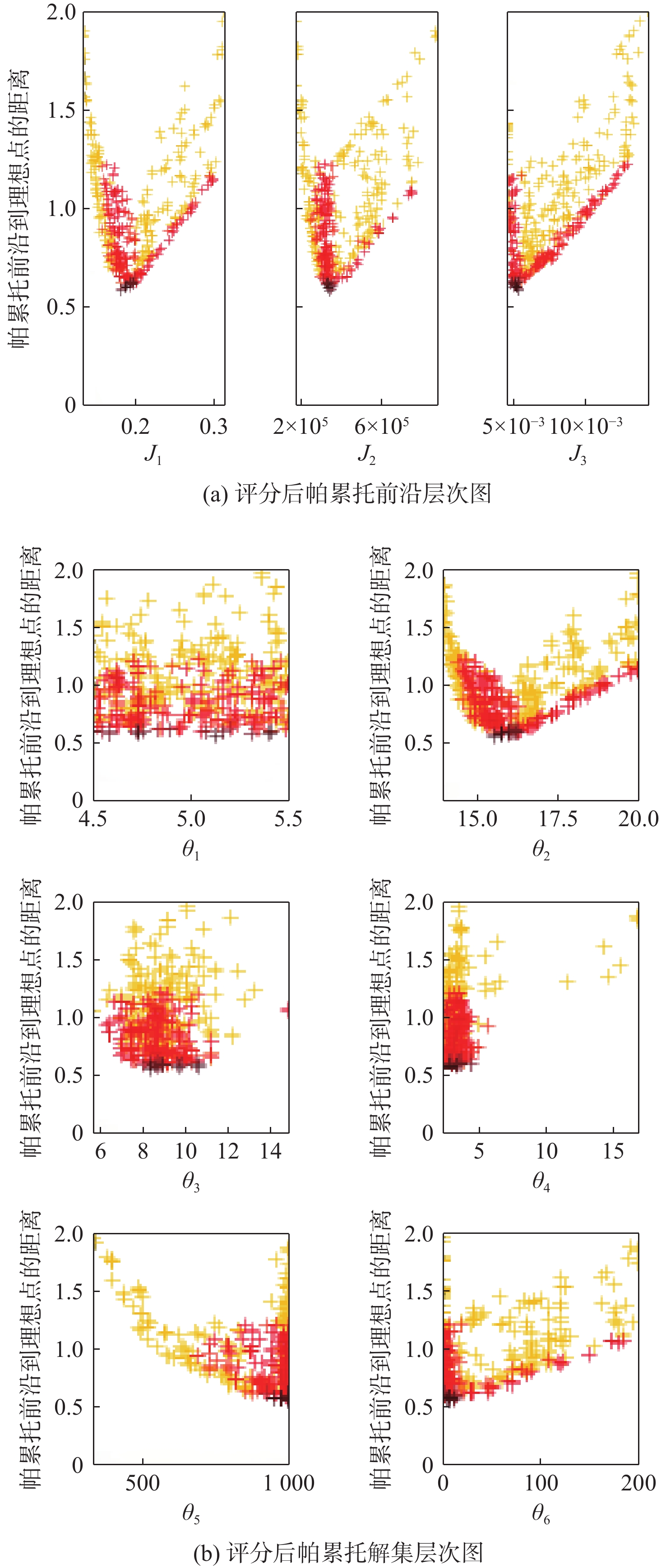
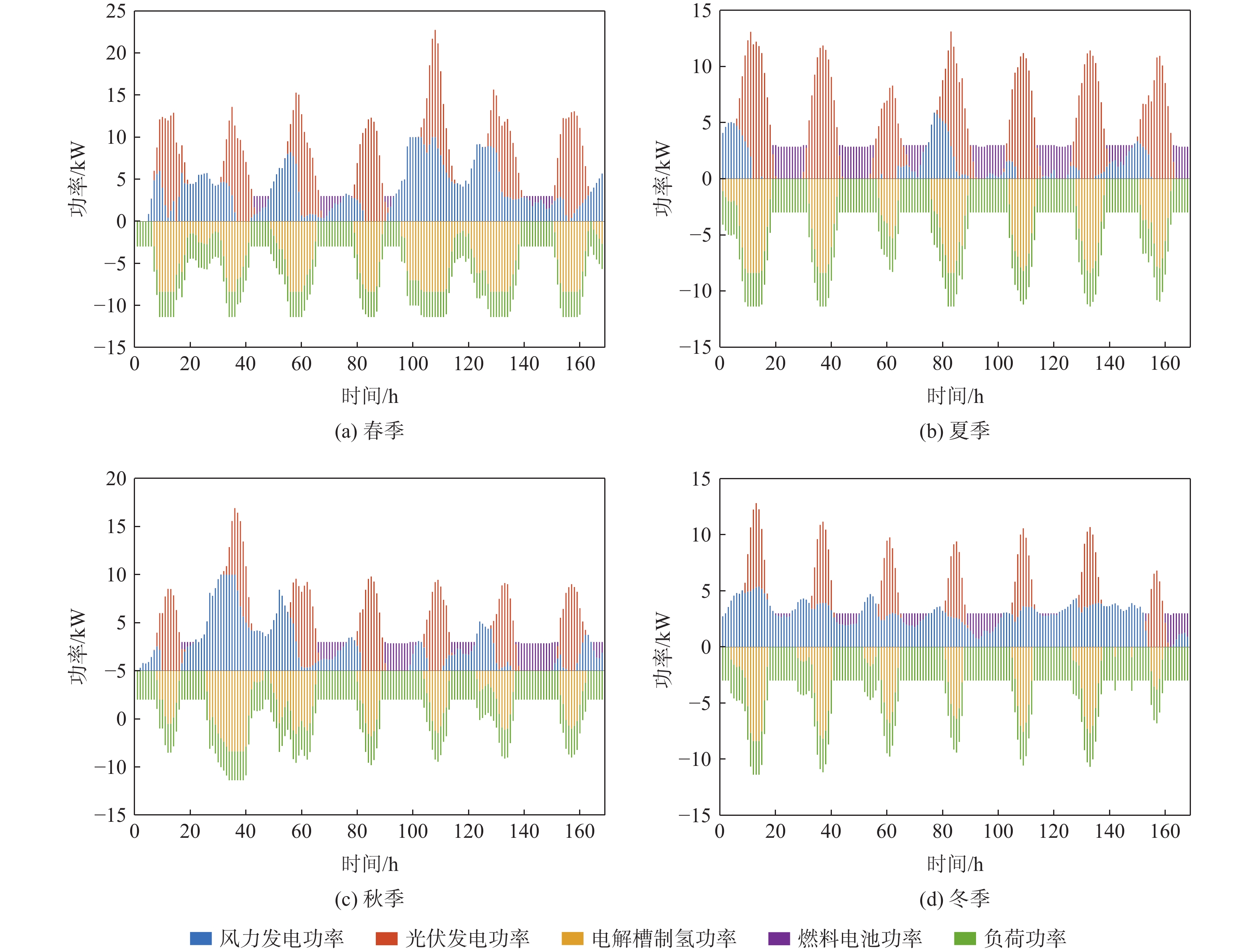
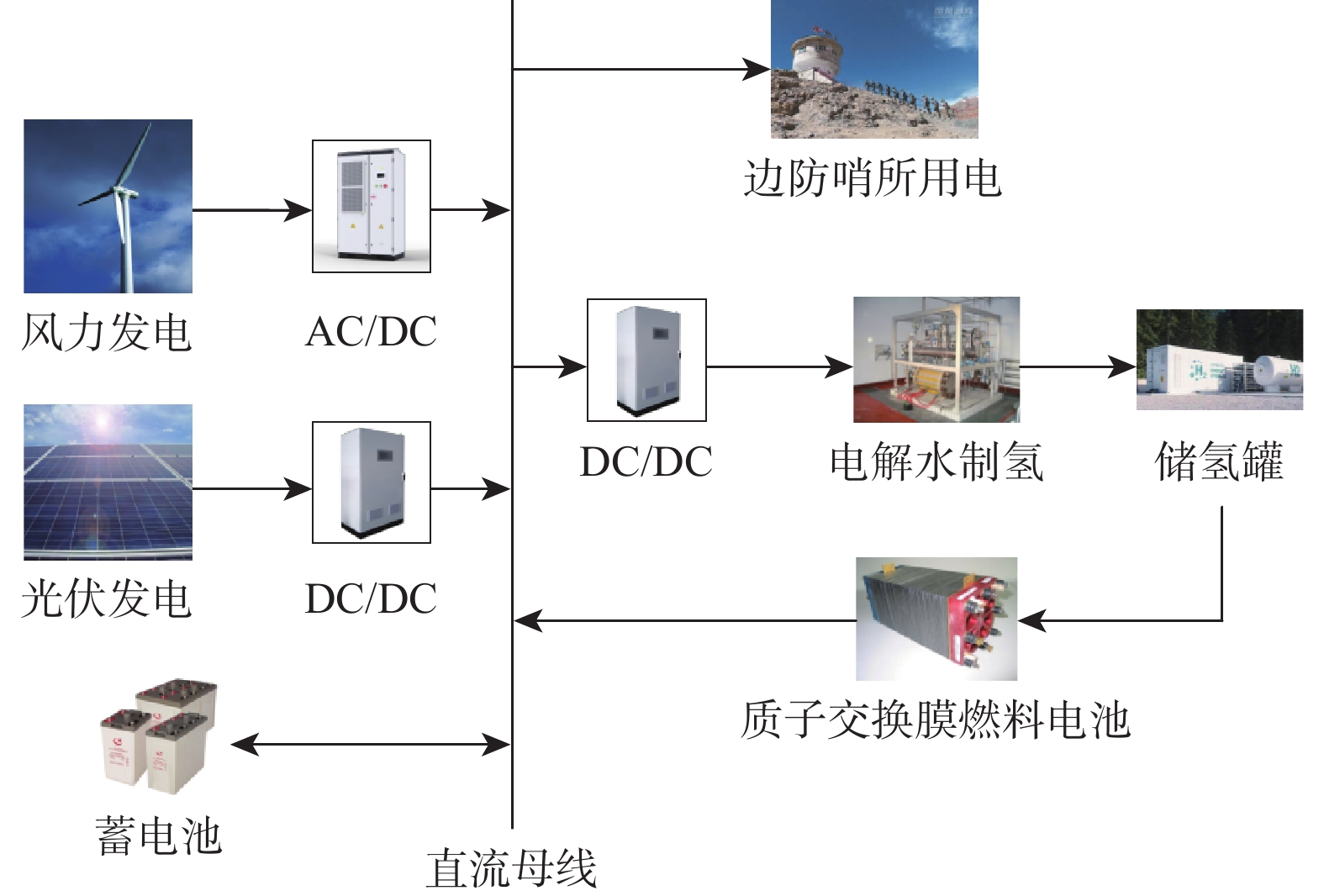
为解决边防哨所地处偏远、环境复杂、对能源需求大且上网成本高的问题,利用风光资源的互补性及氢能的能量密度高、绿色清洁等特点,提出了建立以风能和太阳能作为主要发电能源的风光耦合制氢系统,并选择氢能单元作为系统的储能单元,以满足边防哨所对能源多样性的需求,提高哨所从周边环境获取能量的能力。建立风光耦合制氢系统各子系统数学模型,以减小系统成本、提高可再生能源利用率、增大氢能产量为目标进行系统建设配置优化,选择系统各组件的额定功率作为设计变量,具体地区气象数据作为输入,利用第三代非支配排序遗传算法(NSGA-Ⅲ)进行求解,对优化得到的帕累托解集进行决策。通过层次图的绘制实现多维帕累托前沿可视化,得到了最优配置方案,并与未优化配置方案等进行对比,保障供电可靠性的同时可大幅度提高能源利用率、降低配置成本。
Abstract:In order to solve the problems of the remote location of frontier sentries, complex environment, large energy demand, and high cost of access to the electricity network, the complementary nature of wind/photovoltaic resources, as well as the high energy density and green and clean characteristics of hydrogen energy were used to establish a wind/photovoltaic hydrogen production system with wind and solar energy as the main power generation energy. In addition, hydrogen energy was selected as the energy storage unit of the system to meet the demand for energy diversity of frontier sentries and improve the sentries eability to obtain energy from the surrounding environment. Firstly, the mathematical model of each subsystem of the wind/photovoltaic hydrogen production system was established, and the system construction configuration was optimized to reduce the system cost, improve the utilization rate of renewable energy, and increase hydrogen energy production. The rated power of each component of the system was chosen as the design variable, and the meteorological data of specific regions was used as input. The non-dominated sorting genetic algorithm-Ⅲ (NSGA-Ⅲ) was applied to solve the system, and decision-making was performed on the Pareto solution set obtained by optimization.The visualization of the multi-dimensional Pareto front was realized through the drawing of level diagrams, and the optimal configuration scheme was compared with the unoptimized configuration scheme, the energy utilization rate and configuration cost can be greatly improved while ensuring the reliability of power supply.
-
表 1 不同组件的单位容量成本数据
Table 1. Cost per unit capacity for different components
风力发电机 光伏阵列 电解槽 投资建设成本/
(元·kW−1)运行维护成本/
(元·(kW·年)−1)投资建设成本/
(元·kW−1)运行维护成本/
(元·(kW·年)−1)投资建设成本/
(元·kW−1)运行维护成本/
(元·(kW·年)−1)置换成本/
(元·kW−1)7250 145 9200 184 4465.5 128 4654 燃料电池 储氢罐 蓄电池 投资建设成本/
(元·kW−1)运行维护成本/
(元·(kW·年)−1)置换成本/
(元·kW−1)投资建设成本/
(元·kg−1)运行维护成本/
(元·(kW·h·年)−1)投资建设成本/
(元·(kW·h)−1)运行维护成本/
(元·(kW·h·年)−1)置换成本/
(元·(kW·h)−1)3000 60 2570 42000 170 1190 24 992 表 2 优化配置方案示例
Table 2. Example of optimal configuration scheme
编号 弃风弃光率 系统成本/元 年度氢能产量/Nm3 1 0.134 795453 76.923 2 0.181 346965 200 3 0.277 238842 142.857 4 0.258 339334 250 ⋮ 表 3 理想目标函数取值范围
Table 3. Ideal value range of objective function
优化目标 JiHD JiD JiT JiU JiHD JiHU J1 0.15 0.16 0.17 0.18 0.19 0.2 J2 220000 260000 300000 320000 340000 360000 J3 0.0050 0.0051 0.0052 0.0053 0.0054 0.0055 表 4 最优配置方案
Table 4. Optimal configuration scheme
风力发电机
额定功率/
kW光伏阵列
额定功率/
kW电解槽
额定功率/
kW燃料电池
额定功率/
kW储氢罐
额定容量/
Nm3蓄电池
额定容量/
(kW·h)10 15.52 8.38 2.86 223 8.38 表 5 优化配置方案对比
Table 5. Comparison of optimal configuration schemes
方案 负荷
缺额率/
%弃风
弃光率系统
成本/
(元·年−1)年度
氢能产量/
Nm3风光
互补特性仅风光发电单元 42.9 0.170 耦合氢能下未优化
配置方案1.1 0.737 439674 167.4 5.113 优化配置方案 4.3 0.184 338140 167.6 1.486 -
[1] 孔令国. 风光氢综合能源系统优化配置与协调控制策略研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2017: 1-12.KONG L G. Research on optimal sizing and coordinated control strategy of integrated energy system of wind photovoltaic and hydrogen[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2017: 1-12(in Chinese). [2] 曹蕃, 郭婷婷, 殷爱鸣, 等. 风光氢混合发电系统设计与能量管理策略研究进展[J]. 分布式能源, 2021, 6(4): 1-14.CAO F, GUO T T, YIN A M, et al. Research progress on optimal sizing and energy management strategy of wind-solar-hydrogen hybrid energy systems[J]. Distributed Energy, 2021, 6(4): 1-14(in Chinese). [3] AL BUSAIDI A S, KAZEM H A, AL-BADI A H, et al. A review of optimum sizing of hybrid PV-wind renewable energy systems in Oman[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2016, 53: 185-193. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2015.08.039 [4] KHALILNEJAD A, RIAHY G H. A hybrid wind-PV system performance investigation for the purpose of maximum hydrogen production and storage using advanced alkaline electrolyzer[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2014, 80: 398-406. doi: 10.1016/j.enconman.2014.01.040 [5] BAKHTIARI H, ALI NAGHIZADEH R. Multi-criteria optimal sizing of hybrid renewable energy systems including wind, photovoltaic, battery, and hydrogen storage with ɛ-constraint method[J]. IET Renewable Power Generation, 2018, 12(8): 883-892. doi: 10.1049/iet-rpg.2017.0706 [6] GONZÁLEZ A, RIBA J R, RIUS A, et al. Optimal sizing of a hybrid grid-connected photovoltaic and wind power system[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 154: 752-762. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.04.105 [7] 马榕谷, 陈洁, 赵军超, 等. 非并网风氢互补系统的容量多目标优化[J]. 太阳能学报, 2019, 40(2): 422-429.MA R G, CHEN J, ZHAO J C, et al. Multi-objective optimization for capacity of non-grid-connected wind/hydrogen hybrid power system[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2019, 40(2): 422-429(in Chinese). [8] 王侃宏, 赵政通, 罗景辉. 风光氢储系统的两阶优化匹配分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2020, 20(26): 10790-10794. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.26.035WANG K H, ZHAO Z T, LUO J H. Two-order optimization matching analysis of scenery hydrogen storage system[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2020, 20(26): 10790-10794(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2020.26.035 [9] KHIAREDDINE A, BEN SALAH C, REKIOUA D, et al. Sizing methodology for hybrid photovoltaic/wind/hydrogen/battery integrated to energy management strategy for pumping system[J]. Energy, 2018, 153: 743-762. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2018.04.073 [10] 董伟强. 风光氢蓄混合发电系统的配置及其电池管理研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2017: 10-19.DONG W Q. Optimal sizing and battery management of a stand-alone hybrid power system based on battery/hydrogen[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2017: 10-19(in Chinese). [11] HADIDIAN MOGHADDAM M J, KALAM A, NOWDEH S A, et al. Optimal sizing and energy management of stand-alone hybrid photovoltaic/wind system based on hydrogen storage considering LOEE and LOLE reliability indices using flower pollination algorithm[J]. Renewable Energy, 2019, 135: 1412-1434. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2018.09.078 [12] XU L, RUAN X B, MAO C X, et al. An improved optimal sizing method for wind-solar-battery hybrid power system[J]. IEEE Transactions on Sustainable Energy, 2013, 4(3): 774-785. doi: 10.1109/TSTE.2012.2228509 [13] SKOPLAKI E, PALYVOS J A. Operating temperature of photovoltaic modules: A survey of pertinent correlations[J]. Renewable Energy, 2009, 34(1): 23-29. doi: 10.1016/j.renene.2008.04.009 [14] MORIN D, STEVENIN Y, GROLLEAU C, et al. Evaluation of performance improvement by model predictive control in a renewable energy system with hydrogen storage[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018, 43(45): 21017-21029. [15] GÖTZ M, LEFEBVRE J, MÖRS F, et al. Renewable power-to-gas: A technological and economic review[J]. Renewable Energy, 2016, 85: 1371-1390. [16] SHAW S, PETEVES E. Exploiting synergies in European wind and hydrogen sectors: A cost-benefit assessment[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2008, 33(13): 3249-3263. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2008.02.052 [17] DEB K, JAIN H. An evolutionary many-objective optimization algorithm using reference-point-based nondominated sorting approach, Part I: Solving problems with box constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2014, 18(4): 577-601. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2013.2281535 [18] 耿焕同, 戴中斌, 王天雷, 等. 基于参考点选择策略的改进型NSGA-Ⅲ算法[J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 2020, 33(3): 191-201.GENG H T, DAI Z B, WANG T L, et al. Improved NSGA-Ⅲ algorithm based on reference point selection strategy[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 33(3): 191-201(in Chinese). [19] BLASCO X, HERRERO J M, SANCHIS J, et al. A new graphical visualization of n-dimensional Pareto front for decision-making in multiobjective optimization[J]. Information Sciences, 2008, 178(20): 3908-3924. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2008.06.010 [20] 徐林, 阮新波, 张步涵, 等. 风光蓄互补发电系统容量的改进优化配置方法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2012, 32(25): 88-98.XU L, RUAN X B, ZHANG B H, et al. An improved optimal sizing method for wind-solar-battery hybrid power system[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2012, 32(25): 88-98(in Chinese). [21] 万家豪, 苏浩, 冯冬涵, 等. 计及源荷匹配的风光互补特性分析与评价[J]. 电网技术, 2020, 44(9): 3219-3226.WAN J H, SU H, FENG D H, et al. Analysis and evaluation of the complementarity characteristics of wind and photovoltaic considering source-load matching[J]. Power System Technology, 2020, 44(9): 3219-3226(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: