Influence mechanism of air pressure and heating power on thermal safety of lithium-ion battery
-
摘要:
随着锂离子电池的普及应用,其在航空低气压环境下的热安全问题受到广泛关注。对此,在20~95 kPa的气压环境下,以30~100 W的加热功率诱导电池热失控,通过电池热失控现象、温度及时间的分析,研究航空低气压环境下加热功率对锂离子电池热安全行为的影响机制。研究表明:气压的降低导致电池安全阀打开时间提前,但由于低气压环境下对流换热系数和特征达姆科勒数的减小,电池从安全阀开启到热失控的过渡时间延长;而加热功率的提高显著缩短了电池的热失控时间,加剧了电池热失控燃爆,同时也缩短了电池的加热时间,导致外部热源传递给电池的热量减少,热失控过程中电池表面峰值温度降低;在二者的综合作用下,电池的热失控时间总体呈现出随功率增加而减小的趋势,但气压的作用导致其变化规律呈现出明显差异。为实现气压及加热功率综合影响下电池热失控时间的预测,通过多项式拟合,构建电池热失控时间预测模型,预测精度控制在(3±2) s。
Abstract:With the popularization and application of lithium-ion batteries, the thermal safety problem in aviation low-pressure environments have has attracted wide attention. The lithium-ion batteries were induced to thermal runaway under the heating power of 30−100 W at 20−95 kPa. Through the analysis of the thermal runaway phenomenon, temperature and time, the influence mechanism of the heating power on the thermal safety behavior of lithium-ion batteries in aviation low-pressure environments was discussed. The results showed that the reduction of air pressure caused the opening time of the battery safety valve to advance. However, due to the reduction of the convection heat transfer coefficient and characteristic Damkoler number under low-pressure environments, the transition time from the opening of the safety valve to the thermal runaway of the battery was prolonged. The battery’s thermal runaway period was greatly reduced by the increase in heating power, which also made the battery's thermal runaway explosion worse. The heating time was shortened, resulting in less heat transferred to the batteries from the external heat source, and the peak temperature of the battery surface was reduced. Under the combined action of the heating power and air pressure, the thermal runaway time of the battery generally showed a trend of decreasing with the increase of power. However, due to the effect of air pressure, its change law showed and obvious difference. A prediction model of battery thermal runaway time has been built by polynomial fitting, and the forecast accuracy has been regulated within (3±2) s. This was done in order to achieve the prediction of battery thermal runaway time under the combined impact of air pressure and heating power.
-
Key words:
- low air pressure /
- heating power /
- lithium-ion battery /
- thermal runaway /
- thermal safety
-
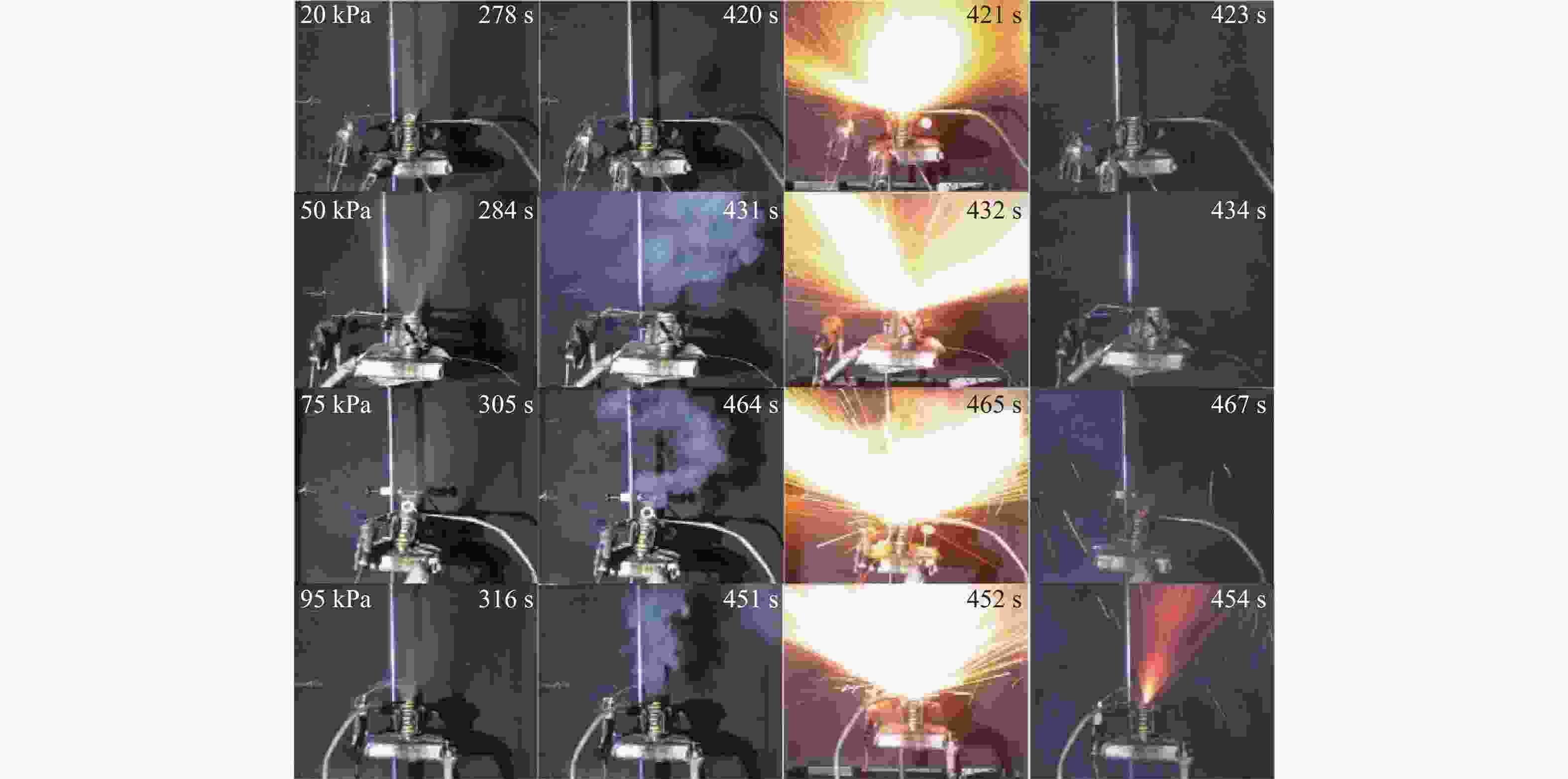
表 1 锂离子电池排气时间
Table 1. Exhausted gas time of lithium-ion battery
气压/kPa 排气时间/s 加热功率30 W 加热功率50 W 加热功率100 W 20 476 278 171 50 480 284 169 75 486 3.5 178 95 495 316 180 表 2 锂离子电池热失控时间
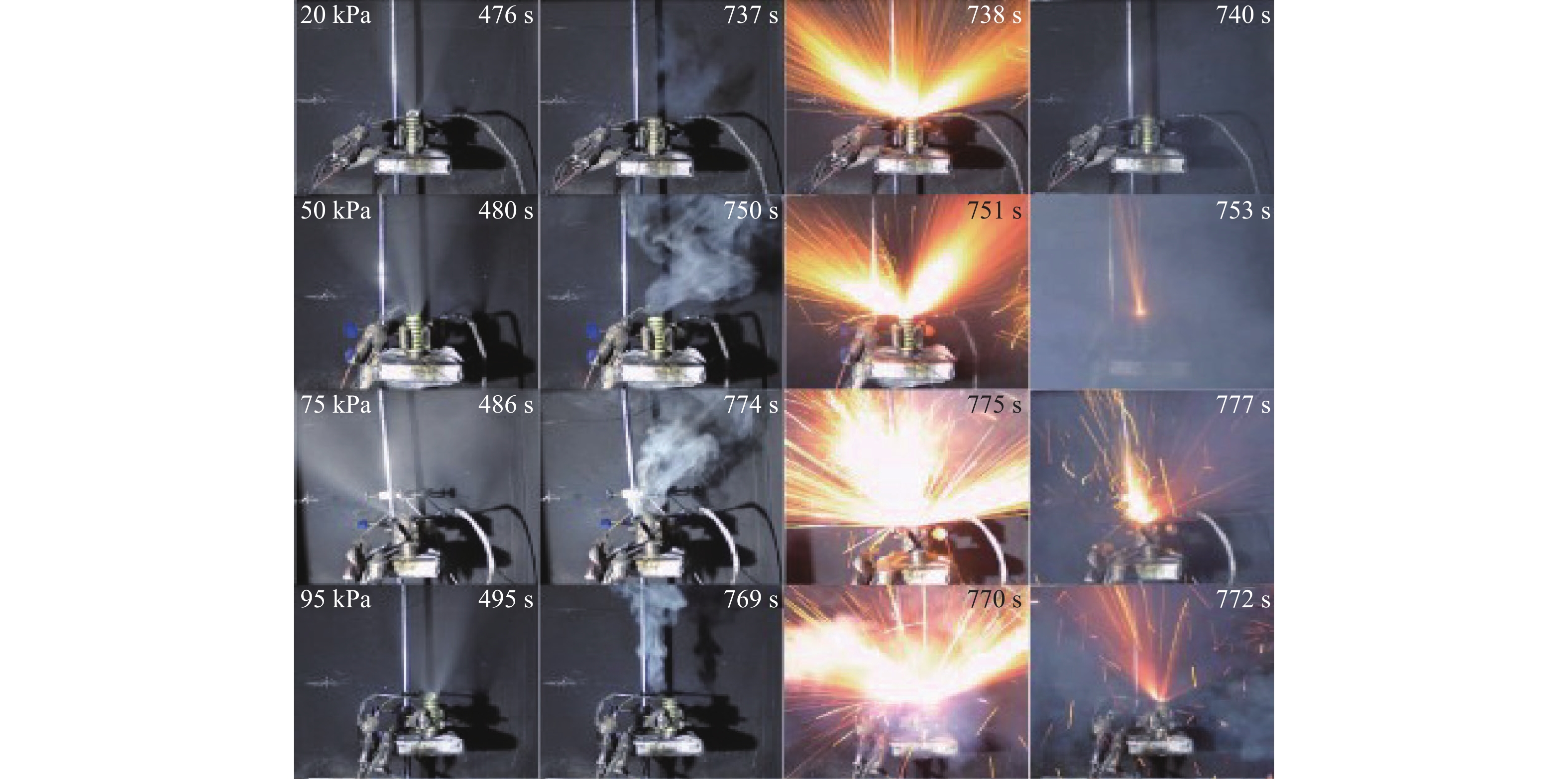
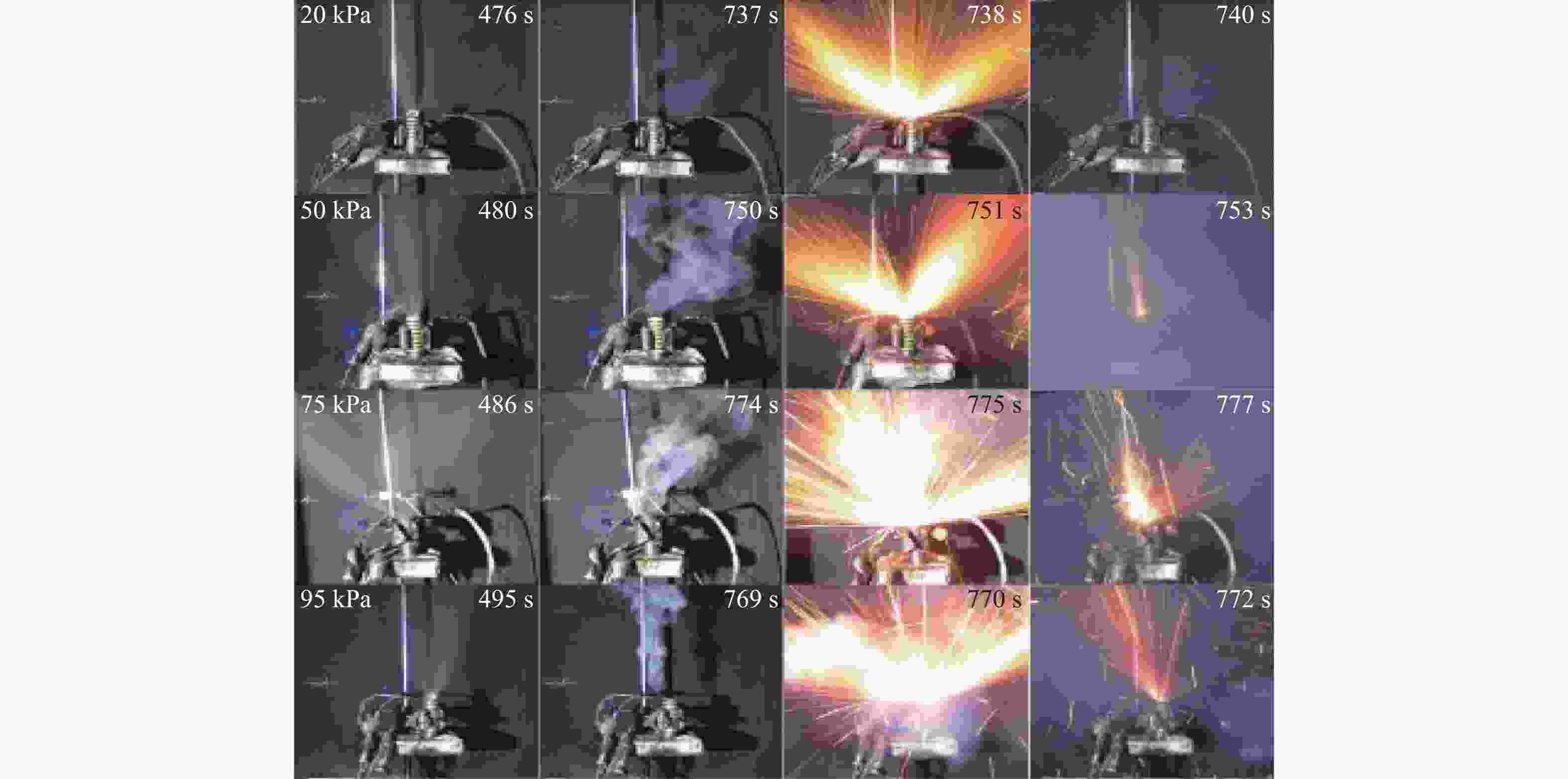
Table 2. Thermal runaway onset time of the lithium-ion battery
气压/kPa 热失控时间/s 加热功率30 W 加热功率50 W 加热功率100 W 20 737 420 224 50 750 431 235 75 774 464 228 95 769 451 223 表 3 热失控时间预测模型系数
Table 3. Predicted model coefficients of thermal runaway onset time
a b c d e f u v 1405 1.231 −27.92 −0.008701 −0.003172 0.1609 6.974 0.4369 -
[1] SABET P S, SAUER D U. Separation of predominant processes in electrochemical impedance spectra of lithium-ion batteries with nickel-manganese-cobalt cathodes[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2019, 425: 121-129. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.03.068 [2] NITTA N, WU F, LEE J T, et al. Li-ion battery materials: present and future[J]. Materials Today, 2015, 18(5): 252-264. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2014.10.040 [3] 谢松, 李明浩, 巩译泽, 等. 航空机载锂离子电池热失控特性研究进展[J]. 科技导报, 2021, 39(11): 118-125. doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2021.11.013XIE S, LI M H, GONG Y Z, et al. Review of the thermal runaway characteristics of airborne lithium-ion batteries[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2021, 39(11): 118-125(in Chinese). doi: 10.3981/j.issn.1000-7857.2021.11.013 [4] CHEN M Y, LIU J H, HE Y P, et al. Study of the fire hazards of lithium-ion batteries at different pressures[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 125: 1061-1074. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.06.131 [5] CHEN M Y, LIU J H, LIN X, et al. Combustion characteristics of primary lithium battery at two altitudes[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2016, 124(2): 865-870. doi: 10.1007/s10973-015-5219-3 [6] JIA Z Z, HUANG Z H, ZHAI U J, et al. Experimental investigation on thermal runaway propagation of 18650 lithium-ion battery modules with two cathode materials at low pressure[J]. Energy, 2022, 251: 123925. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2022.123925 [7] 张青松, 刘添添, 赵子恒. 锂离子电池热失控气体燃烧对热失控传播影响的量化方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(1): 17-22. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2021.0212ZHANG Q S, LIU T T, ZHAO Z H. Quantitative method of the influence of thermal runaway gas combustion on thermal runaway propagation of lithium ion battery[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(1): 17-22. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2021.0212 [8] 孙强, 贾井运, 王海斌, 等. 常压及低压下锂电池热失控随数量变化特性[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2022, 32(2): 145-151. doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.02.020SUN Q, JIA J Y, WANG H B, et al. Research on thermal runaway characteristics of lithium-ion batteries along with cell number changes under standard and low atmospheric pressures[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2022, 32(2): 145-151(in Chinese). doi: 10.16265/j.cnki.issn1003-3033.2022.02.020 [9] 孙强, 王海斌, 谢松, 等. 低压环境对锂电池热失控释放温度影响[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2019, 15(11): 78-83. doi: 10.11731/j.issn.1673-193x.2019.11.012SUN Q, WANG H B, XIE S, et al. Influence of low pressure environment on thermal runaway release temperature of lithium battery[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2019, 15(11): 78-83(in Chinese). doi: 10.11731/j.issn.1673-193x.2019.11.012 [10] 张伟, 郝朝龙, 刘添添, 等. 航空气压环境对锂离子电池热解气体爆炸极限影响[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2022, 18(11): 155-162.ZHANG W, HAO C L, LIU T T, et al. Influence of aviation pressure environment on explosion limit of pyrolysis gas from lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2022, 18(11): 155-162(in Chinese). [11] 陈现涛, 赵一帆, 张旭, 等. 不同外部热源及气压对软包装锂离子电池热失控影响[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2022, 41(1): 15-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2022.01.004CHEN X T, ZHAO Y F, ZHANG X, et al. Influence of different external heat power and air pressure on thermal runaway of pouch lithium-ion batteries[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2022, 41(1): 15-20(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2022.01.004 [12] XIE S, SUN J, CHEN X, et al. Thermal runaway behavior of lithium-ion batteries in different charging states under low pressure[J]. International Journal of Energy Research, 2021, 45(4): 5795-5805. doi: 10.1002/er.6200 [13] XU B, LEE J, KWON D, et al. Mitigation strategies for Li-ion battery thermal runaway: A review[J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2021, 150: 111437. doi: 10.1016/j.rser.2021.111437 [14] 朱鸿章, 吴传平, 周天念, 等. 磷酸铁锂和三元锂电池外部过热条件下的热失控特性[J]. 储能科学与技术, 2022, 11(1): 201-210. doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2021.0369ZHU H Z, WU C P, ZHOU T N, et al. Thermal runaway characteristics of LiFePO4 and ternary lithium batteries with external overheating[J]. Energy Storage Science and Technology, 2022, 11(1): 201-210(in Chinese). doi: 10.19799/j.cnki.2095-4239.2021.0369 [15] 张青松, 曲奕润, 刘添添. 锂离子电池热失控气体毒性风险分析方法研究[J/OL]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022(2022-04-25)[2022-12-27]. https://doi.org/10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2022.0217.ZHANG Q S, QU Y R, LIU T T. A methodology study on risk analysis for thermal runaway gas toxicity of lithium batteries[J/OL]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022(2022-04-25)[2022-12-27]. https://doi.org/10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2022.0217 (in Chinese). [16] 王淮斌, 杜志明. 低压环境下锂离子电池安全性研究进展[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2019, 38(6): 884-890. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2019.06.039WANG H B, DU Z M. Research progress on safety of lithium-ion batteries under low pressure[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2019, 38(6): 884-890(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2019.06.039 [17] MCALLISTER S, FERNANDEZ-PELLO A C, URBAN D, et al. The combined effect of pressure and oxygen concentration on piloted ignition of a solid combustible[J]. Combustion and Flame, 2010, 157(9): 1753-1759. doi: 10.1016/j.combustflame.2010.02.022 [18] LIU Y, NIU H, LI Z, et al. Thermal runaway characteristics and failure criticality of massive ternary Li-ion battery piles in low-pressure storage and transport[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2021, 155: 486-497. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2021.09.031 [19] 沈俊杰, 王海斌, 贺元骅, 等. 低压环境下不同三元圆柱锂电池热失控危险特性对比研究[J]. 中国安全生产科学技术, 2020, 16(6): 110-115. doi: 10.11731/j.issn.1673-193x.2020.06.018SHEN J J, WANG H B, HE Y H, et al. Comparative study on thermal runaway hazardous characteristics of different ternary cylindrical lithium battery under low-pressure environment[J]. Journal of Safety Science and Technology, 2020, 16(6): 110-115(in Chinese). doi: 10.11731/j.issn.1673-193x.2020.06.018 [20] SUN Q, LIU H, ZHI M, et al. Thermal characteristics of thermal runaway for pouch lithium-ion battery with different state of charges under various ambient pressures[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2022, 527: 231175. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2022.231175 [21] 窦文娟, 王栋, 王正超, 等. 三元锂离子电池高温诱导热失控试验研究[J]. 青岛大学学报(工程技术版), 2021, 36(4): 1-7. doi: 10.13306/j.1006-9798.2021.04.001DOU W J, WANG D, WNAG Z C, et al. Experimental study onhigh temperature induced thermal runaway of ternary lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Qingdao University (E & T), 2021, 36(4): 1-7(in Chinese). doi: 10.13306/j.1006-9798.2021.04.001 [22] QUINTIERE J G. On methods to measure the energetics of a lithium ion battery in thermal runaway[J]. Fire Safety Journal, 2020, 111: 102911. doi: 10.1016/j.firesaf.2019.102911 [23] 贺元骅, 刘奕, 孙强, 等. 不同外热部位下18650型锂离子电池热失控研究[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2021, 21(1): 124-132. doi: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2019.0762HE Y H, LIU Y, SUN Q, et al. On the thermal runaway mechanism of 18650 lithium-ion batteries at the different external thermal positions[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2021, 21(1): 124-132(in Chinese). doi: 10.13637/j.issn.1009-6094.2019.0762 [24] RICH D, LAUTENBERGER C, TORERO J L, et al. Mass flux of combustible solids at piloted ignition[J]. Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2007, 31(2): 2653-2660. doi: 10.1016/j.proci.2006.08.055 [25] FERNANDEZ-PELLO A C. Combustion fundamentals of fire[M]. San Diego: Academic Press, 1995: 31-100. -







 下载:
下载: