-
摘要:
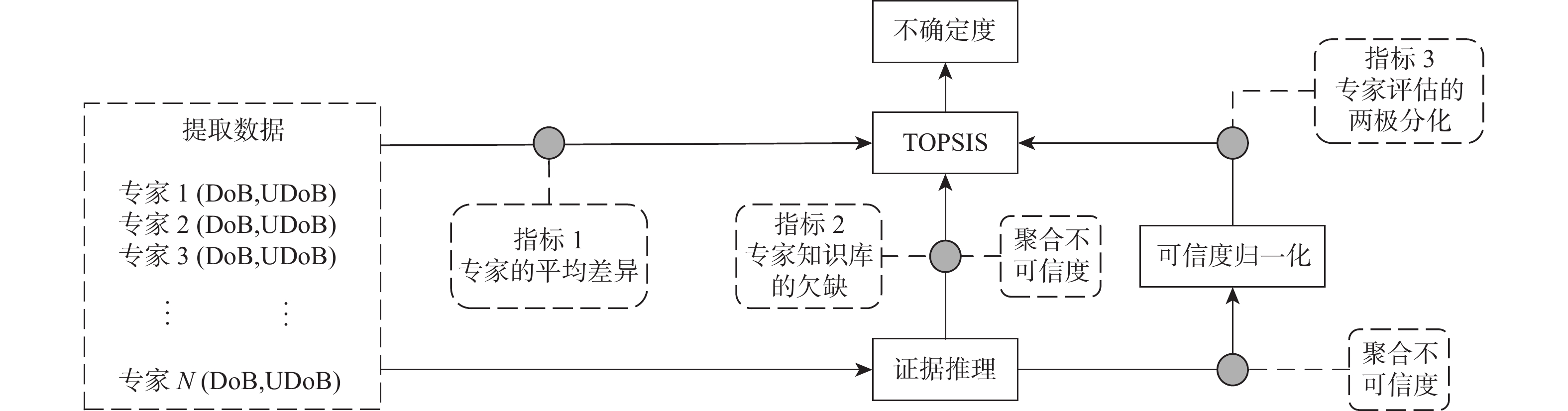
为有效评估航空货运代理人违规行为对航空货物运输的影响,提出一种具有不确定性量化特征的风险评估模型。基于航空货运代理人违规行为的威胁可能性、安全脆弱性、后果严重性构建贝叶斯网络模型;应用专家的平均差异、专家知识库的欠缺及专家评估的两极分化3个不确定性指标量化航空货运代理人违规行为风险评估结果的不确定性。结合深圳宝安国际机场的应用实例,分析航空货运代理人违规行为的风险及风险评估结果的不确定性。结果表明:风险评估结果符合航空货运实际情况,根据风险等级指数和不确定指数确定的航空货运代理人违规行为优先级顺序,为航空公司和机场开启了有序实施风险预防措施的另一个维度。
Abstract:A risk assessment model with quantitative uncertainty features is suggested in order to assess air freight forwarders’ violations on air cargo transportation in an efficient manner. The Bayesian network model is constructed based on the threat possibility, security vulnerability and consequence severity of violations of air freight forwarders. The average difference of experts, the lack of expert knowledge base and the polarization of expert evaluation are used to quantify the uncertainty of risk assessment results of air freight forwarders’ violations. Combined with the application example of Shenzhen Bao’an International Airport, this paper analyzes the risks and uncertainties of risk assessment results of air freight forwarders’ violations. The study’s findings demonstrate that the risk assessment’s conclusions are consistent with the real state of air cargo, and the air freight forwarders’ priority order of violations, which is established based on the risk level and uncertainty indices, offers airlines and airports a new avenue for methodically preventing risks.
-
Key words:
- safety management engineering /
- air freight forwarder /
- violations /
- TOPSIS /
- Bayesian network /
- risk assessment
-
表 1 航空货运代理人违规行为
Table 1. Violations of air freight forwarders
符号 航空货运代理人违规行为 A1 将贵重货物匿报、瞒报、谎报为普通货物 A2 对于需要退运的货物换单重新提交或更换通道提交 A3 不具备危险品运输资质的情况下,提交危险品货物 A4 未按规定粘贴货物标记、标签 A5 蓄意瞒报货物重量 A6 提交的货物运输文件不齐全 A7 申报品名为泛指品名、商品代号 A8 伪造、变造货物运输文件及其他有效证明文件 A9 将危险品匿报、瞒报、谎报为普通货物 A10 在普通货物或快件中夹带违禁品或危险品 A11 代表托运人托运危险品货物 A12 使用过期证件、假证件办理控制区证件或办理货运手续 A13 未按要求包装航空货物 表 2 风险参数的评估状态
Table 2. Evaluation status of risk parameters
参数 评估状态 低 中 高 行为动机 违规行为带来的潜在利益低。实施违规行为对航空货运代理人操作便捷性没有明显影响 违规行为带来的潜在利益适中。实施违规行为使航空货运代理人操作便捷性有提高,但不显著 违规行为带来的潜在利益高。实施违规行为使航空货运代理人操作便捷性显著提高 惩罚力度 检测出违规行为后,航空货运代理人所接受的惩罚力度高 检测出违规行为后,航空货运代理人所接受的惩罚度中等 检测出违规行为后,航空货运代理人所接受的惩罚度低 收运核查 违规行为在收运核查环节依靠现有的技术手段或检查方式被检测的几率很高 违规行为在收运核查环节依靠现有的技术手段或检查方式被检测的几率适中 违规行为在收运核查环节依靠现有的技术手段或检查方式几乎不可能或极难检测 安全检查 违规行为在安全检查环节依靠现有的技术手段或检查方式被检测的几率很高 违规行为在安全检查环节依靠现有的技术手段或检查方式被检测的几率适中 违规行为在安全检查环节依靠现有的技术手段或检查方式几乎不可能或极难检测 财务影响 航空公司或机场经济损失少于10万元。对航空公司或机场的偿付能力或经济流动性产生的负面影响可以忽略不计 航空公司或机场经济损失范围为10万元到100万元。对航空公司或机场的偿付能力或经济流动性有明显的负面影响 航空公司或机场经济损失超过100万元。对航空公司或机场的偿付能力或经济流动性产生重大的负面影响 声誉影响 对航空公司或机场形象无明显损害。对合作伙伴和客户的关系没有明显的影响 对航空公司或机场形象有负面影响,但短期内可恢复。对合作伙伴和客户的关系有显著影响(如收到多次或重大投诉) 严重影响航空公司或机场的形象和信誉。对合作伙伴和客户关系有重大影响(如停止合作、违反合同或协议) 不可信度范围 描述 [0.8,1) 没有经验。影响参数状态和情景发展的关键因素未知或知之甚少,导致在进行评估时严重犹豫 [0.6,0.8) 数据只有在报告中零星提到。对关键的影响因素和相关现象了解甚少;情景的发展难以涵盖,导致在进行评估时出现严重犹豫 [0.4,0.6) 数据可用,但不完整,与当前参数不兼容,或仅限于简短的报告。关键的影响因素和相关现象在一定程度上已被理解,但情景的发展只是一种可疑的推测,导致在给出评估时产生明显的犹豫 [0.2,0.4) 数据可用,与当前参数兼容。可合理地理解关键的影响因素及其相关现象,专家对情景发展的推测较有信心 [0,0.2) 数据可用,与当前参数兼容,并详细记录了关键影响因素和相关现象,专家对情景发展的推测非常有信心 表 4 威胁可能性的评估状态为“低”时风险的条件概率
Table 4. Conditional probability of risk when evaluation status of threat possibility is “low”
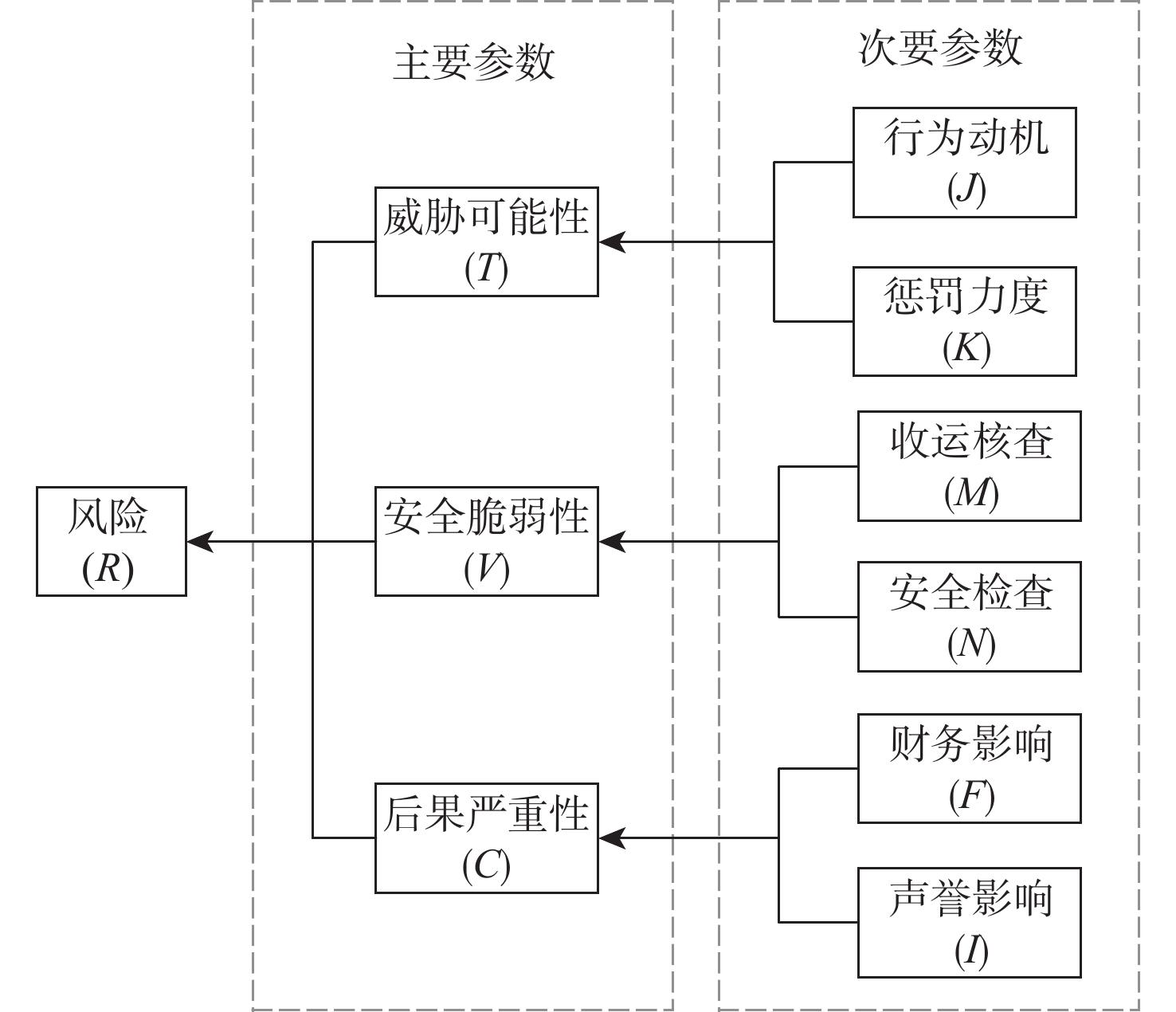
威胁可能性 安全脆弱性 后果严重性 风险 低 中 高 低 中 高 低 中 高 低 中 高 √ √ √ 1 0 0 √ √ √ x+y z 0 √ √ √ x+y 0 z √ √ √ x+z y 0 √ √ √ x y+z 0 √ √ √ x y z √ √ √ x+z 0 y √ √ √ x z y √ √ √ x 0 y+z 表 5 风险参数权重
Table 5. Weight of risk parameters
参数 权重 ωT 0.37 ωV 0.32 ωC 0.31 ωJ 0.59 ωK 0.41 ωM 0.40 ωN 0.60 ωF 0.49 ωI 0.51 表 6 基于不确定指数的航空货运代理人违规行为
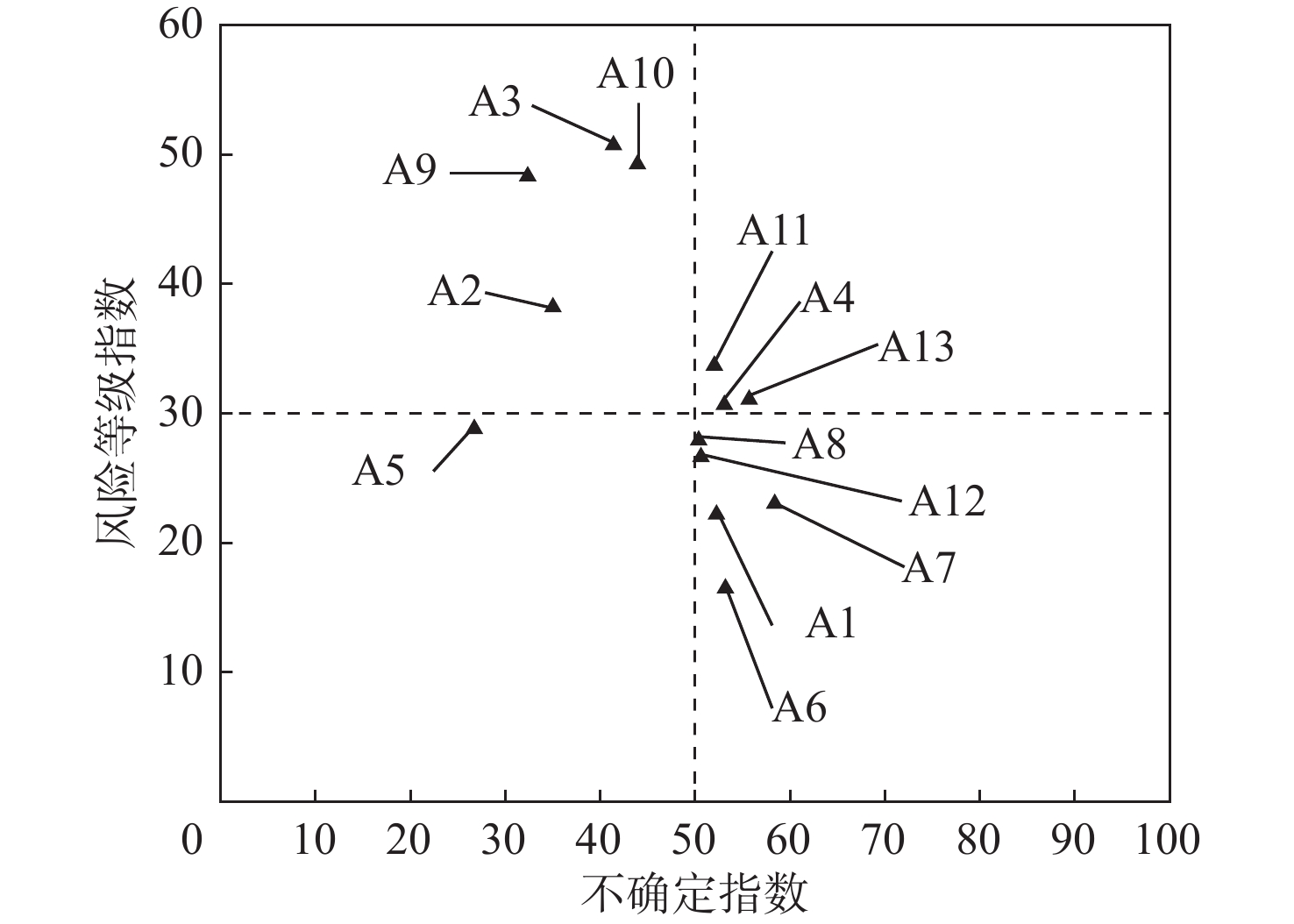
Table 6. Violations of air freight forwarders based on uncertainty index
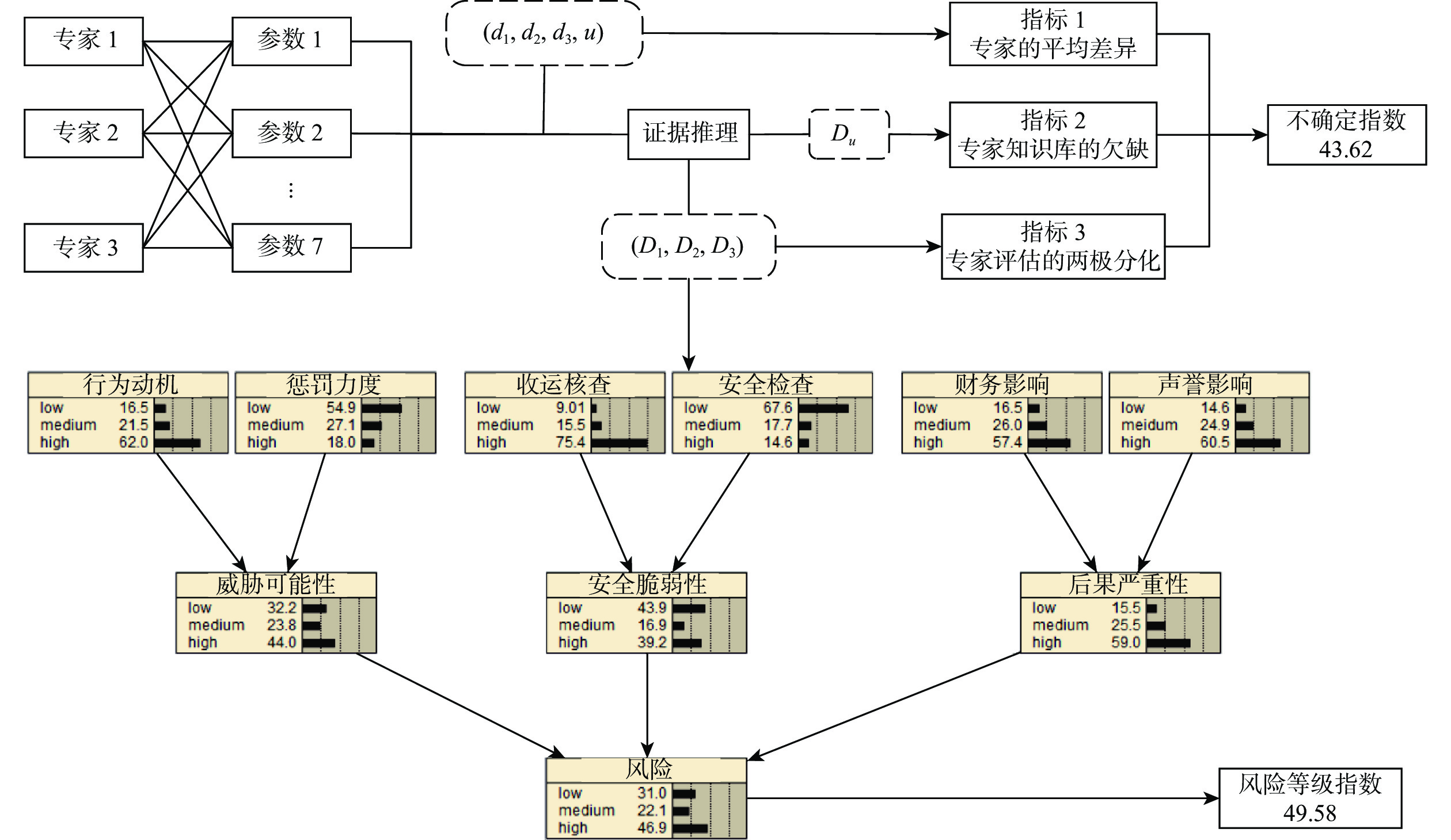
符号 航空货运代理人违规行为 不确定指数 等级 A6 提交的货物运输文件不齐全 60.25 1 A7 申报品名为泛指品名、商品代号 58.37 2 A13 未按要求包装航空货物 55.45 3 A4 未按规定粘贴货物标记、标签 52.70 4 A1 将贵金属货物匿报、瞒报、谎报为普通货物 52.31 5 A11 代表托运人托运危险品货物 51.78 6 A12 使用过期证件、假证件办理控制区证件或办理货运手续 50.64 7 A8 伪造、变造货物运输文件及其他有效证明文件 50.27 8 A10 在普通货物或快件中夹带违禁品或危险品 43.62 9 A3 不具备危险品运输资质的情况下,提交危险品货物 41.17 10 A2 对于需要退运的货物换单重新提交或更换通道提交 34.62 11 A9 将危险品匿报、瞒报、谎报为普通货物 31.95 12 A5 蓄意瞒报货物重量 26.26 13 表 7 基于风险等级指数的航空货运代理人违规行为
Table 7. Violations of air freight forwarders based on risk level index
符号 航空货运代理人违规行为 风险等级指数 等级 A3 不具备危险品运输资质的情况下,提交危险品货物 51.06 1 A10 在普通货物或快件中夹带违禁品或危险品 49.58 2 A9 将危险品匿报、瞒报、谎报为普通货物 48.71 3 A2 对于需要退运的货物换单重新提交或更换通道提交 38.36 4 A11 代表托运人托运危险品货物 33.80 5 A13 未按要求包装航空货物 31.40 6 A4 未按规定粘贴货物标记、标签 30.99 7 A5 蓄意瞒报货物重量 28.96 8 A8 伪造、变造货物运输文件及其他有效证明文件 28.24 9 A12 使用过期证件、假证件办理控制区证件或办理货运手续 27.02 10 A7 申报品名为泛指品名、商品代号 23.22 11 A1 将贵金属货物匿报、瞒报、谎报为普通货物 22.42 12 A6 提交的货物运输文件不齐全 16.81 13 -
[1] KHAN R U, YIN J B, MUSTAFA F S, et al. Analyzing human factor involvement in sustainable hazardous cargo port operations[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 250: 111028. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.111028 [2] ZHAO H L, ZHANG N, GUAN Y. Safety assessment model for dangerous goods transport by air carrier[J]. Sustainability, 2018, 10(5): 1306. doi: 10.3390/su10051306 [3] HSU W K K, HUANG S H S, TSENGW J. Evaluating the risk of operational safety for dangerous goods in airfreights–A revised risk matrix based on fuzzy AHP[J]. Transportation Research Part D: Transport and Environment, 2016, 48: 235-247. doi: 10.1016/j.trd.2016.08.018 [4] 王永刚, 孙瑶. 危险品航空运输事故的改进贝叶斯网络分析[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2010, 10(5): 163-166.WANG Y G, SUN Y. Bayesian networks analysis on the accidents of air transportation of the hazardous goods[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2010, 10(5): 163-166(in Chinese). [5] 陈常美. 销售代理人危险品航空运输风险评价研究[D]. 天津: 中国民航大学, 2016.CHEN C M. Study on risk assessment of air transport of dangerous goods by sales agents[D]. Tianjin: Civil Aviation University of China, 2016(in Chinese). [6] 杜珺, 何家力. 基于社会网络的危险品航空运输违规行为分析[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2018, 14(7): 73-78. doi: 10.11731/j.issn.1673-193x.2018.07.011DU J, HE J L. Analysis on violation behavior in air transportation of dangerous goods based on social network[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2018, 14(7): 73-78(in Chinese). doi: 10.11731/j.issn.1673-193x.2018.07.011 [7] 杨晓乐. 经营人危险品航空运输全流程风险评估研究[D]. 天津: 中国民航大学, 2020.YANG X L. Study on risk assessment of the whole process of air transport of dangerous goods byoperators[D]. Tianjin: Civil Aviation University of China, 2020(in Chinese). [8] 陈晨. 基于故障树分析法的航空运输中隐含危险品安全风险研究[J]. 民航学报, 2022, 6(2): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4994.2022.02.001CHEN C. Research on safety risk of hidden dangerous goods in air transportation based on fault tree analysis[J]. Journal of Civil Aviation, 2022, 6(2): 1-4(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-4994.2022.02.001 [9] 中国民用航空局. 2012年2月至12月危险品航空运输违规行为处罚情况的公告[EB/OL]. (2013-04-12)[2022-07-25].Civil Aviation Administration of China. Announcement on penalties for dangerous goods air transport violations from February to December 2012[EB/OL]. (2013-04-12)[2022-07-25]. [10] 中国民用航空局. 关于2013年危险品航空运输违规行为处罚情况的公告[EB/OL]. (2014-05-21) [2022-07-25].Civil Aviation Administration of China. Announcement on the penalties for dangerous goods air transport violations in 2013[EB/OL]. (2014-05-21) [2022-07-25]. [11] 中国民用航空局. 关于2014年危险品航空运输违规行为处罚情况的公告[EB/OL]. (2015-05-21) [2022-07-25].Civil Aviation Administration of China. Announcement on the penalties for dangerous goods air transport violations in 2014[EB/OL]. (2015-05-21) [2022-07-25]. [12] 中国民用航空局. 关于2015年危险品航空运输违规行为处罚情况的公告[EB/OL]. (2016-05-30) [2022-07-25].Civil Aviation Administration of China. Announcement on the penalties for violations in dangerous goods air transport in 2015[EB/OL]. (2016-05-30) [2022-07-25]. [13] 中国民用航空局.关于2016年危险品航空运输违规行为行政处罚情况的公告[EB/OL].(2017-05-08) [2022-07-25].Civil Aviation Administration of China. Announcement on administrative penalties for violations of dangerous goods air transport in 2016[EB/OL]. (2017-05-08) [2022-07-25]. [14] 中国民用航空局.关于2017年危险品航空运输违规行为行政处罚情况的公告[EB/OL]. (2018-05-04) [2022-07-25].Civil Aviation Administration of China. Announcement on administrative penalties for violations of dangerous goods air transport in 2017[EB/OL]. (2018-05-04) [2022-07-25]. [15] 中国民用航空局. 关于2018年危险品航空运输违规行为行政处罚情况的公告[EB/OL]. (2019-04-30) [2022-07-25].Civil Aviation Administration of China. Announcement on administrative penalties for violations of dangerous goods air transport in 2018[EB/OL]. (2019-04-30) [2022-07-25]. [16] 中国民用航空局. 东北局行政处罚信息统计表(2019年1月至6月)[EB/OL]. (2019-08-13) [2022-09-06].Civil Aviation Administration of China. Statistics of administrative penalties issued by the Northeast Bureau (January to June 2019)[EB/OL]. (2019-08-13) [2022-09-06]. [17] 中国民用航空局. 东北局行政处罚信息统计表(2019年7月至12月)[EB/OL]. (2020-04-02) [2022-09-06].Civil Aviation Administration of China. Statistics of administrative penalties issued by the Northeast Bureau (July-December 2019)[EB/OL]. (2020-04-02) [2022-09-06]. [18] 中国民用航空局. 中国民用航空局关于2020年危险品航空运输违规行为行政处罚情况的公告[EB/OL]. (2021-03-30) [2022-07-25].Civil Aviation Administration of China. Announcement of the Civil Aviation Administration of China on administrative penalties for violations of dangerous goods air transport in 2020[EB/OL]. (2021-03-30) [2022-07-25]. [19] WAN C P, YAN X P, ZHANG D, et al. An advanced fuzzy Bayesian-based FMEA approach for assessing maritime supply chain risks[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2019, 125: 222-240. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2019.03.011 [20] LEVIN R. Uncertainty in risk assessment: Contents and modes of communication[D]. Stockholm: Royal Institute of Technology, 2005. [21] YANG J B, XU D L. On the evidential reasoning algorithm for multiple attribute decision analysis under uncertainty[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part A: Systems and Humans, 2002, 32(3): 289-304. doi: 10.1109/TSMCA.2002.802746 [22] NGUYEN S. A risk assessment model with systematical uncertainty treatment for container shipping operations[J]. Maritime Policy & Management, 2020, 47(6): 778-796. [23] GOERLANDT F, MONTEWKA J. A framework for risk analysis of maritime transportation systems: A case study for oil spill from tankers in a ship-ship collision[J]. Safety Science, 2015, 76: 42-66. doi: 10.1016/j.ssci.2015.02.009 [24] NGUYEN S, CHEN P S L, DU Y Q, et al. An operational risk analysis model for container shipping systems considering uncertainty quantification[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2021, 209: 107362. [25] NGUYEN S, CHEN P S L, DU Y Q, et al. A quantitative risk analysis model with integrated deliberative Delphi platform for container shipping operational risks[J]. Transportation Research Part E: Logistics and Transportation Review, 2019, 129: 203-227. doi: 10.1016/j.tre.2019.08.002 [26] NGUYEN S, WANG H Y. Prioritizing operational risks in container shipping systems by using cognitive assessment technique[J]. Maritime Business Review, 2018, 3(2): 185-206. doi: 10.1108/MABR-11-2017-0029 -







 下载:
下载: