-
摘要:
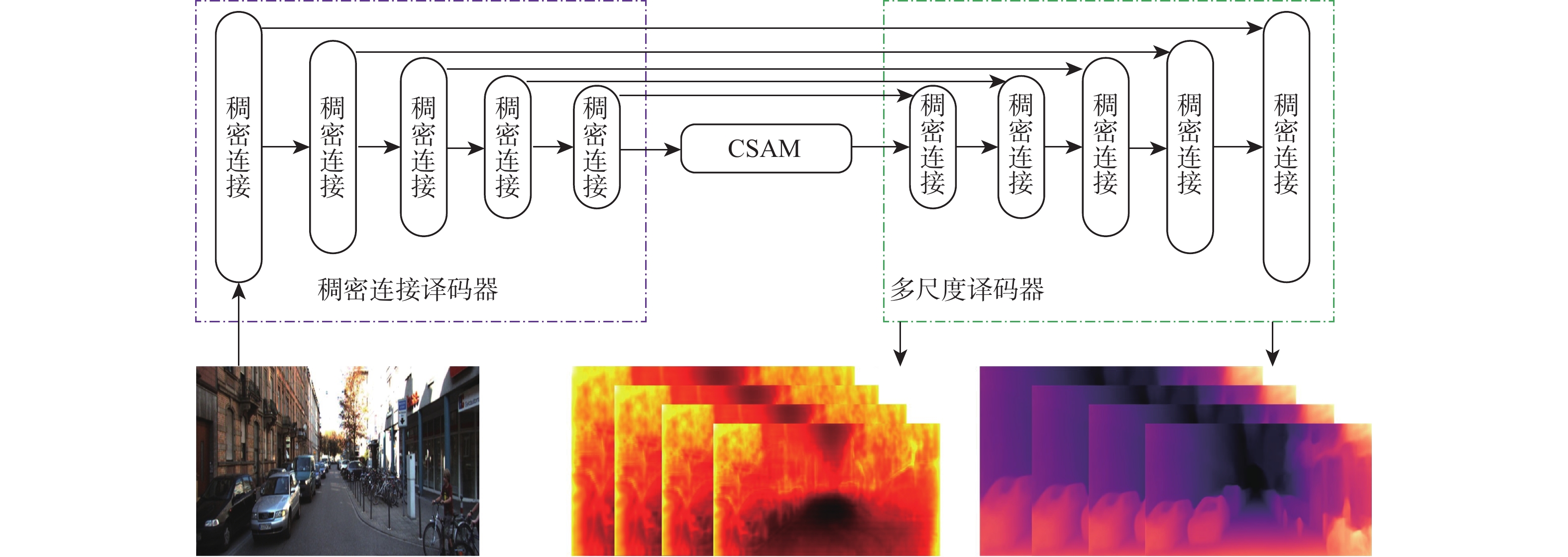
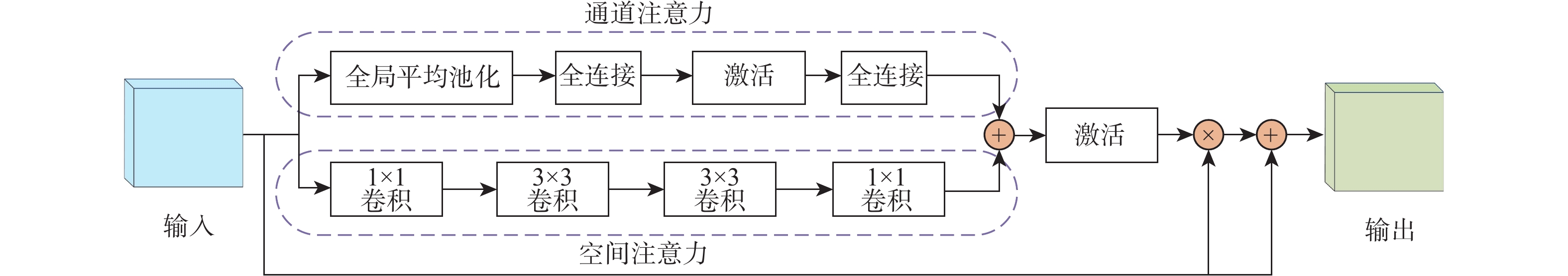
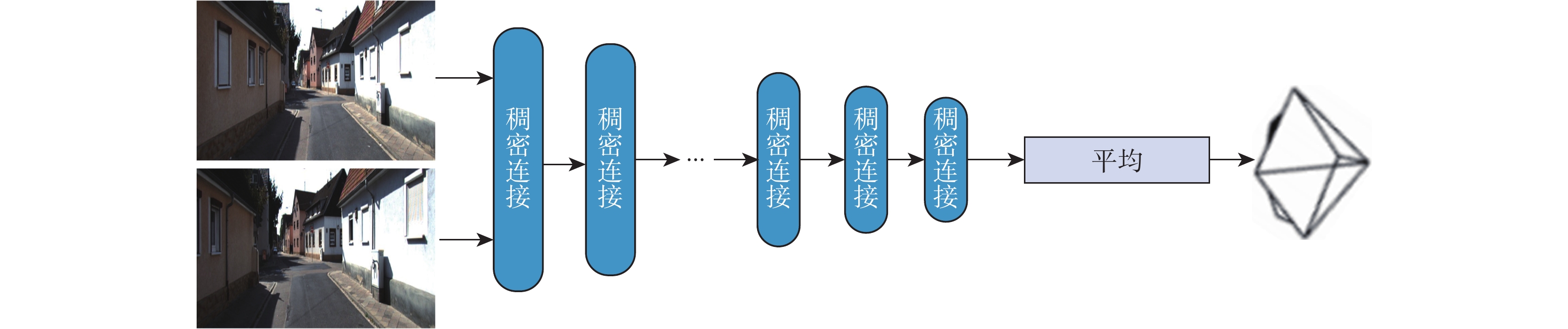
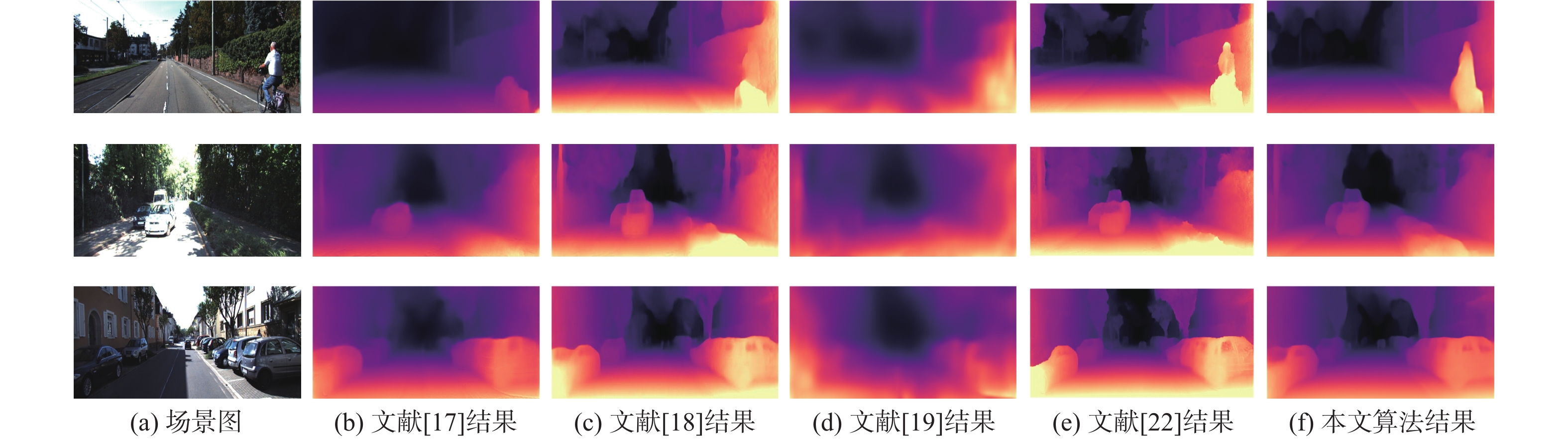
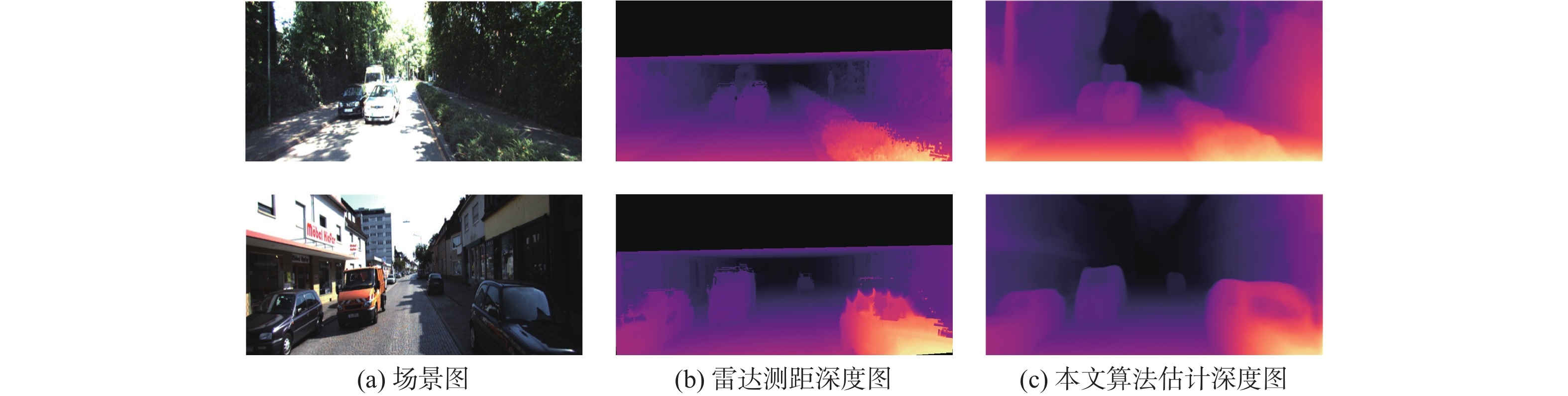
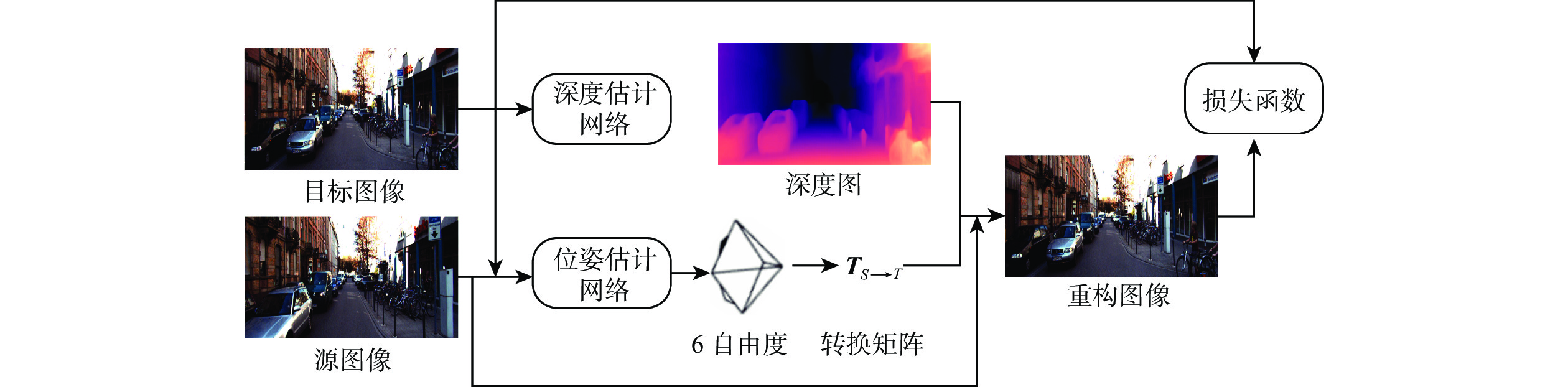
深度信息对于准确理解场景三维结构、分析图像中物体之间的三维关系具有重要作用。结合运动恢复结构、图像重投影和不确定性理论,以端到端的形式提出一种基于不确定性单目图像自监督深度估计算法。利用基于改进稠密连接模块的编码器-解码器深度估计网络得到目标图像的深度图,利用位姿估计网络计算出拍摄目标图像和源图像2个时刻相机位置转换矩阵;根据图像重投影对源图像进行逐像素采样,得到重构目标图像;结合重构目标函数、不确定性目标函数和平滑目标函数对所提算法网络进行优化训练,通过使重构图像和真实目标图像差异最小化实现自监督的深度信息估计。实验结果表明:所提算法在客观指标与主观视觉对比上均取得了比竞争合作估计算法(CC)、Monodepth2、Hr-depth等主流算法更好的深度估计结果。
Abstract:Depth information plays an important role in accurately understanding the three-dimensional scene structure and the three-dimensioual relationship between objects in images. An end-to-end self-supervised depth estimation algorithm based on uncertainty for monocular images was proposed in this paper by combining structure-from-motion, image reprojection, and uncertainty theory. The depth map of the target image was obtained by the encoder-decoder depth estimation network based on an improved densely connected module, and the transformation matrix of camera positions for shooting the target image and source image was calculated by the pose estimation network. Then, the source image was sampled pixel by pixel according to the image reprojection to obtain the reconstructed target image. The proposed algorithm was optimized by the reconstructed objective function, uncertain objective function, and smooth objective function, and the self-supervised depth information estimation was realized by minimizing the difference between the reconstructed image and the real target image. Experimental results show that the proposed algorithm achieves better depth estimation effects than the mainstream algorithms such as competitive collaboration estimation algorithm (CC), Monodepth2, and Hr-depth in terms of both objective indicators and subjective visual comparison.
-
Key words:
- depth estimation /
- deep learning /
- self-supervised /
- image reprojection /
- uncertainty
-
表 1 不同深度估计算法定量结果比较
Table 1. Quantitative result comparison of different depth estimation algorithms
算法 AbsRel SqRel RMSE Rmax δ<1.25 δ<1.252 δ<1.253 文献[17] 0.140 1.070 5.326 0.826 0.941 0.975 文献[18] 0.109 0.873 4.960 0.864 0.948 0.975 文献[19] 0.208 1.768 6.856 0.678 0.885 0.957 文献[21] 0.115 0.871 4.778 0.874 0.963 0.984 文献[22] 0.019 0.792 4.632 0.884 0.962 0.983 文献[23] 0.105 0.842 4.628 0.860 0.973 0.986 本文算法 0.085 0.565 3.856 0.918 0.983 0.998 表 2 不同算法参数量与测试时间对比
Table 2. Comparison of parameter number and testing time of different algorithms
表 3 不确定性对估计结果的影响
Table 3. Effect of uncertainty on estimated results
函数 AbsRel SqRel RMSE Rmax δ<1.25 δ<1.252 δ<1.253 无不确定性目标函数 0.105 0.801 4.641 0.910 0.968 0.984 包含不确定性目标函数 0.096 0.761 4.539 0.918 0.972 0.987 -
[1] 李宏刚, 王云鹏, 廖亚萍, 等. 无人驾驶矿用运输车辆感知及控制方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(11): 2335-2344.LI H G, WANG Y P, LIAO Y P, et al. Perception and control method of driverless mining vehicle[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(11): 2335-2344(in Chinese). [2] CHENG Z Y, ZHANG Y, TANG C K. Swin-depth: Using transformers and multi-scale fusion for monocular-based depth estimation[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 21(23): 26912-26920. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2021.3120753 [3] IZADINIA H, SHAN Q, SEITZ S M. IM2CAD[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2422-2431. [4] ZHANG Y Y, XIONG Z W, YANG Z, et al. Real-time scalable depth sensing with hybrid structured light illumination[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing: A Publication of the IEEE Signal Processing Society, 2014, 23(1): 97-109. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2286901 [5] LEE J, KIM Y, LEE S, et al. High-quality depth estimation using an exemplar 3D model for stereo conversion[J]. IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2015, 21(7): 835-847. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2015.2398440 [6] 邓慧萍, 盛志超, 向森, 等. 基于语义导向的光场图像深度估计[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44(8): 2940-2948.DENG H P, SHENG Z C, XIANG S, et al. Depth estimation based on semantic guidance for light field image[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44(8): 2940-2948(in Chinese). [7] ZHANG J, CAO Y, ZHA Z J, et al. A unified scheme for super-resolution and depth estimation from asymmetric stereoscopic video[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2016, 26(3): 479-493. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2014.2367356 [8] YANG J Y, ALVAREZ J M, LIU M M. Self-supervised learning of depth inference for multi-view stereo[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 7522-7530. [9] FU H, GONG M M, WANG C H, et al. Deep ordinal regression network for monocular depth estimation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 2002-2011. [10] UMMENHOFER B, ZHOU H Z, UHRIG J, et al. DeMoN: Depth and motion network for learning monocular stereo[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 5622-5631. [11] KENDALL A, MARTIROSYAN H, DASGUPTA S, et al. End-to-end learning of geometry and context for deep stereo regression[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 66-75. [12] HAMBARDE P, MURALA S. S2DNet: Depth estimation from single image and sparse samples[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2020, 6: 806-817. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2020.2981761 [13] BADKI A, TROCCOLI A, KIM K, et al. Bi3D: Stereo depth estimation via binary classifications[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1597-1605. [14] DU Q C, LIU R K, PAN Y, et al. Depth estimation with multi-resolution stereo matching[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1-4. [15] JOHNSTON A, CARNEIRO G. Self-supervised monocular trained depth estimation using self-attention and discrete disparity volume[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 4755-4764. [16] SONG M, LIM S, KIM W. Monocular depth estimation using Laplacian pyramid-based depth residuals[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2021, 31(11): 4381-4393. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2021.3049869 [17] RANJAN A, JAMPANI V, BALLES L, et al. Competitive collaboration: Joint unsupervised learning of depth, camera motion, optical flow and motion segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 12232-12241. [18] GODARD C, MAC AODHA O, FIRMAN M, et al. Digging into self-supervised monocular depth estimation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 3827-3837. [19] ZHOU T H, BROWN M, SNAVELY N, et al. Unsupervised learning of depth and ego-motion from video[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 6612-6619. [20] LI K H, FU Z H, WANG H Y, et al. Adv-depth: Self-supervised monocular depth estimation with an adversarial loss[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2021, 28: 638-642. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3065203 [21] ZOU Y L, JI P, TRAN Q H, et al. Learning monocular visual odometry via self-supervised long-term modeling[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 710-727. [22] LYU X Y, LIU L, WANG M M, et al. HR-depth: High resolution self-supervised monocular depth estimation[C]//Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence. Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2021, 35(3): 2294-2301. [23] WAN Y C, ZHAO Q K, GUO C, et al. Multi-sensor fusion self-supervised deep odometry and depth estimation[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(5): 1228. doi: 10.3390/rs14051228 [24] MAHJOURIAN R, WICKE M, ANGELOVA A. Unsupervised learning of depth and ego-motion from monocular video using 3D geometric constraints[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 5667-5675. [25] 刘晓旻, 杜梦珠, 马治邦, 等. 基于遮挡场景的光场图像深度估计方法[J]. 光学学报, 2020, 40(5): 0510002. doi: 10.3788/AOS202040.0510002LIU X M, DU M Z, MA Z B, et al. Depth estimation method of light field image based on occlusion scene[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2020, 40(5): 0510002(in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/AOS202040.0510002 [26] YIN Z C, SHI J P. GeoNet: Unsupervised learning of dense depth, optical flow and camera pose[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1983-1992. [27] KONG C, LUCEY S. Deep non-rigid structure from motion with missing data[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2021, 43(12): 4365-4377. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2020.2997026 [28] HUANG G, LIU Z, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2261-2269. [29] WANG P Q, CHEN P F, YUAN Y, et al. Understanding convolution for semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1451-1460. [30] KENDALL A, GAL Y. What uncertainties do we need in Bayesian deep learning for computer vision[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. California: NIPS, 2017: 5580-5590. [31] GEIGER A, LENZ P, STILLER C, et al. Vision meets robotics: The KITTI dataset[J]. The International Journal of Robotics Research, 2013, 32(11): 1231-1237. doi: 10.1177/0278364913491297 -







 下载:
下载: