-
摘要:
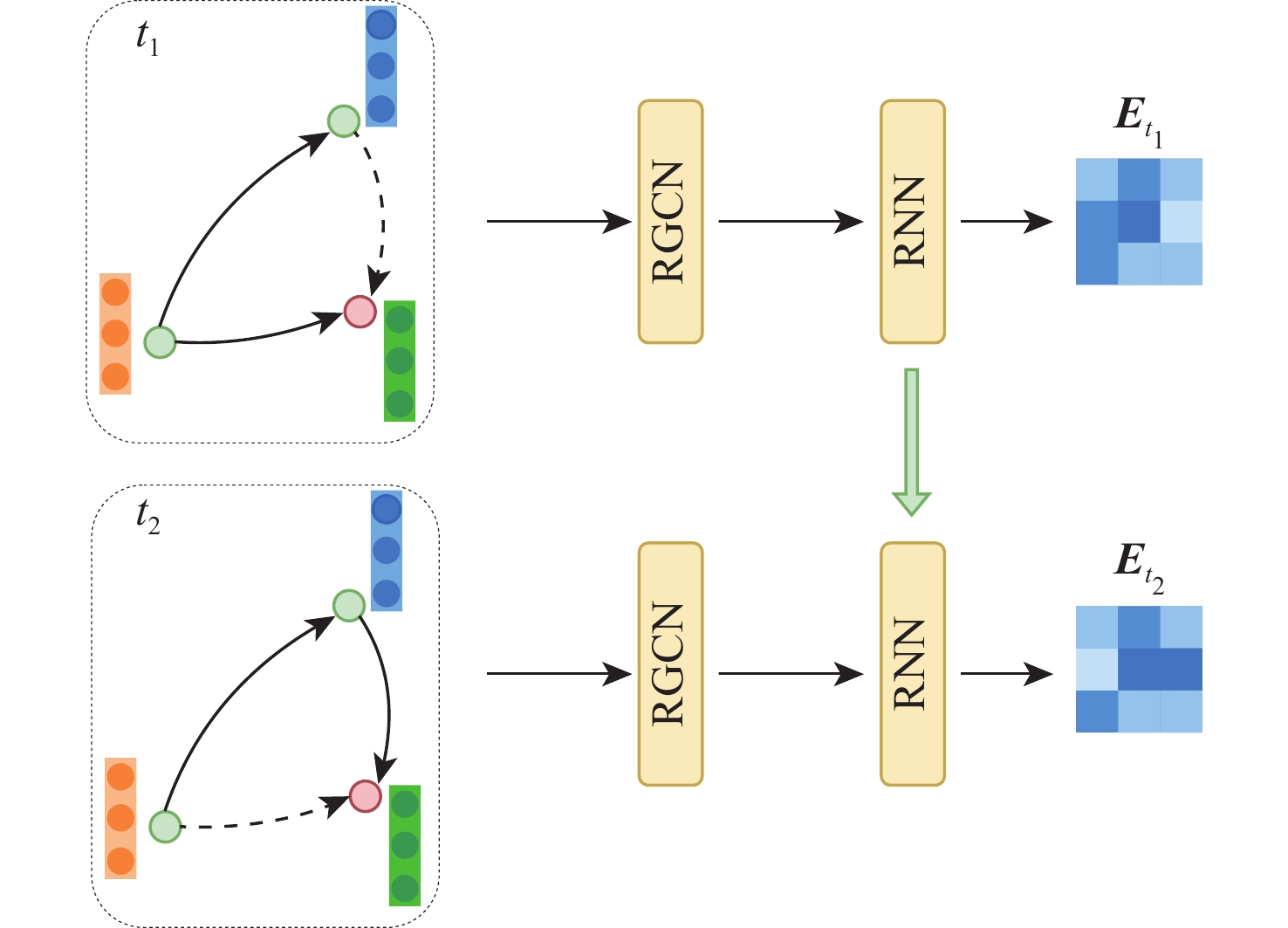
随着电力设施规模的日渐增长,对于电力设备的运行监测成为电力系统管理的一个重要内容。电力设备的缺陷预测是电力系统运行监测的关键步骤。为解决对大规模电力系统中的电力设备进行缺陷预测的问题,结合人工智能技术,提出一种基于时序知识图谱的电力设备缺陷预测模型。通过注意力机制对多模态信息进行融合,利用关系感知的图神经网络和循环神经网络得到实体和关系的时序表示,基于时序表示对电力设备进行缺陷预测。提出基于图神经网络的时序知识图谱推理方法能够充分利用多模态信息,提升电力设备缺陷预测的准确率。实验表明:所提模型性能优于基线模型。
Abstract:Power system management now includes monitoring power equipment operation, which is crucial given the growing size of power facilities. Defect prediction of power equipment is a key step in power system operation monitoring. In order to solve the problem of defect prediction for power equipment in large-scale power systems, we propose a defect prediction model for power equipment based on a temporary knowledge graph. The attention mechanism fuses the multimodal data, and the relationship-aware graph neural network and recurrent neural network are then employed to extract the temporal representation of entities and relations. Finally, we perform defect prediction of power equipment based on the temporal representation. The method proposed in this paper can make full use of multimodal information to improve the accuracy of power equipment defect prediction. Experimental results show that the model has considerable performance improvement compared to the baseline model.
-
Key words:
- temporary knowledge graph /
- graph neural network /
- defect prediction /
- power system /
- power equipment
-
表 1 电力设备及其缺陷类型
Table 1. Electrical equipment and type of defect event
序号 电力设备 缺陷类型 三元组
数量1 主变压器 堵塞,进水,污秽,滑档,生锈,喷油,
油温过高,漏油等1147 2 变压器 堵塞,进水,污秽,滑档,生锈,喷油,
油温过高,漏油等534 3 联变变压器 生锈,无油位,无防雨罩,未绝缘包扎等 160 4 站用变压器 氧气含量超标 220 5 电抗器 连接处震动,压力低,数据未上传,
封堵,硅胶变色,乙炔超标等1234 6 高压电抗器 乙炔、甲烷超标,漏油,操作不当等 456 7 干式电抗器 缺少绝缘试验报告 567 8 其他子部件 生锈,缺少实验报告,无防雨罩,
脏污,堵塞,封堵不当等170 表 2 数据类型和数量
Table 2. Type and quantity of dataset
三元组数 节点数 属性数 4 488 2 463 3 077 表 3 模型主要参数
Table 3. Main parameters of model
参数名 参数介绍 参数值 Learning rate 初始学习率 0.05 Total epochs 总训练轮次 50 Dropout rate 随机丢弃概率 0.1 Regularizer 正则化系数 0.01 Batch size 每批次训练样本的大小 64 Num layers 网络层数 4 Hidden dim 隐藏层维度 256 表 4 缺陷检测性能
Table 4. Defect prediction performance
基线模型 MR/% MRR/% Hits@1/% Hits@10/% DisMult[27] 51.37 61.83 50.92 72.38 ConvE[28] 33.83 52.11 36.83 69.24 RotatE[29] 42.82 44.33 48.85 70.76 TA-DistMult[30] 34.23 65.37 53.21 71.72 HyTE[31] 42.78 53.49 56.19 72.25 Dyngraph2vecAE[32] 36.72 50.02 59.72 70.82 tNodeEmbed[33] 41.83 62.38 50.48 71.63 EvolveGCN[34] 32.28 62.82 54.05 72.32 GCRN[35] 36.83 52.23 51.21 76.22 Know-Evolve[36] 44.32 66.73 51.92 75.38 DyRep[37] 35.83 54.35 44.83 69.24 RE-Net[38] 35.73 68.77 56.48 70.58 本文模型 21.34 68.22 57.82 82.50 表 5 消融实验结果
Table 5. Results of ablation experiments
消融模块 MR/% MRR/% Hits@1/% Hits@10/% 基线模型 44.56 49.17 44.58 74.31 只消融视觉模态 42.61 51.23 45.18 75.21 只消融文本模态 28.88 65.17 52.58 79.31 只消融数值模态 29.43 64.76 51.62 78.66 消融RGCN关系矩阵 25.73 66.14 55.91 80.55 完整模型 21.34 68.22 57.82 82.50 -
[1] 蒲天骄, 乔骥, 韩笑, 等. 人工智能技术在电力设备运维检修中的研究及应用[J]. 高电压技术, 2020, 46(2): 369-383.PU T J, QIAO J, HAN X, et al. Research and application of artificial intelligence in operation and maintenance for power equipment[J]. High Voltage Engineering, 2020, 46(2): 369-383 (in Chinese). [2] 田萱, 陈杭雪. 推荐任务中知识图谱嵌入应用研究综述[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2022, 16(8): 1681-1705. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2112070TIAN X, CHEN H X. Survey on applications of knowledge graph embedding in recommendation tasks[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology, 2022, 16(8): 1681-1705 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2112070 [3] 董天波. 基于知识图谱的智能问答系统实现与应用[J]. 数字技术与应用, 2022, 40(3): 165-167.DONG T B. Realization and application of intelligent question answering system based on knowledge map[J]. Digital Technology & Application, 2022, 40(3): 165-167 (in Chinese). [4] LI J, SUN A X, HAN J L, et al. A survey on deep learning for named entity recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2022, 34(1): 50-70. doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2020.2981314 [5] 田玲, 张谨川, 张晋豪, 等. 知识图谱综述: 表示、构建、推理与知识超图理论[J]. 计算机应用, 2021, 41(8): 2161-2186. doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2021040662TIAN L, ZHANG J C, ZHANG J H, et al. Knowledge graph survey: Representation, construction, reasoning and knowledge hypergraph theory[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2021, 41(8): 2161-2186 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11772/j.issn.1001-9081.2021040662 [6] 付雷杰, 曹岩, 白瑀, 等. 国内垂直领域知识图谱发展现状与展望[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2021, 38(11): 3201-3214.FU L J, CAO Y, BAI Y, et al. Development status and prospect of vertical domain knowledge graph in China[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2021, 38(11): 3201-3214 (in Chinese). [7] 陈烨, 周刚, 卢记仓. 多模态知识图谱构建与应用研究综述[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2021, 38(12): 3535-3543.CHEN Y, ZHOU G, LU J C. Survey on construction and application research for multi-modal knowledge graphs[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2021, 38(12): 3535-3543 (in Chinese). [8] 张吉祥, 张祥森, 武长旭, 等. 知识图谱构建技术综述[J]. 计算机工程, 2022, 48(3): 23-37.ZHANG J X, ZHANG X S, WU C X, et al. Survey of knowledge graph construction techniques[J]. Computer Engineering, 2022, 48(3): 23-37 (in Chinese). [9] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[EB/OL]. (2015-04-10) [2022-05-10]. [10] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [11] DEVLIN J, CHANG M W, LEE K, et al. BERT: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding[EB/OL]. (2019-05-24) [2022-05-10]. [12] MIKOLOV T, CHEN K, CORRADO G, et al. Efficient estimation of word representations in vector space[EB/OL]. (2013-09-17) [2022-05-10]. [13] CHEN S, COWAN C F N, GRANT P M. Orthogonal least squares learning algorithm for radial basis function networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks, 1991, 2(2): 302-309. doi: 10.1109/72.80341 [14] CAI L, YAN B, MAI G C, et al. TransGCN: Coupling transformation assumptions with graph convolutional networks for link prediction[C]//Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Knowledge Capture. New York: ACM, 2019: 131–138. [15] SHANG C, TANG Y, HUANG J, et al. End-to-end structure-aware convolutional networks for knowledge base completion[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 33(1): 3060-3067. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33013060 [16] NATHANI D, CHAUHAN J, SHARMA C, et al. Learning attention-based embeddings for relation prediction in knowledge graphs[EB/OL]. (2019-06-04) [2022-05-10]. [17] XU X R, FENG W, JIANG Y S, et al. Dynamically pruned message passing networks for large-scale knowledge graph reasoning[EB/OL]. (2020-04-07) [2022-05-10]. [18] VOLODYMYR M, NICOLAS H, ALEX G. Recurrent models of visual attention[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2014, 27(2): 2204-2212. [19] ZAREMBA W, SUTSKEVER I, VINYALS O. Recurrent neural network regularization[EB/OL]. (2015-02-19) [2022-05-10]. [20] CAO Y X, LIU Z Y, LI C J, et al. Multi-channel graph neural network for entity alignment[EB/OL]. (2019-08-26) [2022-05-10]. [21] ZHANG Q H, SUN Z Q, HU W, et al. Multi-view knowledge graph embedding for entity alignment[EB/OL]. (2019-06-06) [2022-05-10]. [22] GUO L B, SUN Z Q, HU W. Learning to exploit long-term relational dependencies in knowledge graphs[EB/OL]. (2019-05-13) [2022-05-10]. [23] SUN Z Q, WANG C M, HU W, et al. Knowledge graph alignment network with gated multi-hop neighborhood aggregation[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 34(1): 222-229. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v34i01.5354 [24] ADAM P, SAM G, SOUMITH C, et al. Automatic differentiation in pytorch[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017, 3(6): 1401-1412. [25] ADAM P, SAM G, FRANCISCO M, et al. Pytorch: An imperative style, high-performance deep learning library[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2019, 32(13): 611-624. [26] VISHNU S. Deep Learning with PyTorch: A practical approach to building neural network models using PyTorch[M]. Birmingham: Packt Publishing Ltd, 2018. [27] SCHLICHTKRULL M, KIPF T N, BLOEM P, et al. Modeling relational data with graph convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the European Semantic Web Conference. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 593-607. [28] DETTMERS T, MINERVINI P, STENETORP P, et al. Convolutional 2D knowledge graph embeddings[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2018, 32(1): 1811-1818. [29] SUN Z Q, DENG Z H, NIE J Y, et al. RotatE: Knowledge graph embedding by relational rotation in complex space[EB/OL]. (2019-02-26) [2022-05-10]. [30] GARCÍA-DURÁN A, DUMANČIĆ S, NIEPERT M. Learning sequence encoders for temporal knowledge graph completion[C]// Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2018: 4816-4821. [31] DASGUPTA S S, RAY S N, TALUKDAR P. HyTE: Hyperplane-based temporally aware knowledge graph embedding[C]//Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2018: 2001-2011. [32] GOYAL P, CHHETRI S R, CANEDO A. Dyngraph2vec: Capturing network dynamics using dynamic graph representation learning[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2020, 187: 104816. doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2019.06.024 [33] URIEL S, IDO G, KIRA R. Node embedding over temporal grapns[C]//Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Amsterdam: Morgan Kaufmann, 2019: 4605-4612. [34] PAREJA A, DOMENICONI G, CHEN J, et al. EvolveGCN: Evolving graph convolutional networks for dynamic graphs[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 34(4): 5363-5370. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v34i04.5984 [35] SEO Y, DEFFERRARD M, VANDERGHEYNST P, et al. Structured sequence modeling with graph convolutional recurrent networks[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 362-373. [36] RAKSHIT T, HANJUN D, YICHEN W, et al. Know-Evolve: Deep temporal reasoning for dynamic knowledge graphs[C]//International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2017: 3462-3471. [37] TRIVEDI R, FARAJTABAR M, BISWAL P, et al. Representation learning over dynamic graphs[EB/OL]. (2018-03-16) [2022-05-10]. [38] JIN W, QU M, JIN X S, et al. Recurrent event network: Autoregressive structure inferenceover temporal knowledge graphs[C]// Proceedings of the Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing. Stroudsburg: Association for Computational Linguistics, 2020: 6669-6683. -








 下载:
下载: