Rapid planning method for lunar direct ascent and rendezvous trajectory in emergency cases
-
摘要:
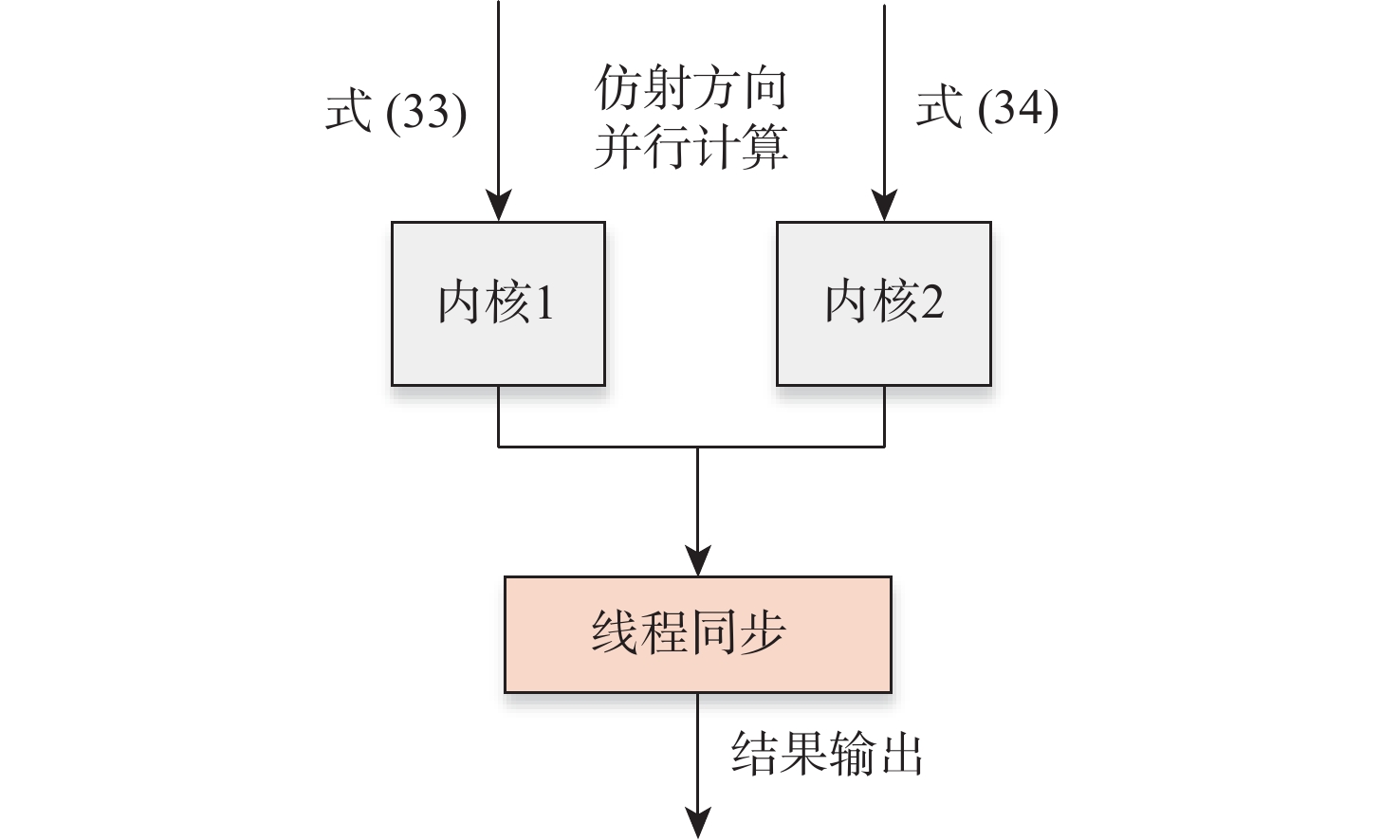
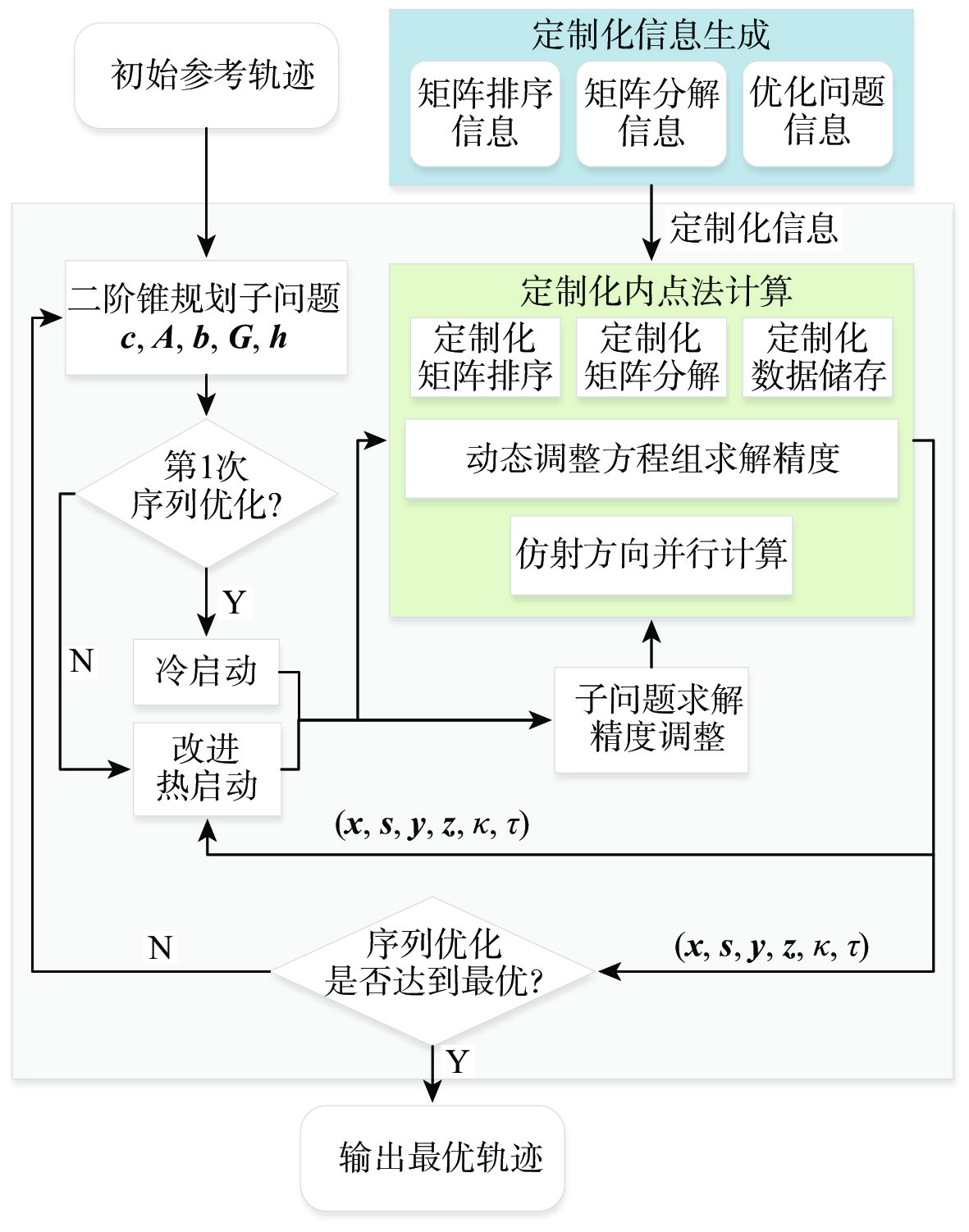
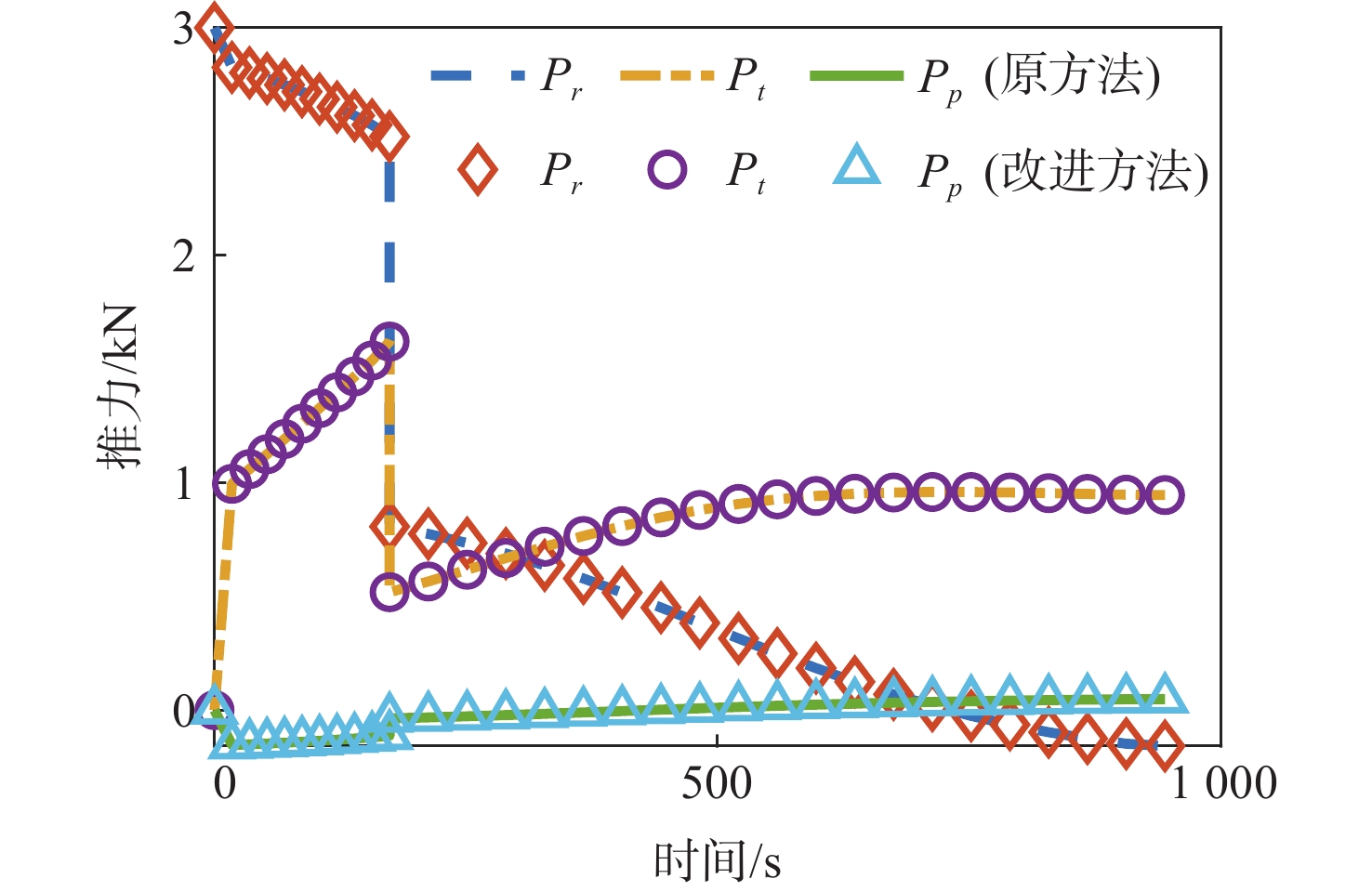
当月面探测器出现某些突发状况而需要返回环月轨道器或地球时,上升器需具备自主规划出合适的应急上升交会轨迹的能力。以上升交会时间最短为目标函数,基于序列二阶锥规划方法,建立直接上升交会轨迹优化模型,并构建求解直接上升交会轨迹优化问题的凸优化算法。为提高计算效率,对内点法进行定制化改进,主要改进有:线性方程组求解过程定制化改进;内点法热启动;二阶锥规划子问题求解精度动态调整。仿真结果表明:所提月面应急上升交会轨迹优化方法可实现上升器的快速上升交会。与采用通用内点法求解器的传统序列二阶锥规划方法相比,在求解精度不变的情况下,所提的序列二阶锥规划问题求解加速方法可达到9.5倍左右的加速比。综合运用所提方法,有望实现月面上升器的自主在线轨迹规划。
Abstract:When a lunar detector encounters unexpected conditions and needs a return to the lunar orbiter or Earth, the lunar ascender should be able to plan an appropriate ascent and rendezvous trajectory independently in emergency cases. In this paper, a direct ascent and rendezvous trajectory optimization model was established based on a successive second-order cone programming method, and minimum ascent and rendezvous time was chosen as the objective function. Additionally, a convex optimization algorithm was proposed to solve the ascent and rendezvous trajectory optimization problem. In order to enhance computational efficiency, the interior point method was customized and modified. The main adaptations included: the process of solving linear equations was customized and modified; a warm starting was used in the interior point method; the second-order cone programming subproblem solving accuracy was adjusted dynamically. Simulation results demonstrate that the proposed lunar ascent and rendezvous trajectory optimization method in emergency cases facilitates the rapid ascent and rendezvous process of the lunar ascender. Moreover, when compared to the traditional successive second-order cone programming method employing a general interior point method solver, the proposed acceleration technique achieves a speedup ratio of approximately 9.5 times while maintaining the same level of solving accuracy. Consequently, the method outlined in this paper holds significant potential for enabling autonomous online trajectory planning of lunar ascenders.
-
表 1 不同排序方法的矩阵非零元素个数对比
Table 1. Number of non-zero elements of matrix for different ordering methods
离散点数(N1+N2) 非零元素个数 近似最小度算法 局部填充最小算法 11+21 8194 7209 21+41 17059 14416 31+61 26977 21709 41+81 34435 28916 表 2 上升器参数
Table 2. Parameters of ascender
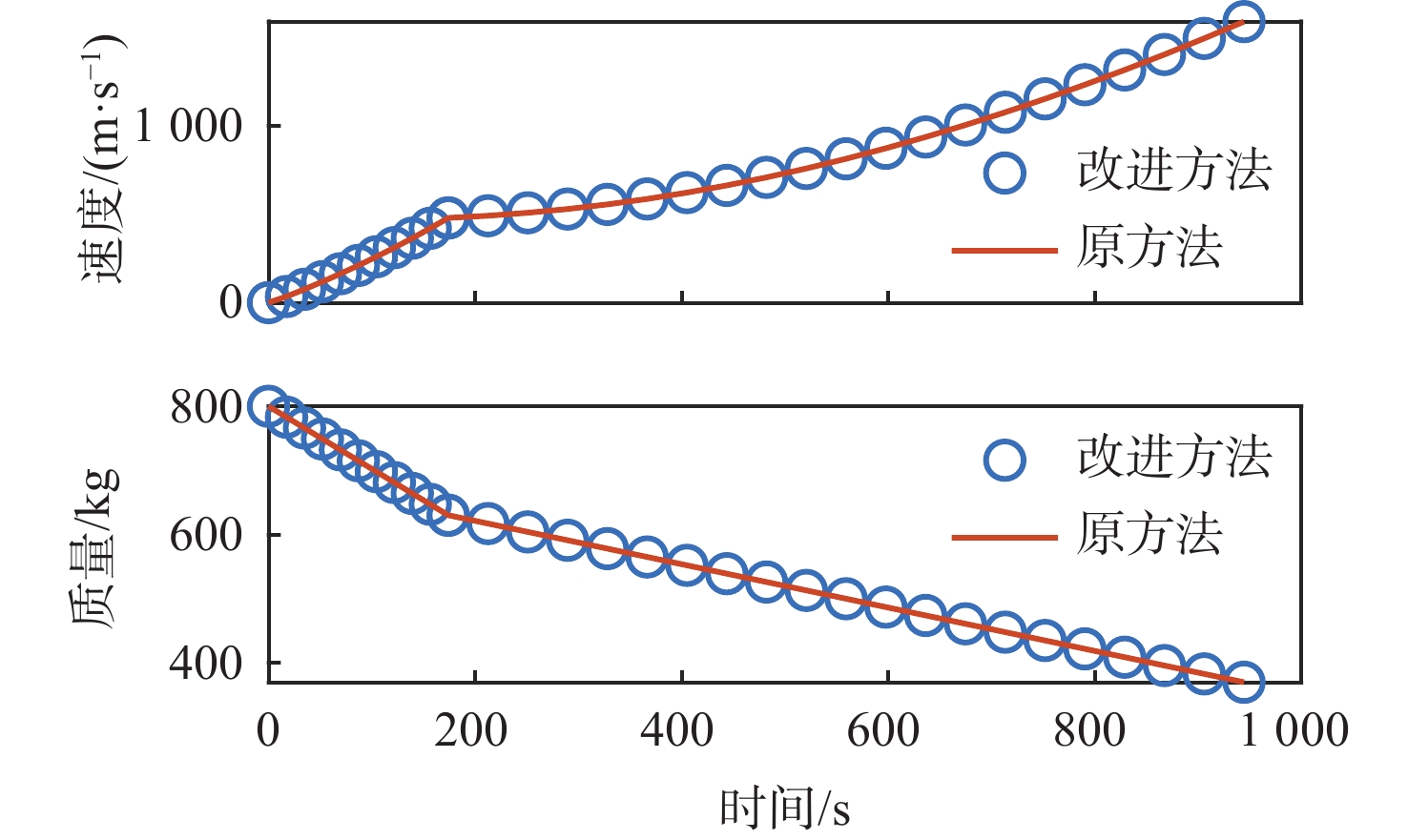
上升器总重mwet/kg 上升器干重mdry/kg 主发动机推力P1/N 主发动机比冲Isp1/s 推力器总推力P2/N 推力器比冲Isp2/s 800 370 3000 313.7 960 290 表 3 不同M值下的计算结果对比
Table 3. Comparison of calculation results under different M values
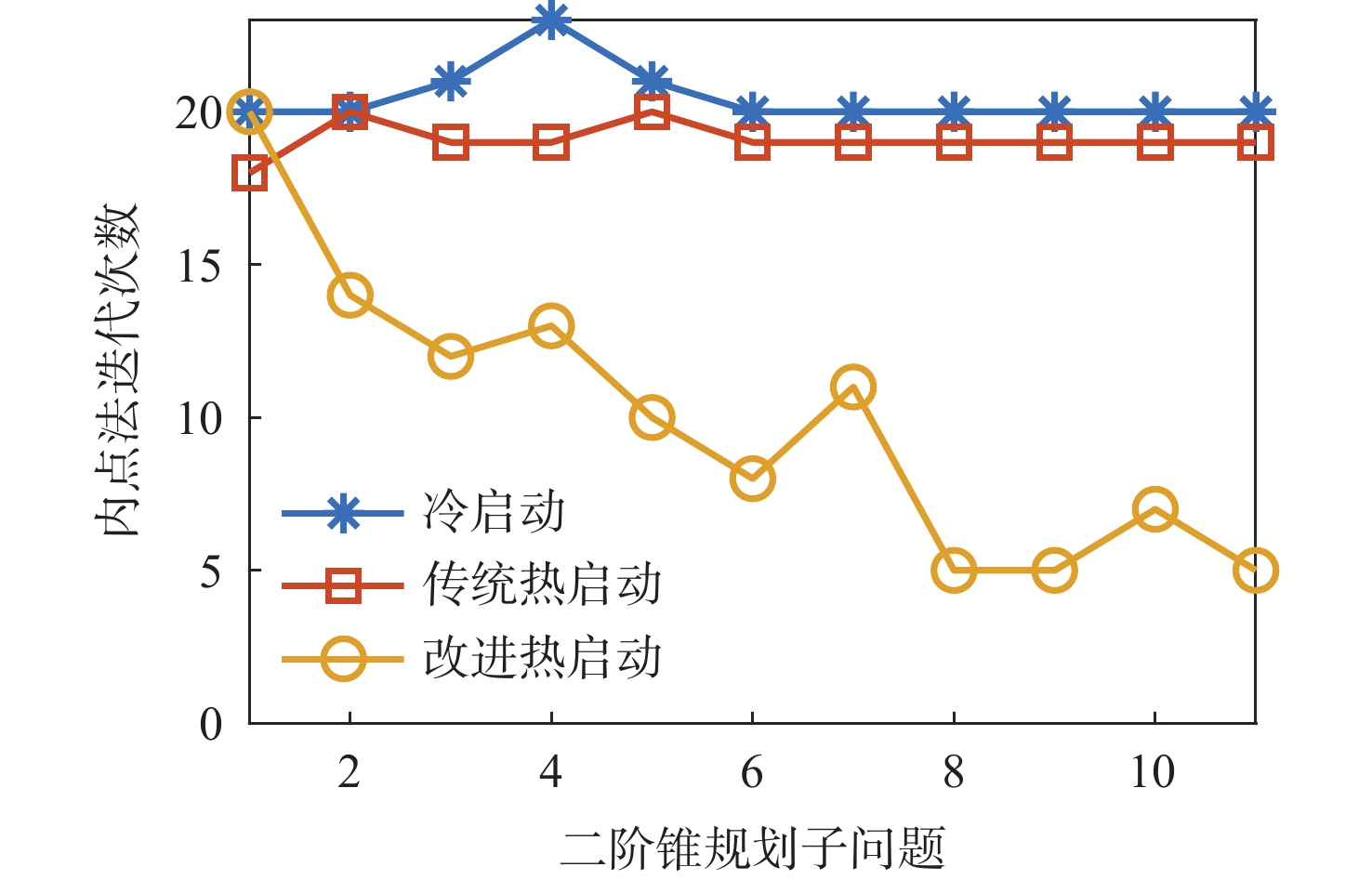
M 序列二阶锥规划
迭代次数内点法
总迭代次数20 15 96 40 15 102 60 15 102 100 10 60 200 10 64 400 10 72 600 12 84 1 000 11 89 表 4 不同离散点数下的参数设置
Table 4. Parameter setting under different discrete points
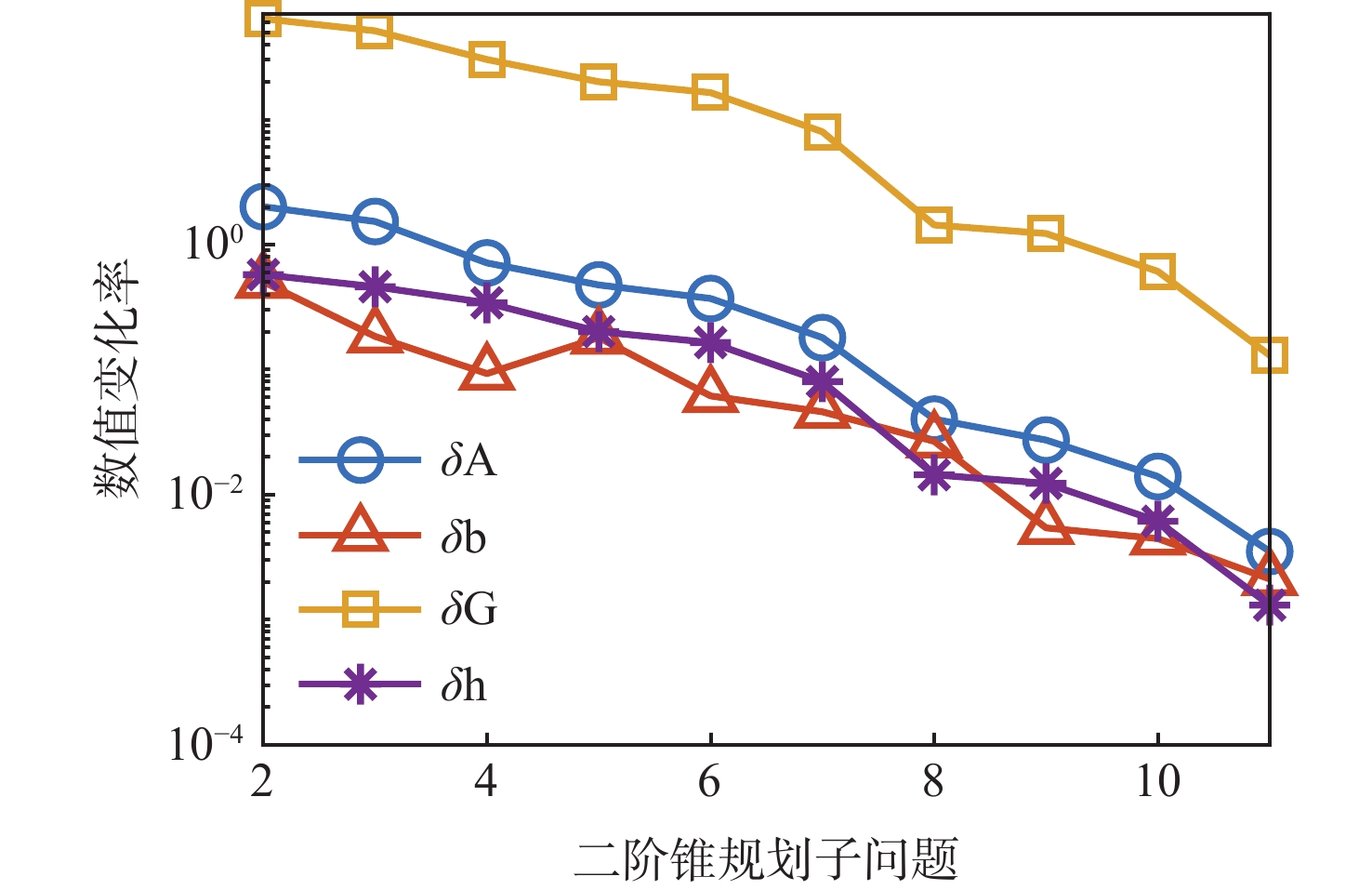
离散点数(N1+N2) 热启动参数ω 精度提高倍数M 11+21 0.992 0 200 21+41 0.999 2 100 31+61 0.999 6 100 41+81 0.999 6 100 表 5 不同方法的求解耗时统计
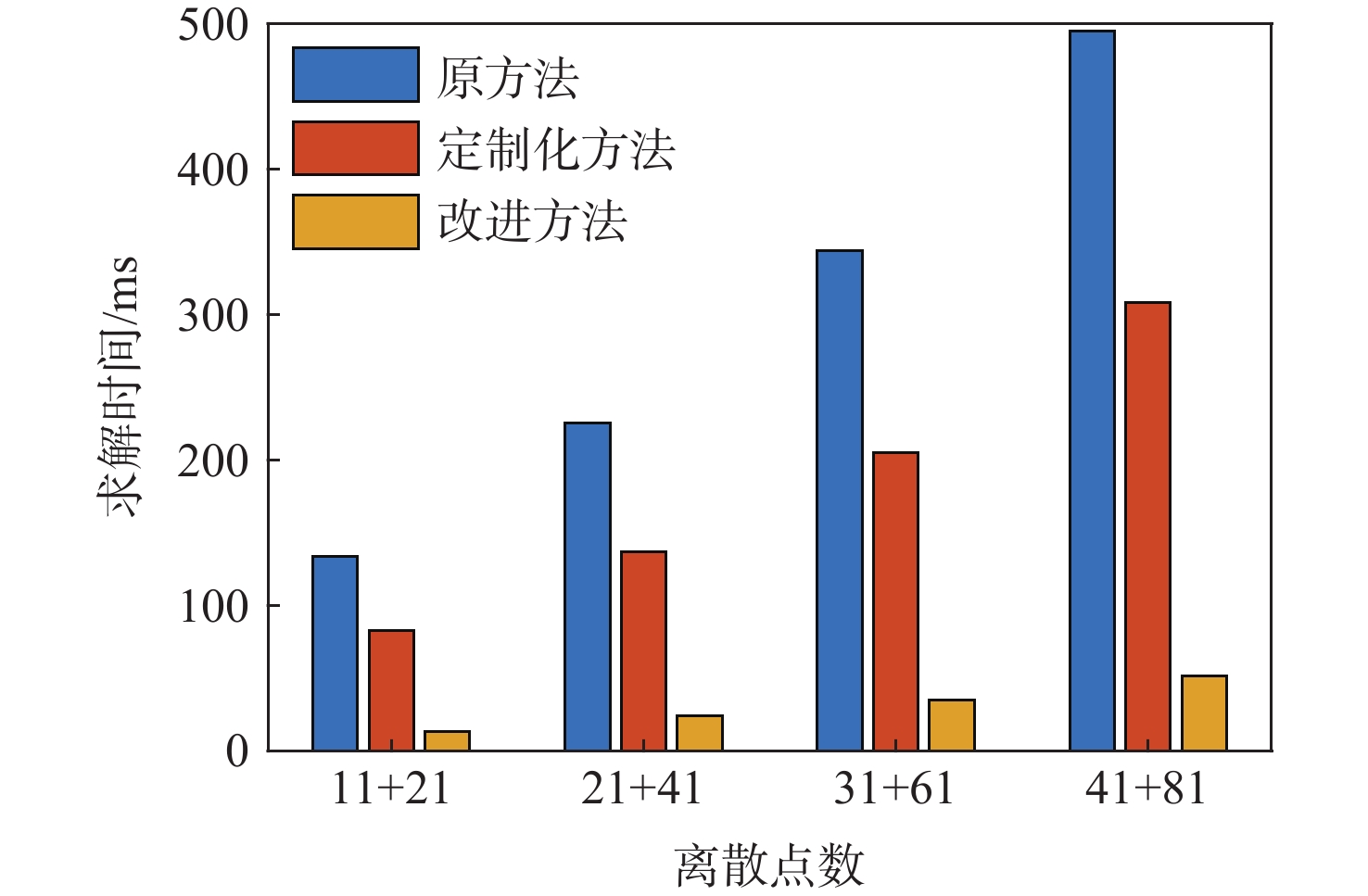
Table 5. Statistics of runtime by different methods
离散点数
(N1+N2)原方法
耗时/ms定制化方法
耗时/ms改进方法
耗时/ms11+21 133.60 82.60 13.15 21+41 225.20 136.70 24.00 31+61 344.10 205.10 35.10 41+81 495.00 308.10 51.60 表 6 不同方法加速比
Table 6. Speedup ratios of different methods
离散点数
(N1+N2)定制化方法
加速比改进方法
加速比11+21 1.62 10.19 21+41 1.65 9.39 31+61 1.68 9.81 41+81 1.61 9.58 表 7 不同方法的求解精度
Table 7. Solving accuracies of different methods
离散点数
(N1+N2)方法 位置误差/km 速度误差/
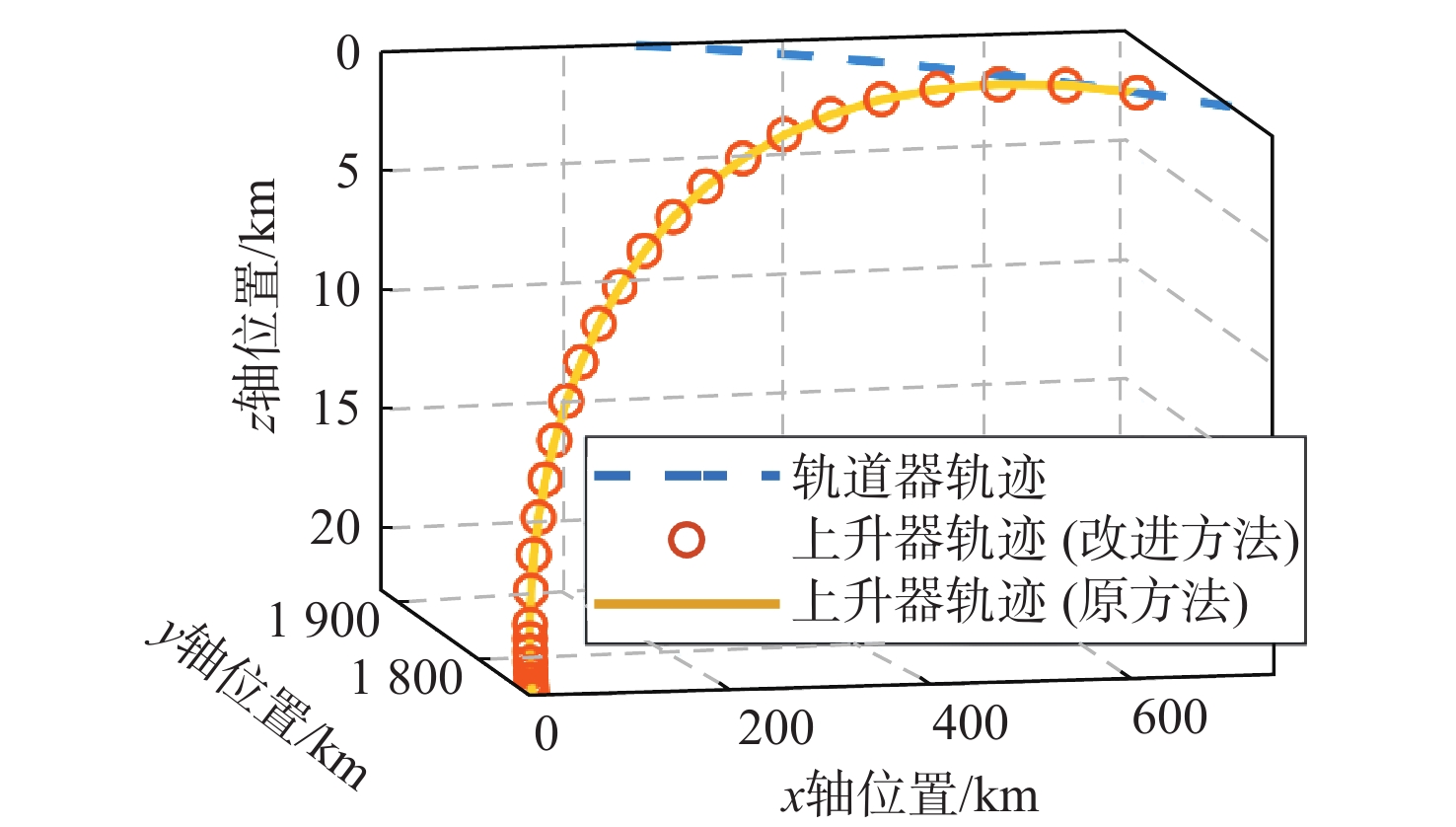
(m·s−1)11+21 原方法 16.280 4 33.529 9 定制化方法[27] 16.280 4 33.529 9 改进方法 16.155 7 33.268 1 21+41 原方法 7.942 4 16.482 4 定制化方法[27] 7.942 4 16.482 4 改进方法 8.118 8 16.841 4 31+61 原方法 5.262 3 10.938 1 定制化方法[27] 5.262 3 10.938 1 改进方法 5.312 4 11.029 8 41+81 原方法 4.080 0 8.472 8 定制化方法[27] 4.080 0 8.472 8 改进方法 3.933 3 8.172 2 -
[1] 欧阳自远. 我国月球探测的总体科学目标与发展战略[J]. 地球科学进展, 2004, 19(3): 351-358. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.03.001OUYANG Z Y. Scientific objectives of Chinese lunar exploration project and development strategy[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2004, 19(3): 351-358(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2004.03.001 [2] 李鑫, 刘莹莹, 周军. 载人登月舱上升入轨段的制导律设计[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2011, 33(11): 2480-2484. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2011.11.26LI X, LIU Y Y, ZHOU J. Design of guidance law for lunar ascent phase of manned lunar module[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2011, 33(11): 2480-2484(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2011.11.26 [3] 马克茂, 陈海朋. 登月舱上升段最优轨迹设计[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2013, 33(2): 54-60. doi: 10.3780/j.issn.1000-758X.2014.02.007MA K M, CHEN H P. Optimal trajectory design for the lunar module in ascent stage[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2013, 33(2): 54-60(in Chinese). doi: 10.3780/j.issn.1000-758X.2014.02.007 [4] HULL D G, HARRIS M W. Optimal solutions for quasiplanar ascent over a spherical moon[J]. Journal of Guidance Control Dynamics, 2012, 35(4): 1218-1224. doi: 10.2514/1.55443 [5] MA L, SHAO Z J, CHEN W F, et al. Three-dimensional trajectory optimization for lunar ascent using Gauss pseudospectral method[C]//Proceedings of the AIAA Guidance, Navigation, and Control Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2016. [6] 张磊. 月面上升的轨迹优化与参数分析[J]. 深空探测学报, 2019, 6(4): 391-397.ZHANG L. Trajectory optimization and parameter analysis for lunar ascent[J]. Journal of Deep Space Exploration, 2019, 6(4): 391-397(in Chinese). [7] 宋征宇, 王聪, 巩庆海. 运载火箭上升段推力下降故障的自主轨迹规划方法[J]. 中国科学(信息科学), 2019, 49(11): 1472-1487. doi: 10.1360/SSI-2019-0132SONG Z Y, WANG C, GONG Q H. Autonomous trajectory planning for launch vehicle under thrust drop failure[J]. Scientia Sinica (Informationis), 2019, 49(11): 1472-1487(in Chinese). doi: 10.1360/SSI-2019-0132 [8] HAO Z M, ZHANG R. Onboard real-time generation of launch vehicle abort orbits[J]. Journal of Guidance Control Dynamics, 2021, 44(8): 1541-1549. doi: 10.2514/1.G004812 [9] BENEDIKTER B, ZAVOLI A, COLASURDO G, et al. Convex approach to three-dimensional launch vehicle ascent trajectory optimization[J]. Journal of Guidance Control Dynamics, 2021, 44(6): 1116-1131. doi: 10.2514/1.G005376 [10] 王华, 唐国金. 用遗传算法求解双冲量最优交会问题[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2003, 23(1): 26-30. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-758X.2003.01.005WANG H, TANG G J. Solving optimal rendezvous using two impulses based on genetic algorithms[J]. Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2003, 23(1): 26-30(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-758X.2003.01.005 [11] 冉茂鹏, 王青. 一种基于EPSO的航天器交会轨迹优化方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2013, 34(9): 1195-1201.RAN M P, WANG Q. Spacecraft rendezvous trajectory optimization method based on EPSO[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2013, 34(9): 1195-1201(in Chinese). [12] 李君龙, 李松洲, 周荻. 一种多约束条件下的三脉冲交会优化设计方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44(8): 2612-2620. doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.08.26LI J L, LI S Z, ZHOU D. Optimization method for three-impulse rendezvous under multi-constraints[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(8): 2612-2620(in Chinese). doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.08.26 [13] 任远, 崔平远, 栾恩杰. 最优两脉冲行星际轨道转移优化算法[J]. 航空学报, 2007, 28(6): 1307-1311. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.2007.06.005REN Y, CUI P Y, LUAN E J. Interplanetary optimum two-impulse transfer trajectories[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2007, 28(6): 1307-1311(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6893.2007.06.005 [14] YUE X C, YANG Y, GENG Z Y. Indirect optimization for finite-thrust time-optimal orbital maneuver[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2010, 33(2): 628-634. doi: 10.2514/1.44885 [15] 武冠群. 在轨服务航天器交会轨迹优化与近距离安全接近控制研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019.WU G Q. Research on rendezvous trajectory optimization and close-range safe approach control of on-orbit service spacecraft[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [16] 管凯颜. 不同质量航天器在连续推力下快速协同交会探讨[D]. 济南: 山东大学, 2021.GUAN K Y. Discussion on rapid cooperative rendezvous of spacecraft with different masses under continuous thrust[D]. Jinan: Shandong University, 2021(in Chinese). [17] 李萌, 龚胜平, 彭坤, 等. 直接优化算法在快速交会组合变轨策略中的应用[J]. 载人航天, 2017, 23(2): 156-162. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5825.2017.02.003LI M, GONG S P, PENG K, et al. Application of direct optimization algorithmin synthetic orbit maneuver strategy of short rendezvous[J]. Manned Spaceflight, 2017, 23(2): 156-162(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-5825.2017.02.003 [18] 周新耀, 陶勇鹏, 曾亮, 等. 空间轨道交会非线性优化方法研究[J]. 上海航天, 2018, 35(1): 54-58.ZHOU X Y, TAO Y P, ZENG L, et al. Study on nonlinear optimization of space orbit interception[J]. Aerospace Shanghai (Chinese & English), 2018, 35(1): 54-58(in Chinese). [19] ORTOLANO N, GELLER D K, AVERY A. Autonomous optimal trajectory planning for orbital rendezvous, satellite inspection, and final approach based on convex optimization[J]. The Journal of the Astronautical Sciences, 2021, 68(2): 444-479. doi: 10.1007/s40295-021-00260-5 [20] 靳锴, 罗建军, 郑茂章, 等. 考虑导航误差和摄动影响的椭圆轨道最优交会制导[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2018, 35(10): 1484-1493. doi: 10.7641/CTA.2018.70887JIN K, LUO J J, ZHENG M Z, et al. Guidance design with navigation errors for relative motion in noncircular perturbed orbits[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2018, 35(10): 1484-1493(in Chinese). doi: 10.7641/CTA.2018.70887 [21] WANG Z B, GRANT M J. Optimization of minimum-time low-thrust transfers using convex programming[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2018, 55(3): 586-598. doi: 10.2514/1.A33995 [22] WANG Z B, GRANT M J. Minimum-fuel low-thrust transfers for spacecraft: a convex approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2018, 54(5): 2274-2290. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2018.2812558 [23] 王访寒, 周如好, 余薛浩, 等. 基于序列凸优化的上面级远程交会轨迹优化[J]. 上海航天(中英文), 2022, 39(2): 45-52.WANG F H, ZHOU R H, YU X H, et al. Trajectory optimization of remote rendezvous for upper stage based on sequential convex optimization[J]. Aerospace Shanghai(Chinese& English), 2022, 39(2): 45-52(in Chinese). [24] 彭祺擘. 考虑应急返回能力的载人登月轨道优化设计及特性分析[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2012.PENG Q B. Optimal design and characteristic analysis of manned moon orbit considering emergency return capability[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2012(in Chinese). [25] STURM J F. Using SeDuMi 1.02, a Matlab toolbox for optimization over symmetric cones[J]. Optimization Methods and Software, 1999, 11(1-4): 625-653. doi: 10.1080/10556789908805766 [26] DOMAHIDI A, CHU E, BOYD S. ECOS: an SOCP solver for embedded systems[C]//Proceedings of the 2013 European Control Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 3071-3076. [27] DUERI D, ACIKMESE B, SCHARF D P, et al. Customized real-time interior-point methods for onboard powered-descent guidance[J]. Journal of Guidance Control Dynamics, 2017, 40(2): 197-212. doi: 10.2514/1.G001480 [28] MATTINGLEY J, BOYD S. CVXGEN: a code generator for embedded convex optimization[J]. Optimization and Engineering, 2012, 13(1): 1-27. doi: 10.1007/s11081-011-9176-9 [29] JUNG J H, O’LEARY D P. Implementing an interior point method for linear programs on a CPU-GPU system[J]. Electronic Transactions on Numerical Analysis, 2008, 28: 174-189. [30] WANG J W, ZHANG R, LI H F. Onboard optimization of multi-arc trajectories with constraints on duration of arcs[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2022, 192: 434-442. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2021.12.023 [31] BOYD S. Distributed optimization and statistical learning via the alternating direction method of multipliers[J]. Foundations and Trends® in Machine Learning, 2010, 3(1): 1-122. [32] O’DONOGHUE B, CHU E, PARIKH N, et al. Conic optimization via operator splitting and homogeneous self-dual embedding[J]. Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications, 2016, 169(3): 1042-1068. doi: 10.1007/s10957-016-0892-3 [33] ELANGO P, KAMATH A, YU Y, et al. A customized first-order solver for real-time powered-descent guidance[C]//Proceedings of the AIAA Scitech Forum. Reston: AIAA, 2022: 0951. [34] SKAJAA A, ANDERSEN E D, YE Y Y. Warmstarting the homogeneous and self-dual interior point method for linear and conic quadratic problems[J]. Mathematical Programming Computation, 2013, 5(1): 1-25. doi: 10.1007/s12532-012-0046-z [35] CHEN Y S, YANG G W, WANG L, et al. Iteration complexity of an infeasible interior point methods for seconder-order cone programming and its warmstarting[EB/OL]. (2023-01-24)[2025-02-04]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2205.03570. [36] ZHANG Z Y, ZHAO Q C, DAI F A. A warm-start strategy in interior point methods for shrinking horizon model predictive control with variable discretization step[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2023, 68(6): 3830-3837. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2022.3201026 [37] CHEN Y S, YANG G W, WANG L, et al. A fast algorithm for onboard atmospheric powered descent guidance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59(5): 6112-6123. [38] 郝泽明, 张冉, 王嘉炜, 等. 大气层内固体火箭实时轨迹优化方法[J]. 宇航学报, 2021, 42(11): 1416-1426. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2021.11.008HAO Z M, ZHANG R, WANG J W, et al. Real-time atmospheric trajectory optimization for solid rockets[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2021, 42(11): 1416-1426(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2021.11.008 [39] VANDENBERGHE L. The CVXOPT linear and quadratic cone program solvers[EB/OL]. (2010-03-20)[2023-03-28]. http://cvxopt.org/documentation/coneprog.pdf. [40] DOMAHIDI A. Methods and tools for embedded optimization and control[D]. Zurich: ETH Zurich, 2013. [41] DAVIS T A, GILBERT J R, LARIMORE S I, et al. A column approximate minimum degree ordering algorithm[J]. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 2004, 30(3): 353-376. doi: 10.1145/1024074.1024079 [42] GEORGE A, LIU J W H. The evolution of the minimum degree ordering algorithm[J]. SIAM Review, 1989, 31(1): 1-19. doi: 10.1137/1031001 [43] DUFF I S, ERISMAN A M, REID J K. Direct methods for sparse matrices[M]. New York: Oxford University Press, 2017. [44] GILL P E, SAUNDERS M A, SHINNERL J R. On the stability of cholesky factorization for symmetric quasidefinite systems[J]. SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications, 1996, 17(1): 35-46. doi: 10.1137/S0895479893252623 [45] DAVIS T A. Algorithm 849[J]. ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 2005, 31(4): 587-591. doi: 10.1145/1114268.1114277 [46] GAO Y, SHAO Z J, SONG Z Y. Enhanced successive convexification based on error-feedback index and line search filter[J]. Journal of Guidance Control Dynamics, 2022, 45(12): 2243-2257. doi: 10.2514/1.G005938 -








 下载:
下载: