Control of combustion oscillation in a central-staged combustor based on Helmholtz resonator
-
摘要:
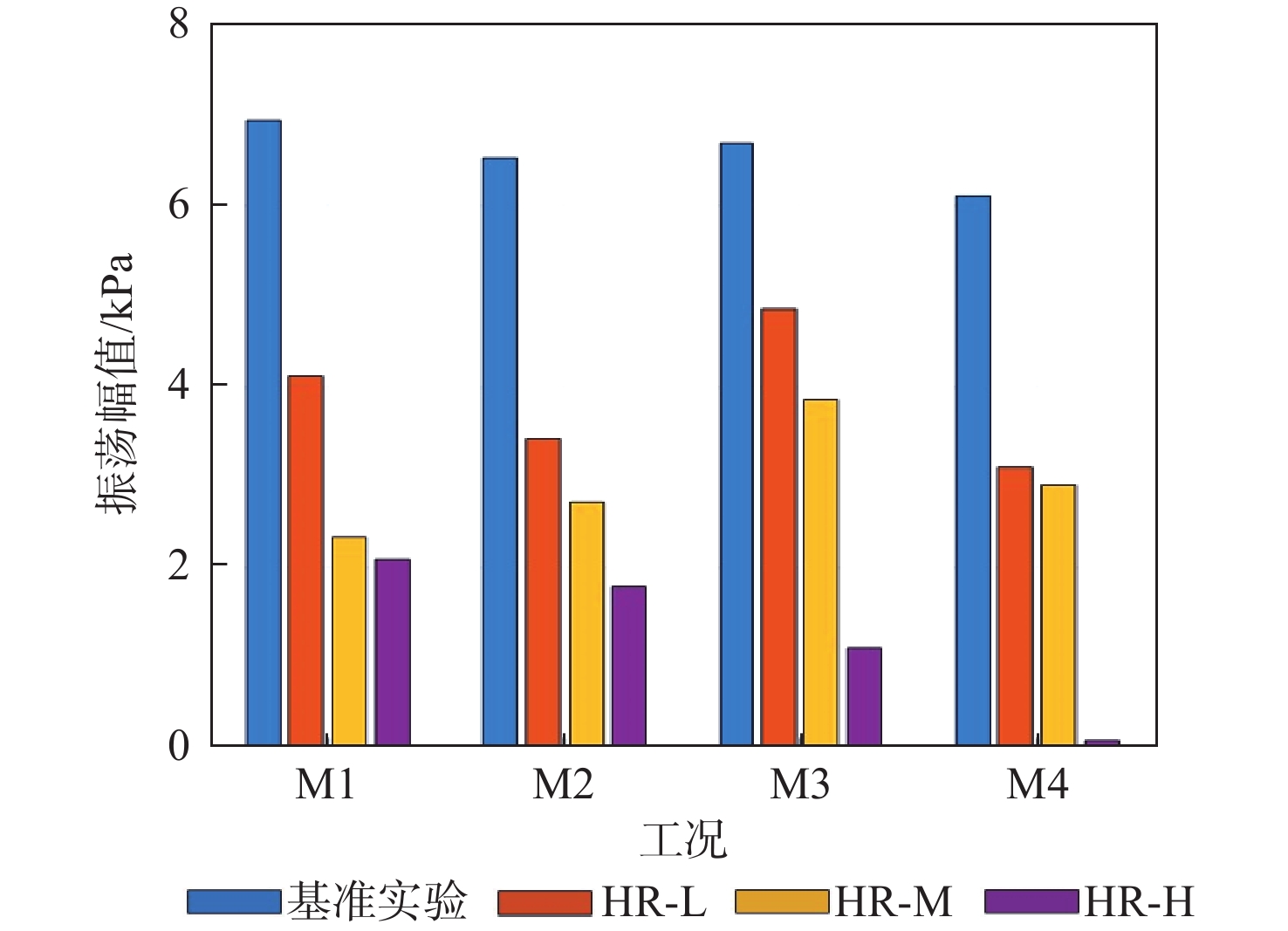
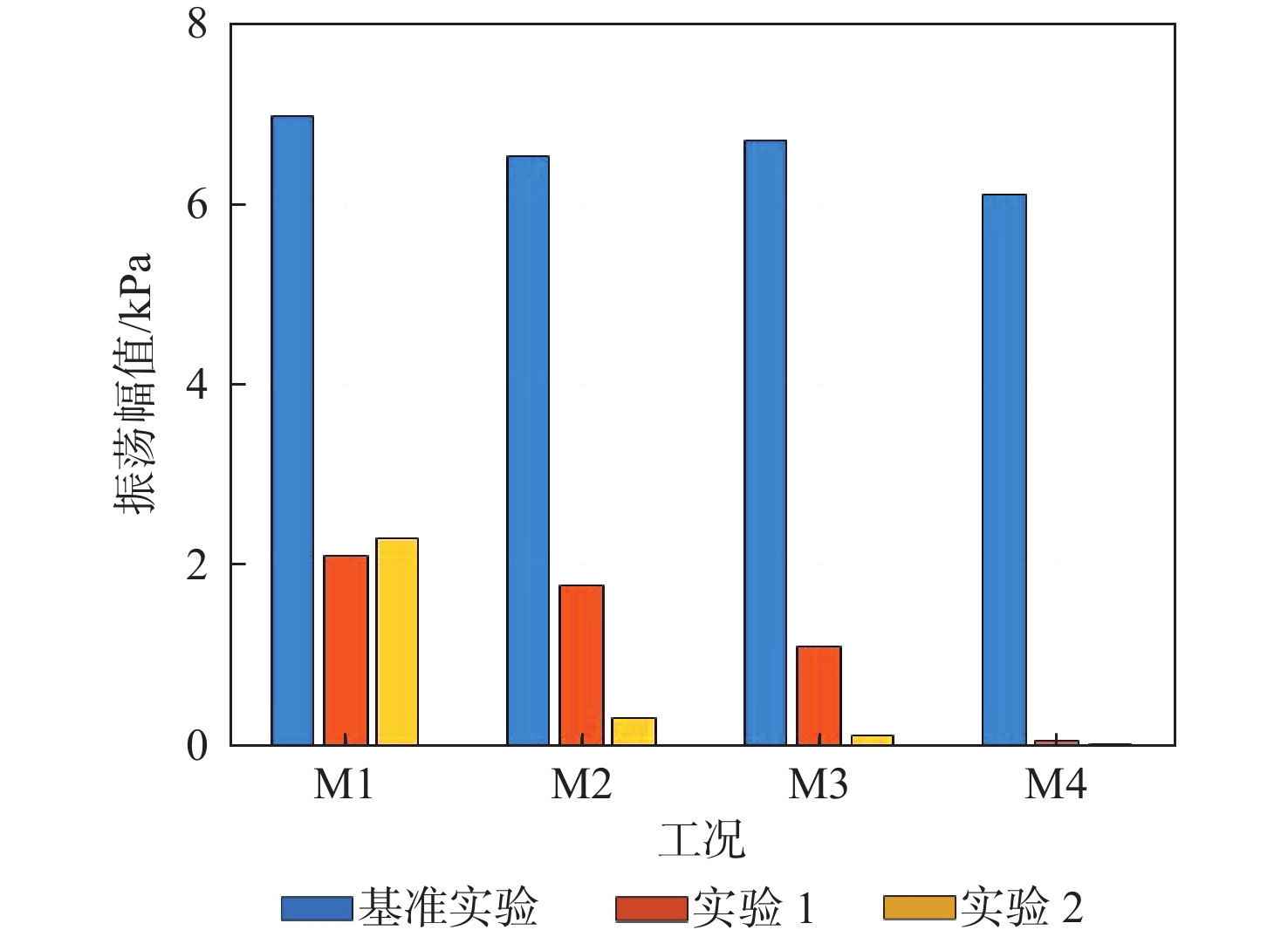
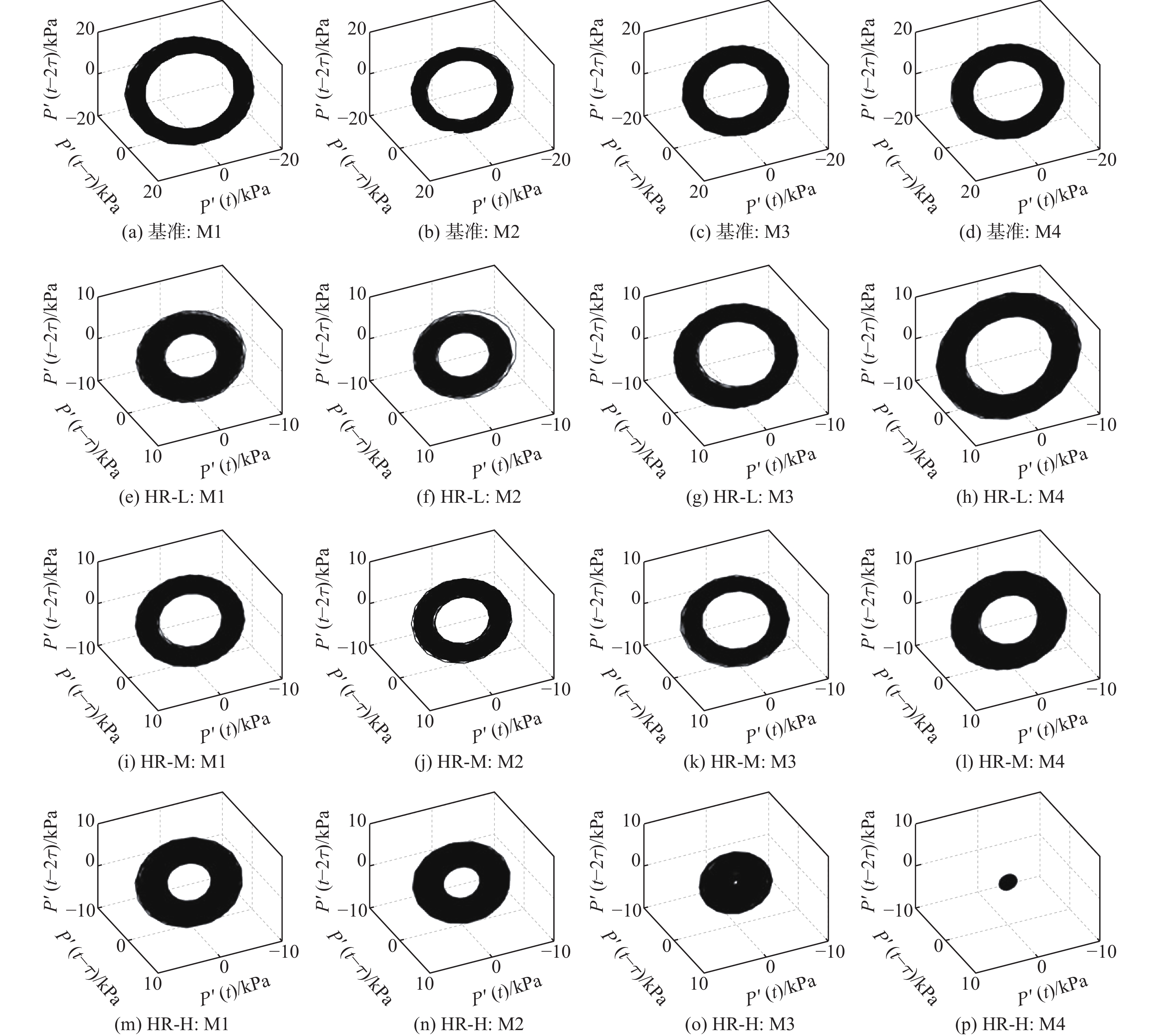
中心分级贫油预混预蒸发(LPP)燃烧室被广泛用于航空发动机和燃气轮机中用于降低排放。但是此类燃烧室在运行过程中遇到了较多的燃烧振荡问题。研究了亥姆霍兹共振器对航空发动机中心分级LPP燃烧室中燃烧振荡的控制效果。实验在以液态航空煤油为燃料的单头部模型燃烧室上开展,涉及中温中压和高温高压2种工况环境。基于声学仿真结果设计了紧凑的亥姆霍兹共振器,体积仅为80 mL和160 mL。实验结果表明,工作频率与燃烧振荡频率相近的亥姆霍兹共振器能显著降低振荡的幅值。中温中压实验中,在火焰分级比25.1%、头部当量比0.6的工况下,亥姆霍兹共振器能完全消除燃烧振荡;高温高压实验中,振荡幅值降低约90%。同时,设计合理的共振器在不同分级比下控制效果略有不同,振荡幅值下降幅度为69.9%~98.9%。另外,声学仿真结果显示,共振器的加入对系统的声学特征模态影响极小,与实验结果吻合。结构紧凑的亥姆霍兹共振器具有在航空发动机LPP燃烧室中抑制燃烧振荡的潜力。
Abstract:Lean premixed pre-vaporized (LPP) combustion technology is widely used in centrally staged combustors of aero engines to reduce pollutant emissions. However, such combustors are prone to combustion instability. The control effect of the Helmholtz resonator on combustion oscillation in a central-staged LPP combustor of an aero-engine was studied. The experiment was carried out on a single-head model combustor with liquid aviation kerosene as fuel, involving two working conditions: medium temperature and medium pressure, as well as high temperature and high pressure. According to the acoustic simulation results, compact Helmholtz resonators were designed, with volumes of 80 mL and 160 mL. The experimental results show that Helmholtz resonators with a working frequency close to the combustion oscillation frequency can significantly reduce the oscillation amplitude. In the medium temperature and medium pressure experiment, the Helmholtz resonator can completely eliminate combustion oscillation under the condition of flame stage ratio of 25.1% and head equivalent ratio of 0.6. In the high temperature and high pressure experiment, the oscillation amplitude is reduced by about 90%. In addition, the reasonably designed resonator has slightly different control effects at different stage ratios, with a decrease in oscillation amplitude in the range of 69.9%~98.9%. Meanwhile, the acoustic simulation results show that the addition of a resonator has little effect on the acoustic characteristic modes of the system, which is consistent with the experimental results. In summary, the Helmholtz resonator with a compact structure has the potential to suppress combustion oscillations in an LPP combustor of aero-engine.
-
Key words:
- Helmholtz resonator /
- passive control /
- combustion oscillation /
- lean-premixed combustor /
- aero-engin
-
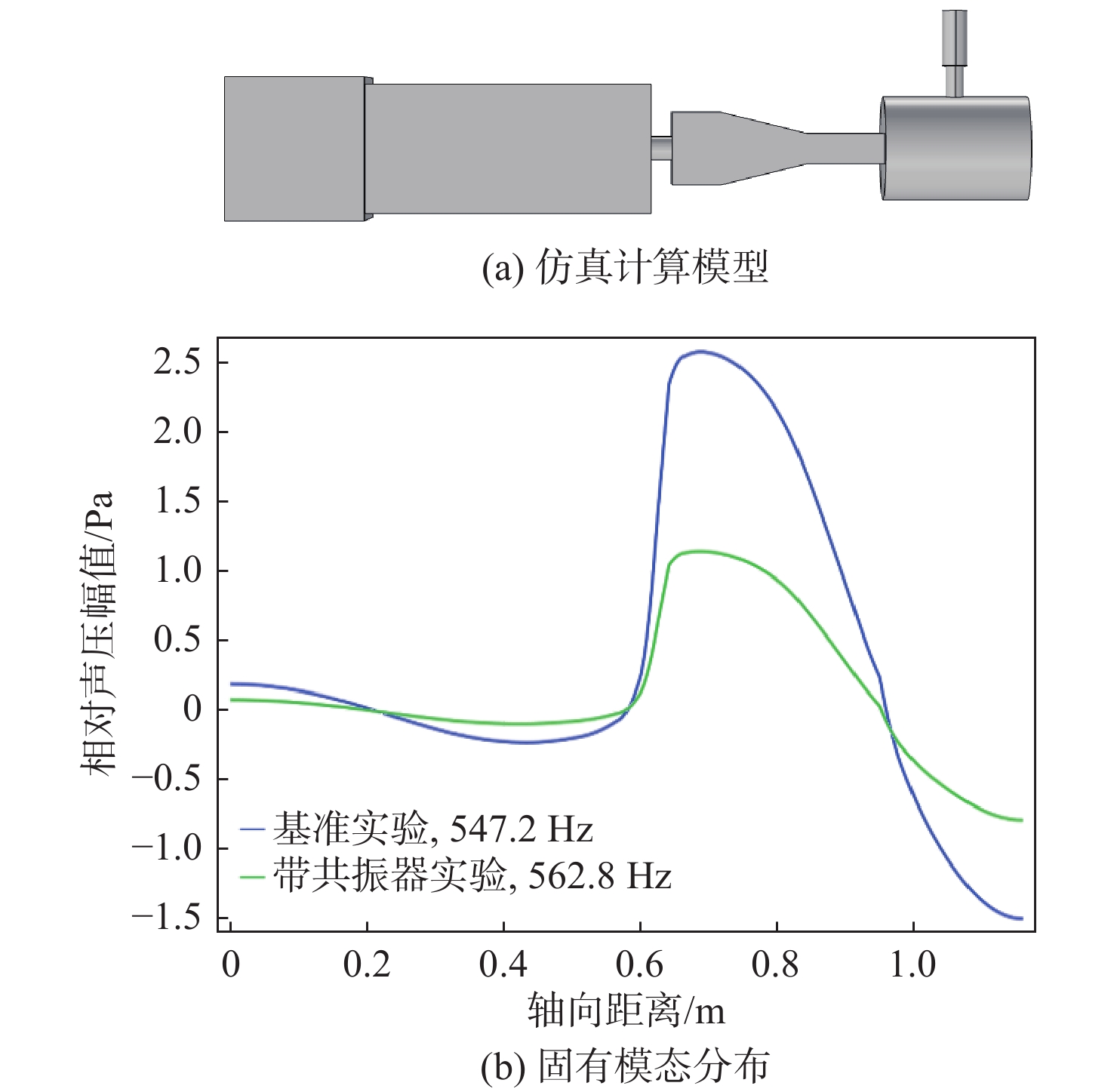
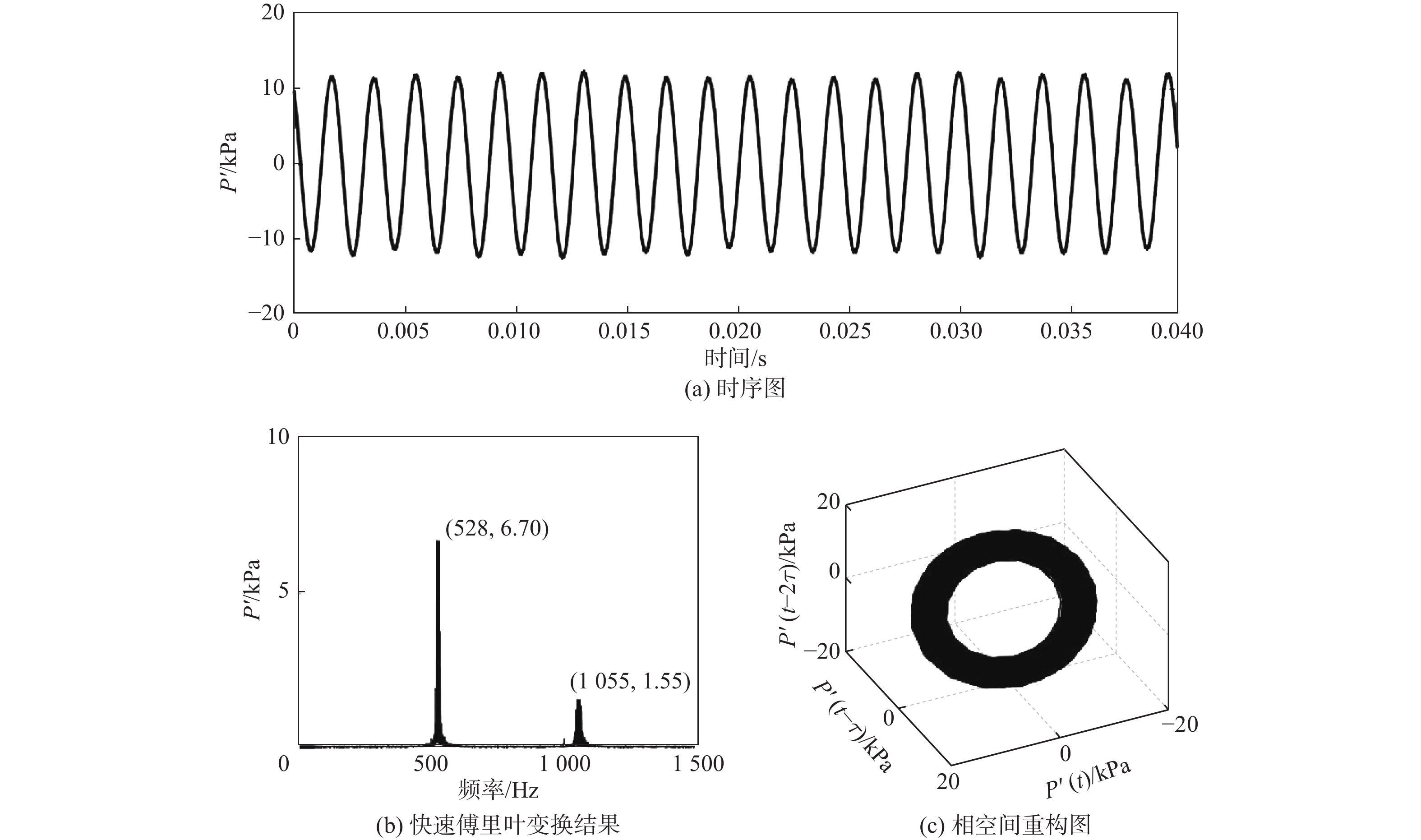
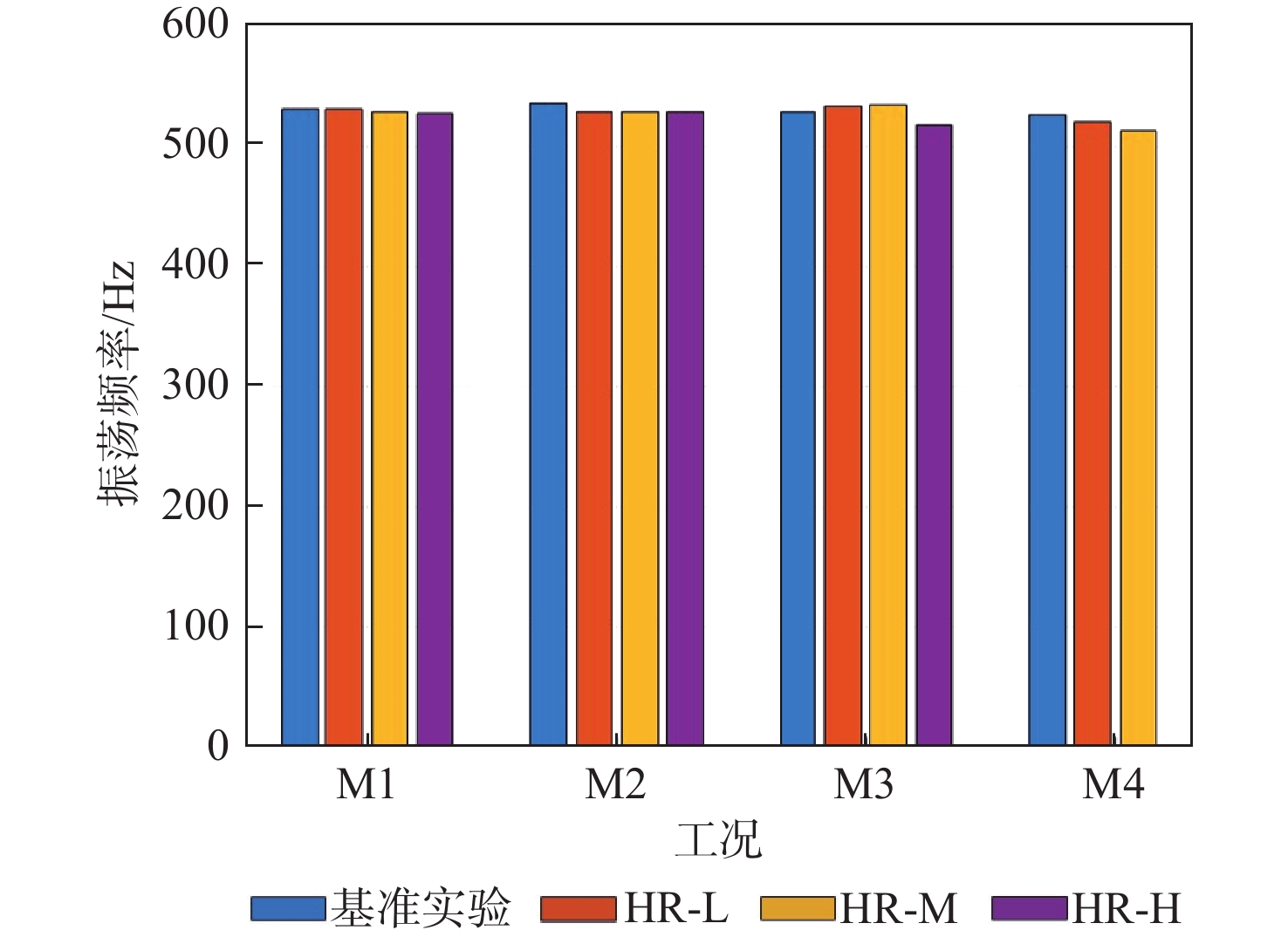
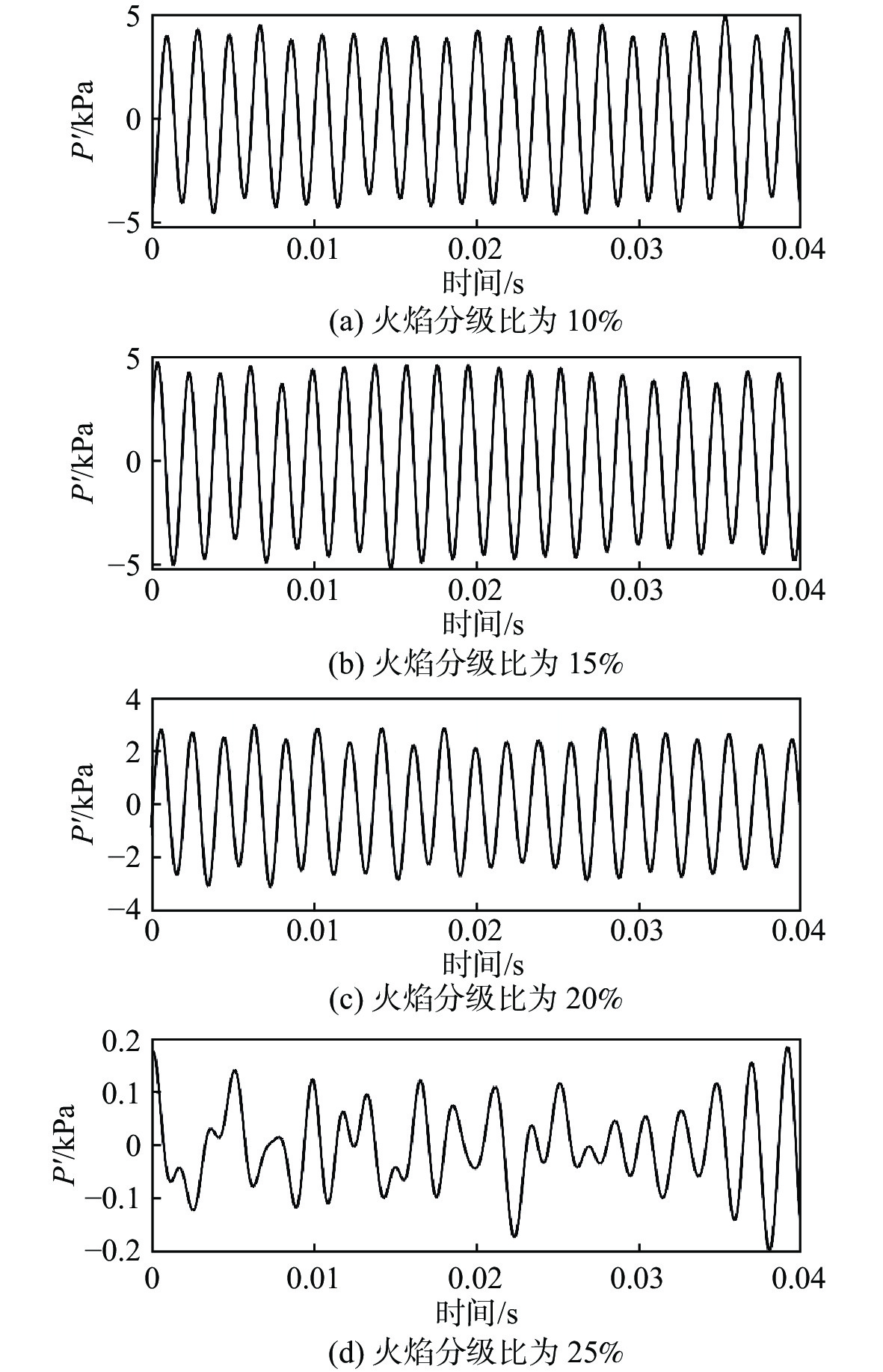
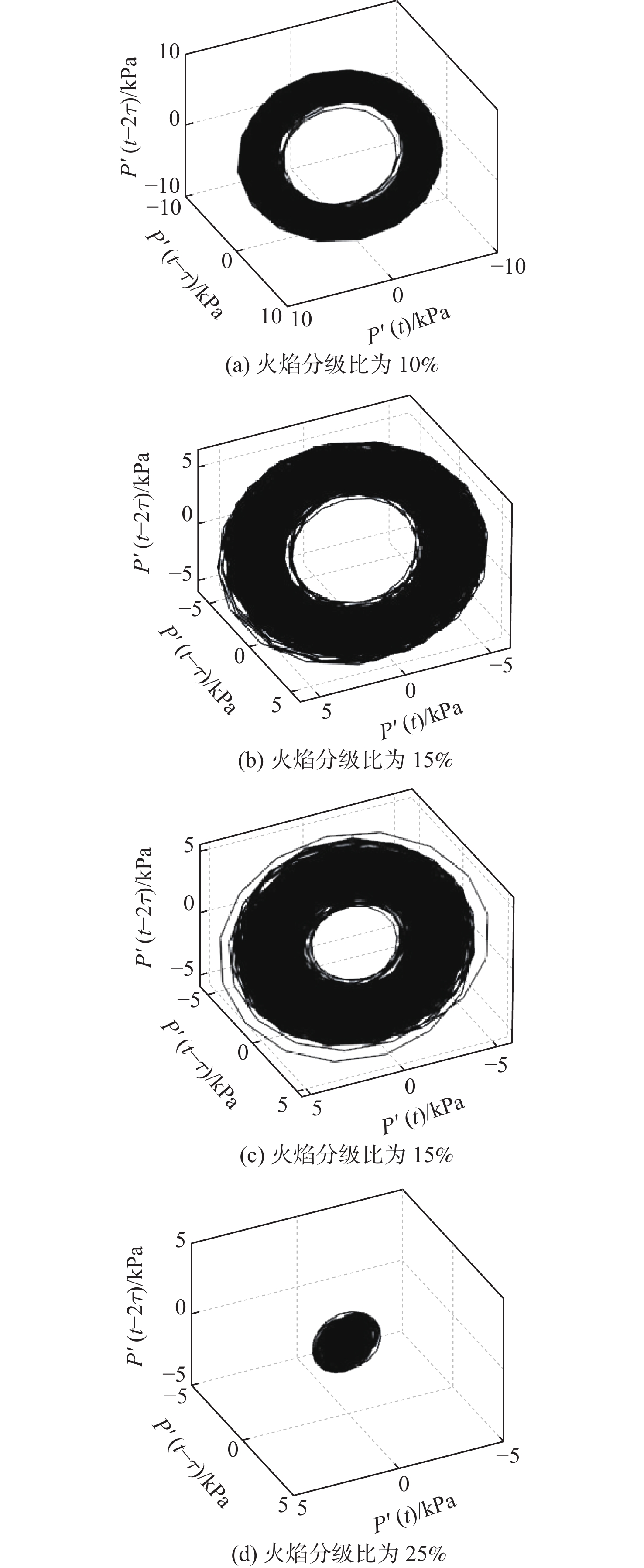
表 1 中温中压实验基准工况和振荡特性
Table 1. Basic operating conditions and oscillation characteristic for medium temperature and medium pressure experiment
工况 质量流量 火焰
分级比/
%头部
当量比振荡
频率/Hz振荡
幅值/
kPa预燃级燃料/
(kg·h−1)主燃级燃料/
(kg·h−1)M1 4.17 35.6 10.5 0.6 531 6.97 M2 6.04 33.4 15.3 0.6 536 6.53 M3 7.85 31.1 20.2 0.6 528 6.7 M4 9.69 28.9 25.1 0.6 526 6.11 表 2 高温高压实验基准工况和振荡特性
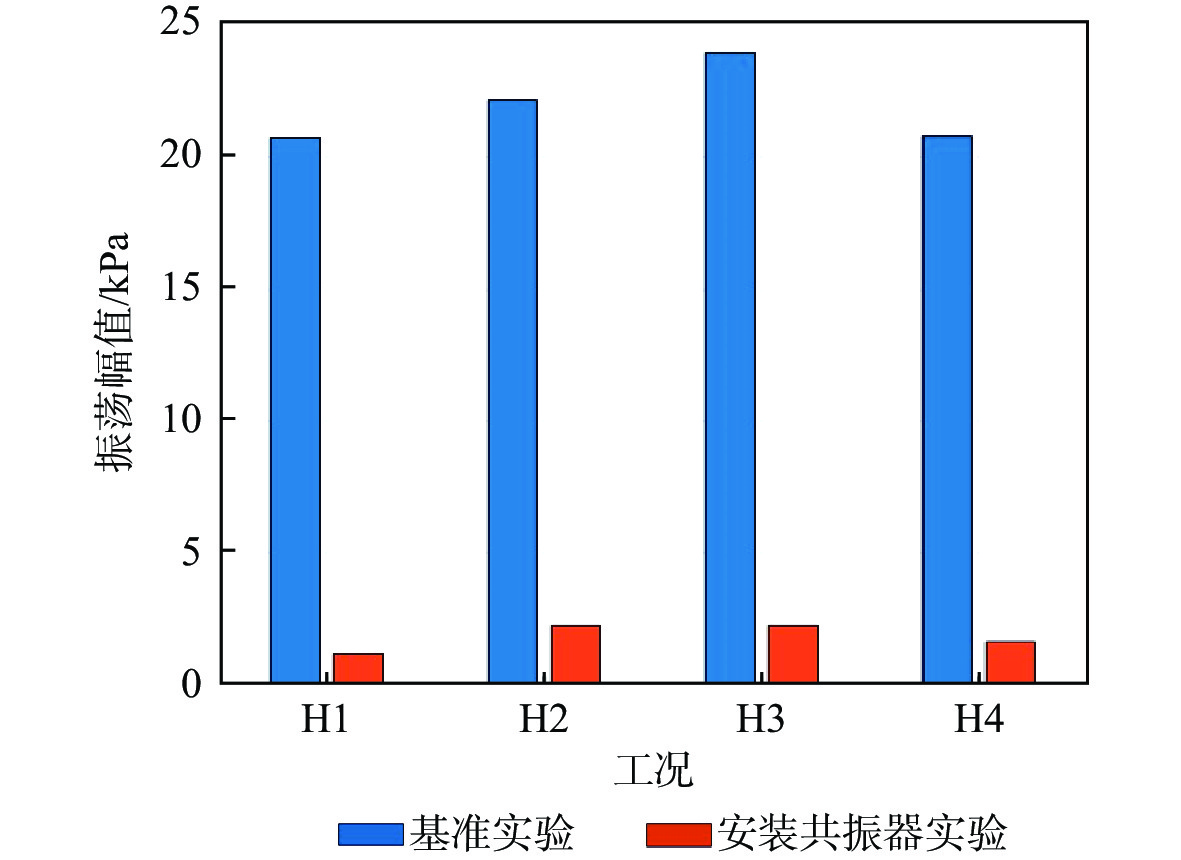
Table 2. Basic operating conditions and oscillation characteristic for high temperature and high pressure experiment
工况 质量流量 火焰
分级比/
%头部
当量比振荡
频率/Hz振荡
幅值/
kPa预燃级燃料/
(kg·h−1)主燃级燃料/
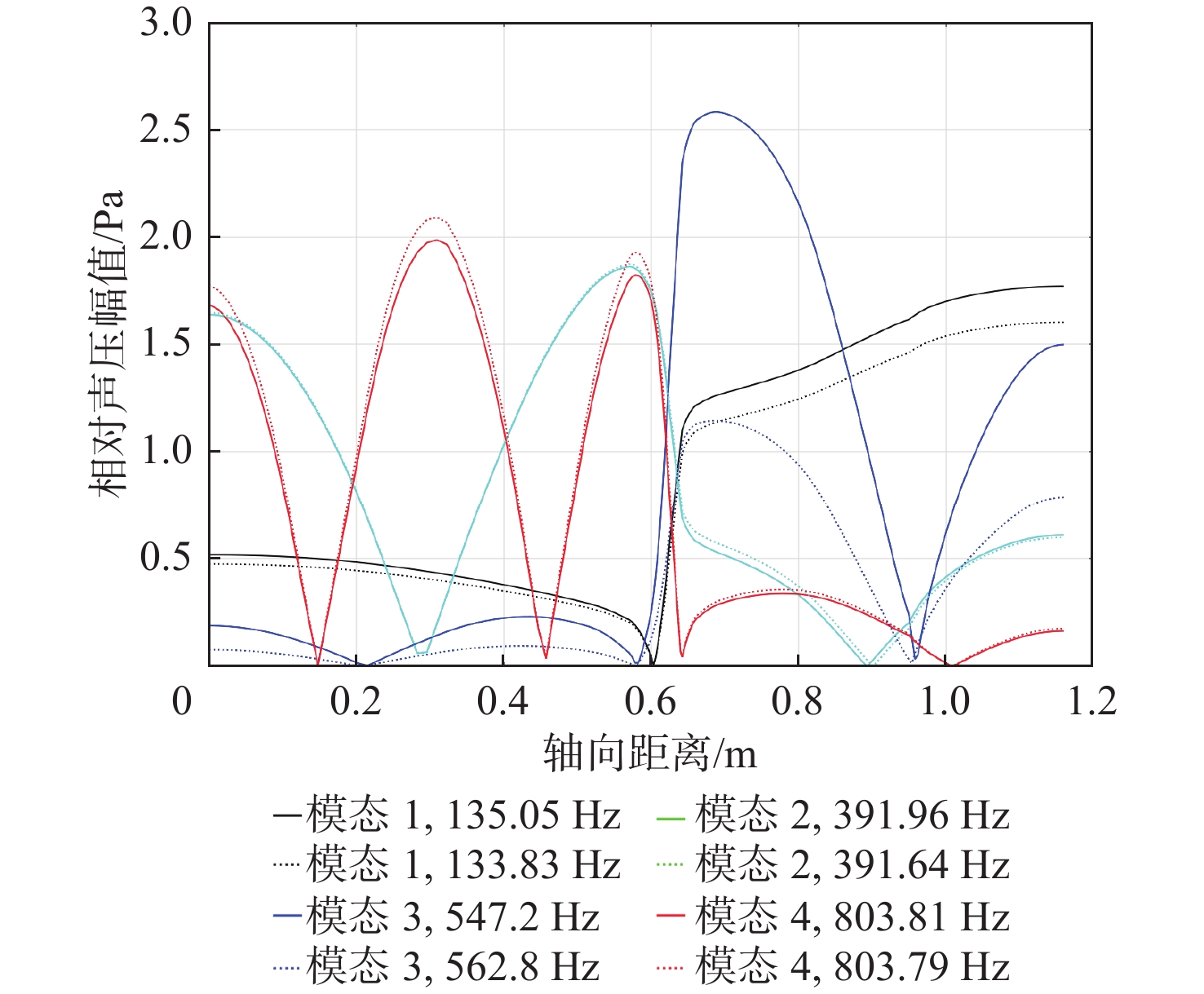
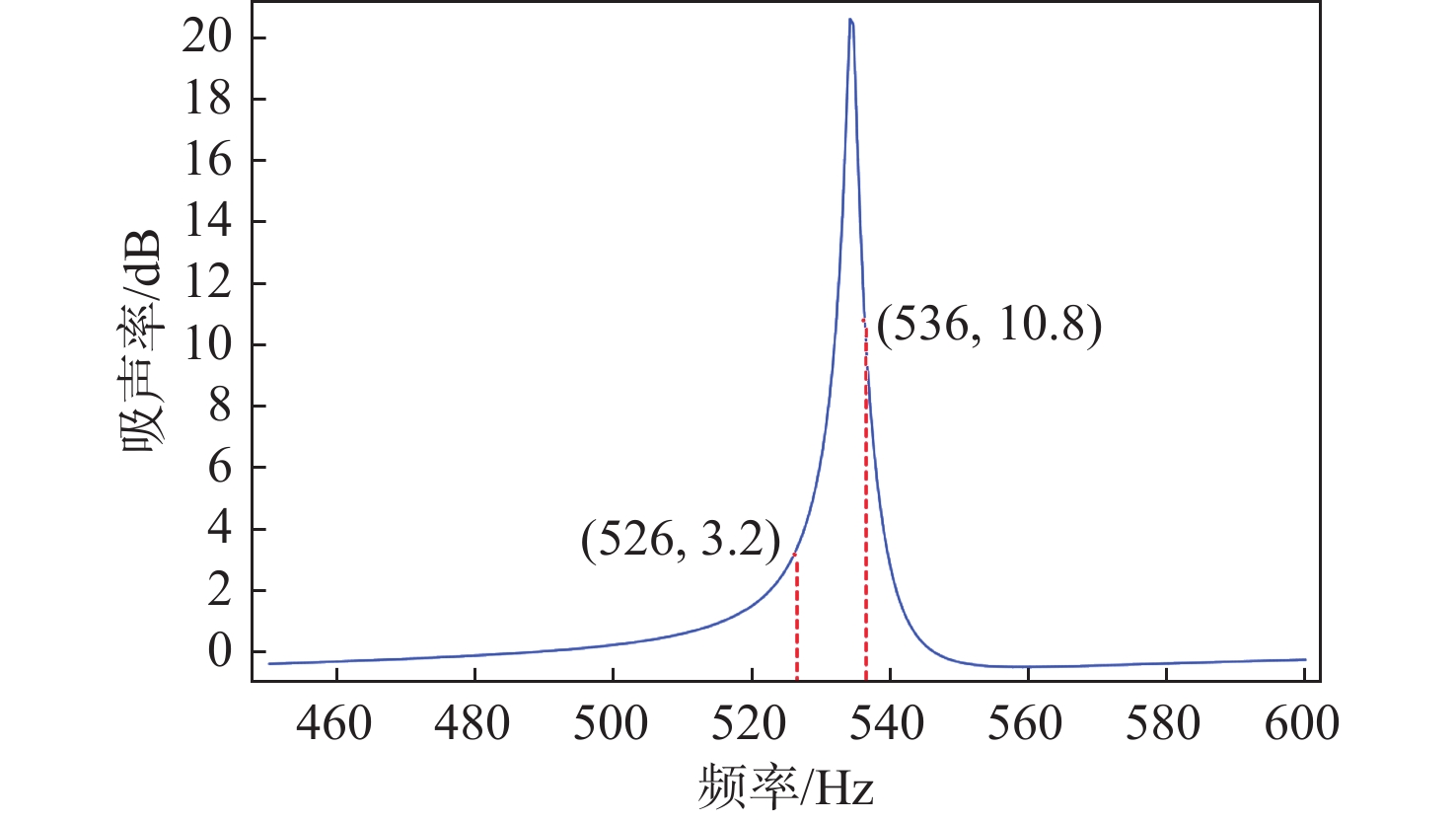
(kg·h−1)H1 22.3 127 14.9 0.58 507 20.79 H2 23.2 132 14.9 0.61 508 22.16 H3 24.4 138 15.1 0.64 508 24 H4 19.8 143 12.2 0.64 509 20.81 表 3 中温中压实验的亥姆霍兹共振器参数
Table 3. Parameters of Helmholtz resonator in medium temperature and medium pressure experiment
共振器 背腔高度/
mm背腔直径/
mm颈部长度/
mm体积/
mL特征频率/
Hz预估
吸声率/dBHR-L 85 36 26 87 496 6.28 HR-M 80 36 26 82 524 9.77 HR-H 75 36 26 76 556 10.91 表 4 中温中压实验工况
Table 4. Operating conditions in medium temperature and medium pressure experiment
工况 质量流量 火焰
分级比/
%振荡
频率/Hz振荡
幅值/
kPa预燃级燃料/
(kg·h−1)主燃级燃料/
(kg·h−1)M5 5.13 39 11.6 534 4.76 M6 7.07 36.14 16.4 530 2.98 M7 8.79 33.83 20.6 524 1.85 M8 10.36 31.33 24.9 0.34 -
[1] 黄勇, 林宇震, 樊未军, 等. 燃烧与燃烧室[M]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 2009.HUANG Y, LIN Y Z, FAN W J, et al. Combustion and combustion chambers[M]. Beijing: Beihang University Press, 2009(in Chinese). [2] STEINBERG A M, BOXX I, STÖHR M, et al. Flow-flame interactions causing acoustically coupled heat release fluctuations in a thermo-acoustically unstable gas turbine model combustor[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2010, 157(12): 2250-2266. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2010.07.011 [3] LIEUWEN T C, YANG V. Combustion instabilities in gas turbine engines: Operational experience, fundamental mechanisms and modeling[M]. Reston: AIAA, 2005. [4] HAN X, LAERA D, MORGANS A S, et al. The effect of stratification ratio on the macrostructure of stratified swirl flames: Experimental and numerical study[C]//Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2018: Turbomachinery Technical Conference and Exposition. New York: ASME, 2018. [5] HAN X, LAERA D, MORGANS A S, et al. Flame macrostructures and thermoacoustic instabilities in stratified swirling flames[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2019, 37(4): 5377-5384. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2018.06.147 [6] ZHAO D, LU Z L, ZHAO H, et al. A review of active control approaches in stabilizing combustion systems in aerospace industry[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2018, 97: 35-60. doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2018.01.002 [7] SOHN C H, PARK J H. A comparative study on acoustic damping induced by half-wave, quarter-wave, and Helmholtz resonators[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2011, 15(8): 606-614. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2010.12.004 [8] 马大猷. 亥姆霍兹共鸣器[J]. 声学技术, 2002, 21(增刊1): 2-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3630.2002.01.001MA D Y. Helmholtz resonators[J]. Technical Acoustics, 2002, 21(Sup1): 2-3(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3630.2002.01.001 [9] 高原, 朱民. 亥姆霍兹共振器抑制振荡燃烧理论分析[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2009, 30(6): 1048-1050. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-231X.2009.06.041GAO Y, ZHU M. Theoretical analysis of combustion oscillation suppression with Helmholtz resonators[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2009, 30(6): 1048-1050(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-231X.2009.06.041 [10] HOWE M S. Influence of cross-sectional shape on the conductivity of a wall aperture in mean flow[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration, 1997, 207(5): 601-616. doi: 10.1006/jsvi.1997.1103 [11] DUPÈRE I D J, DOWLING A P. The use of Helmholtz resonators in a practical combustor[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 2005, 127(2): 268-275. doi: 10.1115/1.1806838 [12] YANG S H, WANG J C, WANG Z C, et al. Experimental investigation of dual-swirl spray flame in a fuel staged optical model combustor with laser diagnostics[C]//Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2021: Turbomachinery Technical Conference and Exposition. New York: ASME, 2021, 84942: V03AT04A015. [13] LIU Z H, ZHOU H, FANG H, et al. Combustion instability control performance of an improved Helmholtz resonator in the presence of bias flow[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2021, 119: 107153. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2021.107153 [14] RICHARDS G A, STRAUB D L, ROBEY E H. Passive control of combustion dynamics in stationary gas turbines[J]. Journal of Propulsion and Power, 2003, 19(5): 795-810. doi: 10.2514/2.6195 [15] STEELE R C, COWELL L H, CANNON S M, et al. Passive control of combustion instability in lean premixed combustors[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 2000, 122(3): 412-419. doi: 10.1115/1.1287166 [16] GYSLING D L, COPELAND G S, MCCORMICK D C, et al. Combustion system damping augmentation with Helmholtz resonators[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 2000, 122(2): 269-274. doi: 10.1115/1.483205 [17] BELLUCCI V, FLOHR P, PASCHEREIT C O, et al. On the use of Helmholtz resonators for damping acoustic pulsations in industrial gas turbines[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 2004, 126(2): 271-275. doi: 10.1115/1.1473152 [18] PANDALAI R, MONGIA H. Combustion instability characteristics of industrial engine dry low emission combustion systems[C]// Proceedings of the 34th AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 1998. [19] WANG Z C, HUI X, WANG J C, et al. Effects of axial velocity of main stage on the performances of a centrally staged LPP combustor[C]//Proceedings of the ASME Turbo Expo 2019: Turbomachinery Technical Conference and Exposition, 2019, 58615: V04AT04A061. [20] ABARBANEL H D I, BROWN R, SIDOROWICH J J, et al. The analysis of observed chaotic data in physical systems[J]. Reviews of Modern Physics, 1993, 65(4): 1331-1392. doi: 10.1103/RevModPhys.65.1331 [21] WANG B, ZHANG C, LIN Y Z, et al. Influence of main swirler vane angle on the ignition performance of TeLESS-II combustor[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 2017, 139(1): 011501. doi: 10.1115/1.4034154 [22] PANTON R L, MILLER J M. Resonant frequencies of cylindrical Helmholtz resonators[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1975, 57(6): 1533-1535. doi: 10.1121/1.380596 -








 下载:
下载: