-
摘要:
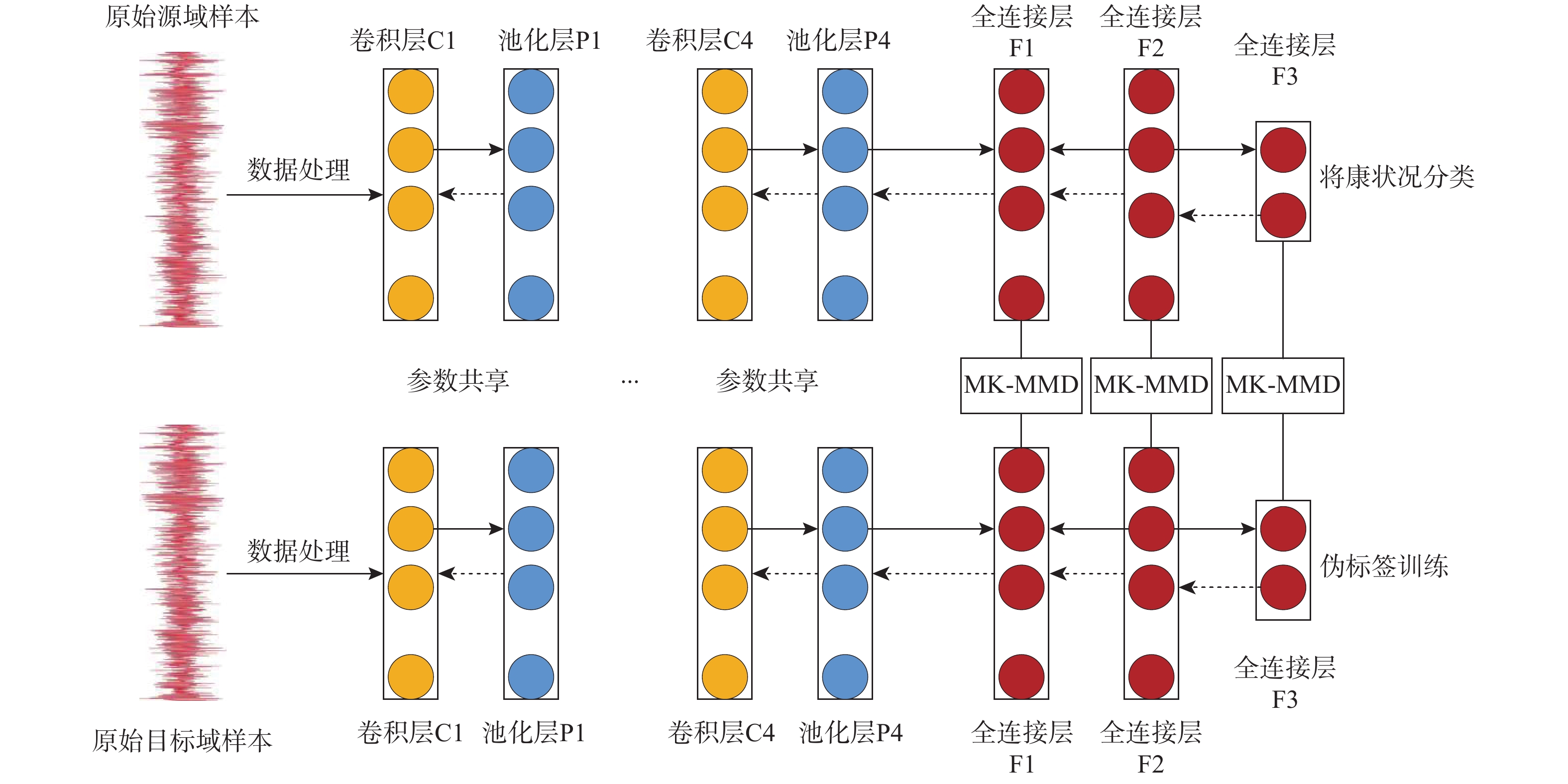
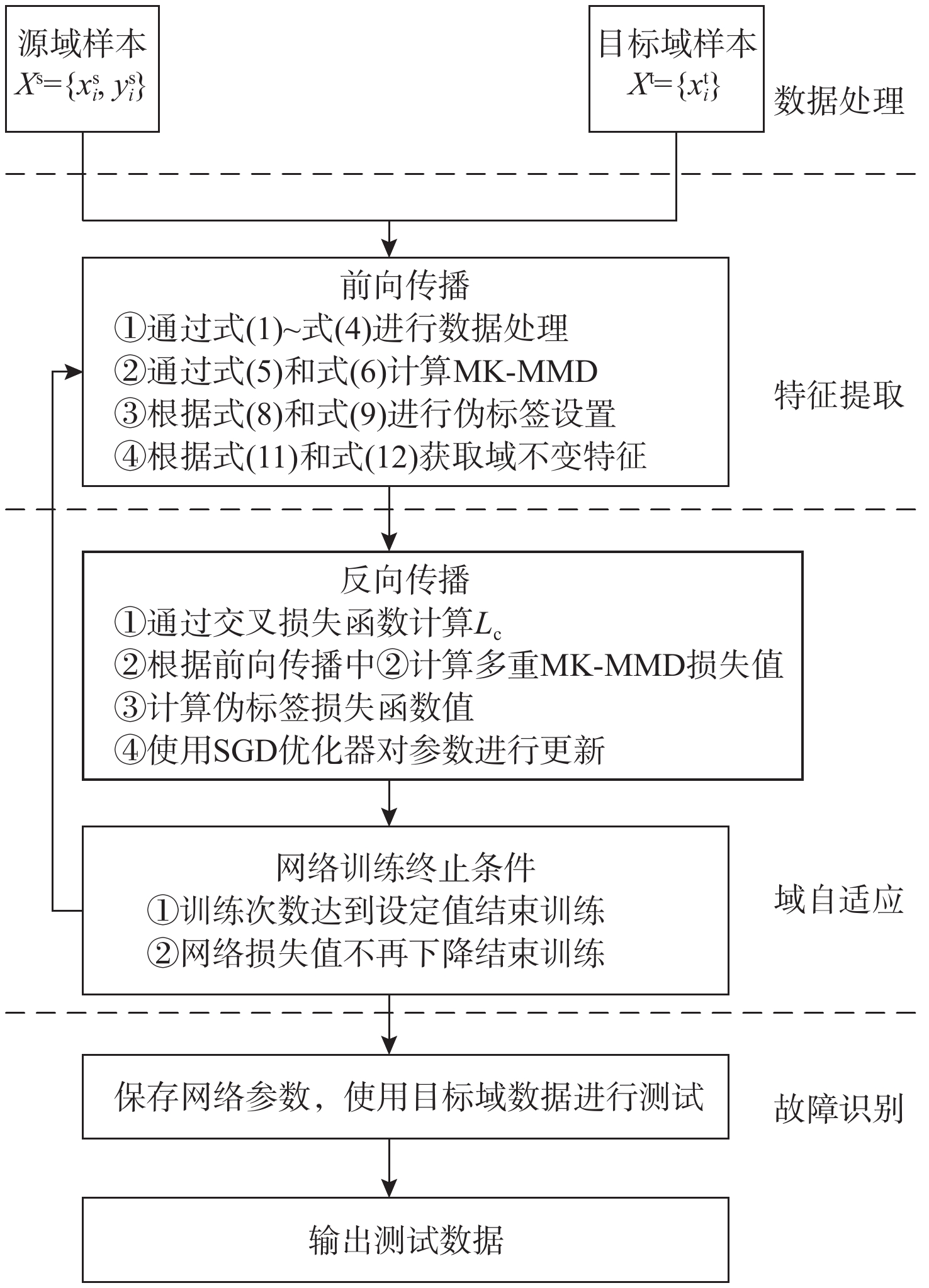
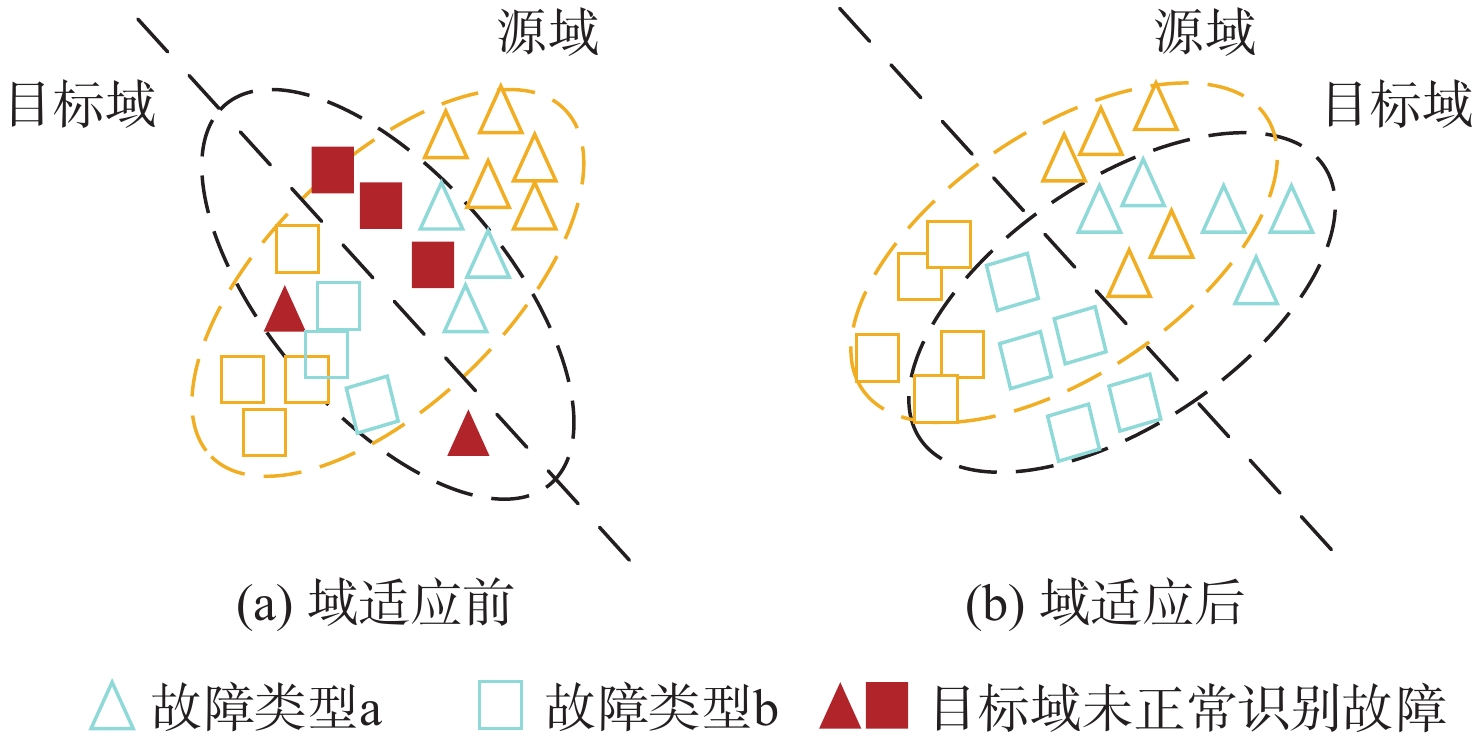
在工业生产中,由于源域数据和目标域数据分布有差异且有标签的故障数据量较少,以至于现有的域适应轴承故障诊断方法大多精度不高。基于此,提出多层域适应神经网络(MDANN)故障诊断方法,用于无标签数据的滚动轴承故障诊断。使用小波包分解与重构(WPT)对原始振动信号进行处理,以降低信号冗余并避免关键信号特征遗失;利用多核最大均值差异(MK-MMD)算法对输入特征值进行差异计算,并通过反向传播更新多层域适应神经网络的参数,使其能够提取域不变特征;为保证无标签目标域数据可以正常参与网络训练,使用最大概率标签作为真实标签的伪标签策略,解决目标域无标签数据无法训练问题,增强模型可靠诊断知识的获取。采用2个公开数据集CWRU和PU进行验证。实验结果表明:所提方法与常见的域适应方法对比具有更高的诊断精度,说明该方法能够有效地学习可迁移特征,拟合2个数据集之间的数据分布差异。
Abstract:in industrial production, due to the difference in the distribution of source domain data and target domain data and the small amount of labeled fault data, the accuracy of domain adaptation-based bearing fault diagnosis algorithms proposed in the past is generally not high. In view of this, the multi-domain adaptation neural network (MDANN) fault diagnosis method was proposed in this paper, which was used for rolling bearing fault diagnosis without labeled data. Firstly, the original vibration signal was processed by using wavelet packet transformation (WPT) to reduce signal redundancy and avoid the loss of key signal features. Secondly, the multi-kernel maximum mean discrepancy (MK-MMD) algorithm was used to calculate the difference of input eigenvalues, and the network parameters of MDANN were updated by backpropagation so that the network can extract domain invariant features. Finally, in order to ensure that unlabeled target domain data can participate in network training normally, the maximum probability label was used as a pseudo-label strategy of the real label to solve the problem that unlabeled target domain data cannot be trained and enhance the acquisition of reliable diagnosis knowledge of the model. Two publicly available datasets, CWRU and PU, were used for validation. The experimental results show that the proposed method has higher diagnosis accuracy compared with common domain adaptation methods, which further shows that the method can effectively learn the transferable features and fit the discrepancy in data distribution between the two datasets.
-
Key words:
- rolling bearing /
- fault diagnosis /
- transfer learning /
- multi-domain adaptation /
- pseudo-label strategy
-
表 1 网络参数详解
Table 1. Detailed explanation of network parameters
网络层 网络参数 激活函数 输出尺寸 输入层 2048 ×1卷积层C1 3×1×20 非线性映射Relu 2046 ×20卷积层C2 3×20×20 非线性映射Relu 1020 ×20卷积层C3 3×20×20 非线性映射Relu 508×20 卷积层C4 3×20×20 非线性映射Relu 252×20 池化层P1~P6 2×1 全连接层F1 5040 ×1全连接层F2 5040 ×256256×1 全连接层F3 256×5 分类函数SoftMax 5×1 表 2 数据集的基本情况
Table 2. Basic information of datasets
数据集 转速/(r·min−1) 负载/N 训练集/测试集
(故障样本数)数据集A(CWRU) 1700 1470 1500 /500数据集B (PU) 1500 1000 1500 /500表 3 不同数据处理方法的诊断精度
Table 3. Diagnosis accuracy of different data processing methods
数据处理方法 输入特征 迁移任务 诊断精度/% 不做处理 2048 ×1A->B 62.23 FFT 2048 ×1A->B 71.48 CWT 2014 ×1A->B 73.65 WPT 2048 ×1A->B 82.14 不做处理 2048 ×1B->A 54.21 FFT 2048 ×1B->A 75.47 CWT 2014 ×1B->A 71.56 WPT 2048 ×1B->A 80.37 表 4 多层域适应对诊断精度的影响
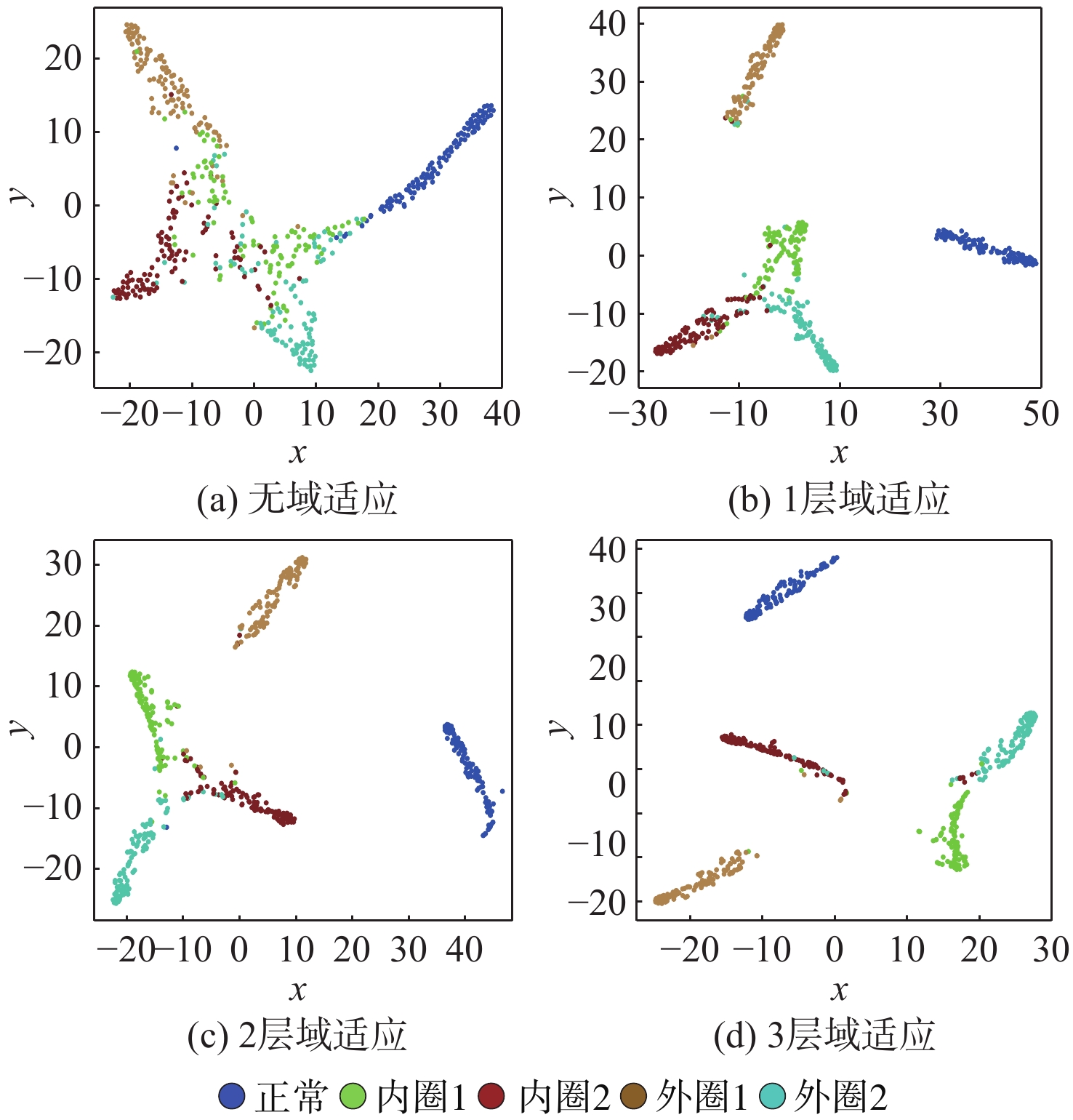
Table 4. Effect of multi-domain adaptation on diagnosis accuracy
处理策略 训练时间/s 训练任务 诊断精度/% 不添加MK-MMD 93 A->B 37.21 F1处添加MK-MMD 108 A->B 71.32 F1,F2处添加MK-MMD 124 A->B 77.56 F1,F2,F3处添加MK-MMD 147 A->B 82.94 不添加MK-MMD 89 B->A 41.83 F1处添加MK-MMD 97 B->A 75.89 F1,F2处添加MK-MMD 123 B->A 79.87 F1,F2,F3处添加MK-MMD 148 B->A 83.21 表 5 不同模型的精度
Table 5. Accuracy of different models
网络模型 是否域适应 迁移任务 输入特征 诊断精度/% TCA 否 A->B 2048 ×147.12 DDC 是 A->B 224×224×3 74.32 DAN 是 A->B 2048 ×176.86 DANN 是 A->B 224×224×3 77.58 MANN 否 A->B 2048 ×132.15 MDANN 是 A->B 2048 ×184.17 TCA 否 B->A 2048 ×128.21 DDC 是 B->A 224×224×3 65.36 DAN 是 B->A 2048 ×174.21 DANN 是 B->A 224×224×3 75.36 MANN 否 B->A 2048 ×136.58 MDANN 是 B->A 2048 ×182.15 -
[1] YU X, LIANG Z T, WANG Y J, et al. A wavelet packet transform-based deep feature transfer learning method for bearing fault diagnosis under different working conditions[J]. Measurement, 2022, 201: 111597. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2022.111597 [2] HU Q, SI X S, QIN A S, et al. Balanced adaptation regularization based transfer learning for unsupervised cross-domain fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(12): 12139-12151. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3174396 [3] 赵小强, 张青青, 陈鹏, 等. 基于PSO-BFA和改进Alexnet的滚动轴承故障诊断方法[J]. 振动与冲击, 2020, 39(7): 21-28.ZHAO X Q, ZHANG Q Q, CHEN P, et al. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on improved Alexnet and PSO-BFA[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2020, 39(7): 21-28(in Chinese). [4] XU W, WAN Y, ZUO T Y, et al. Transfer learning based data feature transfer for fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 76120-76129. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2989510 [5] MA P, ZHANG H L, FAN W H, et al. A novel bearing fault diagnosis method based on 2D image representation and transfer learning-convolutional neural network[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2019, 30(5): 055402. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/ab0793 [6] WU Z H, JIANG H K, ZHAO K, et al. An adaptive deep transfer learning method for bearing fault diagnosis[J]. Measurement, 2020, 151: 107227. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2019.107227 [7] 刘飞, 陈仁文, 邢凯玲, 等. 基于迁移学习与深度残差网络的滚动轴承快速故障诊断算法[J]. 振动与冲击, 2022, 41(3): 154-164.LIU F, CHEN R W, XING K L, et al. Fast fault diagnosis algorithm for rolling bearing based on transfer learning and deep residual network[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2022, 41(3): 154-164(in Chinese). [8] ZOU Y S, LIU Y Z, DENG J L, et al. A novel transfer learning method for bearing fault diagnosis under different working conditions[J]. Measurement, 2021, 171: 108767. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108767 [9] ZHAO M H, ZHONG S S, FU X Y, et al. Deep residual shrinkage networks for fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(7): 4681-4690. [10] SHAO J J, HUANG Z W, ZHU J M. Transfer learning method based on adversarial domain adaption for bearing fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 119421-119430. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3005243 [11] LI B, TANG B P, DENG L, et al. Joint attention feature transfer network for gearbox fault diagnosis with imbalanced data[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2022, 176: 109146. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2022.109146 [12] 张根保, 李浩, 冉琰, 等. 一种用于轴承故障诊断的迁移学习模型[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2020, 50(5): 1617-1626.ZHANG G B, LI H, RAN Y, et al. A transfer learning model for bearing fault diagnosis[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2020, 50(5): 1617-1626(in Chinese). [13] LIU M K, TRAN M Q, WENG P Y. Fusion of vibration and current signatures for the fault diagnosis of induction machines[J]. Shock and Vibration, 2019, 2019(1): 7176482. [14] JIE H J, WANDA P. RunPool: a dynamic pooling layer for convolution neural network[J]. International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, 2020, 13(1): 66-76. doi: 10.2991/ijcis.d.200120.002 [15] YANG Z N, WANG X Y, YANG R. Transfer learning based rolling bearing fault diagnosis[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 10th Data Driven Control and Learning Systems Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 354-359. [16] 徐冰冰, 岑科廷, 黄俊杰, 等. 图卷积神经网络综述[J]. 计算机学报, 2020, 43(5): 755-780. doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2020.00755XU B B, CEN K T, HUANG J J, et al. A survey on graph convolutional neural network[J]. Chinese Journal of Computers, 2020, 43(5): 755-780(in Chinese). doi: 10.11897/SP.J.1016.2020.00755 [17] SHABBEER BASHA S H, DUBEY S R, PULABAIGARI V, et al. Impact of fully connected layers on performance of convolutional neural networks for image classification[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 378: 112-119. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.10.008 [18] 史加荣, 王丹, 尚凡华, 等. 随机梯度下降算法研究进展[J]. 自动化学报, 2021, 47(9): 2103-2119.SHI J R, WANG D, SHANG F H, et al. Research advances on stochastic gradient descent algorithms[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47(9): 2103-2119(in Chinese). [19] CAO X Y, LAI L F. Distributed gradient descent algorithm robust to an arbitrary number of Byzantine attackers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(22): 5850-5864. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2946020 [20] ACHARYA U R, YANTI R, ZHENG J W, et al. Automated diagnosis of epilepsy using CWT, HOS and texture parameters[J]. International Journal of Neural Systems, 2013, 23(3): 1350009. doi: 10.1142/S0129065713500093 [21] SHEN J X, SONG D, MA T C, et al. Blade crack detection based on domain adaptation and autoencoder of multidimensional vibro-acoustic feature fusion[J]. Structural Health Monitoring, 2023, 22(5): 3498-3513. doi: 10.1177/14759217221139134 [22] ZHANG W P, ZHANG P, HE X H, et al. Convolutional neural network based two-layer transfer learning for bearing fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10: 109779-109794. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3213657 [23] LONG M S, ZHU H, WANG J M, et al. Deep transfer learning with joint adaptation networks[C]//Proceedings of the 34th International Conference on Machine Learning. New York: ACM, 2017: 2208-2217. [24] WANG Q, MICHAU G, FINK O. Domain adaptive transfer learning for fault diagnosis[C]//Proceedings of the Prognostics and System Health Management Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 279-285. -







 下载:
下载: