Experimental study on flow and heat transfer of hydrocarbon fuels in additive manufacturing channels at supercritical pressure
-
摘要:
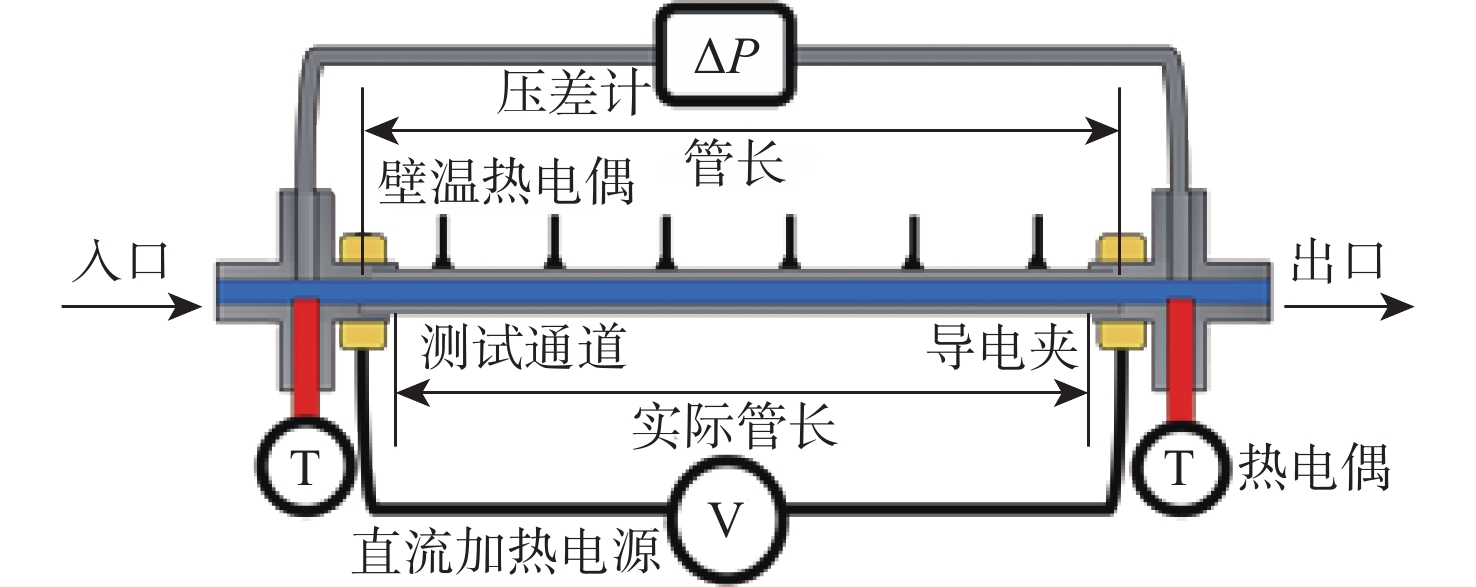
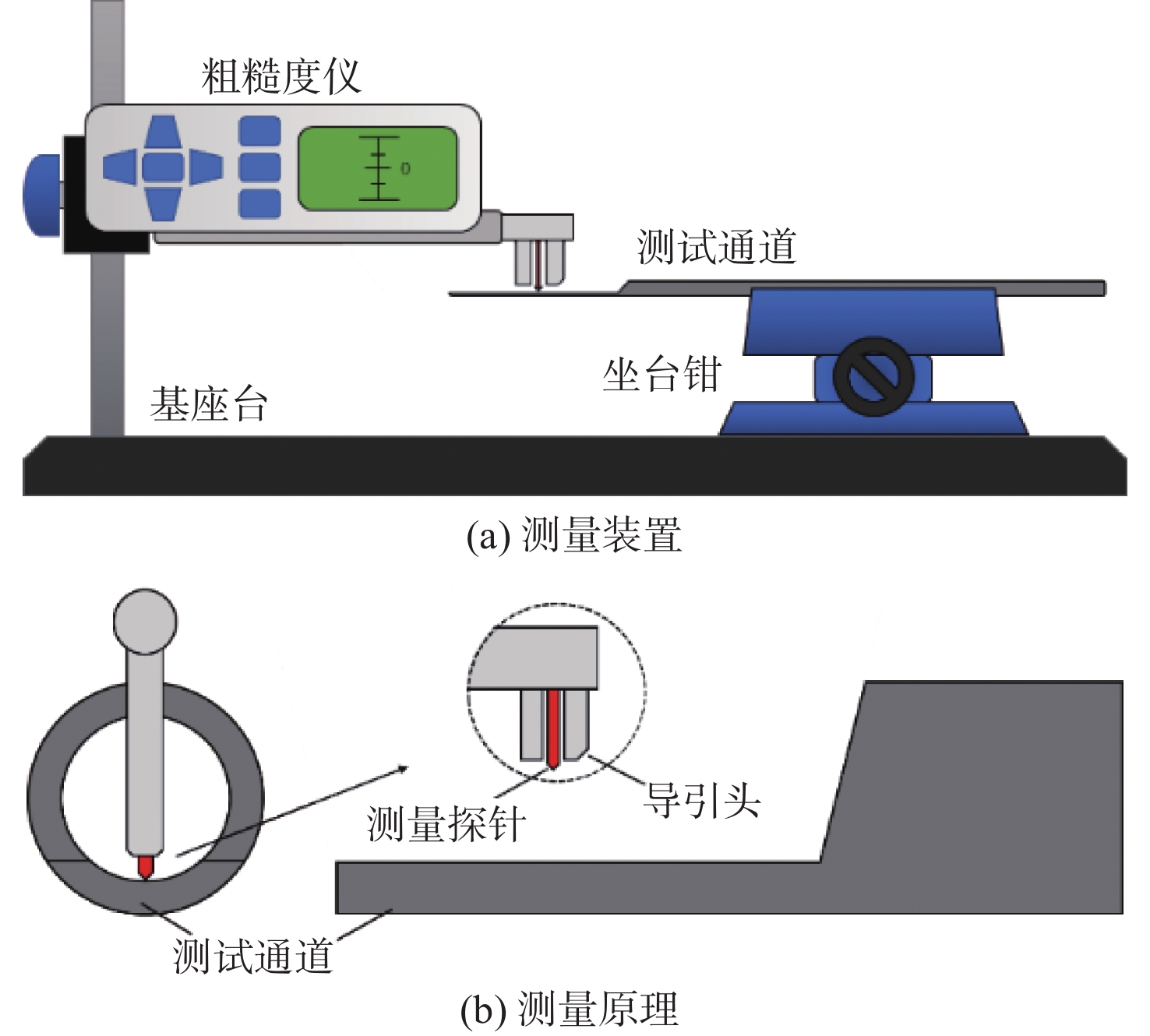
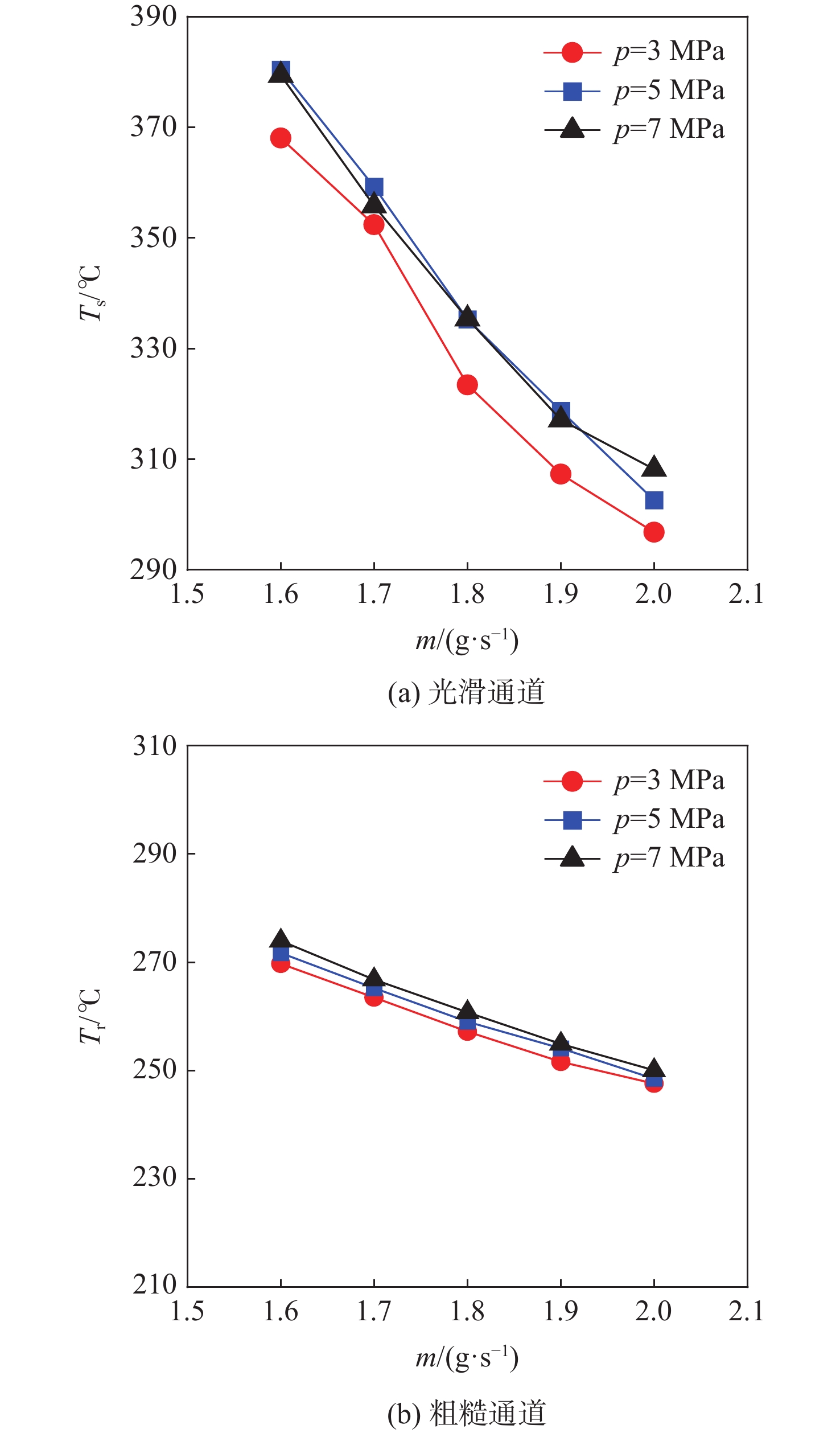
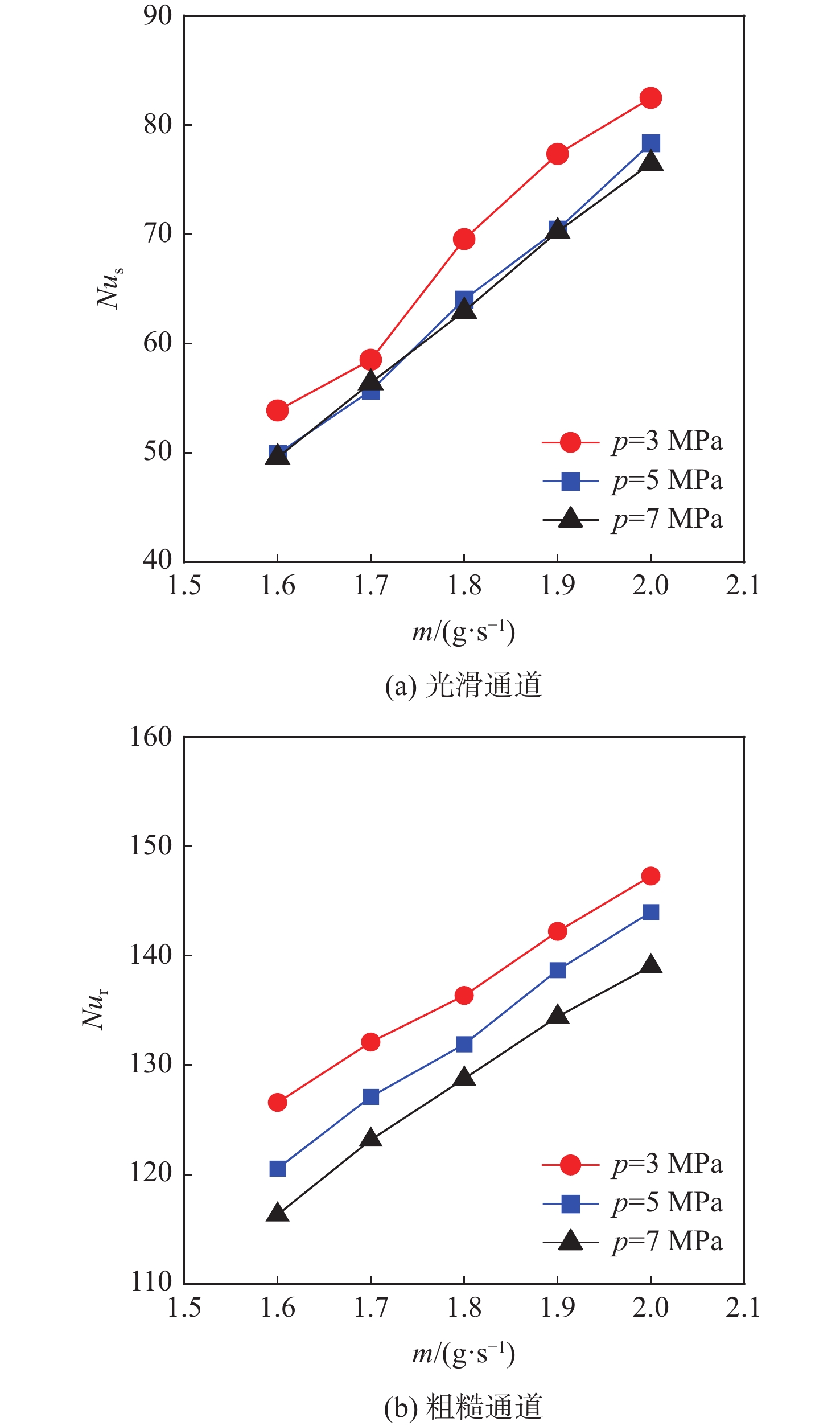
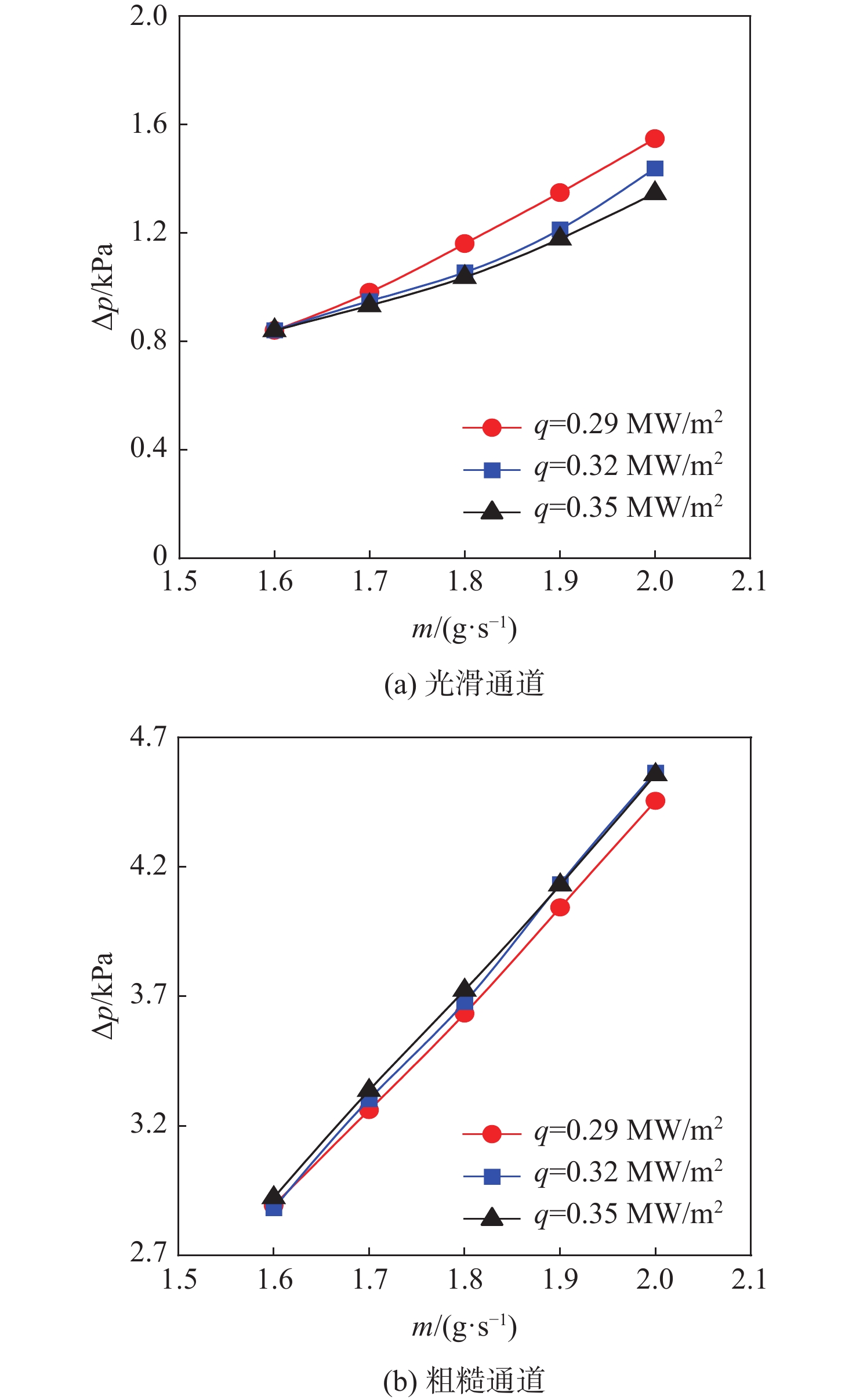
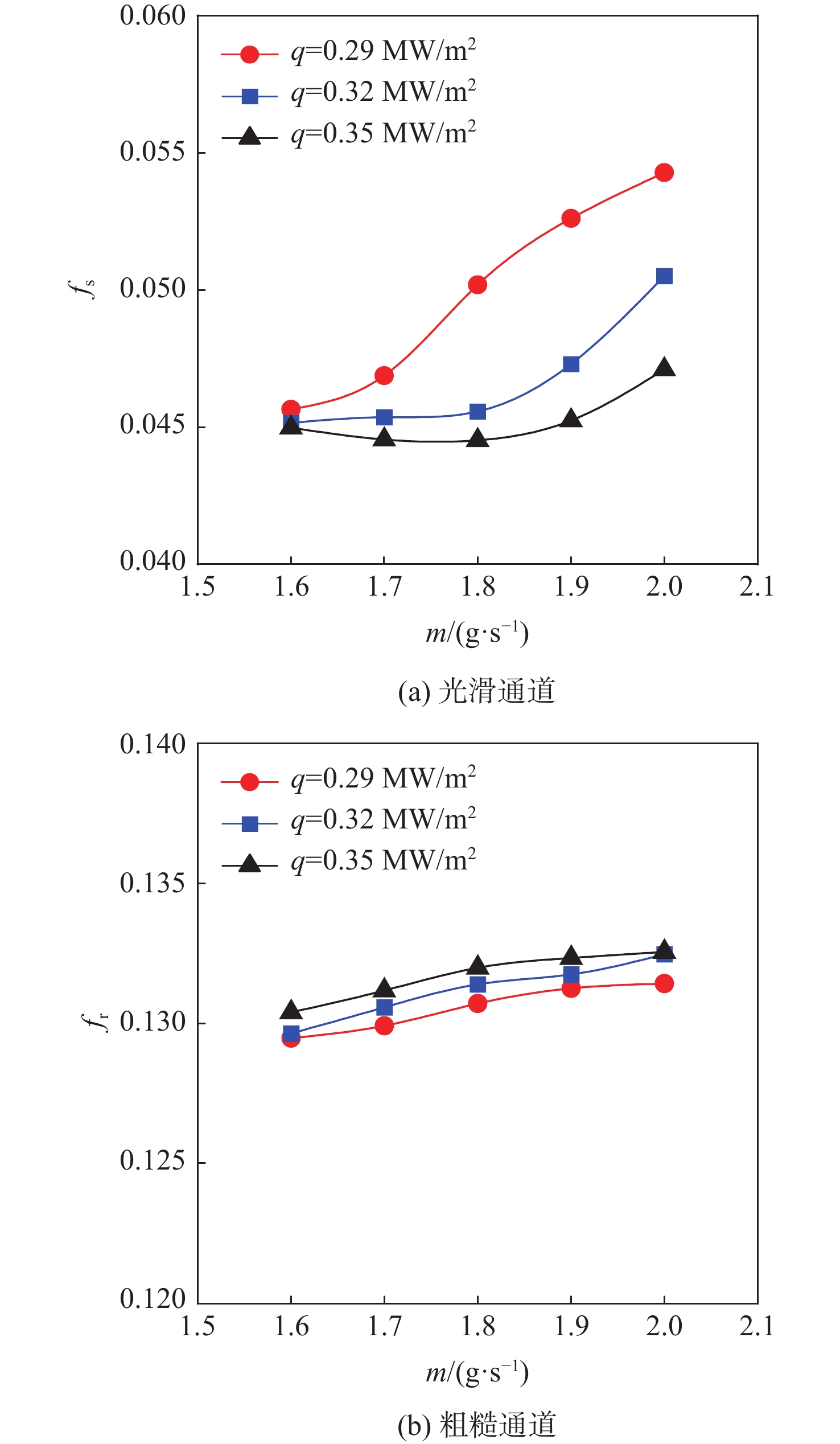
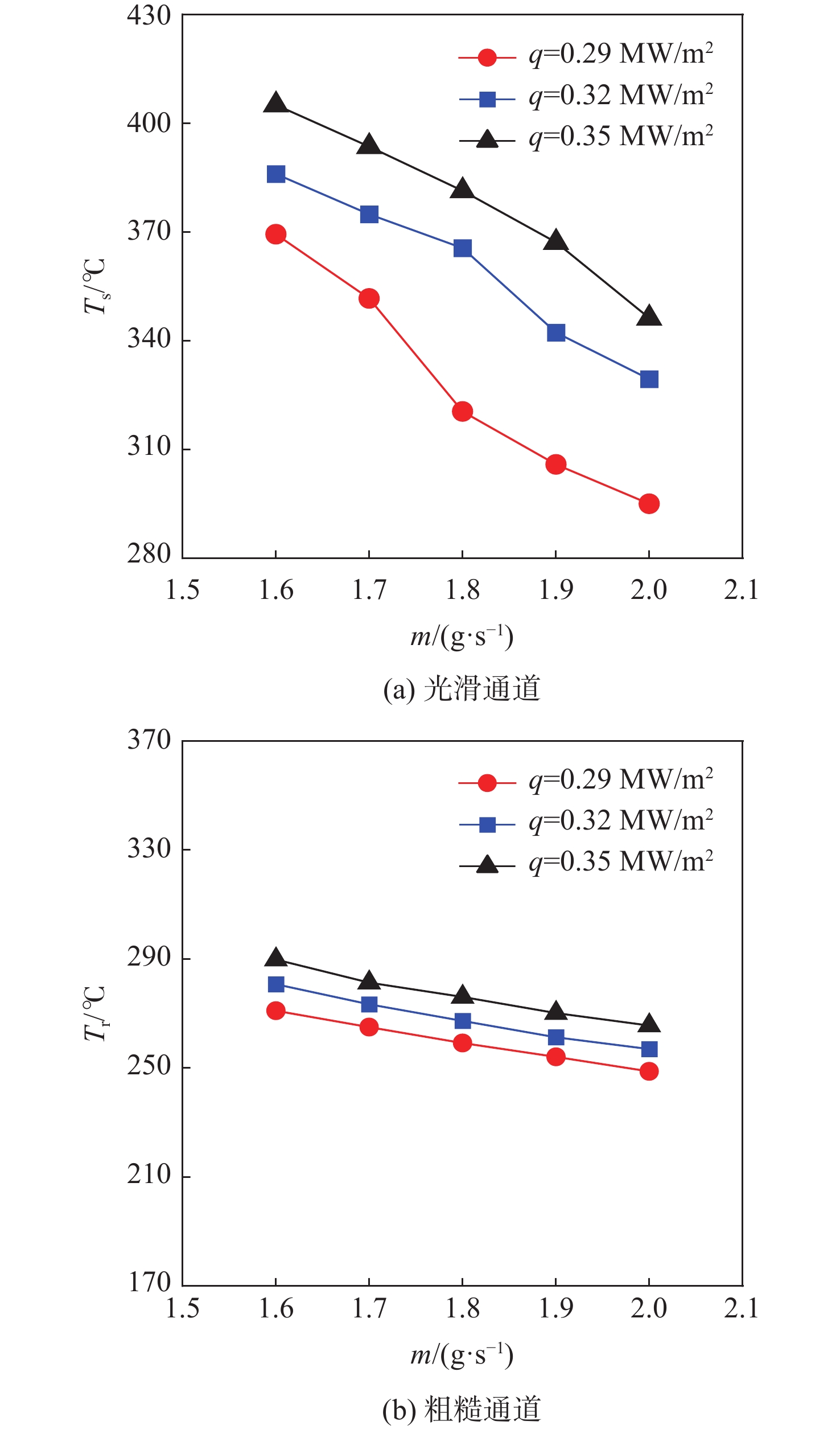
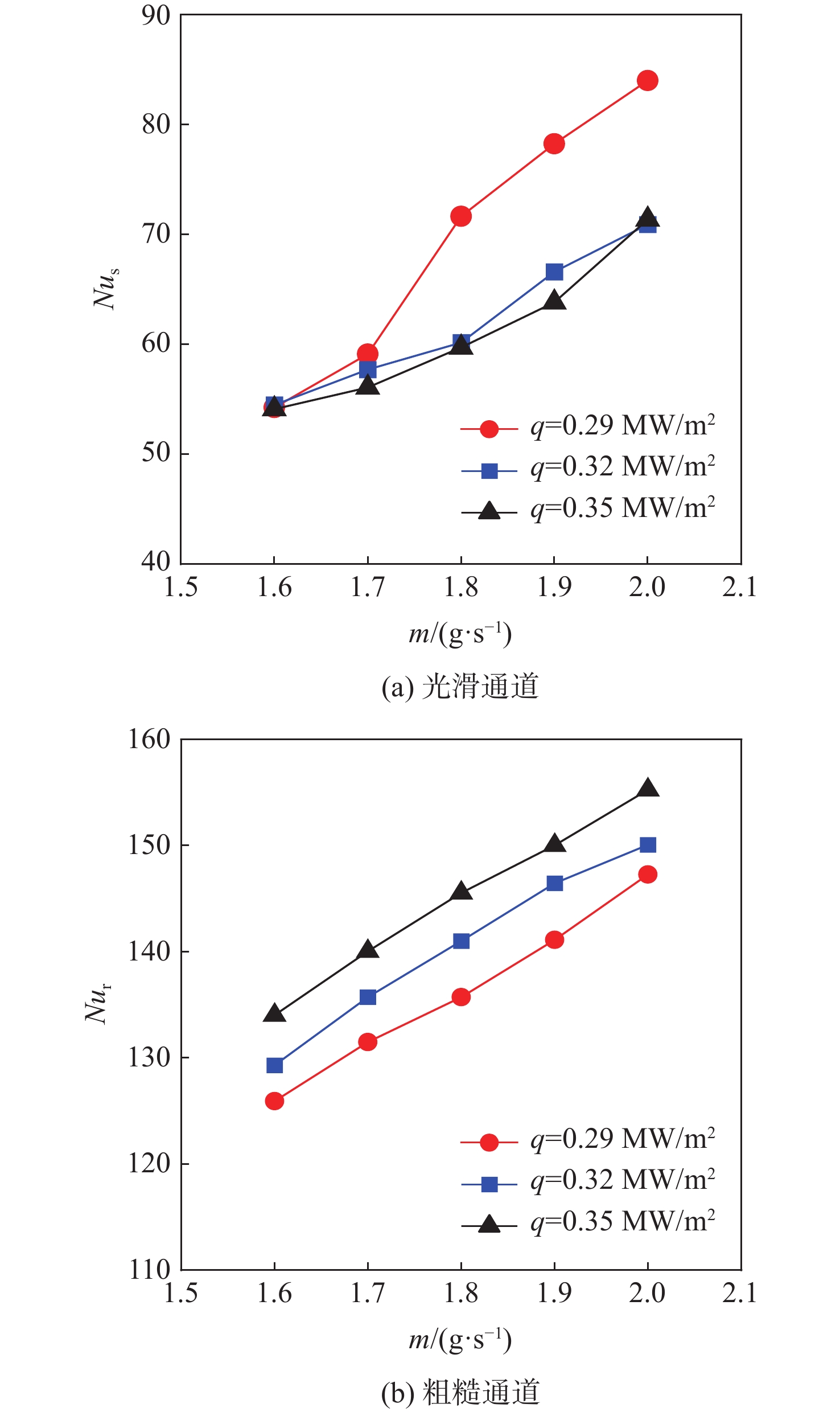
针对超临界压力正癸烷在增材制造(AM)粗糙通道与机械加工光滑通道中的流动和传热性能差异进行对比实验研究。采用粗糙度仪获得AM通道和光滑通道的表面平均粗糙度分别为11 μm和 3 μm。考察不同系统压力(3 MPa、5 MPa和7 MPa)和壁面热流密度(0.29 MW/m2、0.32 MW/m2和0.35 MW/m2)工况下,2种通道摩阻系数
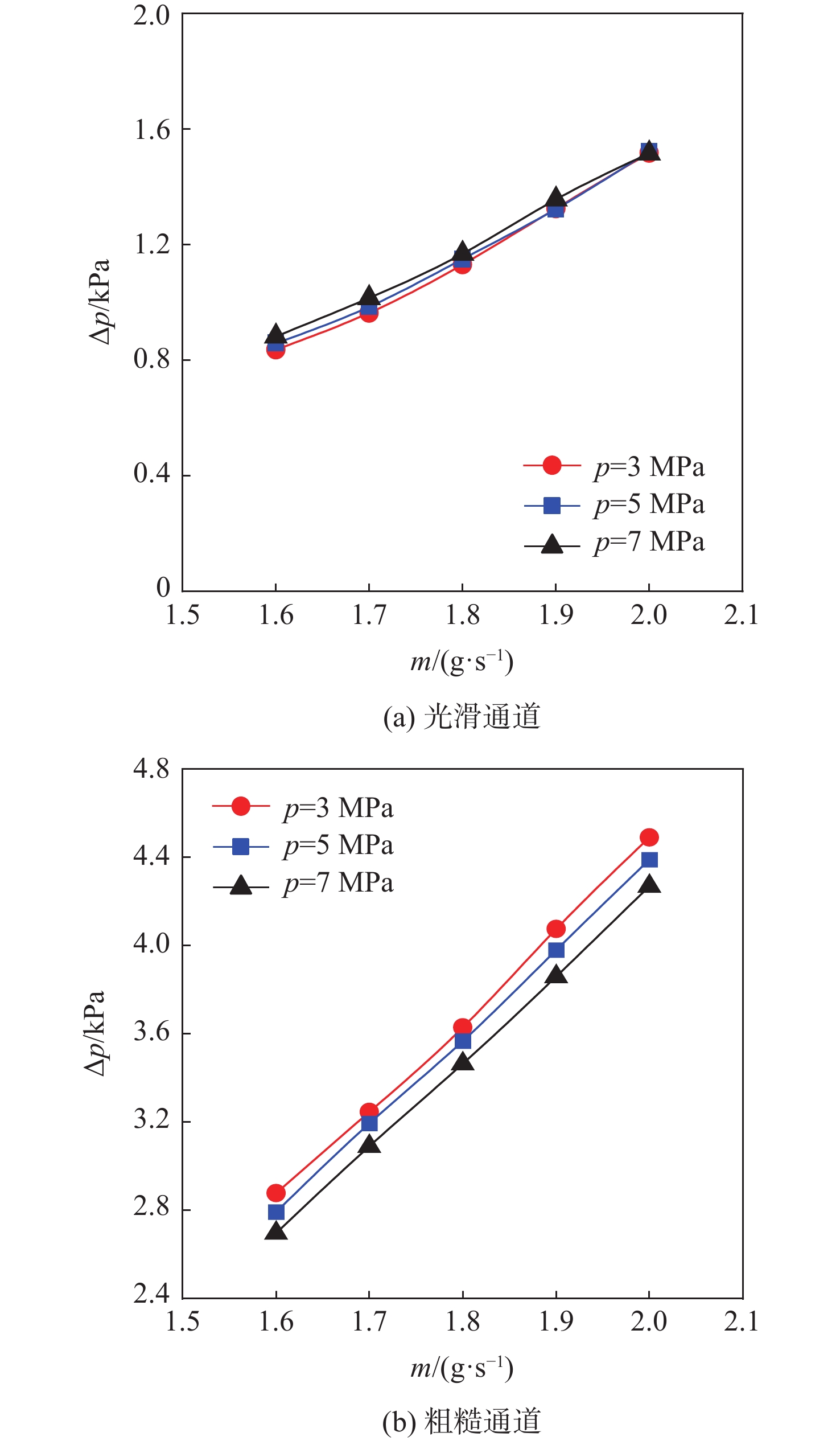
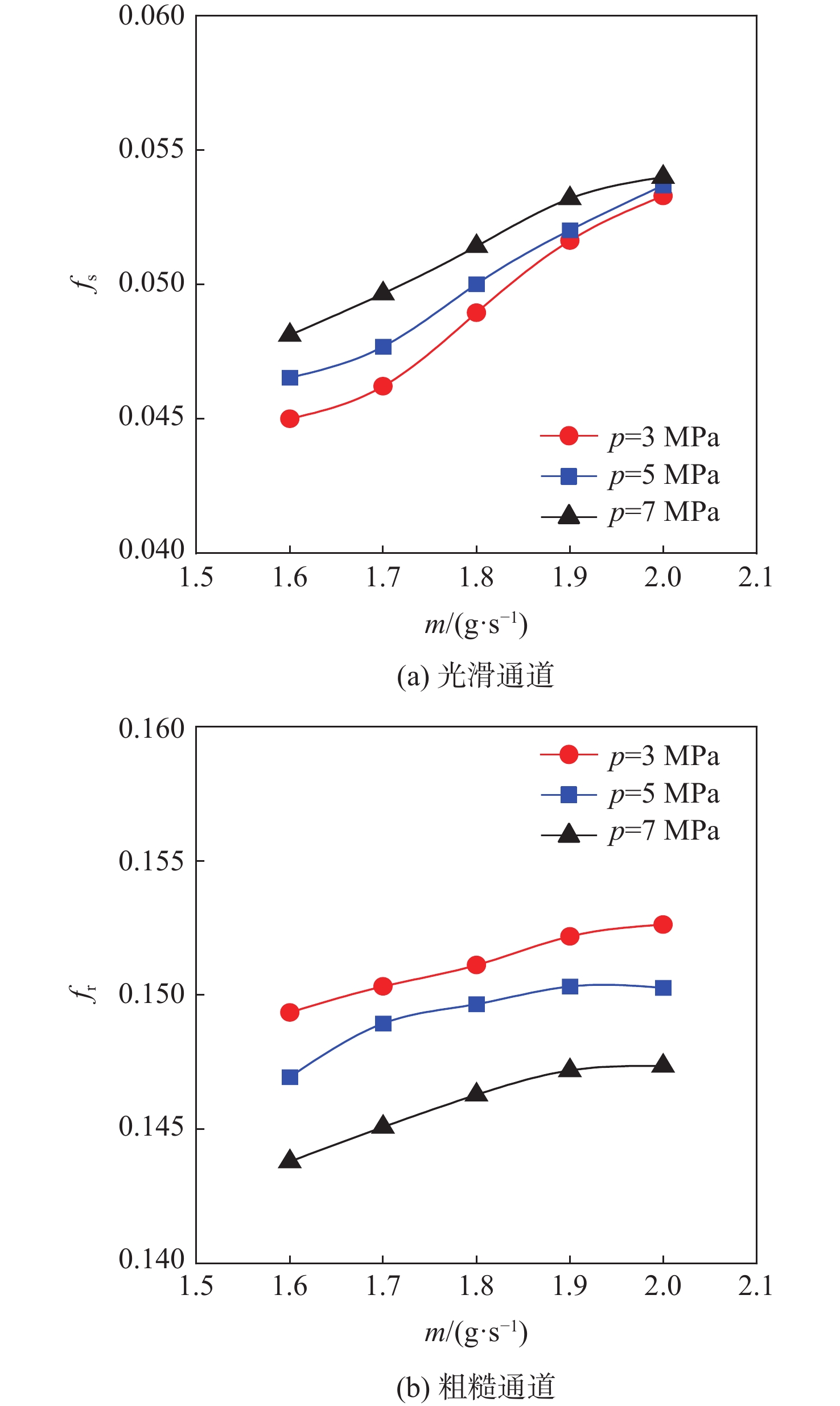
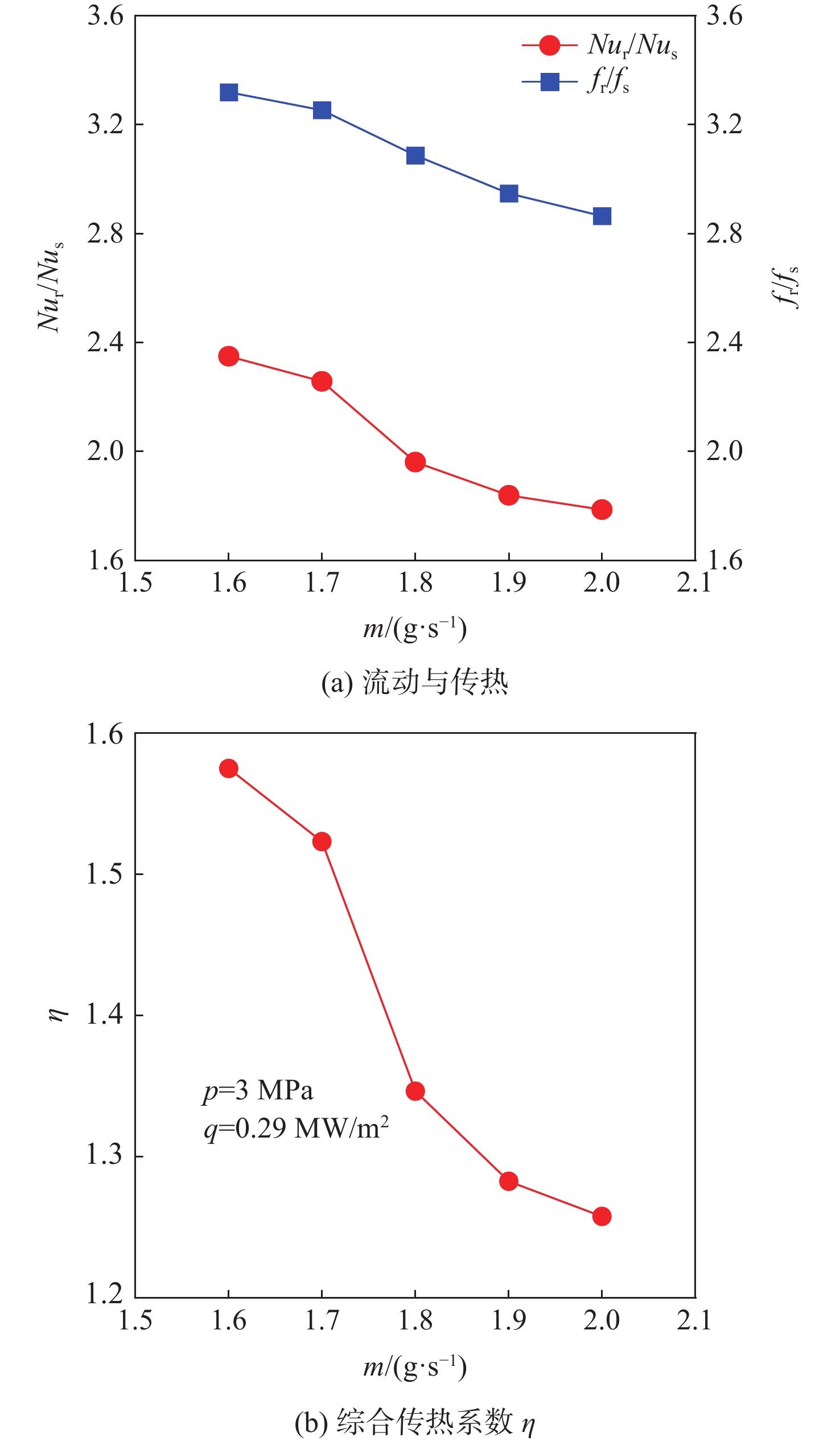
f 和努塞尔特数Nu 在不同流量下的变化规律。结果表明:在选定的流量范围内,AM通道的f 和Nu 皆大于光滑通道,AM通道的f 是光滑通道的2.8~3.5倍,Nu 是光滑通道的1.7~2.3倍;增大系统压力会使AM通道的f 降低,但却使光滑通道增加,而Nu 在AM和光滑通道皆降低;随着壁面热流密度增加,AM通道的f 和Nu 皆降低,而光滑通道皆增加;粗糙通道具有很好的综合传热性能,并且在小流量时效果更好,其综合传热系数为1.2~1.5;提出超临界碳氢燃料在增材制造通道中Nu 和f 的关联式。Abstract:This article presents a comparative experimental study on the flow and heat transfer performance differences between additive manufacturing (AM) rough channels and machined smooth channels for supercritical pressure n-decane. Using a roughness gauge, the surface average roughness of the smooth channel and AM channel were determined to be 3 μm and 11 μm, respectively. The study investigated variations in the friction factor (
f ) and Nusselt number (Nu ) of the two channels under different flow rates, system pressures (3 MPa, 5 MPa, and 7 MPa), and wall heat flux densities (0.29 MW/m2, 0.32 MW/m2, and 0.35 MW/m2). The results showed that, within the selected flow rate range, bothf andNu of the AM channel were higher than those of the smooth channel, withf being 2.8~3.5 times that of the smooth channel, andNu being 1.7~2.3 times that of the smooth channel. Increasing the system pressure reducedf of the AM channel, but increased that of the smooth channel, whileNu decreased for both channels. As the wall heat flux density increased, bothf andNu of the AM channel decreased, while those of the smooth channel increased. The rough channel had a comprehensive heat transfer coefficient of 1.2~1.5, showing outstanding overall heat transfer performance and greater effectiveness at low flow rate. The correlations of theNu andf of supercritical hydrocarbon fuel in additive manufacturing channel are proposed.-
Key words:
- roughness /
- additive manufacturing /
- friction loss /
- heat transfer characteristics /
- experimental study
-
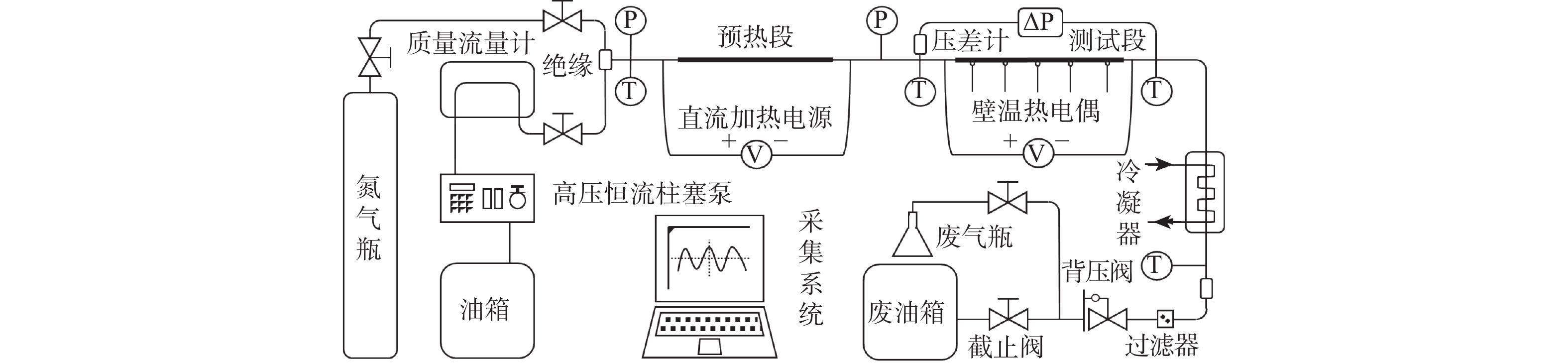
表 1 直接测量误差
Table 1. Direct measurement error
仪器 直接测量参数 误差/% 直流电源 电压U 2.82 电流I 1.64 压差计 压力差Δp 1.16 压力传感器 压力p 0.25 温度传感器 温度T 0.4 流量计 质量流量m 0.62 表 2 间接测量误差
Table 2. Indirect measurement error
间接测量参数 误差/% 物性 0.47 流速 0.77 内壁温度Ti 3.28 对流换热系数h 6.72 摩阻系数f 1.46 努塞尔特数Nu 6.73 -
[1] NOURIN F N, AMANO R S. Review of gas turbine internal cooling improvement technology[J]. Journal of Energy Resources Technology, 2020, 143(8): 080801-080809. [2] SINGH J, ALEJANDRO M C, NIGAM K D P. Process intensification for compact and micro heat exchangers through innovative technologies: a Review[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2019, 58(31): 13819-13847. [3] HASAN M I, RAGEB A A, YAGHOUBI M, et al. Influence of channel geometry on the performance of a counter flow microchannel heat exchanger[J]. International Journal of Thermal Sciences, 2009, 48(8): 1607-1618. doi: 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2009.01.004 [4] 刘洋, 周建平, 张晓天. 增材制造技术在载人航天工程中的应用与展望[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(1): 83-91.LIU Y, ZHOU J P, ZHANG X T. Application and prospect of additive manufacturing technology in manned space engineering[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(1): 83-91(in Chinese). [5] PU H, LI S, DONG M, et al. Convective heat transfer and flow resistance characteristics of supercritical pressure hydrocarbon fuel in a horizontal rectangular mini-channel[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2019(108): 39-53. [6] ZHAO W, SONG Z, LI H, et al. Research on heat transfer characteristics of kerosene at supercritical pressure in circular tubes[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2018(96): 507-515. [7] 黄世璋, 阮波, 高效伟, 等. 超临界压力下碳氢燃料裂解与流动传热模拟的快速算法[J]. 航空学报, 2018, 39(4): 121650.HUANG S Z, RUAN B, GAO X W, et al. A fast algorithm for simulating hydrocarbon fuel heat transfer with endothermic pyrolysis under supercritical pressures[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2018, 39(4): 121650(in Chinese). [8] 阮波. 超临界压力下正癸烷裂解吸热和对流传热现象的数值模拟研究[D]. 浙江: 浙江大学, 2013.RUAN B. A numerical simulation study on the endothermic cracking and convective heat transfer phenomena of n-decane under supercritical pressure[D]. Zhejiang: Zhejiang University, 2013(in Chinses). [9] 张磊, 乐嘉陵, 张若凌, 等. 超临界压力下湍流区碳氢燃料传热研究[J]. 推进技术, 2013, 34(2): 225-229.ZHANG L, LE J L, ZHANG R L, et al. Heat transfer of hydrocarbon fuel in turbulent flow region under supercritical pressure[J]. Journal of Propulsion Technology, 2013, 34(2): 225-229(in Chinese). [10] CORMIER Y, DUPUIS P, FARJAM A, et al. Additive manufacturing of pyramidal pin fins: Height and fin density effects under forced convection[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2014(75): 235-244. [11] HUTTUNEN E, NYKÄNEN M T, ALEXANDERSEN J. Material extrusion additive manufacturing and experimental testing of topology-optimised passive heat sinks using a thermally-conductive plastic filament[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2022(59): 103123. [12] ALTENEIJI M, ALI M, KHAN K A, et al. Heat transfer effectiveness characteristics maps for additively manufactured TPMS compact heat exchangers[J]. Energy Storage and Saving, 2022, 1(3): 9. [13] DELGADO J, CIURANA J, RODRÍGUEZ C A. Influence of process parameters on part quality and mechanical properties for DMLS and SLM with iron-based materials[J]. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2012, 60(5): 601-610. [14] STRANO G, HAO L, EVERSON R M, et al. Surface roughness analysis, modelling and prediction in selective laser melting[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2013, 213(4): 589-597. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2012.11.011 [15] TOWNSEND A, SENIN N, BLUNT L, et al. Surface texture metrology for metal additive manufacturing: a review[J]. Precision Engineering, 2016, 46: 34-47. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2016.06.001 [16] SHEN S, XU J L, ZHOU J J, et al. Flow and heat transfer in microchannels with rough wall surface[J]. Energy Conversion and Management, 2006, 47(11): 1311-1325. [17] HUANG K, WAN J W, CHEN C X, et al. Experimental investigation on friction factor in pipes with large roughness[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2013, 50: 147-153. doi: 10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2013.06.002 [18] 周红秀, 张奥, 刘悦闻, 等. 壁面表面粗糙度对喷孔内空化流动特性的影响[J]. 内燃机与动力装置, 2022, 39(2): 7-13.ZHOU H X, ZHANG A, LIU Y W, et al. The effect of wall surface roughness on cavitation flow characteristics in nozzle[J]. Internal Combustion Engine & PowerPlant, 2022, 39(2): 7-13(in Chinese). [19] LIU Y, XU G, SUN J, et al. Investigation of the roughness effect on flow behavior and heat transfer characteristics in microchannels[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2015, 83: 11-20. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2014.11.060 [20] YUAN Y, TAO Z, LI H, et al. Experimental investigation of surface roughness effects on flow behavior and heat transfer characteristics for circular microchannels[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2016, 29(6): 1575-1581. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2016.10.006 [21] 李虹杨, 郑赟. 粗糙度对涡轮叶片流动转捩及传热特性的影响[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(10): 2038-2047.LI H Y, ZHENG Y. Effect of surface roughness on flow transition and heat transfer of turbine blade[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronsutics, 2016, 42(10): 2038-2047(in Chinese). [22] NATRAJAN V K, CHRISTENSEN K T. The impact of surface roughness on flow through a rectangular microchannel from the laminar to turbulent regimes[J]. Microfluid Nanofluid, 2010(9): 95-121. [23] 郝鹏飞, 姚朝晖, 何枫. 粗糙微管道内液体流动特性的实验研究[J]. 物理学报, 2007, 56(8): 5. doi: 10.7498/aps.56.4728HAO P F, YAO C H, HE F. Experimental study of flow characteristics in rough microchannels[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2007, 56(8): 5(in Chinese). doi: 10.7498/aps.56.4728 [24] 鲁聪达, 薛浩, 吴化平, 等. 随机粗糙微通道内部流动与传质特性[J]. 中国机械工程, 2018, 29(12): 7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2018.12.005LU C D, XUE H, WU H P, et al. Flow and mass transfer characteristics in random roughness surface microchannels[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 29(12): 7(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2018.12.005 [25] ROVENSKAYA O I. Numerical analysis of surface roughness effects on the Poiseuille flow caused by a small pressure drop[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2017, 110: 817-826. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2017.03.084 [26] RAWOOL A S, MITRA S K, KANDLIKAR S G. Numerical simulation of flow through microchannels with designed roughness[J]. Microfluidics and Nanofluidics, 2006, 2(3): 215-221. doi: 10.1007/s10404-005-0064-5 -







 下载:
下载: