-
摘要:
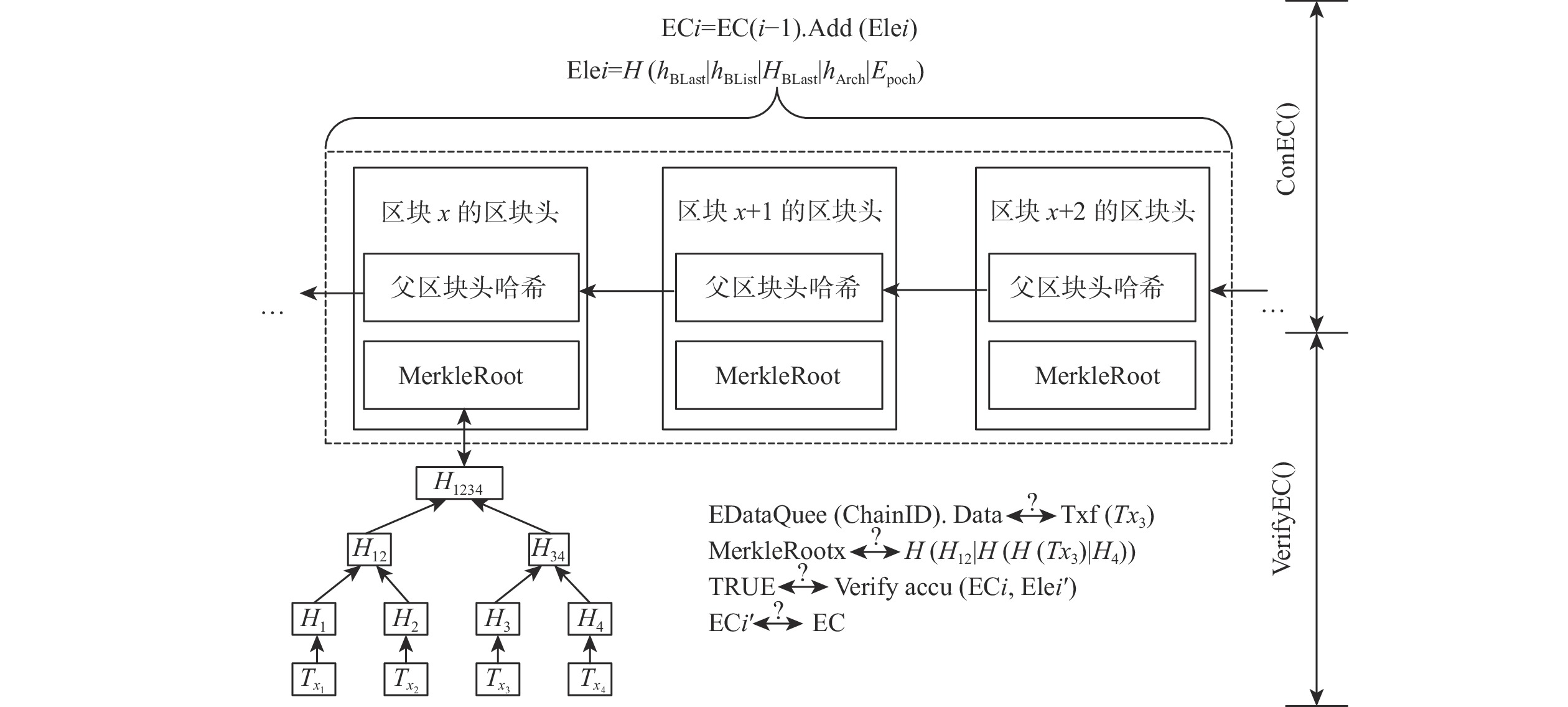
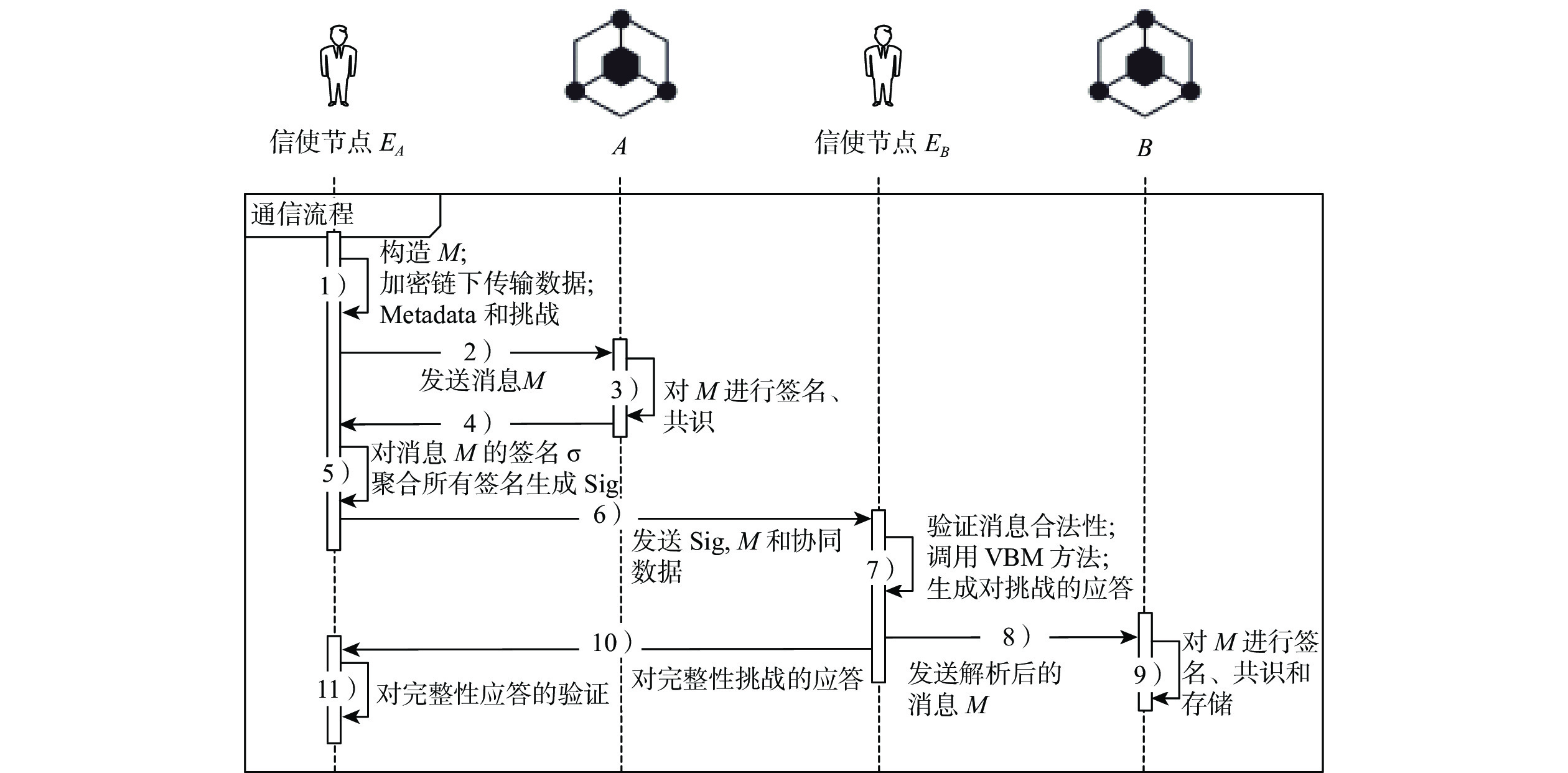
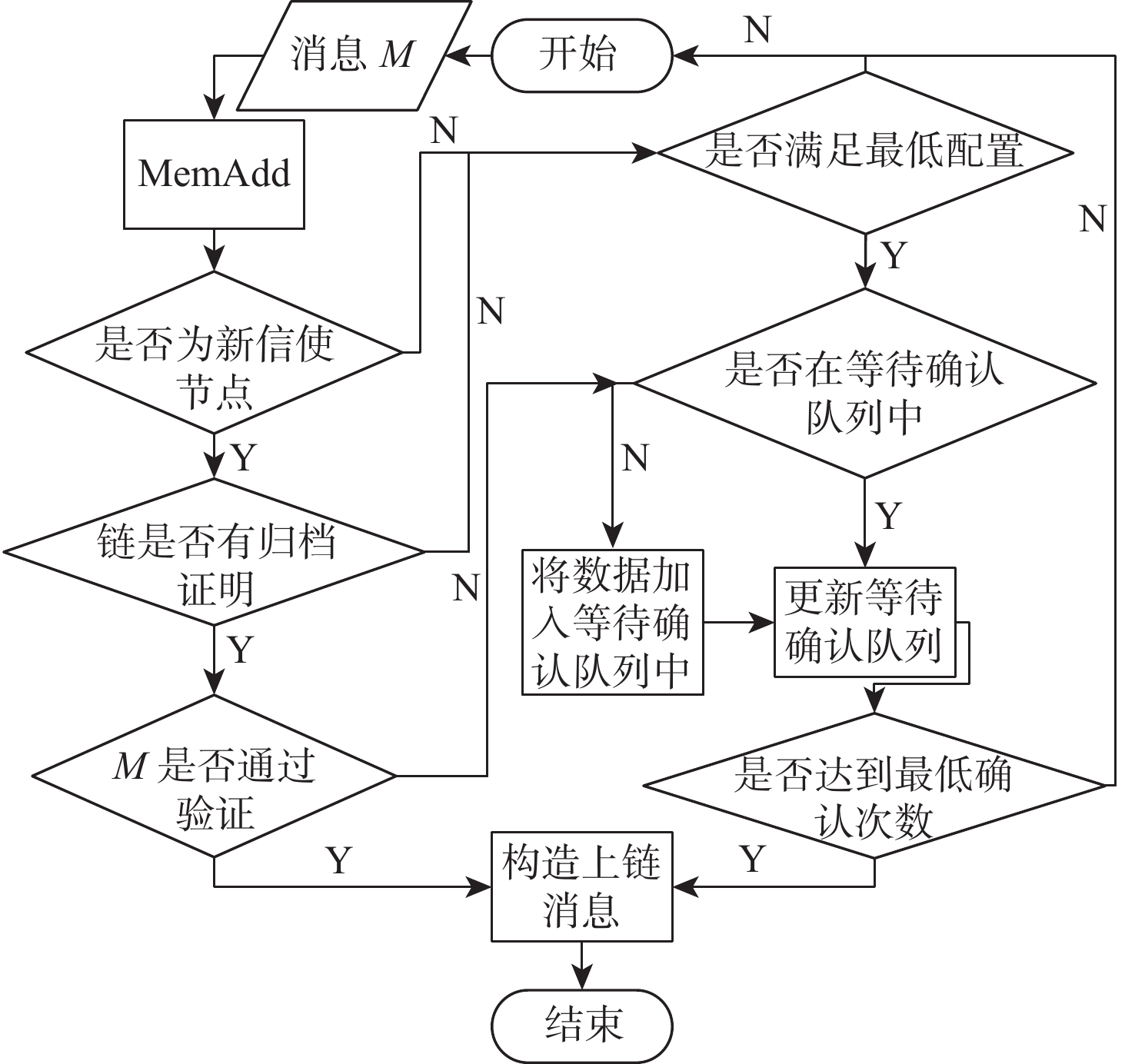
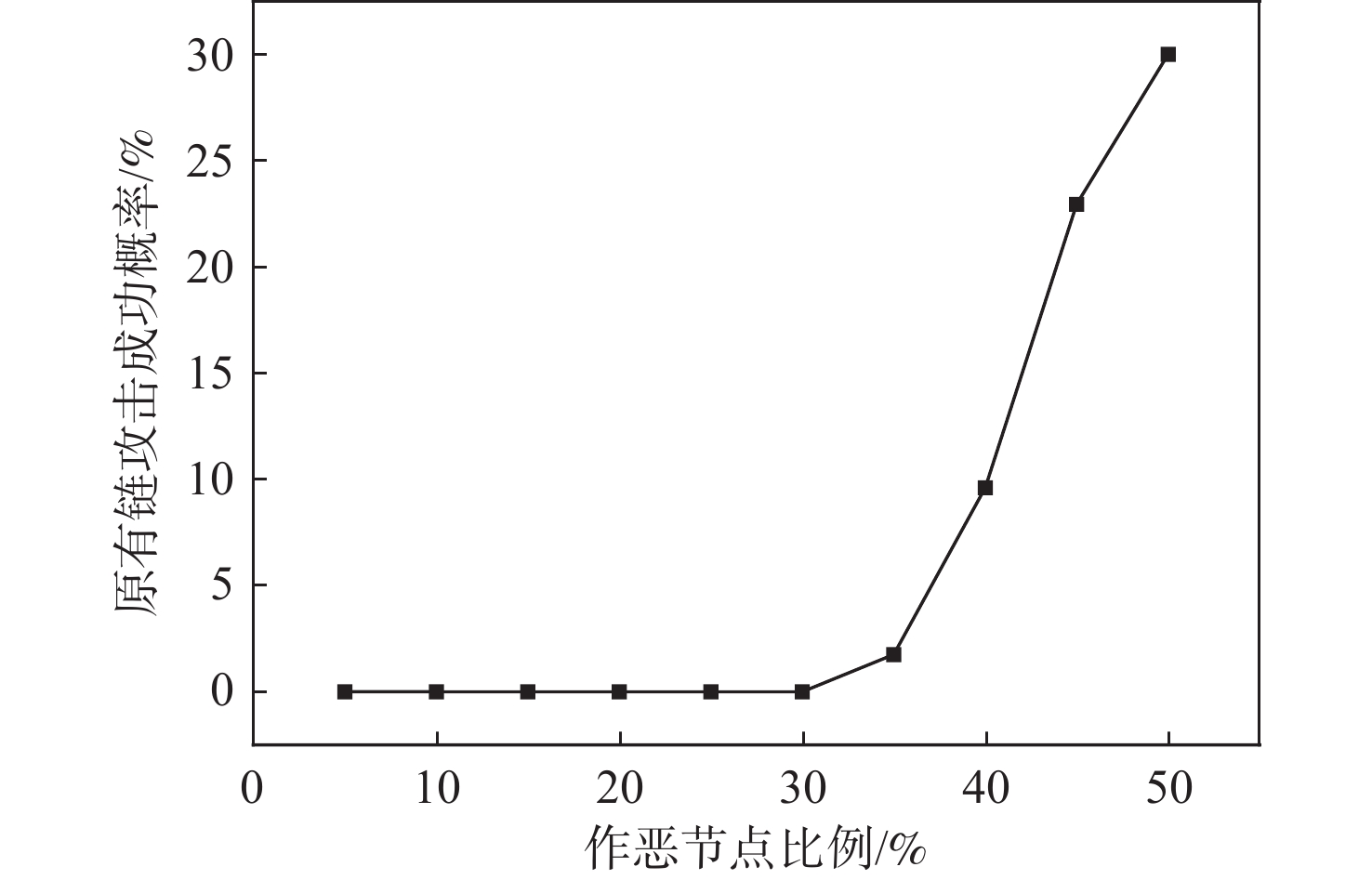
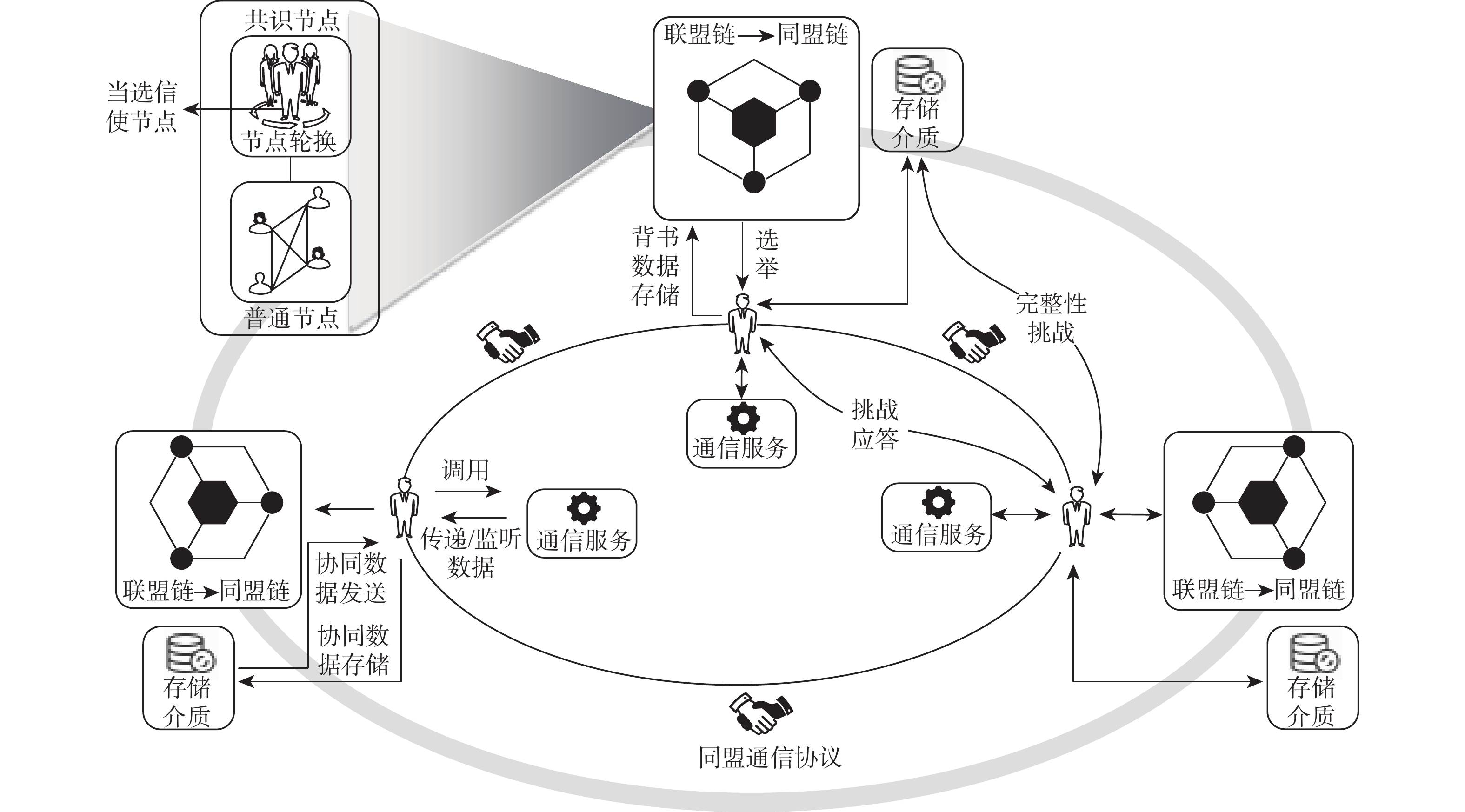
监管友好、性能优异的联盟链是我国政务和商用区块链的首选。然而联盟链通常因为有效节点少、节点独立性低和发展能力弱的原因,降低系统的可靠性。因此提出了同盟链:一种通过协同多个联盟链来提升系统可靠性的模型。同盟链通过联盟链间相互层叠存储链上数据降低联盟链历史数据被篡改的可能性,通过协同存储区块链加密数据保障账本数据恢复能力;使用聚合签名、数据完整性验证等方法解决数据传输完整性、来源真实性问题;设计双向数据存在性验证方法检验传输数据的连续性,确保协同数据相互背书的真实性;通过与现有方案进行通信、存储和计算消耗上的对比来验证本方案的有效性。
Abstract:In recent years, blockchain technology has been developing rapidly, and It plays a critical role in fintech, supply chain, medical health, data security and other fields. Due to friendly supervision and excellent performance, the consortium chain has become China's first choice for government and commercial blockchain. However, it is usually faced with problems such as the small number of effective nodes, low node independence, and weak sustainable development ability, which reduces the system’s reliability. We suggest the alliance model, a blockchain approach that coordinates several consortium chains to increase system stability, in light of the aforementioned issues. The model stores data by overlapping each other between chains to reduce the possibility of data tampering and ensure data recovery. In addition, we use the methods of aggregated signature and data integrity verification to solve the problems of transmission data integrity and source authenticity. In order to verify the legitimacy of reciprocal endorsement of collaborative data and to check the continuation of the sent data, we also develop an existence verification method. To confirm its efficacy, this scheme's communication, storage, and computational usage are compared to those of the current techniques.
-
Key words:
- blockchain /
- consortium chain /
- reliability /
- decentralization /
- data integrity /
- data authenticity
-
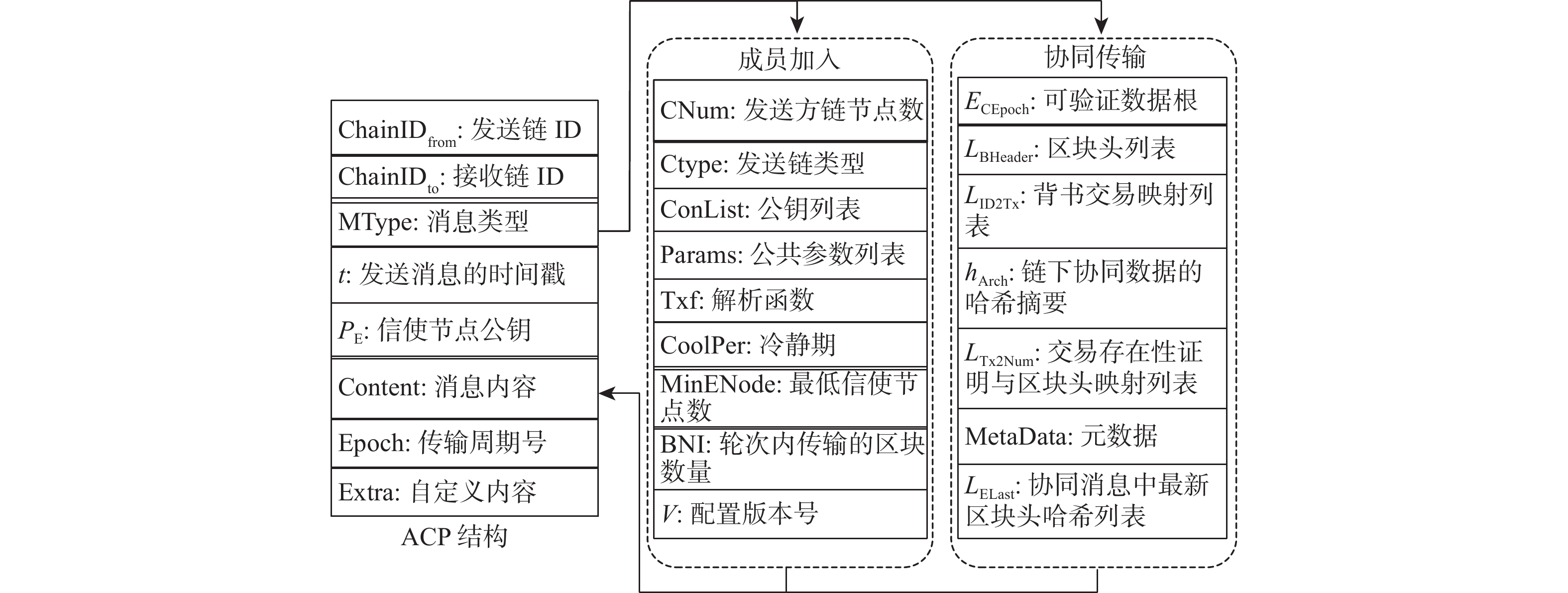
表 1 AIC关键配置项
Table 1. Key configuration items of AIC
配置项 作用 Ecert 现任信使节点当选证明 AEnvInfo 其他联盟链信使节点证书列表和路由信息 AConfigList 其他联盟链配置信息 EDataQuene 收发双方待确认、已确认数据次数映射列表 ECerList 记录每个成员近期传输证明映射列表 BlackNode 记录禁止通信的信使节点名单 BlackChain 记录作恶联盟链唯一标识列表 Miniconfig 所有联盟链确认加入同盟链模型的最低配置 表 2 不同区块链类型对比
Table 2. Comparison of different blockchain types
对比维度 公有链 私有链 联盟链 同盟链 准入机制 无 有 有 有 去中心化程度 高 低 中 较高 交易速度 低 高 高 高 监管难易 难 易 易 易 表 3 不同方案可靠性指标对比
Table 3. Comparison of reliability indicators of different schemes
方案 账本篡改
难度有效节点
数量增幅节点独立
程度账本恢复
能力适用
范围交易体验
影响程度方案1 中 中 低 无 广 中 方案2 高 高 高 无 较广 小 方案3 高 高 高 有 窄 大 本方案 高 高 高 有 广 小 表 4 单节点存储量增幅
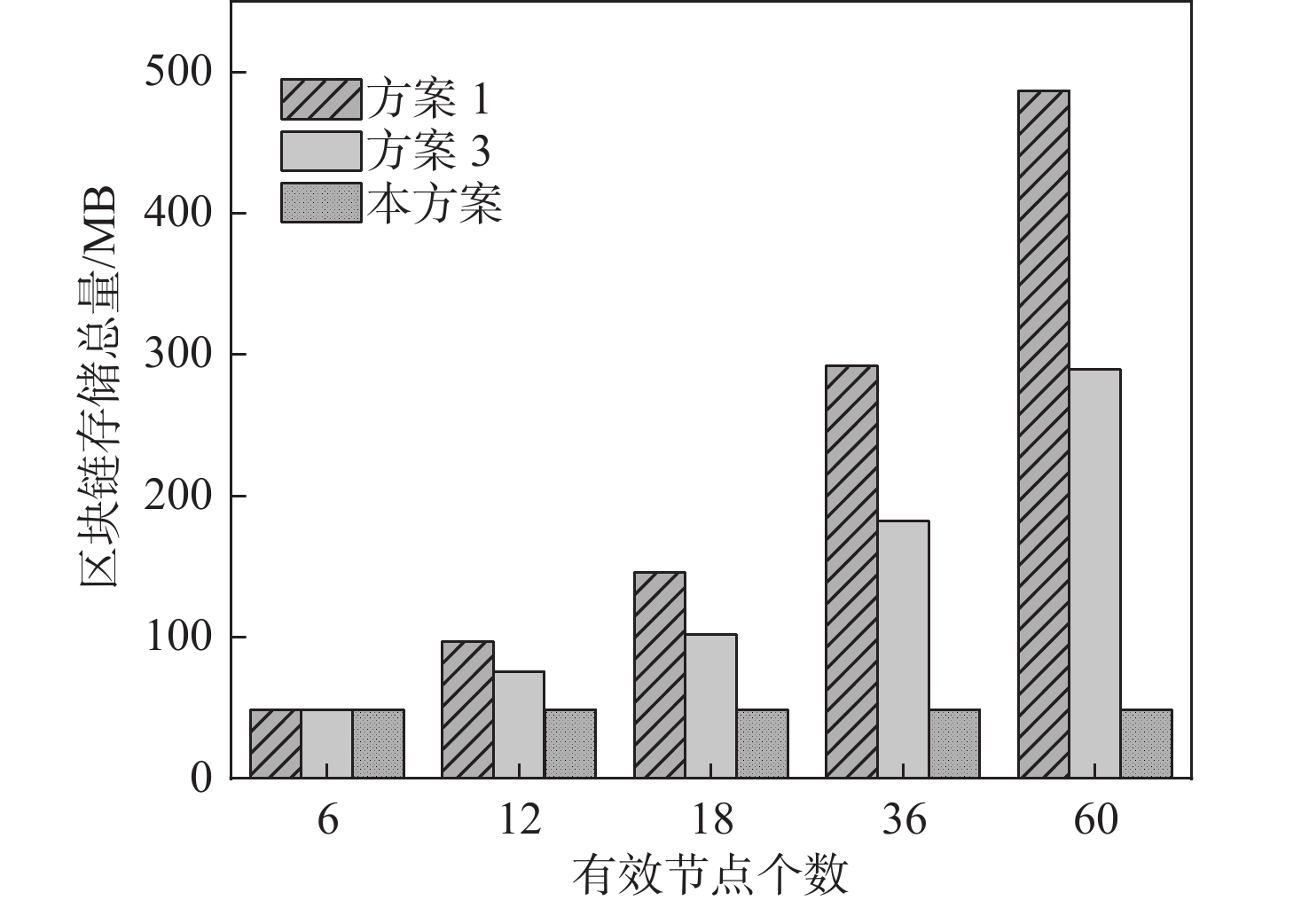
Table 4. Increment of single node storage
% 有效节点个数 方案3 本方案 6 0 0 12 53.4136 0.0024 18 112.1372 0.0048 36 275.9851 0.1205 60 495.2543 0.2169 表 5 计算开销额外总耗时
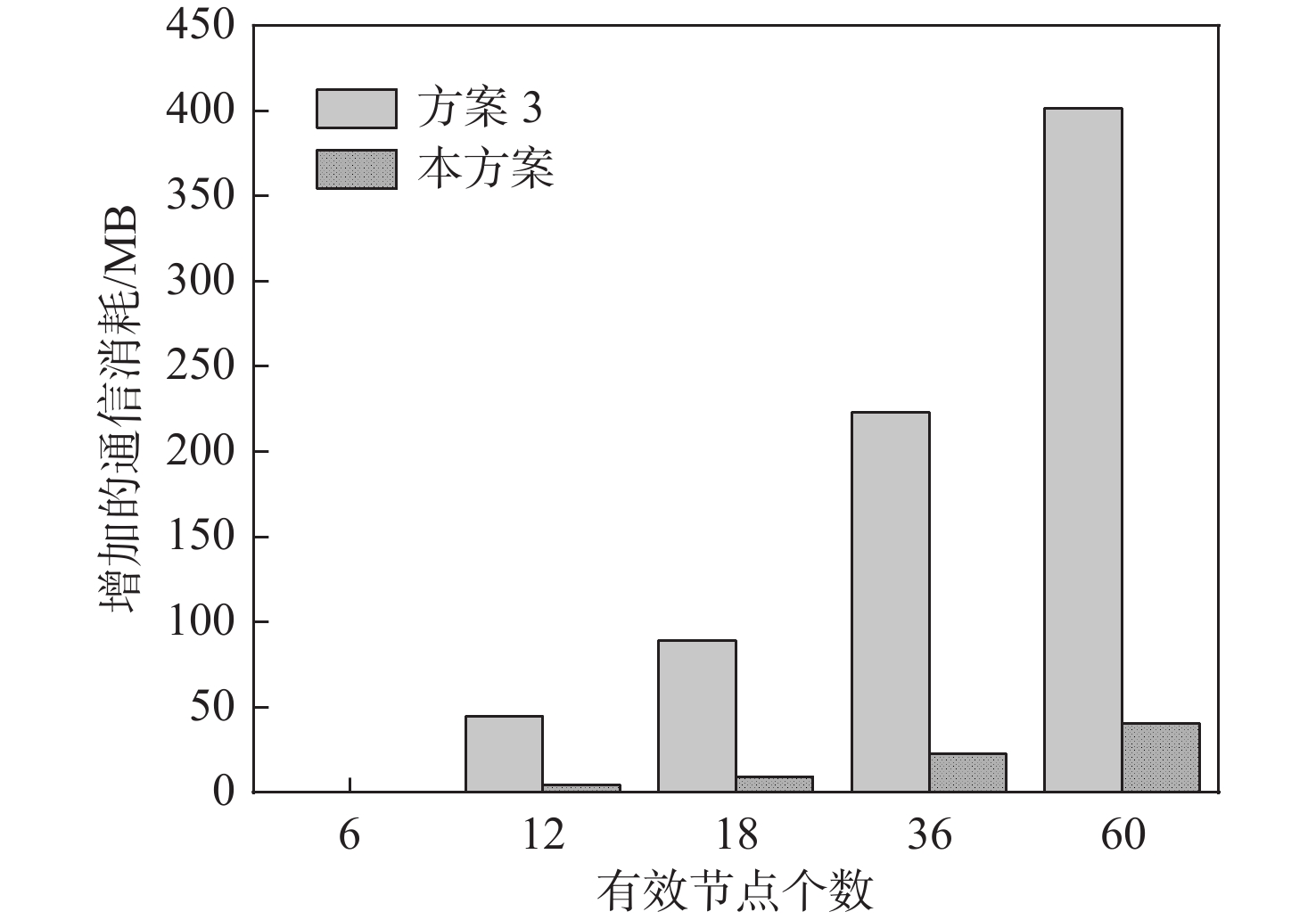
Table 5. Additional total elapsed time spent on computing overhead
s 有效节点
个数方案1额外
总耗时方案3额外
总耗时本方案额外
总耗时6 0 0 0 12 117.5411 0.2466 1.5316 18 209.2531 0.2544 1.5660 36 486.2300 0.2778 2.8357 60 855.9127 0.3090 3.8571 -
[1] ZHENG Z B, XIE S A, DAI H N, et al. An overview of blockchain technology: architecture, consensus, and future trends[C]// 2017 IEEE International Congress on Big Data (BigData Congress). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 557-564. [2] CASTRO M, LISKOV B. Practical Byzantine fault tolerance and proactive recovery[J]. ACM Transactions on Computer Systems, 2002, 20(4): 398-461. doi: 10.1145/571637.571640 [3] ZHU X Y, BADR Y. Identity management systems for the Internet of Things: a survey towards blockchain solutions[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(12): 4215. doi: 10.3390/s18124215 [4] 中国电子信息产业发展研究院. 2021年中国区块链年度发展白皮书[R/OL]. (2022-06-14)[2022-07-24]. [5] 武腾, 薛磊, 郑东, 等. P2P持久存储系统可靠性分析与数据维护优化[J]. 信息安全与通信保密, 2009, 7(8): 149-153. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8054.2009.08.057WU T, XUE L, ZHENG D, et al. Reliability analysis and data maintenance optimization of P2P durable storage system[J]. Information Security and Communications Privacy, 2009, 7(8): 149-153 (in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8054.2009.08.057 [6] GUO H Q, YU X J. A survey on blockchain technology and its security[J]. Blockchain: Research and Applications, 2022, 3(2): 100067. doi: 10.1016/j.bcra.2022.100067 [7] BANDARA H D, XU X W, WEBER I. Patterns for blockchain data migration[C]// Proceedings of the European Conference on Pattern Languages of Programs 2020. New York: ACM, 2020: 1-19. [8] LEI K, ZHANG Q C, XU L M, et al. Reputation-based Byzantine fault-tolerance for consortium blockchain[C]// 2018 IEEE 24th International Conference on Parallel and Distributed Systems (ICPADS). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 604-611. [9] YAN C Y, ZHANG C, LU Z G, et al. Blockchain abnormal behavior awareness methods: a survey[J]. Cybersecurity, 2022, 5(1): 5. doi: 10.1186/s42400-021-00107-4 [10] ARÁOZ M. Proof of existence[R/OL]. [2022-07-24]. [11] 谭海波, 周桐, 赵赫, 等. 基于区块链的档案数据保护与共享方法[J]. 软件学报, 2019, 30(9): 2620-2635.TAN H B, ZHOU T, ZHAO H, et al. Archival data protection and sharing method based on blockchain[J]. Journal of Software, 2019, 30(9): 2620-2635 (in Chinese). [12] HOPE-BAILIE A, THOMAS S. Interledger: creating a standard for payments[C]//Proceedings of the 25th International Conference Companion on World Wide Web-WWW '16 Companion. New York: ACM, 2016: 281-282. [13] 叶少杰, 汪小益, 徐才巢, 等. BitXHub: 基于侧链中继的异构区块链互操作平台[J]. 计算机科学, 2020, 47(6): 294-302. doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.191100055YE S J, WANG X Y, XU C C, et al. BitXHub: side-relay chain based heterogeneous blockchain interoperable platform[J]. Computer Science, 2020, 47(6): 294-302 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/jsjkx.191100055 [14] FLOERSCH K. Ethereum smart contracts in L2: optimistic rollup[R/OL]. (2019-08-28)[2022-11-30]. [15] BUTERIN V. Chain interoperability[R/OL]. R3 research paper, 2016 (2016-09-09)[2022-07-24]. [16] VIGIL M, BUCHMANN J, CABARCAS D, et al. Integrity, authenticity, non-repudiation, and proof of existence for long-term archiving: a survey[J]. Computers & Security, 2015, 50: 16-32. [17] LAKHWANI K, KAUR R, KUMAR P, et al. An extensive survey on data authentication schemes in cloud computing[C]// 2018 4th International Conference on Computing Sciences (ICCS). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 59-66. [18] MERKLE R C. A certified digital signature[M]// Advances in Cryptology — CRYPTO’ 89 Proceedings. New York: Springer New York, 2007: 218-238. [19] BENALOH J, DE MARE M. One-way accumulators: a decentralized alternative to digital signatures[M]// Advances in cryptology — EUROCRYPT ’93. Berlin: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 1994: 274-285. [20] ATENIESE G, DI PIETRO R, MANCINI L V, et al. Scalable and efficient provable data possession[C]// Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Security and Privacy in Communication Netowrks. New York: ACM, 2008: 1-10. [21] Zlib home site[EB/OL]. (1995-05-01)[2022-03-28]. [22] 祁健. 累加器在区块链中的应用研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学, 2020: 22-33.QI J. Research on the application of accumulator in blockchain[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Information Science & Technology, 2020: 22-33 (in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: