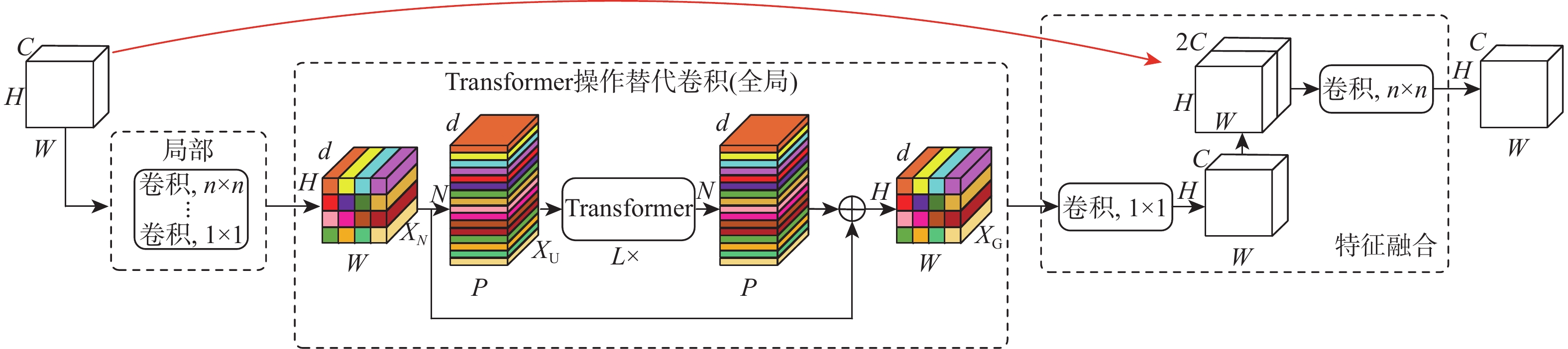
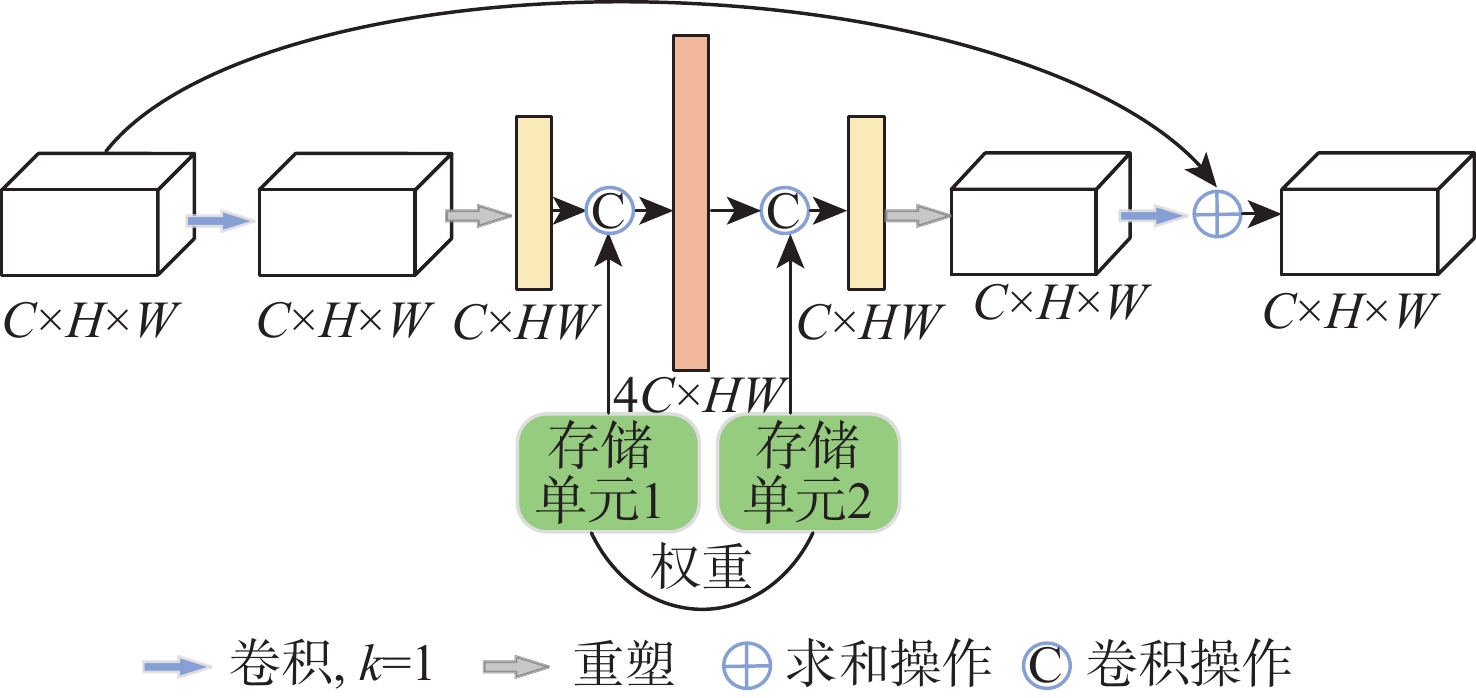
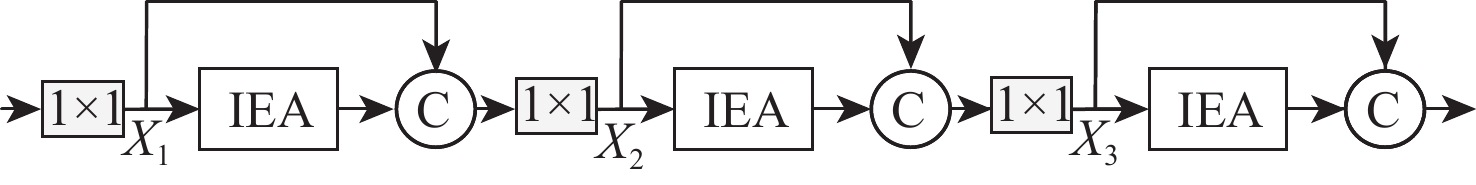
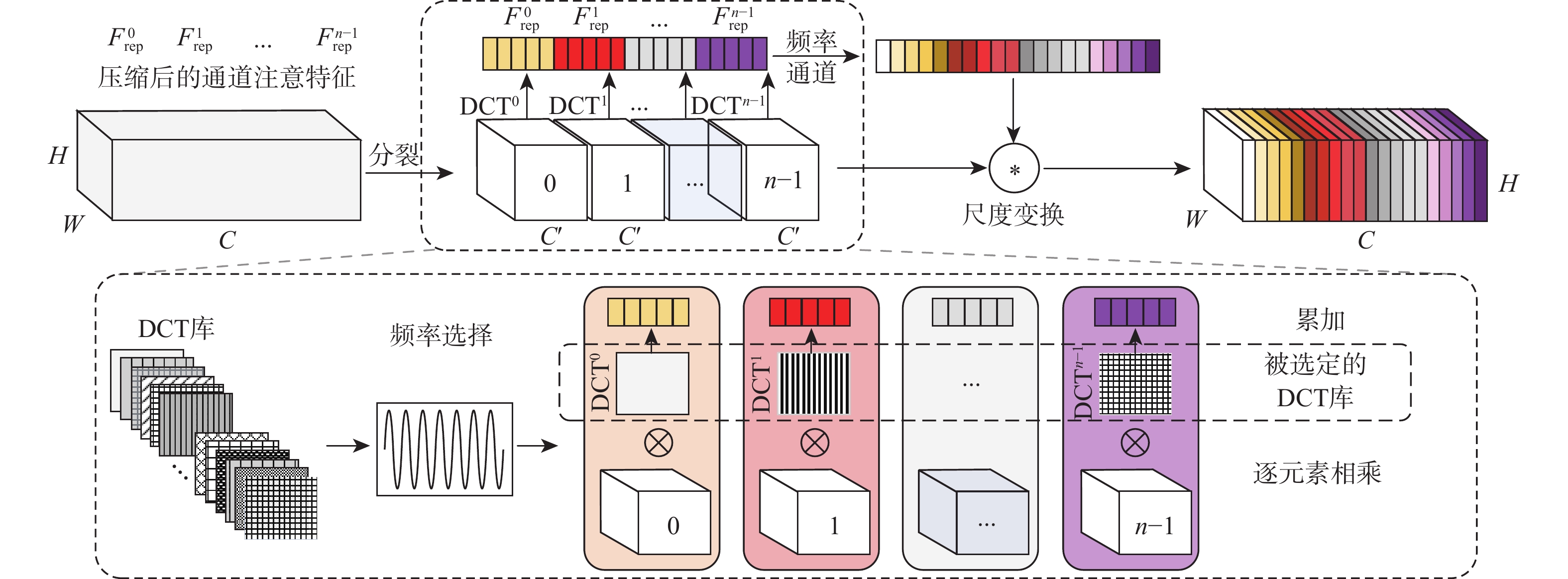
Fusion of Mobile Vit and inverted gated codec retinal vessel segmentation algorithm
-
摘要:
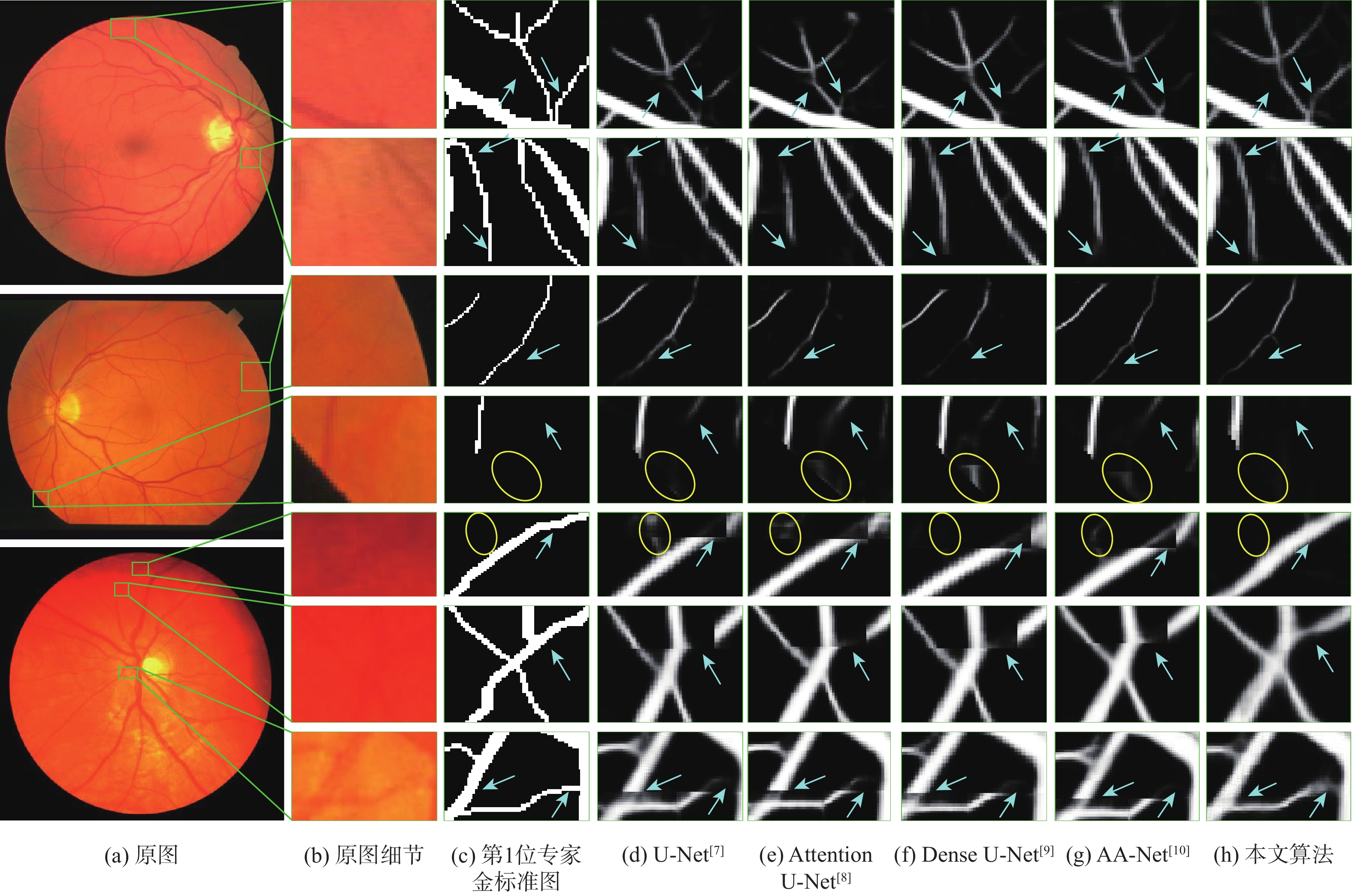
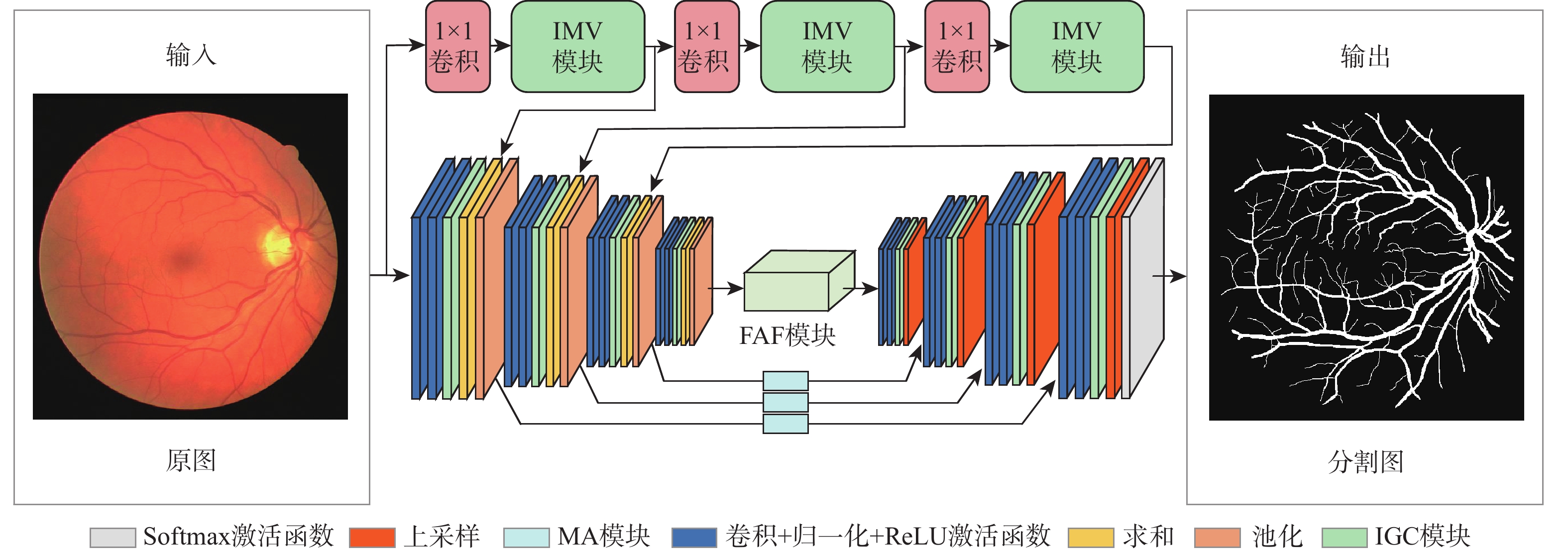
针对视网膜血管分割时存在背景噪声干扰、边界纹理模糊和微细血管提取难等问题,提出一种融合Mobile Vit和倒置门控编解码的视网膜血管分割算法(FMVG-Net)。改进Mobile Vit模块,在编码部分实现双联合特征提取;利用多谱注意力模块,从频域维度减少图像特征信息缺失,精确分割血管前景像素;提出特征自适应融合模块,建立血管纹理上下文依赖关系,提高血管分割灵敏度;优化编解码结构,设计倒置门控编解码模块,进一步捕获空间信息与深层语义信息,提高视网膜血管图像分割精度。在公共数据集DRIVE、STARE和CHASE_DB1上对所提算法进行实验,特异性分别为
0.9863 、0.9897 和0.9873 ,准确度分别为0.9709 、0.9754 和0.9760 ,敏感度分别为0.8109 、0.8010 和0.8079 。仿真实验证明,所提网络对视网膜血管分割具有较好的分割效果,为眼科疾病的诊断提供了新窗口。-
关键词:
- 视网膜血管 /
- Mobile Vit模块 /
- 离散余弦变换 /
- 倒置门控编解码模块 /
- 特征自适应融合
Abstract:An algorithm based on Mobile Vit and inverted gated codec is proposed for retinal vessel segmentation (FMVG-Net), aiming to tackle issues such background noise interference, boundary texture blurring, and challenging extraction of microvascular areas. First, we improve the Mobile Vit module, and realize the double joint feature extraction cleverly in the coding part. Subsequently, we use the multispectral attention module. The module reduces the missing image feature information from the frequency domain dimension, so as to accurately segment the foreground pixel of the vessel. Next, we propose a feature adaptive fusion module to establish the context dependence of vascular texture and improve the sensitivity of vascular segmentation. In order to enhance the precision of retinal vascular picture segmentation, lastly, we have implemented an inverted gated codec module and optimized the codec structure to further collect deep and spatial semantic information. Experiments are performed on the DRIVE, STARE, and CHASE_DB1 datasets,whereby the obtained specificity are
0.9863 ,0.9897 , and0.9873 , respectively; the accuracies are0.9709 ,0.9754 , and0.9760 , respectively; the sensitivity is0.8109 ,0.8010 , and0.8079 , respectively.Simulation experiments reveal that this paper demonstrates a superior segmentation effect on eye lesions images, which opens new avenues for the diagnosis of eye diseases. -
表 1 彩色眼底视网膜数据集血管图像信息
Table 1. Vascular image information of color fundus retinal dataset
数据集 原图 金标准图 掩码图 DRIVE 


STARE 


CHASE_DB1 


表 2 加权调节因子不同取值在DRIVE数据集上的对比
Table 2. Comparison of different values of weighted regulator on DRIVE dataset
AUC 准确度 F1 敏感度 特异性 0.1 0.9 0.9879 0.9708 0.8275 0.7989 0.9873 0.2 0.8 0.9873 0.9706 0.8237 0.7833 0.9886 0.3 0.7 0.9871 0.9706 0.8238 0.7851 0.9884 0.4 0.6 0.9867 0.9698 0.8171 0.7712 0.9888 0.5 0.5 0.9881 0.9709 0.8279 0.7985 0.9875 0.6 0.4 0.9880 0.9710 0.8286 0.8011 0.9873 0.7 0.3 0.9880 0.9709 0.8300 0.8109 0.9863 0.8 0.2 0.9874 0.9702 0.8240 0.7958 0.9870 0.9 0.1 0.9879 0.9709 0.8272 0.7943 0.9879 表 3 不同算法血管分割性能对比
Table 3. Performance comparison of different algorithms for blood vessel segmentation
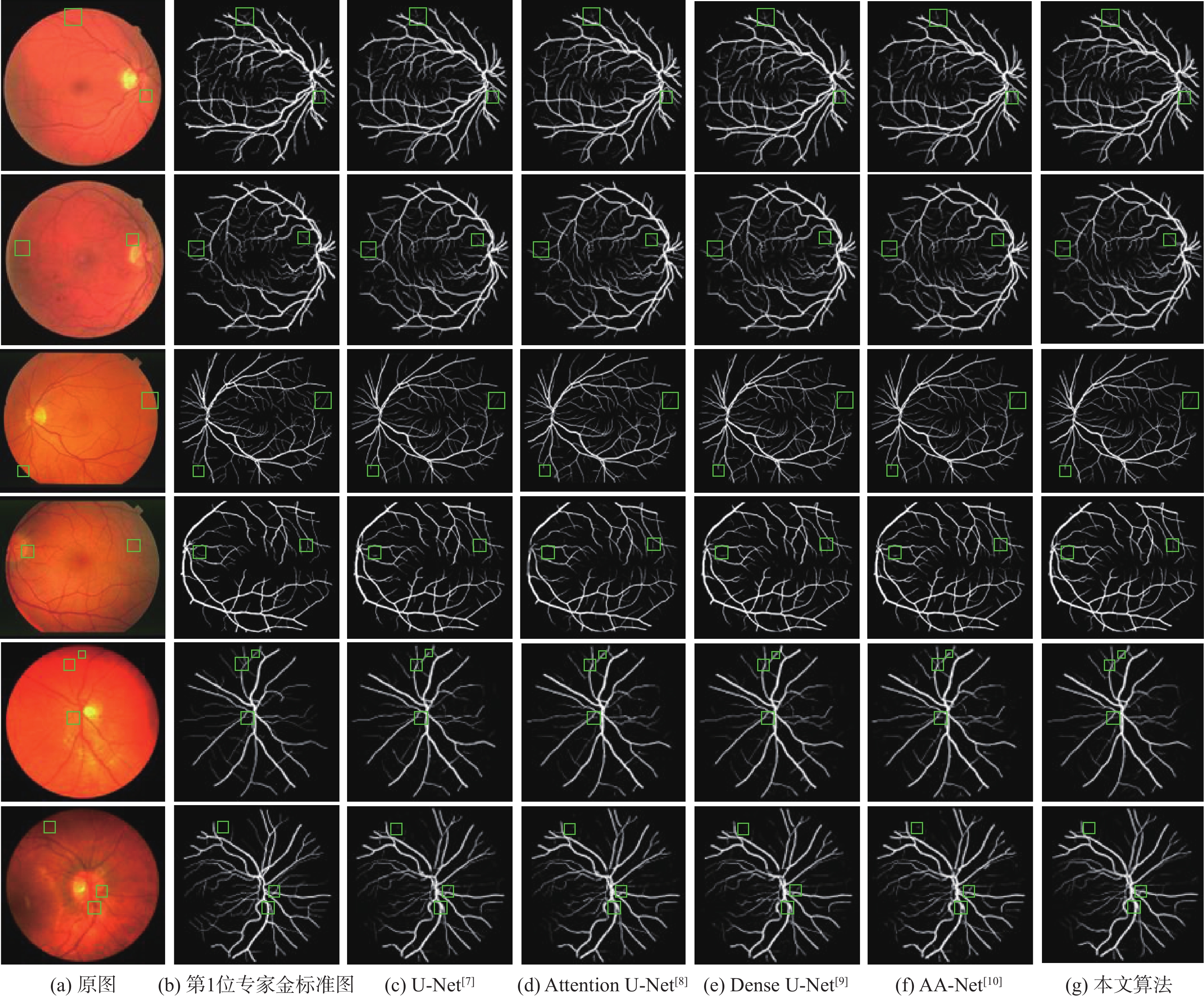
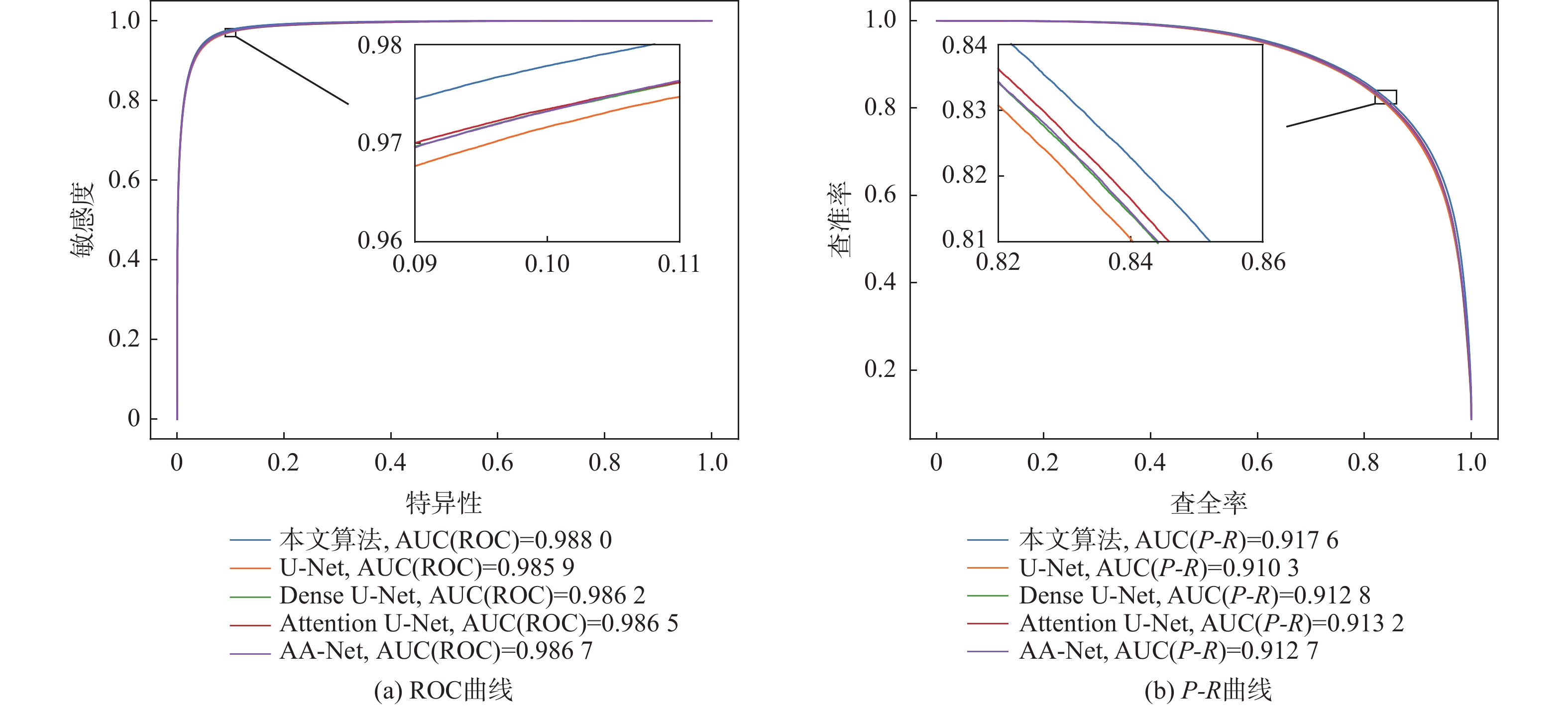
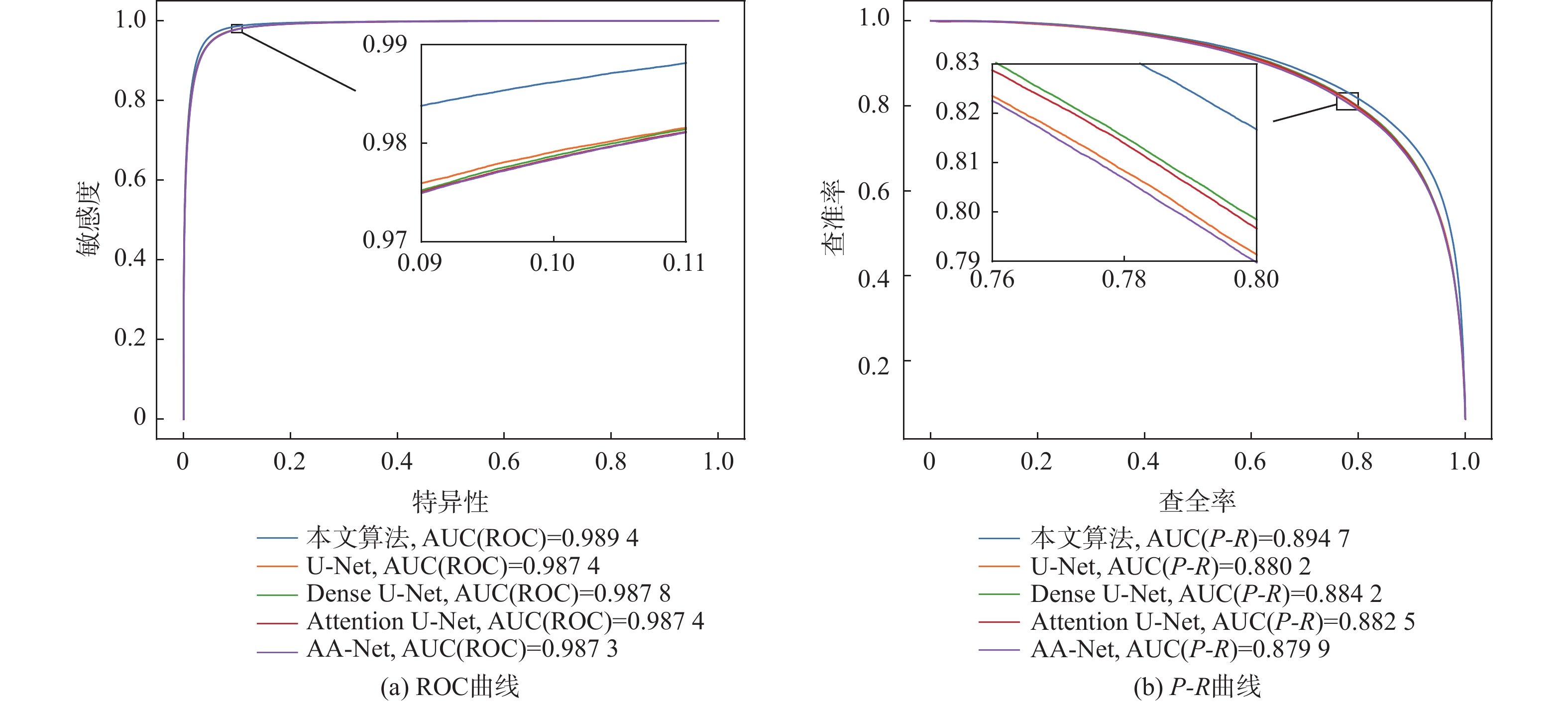
数据集 算法 AUC(ROC) AUC(P-R) F1 准确度 敏感度 特异性 DRIVE U-Net[7] 0.9859 0.9103 0.8228 0.9701 0.7932 0.9871 Attention U-Net[8] 0.9865 0.9132 0.8251 0.9705 0.7953 0.9873 Dense U-Net[9] 0.9862 0.9128 0.8251 0.9704 0.7979 0.9869 AA-Net[10] 0.9867 0.9127 0.8242 0.9703 0.7948 0.9872 本文 0.9880 0.9176 0.8300 0.9709 0.8109 0.9863 STARE U-Net[7] 0.9893 0.9170 0.8265 0.9749 0.7862 0.9904 Attention U-Net[8] 0.9891 0.9151 0.8220 0.9745 0.7743 0.9910 Dense U-Net[9] 0.9891 0.9158 0.8272 0.9749 0.7927 0.9898 AA-Net[10] 0.9901 0.9174 0.8276 0.9746 0.8018 0.9888 本文 0.9907 0.9220 0.8318 0.9754 0.8010 0.9897 CHASE_DB1 U-Net[7] 0.9874 0.8802 0.7945 0.9744 0.7846 0.9872 Attention U-Net[8] 0.9874 0.8825 0.7980 0.9746 0.7950 0.9867 Dense U-Net[9] 0.9878 0.8842 0.7994 0.9745 0.8050 0.9859 AA-Net[10] 0.9873 0.8799 0.7949 0.9732 0.8246 0.9832 本文 0.9894 0.8947 0.8093 0.9760 0.8079 0.9873 表 4 与近年来不同算法在DRIVE数据集上的性能指标对比
Table 4. Compared with performance indexes of different algorithms on DRIVE dataset in recent years
算法 年份 AUC 准确度 敏感度 特异性 文献[24] 2019 0.9750 0.9538 0.7631 0.9820 文献[25] 2020 0.9823 0.9581 0.7991 0.9813 文献[26] 2021 0.9678 0.9480 0.7352 0.9775 文献[27] 2021 0.9871 0.9692 0.8258 0.9829 文献[28] 2021 0.9748 0.9512 0.8060 0.9869 文献[29] 2021 0.9837 0.9697 0.8289 0.9838 文献[30] 2023 0.9820 0.9580 0.8139 0.9818 文献[31] 2022 0.9750 0.9518 0.7580 0.9804 文献[32] 2023 0.9850 0.9659 0.8491 0.9774 文献[33] 2022 0.9610 0.8125 0.9763 文献[34] 2023 0.9807 0.9568 0.8054 0.9789 本文算法 2023 0.9880 0.9709 0.8109 0.9863 表 5 与近年来不同算法在STARE数据集上的性能指标对比
Table 5. Compared with performance indicators of different algorithms in STARE dataset in recent years
算法 年份 AUC 准确度 敏感度 特异性 文献[24] 2019 0.9833 0.9638 0.7735 0.9857 文献[25] 2020 0.9881 0.9673 0.8186 0.9844 文献[26] 2021 0.9686 0.9548 0.7265 0.9759 文献[28] 2021 0.9620 0.9641 0.8230 0.9945 文献[29] 2021 0.9877 0.9736 0.8207 0.9839 文献[30] 2023 0.9902 0.9712 0.7972 0.9779 文献[31] 2022 0.9893 0.9683 0.7747 0.9910 文献[32] 2023 0.9873 0.9719 0.8573 0.9813 文献[33] 2022 0.9586 0.8078 0.9721 文献[34] 2023 0.9850 0.9648 0.8397 0.9795 本文算法 2023 0.9907 0.9754 0.8010 0.9897 表 6 与近年来不同算法在CHASE_DB1数据集上的性能指标对比
Table 6. Compared with performance indicators of different algorithms in CHASE_DB1 dataset in recent years
算法 年份 AUC 准确度 敏感度 特异性 文献[24] 2019 0.9776 0.9607 0.7641 0.9806 文献[25] 2020 0.9871 0.9670 0.8239 0.9813 文献[26] 2021 0.9681 0.9452 0.7279 0.9658 文献[27] 2021 0.9884 0.9745 0.8227 0.9853 文献[29] 2021 0.9867 0.9744 0.8365 0.9839 文献[30] 2023 0.9867 0.9669 0.8194 0.9817 文献[32] 2023 0.9869 0.9731 0.8607 0.9806 文献[33] 2022 0.9578 0.8012 0.9730 文献[34] 2023 0.9836 0.9635 0.8240 0.9775 本文算法 2023 0.9894 0.9760 0.8079 0.9873 表 7 模型参数量与浮点运算数量对比
Table 7. Comparison of number of model parameters and number of floating-point operations
表 8 模型消融实验
Table 8. Model ablation experiment
方法 AUC F1 准确度 敏感度 特异性 M1 0.9859 0.8228 0.9701 0.7932 0.9871 M2 0.9870 0.8265 0.9706 0.7996 0.9870 M3 0.9877 0.8265 0.9709 0.7913 0.9881 M4 0.9876 0.8270 0.9707 0.7993 0.9872 M5 0.9880 0.8300 0.9709 0.8109 0.9863 -
[1] 郑宇祥, 郝鹏翼, 吴冬恩, 等. 结合多层特征及空间信息蒸馏的医学影像分割[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(8): 1409-1417.ZHENG Y X, HAO P Y, WU D E, et al. Medical image segmentation based on multi-layer features and spatial information distillation[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(8): 1409-1417(in Chinese). [2] 梁礼明, 余洁, 陈鑫, 等. 跨级融合门控自适应网络用于视网膜血管分割[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2024, 50(4): 1097-1109.LIANG L M, YU J, CHEN X, et al. Cross-level fusion gated adaptive network for retinal vessel segmentation[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(4): 1097-1109(in Chinese). [3] BEKKERS E, DUITS R, BERENDSCHOT T, et al. A multi-orientation analysis approach to retinal vessel tracking[J]. Journal of Mathematical Imaging and Vision, 2014, 49(3): 583-610. doi: 10.1007/s10851-013-0488-6 [4] LI Q, YOU J, ZHANG D. Vessel segmentation and width estimation in retinal images using multiscale production of matched filter responses[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2012, 39(9): 7600-7610. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2011.12.046 [5] 梁礼明, 黄朝林, 石霏, 等. 融合形状先验的水平集眼底图像血管分割[J]. 计算机学报, 2018, 41(7): 1678-1692. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2018.01678LIANG L M, HUANG C L, SHI F, et al. Retinal vessel segmentation using level set combined with shape priori[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2018, 41(7): 1678-1692(in Chinese). doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2018.01678 [6] ZHANG J, CHEN Y, BEKKERS E, et al. Retinal vessel delineation using a brain-inspired wavelet transform and random forest[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 69: 107-123. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2017.04.008 [7] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T. U-Net: convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention. Berlin: Springer, 2015: 234-241. [8] OKTAY O, SCHLEMPER J, LE FOLGOC L, et al. Attention U-Net: learning where to look for the pancreas[EB/OL]. (2018-05-20)[2023-02-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1804.03999. [9] WANG C, ZHAO Z Y, REN Q Q, et al. Dense U-Net based on patch-based learning for retinal vessel segmentation[J]. Entropy, 2019, 21(2): 168. doi: 10.3390/e21020168 [10] LIANG L M, FENG J, ZHOU L S, et al. U-shaped retinal vessel segmentation based on adaptive aggregation of feature information[J]. Interdisciplinary Sciences: Computational Life Sciences, 2022, 14(2): 623-637. doi: 10.1007/s12539-022-00519-x [11] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]//Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. New York: ACM, 2017: 6000-6010. [12] MEHTA S, RASTEGARI M. MobileViT: light-weight, general-purpose, and mobile-friendly vision transformer[EB/OL]. (2022-03-04)[2023-02-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.02178?context=cs. [13] JIANG Y, LIANG J, CHENG T T, et al. MTPA_Unet: multi-scale Transformer-position attention retinal vessel segmentation network joint Transformer and CNN[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22(12): 4592. doi: 10.3390/s22124592 [14] RUAN J C, XIANG S C, XIE M Y, et al. MALUNet: a multi-attention and light-weight UNet for skin lesion segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 1150-1156. [15] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [16] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Identity mappings in deep residual networks[C]//Proceedings of the14th European Conference. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 630-645. [17] QIN Z Q, ZHANG P Y, WU F, et al. FcaNet: frequency channel attention networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 783-792. [18] HUANG G, LIU Z, VAN DER MAATEN L, et al. Densely connected convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 4700-4708. [19] LIAO T Y, YANG C H, LO Y, et al. HarDNet-DFUS: an enhanced harmonically-connected network for diabetic foot ulcer image segmentation and colonoscopy polyp segmentation[EB/OL]. (2022-09-15)[2023-02-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.07313. [20] STAAL J, ABRÀMOFF M D, NIEMEIJER M, et al. Ridge-based vessel segmentation in color images of the retina[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2004, 23(4): 501-509. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2004.825627 [21] HOOVER A, KOUZNETSOVA V, GOLDBAUM M. Locating blood vessels in retinal images by piecewise threshold probing of a matched filter response[J]. IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2000, 19(3): 203-210. doi: 10.1109/42.845178 [22] OWEN C G, RUDNICKA A R, MULLEN R, et al. Measuring retinal vessel tortuosity in 10-year-old children: validation of the computer-assisted image analysis of the retina (CAIAR) program[J]. Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 2009, 50(5): 2004-2010. [23] LIN T Y, GOYAL P, GIRSHICK R, et al. Focal loss for dense object detection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 2980-2988. [24] YAN Z Q, YANG X, CHENG K T. A three-stage deep learning model for accurate retinal vessel segmentation[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2019, 23(4): 1427-1436. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2018.2872813 [25] WANG D Y, HAYTHAM A, POTTENBURGH J, et al. Hard attention net for automatic retinal vessel segmentation[J]. IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics, 2020, 24(12): 3384-3396. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2020.3002985 [26] TCHINDA B S, TCHIOTSOP D, NOUBOM M, et al. Retinal blood vessels segmentation using classical edge detection filters and the neural network[J]. Informatics in Medicine Unlocked, 2021, 23: 100521. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2021.100521 [27] HU X L, WANG L J, CHENG S L, et al. HDC-Net: a hierarchical dilation convolutional network for retinal vessel segmentation[J]. PLoSOne, 2021, 16(9): e0257013. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257013 [28] WANG C, ZHAO Z Y, YU Y. Fine retinal vessel segmentation by combining Nest U-net and patch-learning[J]. Soft Computing, 2021, 25(7): 5519-5532. doi: 10.1007/s00500-020-05552-w [29] WU H S, WANG W, ZHONG J F, et al. SCS-net: a scale and context sensitive network for retinal vessel segmentation[J]. Medical Image Analysis, 2021, 70: 102025. doi: 10.1016/j.media.2021.102025 [30] LI D Y, PENG L X, PENG S H, et al. Retinal vessel segmentation by using AFNet[J]. The Visual Computer, 2023, 39(5): 1929-1941. doi: 10.1007/s00371-022-02456-8 [31] XU X M, WANG Y X, LIANG Y, et al. Retinal vessel automatic segmentation using SegNet[J]. Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine, 2022, 2022: 3117455. [32] AURANGZEB K, ALHARTHI R S, HAIDER S I, et al. An efficient and light weight deep learning model for accurate retinal vessels segmentation[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 23107-23118. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3217782 [33] KHAN T M, KHAN M A U, REHMAN N U, et al. Width-wise vessel bifurcation for improved retinal vessel segmentation[J]. Biomedical Signal Processing and Control, 2022, 71: 103169. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2021.103169 [34] 梁礼明, 冯骏, 彭仁杰, 等. 融合多标签损失与双注意力的U型视网膜血管分割[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2023, 25(1): 75-86.LIANG L M, FENG J, PENG R J. et al. U-shaped retinal vessel segmentation combining multi-label loss and dual attention[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2023, 25(1): 75-86(in Chinese) . -







 下载:
下载: