Experimental investigation of overcharge caused sodium plating of hard carbon anodes for sodium-ion batteries
-
摘要:
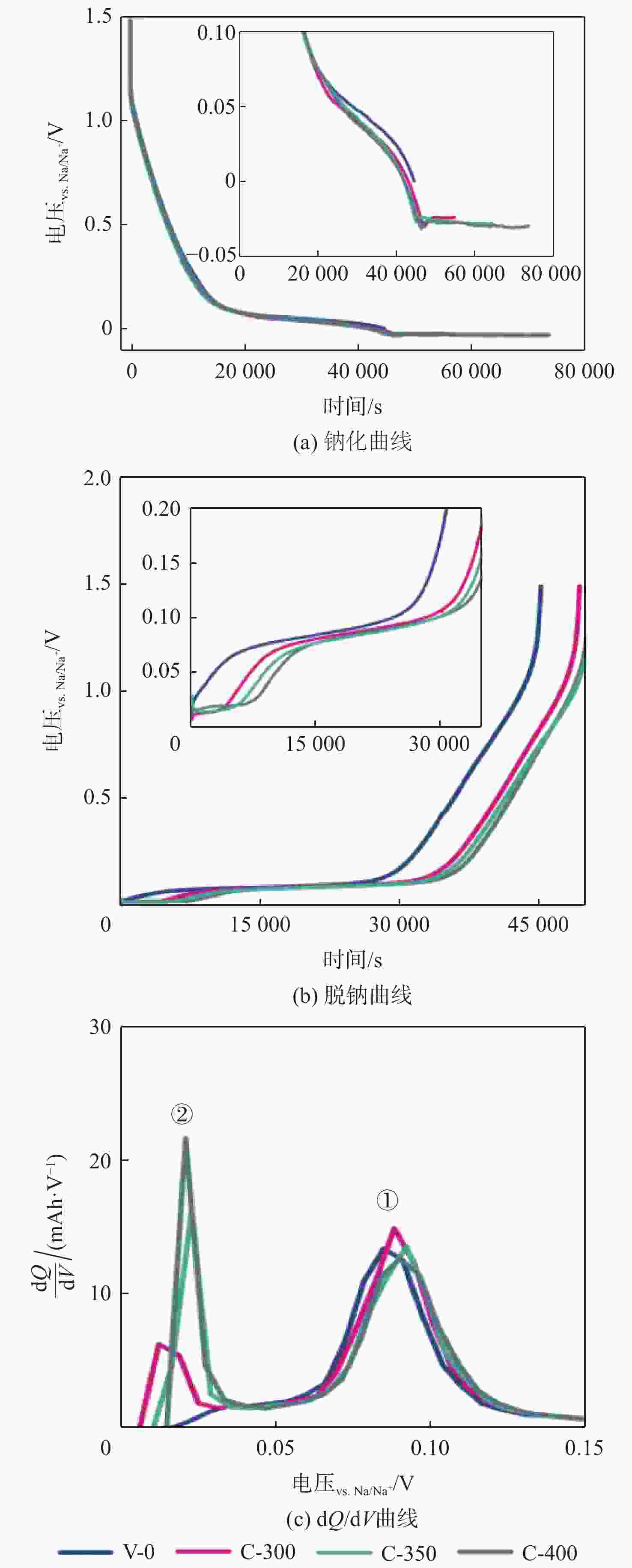
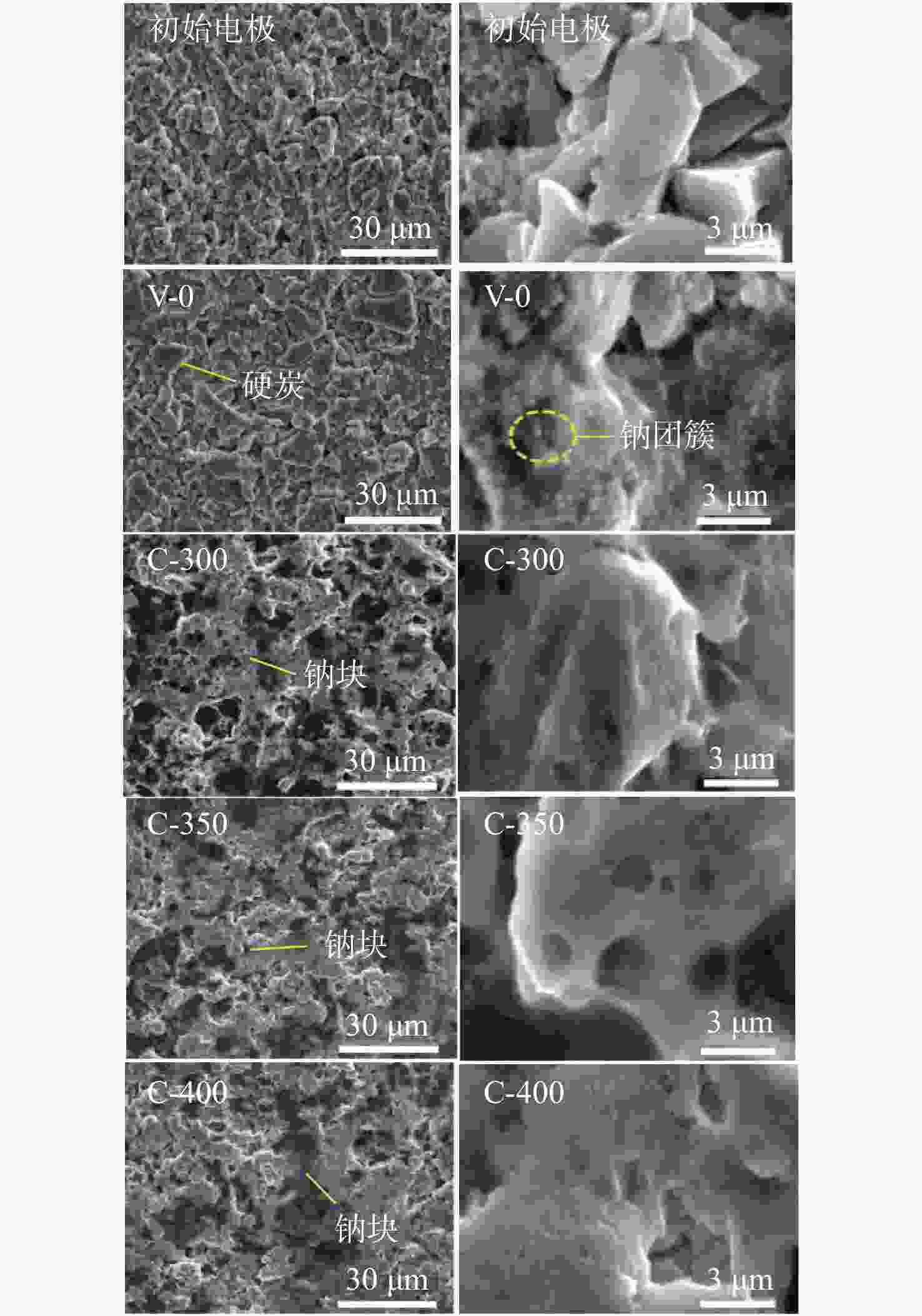
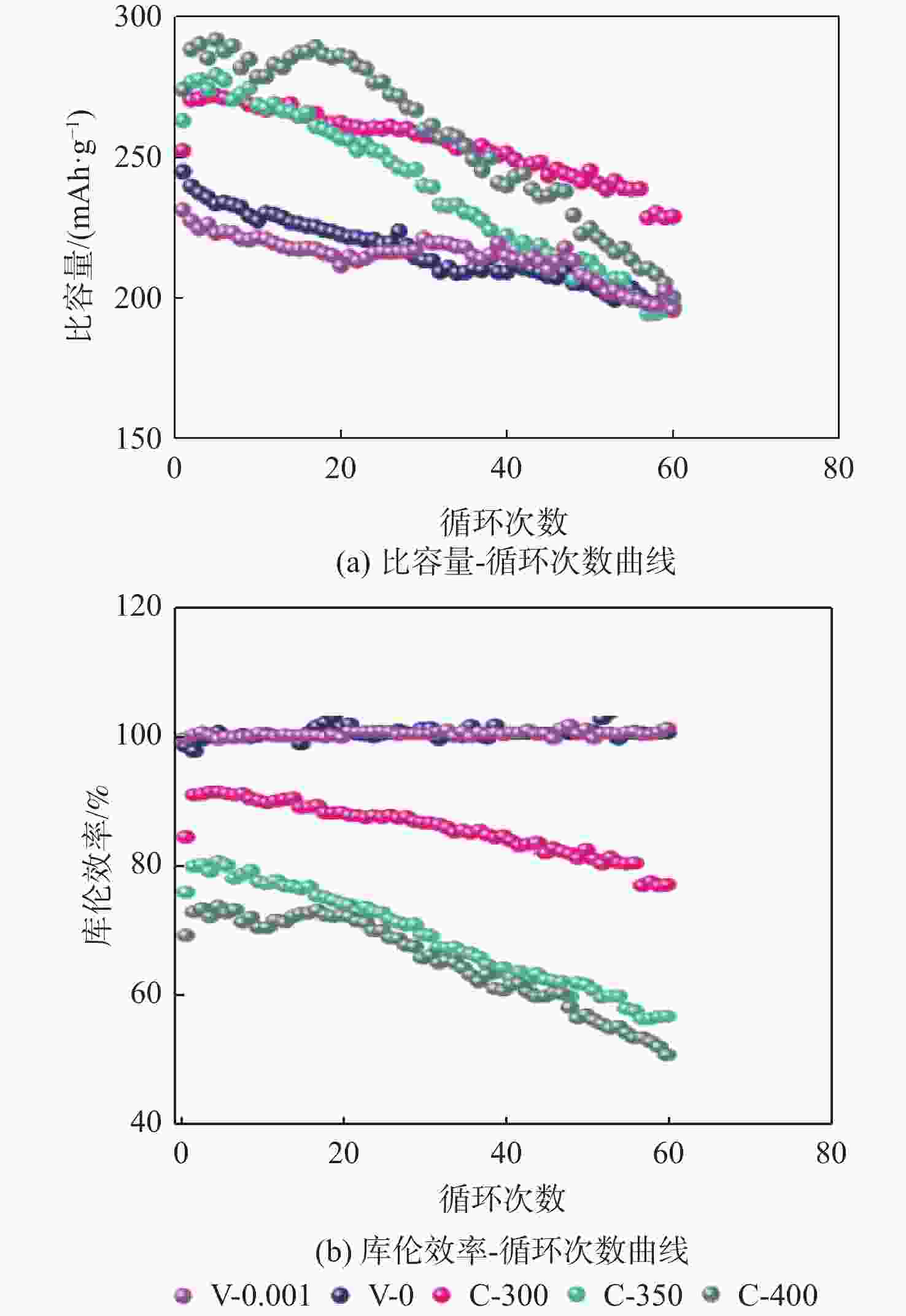
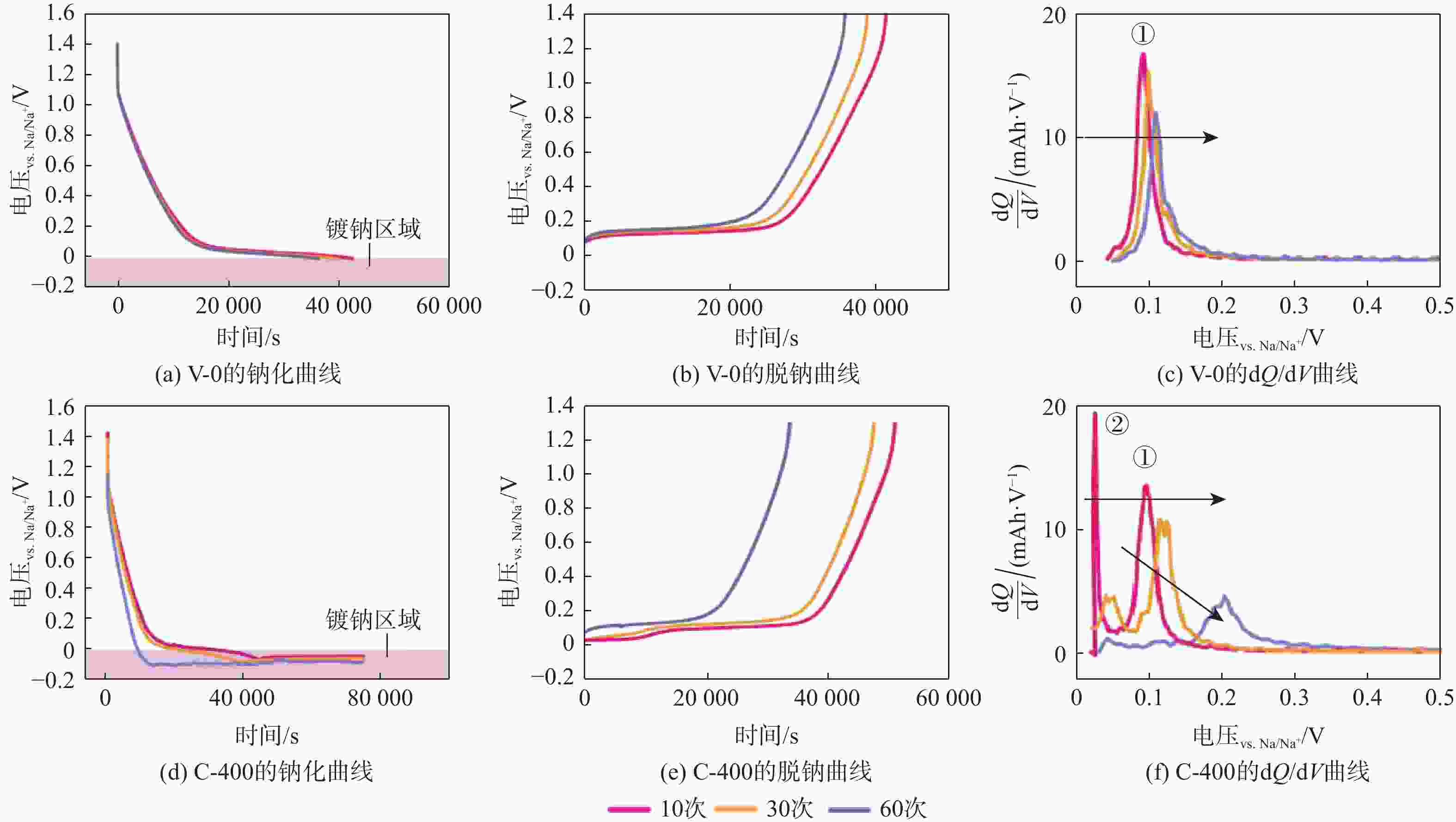
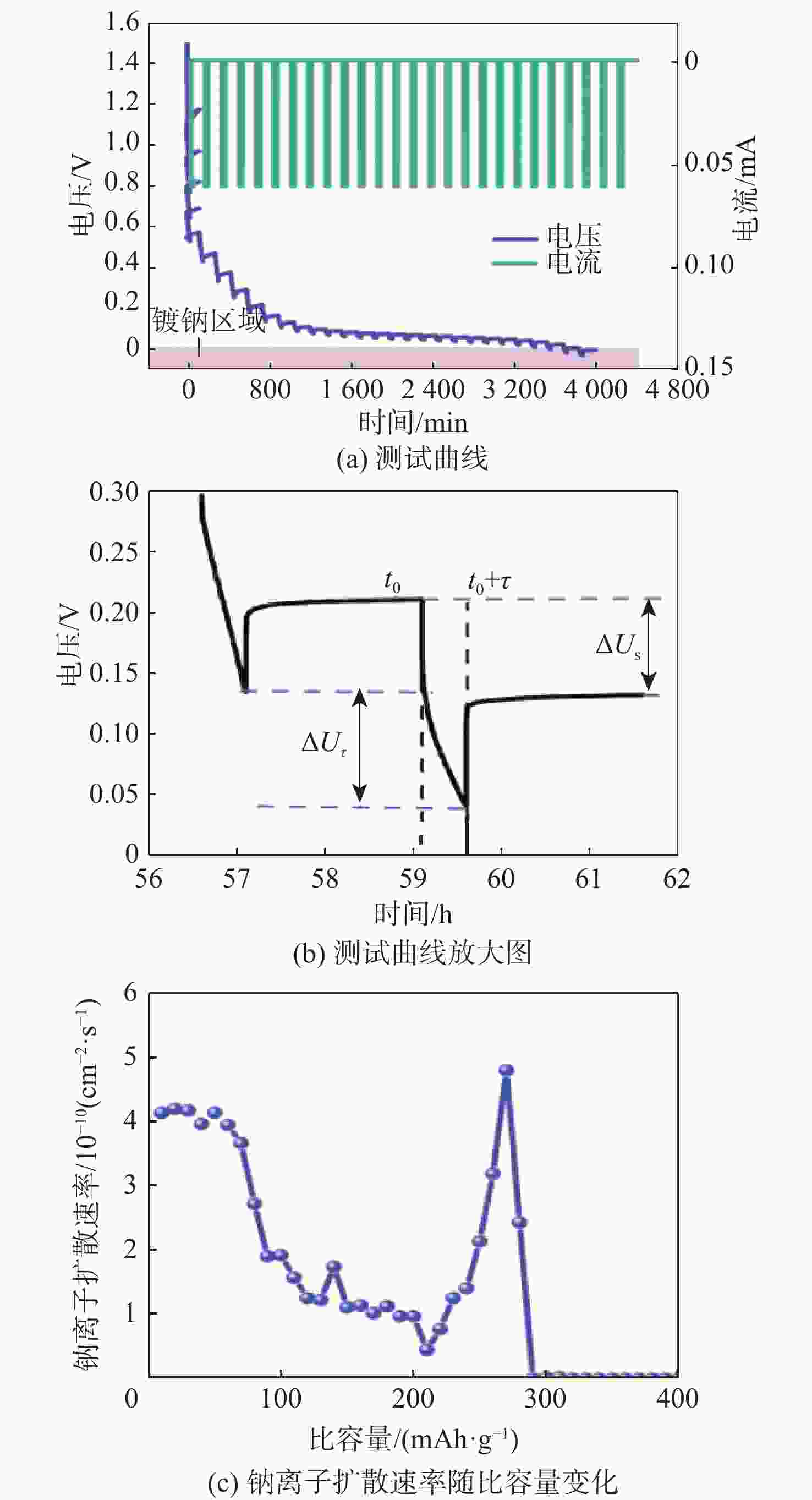
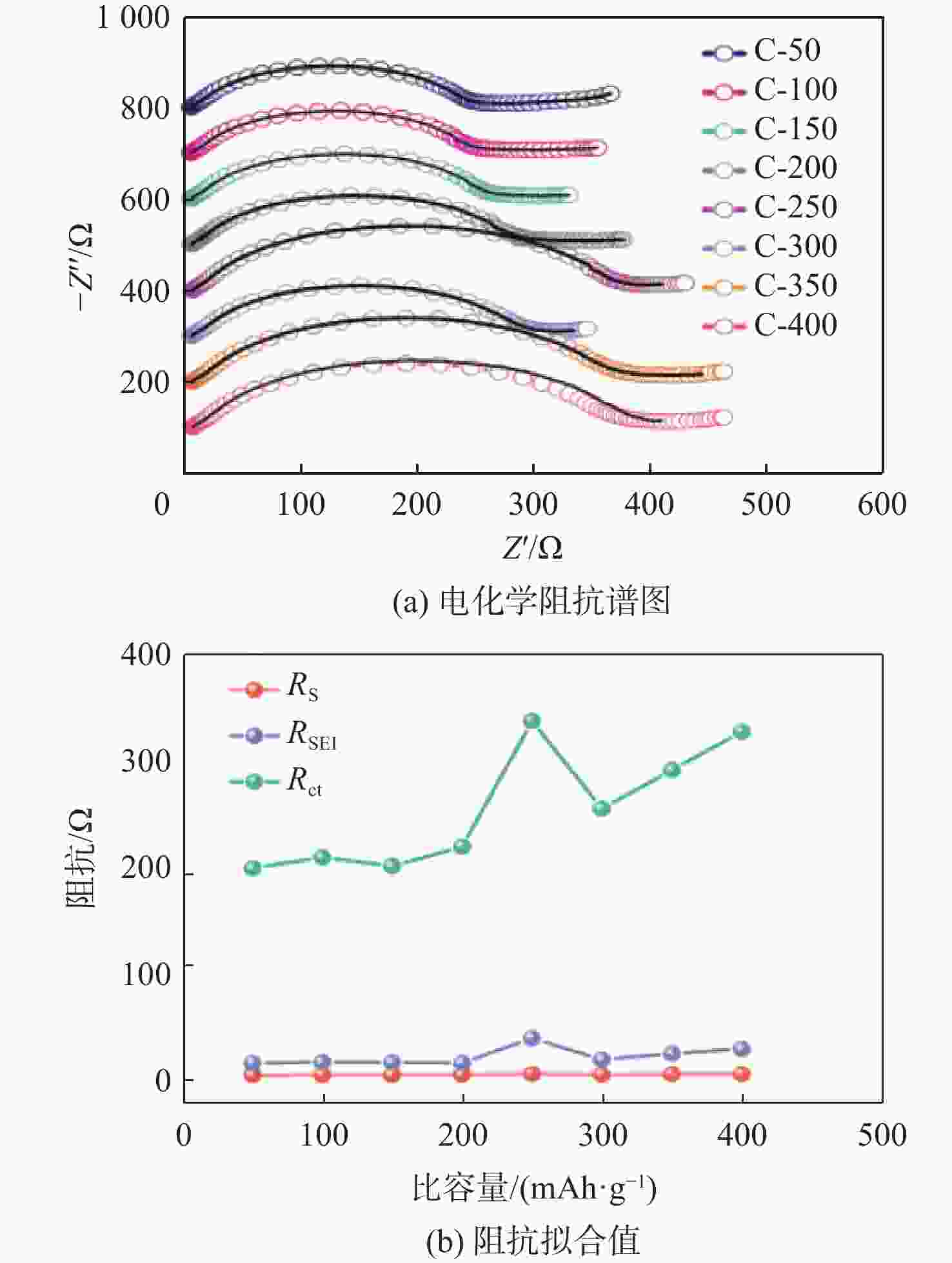
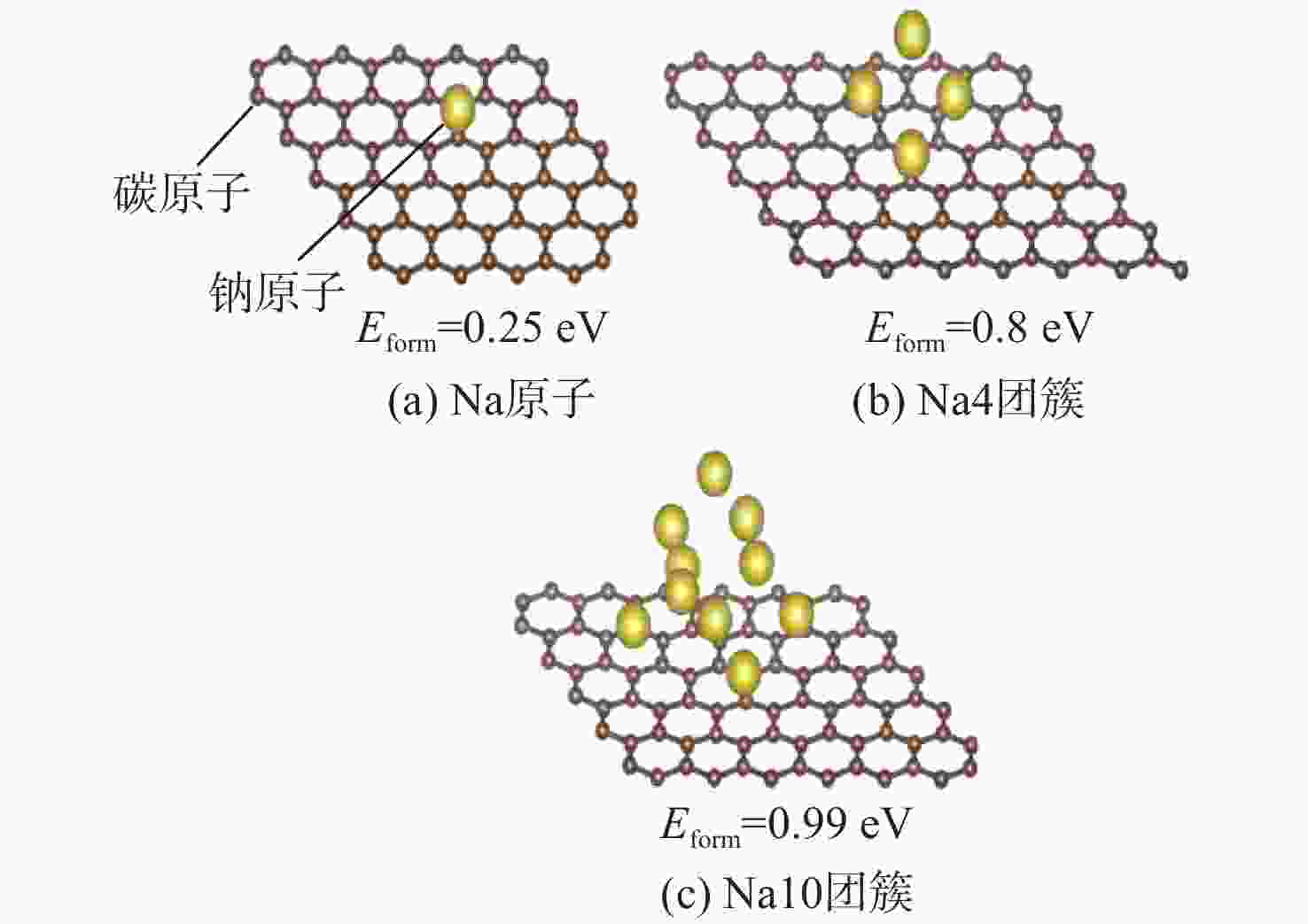
钠离子电池是临近空间飞行器二次电池的有力候选者。关于硬炭负极析钠的监测、失效及析钠机制分析对钠离子电池的管理和使用具有指导意义,但该方面研究较少。对此,通过设置一系列的析钠梯度,利用微分容量曲线,结合扫描电子显微镜(SEM)、恒电流间歇滴定(GITT)等方法对负极析钠行为进行研究。结果表明:在20 mA/g电流密度下放电12.5 h,硬炭表面形成钠团簇,继续钠化2.5 h,钠团簇转变为钠金属,同时,钠金属的脱钠电位可以被微分容量曲线监测;由于钠团簇的脱钠能垒较低,不影响电池循环性能;钠金属块使电池界面阻抗和电荷转移阻抗进一步增加,导致循环容量加速衰减。
Abstract:Sodium-ion batteries are strong candidates for secondary batteries for near-space vehicles. Although there aren’t many reports, the monitoring, failure, and mechanism of sodium plating in hard carbon anodes provide guidelines for the use and management of sodium-ion batteries. For this, a trustworthy understanding of the sodium plating behavior of hard carbons is provided by setting a series of sodium precipitation gradients, using differential capacity curves, combined with scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and galvanostatic intermittent titration technique (GITT). The results show that sodium clusters appear on the surface of the hard carbon at a current density of 20 mA/g for 12.5 h. The sodium clusters are converted into sodium-metal by continuing to sodiate for 2.5 h and the voltage of desodiation of the sodium-metal can be detected by the differential capacity curves. The battery’s cycling performance is not impacted by the sodium clusters because of their low formation energy; however, the sodium-metal causes an increase in the battery’s interfacial impedance and charge transfer impedance, which accelerates the degradation of the battery’s cycling performance.
-
Key words:
- sodium-ion batteries /
- hard carbons /
- anodes /
- sodium plating /
- sodium metal /
- failure
-
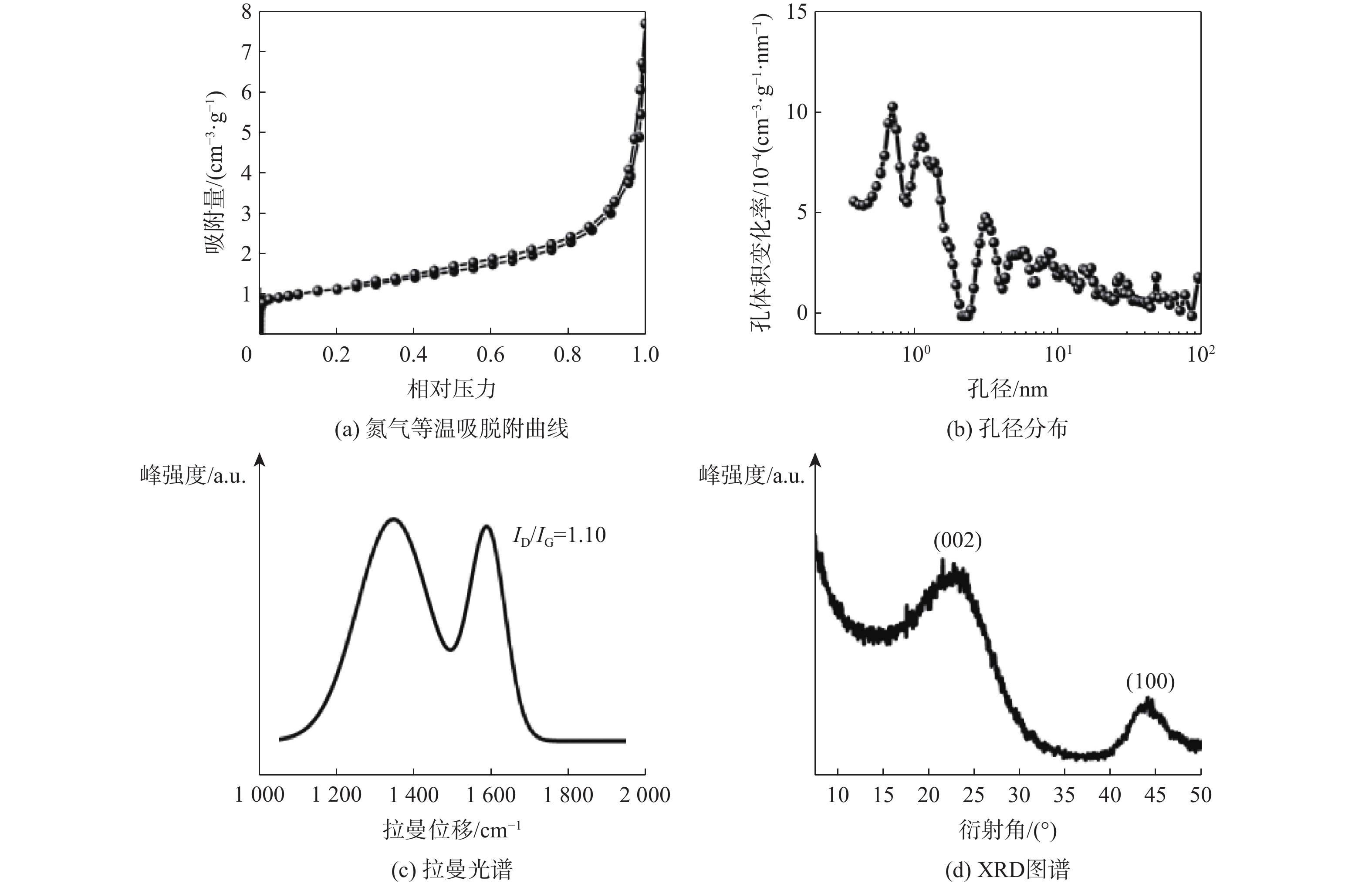
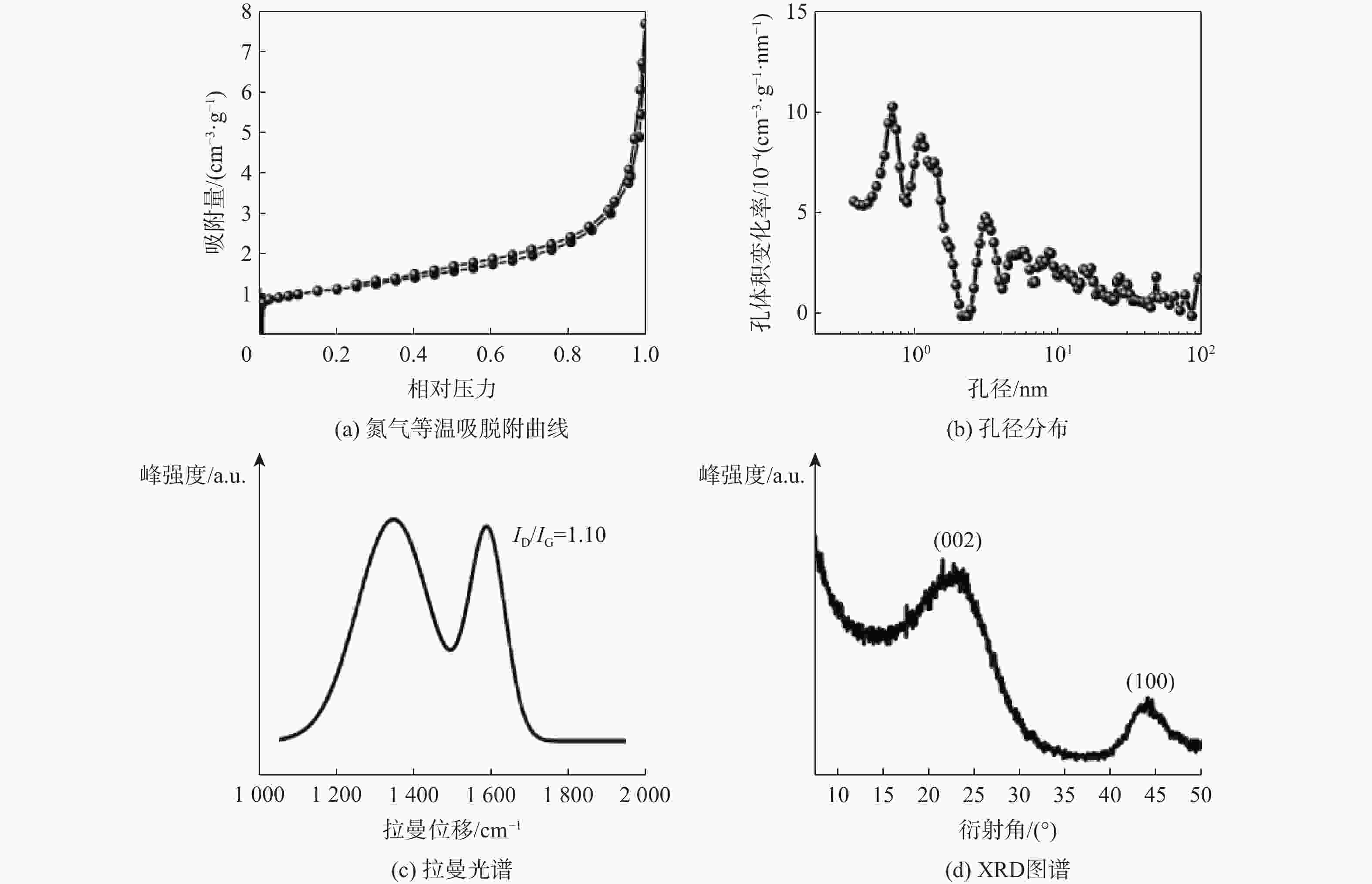
表 1 商用硬炭的结构参数
Table 1. Structure parameters of commercial hard carbons
商业硬炭 赝石墨域的
层间距/nm拉曼光谱D峰和
G峰的相对强度比比表面积/
(m2·g−1)孔体积/
(cm3·g−1)可乐丽 3. 8 1. 10 4.56 0. 011 6 -
[1] KRAUSE F C, RUIZ J P, JONES S C, et al. Performance of commercial Li-ion cells for future NASA missions and aerospace applications[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2021, 168(4): 040504. doi: 10.1149/1945-7111/abf05f [2] 于海江. 共绘钠离子电池“新蓝图”[N]. 中国电力报, 2022-09-15(005).YU H J. Co-creating a new vision for sodium-ion batteries[N]. Chinese Electric Power News, 2022-09-15(005)(in Chinese). [3] WANG Y Y, HOU B H, GUO J Z, et al. An ultralong lifespan and low-temperature workable sodium-ion full battery for stationary energy storage[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(18): 1703252. doi: 10.1002/aenm.201703252 [4] XIA Y, QUE L F, YU F D, et al. Tailoring nitrogen terminals on MXene enables fast charging and stable cycling Na-ion batteries at low temperature[J]. Nano-Micro Letters, 2022, 14(1): 143. doi: 10.1007/s40820-022-00885-7 [5] LI Z, ZHANG Y, ZHANG J H, et al. Sodium-ion battery with a wide operation-temperature range from −70 to 100℃[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2022, 61(13): e202116930. doi: 10.1002/anie.202116930 [6] HU Y Y, WU X W, WEN Z Y, et al. Challenges and thoughts on the development of sodium battery technology for energy storage[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering Science, 2021, 23(5): 94. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2021.05.013 [7] GARCHE J, DYER C K, MOSELEY P T, et al. Preface[M]//JÜRGEN G. Encyclopedia of electrochemical power sources. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2009. [8] ZHANG G X, WEI X Z, CHEN S Q, et al. Comprehensive investigation of a slight overcharge on degradation and thermal runaway behavior of lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2021, 13(29): 35054-35068. [9] CAI W L, YAN C, YAO Y X, et al. The boundary of lithium plating in graphite electrode for safe lithium-ion batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2021, 60(23): 13007-13012. doi: 10.1002/anie.202102593 [10] XU L, XIAO Y, YANG Y, et al. operando quantified lithium plating determination enabled by dynamic capacitance measurement in working Li-ion batteries[J]. Angewandte Chemie (International Edition), 2022, 61(39): e202210365. doi: 10.1002/anie.202210365 [11] 张青松, 罗星娜, 程相静, 等. 基于锂离子电池温降指数的细水雾添加剂筛选方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(6): 1073-1079.ZHANG Q S, LUO X N, CHENG X J, et al. Method for screening fine water mist additive based on temperature drop index of lithium-ion battery[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(6): 1073-1079(in Chinese). [12] MORIKAWA Y, NISHIMURA S I, HASHIMOTO R I, et al. Mechanism of sodium storage in hard carbon: an X-ray scattering analysis[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(3): 1903176. doi: 10.1002/aenm.201903176 [13] CHEN Y X, CHEN K H, SANCHEZ A J, et al. Operando video microscopy of Li plating and re-intercalation on graphite anodes during fast charging[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2021, 9(41): 23522-23536. doi: 10.1039/D1TA06023F [14] YOUN Y, GAO B, KAMIYAMA A, et al. Nanometer-size Na cluster formation in micropore of hard carbon as origin of higher-capacity Na-ion battery[J]. NPJ Computational Materials, 2021, 7: 48. doi: 10.1038/s41524-021-00515-7 [15] FINEGAN D P, QUINN A, WRAGG D S, et al. Spatial dynamics of lithiation and lithium plating during high-rate operation of graphite electrodes[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2020, 13(8): 2570-2584. [16] GAO T, HAN Y, FRAGGEDAKIS D, et al. Interplay of lithium intercalation and plating on a single graphite particle[J]. Joule, 2021, 5(2): 393-414. doi: 10.1016/j.joule.2020.12.020 [17] ALVIN S, CAHYADI H S, HWANG J, et al. Revealing the intercalation mechanisms of lithium, sodium, and potassium in hard carbon[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2020, 10(20): 2000283. doi: 10.1002/aenm.202000283 [18] DESAI P, ABOU-RJEILY J, TARASCON J M, et al. Practicality of methyl acetate as a co-solvent for fast charging Na-ion battery electrolytes[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2022, 416: 140217. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2022.140217 [19] LIN X K, KHOSRAVINIA K, HU X S, et al. Lithium plating mechanism, detection, and mitigation in lithium-ion batteries[J]. Progress in Energy and Combustion Science, 2021, 87: 100953. doi: 10.1016/j.pecs.2021.100953 [20] CHU F L, HU J L, TIAN J, et al. In situ plating of porous Mg network layer to reinforce anode dendrite suppression in Li-metal batteries[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018, 10(15): 12678-12689. [21] LU Y Y, ZHANG Q, HAN M, et al. Stable Na plating/stripping electrochemistry realized by a 3D Cu current collector with thin nanowires[J]. Chemical Communications, 2017, 53(96): 12910-12913. doi: 10.1039/C7CC07485A [22] DONG R Q, ZHENG L M, BAI Y, et al. Elucidating the mechanism of fast Na storage kinetics in ether electrolytes for hard carbon anodes[J]. Advanced Materials, 2021, 33(36): e2008810. doi: 10.1002/adma.202008810 [23] SONG M X, YI Z L, XU R, et al. Towards enhanced sodium storage of hard carbon anodes: regulating the oxygen content in precursor by low-temperature hydrogen reduction[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2022, 51: 620-629. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2022.07.005 [24] JAYAWARDANA W, CARR C L, ZHAO D X, et al. Voltage-relaxation GITT and reverse Monte Carlo to determine lithium diffusion and distribution in TiO2 and highly-ordered nanoporous hard carbons[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2018, 165(11): A2824-A2832. doi: 10.1149/2.1121811jes [25] XIE F, XU Z, GUO Z Y, et al. Disordered carbon anodes for Na-ion batteries: quo vadis?[J]. Science China Chemistry, 2021, 64(10): 1679-1692. doi: 10.1007/s11426-021-1074-8 [26] CAI C C, CHEN Y A, HU P, et al. Regulating the interlayer spacings of hard carbon nanofibers enables enhanced pore filling sodium storage[J]. Small, 2022, 18(6): e2105303. doi: 10.1002/smll.202105303 [27] MEI W X, JIANG L H, LIANG C, et al. Understanding of Li-plating on graphite electrode: detection, quantification and mechanism revelation[J]. Energy Storage Materials, 2021, 41: 209-221. doi: 10.1016/j.ensm.2021.06.013 [28] ZHANG S M, YANG G J, LIU S, et al. Understanding the dropping of lithium plating potential in carbonate electrolyte[J]. Nano Energy, 2020, 70: 104486. doi: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.104486 [29] XU L, YANG Y, XIAO Y, et al. In-situ determination of onset lithium plating for safe Li-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2022, 67: 255-262. doi: 10.1016/j.jechem.2021.10.016 -






 下载:
下载: