-
摘要:
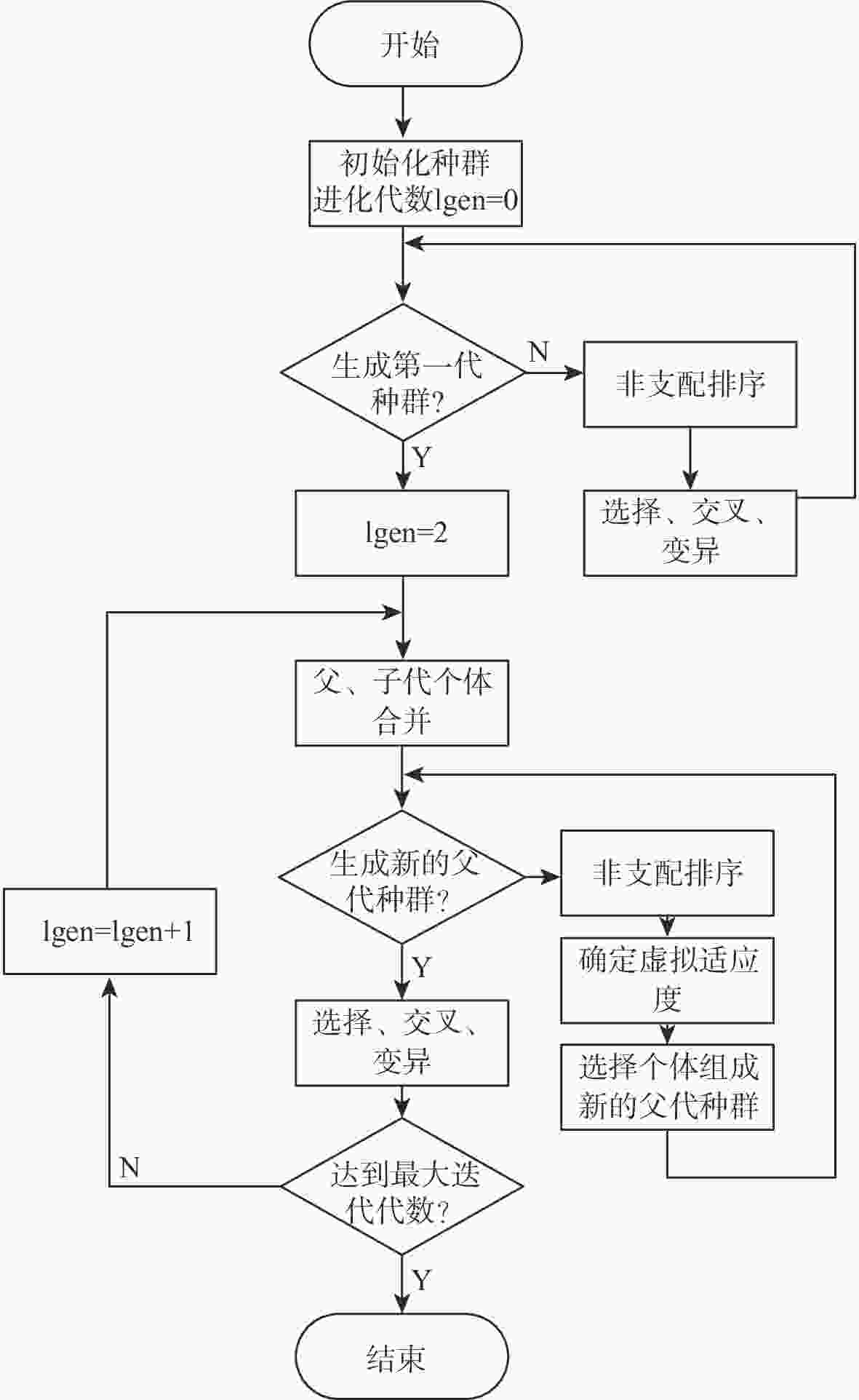
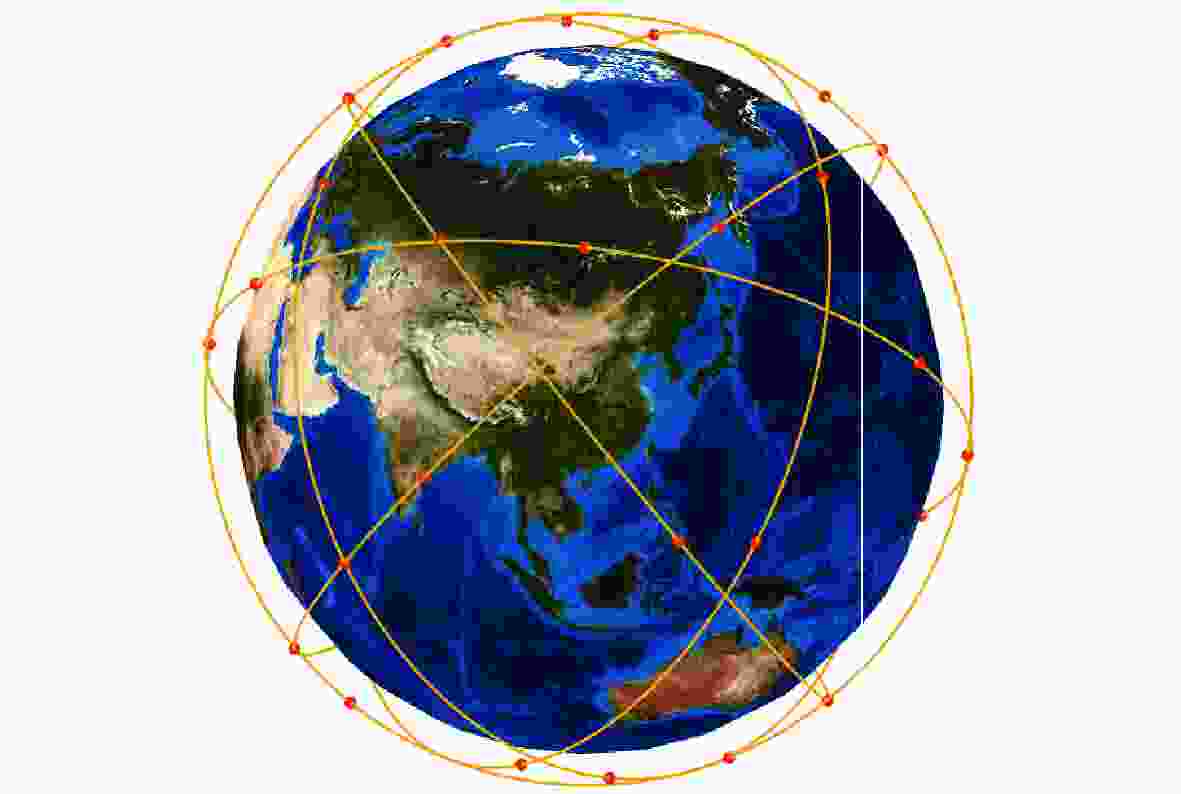
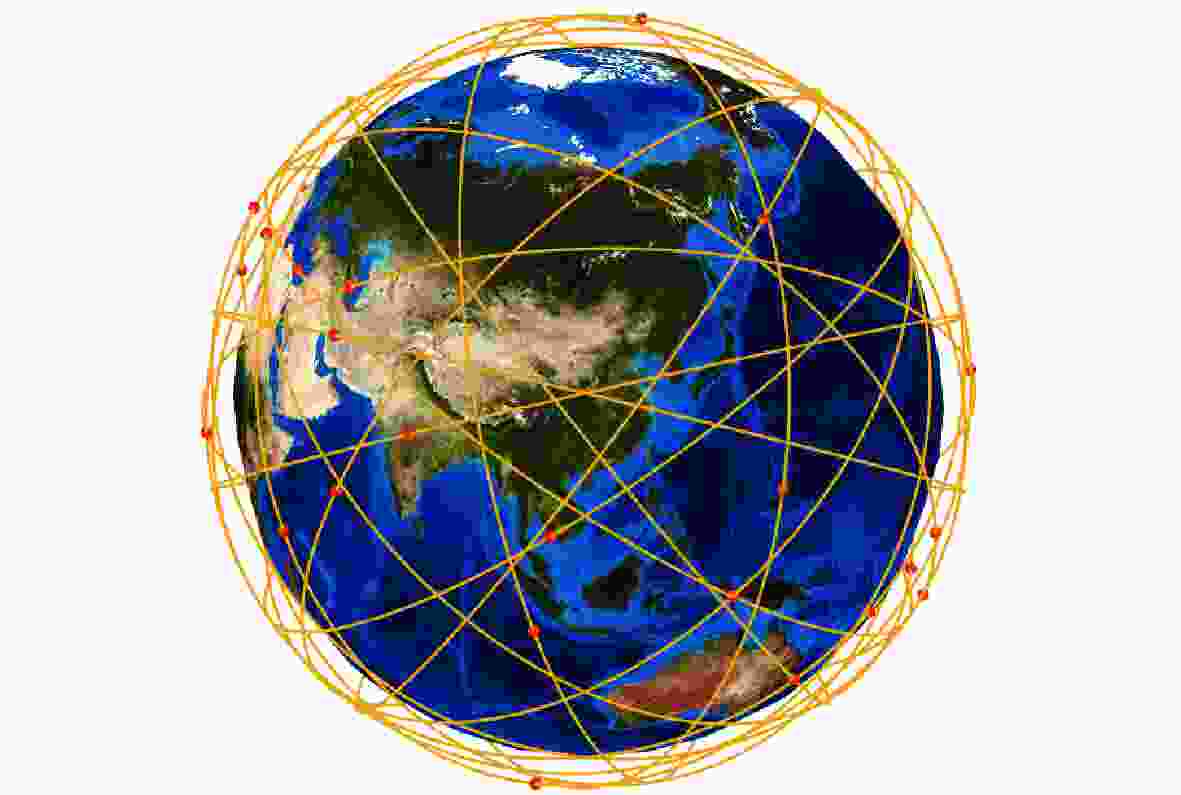
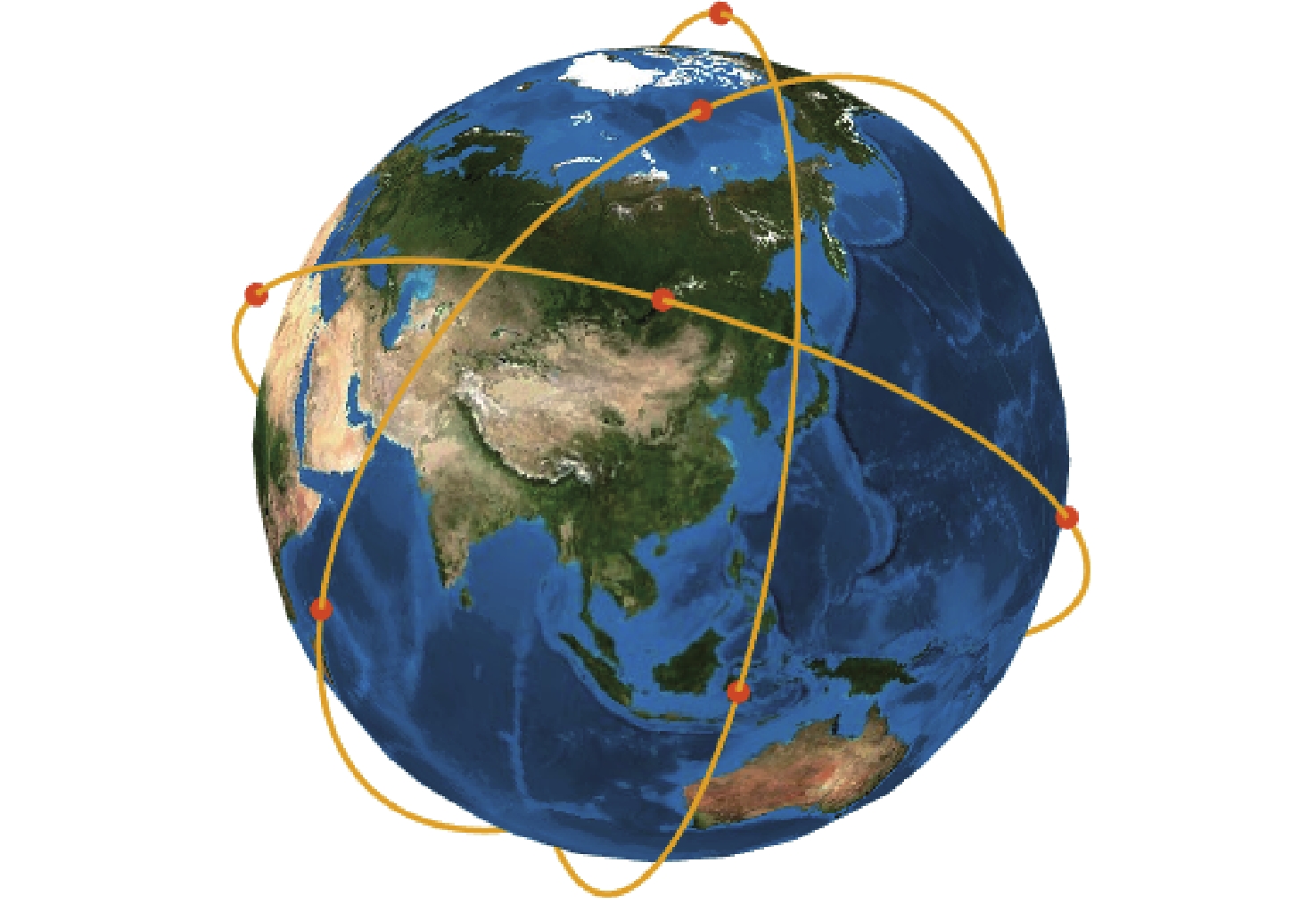
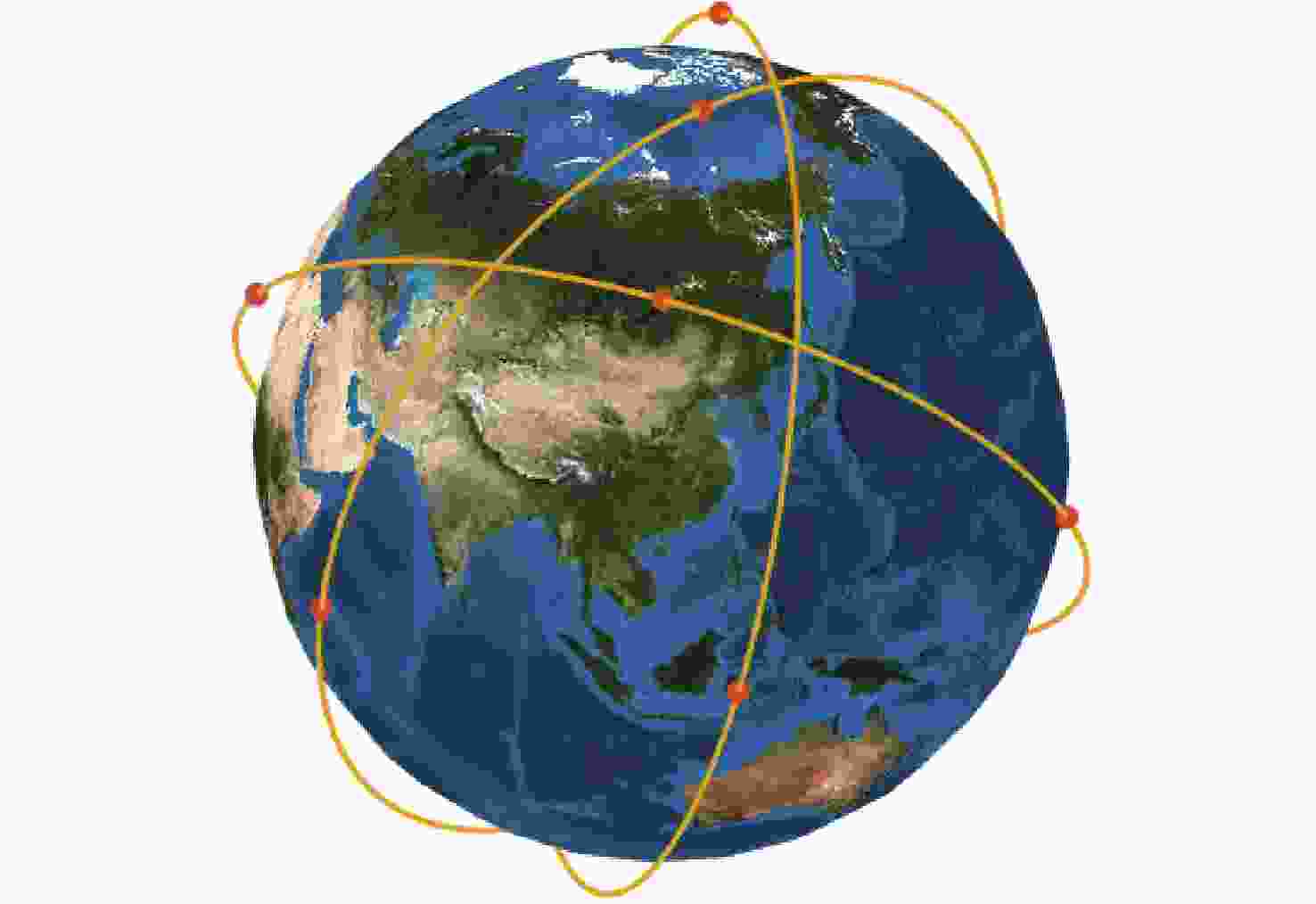
针对遥感卫星星座设计过程中性能-成本的权衡问题和区域覆盖-全球目标覆盖性能权衡问题,提出了一套优化设计方法。对于建设成本和性能间的矛盾,采用多目标优化算法,对成本和性能指标同时进行寻优。优化结果揭示了随着成本增加,性能指标的提升趋势和不同性能指标间可能存在的冲突关系,为星座建设提供依据。为了在增强特定区域的覆盖性能的同时满足全球覆盖性能的一定约束,使用了一种更加灵活的星座模型,并基于非支配排序遗传算法-II(NSGA-II)算法提出适用于此模型的求解方法。结果表明:所提方法在同等的星座规模或成本限制下可达到更好的性能。
Abstract:An ideal design approach is suggested for the trade-offs between performance and cost as well as between regional coverage and worldwide target coverage in the design of a constellation of remote sensing satellites. For the contradiction between construction cost and performance, a multi-objective optimization algorithm is used to optimize the cost and performance at the same time. The optimization results represent the increasing trend of performance and the possible conflicts between different performance indicators as the cost increases. A solution method based on the non-dominated sorting gonetic algorithims-II(NSGA-II) algorithm is suggested for this more flexible constellation model, which is used to meet specific limitations of the global coverage performance and improve the coverage performance of a particular area. The results show that after applying the new constellation model and algorithm, better performance can be achieved under the same constellation size or cost constraints.
-
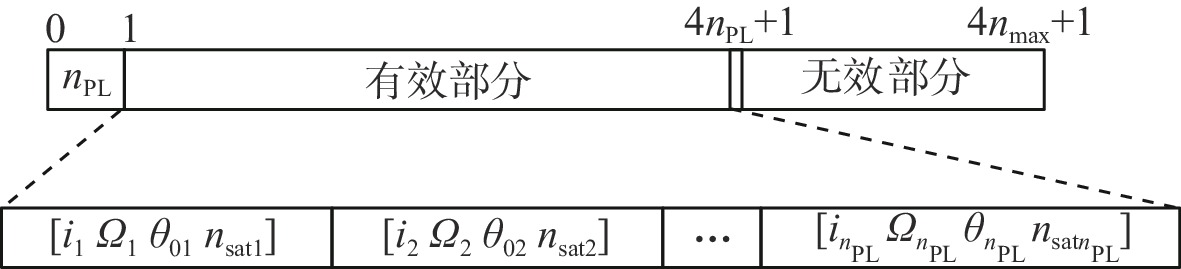
表 1 使用标识符描述变量数的变化(Nmax=6)
Table 1. Variable number of variables represented by bool flags (Nmax=6)
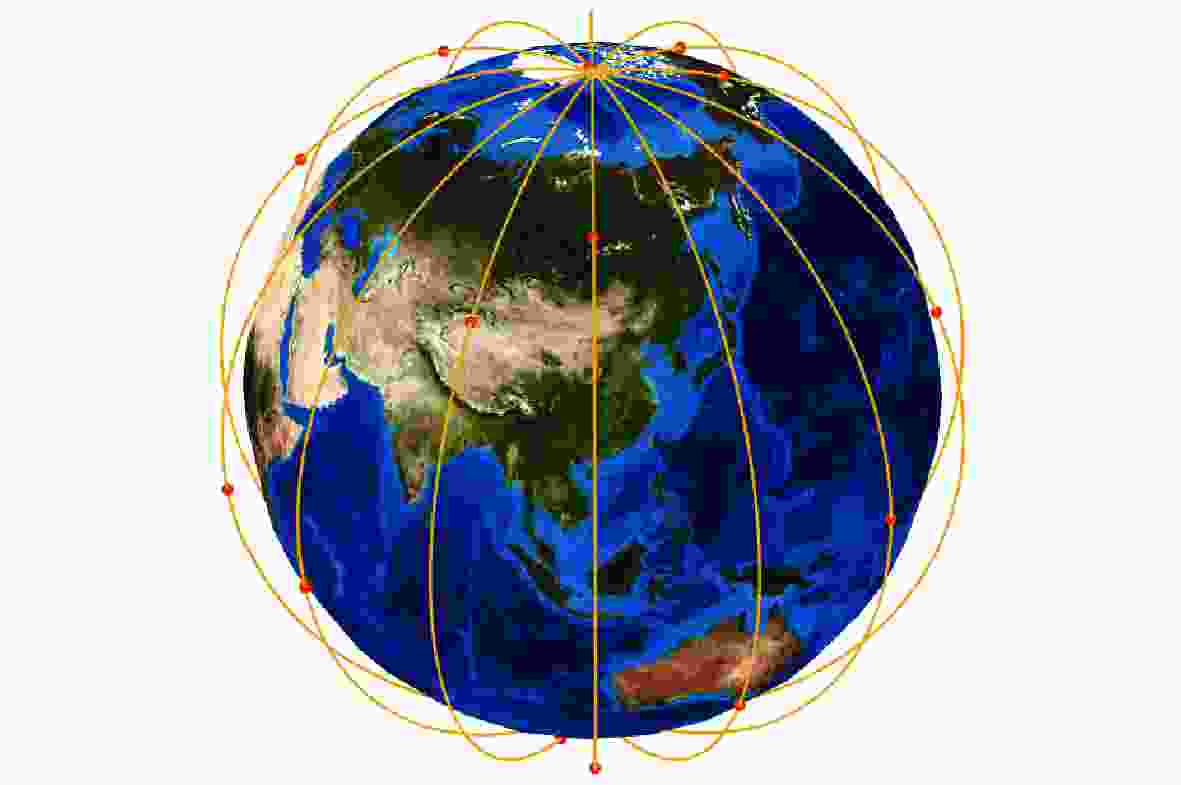
轨道面编号 i/(°) Ω/(°) θ0/(°) nsat B 1 91.86 303.8 63.50 2 TRUE 2 89.11 163.7 279.0 2 FALSE 3 89.42 50.17 339.2 2 TRUE 4 53.28 337.5 40.43 2 TRUE 5 95.18 174.2 208.3 2 FALSE 6 38.55 290.1 22.09 1 FALSE 表 2 目标区域边界
Table 2. Target area boundary
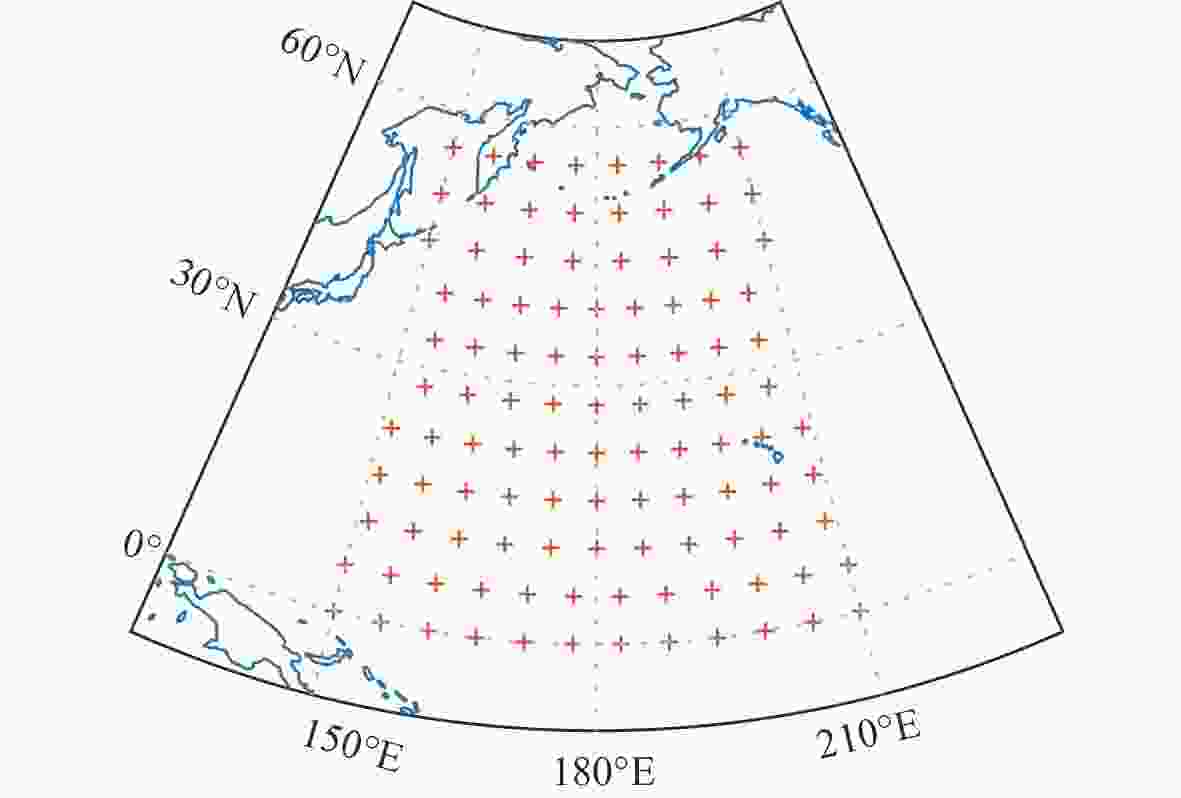
编号 纬度/(°) 经度/(°) 1 28 122 2 28 127 3 32 127 4 32 122 表 3 区域目标网格点信息
Table 3. Area target grid points information
编号 纬度/(°) 经度/(°) 编号 纬度/(°) 经度/(°) 1 28.24 122.8 11 30.09 125.0 2 28.24 123.9 12 30.09 126.1 3 28.24 125.0 13 31.02 122.8 4 28.24 126.1 14 31.02 123.9 5 29.16 122.8 15 31.02 125.0 6 29.16 123.9 16 31.02 126.1 7 29.16 125.0 17 31.94 122.8 8 29.16 126.1 18 31.94 123.9 9 30.09 122.8 19 31.94 125.0 10 30.09 123.9 20 31.94 126.1 表 4 变量取值范围
Table 4. Variable value range
数值 i/(°) Ω/(°) θ0/(°) nsat 最大值 0 0 0 1 最小值 110 360 360 8 表 5 目标区域重访时间
Table 5. Revisit time of target area
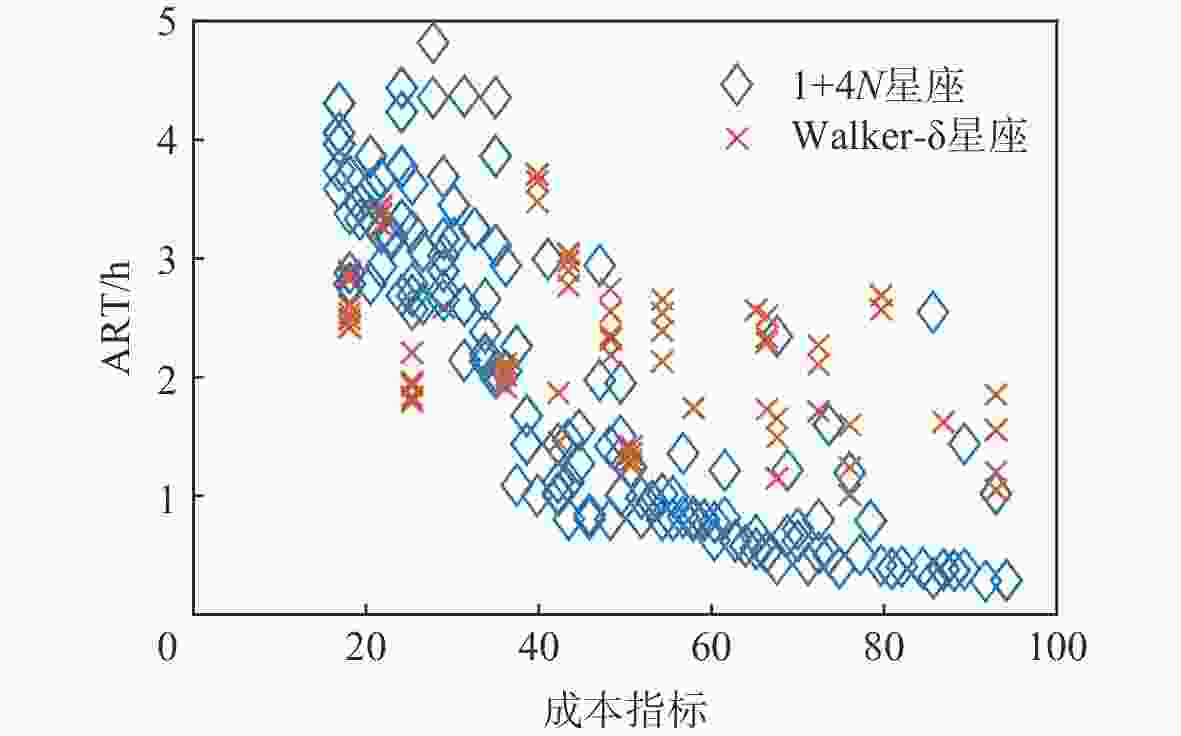
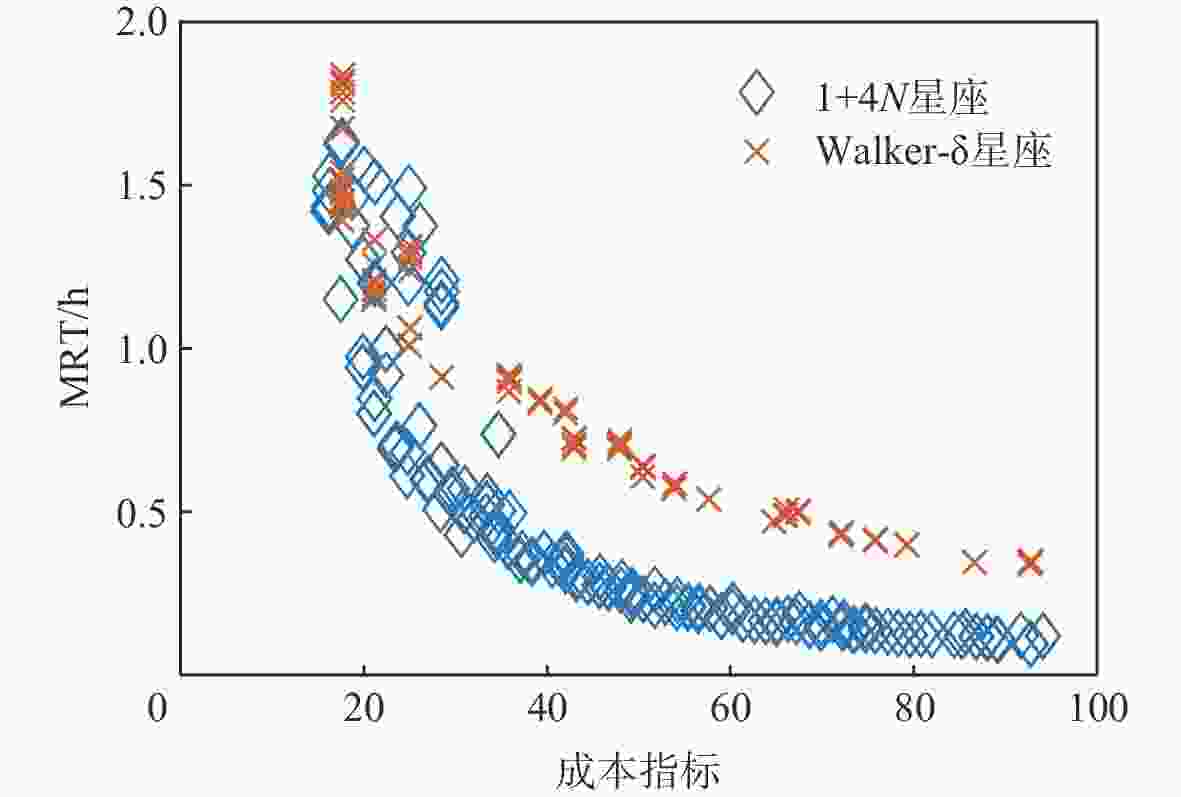
星座模型 卫星个数 成本指标 MRT/h ART/h Walker-δ 21 42.28 1.4201 0.8913 1+4N 23 42.24 1.0247 0.3571 表 6 全球平均重访时间
Table 6. Global average revisit time
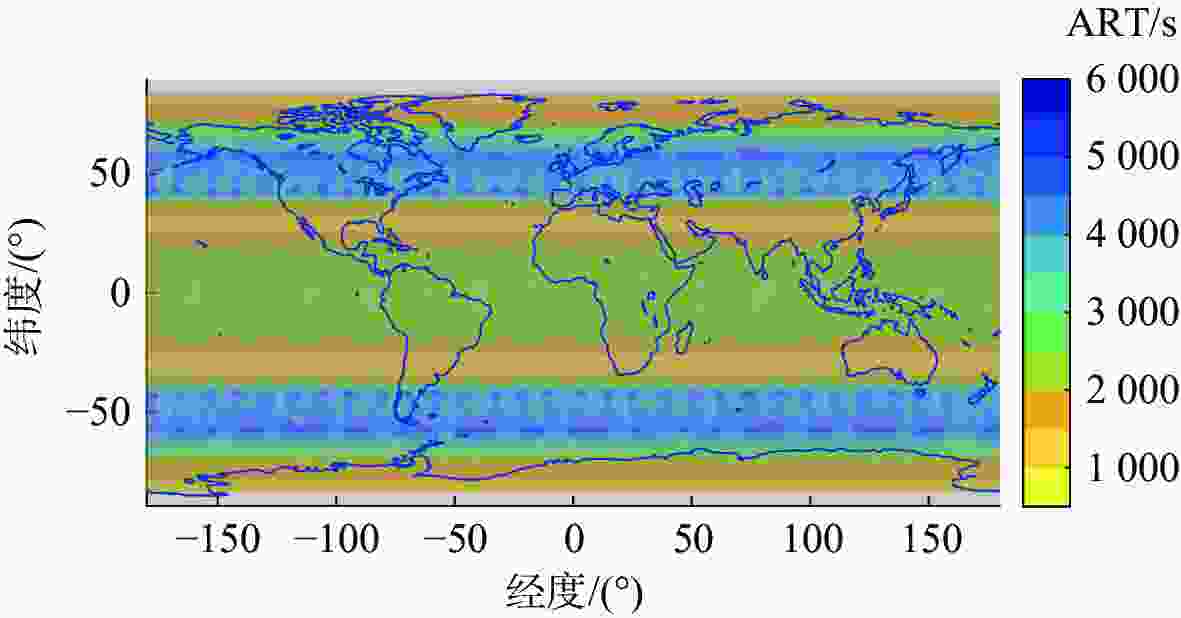
纬度范围 Walker-δ星座 1+4N星座 [−90°, −80°) 0.08 0.38 [−80°, −70°) 0.22 0.49 [−70°, −60°) 0.43 0.93 [−60°, −50°) 0.56 1.19 [−50°, −40°) 0.71 1.10 [−40°, −30°) 0.83 0.48 [−30°, −20°) 0.93 0.45 [−20°, −10°) 1.00 0.62 [−10°, 0°) 1.03 0.67 [0°, 10°) 1.03 0.67 [10°, 20°) 0.99 0.61 [20°, 30°) 0.92 0.43 [30°, 40°) 0.82 0.54 [40°, 50°) 0.70 1.12 [50°, 60°) 0.55 1.20 [60°, 70°) 0.41 0.88 [70°, 80°) 0.21 0.47 [80°, 90°] 0.07 0.38 表 7 较大范围目标区域边界
Table 7. Larger target area boundary
编号 纬度/(°) 经度/(°) 1 0 150 2 60 150 3 60 −150 4 0 −150 表 8 优化设计结果
Table 8. Results of optimization
星座模型 卫星个数 成本指标 MRT/h ART/h Walker-δ 36 65.16 3.1826 0.4907 1+4N 36 65.16 1.2725 0.4376 -
[1] CRISP N H, ROBERTS P C E, LIVADIOTTI S, et al. The benefits of very low earth orbit for earth observation missions[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2020, 117: 100619. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2020.100619 [2] 孙伟伟, 杨刚, 陈超, 等. 中国地球观测遥感卫星发展现状及文献分析[J]. 遥感学报, 2020, 24(5): 479-510. doi: 10.11834/jrs.20209464SUN W W, YANG G, CHEN C, et al. Development status and literature analysis of China’s earth observation remote sensing satellites[J]. National Remote Sensing Bulletin, 2020, 24(5): 479-510 (in Chinese). doi: 10.11834/jrs.20209464 [3] 陈全, 杨磊, 郭剑鸣, 等. 低轨巨型星座网络: 组网技术与研究现状[J]. 通信学报, 2022, 43(5): 177-189.CHEN Q, YANG L, GUO J M, et al. LEO mega-constellation network: Networking technologies and state of the art[J]. Journal on Communications, 2022, 43(5): 177-189 (in Chinese). [4] 王许煜, 胡敏, 赵玉龙, 等. 中轨道Walker导航星座在轨备份方案优化设计[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2021, 41(1): 91-99.WANG X Y, HU M, ZHAO Y L, et al. Optimization of in-orbit backup scheme for medium orbit Walker navigation constellation[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2021, 41(1): 91-99 (in Chinese). [5] 王瑞, 马兴瑞, 李明. 采用遗传算法进行区域覆盖卫星星座优化设计[J]. 宇航学报, 2002, 23(3): 24-28.WANG R, MA X R, LI M. Optimization of regional coverage satellite constellations by genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2002, 23(3): 24-28 (in Chinese). [6] HAN Y, WANG L, FU W J, et al. LEO navigation augmentation constellation design with the multi-objective optimization approaches[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2021, 34(4): 265-278. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2020.09.005 [7] ZHENG C, ZHAO B, GUO D X. A local high-capacity LEO satellite constellation design based on an improved NSGA-II algorithm[M]. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2021: 391-403. [8] YAN D W, LIU C, YOU P, et al. Multi-objective optimization design of extended Walker constellation for global coverage services[C]// 2016 2nd IEEE International Conference on Computer and Communications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1309-1313. [9] MEZIANE-TANI I, MÉTRIS G, LION G, et al. Optimization of small satellite constellation design for continuous mutual regional coverage with multi-objective genetic algorithm[J]. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, 2016, 9(4): 627. doi: 10.1080/18756891.2016.1204112 [10] HITOMI N, SELVA D. Constellation optimization using an evolutionary algorithm with a variable-length chromosome[C]// 2018 IEEE Aerospace Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1-12. [11] 王浩, 张占月, 张海涛, 等. 多等级区域侦察弹性星座设计方法[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2021, 41(4): 85-94.WANG H, ZHANG Z Y, ZHANG H T, et al. Design method of multi-level regional reconnaissance elastic constellation[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2021, 41(4): 85-94 (in Chinese). [12] 李怀建, 韦彦伯, 杜小菁. 基于遗传算法的低轨导航星座构形优化设计[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2021, 41(4): 74-78.LI H J, WEI Y B, DU X Q. LEO Navigation constellation configuration optimization based on genetic algorithm[J]. Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2021, 41(4): 74-78 (in Chinese). [13] 沈欣, 刘钰霖, 李仕学, 等. 一种基于改进PSO算法的高时间分辨率遥感卫星星座优化设计方法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2018, 43(12): 1986-1993.SHEN X, LIU Y L, LI S X, et al. An optimization design method for high temporal resolution remote sensing satellite constellation based on improved PSO algorithm[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2018, 43(12): 1986-1993 (in Chinese). [14] DEB K, PRATAP A, AGARWAL S, et al. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(2): 182-197. doi: 10.1109/4235.996017 [15] 路艳雪, 赵超凡, 吴晓锋, 等. 基于改进的NSGA-Ⅱ多目标优化方法研究[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2018, 35(6): 1733-1737.LU Y X, ZHAO C F, WU X F, et al. Multi-objective optimization method research based on improved NSGA-Ⅱ[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2018, 35(6): 1733-1737 (in Chinese). [16] 戴光明, 王茂才. 多目标优化算法及在卫星星座设计中的应用[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2009.DAI G M, WANG M C. Multi-objective optimization algorithm and its application in satellite constellation design[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2009 (in Chinese). [17] GOLDBERG D E, KORB B, DEB K. Messy genetic algorithms: Motivation, analysis, and first results[J]. Complex Systems, 1989, 3(3): 493-530. -






 下载:
下载: