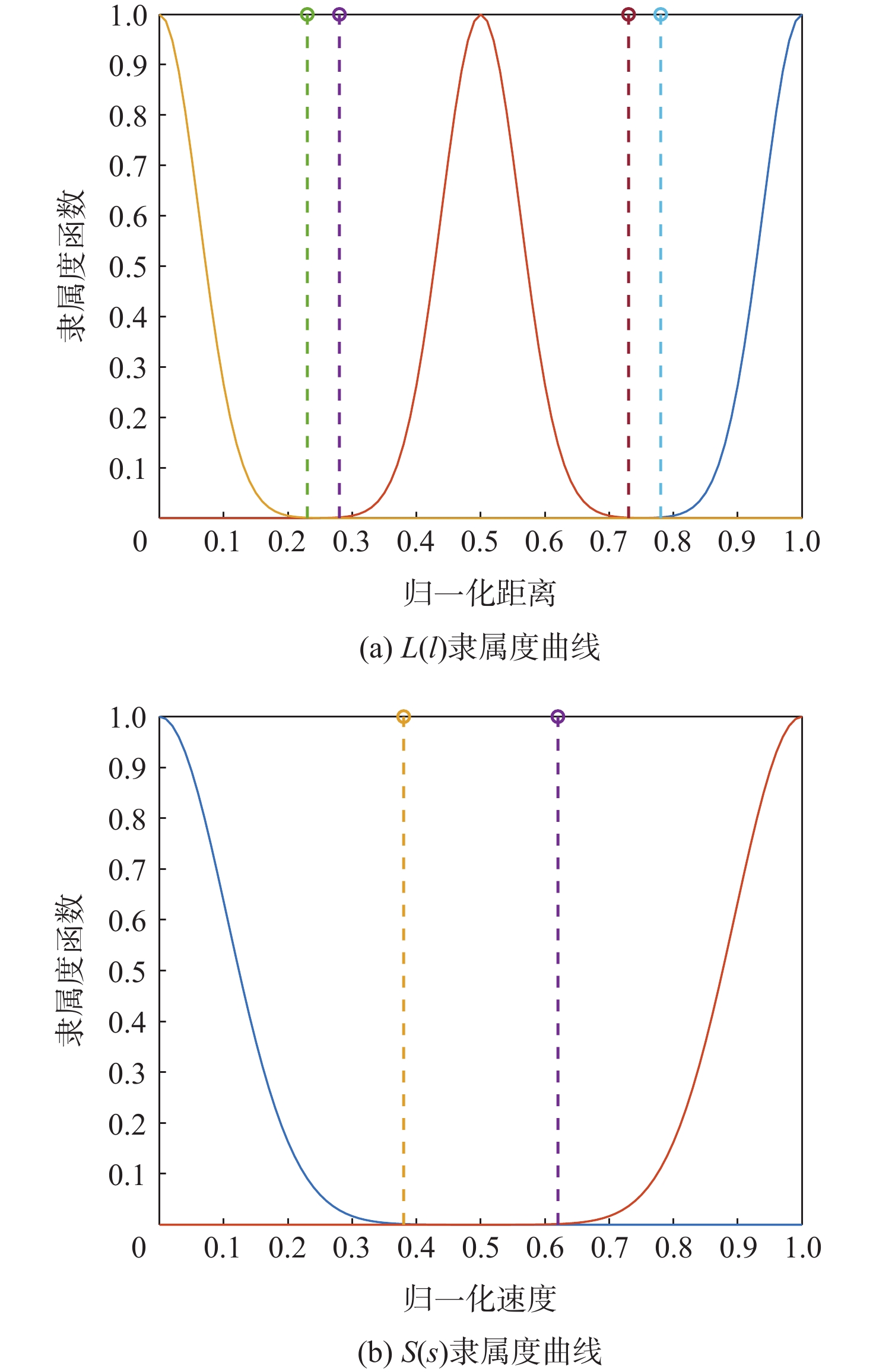
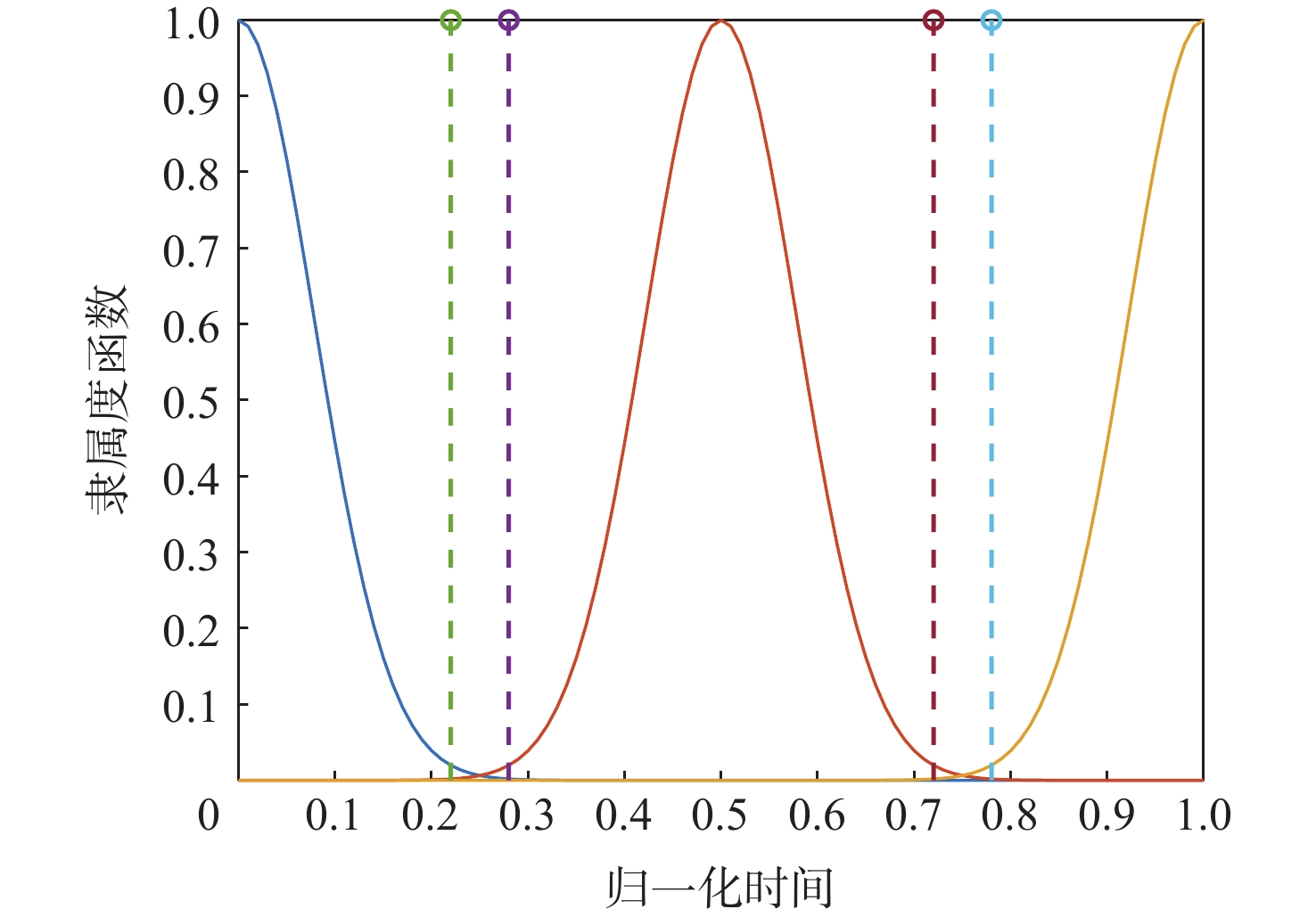
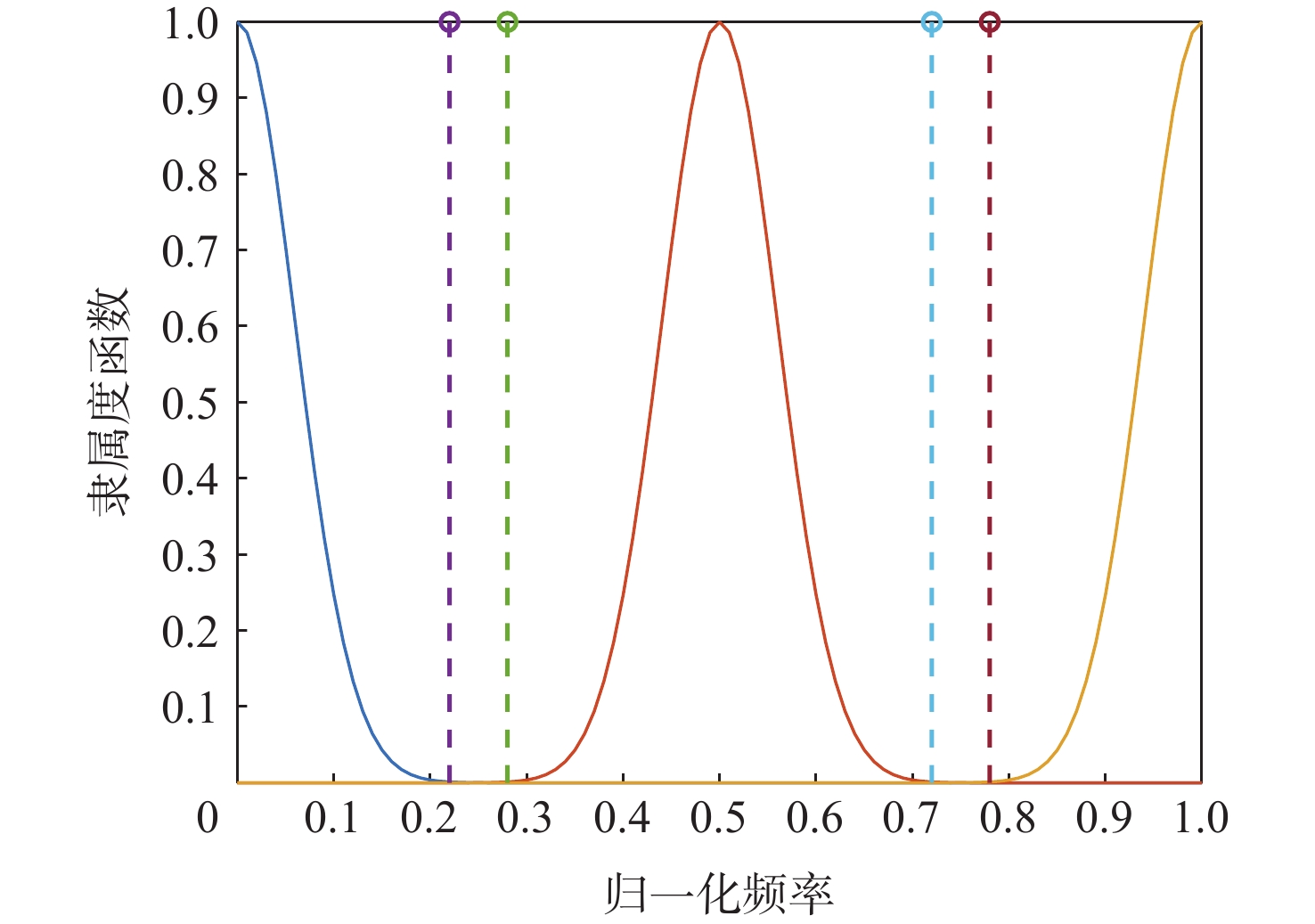
-
摘要:
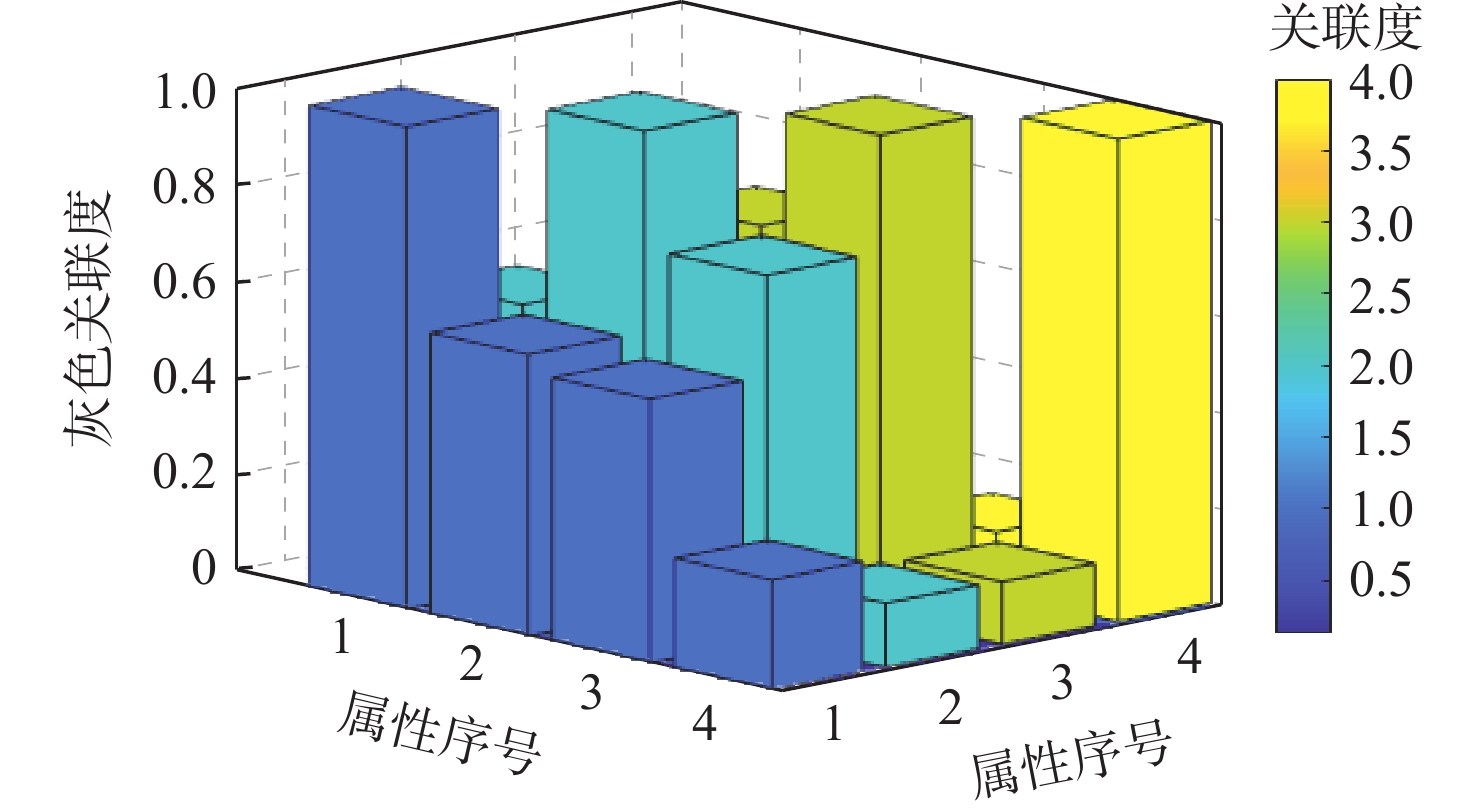
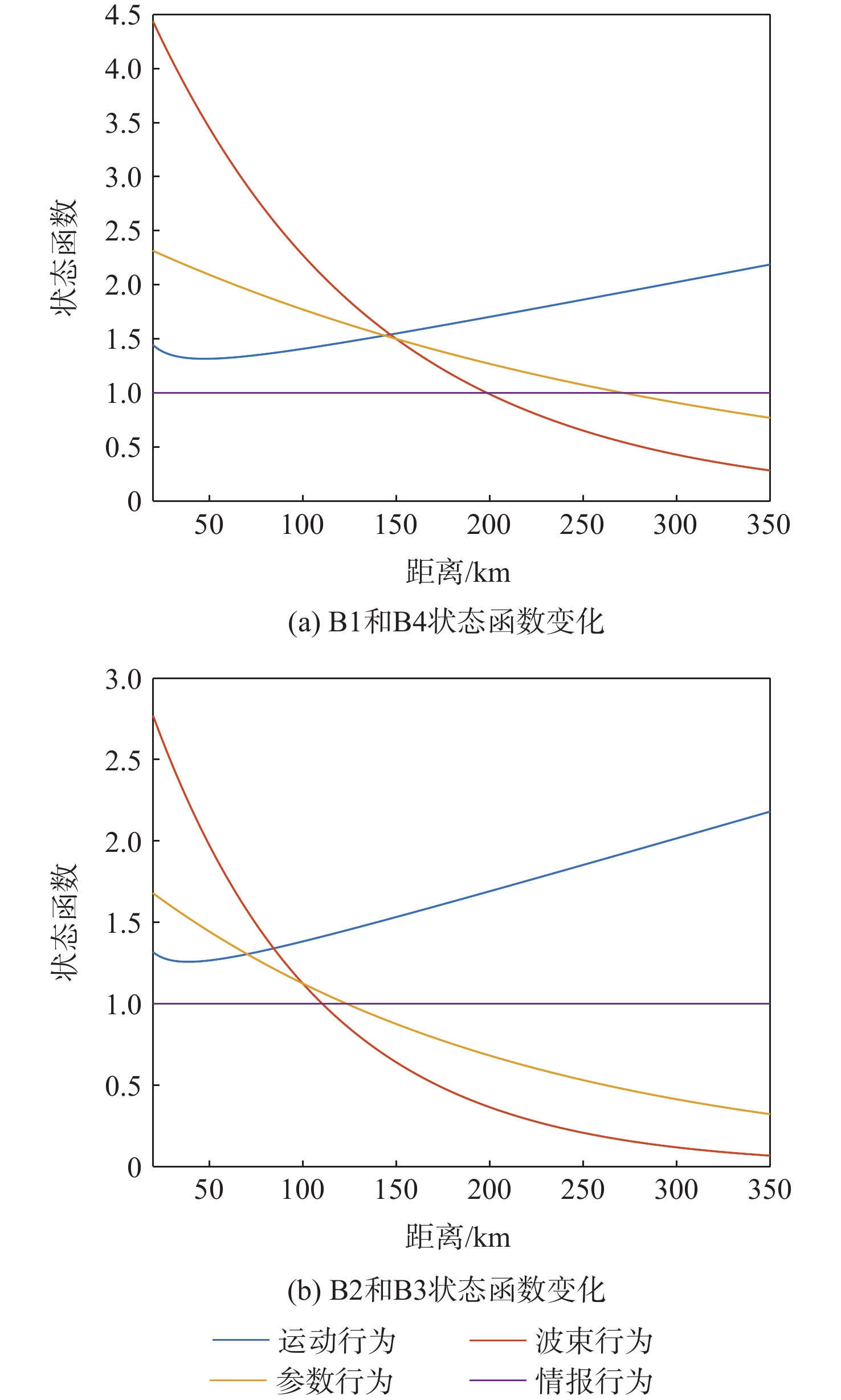
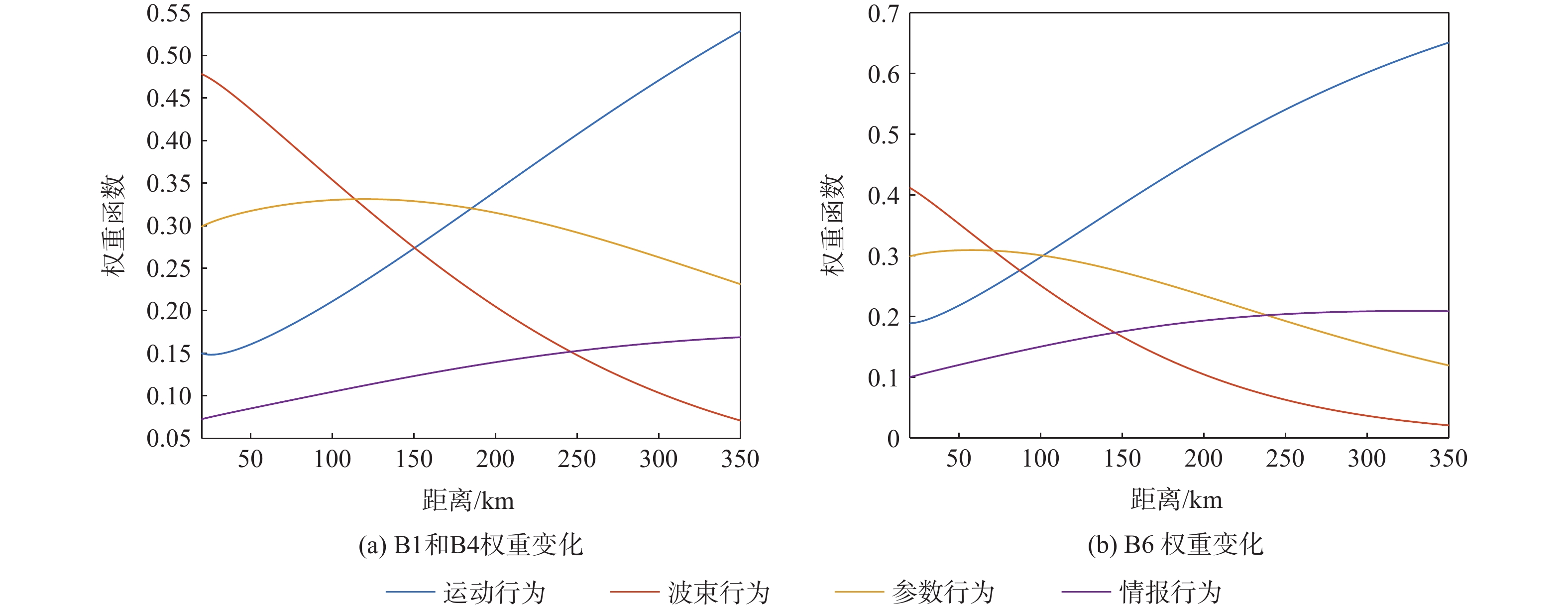
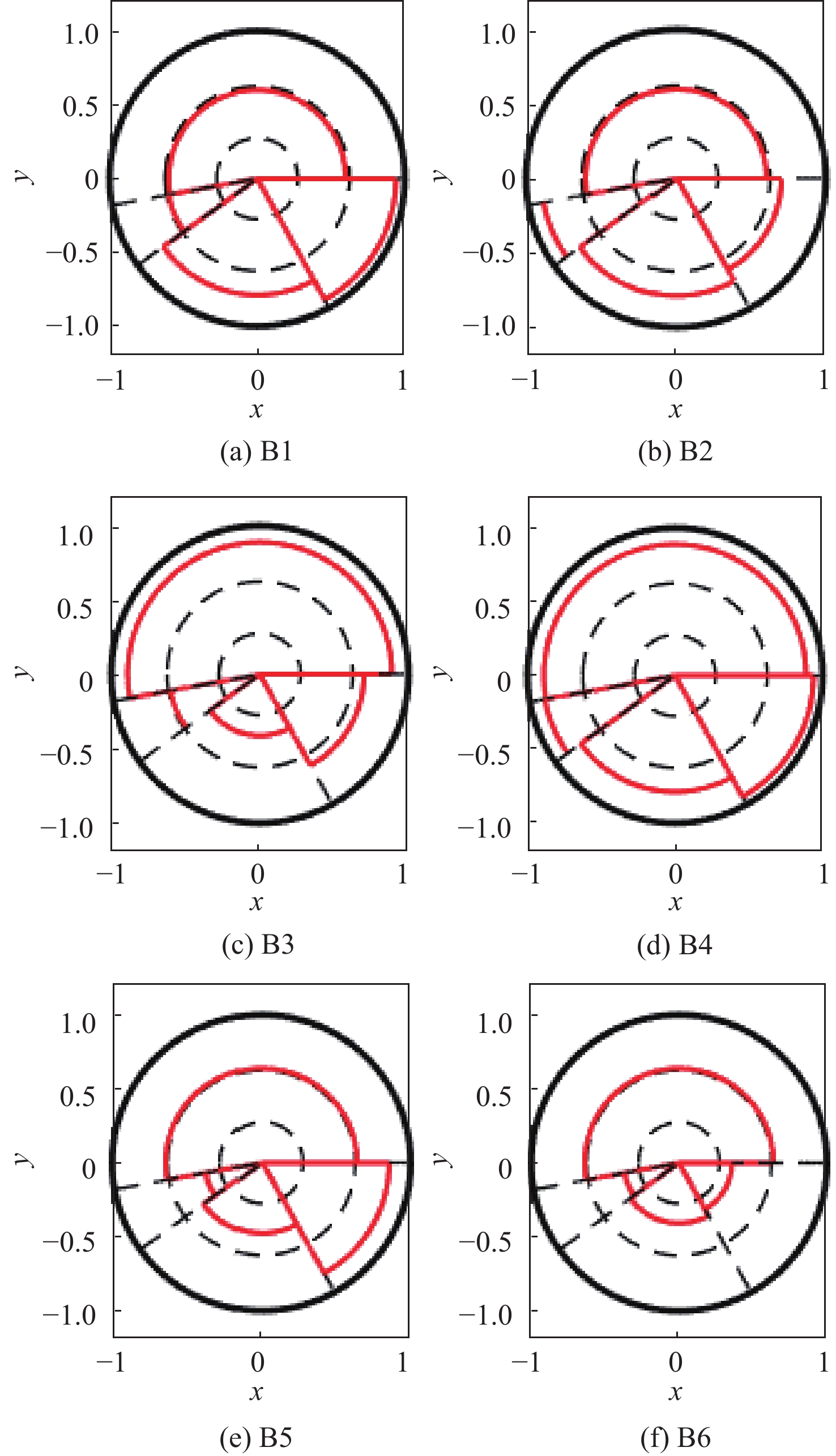
针对当前雷达辐射源威胁评估对精确侦察数据依赖性较大的问题,提出一种基于行为特征的雷达辐射源威胁评估算法。从辐射源目标行为特征和数据融合理论出发,建立基于行为特征的辐射源威胁评估体系,并采用模糊理论和Vague数据集对各子行为进行表示;考虑到指标间的耦合性和空战的高动态性,利用改进的区间灰色关联度修正初始权重,建立以距离为自变量的态势状态函数,为各子行为动态赋权;采用改进的雷达图法计算威胁目标的威胁程度。仿真结果表明:所提算法具有较好的准确性和适应性。
Abstract:This paper studies the problem that the current radar radiation source threat assessment algorithm relies heavily on accurate reconnaissance data. Firstly, a radiation source threat assessment system based on behavior characteristics is constructed, starting from the radiation source target behavior characteristics and data fusion theory. Also, fuzzy theory and Vague datasets are employed to represent each sub-behavior. A situational state function with distance as an independent variable is constructed by using the modified starting weight of interval gray correlation degree to solve the coupling between indicators and the high dynamics of air warfare. Finally, an improved radar map method is adopted to calculate the threat level of the threatening target. The simulation results show that the algorithm in this paper has good accuracy and adaptability.
-
表 1 运动行为模糊评价语言与Vague转换
Table 1. Fuzzy evaluation language of motor behavior and Vague transition
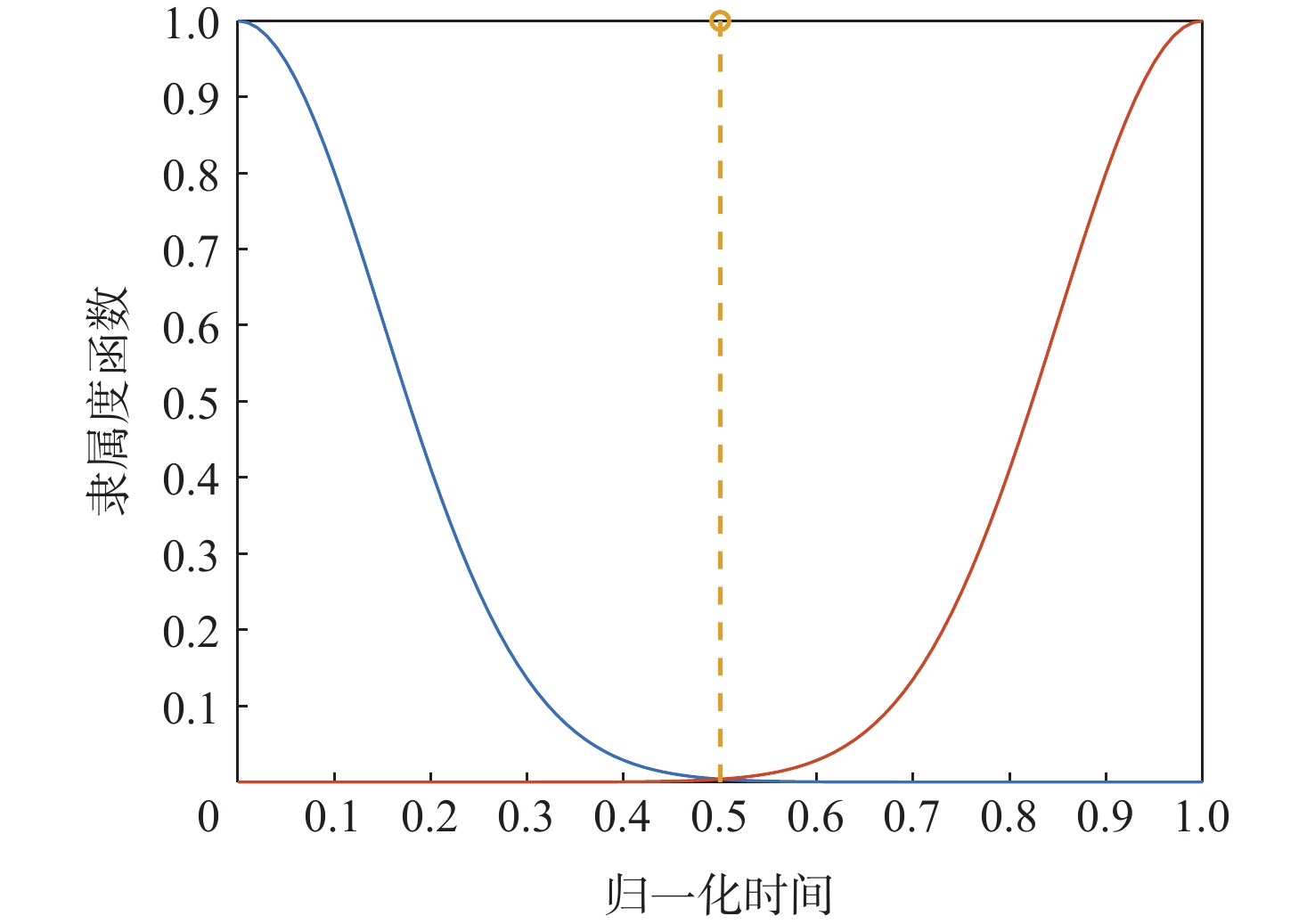
威胁等级 Vague数据集数值 高速远离 [0,0.305] 中低速远离 [0.31,0.615] 盘旋 [0.28,0.73] 中低速接近 [0.39,0.69] 高速接近 [0.7,1] 表 2 波束行为模糊评价语言与Vague转换
Table 2. Fuzzy evaluation language of beam behavior and Vague transition
威胁等级 Vague数据集数值 短暂驻留 [0,0.28] 循环驻留 [0.22,0.78] 长时间驻留 [0.72,1] 表 3 参数行为模糊评价语言与Vague转换
Table 3. Fuzzy evaluation language of parameter behavior and Vague transition
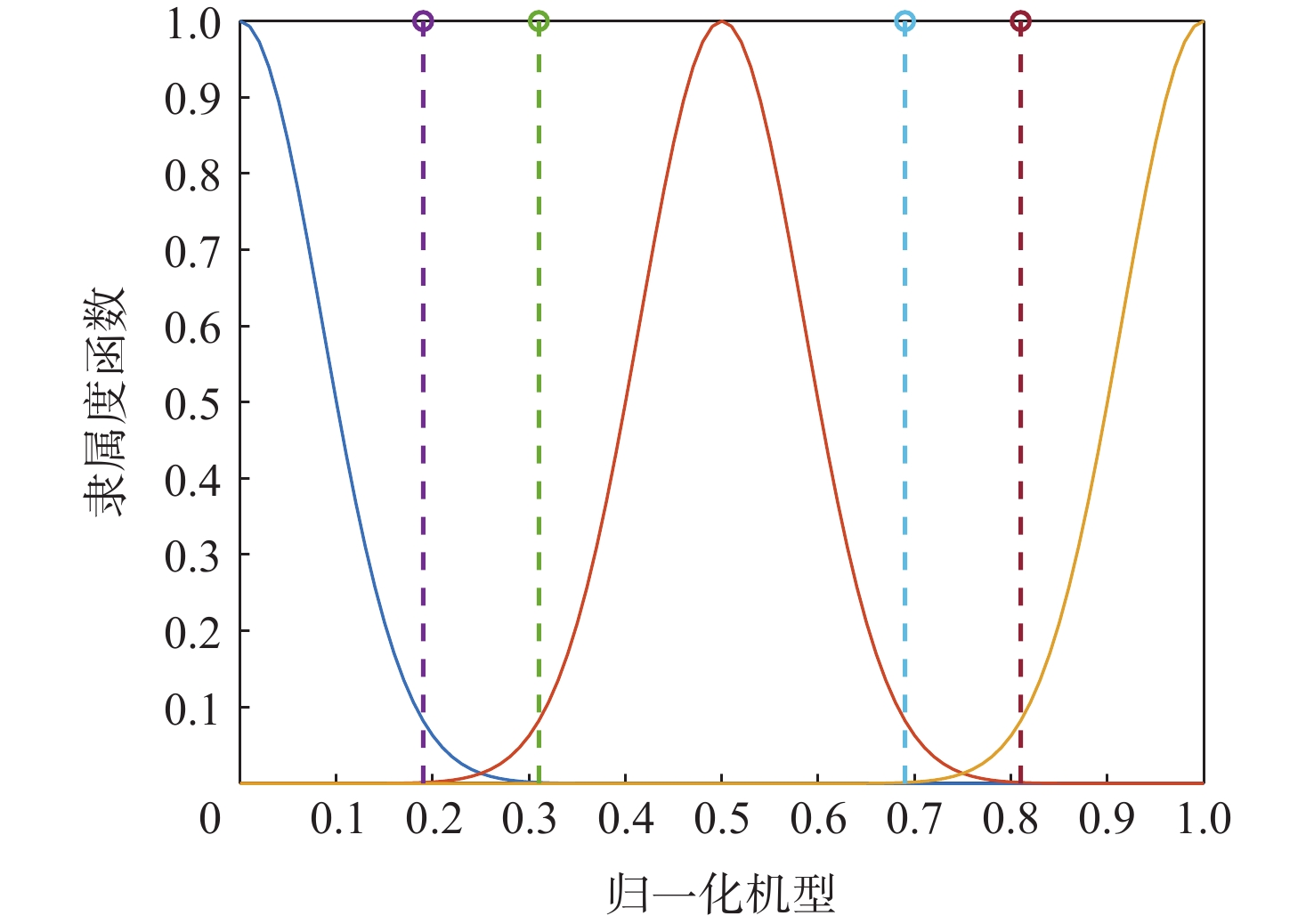
威胁等级 Vague数据集数值 低载频低占空比 [0,0.11] 低载频高占空比 [0,0.22] 中载频低占空比 [0,0.36] 中载频高占空比 [0.14,0.72] 高载频低占空比 [0,0.5] 高载频高占空比 [0.39,1] 表 4 蓝方情报信息
Table 4. Blue intelligence information
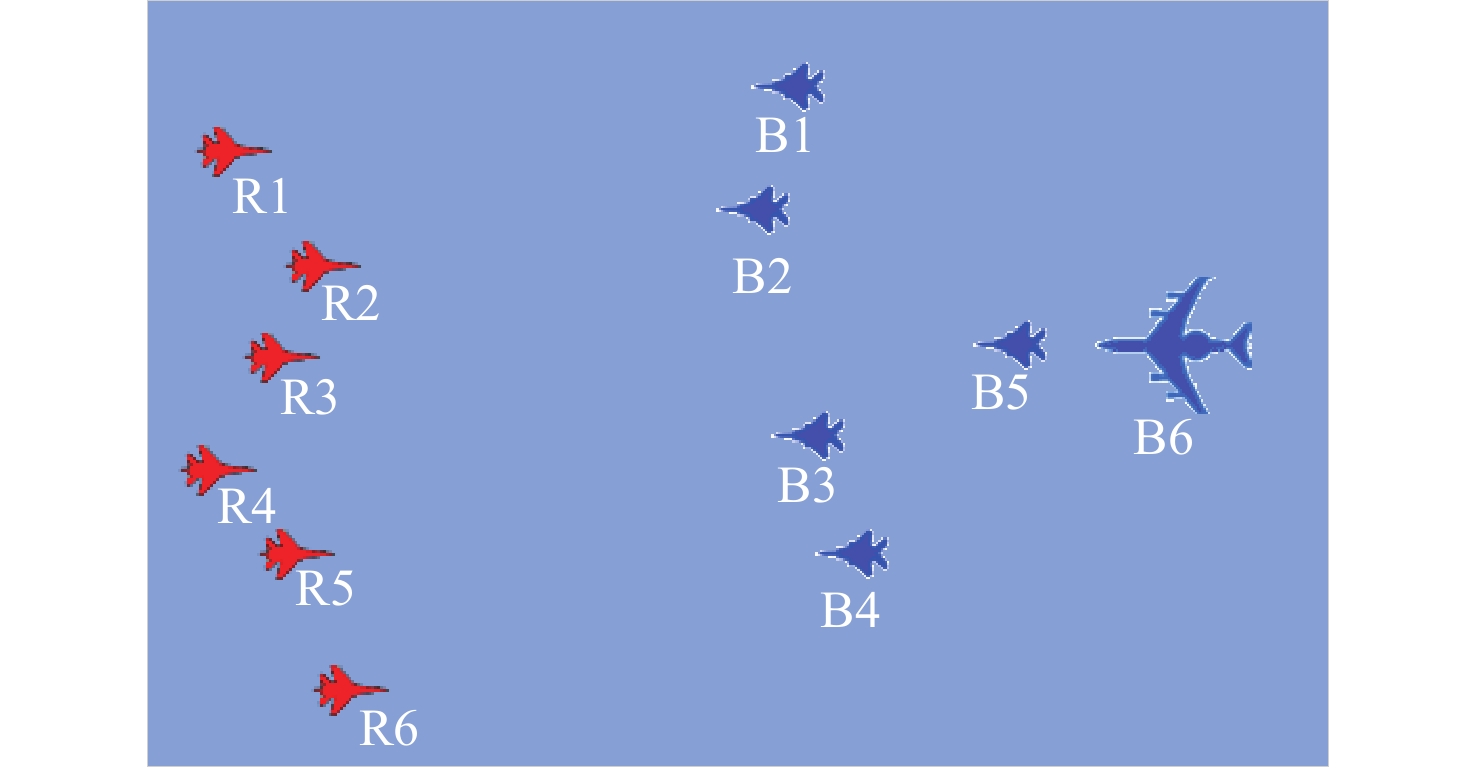
编号 飞机型号 载弹类型 空空弹最大射程/km B1 F-22战机 空对空红外制导导弹、空对空雷达制导导弹 150 B2 F-15战机 空对空红外制导导弹、空对空雷达制导导弹 100 B3 F-15战机 空对空红外制导导弹、空对空雷达制导导弹 100 B4 F-22战机 空对空红外制导导弹、空对空雷达制导导弹 150 B5 F-22战机 空对地反辐射导弹、空对空雷达制导导弹 150 B6 预警机 表 5 蓝方行为指标数据
Table 5. Blue square behavior indicator data
编号 运动行为 载频/MHz 占空比/% Ts/μs Te/μs N B1 中低速接近 9800 40 1 3071 512 B2 中低速接近 9200 20 7910.00 9446.00 1024 B3 高速接近 9100 20 4510 6097.2 512 B4 高速接近 9500 40 3 3071 1024 B5 盘旋 9000 20 1340.2 2799.4 512 B6 盘旋 1500 2 4670 11070.00 64 表 6 蓝方行为模糊评价语言与Vague转换
Table 6. Fuzzy evaluation language of blue square behavior and Vague transition
编号 运动行为 波束行为 参数行为 情报行为 B1 [0.39,0.69] [0.22,0.78] [0.39,1] [0.82,1] B2 [0.39,0.69] [0.72,1] [0.39,1] [0.56,0.76] B3 [0.7,1] [0.22,0.78] [0,0.5] [0.56,0.76] B4 [0.7,1] [0.72,1] [0.39,1] [0.82,1] B5 [0.28,0.73] [0,0.28] [0,0.5] [0.72,0.86] B6 [0.28,0.73] [0,0.28] [0,0.36] [0,0.23] 表 7 行为评估初始权重
Table 7. Initial weights of behavior evaluation
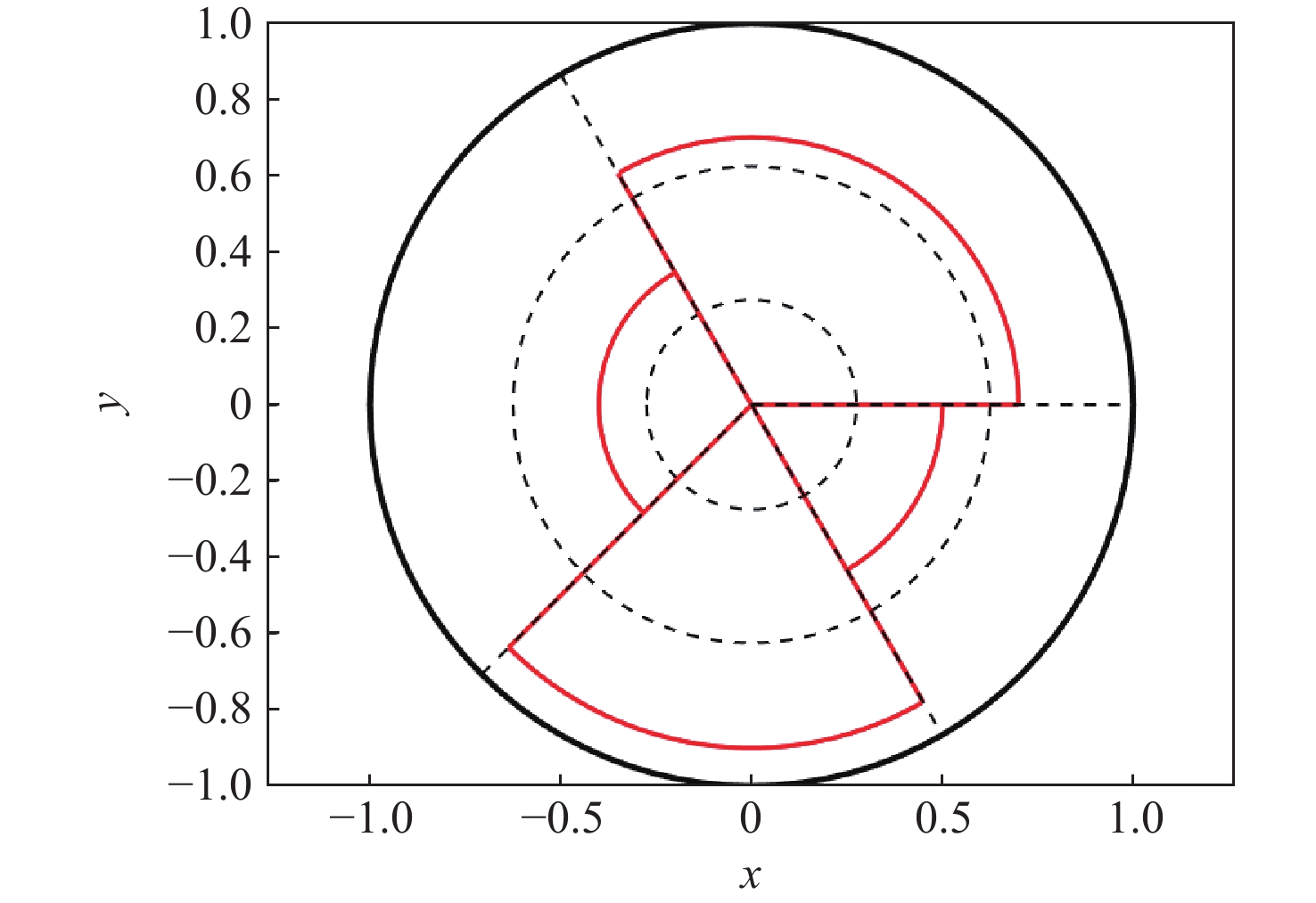
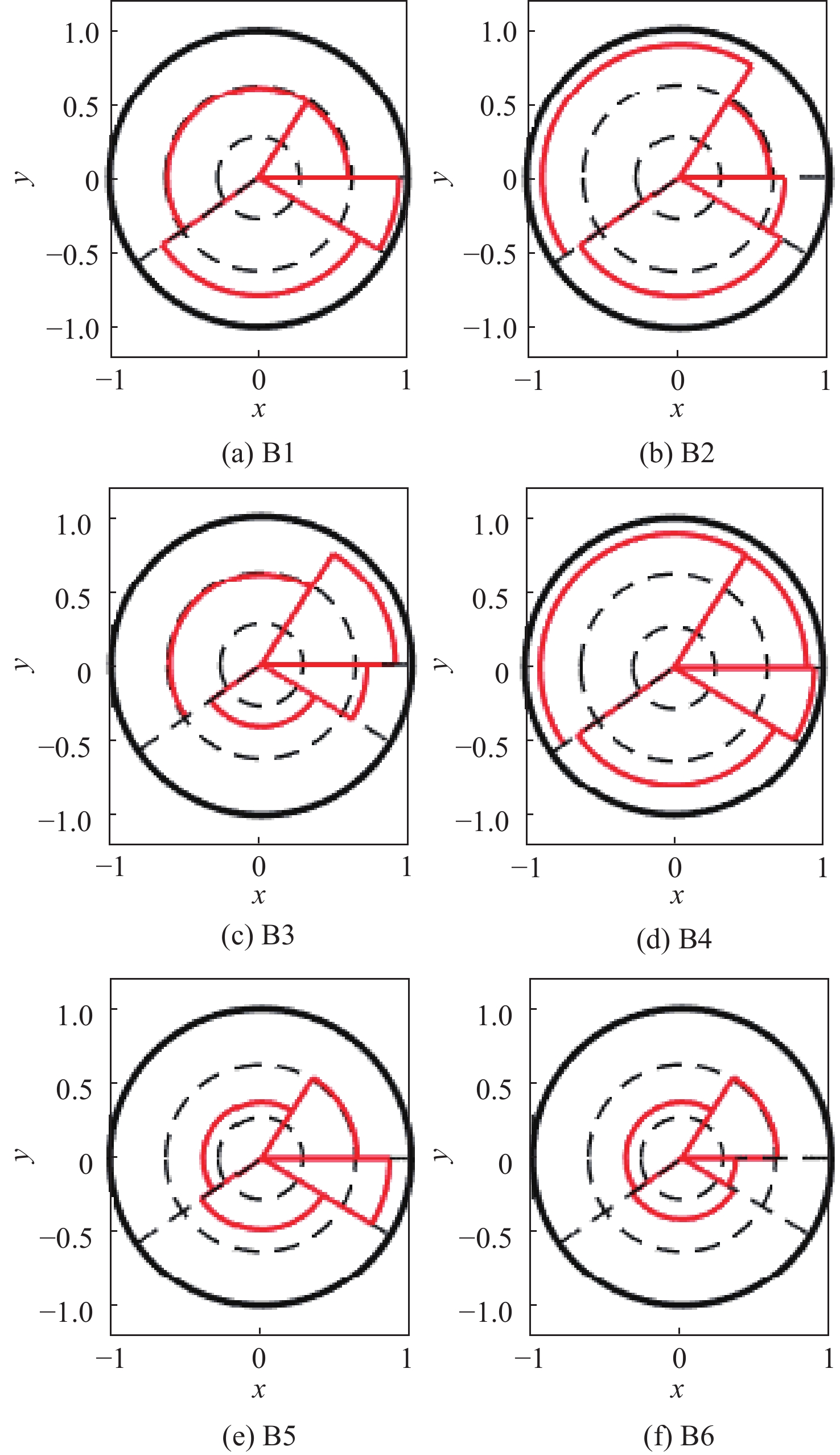
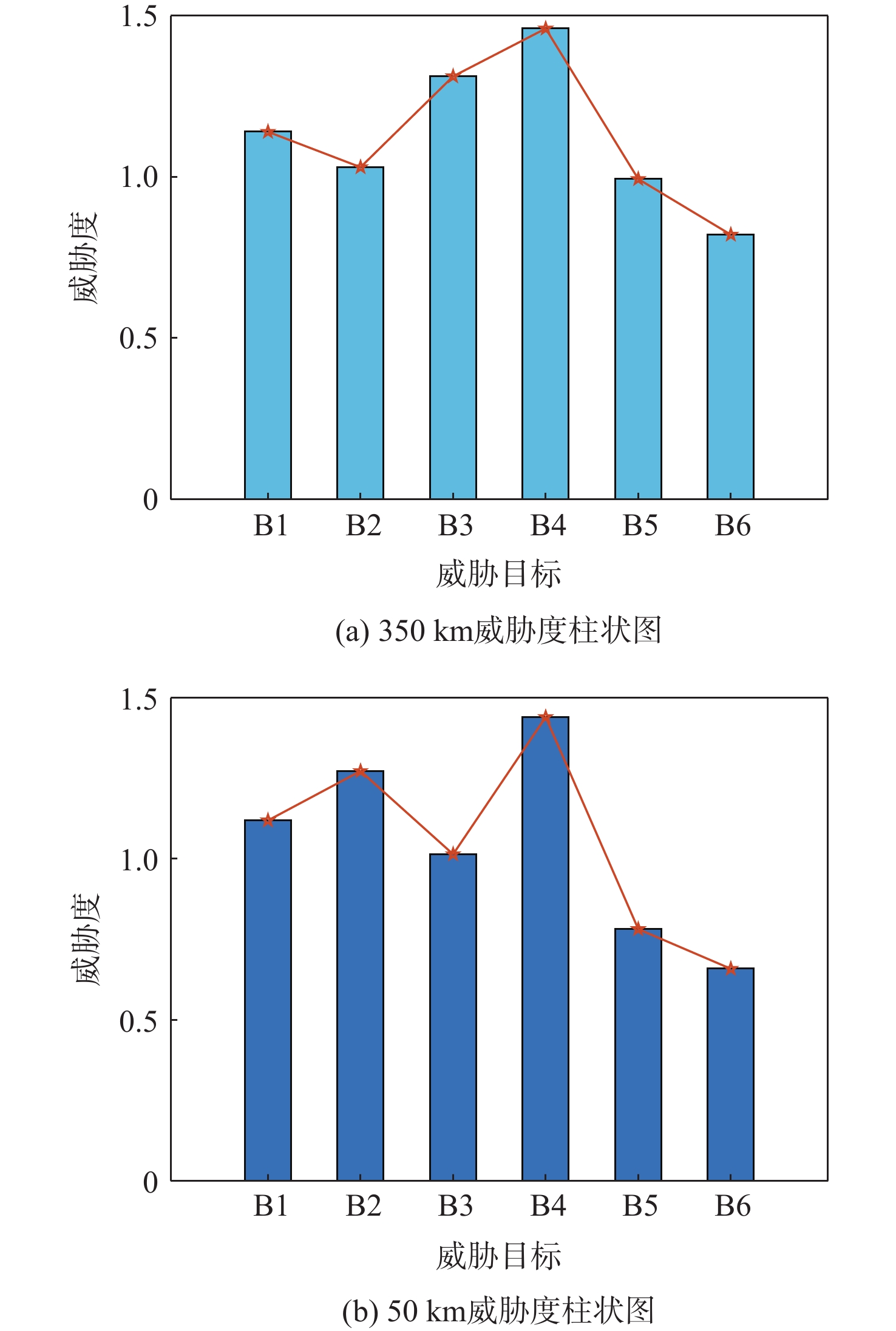
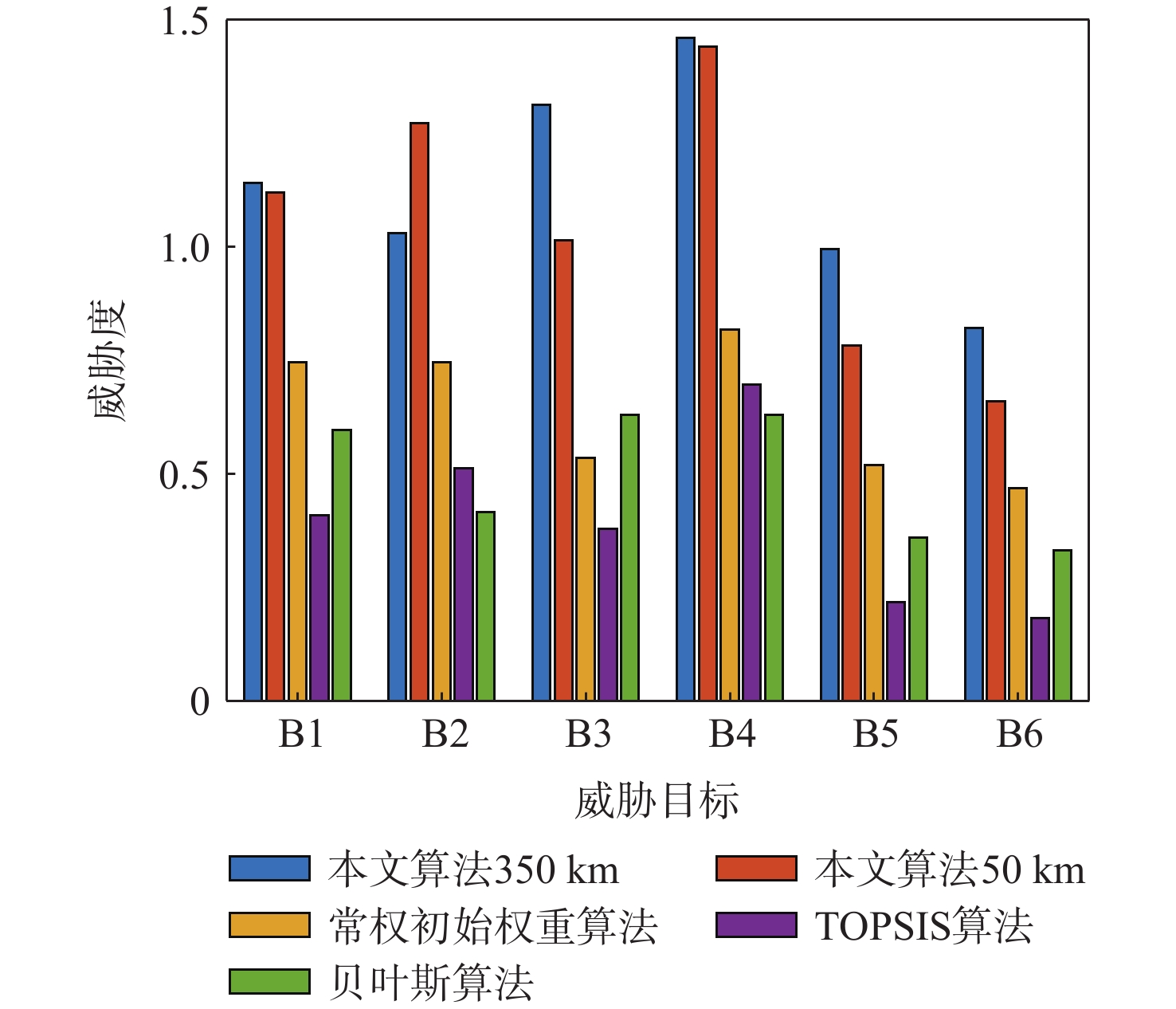
行为 权重 运动行为 0.251 3 波束行为 0.260 6 参数行为 0.312 3 情报行为 0.175 8 表 8 各威胁目标威胁度
Table 8. Threat level of each threat target
目标距离/km 威胁度 B1 B2 B3 B4 B5 B6 350 1.14 1.03 1.31 1.46 0.99 0.821 50 1.119 1.272 1.014 1.44 0.781 0.658 -
[1] ZHANG K, KONG W R, LIU P P, et al. Assessment and sequencing of air target threat based on intuitionistic fuzzy entropy and dynamic VIKOR[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 29(2): 305-310. [2] DENG Y. A threat assessment model under uncertain environment[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2015, 2015: 878024. [3] ZHAO R J, YANG F B, JI L N, et al. Dynamic air target threat assessment based on interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy sets, game theory, and evidential reasoning methodology[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2021, 2021: 6652706. [4] LU Y L, LEI X L, ZHOU Z P, et al. Approximate reasoning based on IFRS and DS theory with its application in threat assessment[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 160558-160568. [5] DI R H, GAO X G, GUO Z G, et al. A threat assessment method for unmanned aerial vehicle based on Bayesian networks under the condition of small data sets[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2018, 2018: 8484358. [6] HUANG L D, CAI G, YUAN H Y, et al. A hybrid approach for identifying the structure of a Bayesian network model[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2019, 131: 308-320. [7] GAO Y, LI D S, ZHONG H. A novel target threat assessment method based on three-way decisions under intuitionistic fuzzy multi-attribute decision making environment[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 87: 103276. [8] 翟翔宇. 基于全连接神经网络的空战目标威胁评估方法研究[D]. 太原: 中北大学, 2020.ZHAI X Y. Research on threat assessment method of air combat turget based on fully connected neural network[D]. Taiyuan: North University of China, 2020(in Chinese). [9] 郭辉, 徐浩军, 刘凌. 基于回归型支持向量机的空战目标威胁评估[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2010, 36(1): 123-126.GUO H, XU H J, LIU L. Target threat assessment of air combat based on support vector machines for regression[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2010, 36(1): 123-126(in Chinese). [10] ZHAO R J, YANG F B, JI L N. An extended fuzzy CPT-TODIM model based on possibility theory and its application to air target dynamic threat assessment[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 21655-21669. [11] 奚之飞, 徐安, 寇英信, 等. 基于改进GRA-TOPSIS的空战威胁评估[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(2): 388-397.XI Z F, XU A, KOU Y X, et al. Air combat threat assessment based on improved GRA-TOPSIS[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(2): 388-397(in Chinese). [12] 胡涛, 王栋, 孙曜, 等. 基于改进CRITIC-LRA和灰色逼近理想解排序法的空战威胁评估[J]. 兵工学报, 2020, 41(12): 2561-2569. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2020.12.022HU T, WANG D, SUN Y, et al. Air combat threat assessment of improved CRITIC-LRA and grey TOPSIS[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2020, 41(12): 2561-2569(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2020.12.022 [13] 杨爱武, 李战武, 李宝, 等. 基于动态变权重的空战态势评估[J]. 兵工学报, 2021, 42(7): 1553-1563. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2021.07.023YANG A W, LI Z W, LI B, et al. Air combat situation assessment based on dynamic variable weight[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2021, 42(7): 1553-1563(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2021.07.023 [14] ZHANG H, XIE J, SONG Y, et al. A novel ranking method for intuitionistic fuzzy set based on information fusion and application to threat assessment[J]. Iranian Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 2020, 17: 91-104. [15] ZHANG Q, HU J H, FENG J F, et al. Air multi-target threat assessment method based on improved GGIFSS[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 36(5): 4127-4139. [16] MA S D, ZHANG H Z, YANG G Q. Target threat level assessment based on cloud model under fuzzy and uncertain conditions in air combat simulation[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2017, 67: 49-53. [17] 杨远志, 王红卫, 索中英, 等. 基于粗糙集-逼近理想解排序的辐射源威胁排序方法[J]. 兵工学报, 2016, 37(5): 945-952. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2016.05.024YANG Y Z, WANG H W, SUO Z Y, et al. An emitter threat evaluation method based on rough set and TOPSIS[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2016, 37(5): 945-952(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2016.05.024 [18] 张晓雷, 单洁, 王刚. 基于云重心评价法的雷达辐射源威胁评估[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2017, 42(8): 10-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2017.08.003ZHANG X L, SHAN J, WANG G. Research on threat assessment of radar radiation source based on cloud gravity center evaluation method[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2017, 42(8): 10-14(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2017.08.003 [19] 张莹, 王红卫, 陈游. 基于ICW-RCM的辐射源组合威胁评估[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(3): 557-562. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.03.11ZHANG Y, WANG H W, CHEN Y. Combined emitter threat assessment based on ICW-RCM[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(3): 557-562(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.03.11 [20] 徐宇恒, 程嗣怡, 周一鹏, 等. 基于Shapley-TOPSIS的辐射源威胁评估[J]. 空军工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 21(2): 91-96.XU Y H, CHENG S Y, ZHOU Y P, et al. Radiator threat evaluating based on Shapley-TOPSIS[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 21(2): 91-96(in Chinese). [21] 董鹏宇, 王红卫, 陈游. 基于博弈论的GRA-TOPSIS辐射源威胁评估方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(10): 1973-1981.DONG P Y, WANG H W, CHEN Y. GRA-TOPSIS emitter threat assessment method based on game theory[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(10): 1973-1981(in Chinese). [22] 董鹏宇, 王红卫, 陈游. 区间条件下基于GRA和TOPSIS的辐射源威胁评估[J]. 控制与决策, 2021, 36(6): 1516-1522.DONG P Y, WANG H W, CHEN Y. Combining TOPSIS and GRA for emitter threat evaluation with interval number[J]. Control and Decision, 2021, 36(6): 1516-1522(in Chinese). [23] 陈振坤, 程嗣怡, 徐宇恒, 等. 数据缺失下基于IOWA-TOPSIS的辐射源威胁评估[J]. 空军工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 22(1): 105-111.CHEN Z K, CHENG S Y, XU Y H, et al. A radiator threat assessment based on IOWA-TOPSIS under conditions of missing data[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 22(1): 105-111(in Chinese). [24] 黄旭佳. 自适应雷达行为分析与辨识技术研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2015.HUANG X J. Research on analysis and identification techniques for adaptive radar behavior[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2015(in Chinese). [25] 欧健. 多功能雷达行为辨识与预测技术研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2017.OU J. Research on behavior recognition and prediction techniques against multi-function radar[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2017(in Chinese). [26] 肖冰松, 方洋旺, 胡诗国, 等. 一种新的超视距空战威胁评估方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2009, 31(9): 2163-2166. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2009.09.030XIAO B S, FANG Y W, HU S G, et al. New threat assessment method in beyond-the-horizon range air combat[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2009, 31(9): 2163-2166(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2009.09.030 [27] 熊升华, 吴胜, 陈振颂, 等. 广义直觉模糊熵及其在权重确定中的应用[J]. 控制与决策, 2017, 32(5): 845-854.XIONG S H, WU S, CHEN Z S, et al. Generalized intuitionistic fuzzy entropy and its application in weight determination[J]. Control and Decision, 2017, 32(5): 845-854(in Chinese). [28] 张莹, 王红卫, 郭晓陶, 等. IFS-BN结合的辐射源威胁评估方法[J]. 空军工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 18(1): 63-68.ZHANG Y, WANG H W, GUO X T, et al. An assessment method of emitter threat based on intuitional fuzzy sets and Bayesian network[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 18(1): 63-68(in Chinese). -








 下载:
下载: