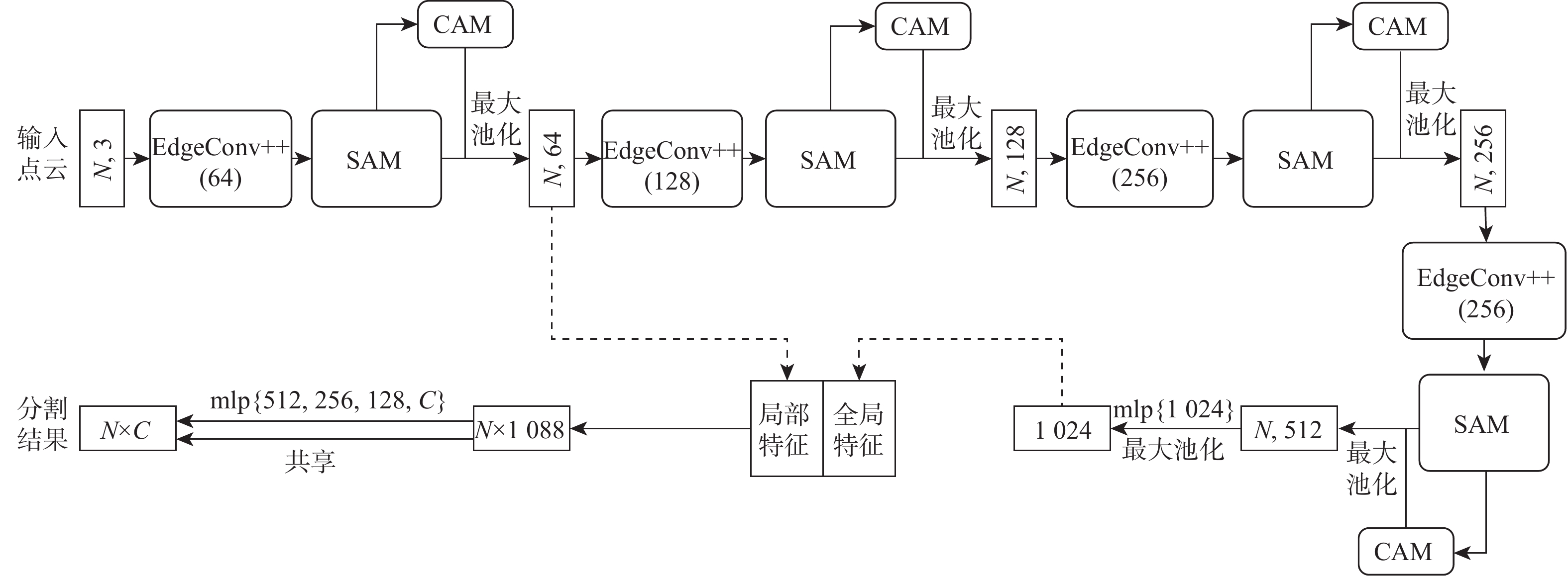
Semantic segmentation of point clouds by fusing dual attention mechanism and dynamic graph convolution
-
摘要:
针对现有基于深度学习的三维点云语义分割算法通常在提取局部特征时忽略邻域点间深层次语义信息,聚合局部邻域特征时忽略其他邻域特征中有用信息的问题,提出融合双注意力机制和动态图卷积神经网络(DGCNN)的三维点云语义分割算法。通过动态图卷积操作构造边缘特征,并将中心点与邻域点的相对距离输入到核点卷积操作得到增强后的边缘特征,进一步加强中心点与邻域点之间的联系;引入空间注意力模块以建立邻域点之间的依赖关系,将特征相似点相互关联,从而在局部邻域内提取到更深层次的上下文信息,丰富邻域点的几何特征;在聚合局部邻域特征时引入通道注意力模块,通过给不同通道赋予不同的权值以达到增强有用通道同时抑制无用通道的目的,从而提高语义分割的准确率。在S3DIS数据集和SemanticKITTI数据集上的实验结果表明:所提算法的语义分割精度分别达到了66.0%和59.4%,与其他经典的网络模型相比,取得了更好的点云分割效果。
Abstract:The existing semantic segmentation methods of 3D point clouds based on deep learning usually ignore the profound semantic information between neighboring points when extracting local features and fail to consider the useful information in other neighboring features when aggregating local neighboring features. To solve these problems, a semantic segmentation algorithm of 3D point clouds fusing dual attention mechanism and dynamic graph convolution neural network (DGCNN) was proposed. Firstly, edge features were constructed by dynamic graph convolution operation, and the relative distance between the center point and the neighboring points was input to the kernel point convolution operation to obtain enhanced edge features, further strengthening the relationship between the center point and the neighboring points. Secondly, the spatial attention module was introduced to establish the dependence between neighboring points, and the similar feature points were intercorrelated, so as to extract profound context information in the local neighborhood and enrich the geometric features of neighboring points. Finally, the channel attention module was introduced when local neighboring features were aggregated. By giving different weights to different channels, the purpose of enhancing useful channels and suppressing useless channels was achieved, so as to improve the accuracy of semantic segmentation. The experimental results on the S3DIS dataset and SemanticKITTI dataset show that the semantic segmentation accuracy of this algorithm has reached 66.0% and 59.4%, respectively. Compared with other classical network models, this algorithm has achieved a better point cloud segmentation effect.
-
Key words:
- 3D point cloud /
- semantic segmentation /
- deep learning /
- attention mechanism /
- dynamic graph convolution
-
表 1 不同算法在S3DIS数据集上的分割精度对比(Area 5作为测试)
Table 1. Comparison of segmentation accuracy of different algorithms on S3DIS dataset (Area 5 as a test)
% 算法 OA mIoU IoU ceiling floor wall beam column window door table chair sofa bookcase board clutter PointNet[6] 79.3 41.1 88.8 97.3 69.8 0.1 3.9 46.3 10.8 59.0 52.6 5.9 40.3 26.4 33.2 TangentConv[8] 82.5 52.6 90.5 97.7 74.0 0 20.7 39.0 31.3 77.5 69.4 57.3 38.5 48.8 39.8 PointCNN[28] 85.9 57.3 92.3 98.2 79.4 0 17.6 22.8 62.1 74.4 80.6 31.7 66.7 62.1 56.7 SPG[29] 86.4 58.0 89.4 96.9 78.1 0 42.8 48.9 61.6 84.7 75.4 69.8 52.6 2.1 52.2 PCCN[30] 58.3 92.3 96.2 75.9 0.3 6.0 69.5 63.5 66.9 65.6 47.3 68.9 59.1 46.2 PointWeb[18] 87.0 60.3 92.0 98.5 79.4 0 21.1 59.7 34.8 76.3 88.3 46.9 69.3 64.9 52.5 HPEIN[31] 87.2 61.9 91.5 98.2 81.4 0 23.3 65.3 40.0 75.5 87.7 58.5 67.8 65.6 49.4 RandLA-Net[32] 87.2 62.4 91.1 95.6 80.2 0 24.7 62.3 47.7 76.2 83.7 60.2 71.1 65.7 53.8 GACNet[19] 87.8 62.8 92.3 98.3 81.9 0 20.3 59.1 40.8 78.5 85.8 61.7 70.7 74.7 52.8 BAAF-Net[33] 88.9 65.4 92.9 97.9 82.3 0 23.1 65.5 64.9 78.5 87.5 61.4 70.7 68.7 57.2 KPConv[20] 67. 1 92.8 97.3 82.4 0 23.9 58.0 69.0 81.5 91.0 75.4 75.3 66.7 58.9 本文 92.8 66.0 92.9 98.3 82.8 0 21.2 56.6 68.5 91.3 81.3 74.4 64.2 68.9 57.8 表 2 不同算法在SemanticKITTTI数据集上的分割精度对比
Table 2. Comparison of segmentation accuracy of different algorithms on SemanticKITTI dataset
% 算法 mIoU IoU road sidewalk parking other-ground building car truck bicycle motorcycle PointNet [6] 14.6 61.6 35.7 15.8 1.4 41.4 46.3 0.1 1.3 0.3 SPG[29] 17.4 45.0 28.5 1.6 0.6 64.3 49.3 0.1 0.2 0.2 PointNet++ [16] 20.1 72.0 41.8 18.7 5.6 62.3 53.7 0.9 1.9 0.2 TangentConv[8] 40.9 83.9 63.9 33.4 15.4 83.4 90.8 15.2 2.7 16.5 SpSequenceNet[34] 43.1 90.1 73.9 57.6 27.1 91.2 88.5 29.2 24.0 0 PointASNL[35] 46.8 87.4 74.3 24.3 1.8 83.1 87.9 39.0 0 25.1 HPGCNN[36] 50.5 89.5 73.6 58.8 34.6 91.2 93.1 21.0 6.5 17.6 RangeNet++ [11] 52.2 91.8 75.2 65.0 27.8 87.4 91.4 25.7 25.7 34.4 RandLA-Net[32] 53.9 90.7 73.7 60.3 20.4 86.9 94.2 40.1 26.0 25.8 PolarNet[37] 54.3 90.8 74.4 61.7 21.7 90.0 93.8 22.9 40.3 30.1 3D-MiniNet [38] 55.8 91.6 74.5 64.2 25.4 89.4 90.5 28.5 42.3 42.1 SAFFGCNN[39] 56.6 89.9 73.9 63.5 35.1 91.5 95 38.3 33.2 35.1 KPConv[20] 58.8 88.8 72.7 61.3 31.6 90.5 96.0 33.4 30.2 42.5 BAAF-Net[33] 59.9 90.9 74.4 62.2 23.6 89.8 95.4 48.7 31.8 35.5 本文 59.4 92.0 77.4 70.1 35.2 89.7 94.4 38.4 43.7 40.3 算法 IoU other-vehicle vegetation trunk terrain person bicyclist motorcyclist fense pole traffic-sign PointNet [6] 0.8 31.0 4.6 17.6 0.2 0.2 0 12.9 2.4 3.7 SPG[29] 0.8 48.9 27.2 24.6 0.3 2.7 0.1 20.8 15.9 0.8 PointNet++ [16] 0.2 46.5 13.8 30.0 0.9 1.0 0 16.9 6.0 8.9 TangentConv[8] 12.1 79.5 49.3 58.1 23.0 28.4 8.1 49.0 35.8 28.5 SpSequenceNet[34] 22.7 84.0 66.0 65.7 6.3 0 0 67.7 50.8 48.7 PointASNL[35] 29.2 84.1 52.2 70.6 34.2 57.6 0 43.9 57.8 36.9 HPGCNN[36] 23.3 84.4 65.9 70.0 32.1 30.0 14.7 65.5 45.5 41.5 RangeNet++ [11] 23.0 80.5 55.1 64.6 38.3 38.8 4.8 58.6 47.9 55.9 RandLA-Net[32] 38.9 81.4 61.3 66.8 49.2 48.2 7.2 56.3 49.2 47.7 PolarNet[37] 28.5 84.0 65.5 67.8 43.2 40.2 5.6 61.3 51.8 57.5 3D-MiniNet [38] 29.4 82.8 60.8 66.7 47.8 44.1 14.5 60.8 48.0 56.6 SAFFGCNN[39] 28.7 84.4 67.1 69.5 45.3 43.5 7.3 66.1 54.3 53.7 KPConv[20] 31.6 84.8 69.2 69.1 61.5 61.6 11.8 64.2 56.4 48.4 BAAF-Net[33] 46.7 82.7 63.4 67.9 49.5 55.7 53.0 60.8 53.7 52.0 本文 30.3 84.3 64.9 70.0 60.1 47.4 7.6 66.9 53.1 62.4 表 3 不同模块在S3DIS数据集上的消融实验
Table 3. Ablation experiments of different modules on S3DIS dataset
网络模型 模块名 mIoU/% Net Model-1 CAM 62.8 Net Model-2 SAM 65.2 Net Model-3 SAM+CAM 66.0 表 4 改进的动态图卷积模块有效性验证
Table 4. Effectiveness verification of improved dynamic graph convolution module
网络模型 模块名 mIoU/% Net Model-4 EdgeConv++ 64.2 Net Model-5 KPConv 64.7 Net Model-6 KPConv+EdgeConv++ 66.0 Net Model-7 KPConv rigid 65.4 表 5 核心点数量对分割结果的影响
Table 5. Influence of number of kernel points on segmentation results
d mIoU/% 11 64.8 13 65.3 15 66.0 17 65.7 -
[1] ZHU Y K, MOTTAGHI R, KOLVE E, et al. Target-driven visual navigation in indoor scenes using deep reinforcement learning[C]// Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 3357-3364. [2] ZHANG K G, XIONG C H, ZHANG W, et al. Environmental features recognition for lower limb prostheses toward predictive walking[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2019, 27(3): 465-476. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2019.2895221 [3] QI C R, LIU W, WU C X, et al. Frustum PointNets for 3D object detection from RGB-D data[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 918-927. [4] ZHANG G C, YU J, WANG Z H, et al. Visual 3D reconstruction system based on RGBD camera[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 4th Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 908-911. [5] 姜枫, 顾庆, 郝慧珍, 等. 基于内容的图像分割方法综述[J]. 软件学报, 2017, 28(1): 160-183.JIANG F, GU Q, HAO H Z, et al. Survey on content-based image segmentation methods[J]. Journal of Software, 2017, 28(1): 160-183(in Chinese). [6] CHARLES R Q, HAO S, MO K C, et al. PointNet: Deep learning on point sets for 3D classification and segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 77-85. [7] WANG Y, SUN Y B, LIU Z W, et al. Dynamic graph CNN for learning on point clouds[J]. ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2019, 38(5): 1-12. [8] TATARCHENKO M, PARK J, KOLTUN V, et al. Tangent convolutions for dense prediction in 3D[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 3887-3896. [9] WU B C, WAN A, YUE X Y, et al. SqueezeSeg: Convolutional neural nets with recurrent CRF for real-time road-object segmentation from 3D LiDAR point cloud[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1887-1893. [10] WU B C, ZHOU X Y, ZHAO S C, et al. SqueezeSegV2: Improved model structure and unsupervised domain adaptation for road-object segmentation from a LiDAR point cloud[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 4376-4382. [11] MILIOTO A, VIZZO I, BEHLEY J, et al. RangeNet++: Fast and accurate LiDAR semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 4213-4220. [12] MATURANA D, SCHERER S. VoxNet: A 3D convolutional neural network for real-time object recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 922-928. [13] TCHAPMI L, CHOY C, ARMENI I, et al. SEGCloud: Semantic segmentation of 3D point clouds[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on 3D Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 537-547. [14] RIEGLER G, ULUSOY A O, GEIGER A. OctNet: Learning deep 3D representations at high resolutions[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 6620-6629. [15] ZENG W, GEVERS T. 3DContextNet: k-d tree guided hierarchical learning of point clouds using local and global contextual cues[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 314-330. [16] QI C R, YI L, SU H, et al. PointNet++: Deep hierarchical feature learning on point sets in a metric space[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2017: 5099-5108. [17] 党吉圣, 杨军. 多特征融合的三维模型识别与分割[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2020, 47(4): 149-157.DANG J S, YANG J. 3D model recognition and segmentation based on multi-feature fusion[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2020, 47(4): 149-157(in Chinese). [18] ZHAO H S, JIANG L, FU C W, et al. PointWeb: Enhancing local neighborhood features for point cloud processing[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 5560-5568. [19] WANG L, HUANG Y C, HOU Y L, et al. Graph attention convolution for point cloud semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 10288-10297. [20] THOMAS H, QI C R, DESCHAUD J E, et al. KPConv: Flexible and deformable convolution for point clouds[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 6410-6419. [21] FU J, LIU J, TIAN H J, et al. Dual attention network for scene segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 3141-3149. [22] LE T, DUAN Y. PointGrid: A deep network for 3D shape understanding[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 9204-9214. [23] ZHANG Z Y, HUA B S, YEUNG S K. ShellNet: Efficient point cloud convolutional neural networks using concentric shells statistics[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1607-1616. [24] HU J, SHEN L, ALBANIE S, et al. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 42(8): 2011-2023. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913372 [25] WOO S, PARK J C, LEE J Y, et al. CBAM: Convolutional block attention module[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 3-19. [26] ARMENI I, SENER O, ZAMIR A R, et al. 3D semantic parsing of large-scale indoor spaces[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1534-1543. [27] BEHLEY J, GARBADE M, MILIOTO A, et al. SemanticKITTI: A dataset for semantic scene understanding of LiDAR sequences[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 9296-9306. [28] LI Y Y, BU R, SUN M C, et al. PointCNN: Convolution on X-transformed points[C]//Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2018, 31: 828-838. [29] LANDRIEU L, SIMONOVSKY M. Large-scale point cloud semantic segmentation with superpoint graphs[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 4558-4567. [30] WANG S L, SUO S, MA W C, et al. Deep parametric continuous convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 2589-2597. [31] JIANG L, ZHAO H S, LIU S, et al. Hierarchical point-edge interaction network for point cloud semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 10432-10440. [32] HU Q Y, YANG B, XIE L H, et al. RandLA-Net: Efficient semantic segmentation of large-scale point clouds[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 11105-11114. [33] QIU S, ANWAR S, BARNES N. Semantic segmentation for real point cloud scenes via bilateral augmentation and adaptive fusion[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 1757-1767. [34] SHI H Y, LIN G S, WANG H, et al. SpSequenceNet: Semantic segmentation network on 4D point clouds[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 4573-4582. [35] YAN X, ZHENG C D, LI Z, et al. PointASNL: Robust point clouds processing using nonlocal neural networks with adaptive sampling[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 5588-5597. [36] DANG J S, YANG J. HPGCNN: Hierarchical parallel group convolutional neural networks for point clouds processing[C]//Proceedings of the Asian Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 20-37. [37] ZHANG Y, ZHOU Z X, DAVID P, et al. PolarNet: An improved grid representation for online LiDAR point clouds semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 9598-9607. [38] ALONSO I, RIAZUELO L, MONTESANO L, et al. 3D-MiniNet: Learning a 2D representation from point clouds for fast and efficient 3D LiDAR semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2020, 5(4): 5432-5439. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2020.3007440 [39] 杨军, 李博赞. 基于自注意力特征融合组卷积神经网络的三维点云语义分割[J]. 光学 精密工程, 2022, 30(7): 840-853. doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223007.0840YANG J, LI B Z. Semantic segmentation of 3D point cloud based on self-attention feature fusion group convolutional neural network[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2022, 30(7): 840-853(in Chinese). doi: 10.37188/OPE.20223007.0840 -







 下载:
下载: