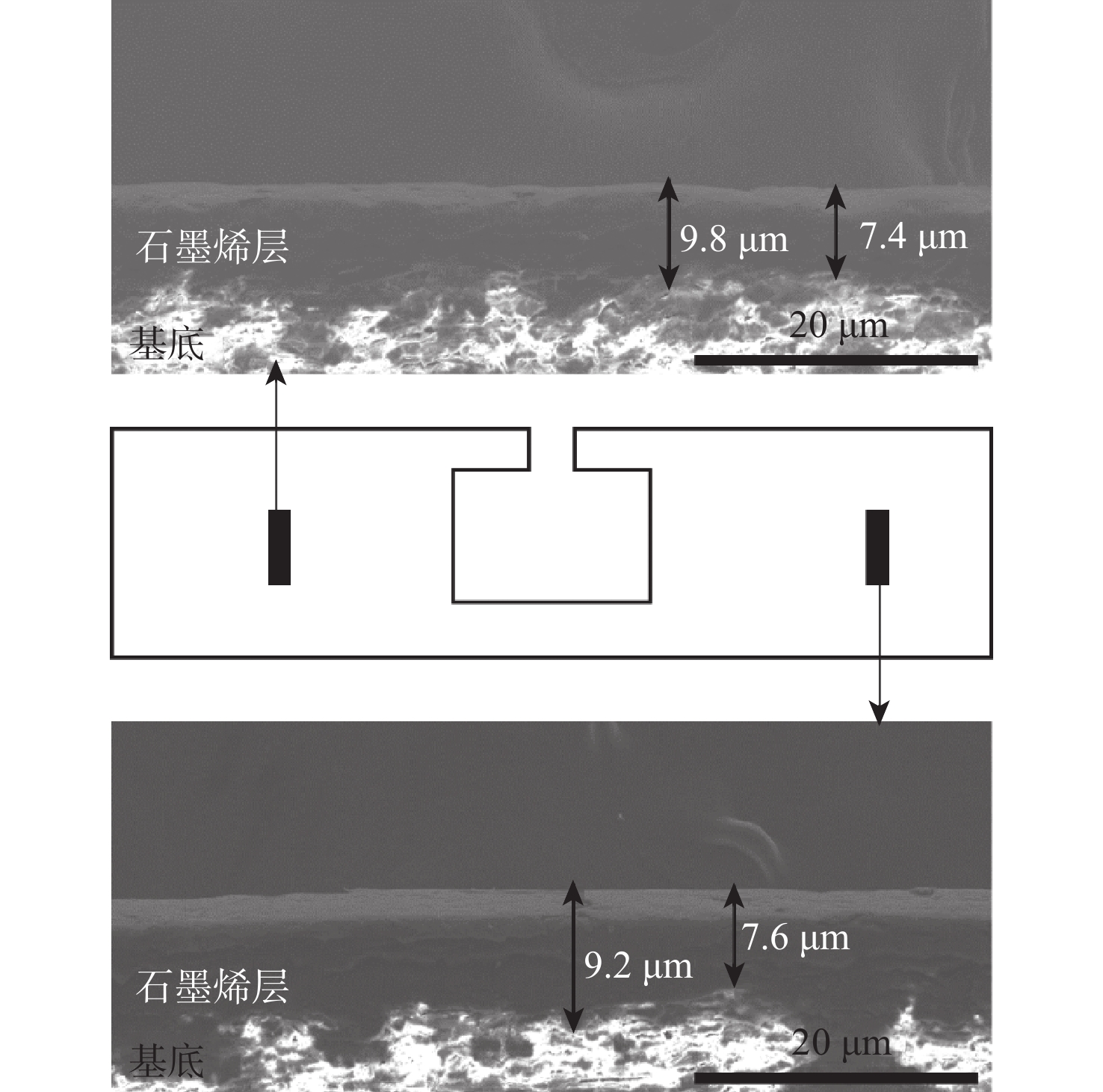
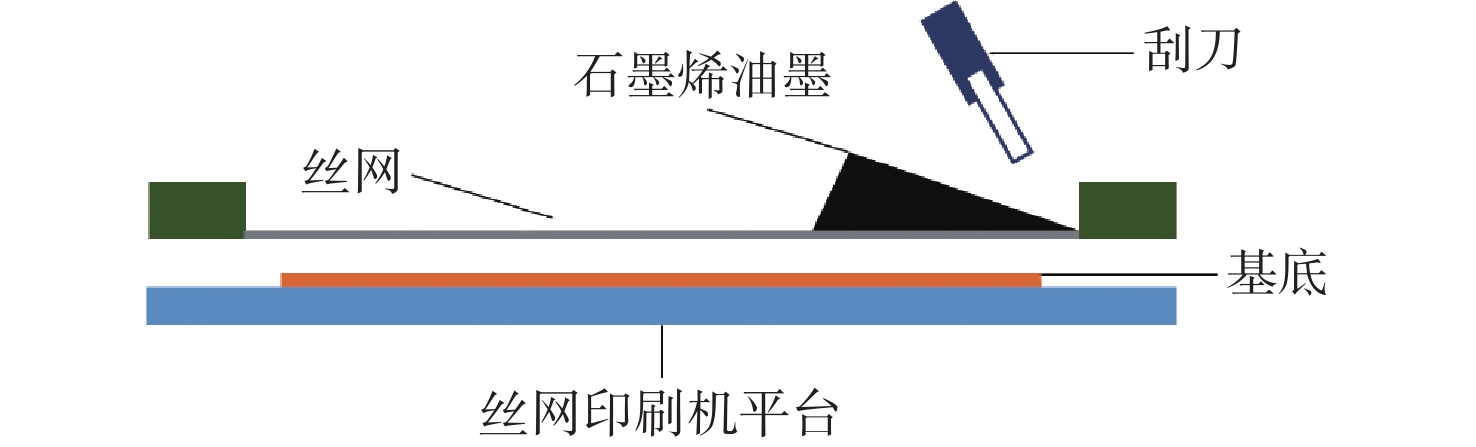
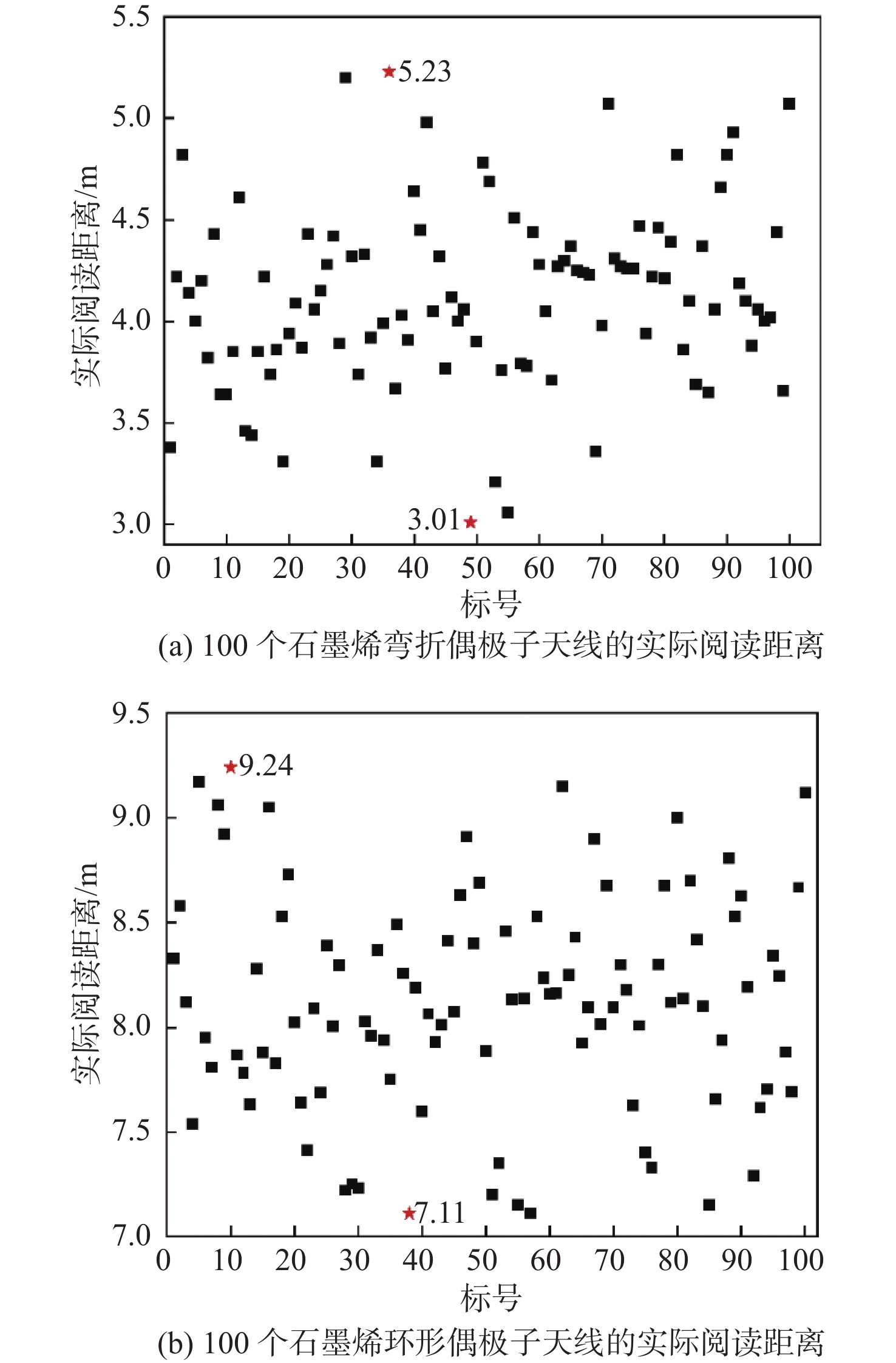
-
摘要:
石墨烯标签天线因具有价格低廉和环境友好的优势而有望替代金属标签天线。然而,石墨烯标签天线在制备过程中受到丝网印刷工艺和石墨烯油墨的影响,不可避免地引入不确定性,使得实际阅读距离与理论值不符。为指导包含不确定性的石墨烯标签天线的设计,使天线阅读距离处于特定范围内,提出一种基于区间分析的算法。通过分析天线理论公式,得到不确定性参数;根据制备经验,为每个不确定性参数估计区间范围,使用区间分析算法(包括区间数学建模和顶点法)计算阅读距离的上下限;通过实验测量了石墨烯标签天线的阅读距离,验证了所提算法。结果表明:所提算法可以有效地计算石墨烯标签天线的阅读距离区间,有助于石墨烯标签天线的实际使用,并为制造过程中的不确定性分析提供指导。
Abstract:Graphene tag antenna, owing to its low price and environmental friendliness, is a promising alternative to metal tag antenna. However, graphene antennas inevitably suffer from property uncertainties due to the manufacturing process of screen printing and the properties of graphene inks, making their real read range different from the theoretical one. A unique interval-based computation algorithm is proposed to guide the design of graphene antennas with uncertainties considered, as well as to make the read range particular. Firstly, uncertainty parameters are obtained by analyzing the theoretical formulas of antennas. Second, using an interval analysis approach that includes the interval mathematical modeling and the vertex algorithm, the upper and lower bounds of the read range are determined based on preparation experience, with each uncertainty parameter approximated as an interval set. In the end, experiments are carried out to measure the read range of graphene antennas to verify the proposed algorithm. Results show that the proposed algorithm can calculate the read range of graphene antennas effectively. Thus, this research facilitates the practical use of graphene antennas and provides guidance for uncertainty analysis during manufacture.
-
Key words:
- graphene /
- tag antenna /
- read range /
- interval analysis /
- uncertainty
-
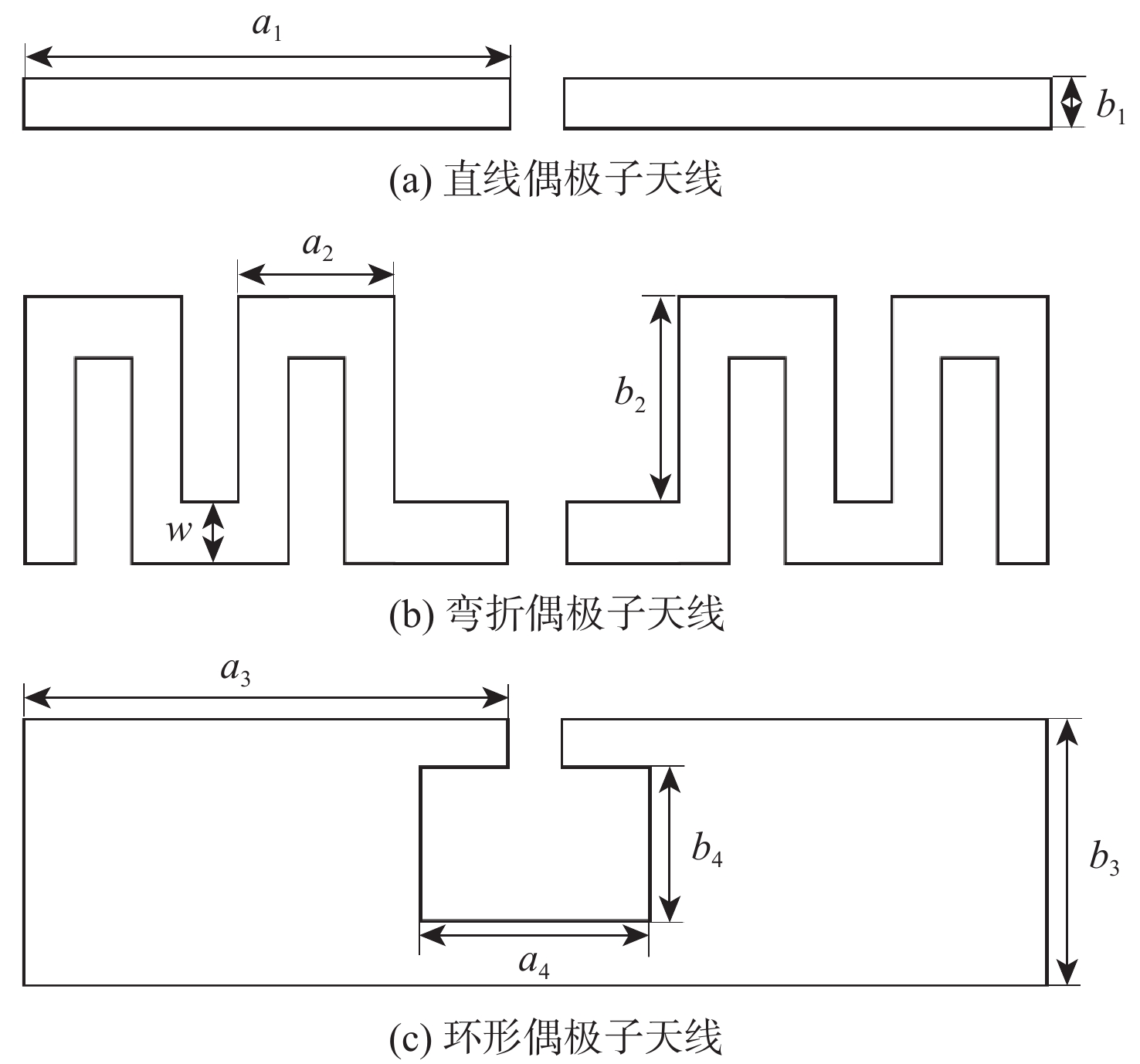
表 1 3种偶极天线的参数
Table 1. Parameters of the three types of dipole antennas
mm 参数 数值 参数 数值 a1 80 b1 10 a2 15 b2 17 a3 50 b3 25 a4 13 b4 14 w 5 t 0.01 表 2 弯折偶极子天线不确定性参数的灵敏度分析
Table 2. Sensitivity analysis of uncertainty parameters for meandered-line dipole antenna
不确定参数的增量式 理论阅读距离增量/m a2+0.8 mm 0.6195 b2+0.8 mm 0.0327 w+0.8 mm 1.314 t+6 μm 2.9177 σ+ 6000 S/m0.8939 表 3 环形偶极子天线不确定性参数的灵敏度分析
Table 3. Sensitivity analysis of uncertainty parameters for loop dipole antenna
不确定参数的增量式 理论阅读距离增量/m a3+0.8 mm 0.1532 b3+0.8 mm 0.1840 a4+0.8 mm 0.0449 b4+0.8 mm 0.0435 t+6 mm 2.7533 σ+ 6000 S/m1.3478 -
[1] LANDT J. The history of RFID[J]. IEEE Potentials, 2005, 24: 8-11. doi: 10.1109/MP.2005.1549751 [2] KIM Y, LEE B, YANG S, et al. Use of copper ink for fabricating conductive electrodes and RFID antenna tags by screen printing[J]. Current Applied Physics, 2012, 12(2): 473-478. doi: 10.1016/j.cap.2011.08.003 [3] SALMERÓN J F, MOLINA-LOPEZ F, BRIAND D, et al. Properties and printability of inkjet and screen-printed silver patterns for RFID antennas[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2014, 43(2): 604-617. doi: 10.1007/s11664-013-2893-4 [4] WOLF F M, PERELAER J, STUMPF S, et al. Rapid low-pressure plasma sintering of inkjet-printed silver nanoparticles for RFID antennas[J]. Journal of Materials Research, 2013, 28(9): 1254-1261. doi: 10.1557/jmr.2013.73 [5] LI Y, LU D, WONG C P. Electrical conductive adhesives with nanotechnologies [M]. Berlin: Springer, 2010. [6] BJÖRNINEN T, MERILAMPI S, UKKONEN L, et al. The effect of fabrication method on passive UHF RFID tag performance[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2009, 2009: 920947. [7] YI M, SHEN Z G. A review on mechanical exfoliation for the scalable production of graphene[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(22): 11700-11715. doi: 10.1039/C5TA00252D [8] KOPYT P, SALSKI B, OLSZEWSKA-PLACHA M, et al. Graphene-based dipole antenna for a UHF RFID tag[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2016, 64(7): 2862-2868. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2016.2565696 [9] HUANG X J, LENG T, ZHANG X, et al. Binder-free highly conductive graphene laminate for low cost printed radio frequency applications[J]. Applied Physics Letters, 2015, 106(20): 203105. doi: 10.1063/1.4919935 [10] LENG T, HUANG X J, CHANG K, et al. Graphene nanoflakes printed flexible meandered-line dipole antenna on paper substrate for low-cost RFID and sensing applications[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2016, 15: 1565-1568. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2016.2518746 [11] AKBARI M, KHAN M W A, HASANI M, et al. Fabrication and characterization of graphene antenna for low-cost and environmentally friendly RFID tags[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2015, 15: 1569-1572. [12] ARAPOV K, JAAKKOLA K, ERMOLOV V, et al. Graphene screen-printed radio-frequency identification devices on flexible substrates[J]. Physica Status Solidi (RRL) - Rapid Research Letters, 2016, 10(11): 812-818. doi: 10.1002/pssr.201600330 [13] MERILAMPI S L, BJÖRNINEN T, VUORIMÄKI A, et al. The effect of conductive ink layer thickness on the functioning of printed UHF RFID antennas[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2010, 98(9): 1610-1619. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2010.2050570 [14] JAULIN L, KIEFFER M, DIDRIT O, et al. Applied interval analysis[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2001. [15] HICKEY T, JU Q, VAN EMDEN M H. Interval arithmetic: from principles to implementation[J]. Journal of the ACM, 2001, 48(5): 1038-1068. doi: 10.1145/502102.502106 [16] ALEFELD G, CLAUDIO D. The basic properties of interval arithmetic, its software realizations and some applications[J]. Computers & Structures, 1998, 67(1-3): 3-8. [17] RAO K V S, NIKITIN P V, LAM S F. Antenna design for UHF RFID tags: a review and a practical application[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2005, 53(12): 3870-3876. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2005.859919 [18] KRAUS J D, MARHEFKA R J. Antennas for all applications [M]. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2002: 9-14. [19] BALANIS C A. Antenna theory: analysis and design[J]. IEEE Antennas & Propagation Society Newsletter, 2003, 24(6): 28-29. [20] 田川, 尹祖伟. 无源超高频标签天线工程设计案例教程[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2019: 20-25.TIAN C, YIN Z W. Engineering design case studies of passive UHF tag antennas[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2019: 20-25(in Chinese). [21] ENDO T, SUNAHARA Y, SATOH S, et al. Resonant frequency and radiation efficiency of meander line antennas[J]. Electronics and Communications in Japan (Part II: Electronics), 2000, 83(1): 52-58. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1520-6432(200001)83:1<52::AID-ECJB7>3.0.CO;2-7 [22] BLAYO A, PINEAUX B. Printing processes and their potential for RFID printing[C]// Proceedings of the Joint Conference on Smart Objects and Ambient Intelligence: Innovative Context-Aware Services: Usages and Technologies. New York: ACM, 2005: 27-30. [23] FADDOUL R, REVERDY-BRUAS N, BLAYO A. Formulation and screen printing of water based conductive flake silver pastes onto green ceramic tapes for electronic applications[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: B, 2012, 177(13): 1053-1066. doi: 10.1016/j.mseb.2012.05.015 [24] HUSSEIN M T. A novel algorithm to compute all vertex matrices of an interval matrix: a computational approach[J]. International Journal of Computing & Information Sciences, 2005, 2(3): 137-142. [25] CAI Z. Analysis of structures with uncertain parameters using interval method[J]. Mechanics Research Communications, 2012, 47(3): 24-31. [26] MOORE R E. Interval analysis [M]. Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey: Prentice-Hall Inc, 1966: 8-13. [27] HANSEN E. Interval arithmetic in matrix computations, part I[J]. Journal of the Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics Series B Numerical Analysis, 1965, 2(2): 308-320. doi: 10.1137/0702025 [28] CSENDES T. Interval analysis and verification of mathematical models [C]// Uncertainties in Environmental Modelling and Consequences for Policy Making. Berlin: Springer, 2009: 79-100. [29] PARUGGIA M. Sensitivity analysis in practice: a guide to assessing scientific models[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2006, 101(473): 398-399. [30] SALTELLI A, TARANTOLA S, CAMPOLONGO F, et al. Sensitivity analysis practices: strategies for model-based inference.[J]. Reliability Engineering & System Safety, 2006, 91: 1109-1125. [31] ROKNE J. Optimal computation of the Bernstein algorithm for the bound of an interval polynomial[J]. Computing, 1982, 28(3): 239-246. doi: 10.1007/BF02241751 [32] BERLEANT D, XIE L Z, ZHANG J Z. Statool: a tool for distribution envelope determination (DEnv), an interval-based algorithm for arithmetic on random variables[J]. Reliable Computing, 2003, 9(2): 91-108. doi: 10.1023/A:1023082100128 -







 下载:
下载: