Thermal control design and verification for high resolution stereo mapping camera system
-
摘要:
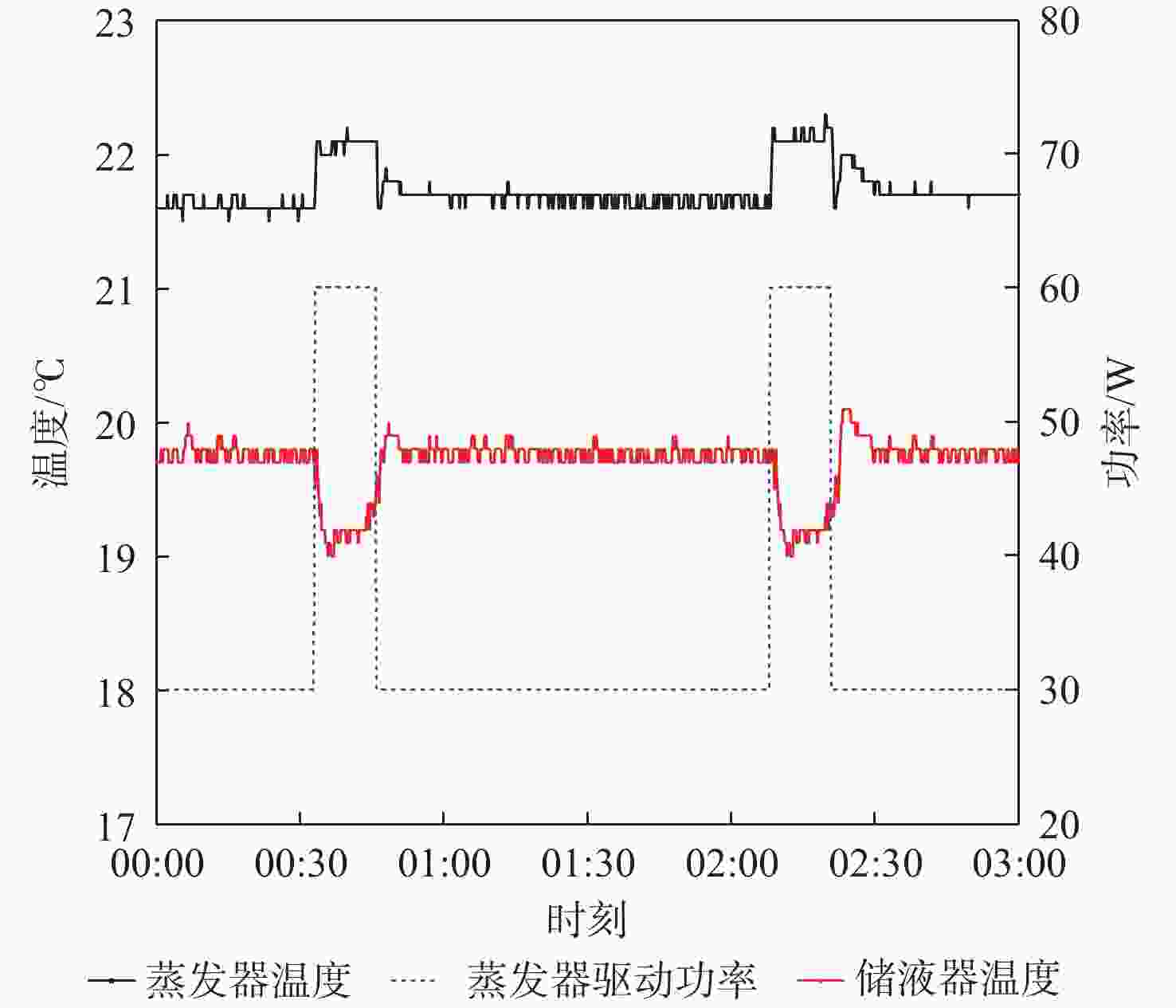
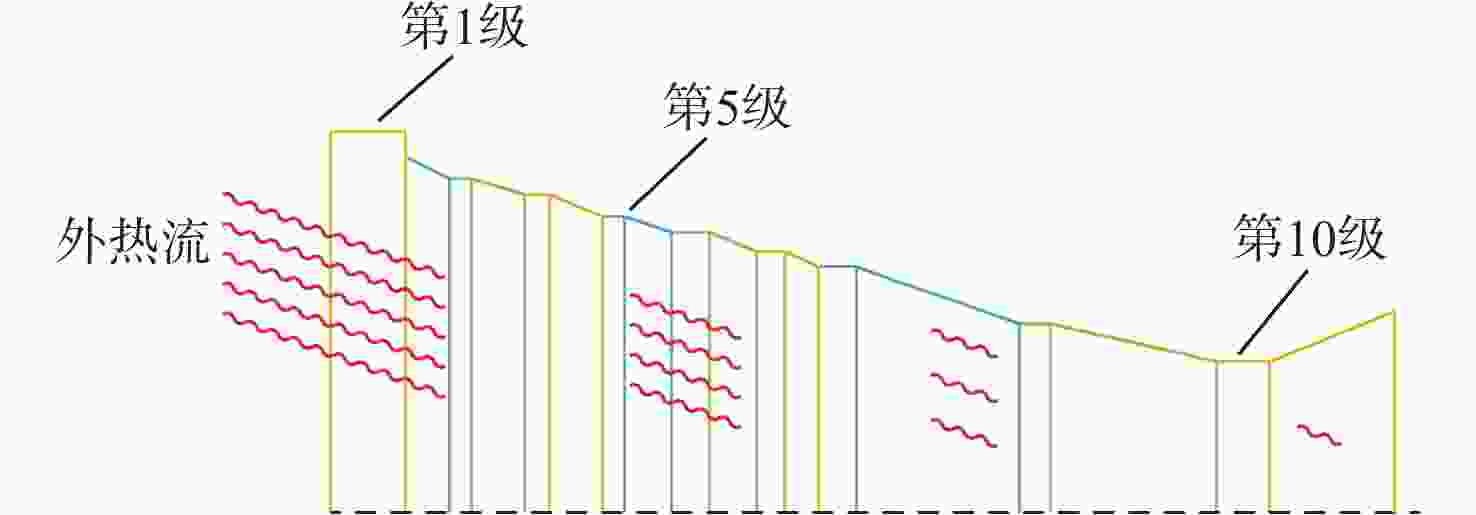
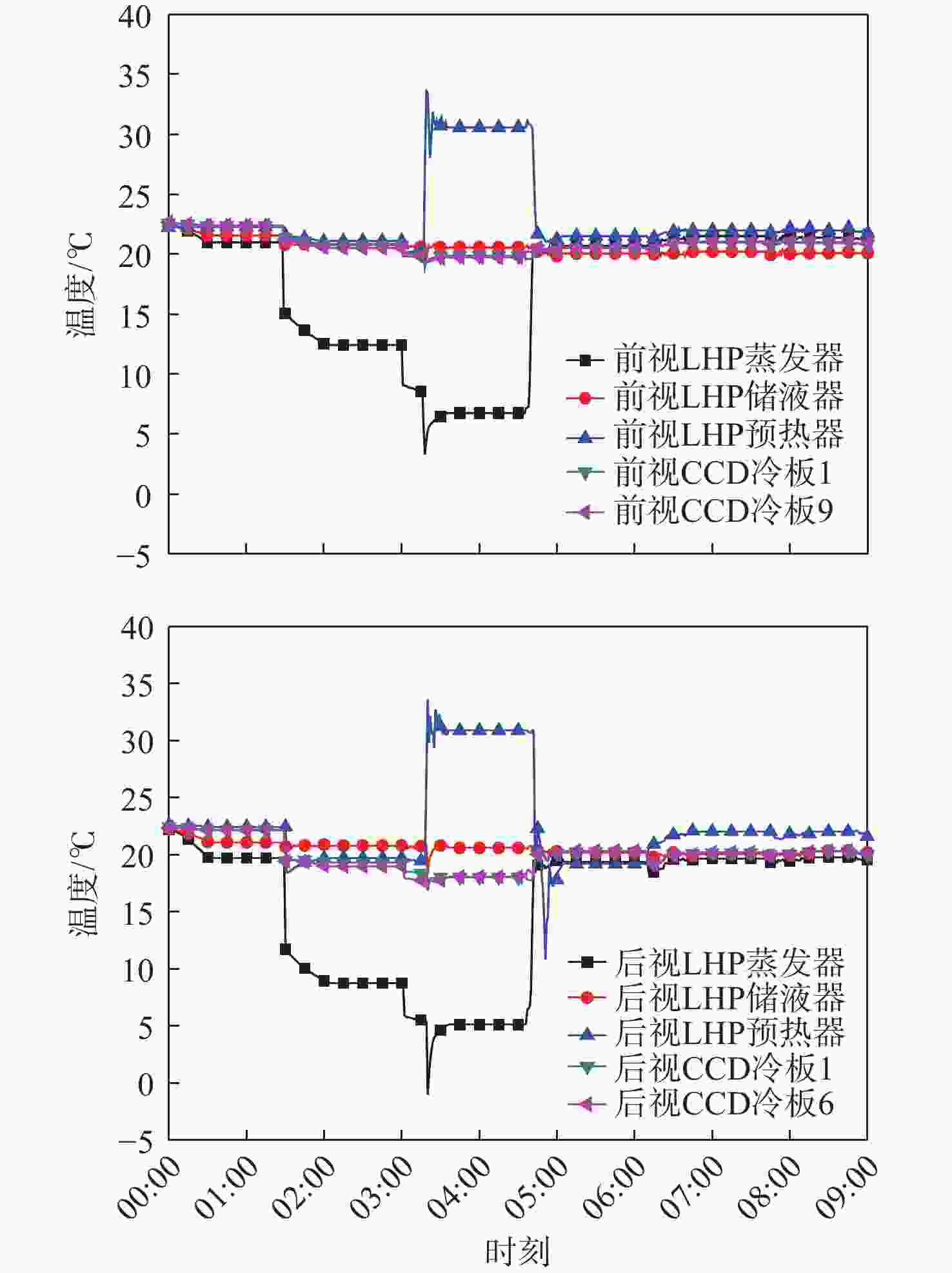
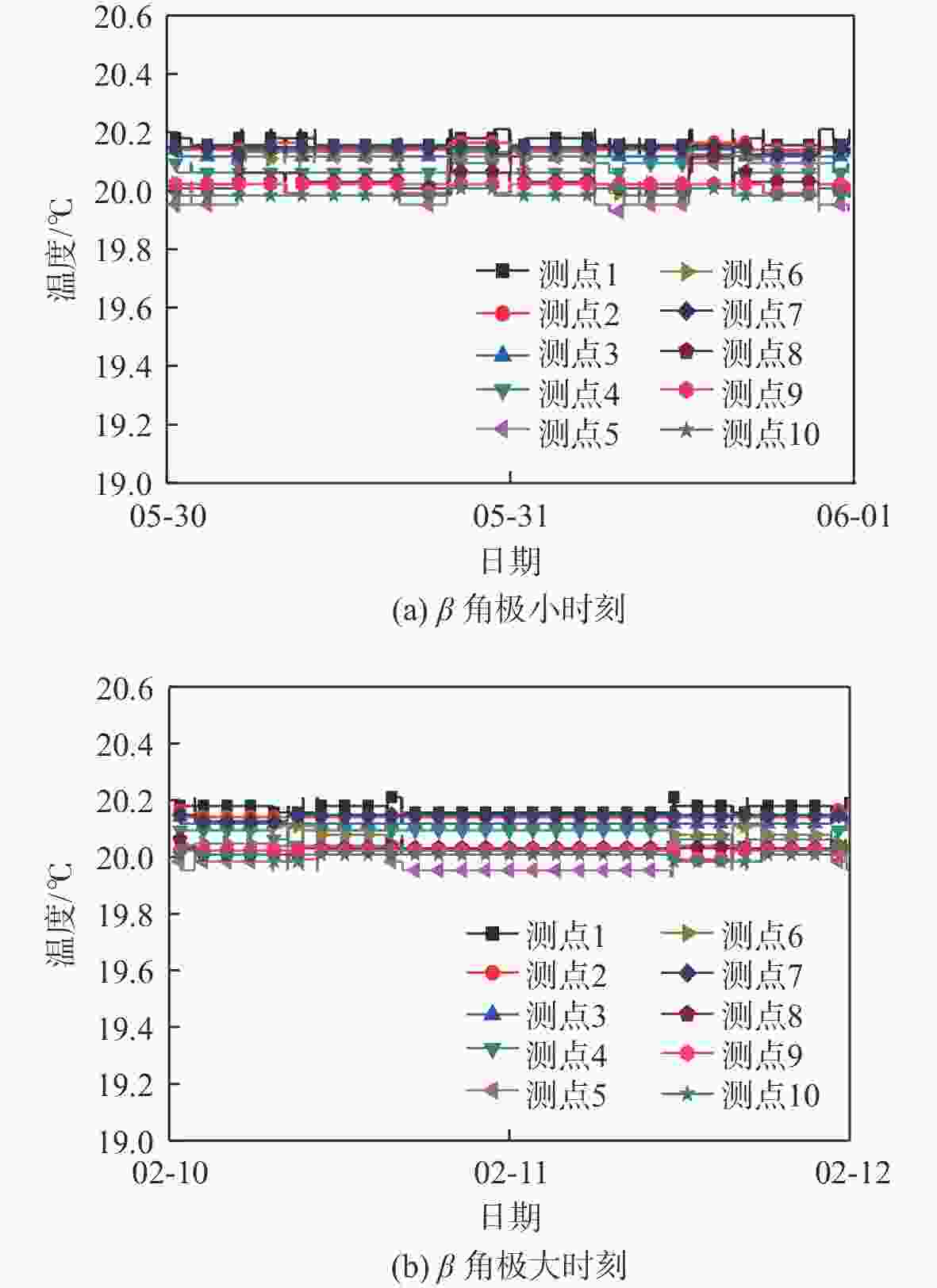
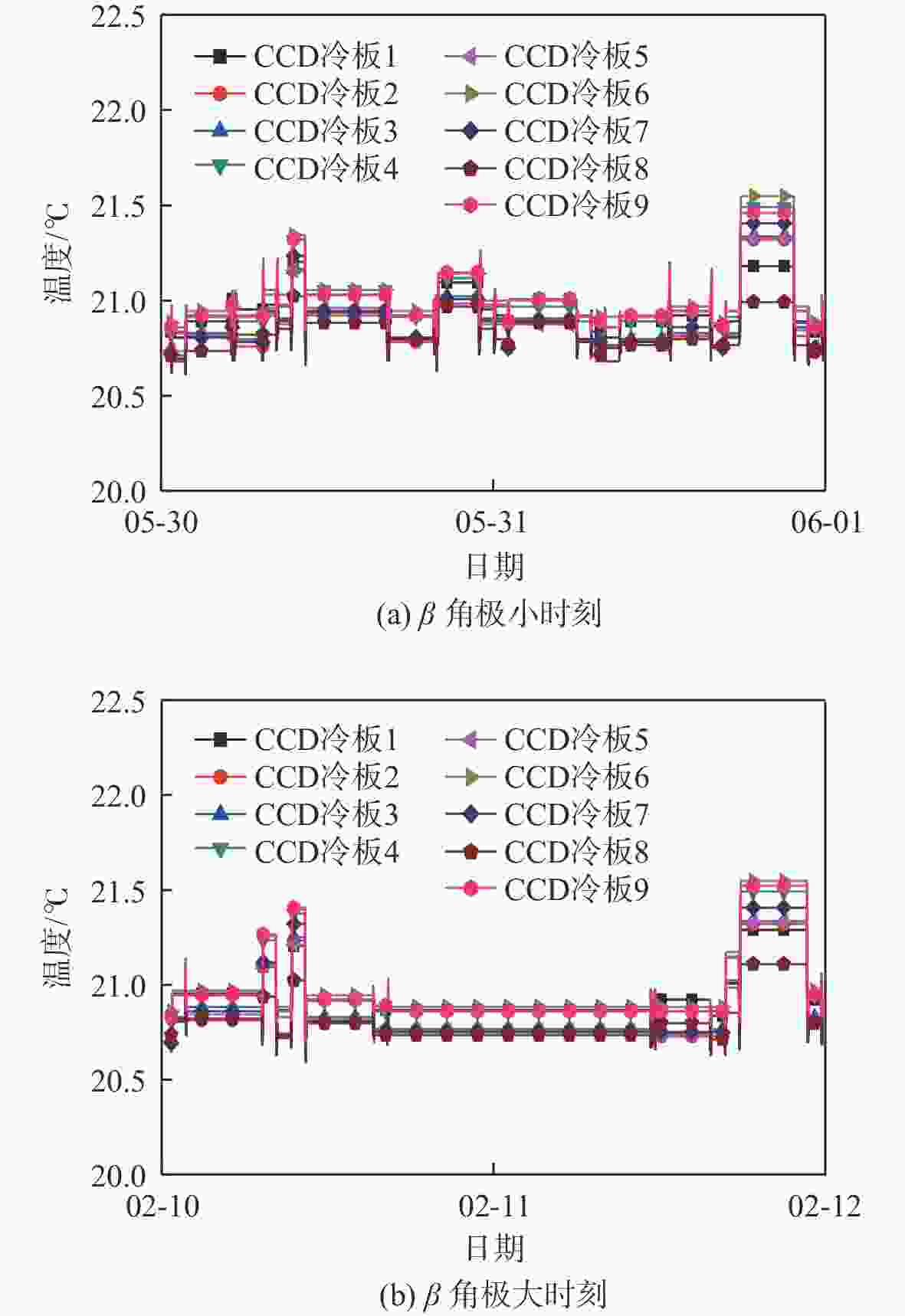
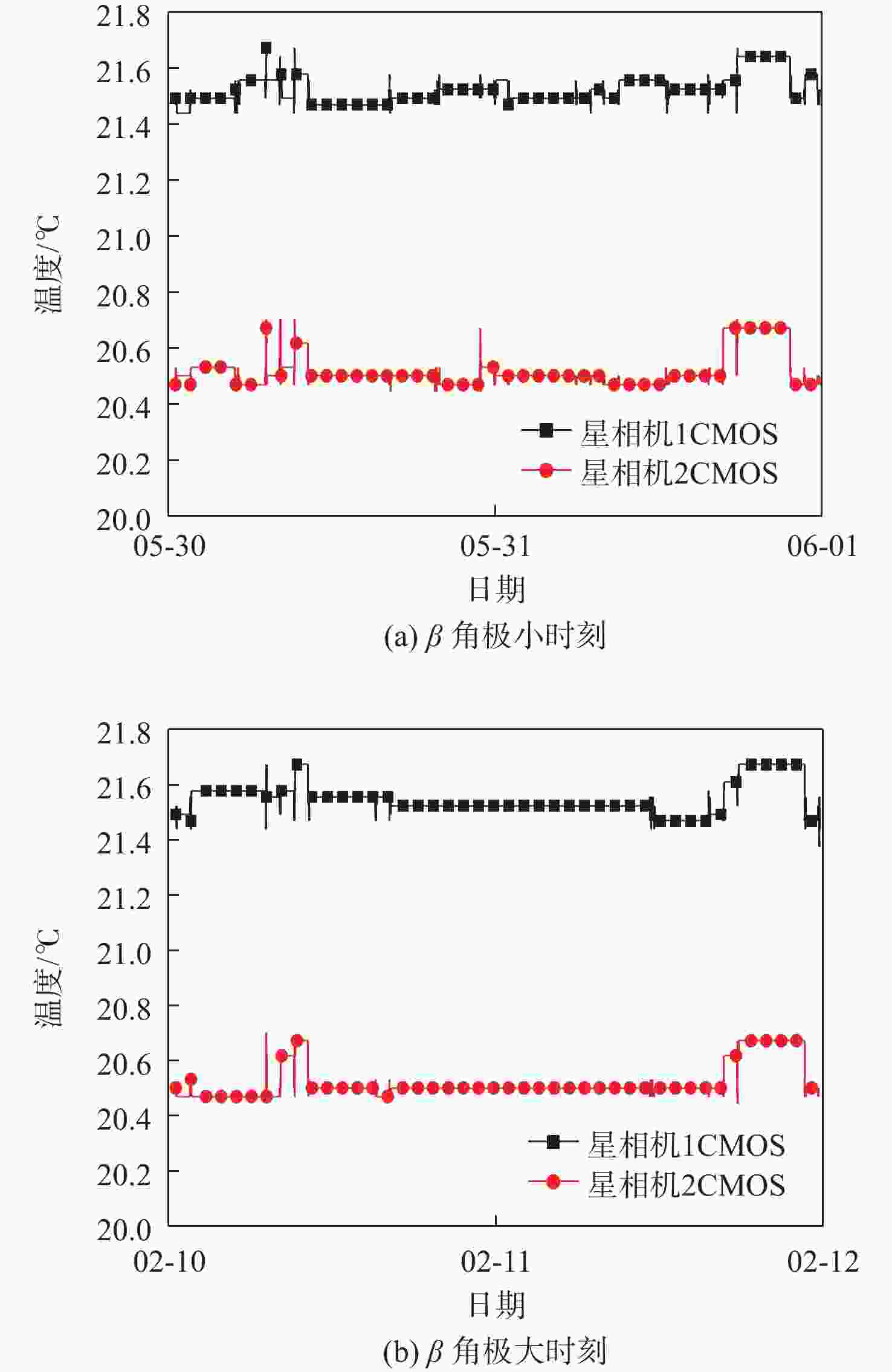
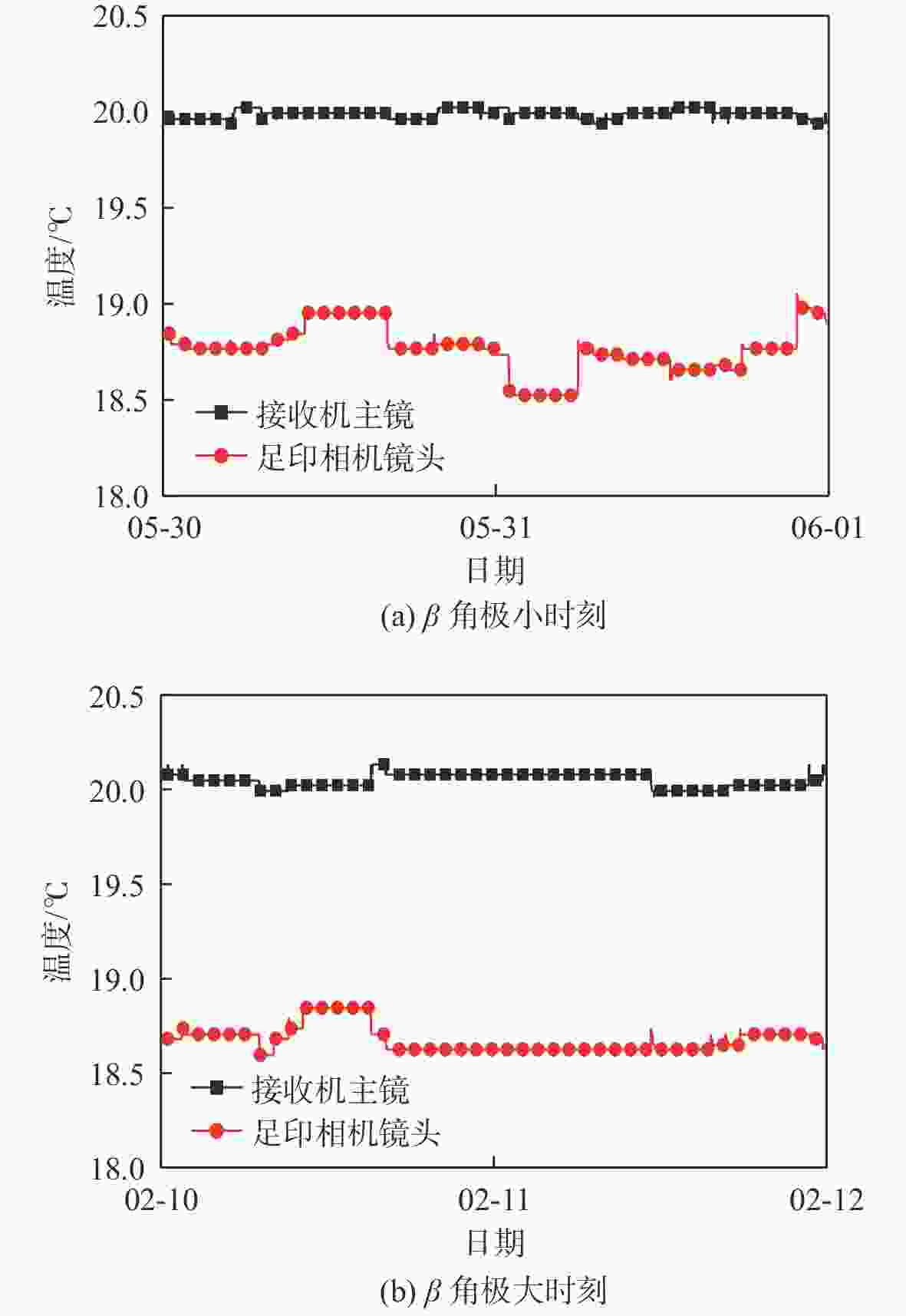
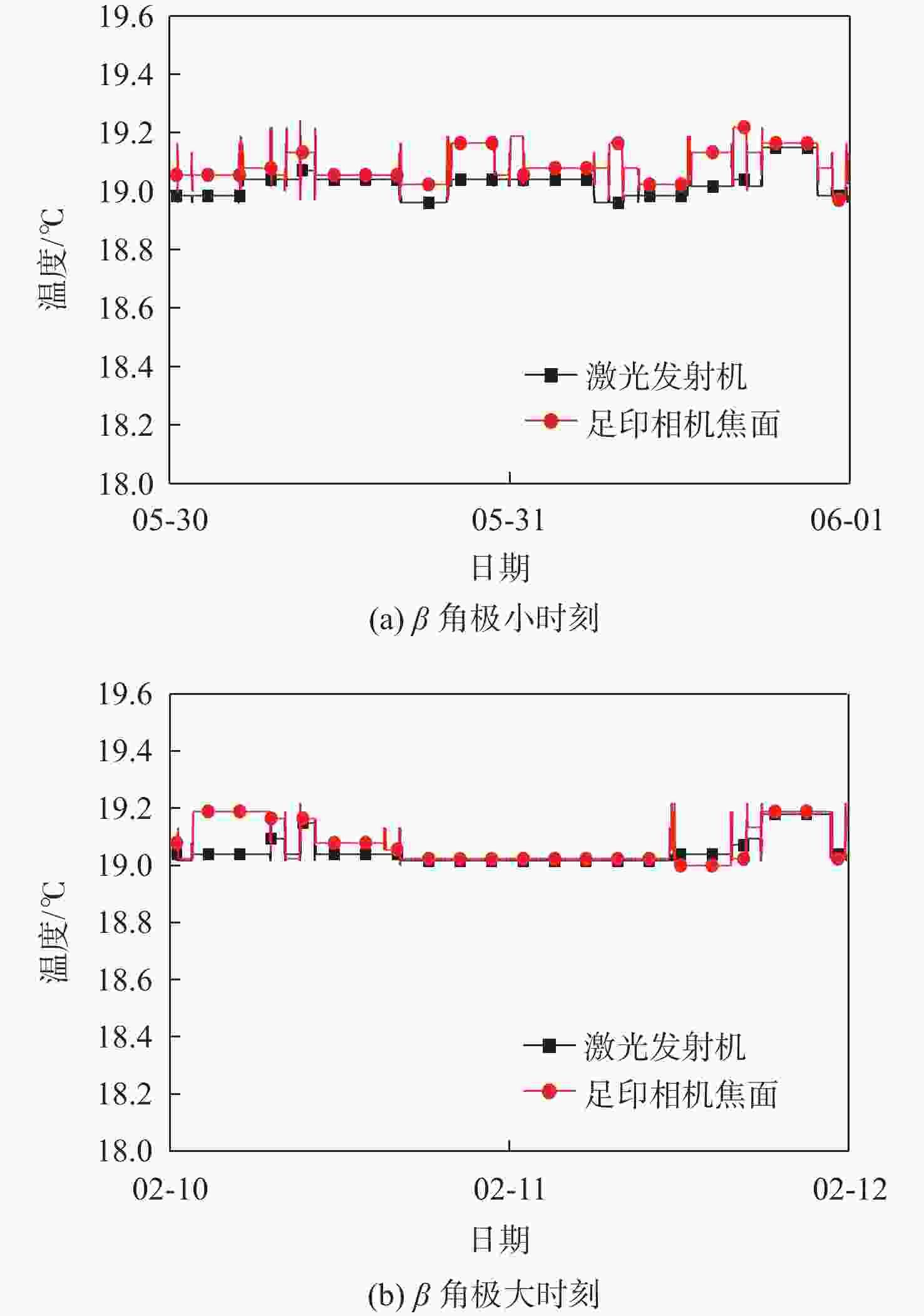
高分辨率立体测绘相机的光学系统及探测器的温度稳定性影响测绘相机的测绘精度。针对透射式光学系统,采用多级外热流抑制技术,使星相机透镜的温度稳定性提高了6倍;针对反射式光学系统,采用间接辐射式控温等热控技术,使主镜、次镜的温度稳定性达到±0.3 ℃;针对大功率电荷耦合元件(CCD),采用基于环路热管(LHP)的节能型控温技术,在满足温度指标的前提下使环路热管驱动功率的周期平均值由60 W降低至33.8 W,同时节省约40%的主冷凝器面积及质量;针对CMOS,采用两级温度波动抑制技术,使其温度稳定性达到±0.3 ℃。研究了地面热试验的方法,报告了测绘相机系统关键部组件在极端空间环境下的在轨数据,全面验证了热控设计方法的正确性。
Abstract:The temperature stability of optical system and detector of high precision stereo mapping camera affects the mapping accuracy of mapping camera. For transmission optical system, multi-stage external heat flow suppression technology is adopted to improve the temperature stability of the star camera lens by 6 times; for reflective optical system, thermal control technologies such as indirect radiation temperature control are adopted to make the temperature stability of the primary and secondary mirrors reach ±0.3 ℃; for high-power charge-coupled device (CCD), energy-saving temperature control technology based on loop heat pipe (LHP) is adopted to make the LHP driving power cycle average from 60 W to 33.8 W, while saving about 40% of the primary condenser area and mass; for CMOS, using two-stage temperature fluctuation suppression technology, the temperature stability is ±0.3 ℃. The method of ground thermal test was investigated, and the flight temperature data of key components of the mapping camera system under extreme space environment were reported, which fully verified the correctness of the thermal control design method.
-
表 1 测绘相机热源工作模式与热耗
Table 1. Operating mode and heat consumption of mapping camera heat source
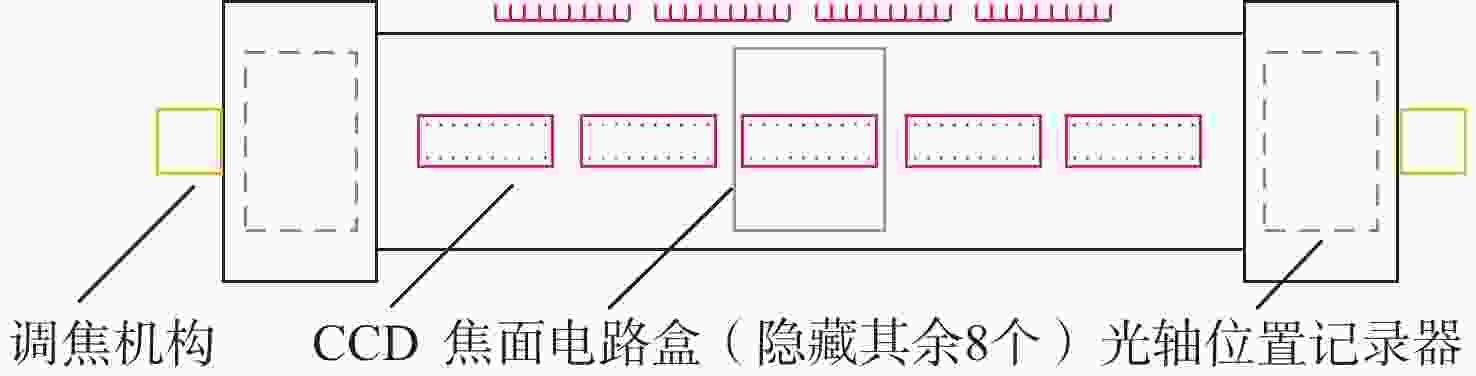
分系统 部组件 单个部组件热耗/W 工作模式/(min·轨−1) 测绘相机 前视CCD 3 8 前视焦面电路 9 8 后视CCD 9 8 后视焦面电路 21 8 坐标测量 星相机CMOS 1 8 星相机焦面电路 36 15 光轴位置记录器 7 15 激光测距 发射机LD阵列 3.7 16 发射机驱动源 67.1 16 接收机APD探测器 4 16 足印相机 30 16 表 2 各部组件温度指标
Table 2. Temperature requirements of each components
分系统 部组件 温度范围/℃ 在轨长期
温度波动/℃测绘相机 主框架 10~22 ±0.5 反射镜 18~22 ±0.25 主承力结构 18~22 ±0.25 CCD 18~22 电路盒 −20~30 坐标测量 星相机透镜 19~21 ±0.25 星相机CMOS 20~27 ±1 激光测距 发射镜头 17~21 发射机腔体 17~21 接收机主、次镜 17~21 APD探测器 14~24 足印镜头 17~21 足印焦面 17~21 主承力结构 14~24 表 3 LHP主要特性参数
Table 3. Main characteristics of LHP
参数 工质
种类质量流量/
(g·s−1)蒸发器
加热功率/W储液器
加热功率/W预热器
加热功率/W前视主冷凝器
面积/m2前视副冷凝器
面积/m2后视主冷凝器
面积/m2后视副冷凝器
面积/m2数值 氨 0.05 60 15 15 0.27 0.20 0.38 0.32 表 4 热平衡试验各部组件温度结果
Table 4. Temperature results of each component in thermal balance test
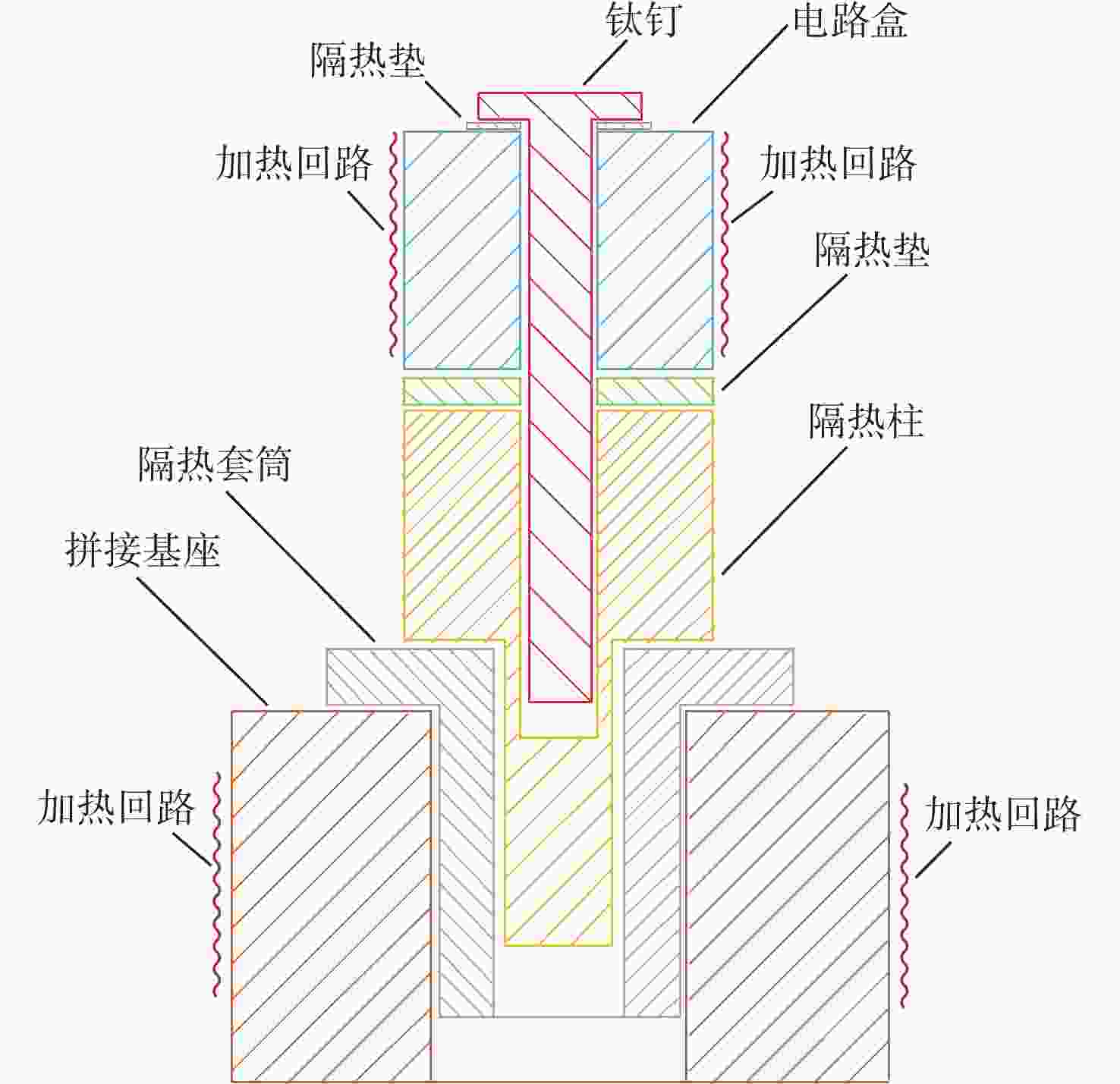
分系统 部组件 试验温度范围/℃ 测绘相机 主框架 16.0~16.3 反射镜 19.7~20.0 主承力结构 20.0~20.2 拼接基座 20.0~20.4 前视CCD 19.6~20.8 电路盒 15.2~19.3 坐标测量 透镜 19.7~20.2 星相机CMOS 21.2~21.8 电路盒 9.0~15.6 激光测距 发射镜头 19.3~20.2 发射机腔体 18.9~19.4 接收机主镜、次镜 19.7~20.2 APD探测器 15.8~20.9 足印镜头 18.2~19.2 足印焦面 18.5~19.6 主承力结构 18.4~19.1 -
[1] 黎明, 吴清文, 江帆, 等. 三线阵立体测绘相机热控系统的设计[J]. 光学精密工程, 2010, 18(6): 1367-1373.LI M, WU Q W, JIANG F, et a1. Design of thermal control system for three-linear array mapping cameras[J]. Optics and Precision Engineering, 2010, 18(6): 1367-1373(in Chinese). [2] 胡莘, 曹喜滨. 三线阵立体测绘卫星的测绘精度分析[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报, 2008, 40(5): 695-699.HU X, CAO X B. Analysis on precision of stereo mapping microsatellite using three-line array CCD images[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2008, 40(5): 695-699(in Chinese). [3] 曹海翊, 刘付强, 赵晨光, 等. 高分辨率立体测绘卫星技术研究[J]. 遥感学报, 2021, 25(7): 1400-1410.CAO H Y, LIU F Q, ZHAO C G, et a1. The study of high resolution stereo mapping satellite[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2021, 25(7): 1400-1410(in Chinese). [4] 赵振明, 孟庆亮, 张焕冬, 等. CCD器件用机械泵驱动两相流体回路仿真与试验[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(5): 893-901. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0519ZHAO Z M, MENG Q L, ZHANG H D, et al. Simulation and experimental study of mechanically pumped two-phase loop for CCD[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(5): 893-901(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0519 [5] CHOI M K. Thermal design to meet stringent temperature gradient/stability requirements of SWIFT BAT detectors: AIAA-2000-2905[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2000. [6] HOANG T T, O’CONNELL T A, KU J, et al. Large area cryocooling for far infrared telescope[C]//Proceedings Volume 5172-Cryogenic Optical Systems and Instruments X. Bellingham: SPIE, 2003, 5172: 77-85. [7] 黄金印, 潘福明, 傅伟纯, 等. 高分七号卫星激光测高仪热设计及验证[J]. 航天器工程, 2020, 29(3): 138-143.HUANG J Y, PAN F M, FU W C, et al. Thermal design and verification of laser altimeter for GF-7 satellite[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2020, 29(3): 138-143(in Chinese). [8] 杨涛, 赵石磊, 高腾, 等. 航天分散热源控温用环路热管设计及飞行应用[J]. 宇航学报, 2021, 42(6): 798-806.YANG T, ZHAO S L, GAO T, et al. Design and in-orbit application of temperature controlled loop heat pipe for aerospace distributed heat sources[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2021, 42(6): 798-806(in Chinese). [9] 杨昌鹏, 赵欣, 辛强. 倾斜轨道星敏感器热控设计及在轨分析[J]. 航天器工程, 2013, 22(6): 59-64.YANG C P, ZHAO X, XIN Q. Thermal design and on-orbit thermal analysis on star sensor of inclined-orbit satellite[J]. Spacecraft Engineering, 2013, 22(6): 59-64(in Chinese). [10] 江帆, 王忠素, 陈立恒, 等. 星敏感器组件的热设计[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2014, 43(11): 3740-3745. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.11.041JIANG F, WANG Z S, CHEN L H, et al. Thermal design of star sensor assembly[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2014, 43(11): 3740-3745(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2014.11.041 [11] 孙鹏, 魏然, 赵欣, 等. 分体式主动像元星敏感器高温度稳定度热设计及在轨验证[J]. 航天器环境工程, 2019, 36(4): 380-386.SUN P, WEI R, ZHAO X, et al. High temperature-stability thermal design of separated type aps star sensor and the on-orbit test[J]. Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2019, 36(4): 380-386(in Chinese). [12] 王伟之, 王妍, 于艳波, 等. 亚角秒级星相机的精度测定[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2018, 47(9): 1605-1609.WANG W Z, WANG Y, YU Y B, et a1. Accuracy determination for sub-arcsec star camera[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2018, 47(9): 1605-1609(in Chinese). [13] 贾永丹, 王伟之, 孙建, 等. 高精度星相机光学系统像质评价及实现[J]. 空间控制技术与应用, 2018, 44(3): 897-906.JIA Y D, WANG W Z, SUN J, et a1. Evaluation and implementation of image quality in high-precision star camera optical system[J]. Aerospace Control and Application, 2018, 44(3): 897-906(in Chinese). [14] 邓永涛, 李旭, 颜凡江. 一种星载激光测距仪姿态的确定方法及误差分析[J]. 航天返回与遥感, 2015, 36(3): 86-91. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2015.03.012DENG Y T, LI X, YAN F J. Attitude determination method and error analysis of spaceborne laser range finder[J]. Spacecraft Recovery & Remote Sensing, 2015, 36(3): 86-91(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2015.03.012 [15] 孟恒辉, 耿利寅, 李国强. 激光通信器热设计与热试验[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2014, 43(7): 2295-2299.MENG H H, GENG L Y, LI G Q. Thermal control design and experiment for laser communication equipment[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2014, 43(7): 2295-2299(in Chinese). [16] 高腾, 杨涛, 赵石磊, 等. 环路热管在低温真空环境下的控温性能试验研究[J]. 航天返回与遥感, 2019, 40(4): 38-47.GAO T, YANG T, ZHAO S L, et al. Experimental research on temperature controlling performance of loop heat pipe in vacuum and low temperature environment[J]. Spacecraft Recovery & Remote Sensing, 2019, 40(4): 38-47(in Chinese). [17] KU J. Operating characteristics of loop heat pipes[C]//29th International Conference on Environmental System, 1999: 1-17. [18] KAYA T, HOANG T T. Mathematical modeling of loop heat pipes and experimental validation[J]. Journal of Thermophysics and Heat Transfer, 1999, 13(3): 314-320. doi: 10.2514/2.6461 [19] MAYDANIK Y F. Loop heat pipes[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2005, 25(5-6): 635-657. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2004.07.010 [20] MAJDANIK Y G, FERSHTATER Y G, PASTUKTOV V G, et al. Thermoregulation of loops with capillary pumping for space use[C]//22nd International Conference on Environmental Systems, 1992: 921169. [21] LAUNAY S, SARTRE V, BONJOUR J. Parametric analysis of loop heat pipe operation: A literature review[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2007, 46(7): 621-636. doi: 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2006.11.007 [22] 沈维道, 蒋智敏, 童钧耕. 工程热力学[M]. 3版. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2006: 205.SHEN W D, JIANG Z M, TONG J G. Engineering thermodynamics[M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2006: 205(in Chinese) . [23] 柏立战, 林贵平, 张红星. 环路热管稳态建模及运行特性分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2006, 32(8): 894-898.BAI L Z, LIN G P, ZHANG H X. Steady state modeling of loop heat pipes and operating characteristics analysis[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2006, 32(8): 894-898(in Chinese). [24] 宋欣阳, 高娟, 赵振明, 等. 间接热控在高分辨率光学遥感器恒温控制中的应用[J]. 航天返回与遥感, 2015, 36(2): 46-52.SONG X Y, GAO J, ZHAO Z M, et a1. Application of indirect thermal control technology for constant temperature control of HR optical remote sensor[J]. Spacecraft Recovery & Remote Sensing, 2015, 36(2): 46-52(in Chinese). [25] 张超, 邢辉, 宋俊儒, 等. 大口径凹椭球面反射镜光轴偏心测量方法[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2021, 50(12): 386-392.ZHANG C, XING H, SONG J R, et al. Measurement of optical axis eccentricity of a large-aperture concave ellipsoid mirror[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2021, 50(12): 386-392 (in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: