-
摘要:
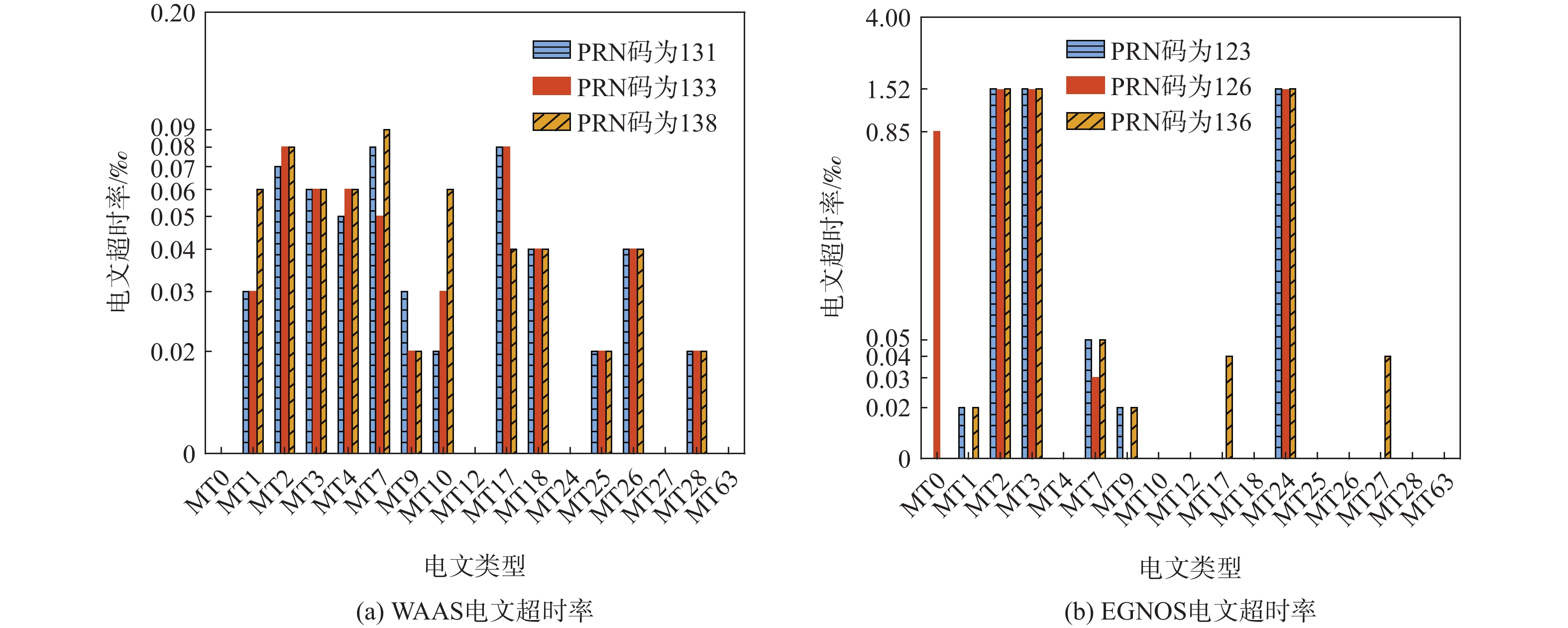
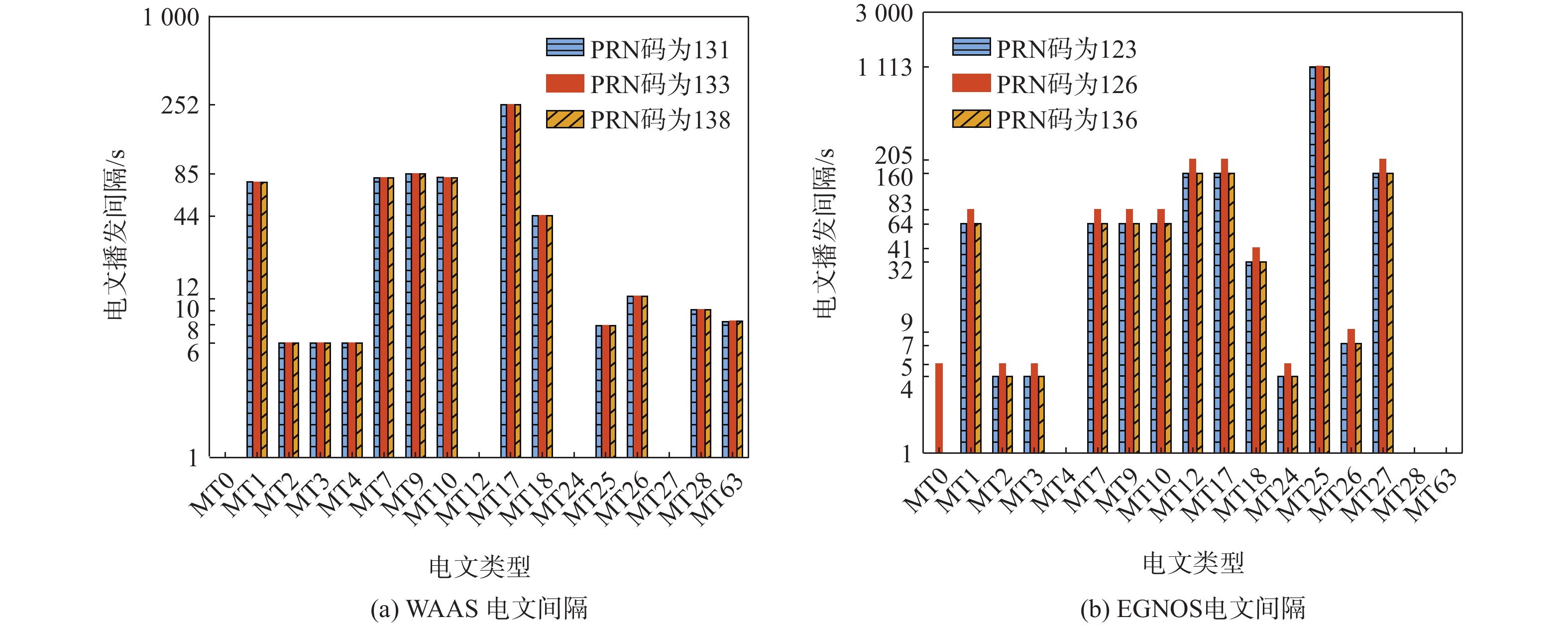
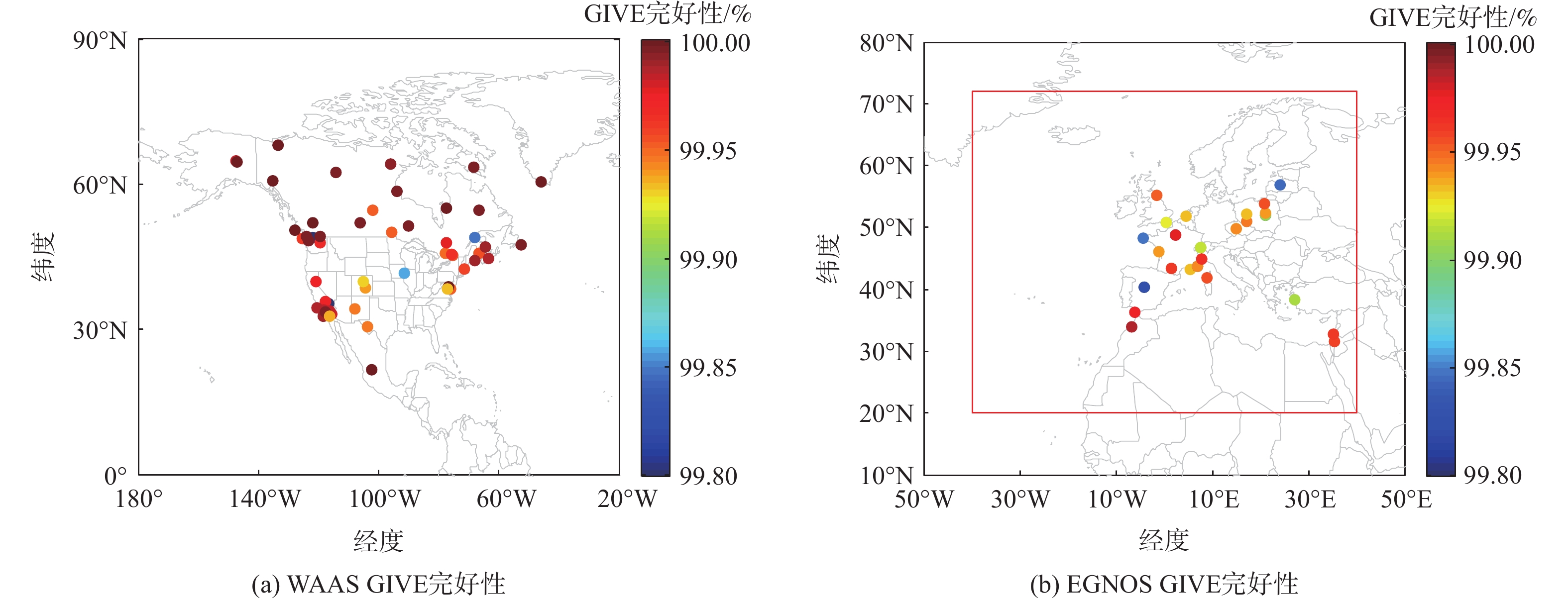
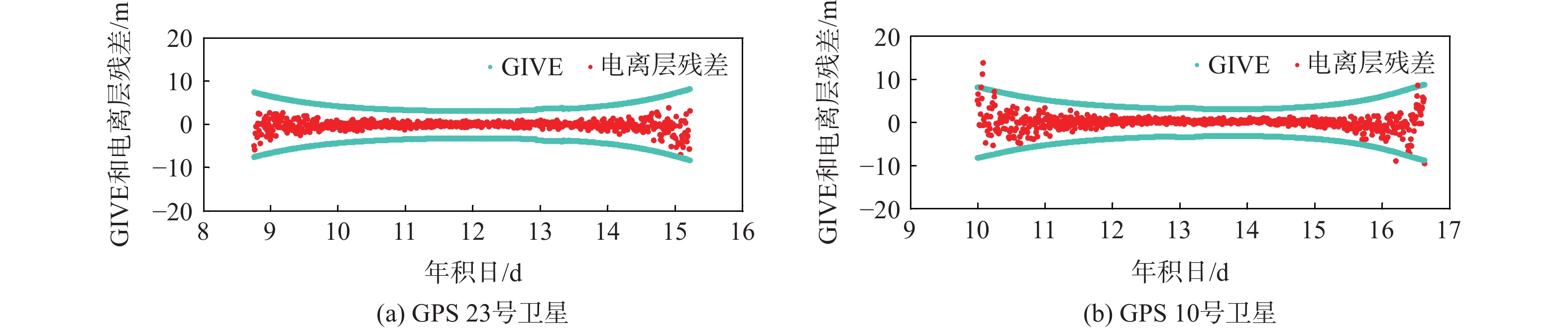
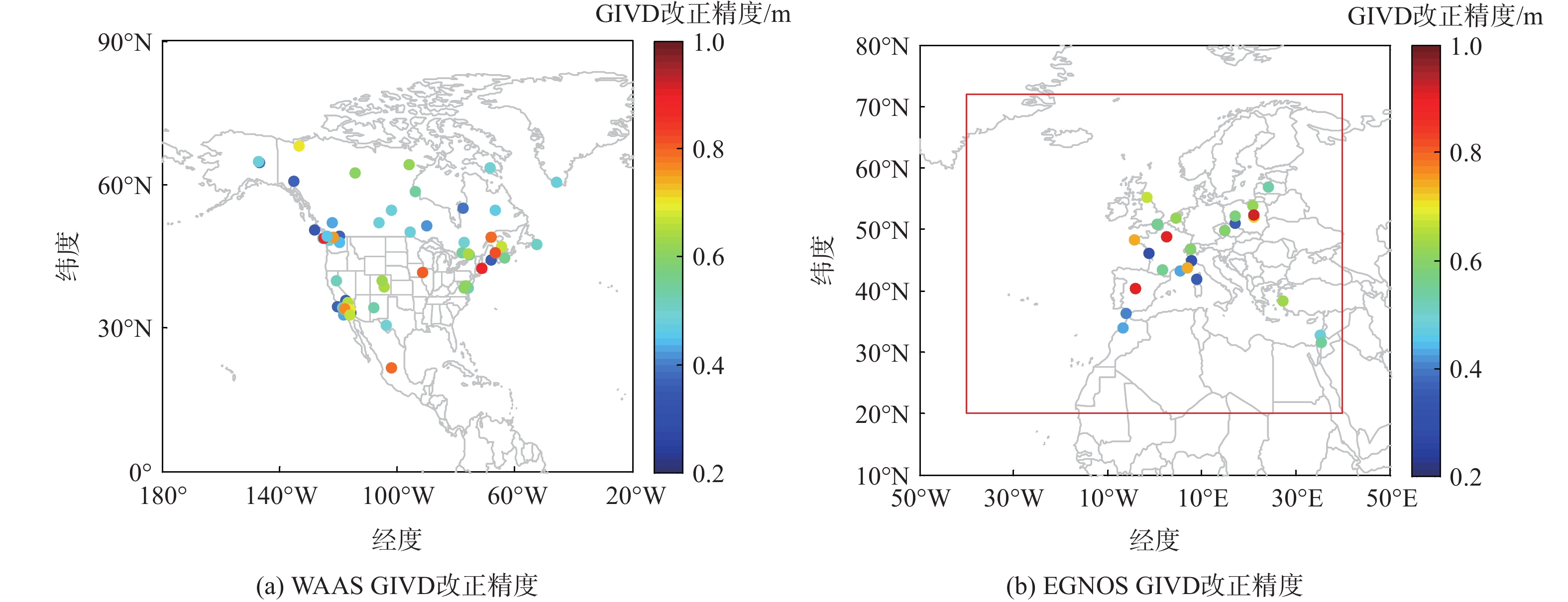
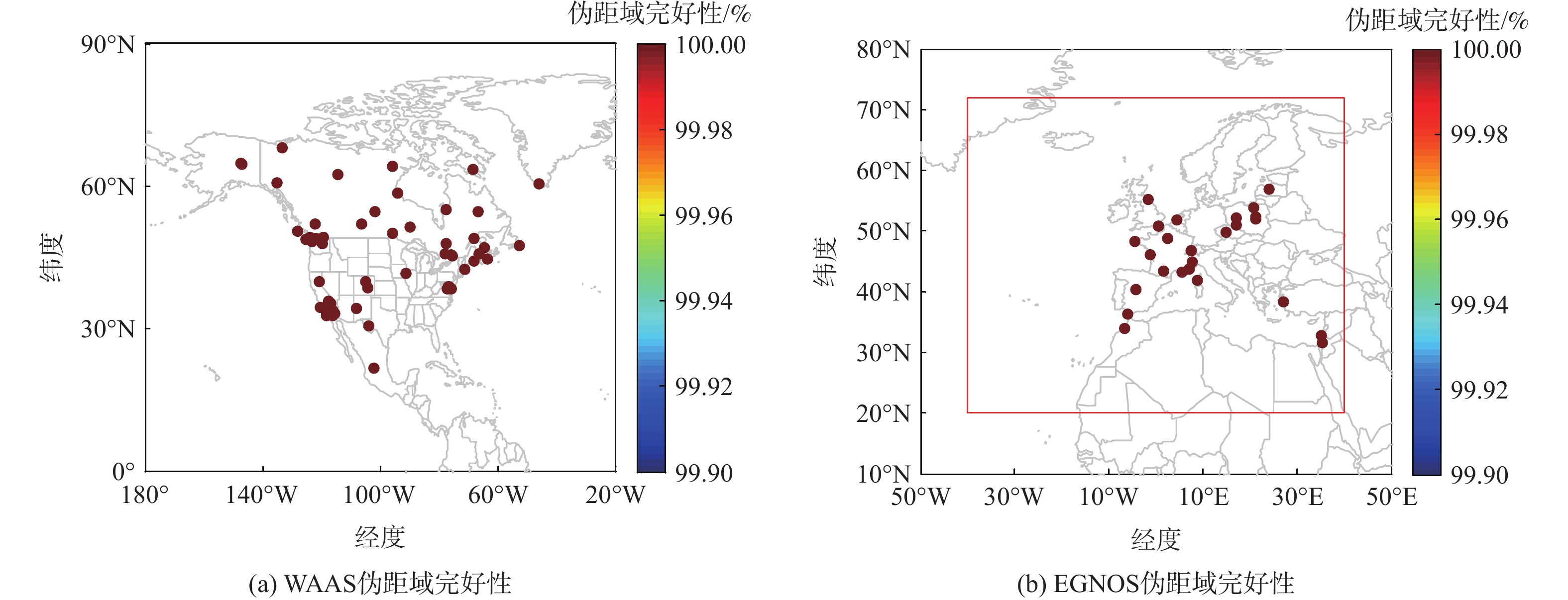
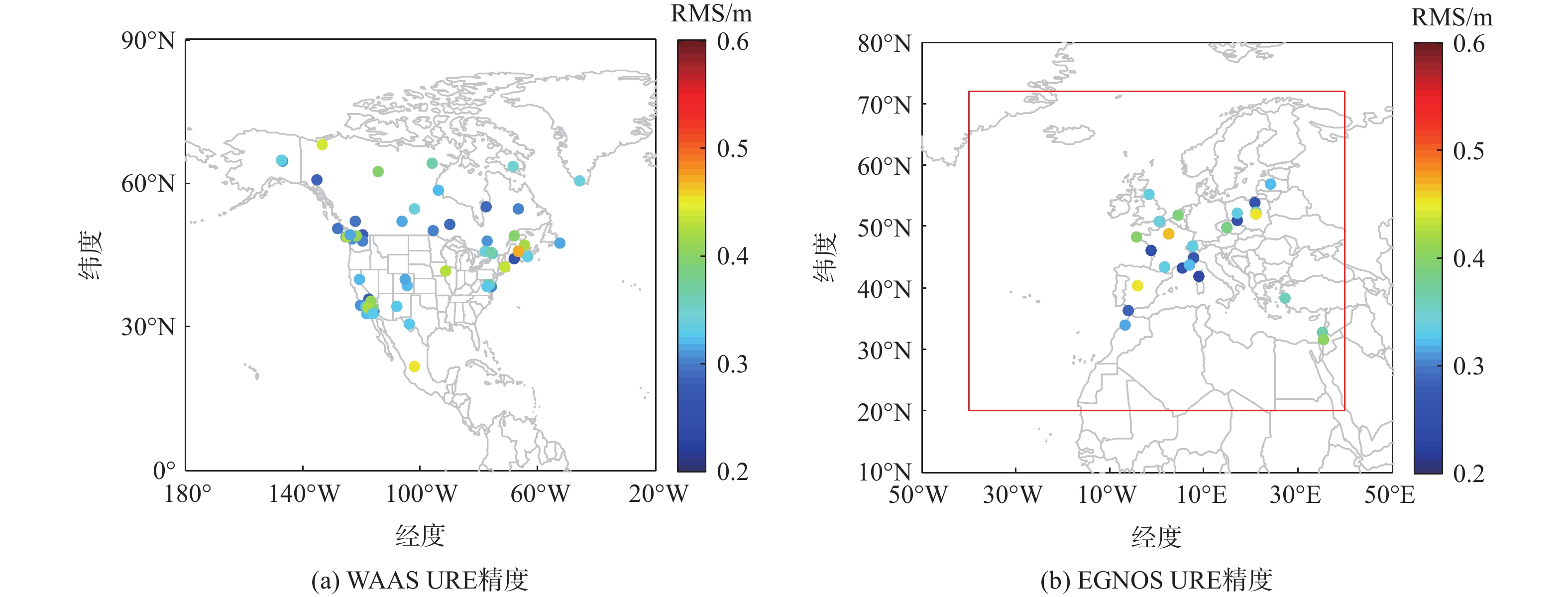
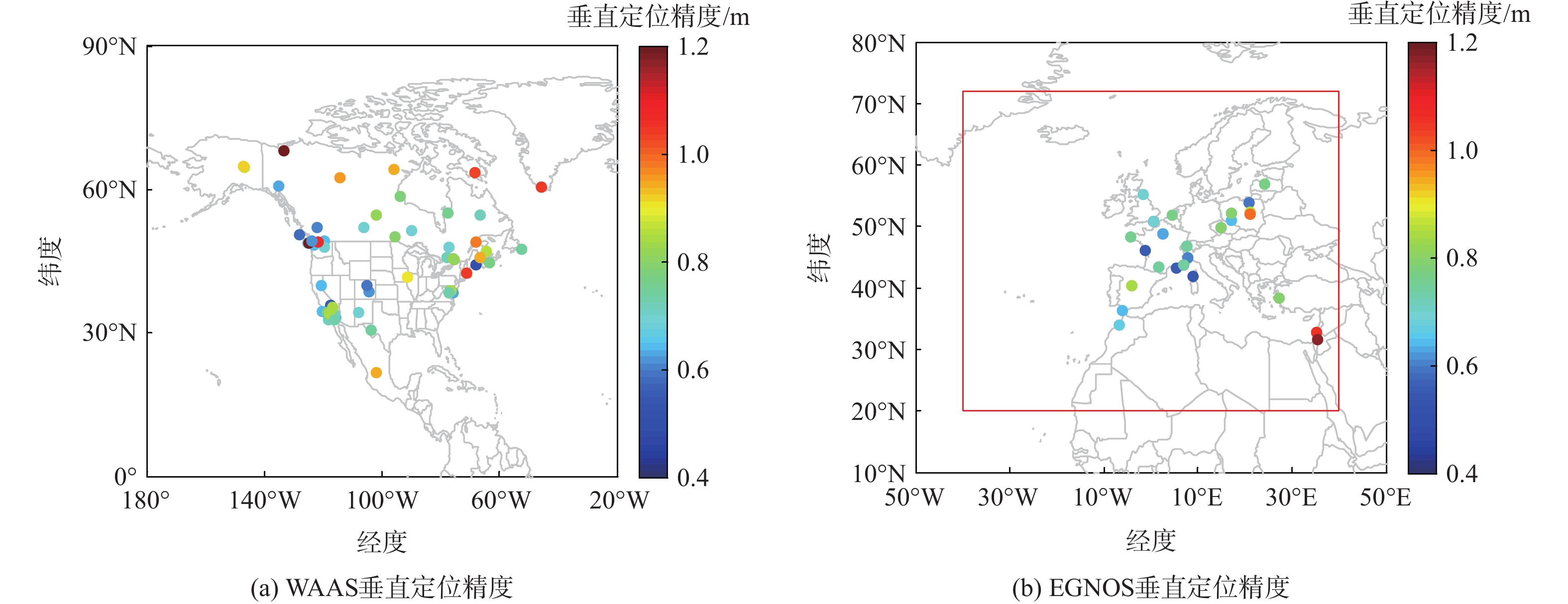
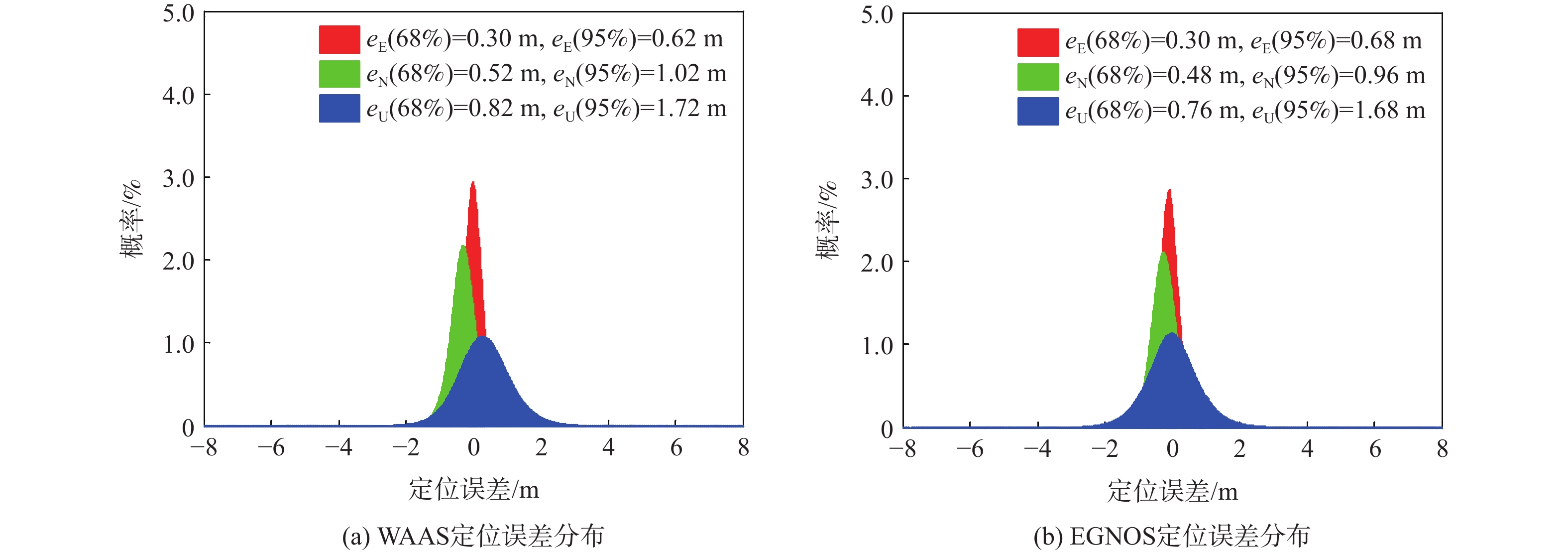
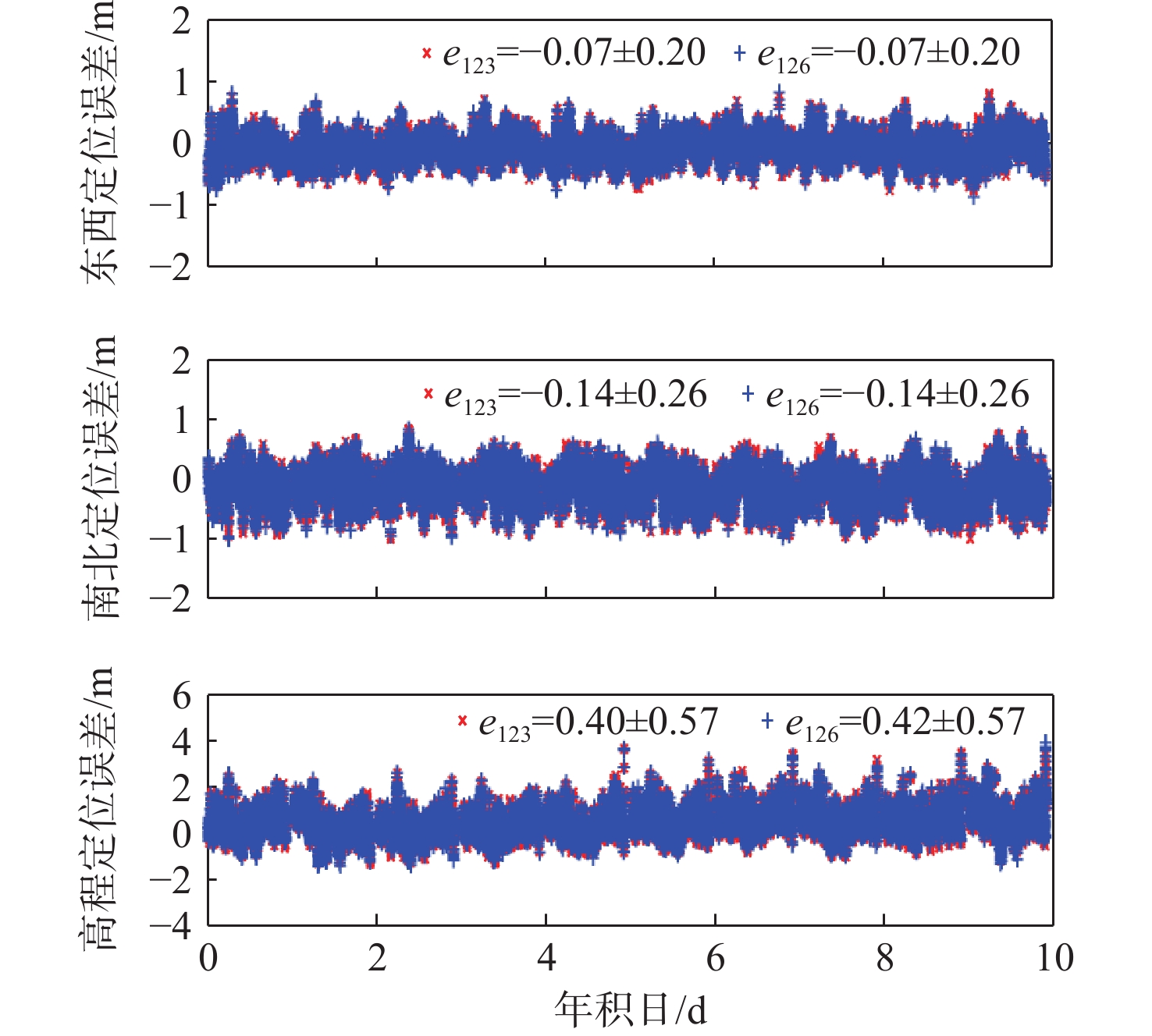
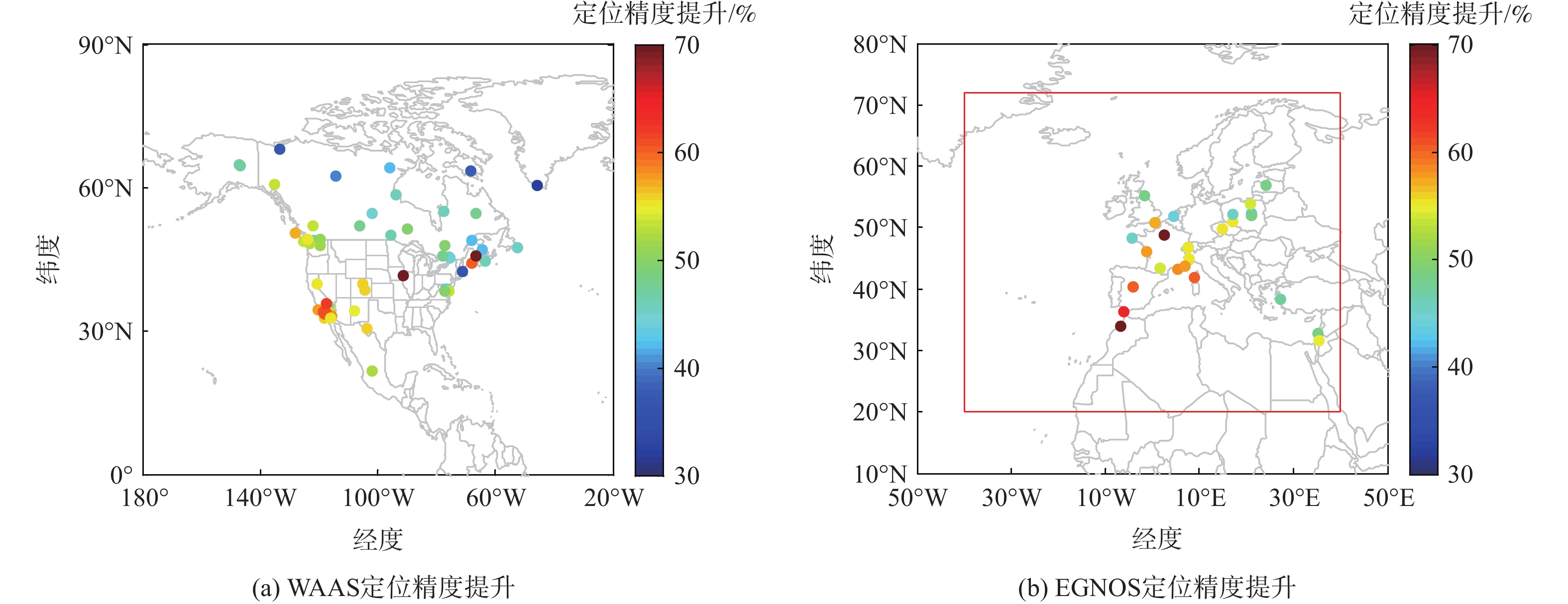
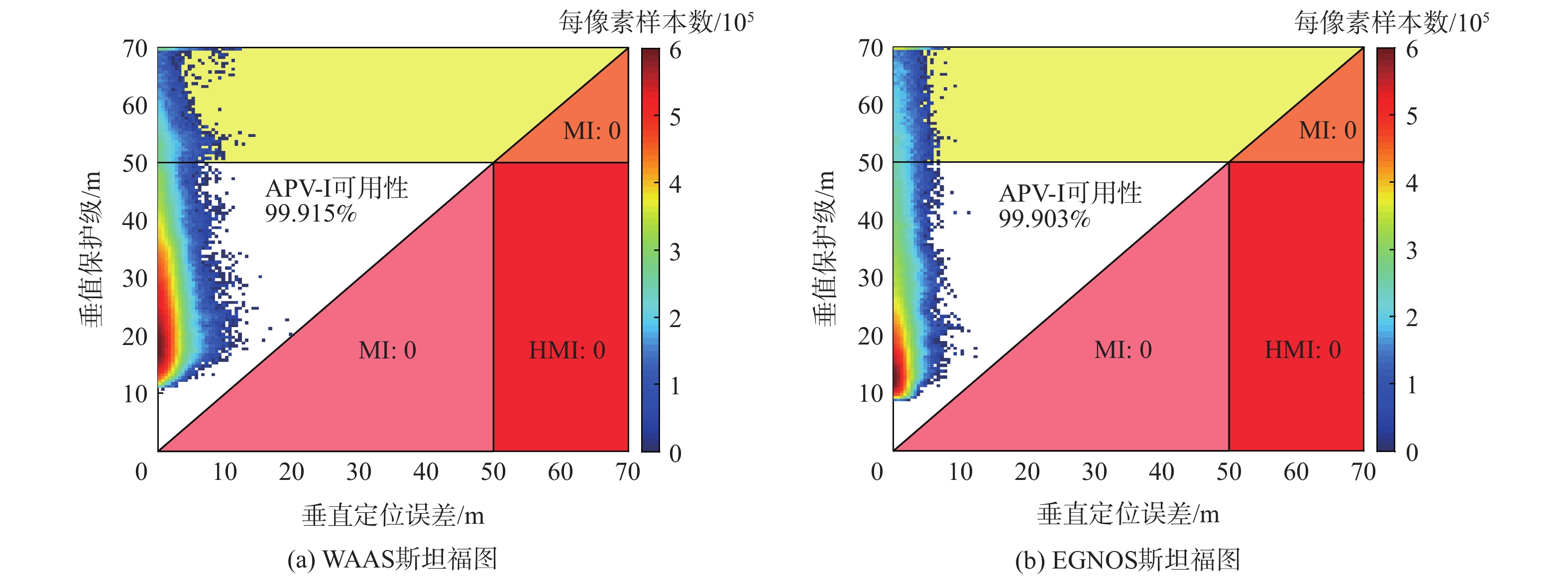
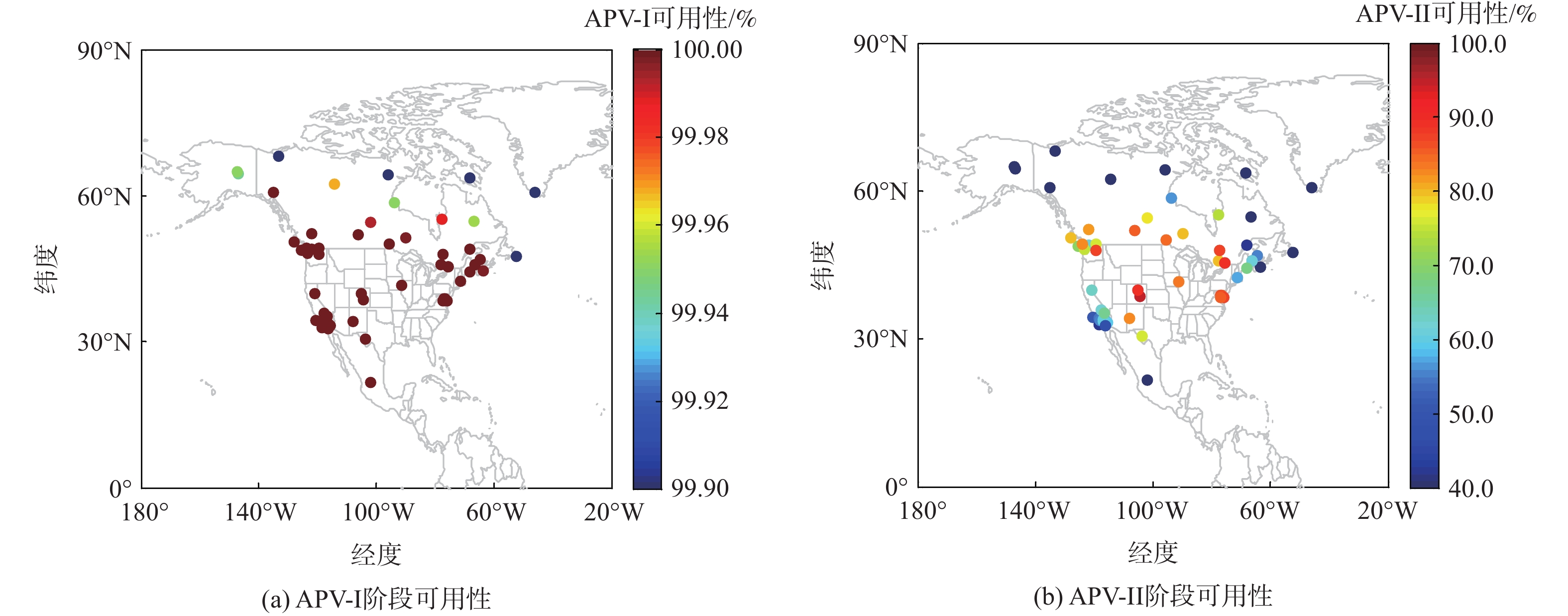
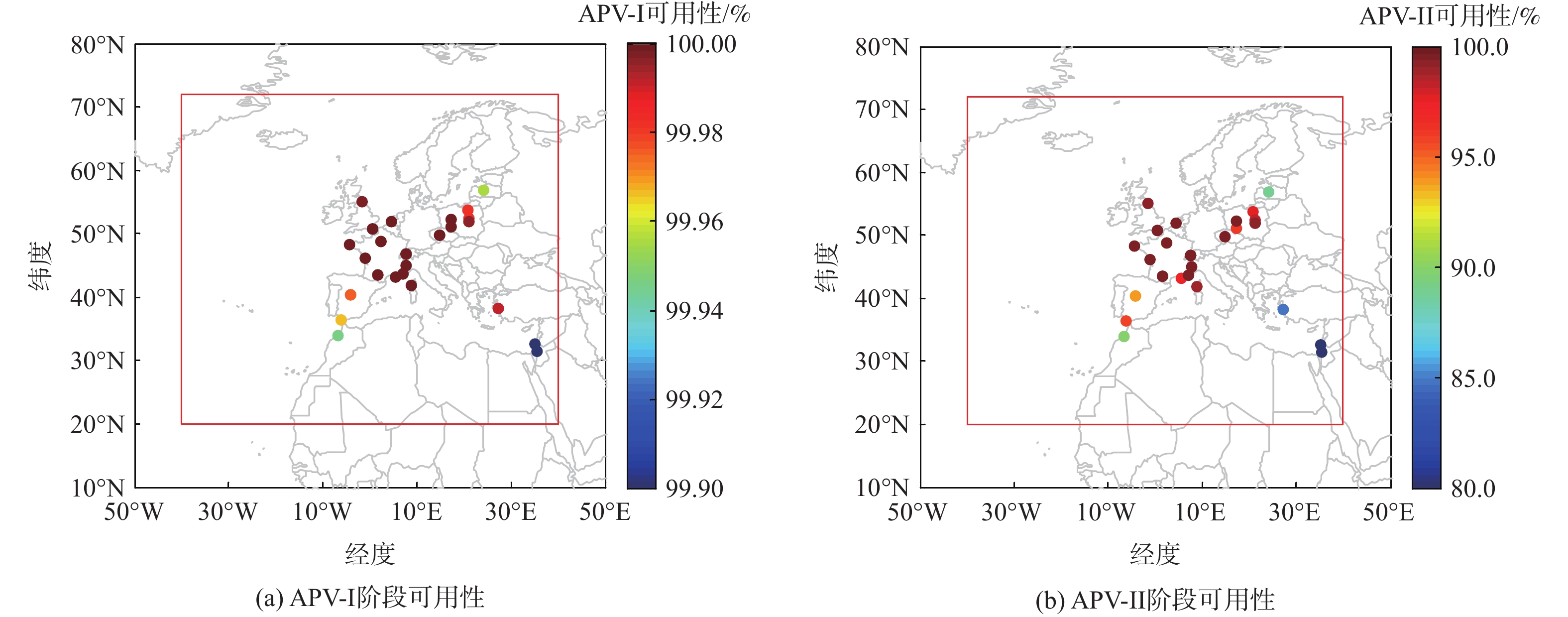
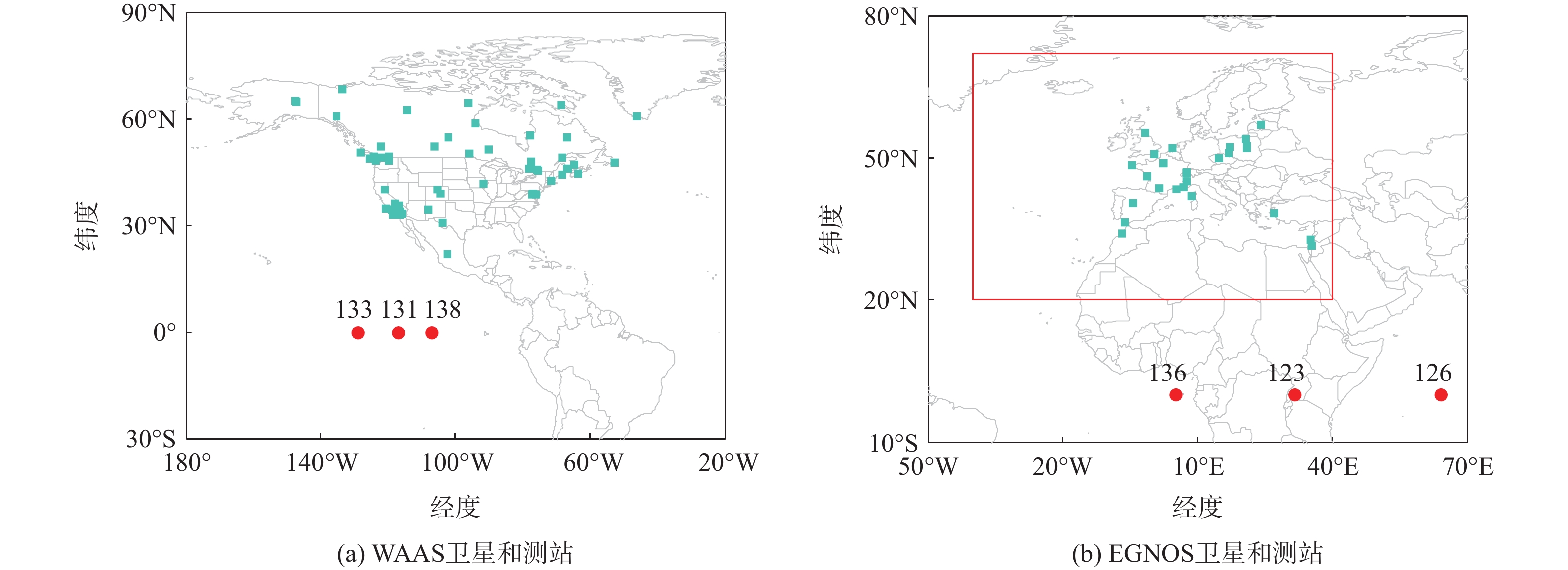
针对星基增强系统(SBAS)用户差分距离误差(UDRE)完好性参数评估时双频无电离层组合放大观测噪声的问题,提出伪距域完好性评估方法,该方法反映了SBAS电离层改正数和星历时钟改正数的综合影响。利用240天共100个国际全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)服务组织(IGS)测站的数据对美国广域增强系统(WAAS)和欧洲地球静止轨道导航重叠服务(EGNOS)的性能进行评估。结果表明:WAAS和EGNOS格网电离层垂直误差(GIVE)参数的完好性分别为99.96%和99.91%,电离层延迟改正精度达到0.56 m。WAAS和EGNOS伪距域完好性优于99.999%,经改正后的GPS用户测距误差(URE)精度达到0.34 m。WAAS 95%的水平和垂直定位误差为1.19 m和1.72 m,EGNOS的则为1.18 m和1.68 m。评估时段内均未发生完好性风险事件,验证了测地型接收机用于SBAS服务性能评估的可行性。WAAS在一类垂直引导进近(APV-I)阶段的定位精度平均可用性为99.9%,二类垂直引导进近(APV-II)阶段在服务中心区域的定位精度可用性为80%~95%;EGNOS APV-I阶段平均定位精度可用性为99.9%,APV-II阶段平均定位精度可用性为94.2%,可用性较高,主要是由于EGNOS评估测站多处于服务区中心。SBAS定位精度可用性在服务区边缘部分下降较明显。
Abstract:Dual frequency ionosphere-free observations are usually applied to evaluate the satellite based augmentation system (SBAS) user differential range error (UDRE) integrity with the drawback of noise amplification. Instead, a range domain integrity method is proposed to assess the combined effect of SBAS ionospheric corrections, ephemeris and clock corrections. 240 days data of from 100 international global navigation satellite system(GNSS)service (IGS) stations are employed to evaluate the service performance of wide area augmentation system (WAAS) and European geostationary navigation overlay service (EGNOS). Results show that: The grid ionospheric vertical error (GIVE) integrity of WAAS and EGNOS achieves 99.96% and 99.91% respectively and the accuracy of ionospheric correction is 0.56 m. The range domain integrity of WAAS and EGNOS is better than 99.999% and the GPS user range error (URE) after applying the corrections achieves 0.34 m. For WAAS, the 95% horizontal and vertical positioning error is 1.19 m and 1.72 m, whereas for EGNOS, it is 1.18 m and 1.68 m. During the test, there were no integrity risk events. It is confirmed that it is feasible to evaluate the SBAS performance—particularly the integrity—using a geodetic receiver. The average availability of positioning accuracy for WAAS during approach with vertical guidance I (APV-I) is 99.9%, while for approach with vertical guidance II (APV-II), it ranges from 80% to 95% within the center of the service area. The average availability of positioning accuracy for APV-I of EGNOS is 99.9%, and for APV-II, it is 94.2%, indicating a higher level of availability, largely because most of the EGNOS assessment stations are located in the center of the service area. The SBAS availability noticeably decreases at the edge of the service area.
-
-
[1] WALTER T, SHALLBERG K, ALTSHULER E, et al. WAAS at 15[J]. Navigation, 2018, 65(4): 581-600. doi: 10.1002/navi.252 [2] TABTI L, KAHLOUCHE S, BENADDA B, et al. Improvement of single-frequency GPS positioning performance based on EGNOS corrections in Algeria[J]. Journal of Navigation, 2020, 73(4): 846-860. doi: 10.1017/S037346331900095X [3] DAMMALAGE T, DE SILVA D N, SATIRAPOD C. Performance analysis of GPS aided geo augmented navigation (GAGAN) over Sri Lanka[J]. Engineering Journal, 2017, 21(5): 305-314. doi: 10.4186/ej.2017.21.5.305 [4] SAITO S. MSAS system development [EB/OL]. (2019-06-05) [2022-08-25]. [5] CHEN S S, JIN B, LI D J, et al. Study on the prediction method of single and dual frequency service area for BDSBAS[C]//Proceedings of the China Satellite Navigation Conference. Berlin: Springer, 2019: 228-237. [6] ZHAO L Q, HU X G, TANG C P, et al. Generation of DFMC SBAS corrections for BDS-3 satellites and improved positioning performances[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2020, 66(3): 702-714. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2020.04.032 [7] WU J Z, WANG K, EL-MOWAFY A. Preliminary performance analysis of a prototype DFMC SBAS service over Australia and Asia-Pacific[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2020, 66(6): 1329-1341. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2020.05.026 [8] LEE E. System development-KASS[EB/OL]. (2019-06-05)[2022-08-25]. [9] JIN B, CHEN S S, LI D J, et al. Ionospheric correlation analysis and spatial threat model for SBAS in China region[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2020, 66(12): 2873-2887. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2020.05.010 [10] 金彪, 魏巍, 陈姗姗, 等. SBAS星历改正数及UDRE参数生成算法分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2021, 46(1): 111-117.JIN B, WEI W, CHEN S S, et al. Analysis of SBAS ephemeris correction and UDRE generation algorithm[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2021, 46(1): 111-117 (in Chinese). [11] JIN B, CHEN S S, LI D J, et al. Performance analysis of SBAS ephemeris corrections and integrity algorithms in China region[J]. Satellite Navigation, 2021, 2(1): 15. doi: 10.1186/s43020-021-00045-z [12] WU J T, PECK S. An analysis of satellite integrity monitoring improvement for WAAS[C]//Proceedings of the 15th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation. Washington, D. C. : Institute of Navigation, 2002: 756-765. [13] BLANCH J, WALTER T, ENGE P. A Clock and ephemeris algorithm for dual frequency SBAS[C]//Proceedings of the 24th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation. Washington, D. C. : Institute of Navigation, 2011: 2513-2519. [14] BLANCH J, WALTER T, ENGE P. Evaluation of a covariance-based clock and ephemeris error bounding algorithm for SBAS[C]//Proceedings of the 27th International Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation. Washington, D. C.: Institute of Navigation, 2014: 3270-3276. [15] SHAO B, DING Q, WU X B. Estimation method of SBAS dual-frequency range error integrity parameter[J]. Satellite Navigation, 2020, 1(1): 1-8. doi: 10.1186/s43020-020-00011-1 [16] WALTER T, HANSEN A, BLANCH J, et al. Robust detection of ionospheric irregularities[J]. Navigation, 2001, 48(2): 89-100. doi: 10.1002/j.2161-4296.2001.tb00231.x [17] SPARKS L, BLANCH J, PANDYA N. Estimating ionospheric delay using Kriging: 1. Methodology[J]. Radio Science, 2011, 46(06): 1-13. [18] SPARKS L, BLANCH J, PANDYA N. Estimating ionospheric delay using Kriging: 2. Impact on satellite-based augmentation system availability[J]. Radio Science, 2011, 46(6): 1-10. [19] WALTER T, KEE C, CHAO Y, et al. Flight trials of the wide area augmentation system (WAAS)[C]//Proceedings of the 7th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of The Institute of Navigation. Washington, D. C.: Institute of Navigation, 1994: 1537-1546. [20] PERRIN O, SCARAMUZZA M, BUCHANAN T, et al. Flying EGNOS approaches in the Swiss Alps[J]. Journal of Navigation, 2006, 59(2): 177-185. doi: 10.1017/S0373463306003754 [21] SPECHT C, PAWELSKI J, SMOLAREK L, et al. Assessment of the positioning accuracy of DGPS and EGNOS systems in the bay of gdansk using maritime dynamic measurements[J]. Journal of Navigation, 2019, 72(3): 575-587. doi: 10.1017/S0373463318000838 [22] HEßELBARTH A, WANNINGER L. SBAS orbit and satellite clock corrections for precise point positioning[J]. GPS Solutions, 2013, 17(4): 465-473. doi: 10.1007/s10291-012-0292-6 [23] 楼益栋, 郑福, 龚晓鹏, 等. QZSS系统在中国区域增强服务性能评估与分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2016, 41(3): 298-303.LOU Y D, ZHENG F, GONG X P, et al. Evaluation of QZSS system augmentation service performance in China region[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2016, 41(3): 298-303 (in Chinese). [24] HIRSCHBERGER M J, LO S, WALTER T. Reevaluating the message loss rate of the wide area augmentation system (WAAS) in flight[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 International Technical Meeting of The Institute of Navigation. Washington, D. C. : Institute of Navigation, 2021: 218-228. [25] 陈姗姗, 金彪, 赵立谦, 等. SBAS电文时序动态编排算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(10): 1996-2005.CHEN S S, JIN B, ZHAO L Q, et al. Dynamic SBAS message scheduler algorithm[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(10): 1996-2005 (in Chinese). [26] 常志巧, 陈金平, 刘利, 等. WAAS电离层格网播发特性及其性能评估[J]. 天文学进展, 2021, 39(2): 265-275. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8349.2021.02.07CHANG Z Q, CHEN J P, LIU L, et al. Broadcast characteristics and performance evaluation of WAAS ionospheric grid[J]. Progress in Astronomy, 2021, 39(2): 265-275 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8349.2021.02.07 [27] 金彪, 陈姗姗, 李祝莲, 等. SBAS GEO卫星URE精度及定位增强研究[J/OL]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), (2021-09-16)[2022-08-27].JIN B, CHEN S S, LI Z L, et al. SBAS GEO satellite user range error and position augmentation research[J/OL]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, (2021-09-16)[2022-08-27]. [28] 蔡洪亮, 孟轶男, 耿长江, 等. 北斗三号全球导航卫星系统服务性能评估: 定位导航授时、星基增强、精密单点定位、短报文通信与国际搜救[J]. 测绘学报, 2021, 50(4): 427-435.CAI H L, MENG Y N, GENG C J, et al. BDS-3 performance assessment: PNT, SBAS, PPP, SMC and SAR[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2021, 50(4): 427-435 (in Chinese). [29] International Civil Aviation Organization. International standards and recommended practices annex 10 Vol. I. radio navigation aids: ISBN 978-92-9258-504-4[S]. Quebec: ICAO, 2018. [30] RTCA. Minimum operational performance standards for global positioning system/wide area augmentation system airborne equipment: RTCA-DO-229D[S]. Washington, D. C. : RTCA, 2006. [31] REN X D, CHEN J, LI X X, et al. Ionospheric total electron content estimation using GNSS carrier phase observations based on zero-difference integer ambiguity: methodology and assessment[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(1): 817-830. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.2989131 [32] WANG N B, LI Z S, DUAN B B, et al. GPS and GLONASS observable-specific code bias estimation: comparison of solutions from the IGS and MGEX networks[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2020, 94(8): 74. doi: 10.1007/s00190-020-01404-5 [33] LIU J B, HERNANDEZ-PAJARES M, LIANG X L, et al. Temporal and spatial variations of global ionospheric total electron content under various solar conditions[J]. Journal of Geodesy, 2017, 91(5): 485-502. doi: 10.1007/s00190-016-0977-7 [34] European GNSS Agency. EGNOS safety of life (SoL) service definition document: 9789292060510[S]. Luxembourg: European GNSS Agency, 2021: 53-57. [35] NIE Z X, ZHOU P Y, LIU F, et al. Evaluation of orbit, clock and ionospheric corrections from five currently available SBAS L1 services: Methodology and analysis[J]. Remote Sensing, 2019, 11(4): 411. doi: 10.3390/rs11040411 [36] FAA. Wide area augmentation system performance analysis report: NJ08405 [R]. Washton, D. C.: Federal Aviation Administration, 2022. [37] European Satellite Services Provider. Monthly performance report: ESSP-DRD-24152 [R]. Toulouse: ESSP SAS, 2019. -







 下载:
下载: