-
摘要:
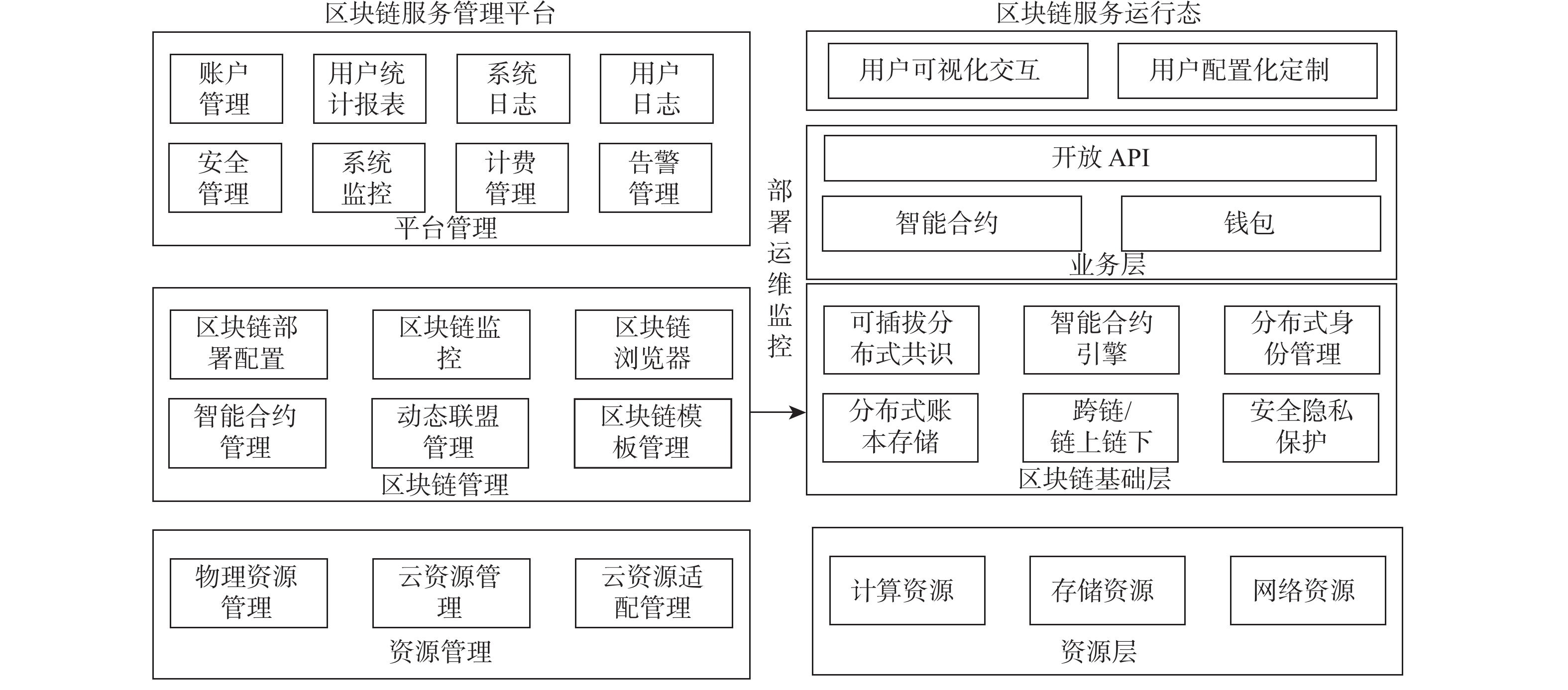
智能合约是区块链上的一种软件服务,具有价值传导、契约性和可信性等特点,当前各区块链系统上的智能合约数量越来越多,应用范围越来越广泛,传统智能合约的局限性也日益增大。隔离沙箱环境执行使智能合约与外界交互困难、资源受限、从而限制了智能合约的使用场景和性能。同时,传统的云服务等链下服务存在中心化风险,缺乏信任机制保障。提出智能合约即服务方案,提供链上合约与链下服务协同的方法,通过链下服务的链上认证,将服务生命周期纳入区块链管理,使之具有合约服务的可信化特点,以支持服务的注册、定制和组合;提出基于交易触发与事件驱动的通信与协同方法,在面对复杂业务场景或高资源需求任务时智能合约可与扩展服务组合构建工作流。经实验验证表明,智能合约即服务可以极大地拓展合约应用场景,通过将合约内执行的高资源耗费任务卸载到计算型扩展服务可提供更高的性能,性能优势与链下加速比正相关,如在执行1 200维矩阵乘法运算的任务时,性能可提升64%。
Abstract:A smart contract is a software service on blockchain with the characteristics of value transfer, contractuality, and trustworthiness. The quantity of smart contracts on blockchain systems is currently rising, together with the application scope's expansion and the restrictions of conventional smart contracts' growing number. Isolated sandbox environment execution makes it difficult for smart contracts to interact with the outside world, and resources are limited, limiting the use scenarios and performance of smart contracts. At the same time, off-chain services have the risk of centralization and lack of trust mechanisms to protect them. We propose a Smart Contract-as-a-Service solution, which provides a method for on-chain contracts to collaborate with off-chain services. Through on-chain authentication of off-chain services, the service lifecycle is incorporated into blockchain management, so that it has the trustworthy characteristics of contract services and supports the registration, customization and combination of services. We proposes a communication and collaboration method based on transaction triggering and event-driven mechanisms, where smart contracts can be combined with extended services to construct workflows in the face of complex business scenarios or tasks with high resource demands. Empirical verification demonstrates that Smart Contracts-as-a-Service can significantly expand contract application scenarios and boost performance by shifting resource-intensive tasks from within the contract to computational extension services. The benefit of increased performance is positively correlated with the off-chain speedup ratio, for example, a 64% improvement in performance when performing multiplication of a
1200 -dimensional matrix. -
表 1 链下扩展服务的数字身份字段
Table 1. Digital identity fields for off-chain scaling services
字段名 作用 服务名称name 统一资源定位符URL 唯一指定服务 方法参数params 形参列表 服务提供商provider 服务注册时间regi_time 描述元信息meta_info 其他服务信息 codeBytes 服务状态快照 表 2 自定义消息格式表
Table 2. Message format table
字段名 长度/字节 描述 Header 4 对消息体类型的标识 Body Not-fixed 承载交易执行状态 表 3 扩展服务执行结果
Table 3. Extended service implementation results
应用场景 图像识别 机器翻译 阿里云 猫(置信度:70%) warmly celebrate the 70th anniversary of the founding of the school 华为云 这是一只猫 celebrating the 70th anniversary of the School 腾讯云 猫为56% ,美国短毛猫为25%,英国短毛猫为15% warmly celebrate the 70th anniversary of the founding of the school 表 4 与业界其他相关工作成果的对比
Table 4. Comparison of characteristics with related work
解决方案 蚂蚁链 BaaS Oracle BaaS ChainLink Mictract SCaaS 适配链 Antchain和FabricBCOS Fabric Ethereum Fabric 北航链 即时通信 否 否 否 否 是 合约扩展性 否 否 是 是 是 链下协同 否 否 是 否 是 协同方式 预言机共识网络 扩展服务认证管理 响应速度 慢 快 -
[1] VACCA A, DI SORBO A, VISAGGIO C A, et al. A systematic literature review of blockchain and smart contract development: techniques, tools, and open challenges[J]. Journal of Systems and Software, 2021, 174: 110891. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2020.110891 [2] MOHANTA B K, PANDA S S, JENA D. An overview of smart contract and use cases in blockchain technology[C]// 2018 9th International Conference on Computing, Communication and Networking Technologies (ICCCNT). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1-4. [3] 袁勇, 王飞跃. 区块链技术发展现状与展望[J]. 自动化学报, 2016, 42(4): 481-494.YUAN Y, WANG F Y. Blockchain: the state of the art and future trends[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42(4): 481-494 (in Chinese). [4] 王鹏, 魏必, 王聪. 区块链技术在政务数据共享中的应用[J]. 大数据, 2020, 6(4): 105-114. doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-0271.2020037WANG P, WEI B, WANG C. Application of blockchain technology in government data sharing[J]. Big Data Research, 2020, 6(4): 105-114 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11959/j.issn.2096-0271.2020037 [5] 周立群, 李智华. 区块链在供应链金融的应用[J]. 信息系统工程, 2016(7): 49-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2362.2016.07.033ZHOU L Q, LI Z H. Application of blockchain in supply chain finance[J]. China CIO News, 2016(7): 49-51 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2362.2016.07.033 [6] ZOU W Q, LO D, KOCHHAR P S, et al. Smart contract development: challenges and opportunities[J]. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, 2021, 47(10): 2084-2106. doi: 10.1109/TSE.2019.2942301 [7] BUTERIN V. A next generation smart contract & decentralized application platform[EB/OL]. ( 2022-07-29)[ 2022-09-05]. https://ethereum.org/zh/whitepaper/. [8] GANESHBABU S N, SRIRAM S, RANGARAJU K G. Smart cyber physical systems: advances, challenges and opportunities[M]. Abingdon: Taylor & Francis, 2020: 255-268. [9] Spring Cloud. Service registration and discovery[EB/OL]. (2022-05-10)[2022-09-05]. https://spring.io/guides/gs/service-registration-and-discovery. [10] Nacos. An easy-to-use dynamic service discovery, configuration and service management platform for building cloud native applications[EB/OL]. (2022-06-12)[2022-09-14]. https://nacos.io/en/docs/v1/what-is-nacos/. [11] HARN L, REN J. Generalized digital certificate for user authentication and key establishment for secure communications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, 2011, 10(7): 2372-2379. doi: 10.1109/TWC.2011.042211.101913 [12] PARK J S, YOUN T Y, KIM H B, et al. Smart contract-based review system for an IoT data marketplace[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(10): 3577. doi: 10.3390/s18103577 [13] ABDELMABOUD A , AHMED A I A , ABAKER M, et al. Blockchain for IoT applications: taxonomy, platforms, recent advances, challenges and future research directions[J]. Electronics, 2022, 11(4): 11040630. [14] ZHENG Z B, XIE S A, DAI H N, et al. An overview on smart contracts: challenges, advances and platforms[J]. Future Generation Computer Systems, 2020, 105(C): 475-491. [15] SUNYAEV A, SUNYAEV A. Internet computing: principles of distributed systems and emerging internet-based technologies [M]. Switzerland: Springer Cham, 2020: 195-236. [16] ZHENG W L, ZHENG Z B, CHEN X P, et al. NutBaaS: a blockchain-as-a-service platform[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 134422-134433. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2941905 [17] 魏凯, 卿苏德, 杨白雪, 等. 区块链即服务平台BaaS白皮书[R]. 北京: 中国信息通信研究院, 2019.WEI K, QING S D, YANG B X, et al. Blockchain as a service platform baas white paper [R]. Beijing: China Institute of Information and Communications, 2019(in Chinese). [18] 张富利, 侯培宇, 李杉杉, 等. 一种智能合约微服务化框架[J]. 软件学报, 2021, 32(11): 3423-3439.ZHANG F L, HOU P Y, LI S S, et al. Framework for architecting smart contracts using microservices[J]. Journal of Software, 2021, 32(11): 3423-3439 (in Chinese). [19] TONELLI R, PINNA A, BARALLA G, et al. Ethereum smart contracts as blockchain-oriented microservices[C]// Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Agile Software Development: Companion. New York: ACM, 2018: 1-2. [20] HU K, WAN J, LUO K, et al. Verification algebra for multi-tenant applications in VaaS architecture[J]. Software Testing, Verification and Reliability, 2021, 31(6): e1763. doi: 10.1002/stvr.1763 [21] 王子凯, 朱健, 张伯钧, 等. 区块链与智能合约并行方法研究与实现[J]. 计算机科学, 2022, 49(9): 318-323. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.220300190WANG Z K, ZHU J, ZHANG B J, et al. Research and implementation of blockchain and smart contract parallel methods[J]. Computer Science, 2022, 49(9): 318-323(in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.220300190 [22] MIR U B, KAR A K, DWIVEDI Y K, et al. Realizing digital identity in government: Prioritizing design and implementation objectives for Aadhaar in India[J]. Government Information Quarterly, 2020, 37(2): 101442. doi: 10.1016/j.giq.2019.101442 [23] SALAH K, REHMAN M H U, NIZAMUDDIN N, et al. Blockchain for AI: review and open research challenges[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 10127-10149. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2890507 -







 下载:
下载: