-
摘要:
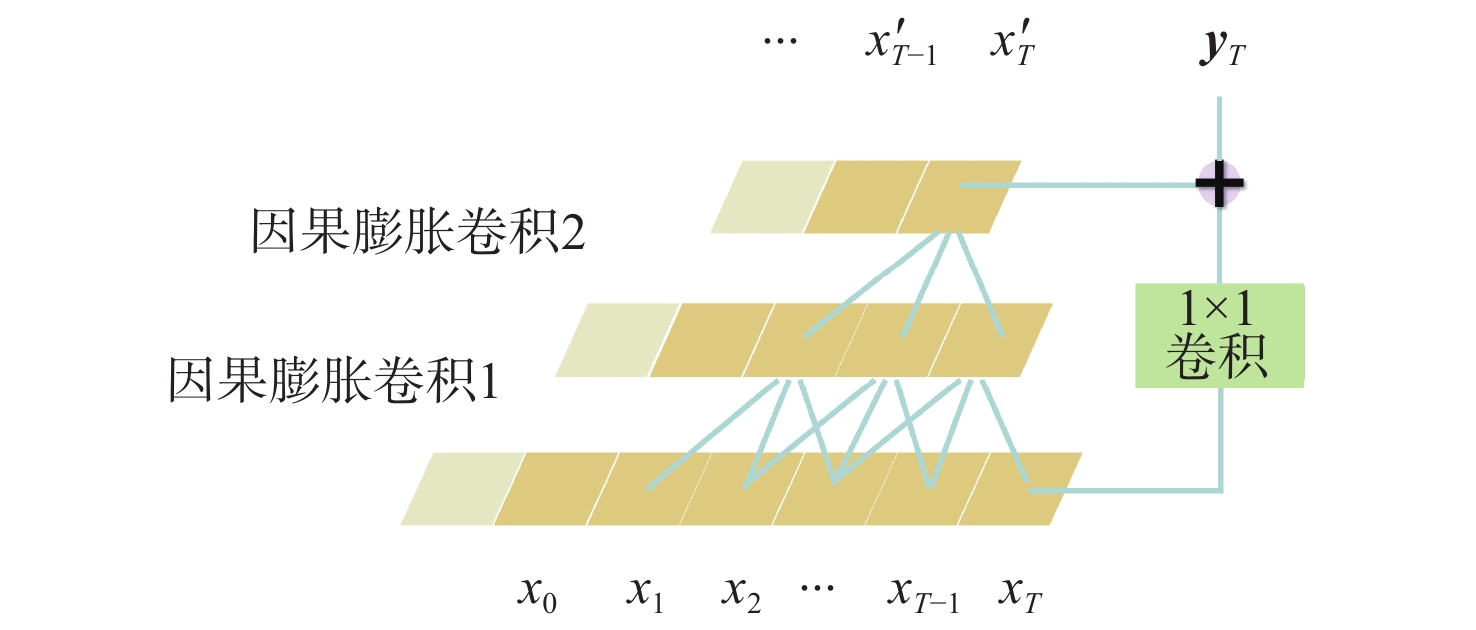
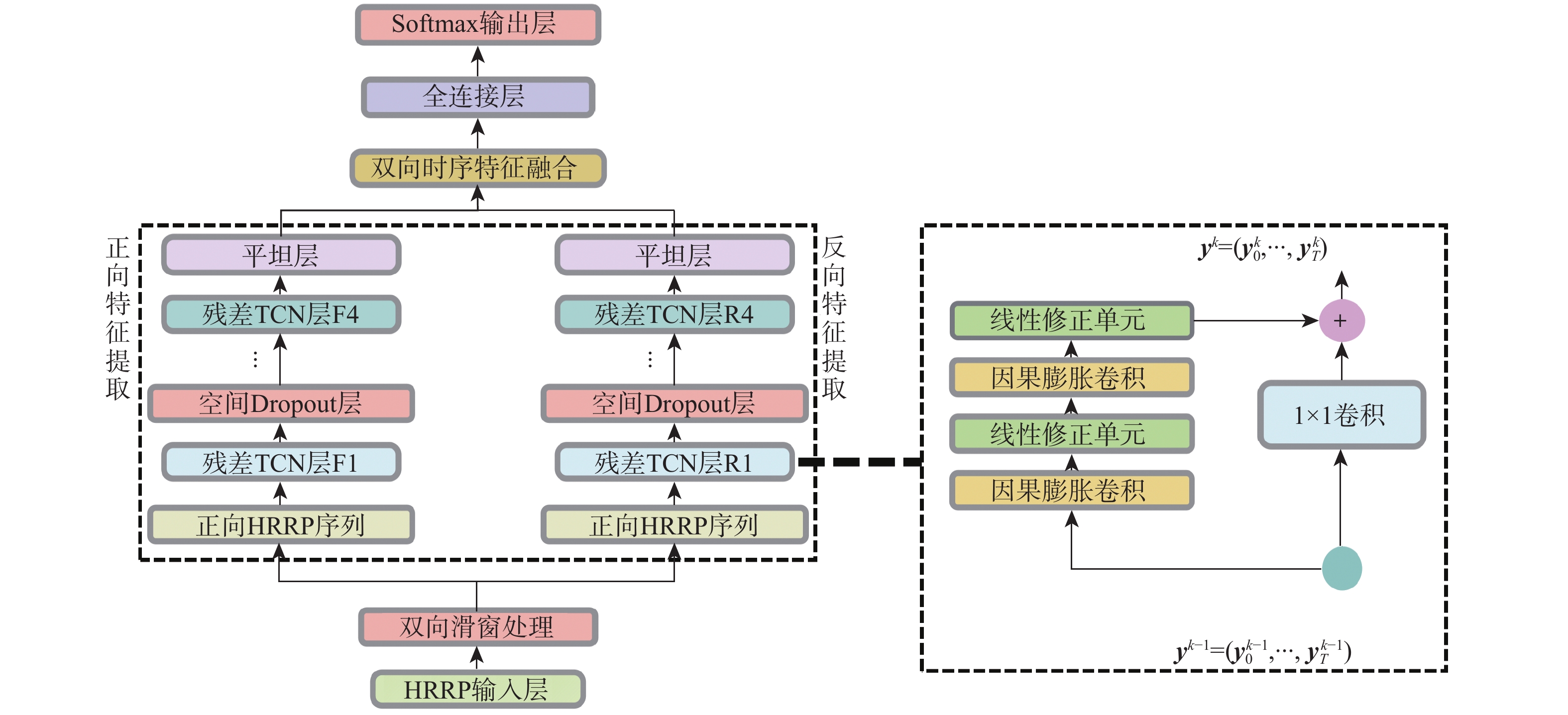
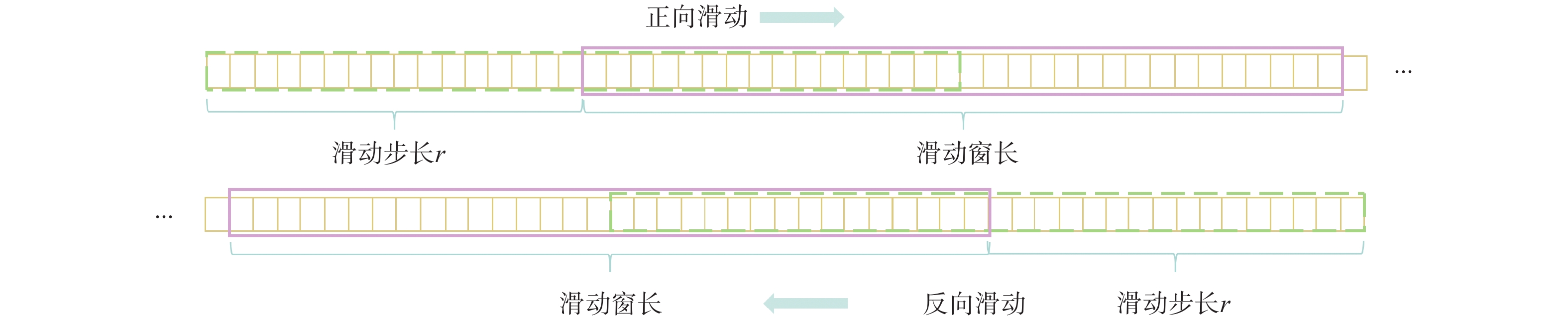
针对弹道中段目标高分辨距离像(HRRP)的时序特征提取和识别问题,为充分利用弹道中段目标HRRP的双向时序信息,进一步提高识别性能,提出一种基于加性融合双向时间卷积神经网络(AF-BiTCN)的识别方法。对HRRP数据采用双向时序滑窗法处理为双向序列;构建BiTCN逐层提取HRRP的双向深层时序特征,并将双向时序特征采用加性策略融合;利用更加稳健的融合特征实现对弹道中段目标的识别,并使用Adam算法优化AF-BiTCN的收敛速度和稳定性。实验结果表明:所提的基于AF-BiTCN的弹道中段目标HRRP识别方法较堆叠选择长短期记忆网络(SLSTM)、堆叠门控循环单元(SGRU)等6种时序方法具有更高的准确率和更快的识别速度,在测试集上达到了96.60%的准确率,并且在噪声数据集上表现出更好的鲁棒性。
-
关键词:
- 双向时间卷积神经网络 /
- 弹道目标识别 /
- 特征融合 /
- 高分辨距离像 /
- 滑窗算法
Abstract:To address the problem of temporal feature extraction and recognition of high-resolution range profiles (HRRP) of midcourse ballistic targets, a recognition method based on bidirectional temporal convolutional networks with additive fusion (AF-BiTCN) was proposed, which could make full use of the bidirectional temporal information of HRRP of midcourse ballistic targets and further improve the recognition performance. Firstly, the HRRP data was processed into a bidirectional sequence by the bidirectional sliding window algorithm. Then, the BiTCN was constructed to extract bidirectional deep temporal features of HRRP in each layer, and the bidirectional features were fused by an additive strategy. Finally, more robust fusion features were utilized to recognize ballistic targets, and the Adam algorithm was used to optimize the convergence speed and stability of AF-BiTCN. The experimental results show that the proposed HRRP recognition method of midcourse ballistic targets based on AF-BiTCN in this paper has higher accuracy and faster recognition speed compared with six methods such as stack long short-term memory (SLSTM), stack gate recurrent unit (SGRU) and so on, and it achieves an accuracy of 96.60% on the test set. Moreover, the proposed method indicates better robustness on noise datasets.
-
表 1 AF-BiTCN参数设置
Table 1. AF-BiTCN parameters setting
参数 数值 损失函数 交叉熵 优化器 Adam[24] 批量大小 256 学习率 0.000 3 一阶矩衰减率 0.9 二阶矩衰减率 0.999 滑窗窗长 32 滑窗间隔 16 迭代次数 400 卷积核 256,128,64,64 卷积核尺寸 1×3 膨胀系数 1,2,8,16 Dropout率 0.5 表 2 不同方法性能对比
Table 2. Performance comparison of different methods
模型 准确率/% 参数量 识别速度/μs AF-BiTCN 96.60 1.16×106 334 CNN-BiGRU 95.78 1.76×106 792 Attention-BiGRU 95.57 1.15×106 708 BiGRU 95.37 1.15×106 670 BiLSTM 94.70 1.52×106 884 SGRU 94.17 0.56×106 374 SLSTM 93.87 0.58×106 392 表 3 不同信噪比条件下鲁棒性对比实验的识别准确率
Table 3. Recognition accuracy of robustness comparison experiments under different signal-to-noise ratios
% 信噪比/dB SLSTM SGRU BiLSTM BiGRU Attention-BiGRU CNN-BiGRU AF-BiTCN −10 56.69 56.08 54.00 56.11 56.22 55.58 56.88 −5 66.02 66.00 67.67 68.25 67.81 66.56 69.22 0 75.86 75.61 74.83 75.55 77.02 75.33 77.21 5 82.83 81.61 81.00 82.22 83.13 82.94 83.64 10 86.33 86.64 84.78 86.05 87.50 87.89 89.03 20 89.91 91.86 88.33 90.97 91.61 92.36 92.45 表 4 不同融合方法的性能对比
Table 4. Performance comparison of different fusion methods
% 融合方法 弹道目标类别 准确率 精确率 召回率 F1分数 加性融合 弹头 91.60 92.74 91.74 92.24 高仿诱饵 95.92 93.04 95.91 94.46 简单诱饵 97.33 98.40 97.25 97.82 球形诱饵 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 母舱 98.08 98.90 98.08 98.49 同维度连接 弹头 89.75 93.24 89.82 91.50 高仿诱饵 94.33 93.16 94.33 93.74 简单诱饵 98.58 94.94 98.50 96.68 球形诱饵 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 母舱 97.92 99.23 97.91 98.57 乘性融合 弹头 87.42 95.01 87.48 91.09 高仿诱饵 95.75 92.28 95.75 93.98 简单诱饵 99.33 93.27 99.25 96.16 球形诱饵 100.00 100.00 100.00 100.00 母舱 97.58 99.82 97.58 98.69 表 5 AF-BiTCN消融实验结果
Table 5. Ablation experiments results of AF-BiTCN
% 模型 准确率 召回率 精确率 F1分数 AF-BiTCN 96.60 96.62 96.60 96.60 正向TCN 96.00 96.00 96.01 95.98 反向TCN 96.33 96.33 96.38 96.31 -
[1] EZUMA M, ANJINAPPA C K, FUNDERBURK M, et al. Radar cross section based statistical recognition of UAVs at microwave frequencies[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58(1): 27-46. [2] CHOI I O, PARK S H, KIM M, et al. Efficient discrimination of ballistic targets with micromotions[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(2): 1243-1261. [3] ZHANG H, RAO P, XIA H, et al. Modeling and analysis of infrared radiation dynamic characteristics for space micromotion target recognition[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2021, 116: 103795. [4] XUE B, YI W J, JING F, et al. Complex ISAR target recognition using deep adaptive learning[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 97: 104025. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2020.104025 [5] PERSICO A R, ILIOUDIS C V, CLEMENTE C, et al. Novel classification algorithm for ballistic target based on HRRP frame[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2019, 55(6): 3168-3189. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2905281 [6] 付哲泉, 李相平, 李尚生, 等. 深度学习在雷达目标高分辨距离像识别中的研究综述[J]. 航空兵器, 2020, 27(3): 37-43. doi: 10.12132/ISSN.1673-5048.2019.0118FU Z Q, LI X P, LI S S, et al. Review of radar HRRP target recognition based on deep learning[J]. Aero Weaponry, 2020, 27(3): 37-43(in Chinese). doi: 10.12132/ISSN.1673-5048.2019.0118 [7] 王彩云, 黄盼盼, 李晓飞, 等. 基于AEPSO-SVM算法的雷达HRRP目标识别[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(9): 1984-1989. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.09.10WANG C Y, HUANG P P, LI X F, et al. Radar HRRP target recognition based on AEPSO-SVM algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(9): 1984-1989(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2019.09.10 [8] ZHAO D B, HUI L. Radar target recognition based on central moment feature and GA-BP neural network[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2018, 47(8): 826005. [9] LI C, DU L, DENG S, et al. Point-wise discriminative auto-encoder with application on robust radar automatic target recognition[J]. Signal Processing, 2020, 169: 107385. [10] WANG X D, LI R, WANG J, et al. One-dimension hierarchical local receptive fields based extreme learning machine for radar target HRRP recognition[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 418: 314-325. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.08.050 [11] TU J, HUANG T, LIU X S, et al. A novel HRRP target recognition method based on LSTM and HMM decision-making[C]//Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Automation and Computing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1-6. [12] PAN M, DU L, WANG P H, et al. Multi-task hidden Markov modeling of spectrogram feature from radar high-resolution range profiles[J]. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Processing, 2012, 2012: 86. [13] LIU J Q, CHEN B, CHEN W C, et al. Radar HRRP target recognition with target aware two-dimensional recurrent neural network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communications and Computing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1-6. [14] CHU Y C, GUO Z H. Attention enhanced spatial temporal neural network for HRRP recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 3805-3809. [15] 刘家麒, 陈渤, 介茜. 基于注意力机制和双向GRU模型的雷达HRRP目标识别[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8(5): 589-597. doi: 10.12000/JR19014LIU J Q, CHEN B, JIE X. Radar high-resolution range profile target recognition based on attention mechanism and bidirectional gated recurrent[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8(5): 589-597(in Chinese). doi: 10.12000/JR19014 [16] 沈梦启. 基于卷积-循环神经网络的雷达高分辨距离像目标识别方法研究[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2019: 37-48.SHEN M Q. Research on target recognition method of radar high resolution range profile based on convolution-cyclic neural network[D]. Xi’an: Xidian University, 2019: 37-48(in Chinese). [17] 陶志勇, 闫明豪, 刘影. 基于时序卷积网络的信道编码闭集识别[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2022, 50(3): 12-17.TAO Z Y, YAN M H, LIU Y. Channel coding closed set recognition based on temporal convolutional network[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(3): 12-17(in Chinese). [18] ZHAO W T, GAO Y Y, JI T X, et al. Deep temporal convolutional networks for short-term traffic flow forecasting[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 114496-114507. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2935504 [19] BAI S J, KOLTER J Z, KOLTUN V, et al. An empirical evaluation of generic convolutional and recurrent networks for sequence modeling[EB/OL]. (2018-04-19)[2023-01-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1803.01271v2. [20] SRIVASTAVA N, HINTON G, KRIZHEVSKY A, et al. Dropout: A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting[J]. Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2014, 15: 1929-1958. [21] SALIMANS T, KINGMA D P. Weight normalization: A simple reparameterization to accelerate training of deep neural networks[C]// Proceedings of the 30th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. La Jolla: NIPS, 2016, 29: 901-909. [22] 徐彬, 陈渤, 刘家麒, 等. 采用双向LSTM模型的雷达HRRP目标识别[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2019, 46(2): 29-34.XU B, CHEN B, LIU J Q, et al. Radar HRRP target recognition by the bidirectional LSTM model[J]. Journal of Xidian University, 2019, 46(2): 29-34(in Chinese). [23] 向前, 王晓丹, 李睿, 等. 基于DCNN的弹道中段目标HRRP图像识别[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2020, 42(11): 2426-2433. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.11.03XIANG Q, WANG X D, LI R, et al. HRRP image recognition of midcourse ballistic targets based on DCNN[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(11): 2426-2433(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.11.03 [24] KINGMA D P, BA J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[EB/OL]. (2017-01-30)[2023-01-12]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1412.6980. -








 下载:
下载: