Lightweight video crowd counting with spatial shuffling and chain residual enhancement
-
摘要:
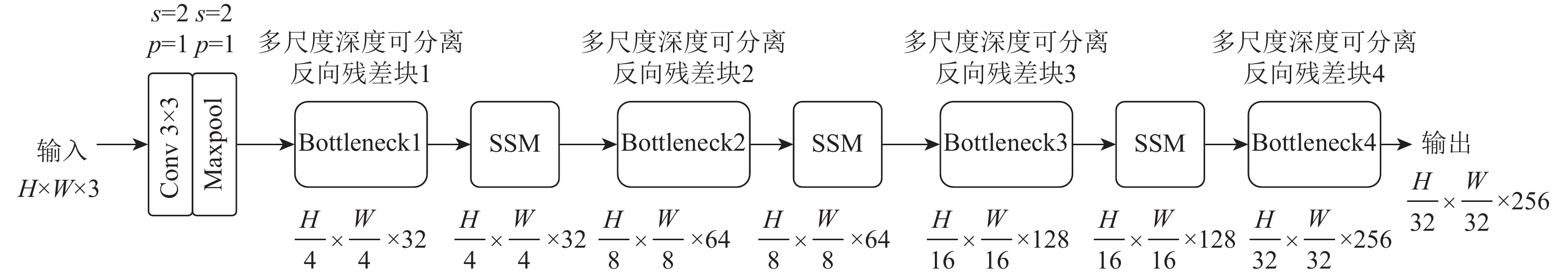
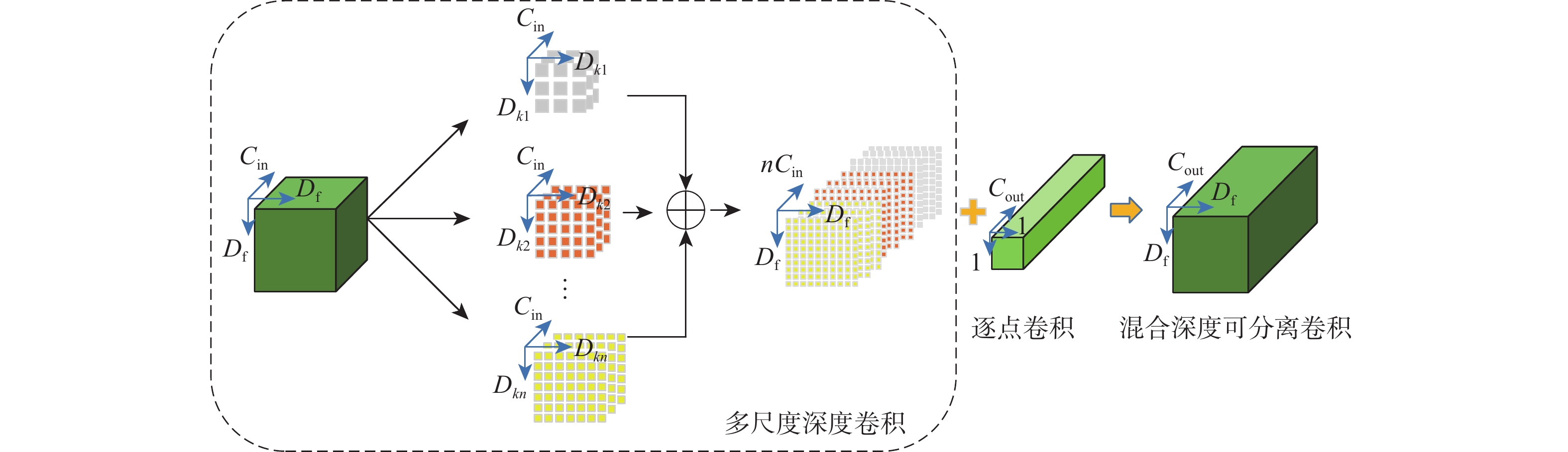
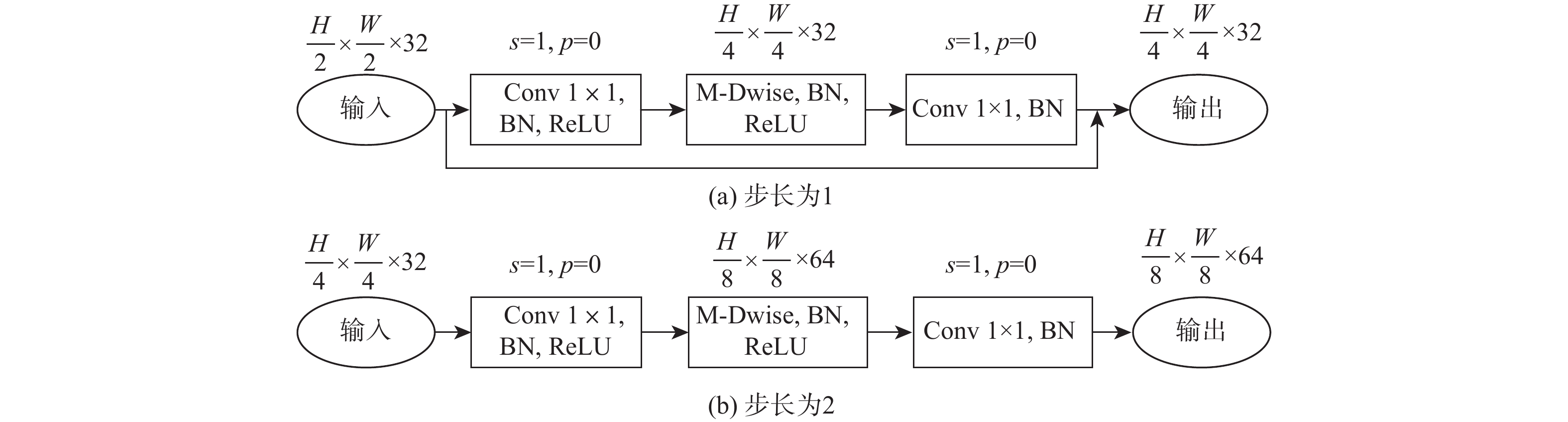
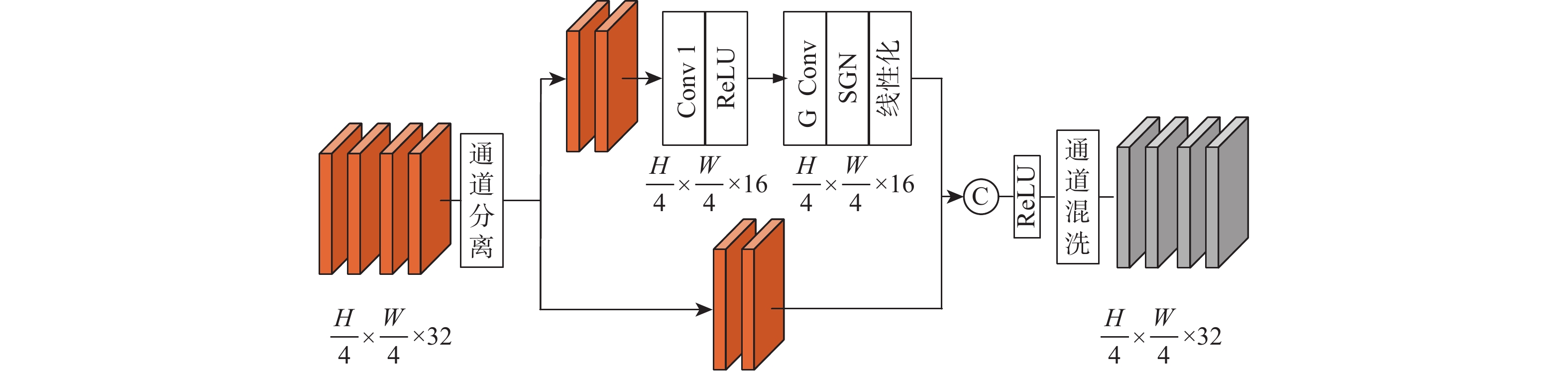
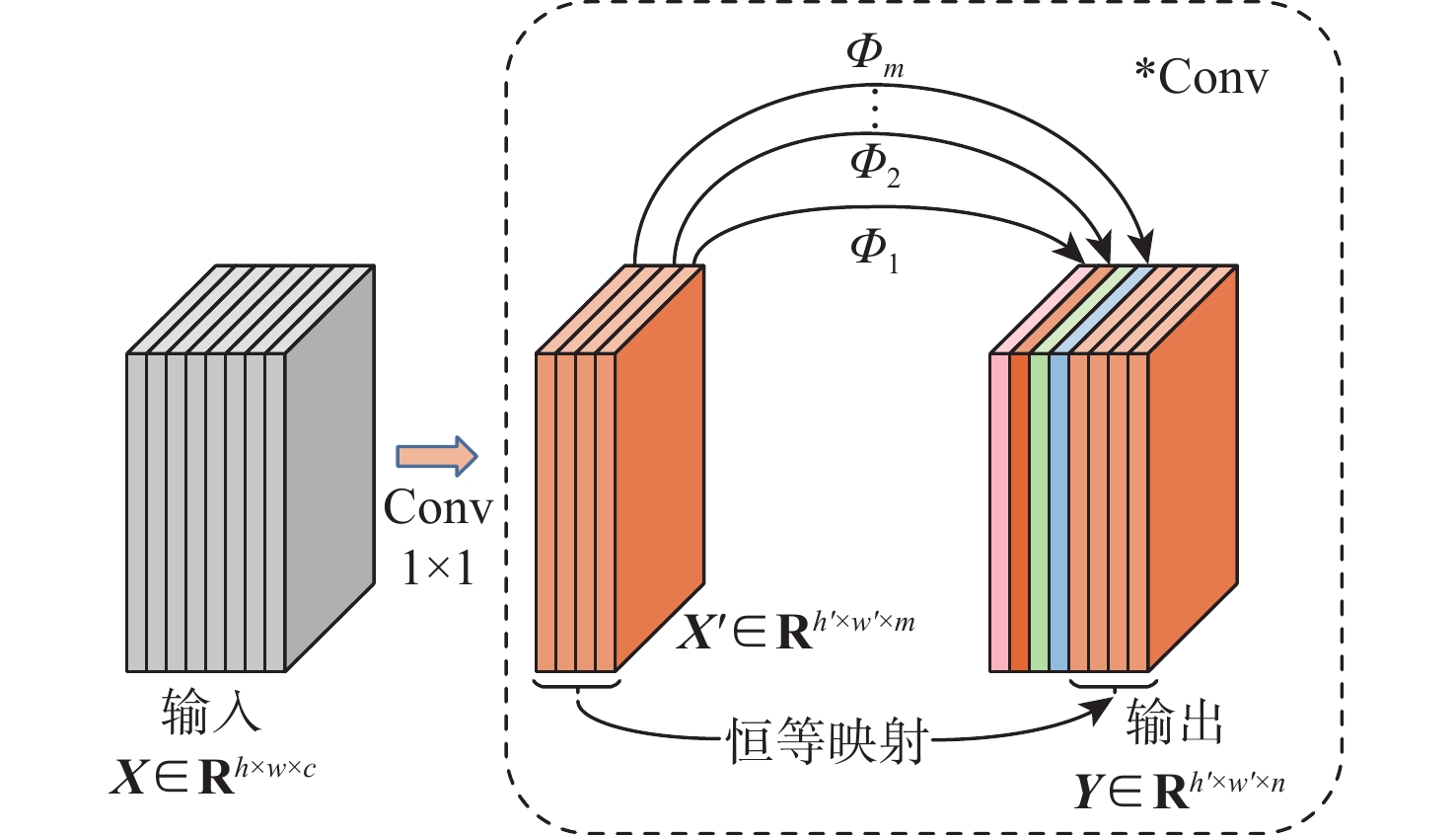
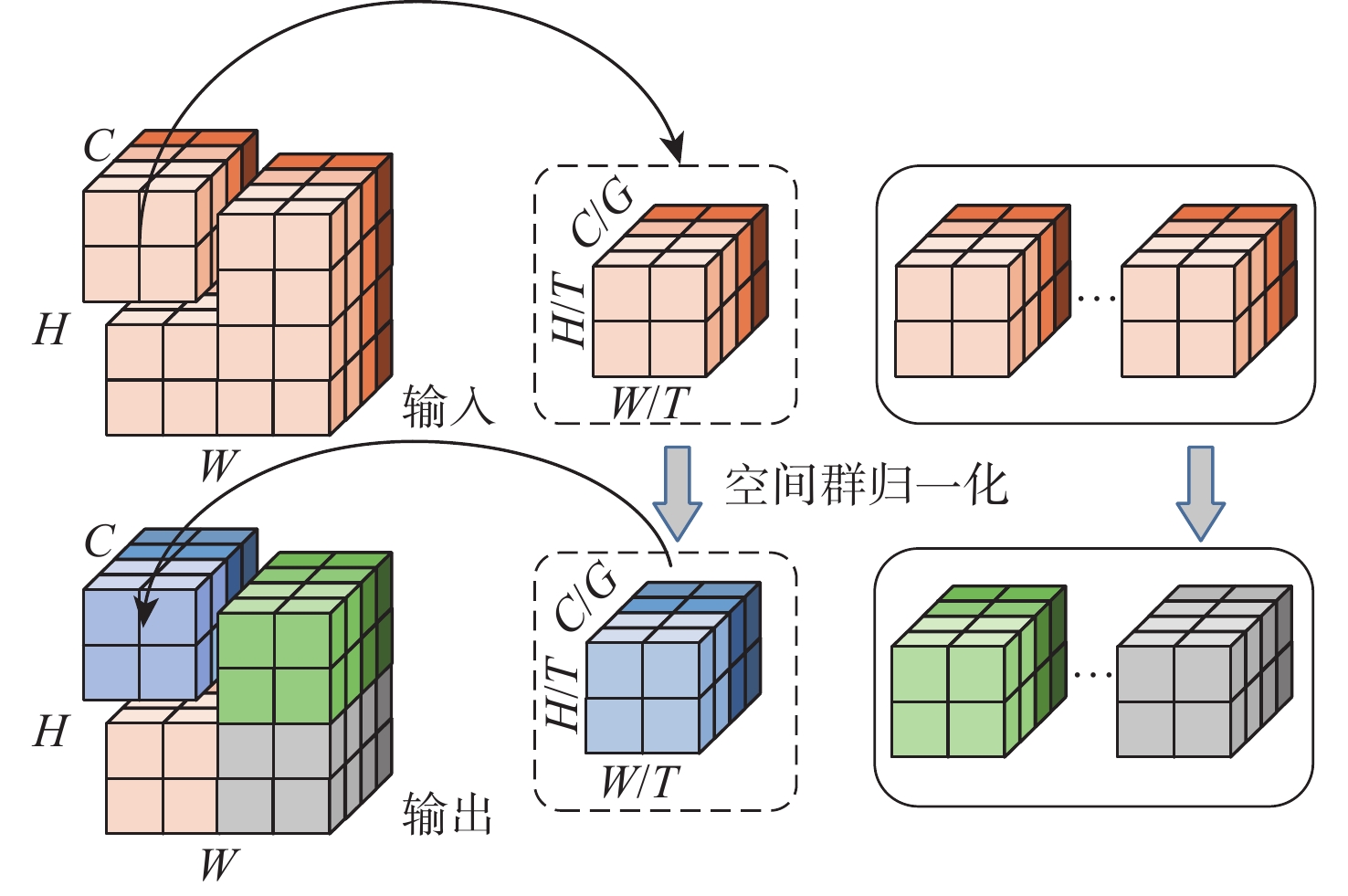
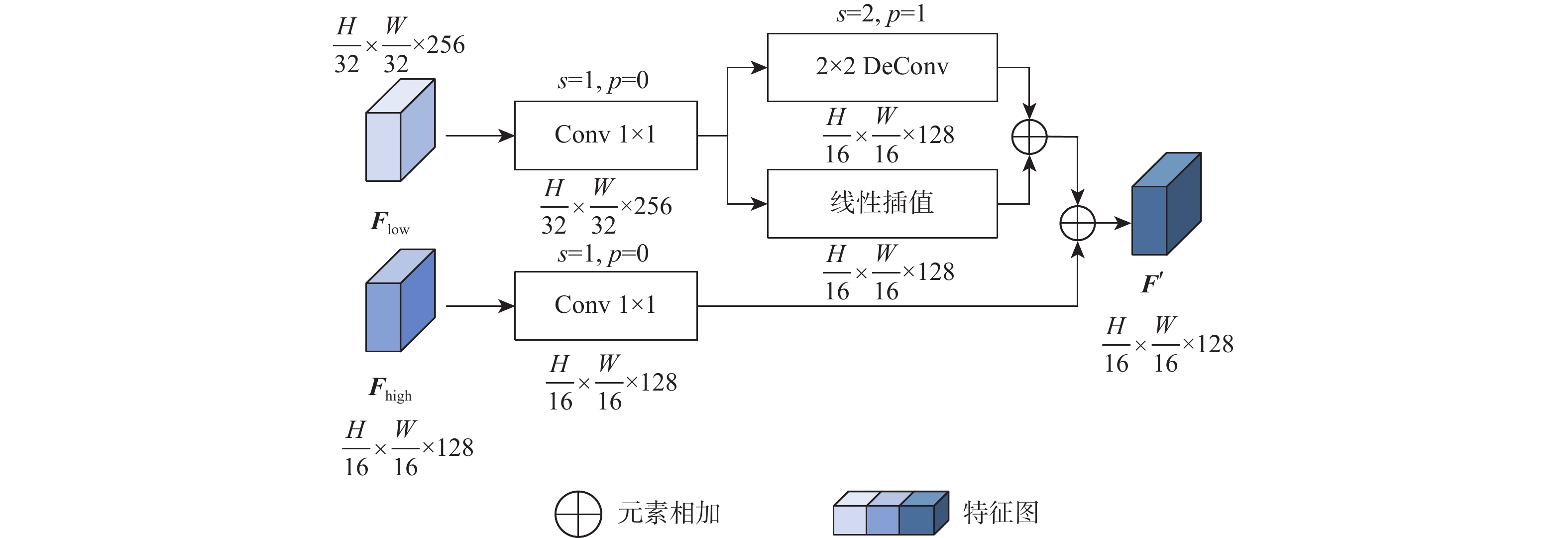
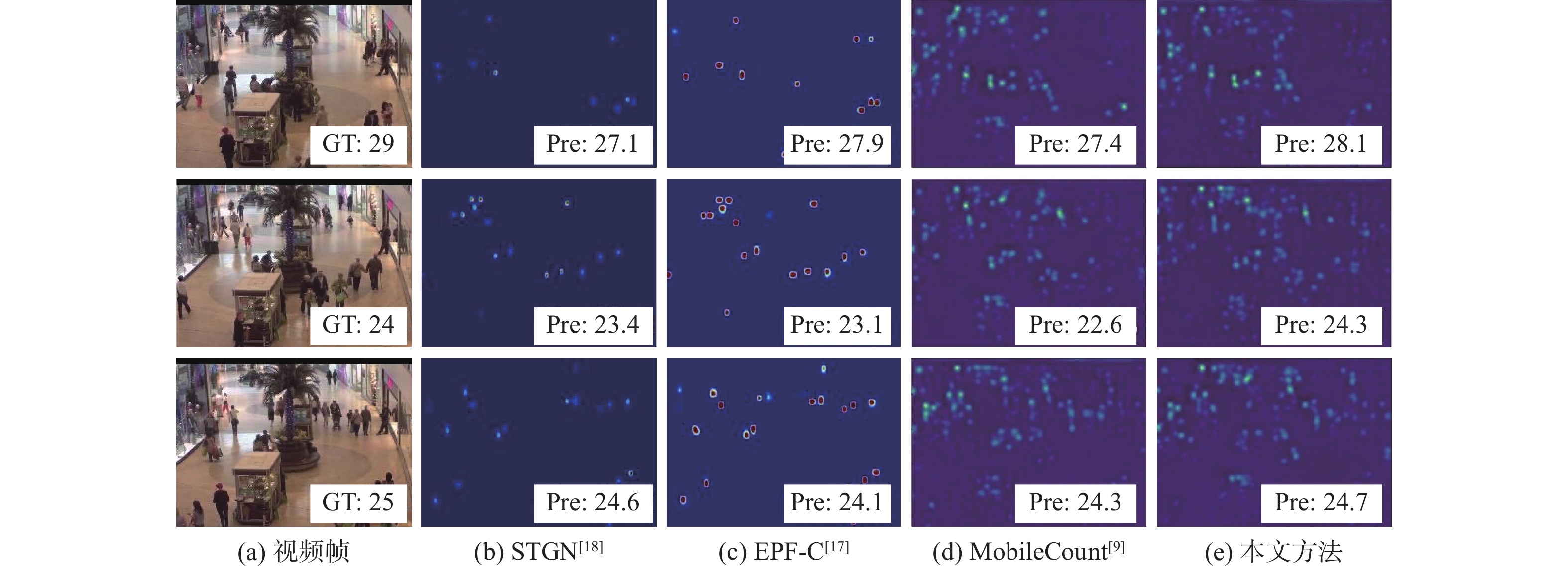
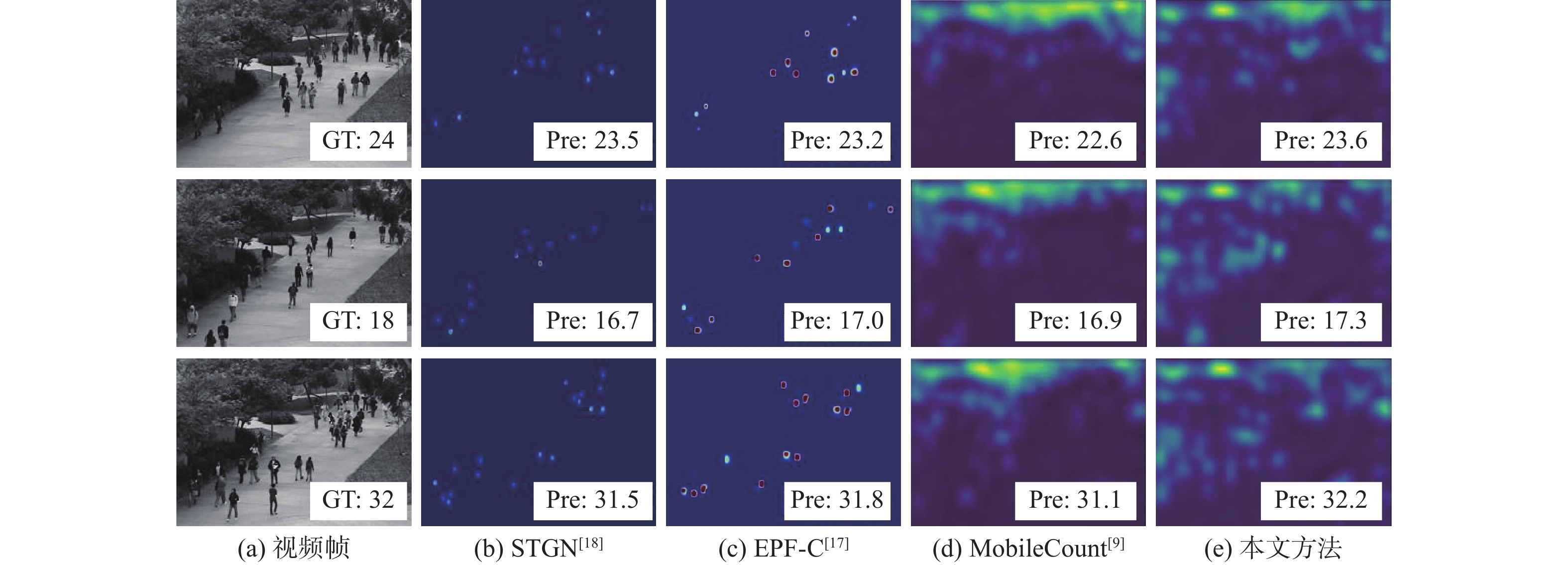
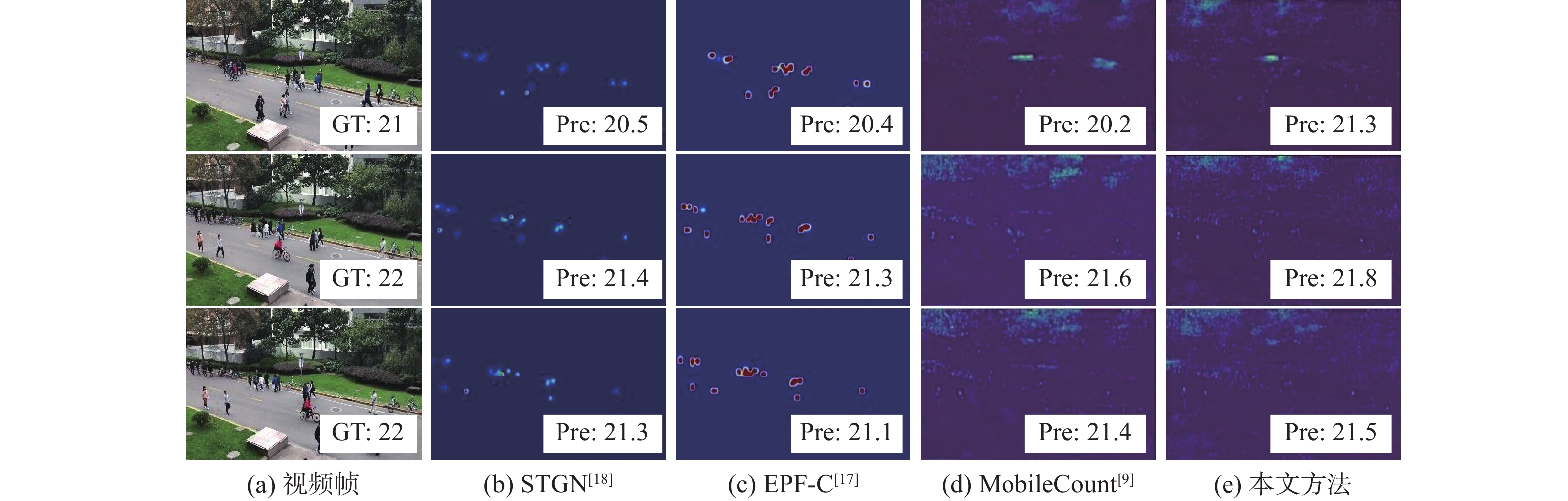
针对现有视频人群计数方法网络模型复杂度高、精确度和实时性差的问题,提出了一种空间混洗与链式残差增强的轻量级视频人群计数方法。所提模型由多尺度深度可分离反向卷积编码器、尺度回归解码器和预测输出层构成。在编码器部分,设计多尺度深度可分离反向残差块,提取不同分辨率的人群特征及相邻帧之间的时域特征信息,提高模型的轻量化程度;提出空间混洗模块嵌入到编码骨干网络中,增强不同尺度人群特征提取能力。在解码器部分,改进多分辨率融合模块及链式残差模块,对编码器输出的不同分辨率特征逐层聚合,减少细节特征丢失。通过解码器预测输出,得到回归人群密度图,并通过对密度图逐像素求和输出计数结果。所提方法在Mall、UCSD、FDST、ShanghaiTech等人群视频数据集上进行对比实验,结果表明:所提方法检测帧率和参数量等评价指标均优于对比方法;在Mall数据集上,相较于ConvLSTM人群计数方法,所提方法的平均绝对误差(MAE)、均方误差(MSE)的误差值分别降低了43.75%、72.71%,对不同场景视频人群计数具有更高的准确率和实时性。
Abstract:The problems with the large complexity, low accuracy, and slow real-time performance of the current video crowd counting techniques in network models are addressed by a lightweight solution based on spatial shuffling and chain residual augmentation. The proposed model consists of an encoder, decoder, and prediction network. In the encoder section, firstly, a multi-scale deep separable reverse residual block is designed to extract crowd features of different resolutions and temporal feature information between adjacent frames, thereby improving the lightweight of the model. Then, a spatial shuffling module is proposed to be embedded in the coding backbone network to enhance the ability to extract features of people at different scales. Next, to reduce the loss of detail features in the decoder section, enhance the fusion module and chain residual module to combine the various resolution characteristics that the encoder produces layer by layer. Finally, by predicting the output through the decoder, a regression population density map is obtained, and the counting result is output by summing the density map pixel by pixel. The method proposed in this paper was compared on population datasets such as Mall, UCSD, FDST, and ShanghaiTech. The results showed that the model outperformed the comparison algorithm in terms of detection frame rate and parameter quantity. For example, on the Mall dataset, compared to the ConvLSTM population counting algorithm, the error values of mean absolute error (MAE) and mean square error (MSE) in this method were reduced by 43.75% and 72.71%, respectively, showing higher accuracy and real-time performance for crowd counting in different scene videos.
-
表 1 Mall数据集评价指标对比
Table 1. Comparison of evaluation indicators of Mall dataset
表 2 UCSD数据集评价指标对比
Table 2. Comparison of evaluation indicators of UCSD dataset
表 3 FDST数据集评价指标对比
Table 3. Comparison of evaluation indicators of FDST dataset
表 4 hanghaiTech数据集评价指标对比
Table 4. Comparison of evaluation indicators of ShanghaiTech dataset
表 5 模型轻量化指标对比
Table 5. Comparison of model lightweight indicators
表 6 消融实验指标对比
Table 6. Comparison of ablation experimental indicators
MS-DSR SSM G-SSM SGN CRP MAE MSE 89.4 146.0 √ 87.1 133.8 √ √ 82.0 128.2 √ √ √ 75.9 119.9 √ √ √ √ 71.5 113.7 √ √ √ √ √ 65.4 102.0 -
[1] GAO H, ZHAO W J, ZHANG D X, et al. Application of improved Transformer based on weakly supervised in crowd localization and crowd counting[J]. Scientific Reports, 2023, 13(1): 1144. [2] 余鹰, 朱慧琳, 钱进, 等. 基于深度学习的人群计数研究综述[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2021, 58(12): 2724-2747. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2021.20200699YU Y, ZHU H L, QIAN J, et al. Survey on deep learning based crowd counting[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2021, 58(12): 2724-2747(in Chinese). doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2021.20200699 [3] CHAN A B, VASCONCELOS N. Bayesian Poisson regression for crowd counting[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2009: 545-551. [4] MIAO Y Q, HAN J G, GAO Y S, et al. ST-CNN: Spatial-temporal convolutional neural network for crowd counting in videos[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2019, 125: 113-118. doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2019.04.012 [5] WU X J, XU B H, ZHENG Y B, et al. Fast video crowd counting with a temporal aware network[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 403: 13-20. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.04.071 [6] BAI H Y, CHAN S H G. Motion-guided non-local spatial-temporal network for video crowd counting[EB/OL]. (2021-04-28)[2023-02-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.13946v1. [7] CAI Y Q, MA Z W, LU C H, et al. Global representation guided adaptive fusion network for stable video crowd counting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2022, 25: 5222-5233. [8] TAN M X, LE Q V. MixConv: Mixed depthwise convolutional kernels[EB/OL]. (2019-12-01)[2023-02-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1907.09595v3. [9] WANG P, GAO C Y, WANG Y, et al. MobileCount: An efficient encoder-decoder framework for real-time crowd counting[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 407: 292-299. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.05.056 [10] CHAN A B, LIANG Z S J, VASCONCELOS N. Privacy preserving crowd monitoring: Counting people without people models or tracking[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2008: 1-7. [11] CHEN K, LOY C C, GONG S G, et al. Feature mining for localised crowd counting[C]//Proceedings of the British Machine Vision Conference. Guildford: British Machine Vision Association, 2012. [12] FANG Y Y, ZHAN B Y, CAI W D, et al. Locality-constrained spatial Transformer network for video crowd counting[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 814-819. [13] ZHANG Y Y, ZHOU D S, CHEN S Q, et al. Single-image crowd counting via multi-column convolutional neural network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 589-597. [14] CHEN K, GONG S G, XIANG T, et al. Cumulative attribute space for age and crowd density estimation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 2467-2474. [15] XIONG F, SHI X J, YEUNG D Y. Spatio temporal modeling for crowd counting in videos[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 5161-5169. [16] MA Y J, SHUAI H H, CHENG W H. Spatio temporal dilated convolution with uncertain matching for video-based crowd estimation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2021, 24: 261-273. [17] LIU WZ, SALZMANN M, FUA P. Estimating people flows to better count them in crowded scenes[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2020: 723-740. [18] WU Z, ZHANG X F, TIAN G, et al. Spatial-temporal graph network for video crowd counting[J]. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2023, 33(1): 228-241. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2022.3187194 [19] WEN L Y, DU D W, ZHU P F, et al. Drone-based joint density map estimation, localization and tracking with space-time multi-scale attention network[EB/OL]. (2019-12-04)[2023-02-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1912.01811. [20] LI H P, LIU L B, YANG K L, et al. Video crowd localization with multifocus Gaussian neighborhood attention and a large-scale bench-mark[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2022, 31: 6032-6047. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2022.3205210 [21] SINDAGI V A, PATEL V M. CNN-based cascaded multi-task learning of high-level prior and density estimation for crowd counting[C]//Proceedings of the 14th IEEE International Conference on Advanced Video and Signal Based Surveillance. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1-6. [22] LI Y H, ZHANG X F, CHEN D M. CSRNet: Dilated convolutional neural networks for understanding the highly congested scenes[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 1091-1100. [23] CAO X K, WANG Z, P ZHAOY Y, et al. Scale aggregation network for accurate and efficient crowd counting[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 757-773. [24] JIANG G Q, WU R, HUO Z Q, et al. LigMSANet: Lightweight multi-scale adaptive convolutional neural network for dense crowd counting[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2022, 197: 116662. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.116662 [25] YOU Z Y, YANG K, LUO W H, et al. Few-shot object counting with similarity-aware feature enhancement[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2023: 6304-6313. -








 下载:
下载: