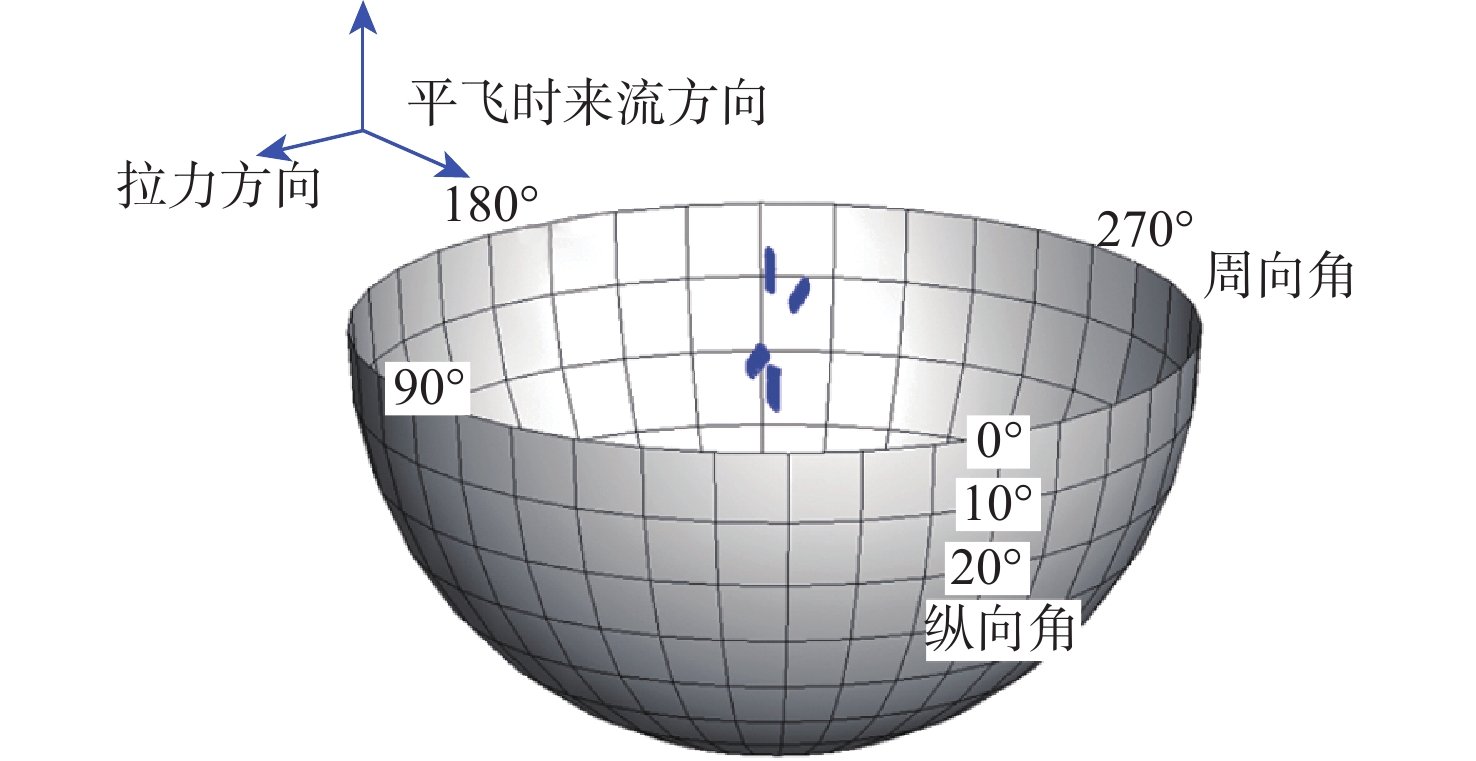
Computation on aerodynamic and aeroacoustic characteristics of scissor tail-rotor under sideslip condition
-
摘要:
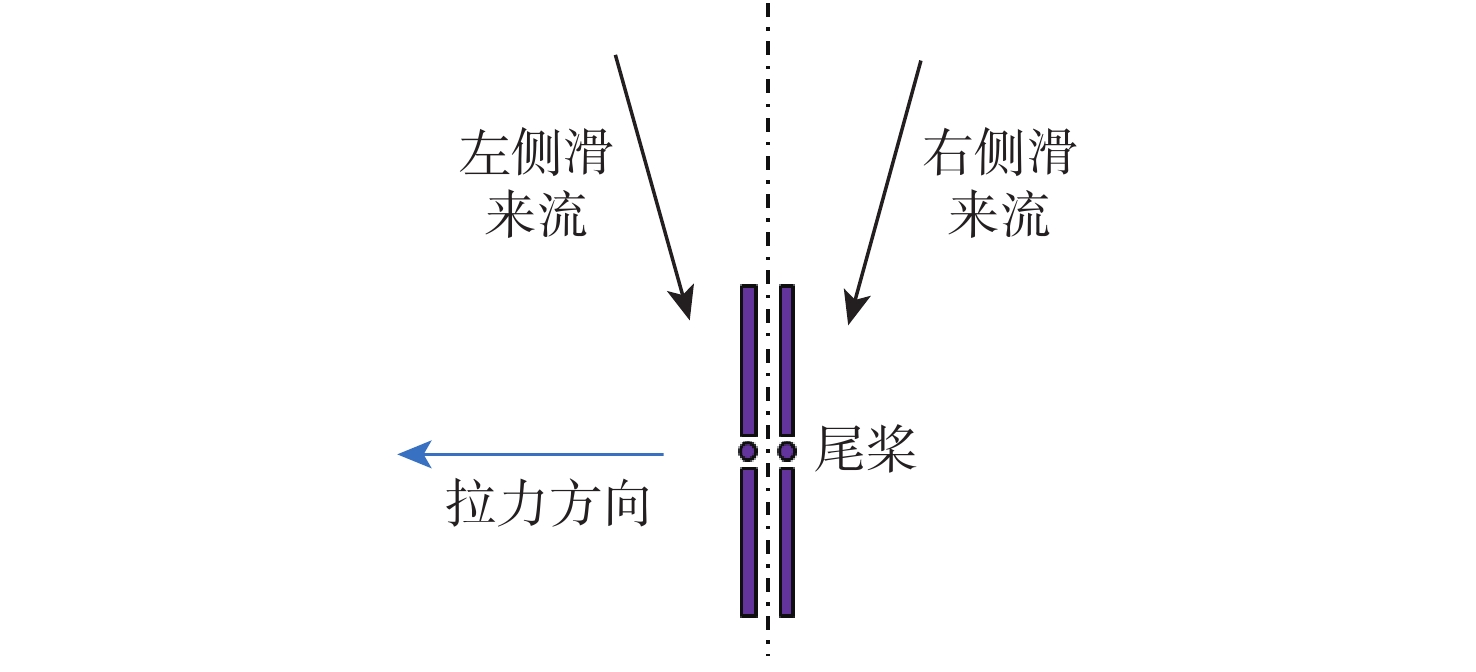
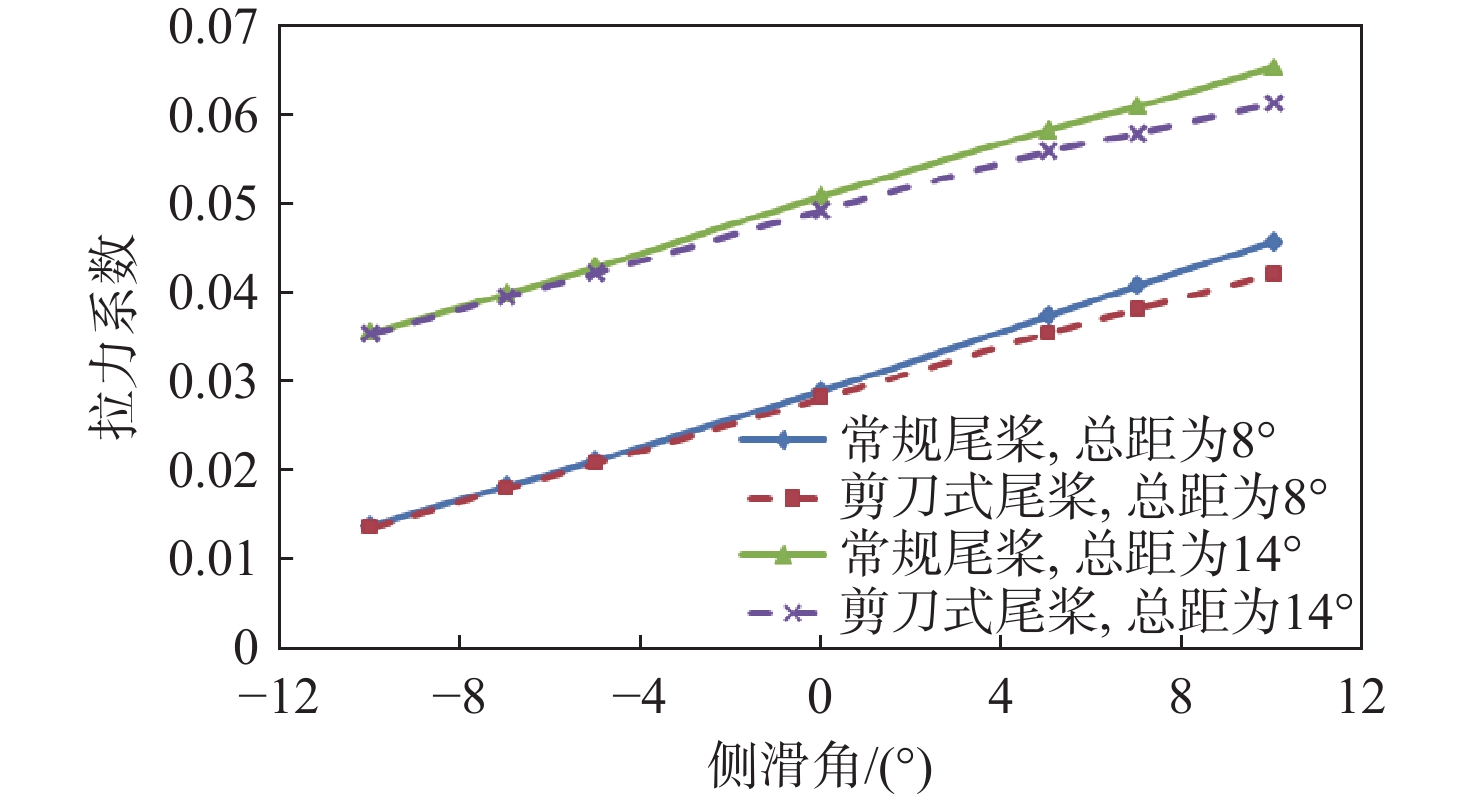
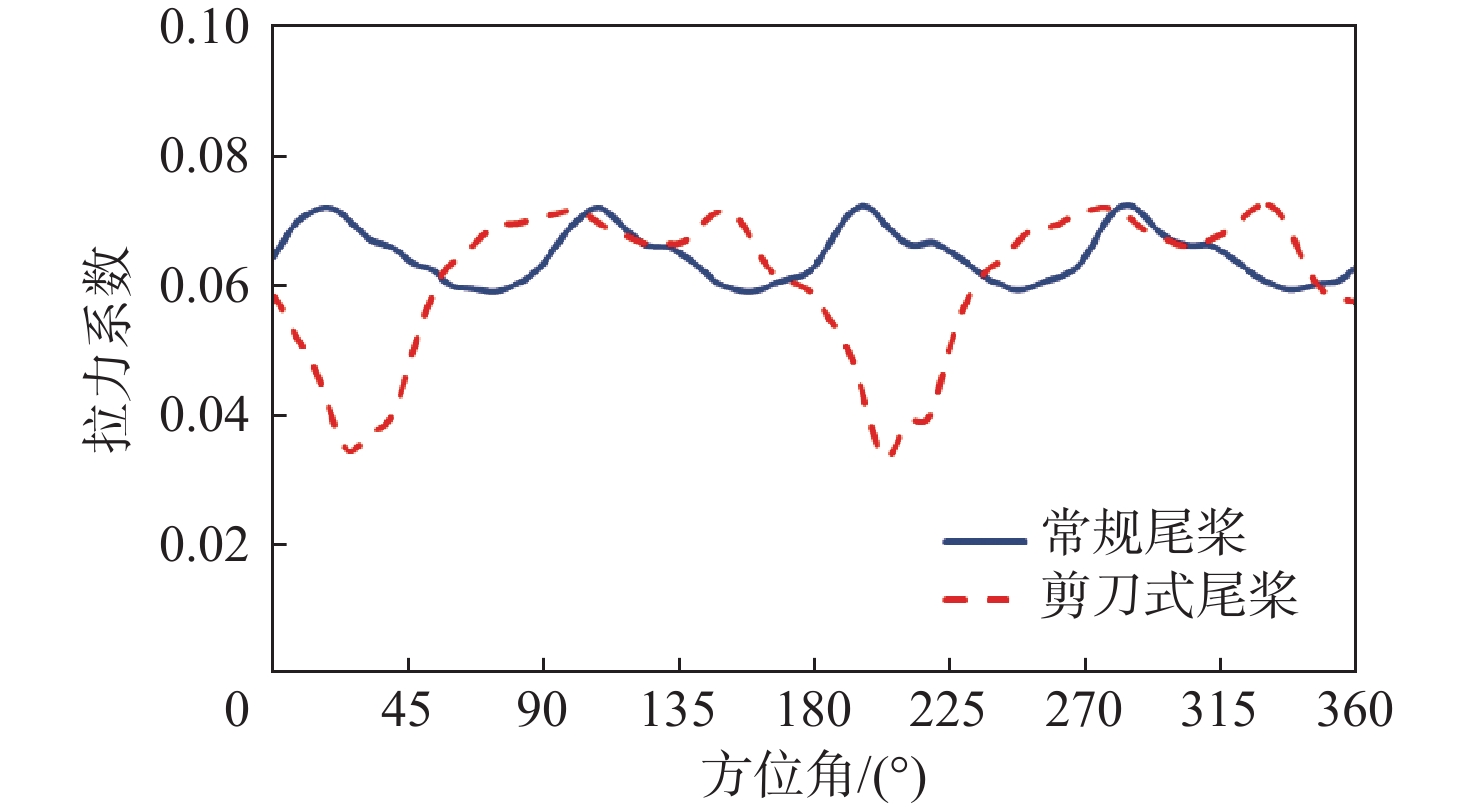
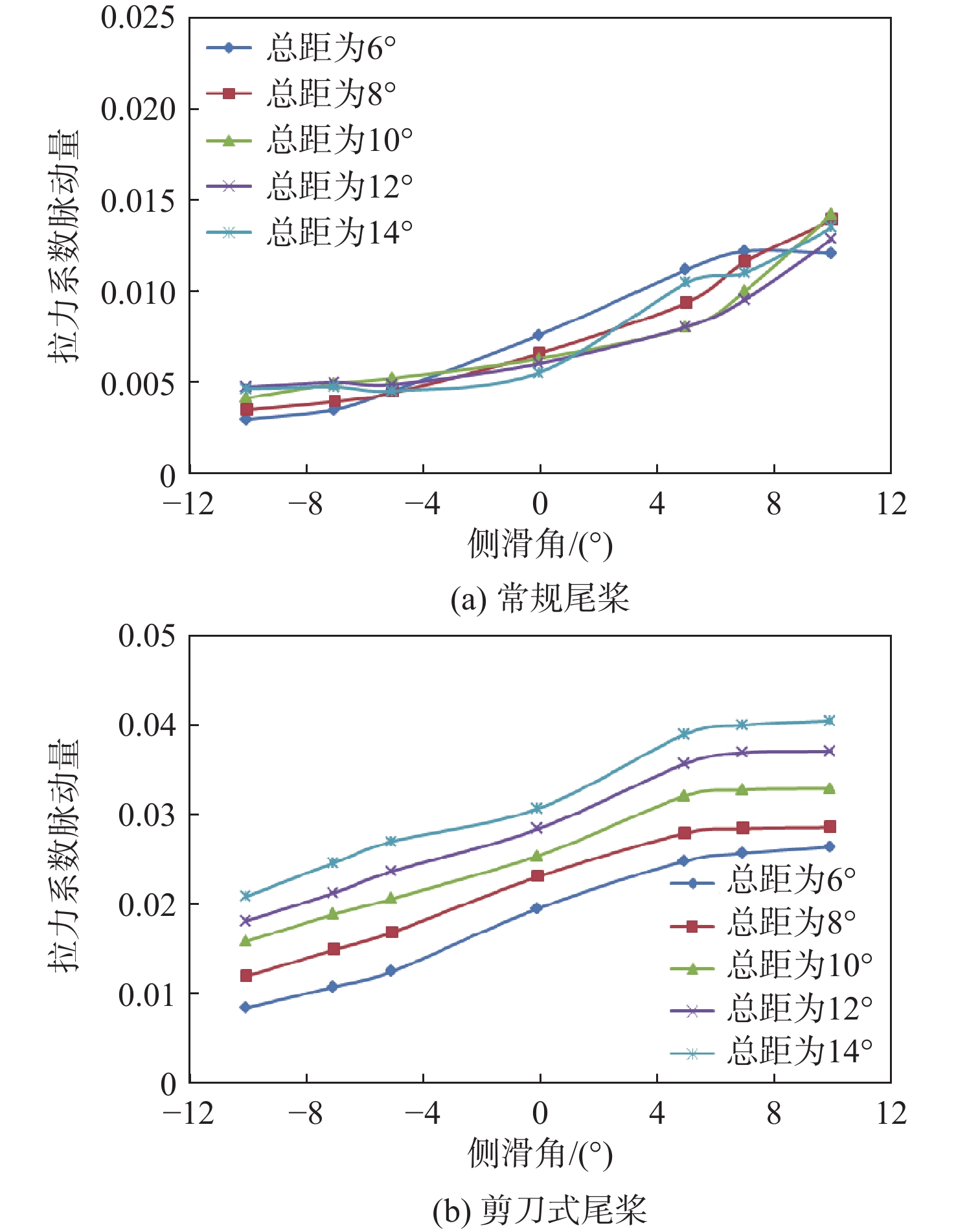
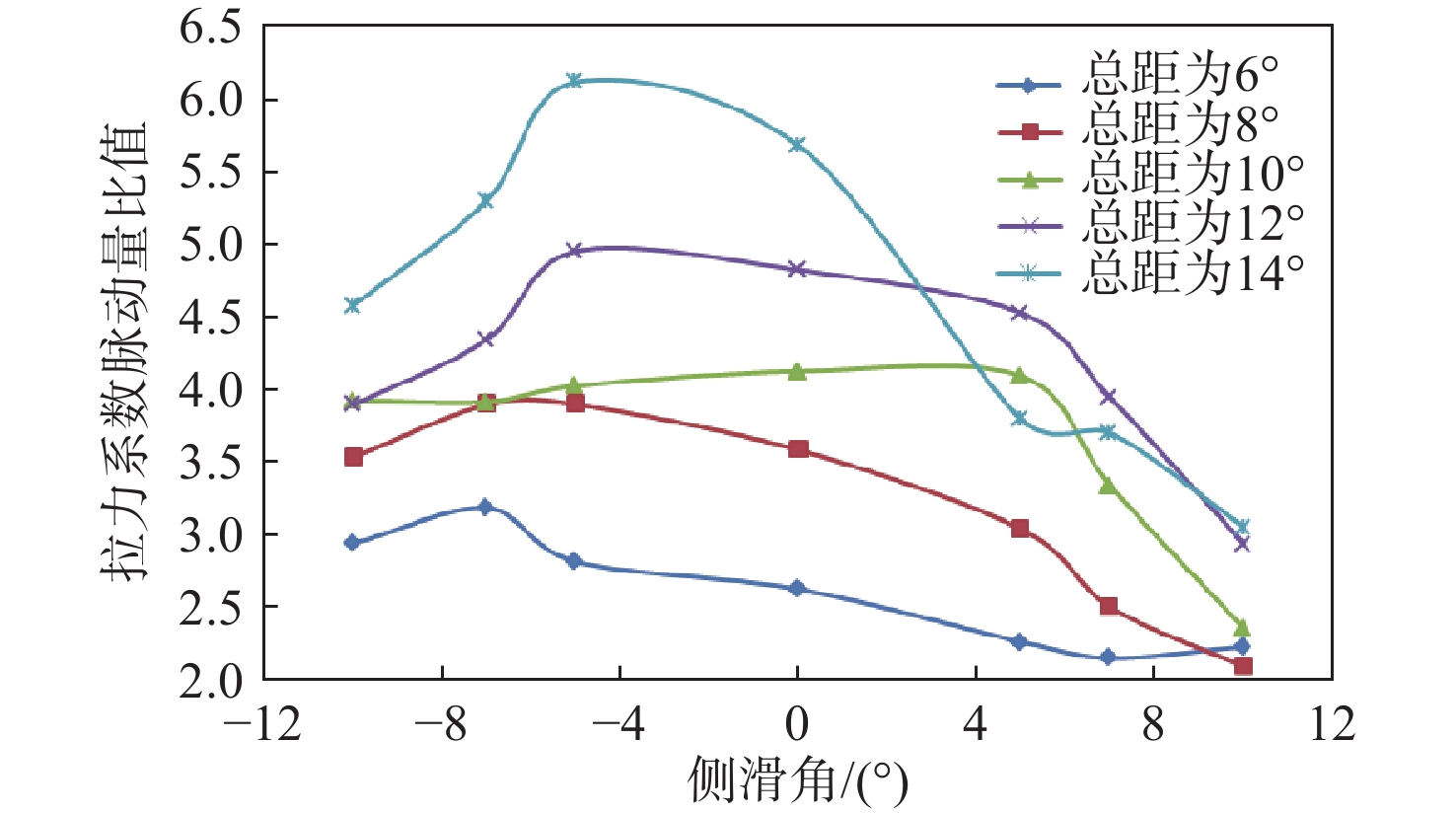
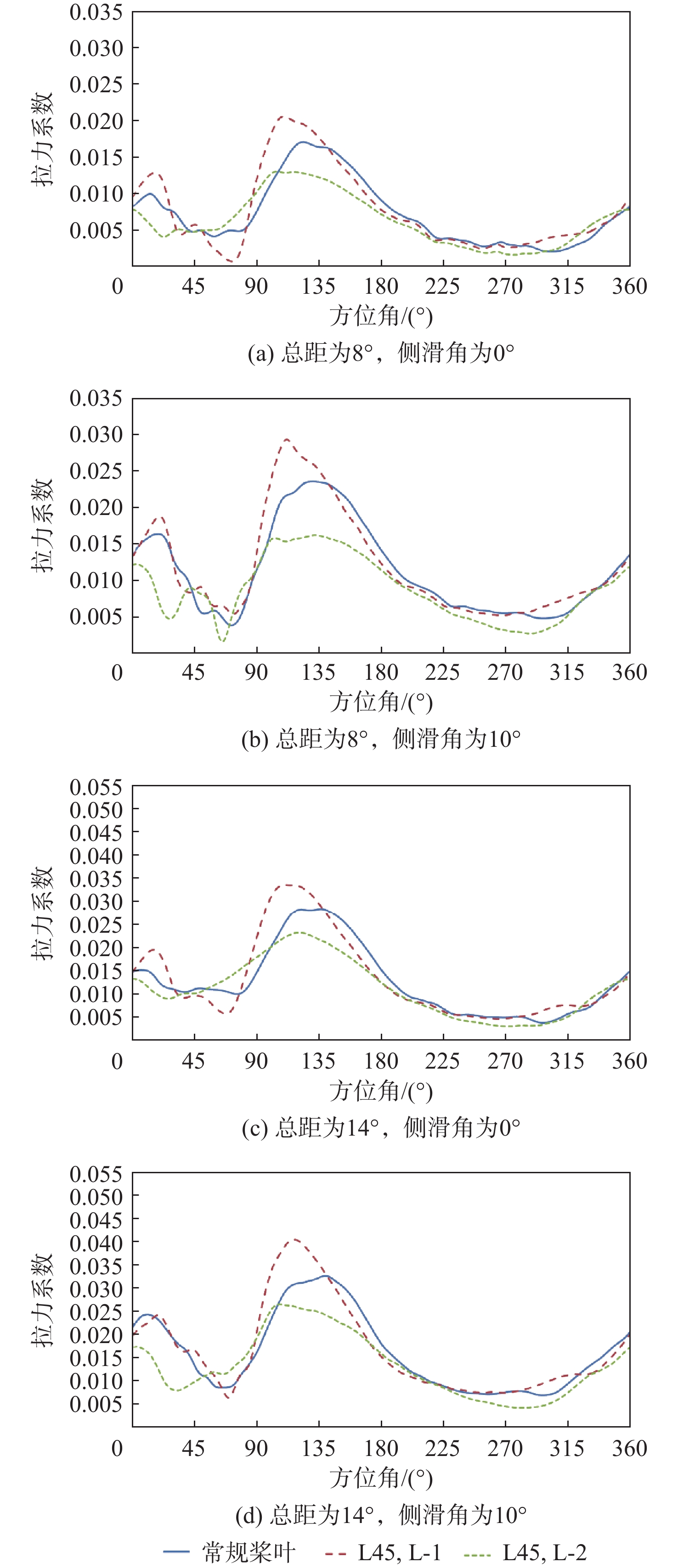
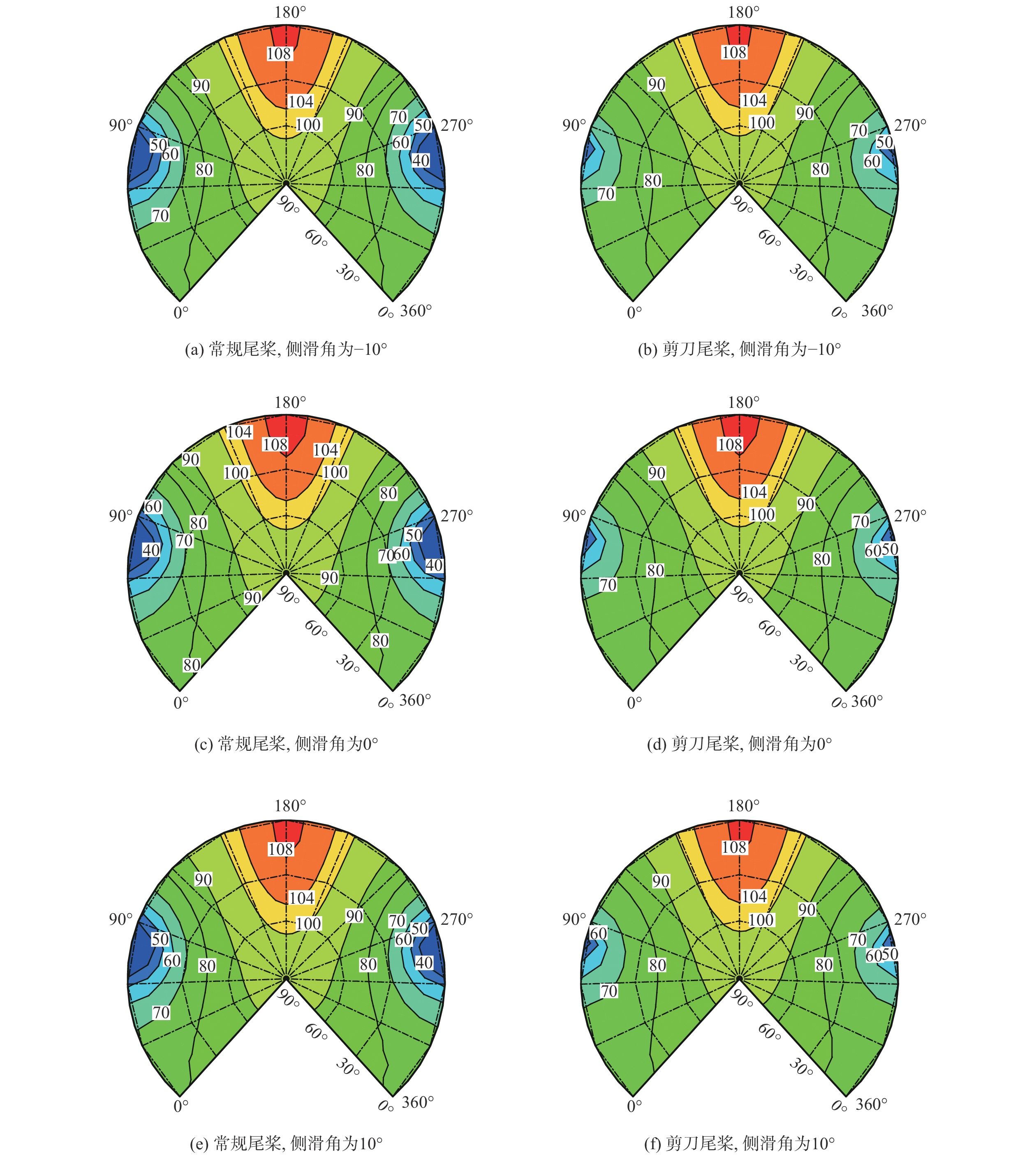
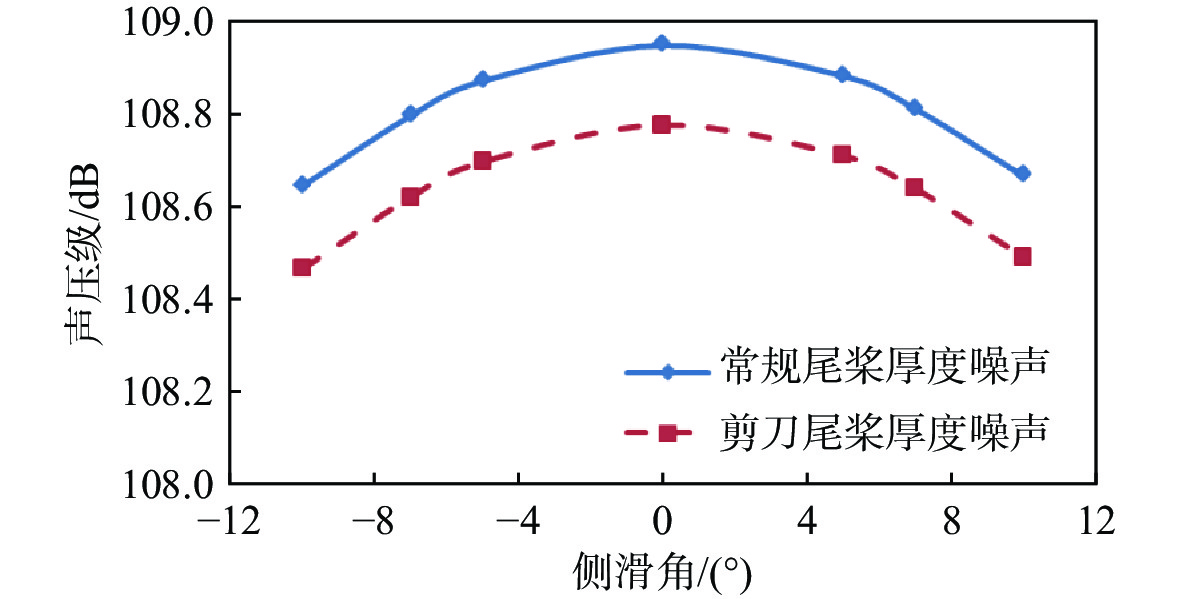
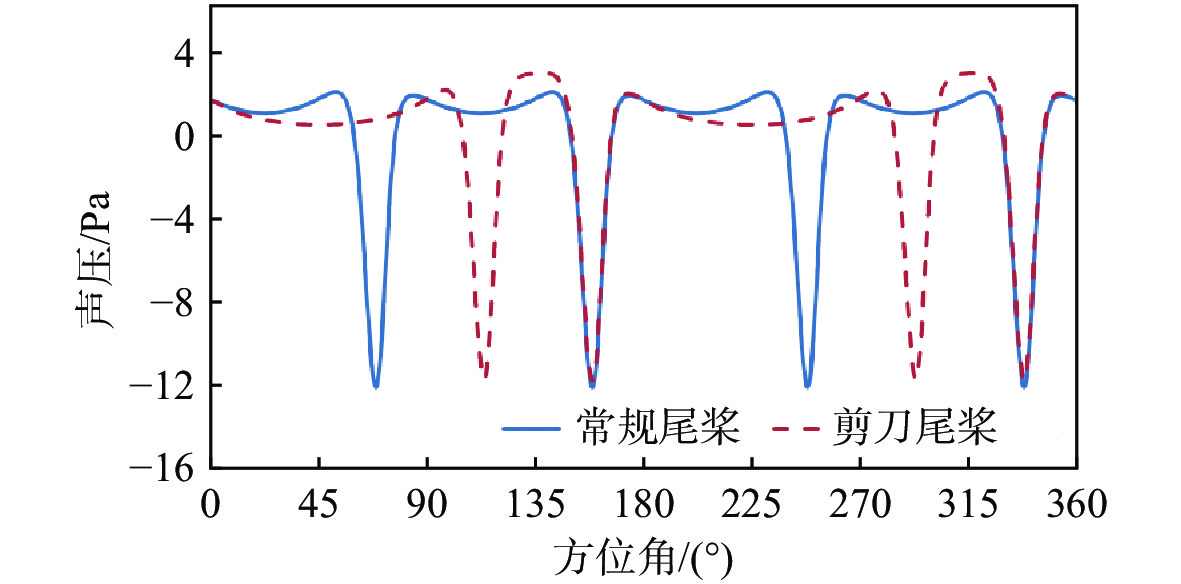
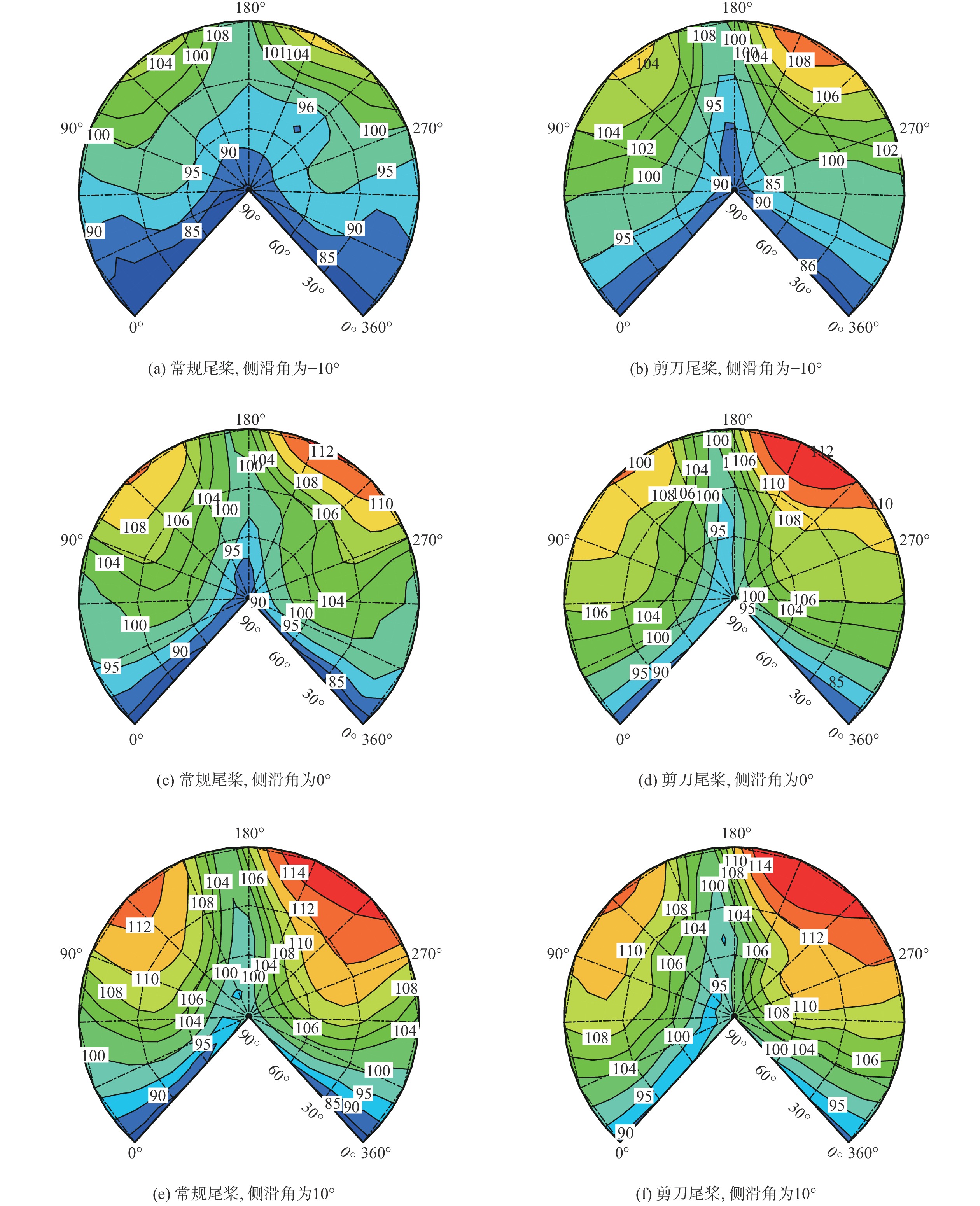
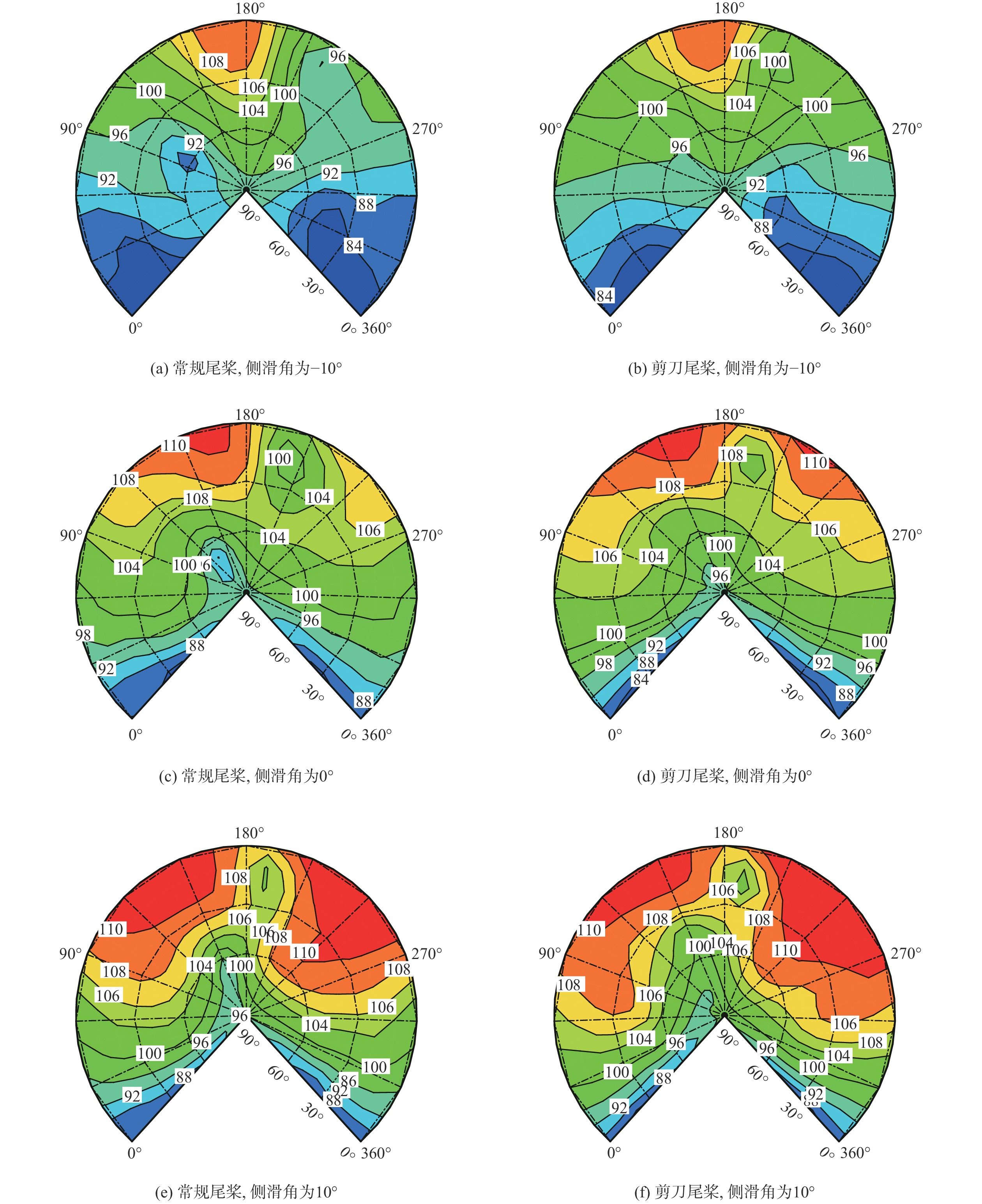
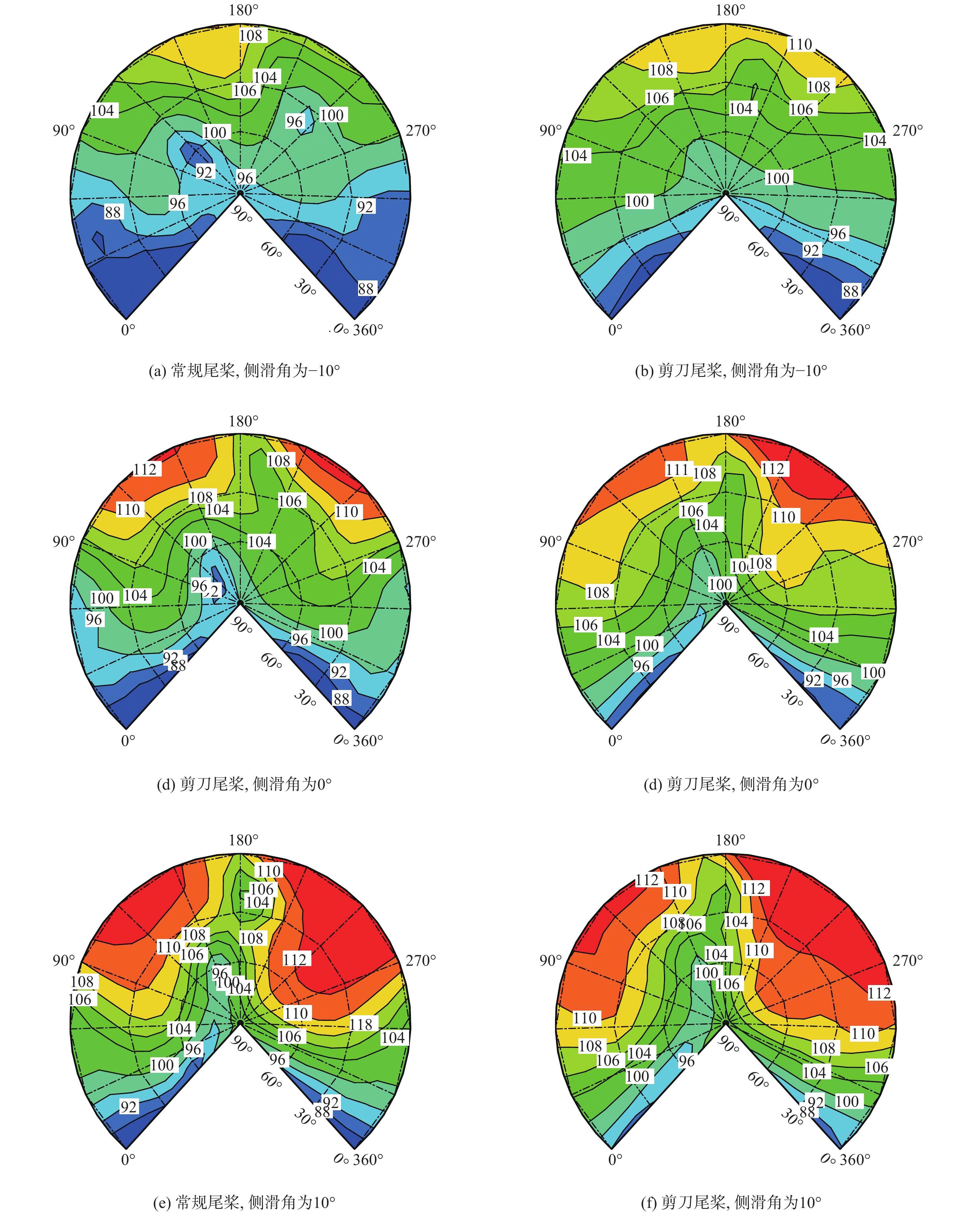
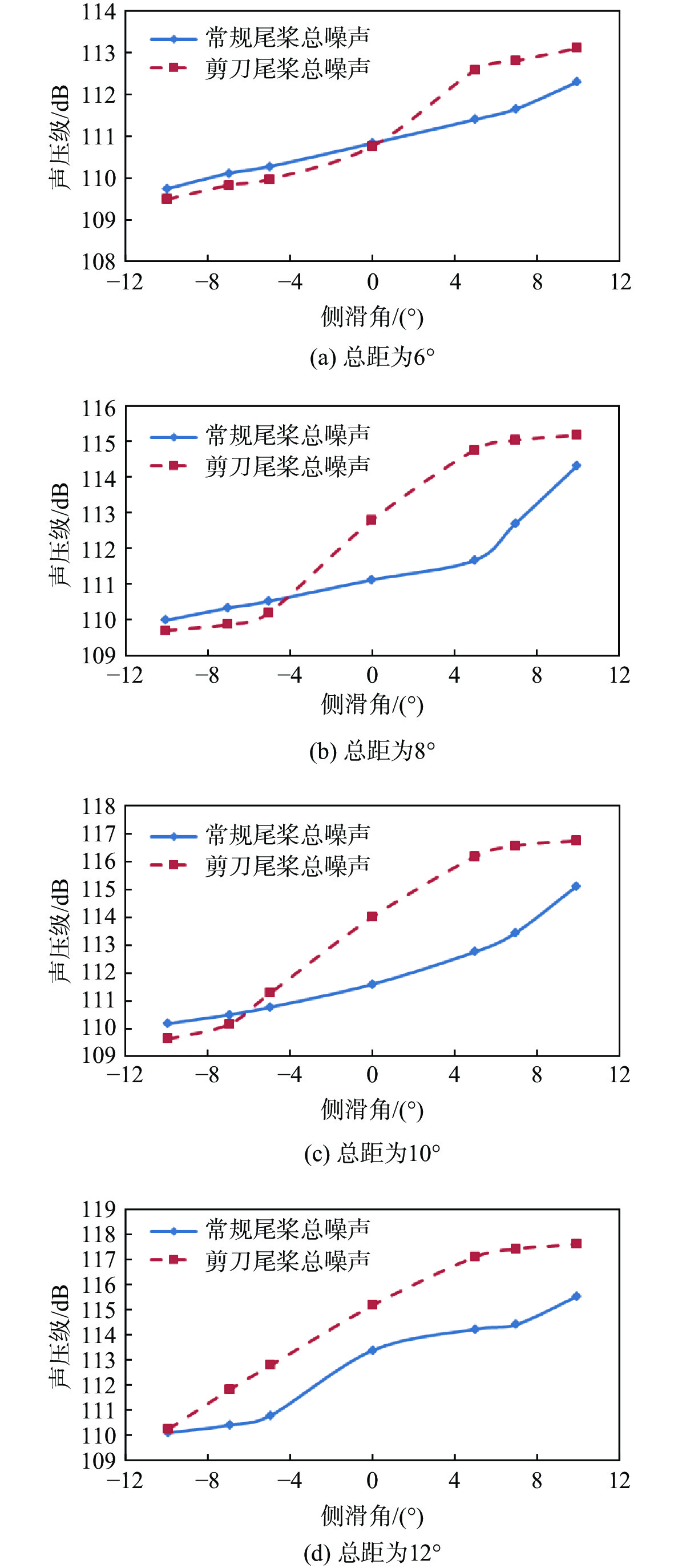
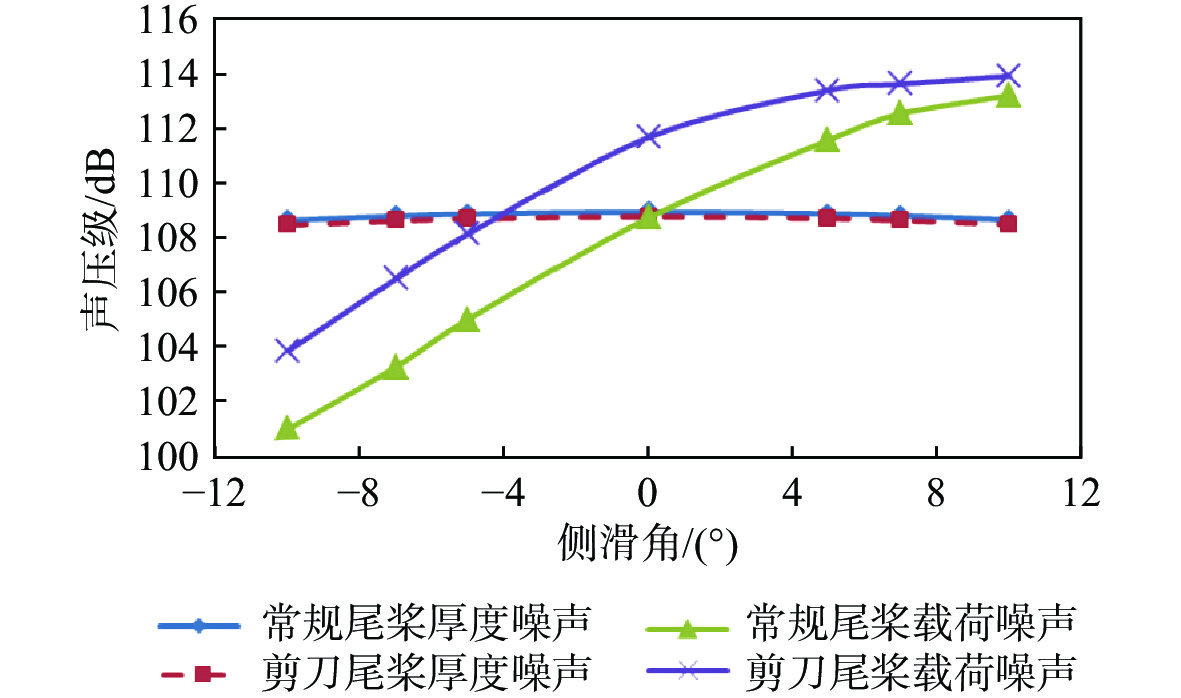
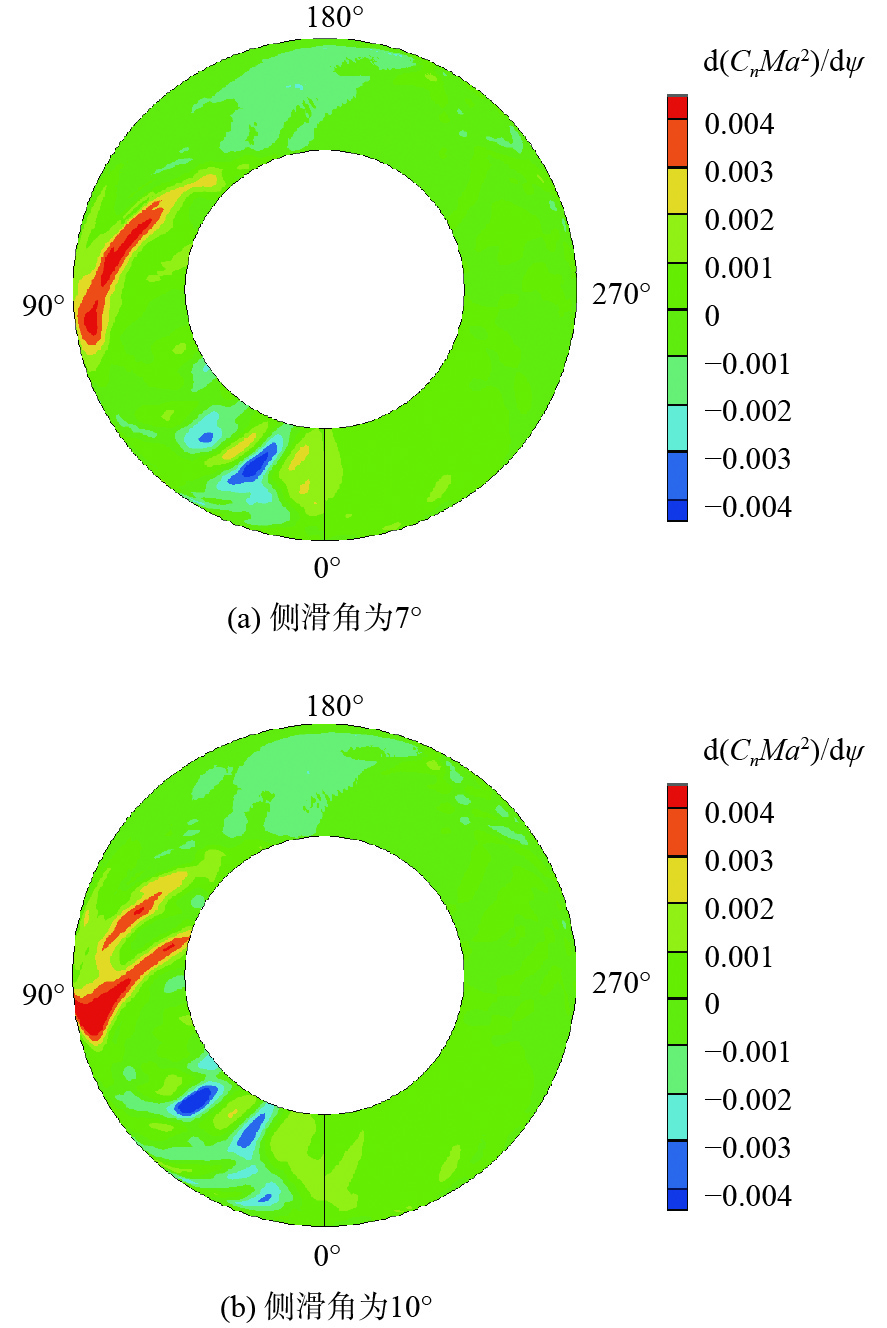
针对侧滑状态下剪刀式尾桨气动环境和噪声特性复杂的问题,提出一套基于计算流体力学(CFD)和 FW-H方程的剪刀式尾桨气动噪声预估方法。通过求解可压缩雷诺平均Navier-Stokes(RANS)方程对剪刀式尾桨的流场进行数值模拟,在此基础上,采用基于固体表面积分面的FW-H方程来求解剪刀式尾桨气动噪声。应用所提方法研究了侧滑状态下剪刀式尾桨(L45)和常规形式尾桨的气动力和噪声特性。数值模拟结果表明:随着侧滑角增大,剪刀式尾桨拉力脉动量增大幅度大于常规尾桨;相同侧滑角状态,剪刀式尾桨的拉力脉动量明显大于常规尾桨,普遍达到2倍以上。在设计时应充分考虑剪刀式尾桨对直升机平衡和操纵带来的不利影响。在大多数计算状态,剪刀式尾桨的最大总噪声大于常规尾桨。
Abstract:In view of the complex aerodynamic environment and noise characteristics of the scissors tail rotor under the condition of sideslip, an aeroacoustic prediction method was proposed based on computational fluid dynamics (CFD)/FW-H equation. Firstly, the flow field of the scissor tail-rotor was numerically simulated by solving the Reynolds averaged Navier-Stokes (RANS) equation. Then, the FW-H equation based on the integral surface of the solid surface was used to solve the aeroacoustic. Under sideslip circumstances, the aerodynamic and aeroacoustic properties of the standard tail rotor and the scissor tail rotor (L45) were examined. The numerical results show that with the increase of sideslip angle, the thrust fluctuation of the scissor tail-rotor increased more than that of the conventional tail-rotor. Under the same condition, the thrust fluctuation of a scissor tail-rotor is obviously larger than that of a conventional tail-rotor, which is generally more than 2 times. Therefore, the design should adequately account for the detrimental effects of the scissors tail rotor on the helicopter’s balance and control. In most states, the maximum total noise of a scissors tail-rotor is bigger than that of a conventional tail-rotor.
-
Key words:
- scissor tail-rotor /
- sideslip condition /
- computational fluid dynamics /
- FW-H equation /
- aerodynamic /
- aeroacoustic
-
-
[1] YIN J, DUMMEL A, FALCHERO D, et al. Analysis of tail rotor noise reduction benefits using HELINOVI aeroacoustic main/tail rotor test and posttest prediction results[C]//Proceedings of the 32th European Rotorcraft Forum. Southampton: ERF, 2006: AC05. [2] ROZHDESTENSKY M G. Scissor rotor concept: New results obtained[C]//Proceedings of the American Helicopter Society 52nd Annual Forum. Washington, D. C.: American Helicopter Society, 1996: 1231-1241. [3] SAMUELS T, XUE S. Helicopter noise prediction and validation: First look at combined main and tail rotors[J]. Journal of the American Helicopter Society, 2008, 64(3): 2233-2241. [4] FLETCHER T M, DURAISAMY K, BROWN R E. Sensitivity of tail rotor noise to helicopter configuration in forward flight[C]// Proceedings of the 65th Annual Forum American Helicopter Society. Washington, D. C.: American Helicopter Society, 2009: 40-51. [5] EDWARDS B. Psvchoacoustic testing of modulated blade spacing for main rotor: NASA /CR-2002-211651[R]. Washington, D. C. : NASA, 2002: 1-50. [6] SULLIVAN B M, EDWARDS B D, BRENTNER K S, et al. A subjective test of modulated blade spacing for helicopter main rotors[J]. Journal of the American Helicopter Society, 2005, 50(1): 26-32. doi: 10.4050/1.3092840 [7] XU G H, ZHAO Q J, PENG Y H. Study on the induced velocity and noise characteristics of a scissors rotor[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2007, 44(3): 806-811. doi: 10.2514/1.24460 [8] FAN F, XU G H, SHI Y J, et al. Numerical calculations of aerodynamic and acoustic characteristics for scissored tail-rotors in forward flight[J]. Transactions of Nanjing University of Aeronautics, 2016, 33(3): 285-293. [9] 陈丝雨, 招启军, 范俊, 等. 悬停状态剪刀式尾桨气动/噪声特性优化分析[J]. 航空动力学报, 2019, 34(5): 1050-1060.CHEN S Y, ZHAO Q J, FAN J, et al. Optimization analysis for aerodynamic noise characteristics of scissors tail rotor in hover[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2019, 34(5): 1050-1060(in Chinese). [10] XU G H, WANG S C, ZHAO Q J. Experimental and analytical investigation on aerodynamic characteristics of helicopter scissors tail rotor[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2001, 14(4): 193-199. [11] 樊枫, 史勇杰, 徐国华. 剪刀式尾桨悬停状态气动力及噪声特性计算研究[J]. 航空学报, 2013, 34(9): 2100-2109.FAN F, SHI Y J, XU G H. Computational research on areodynamic and aeroacoustic characteristics of scissors tail-rotor in hover[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2013, 34(9): 2100-2109 (in Chinese). [12] 朱正, 招启军, 王博. 剪刀式尾桨涡流干扰机理和气动特性研究[J]. 力学学报, 2016, 48(4): 886-896.ZHU Z, ZHAO Q J, WANG B. Studies on vortex interaction mechanism and aerodynamic characteristic of scissors tail rotor[J]. Chinese Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, 2016, 48(4): 886-896(in Chinese). [13] 樊枫. 直升机非定常干扰流场与声场的计算方法研究与应用[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2013.FAN F. Research and application of computational methods for unsteady flow filed and sound field of helicopter[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013(in Chinese). [14] 李志彬, 杨永飞, 孙伟, 等. 剪刀式尾桨前飞状态气动噪声特性计算[J]. 航空动力学报, 2022, 37(12): 2691-2706.LI Z B, YANG Y F, SUN W, et al. Computation on aeroacoustic characteristics of scissors tail-rotor in forward flight[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2022, 37(12): 2691-2706(in Chinese). [15] FARASSAT F. Linear acoustic formulas for calculation of rotating blade noise[J]. AIAA Journal, 1981, 19(9): 1122-1130. doi: 10.2514/3.60051 [16] 江露生, 曹亚雄, 刘婷, 等. 共轴刚性旋翼悬停状态桨叶表面压力测量试验与计算研究[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2021, 47(12): 2484-2493.JIANG L S, CAO Y X, LIU T, et al. Experimental and computional study on blade surface pressure measurement of coaxial rigid rotor in hovering state[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2021, 47(12): 2484-2493(in Chinese). -







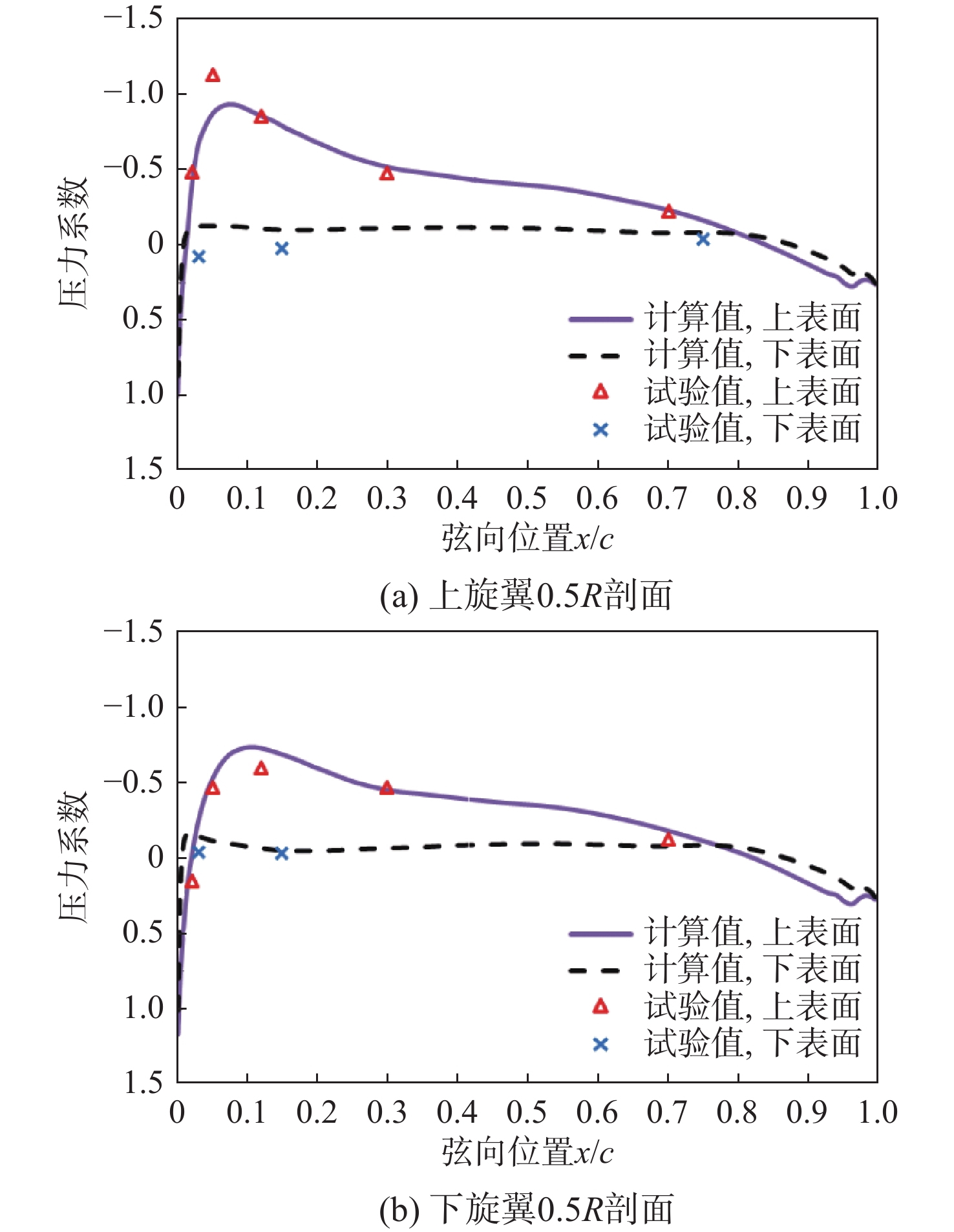
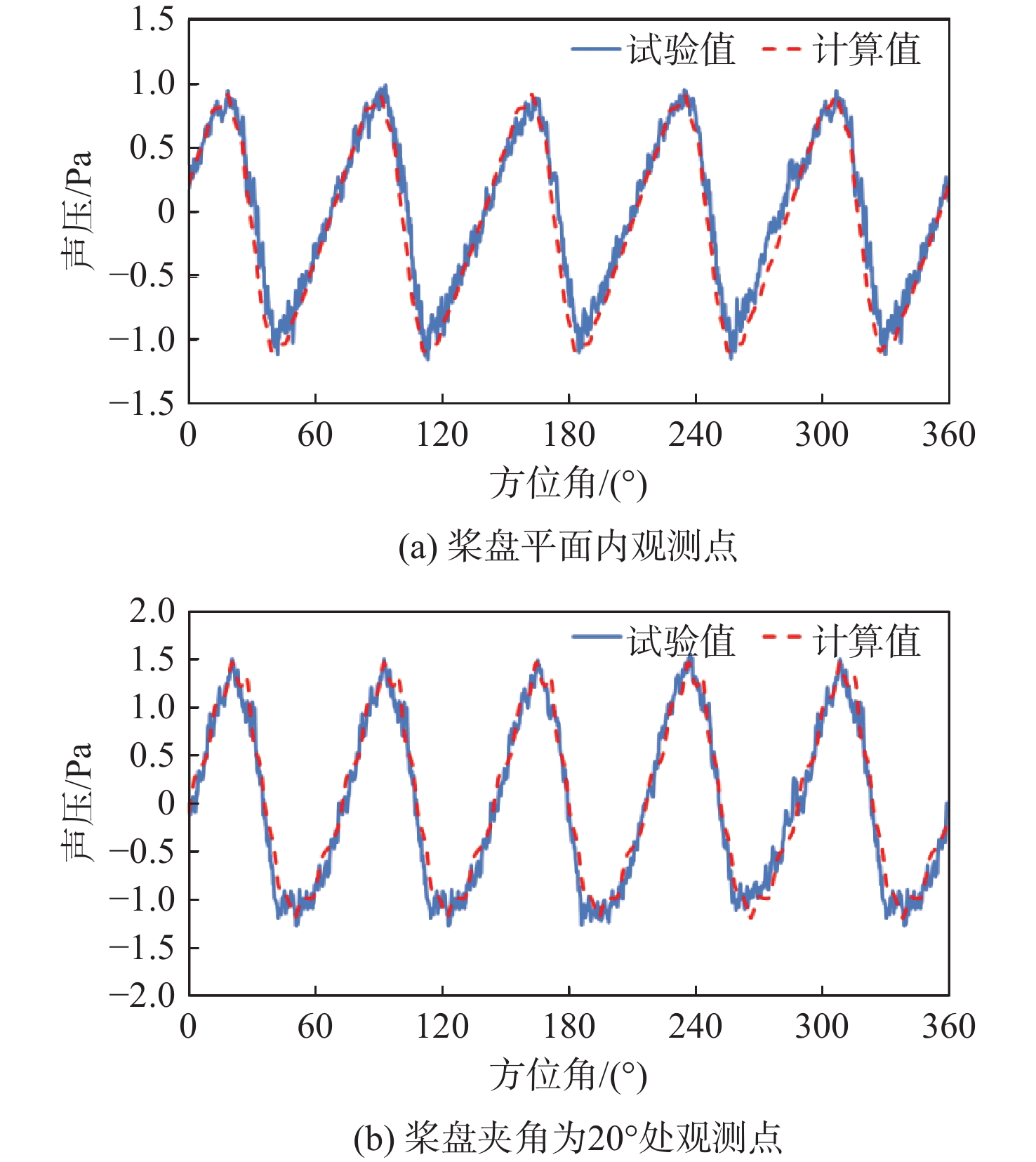
 下载:
下载: