Physiological signal denoising method based on multi-spectrum adaptive wavelet and blind source separation
-
摘要:
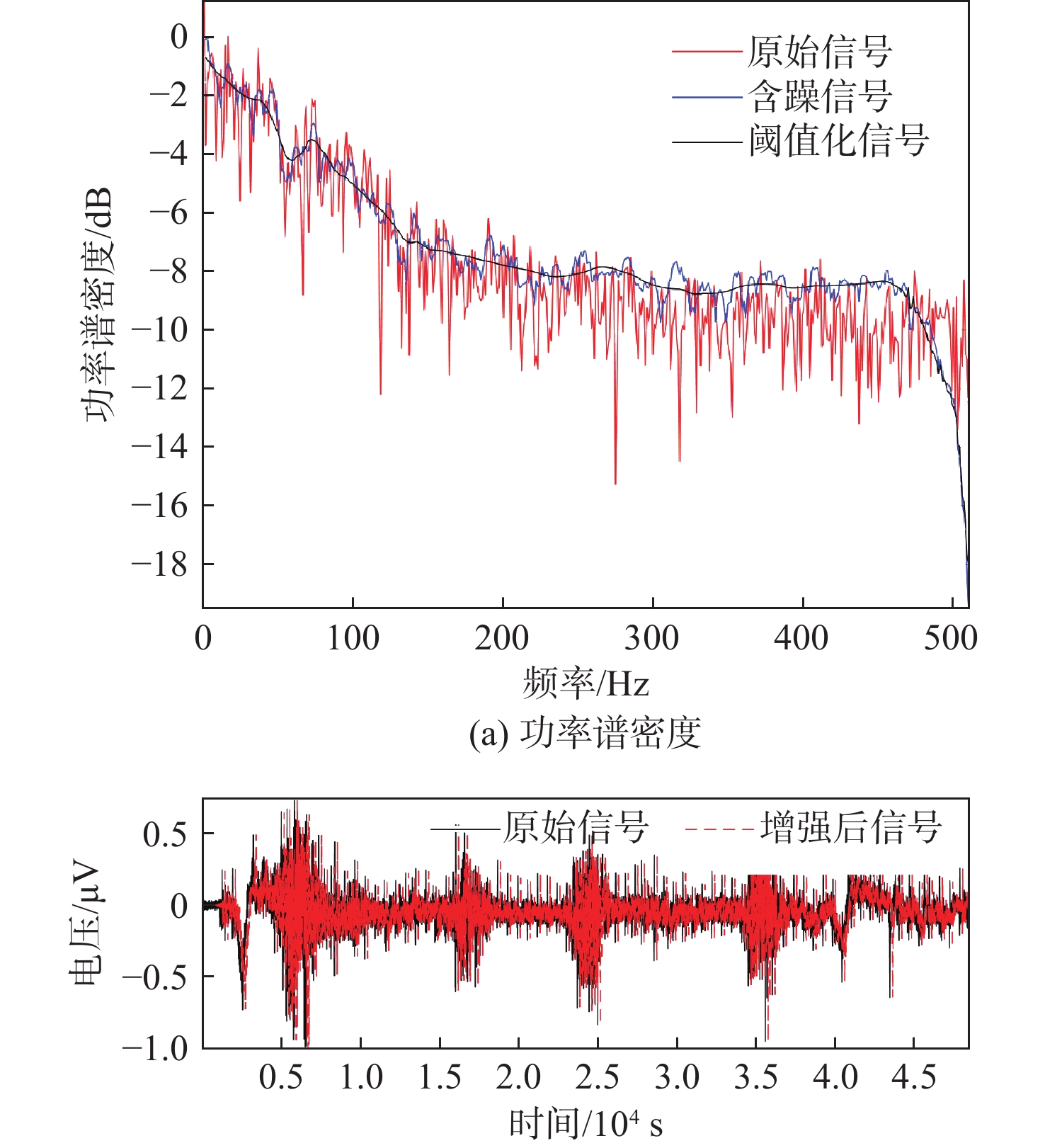
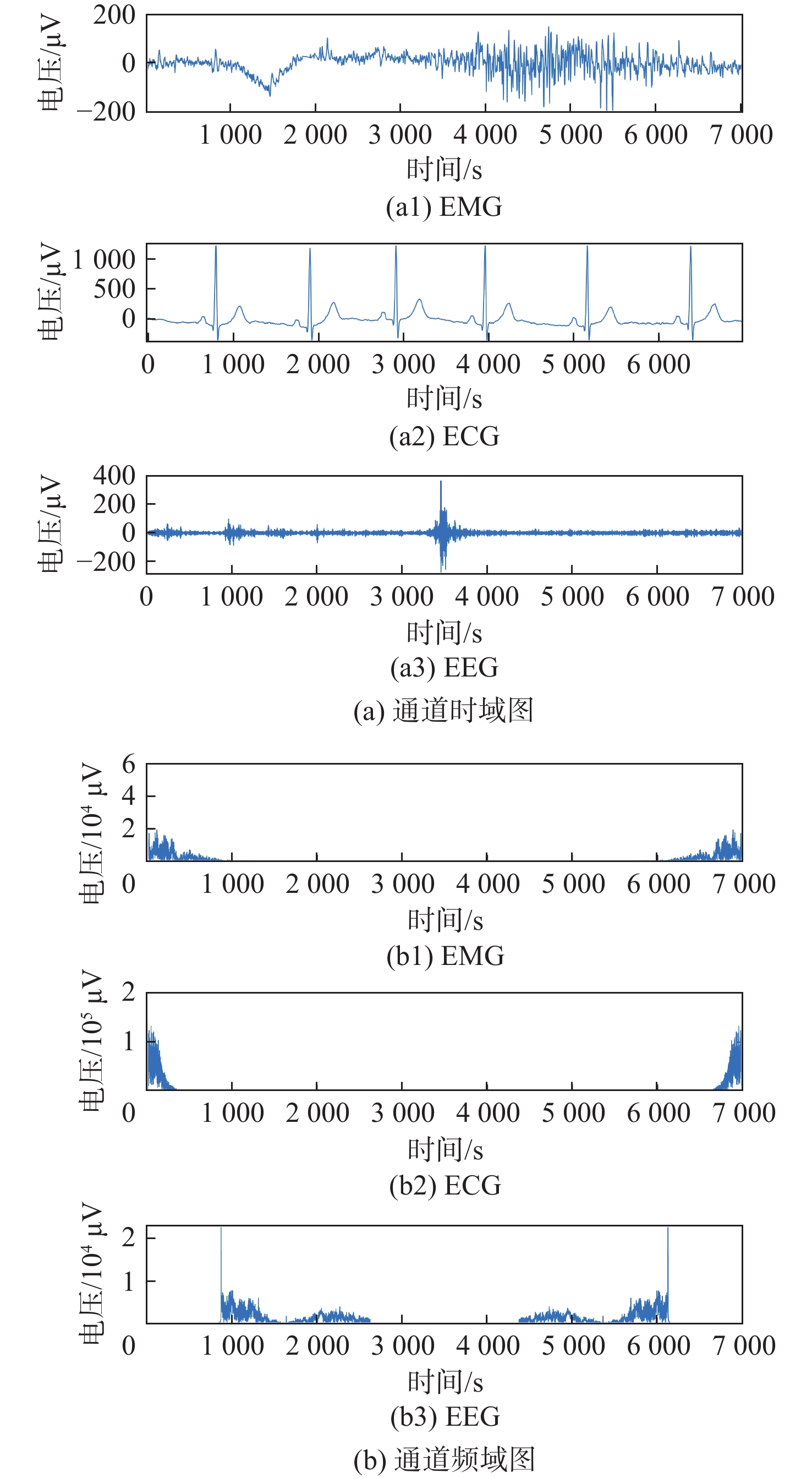
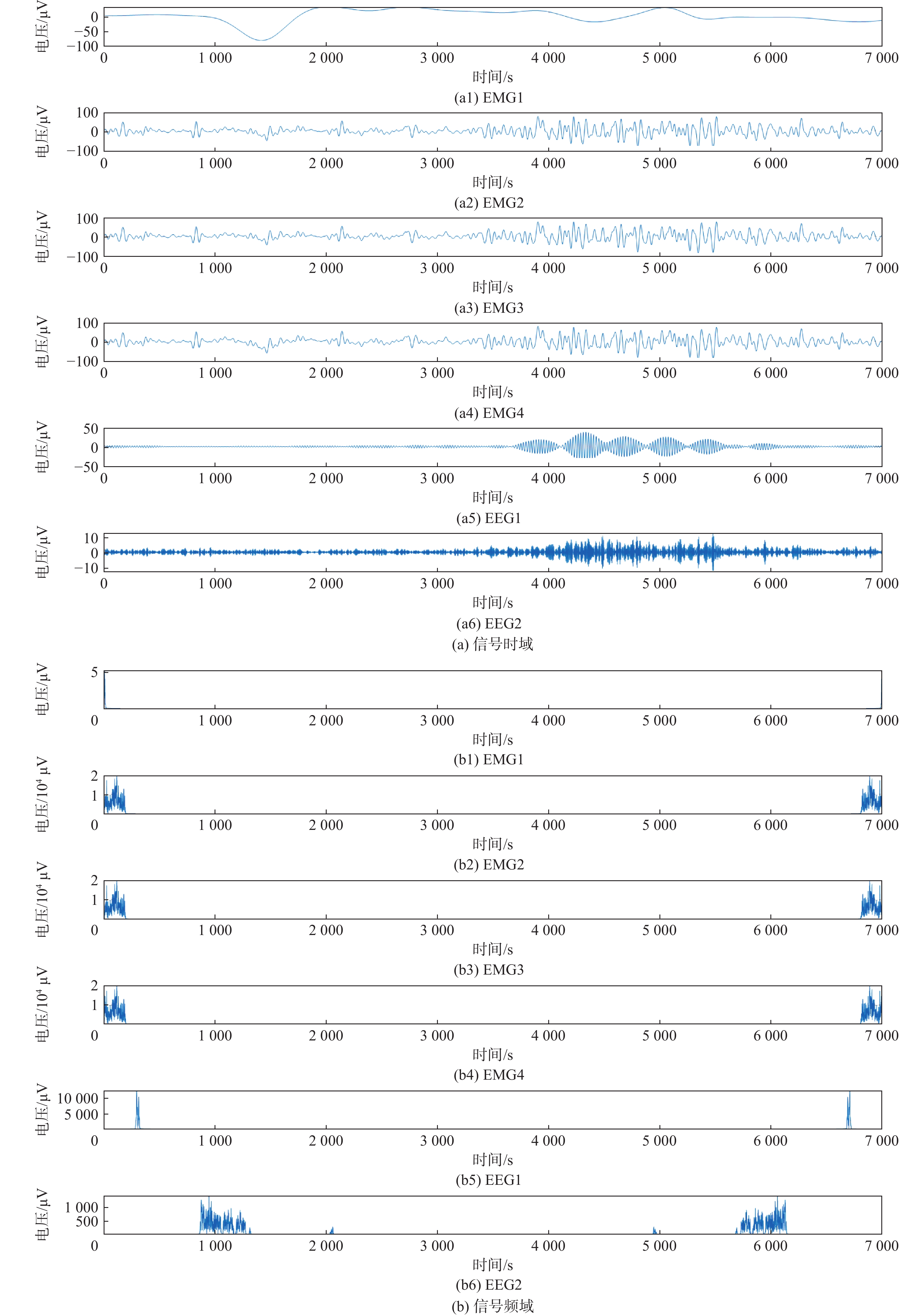
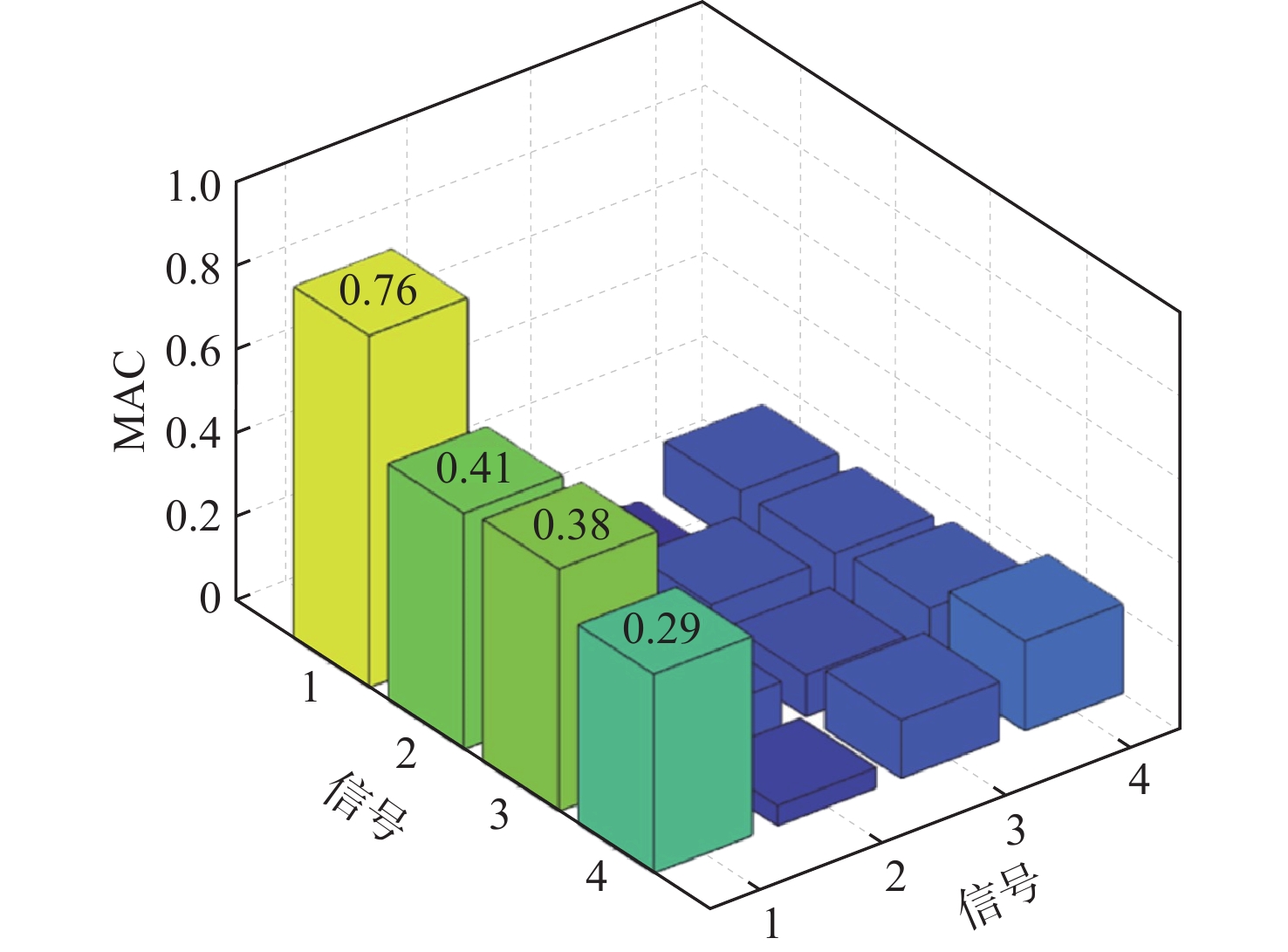
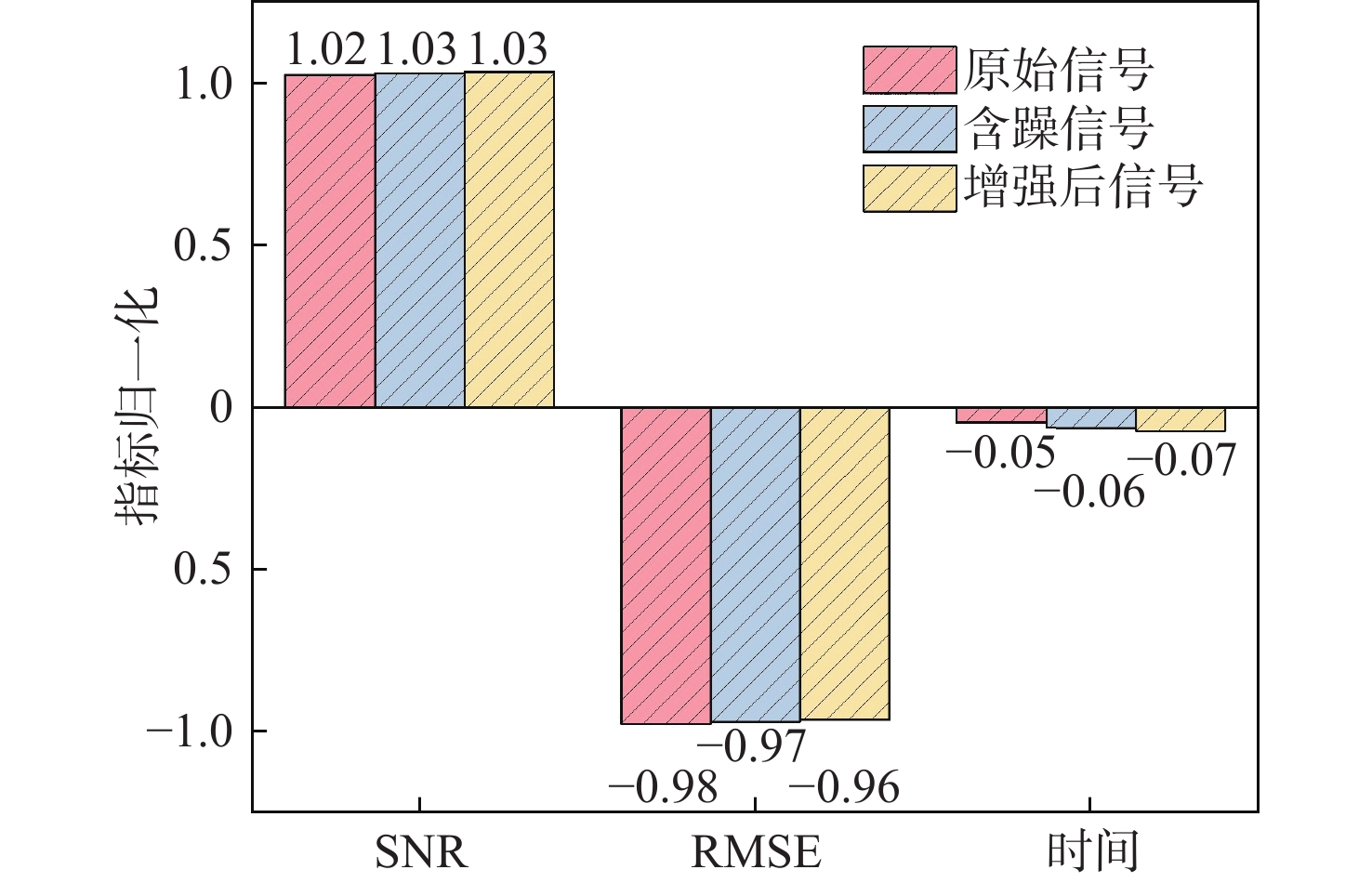
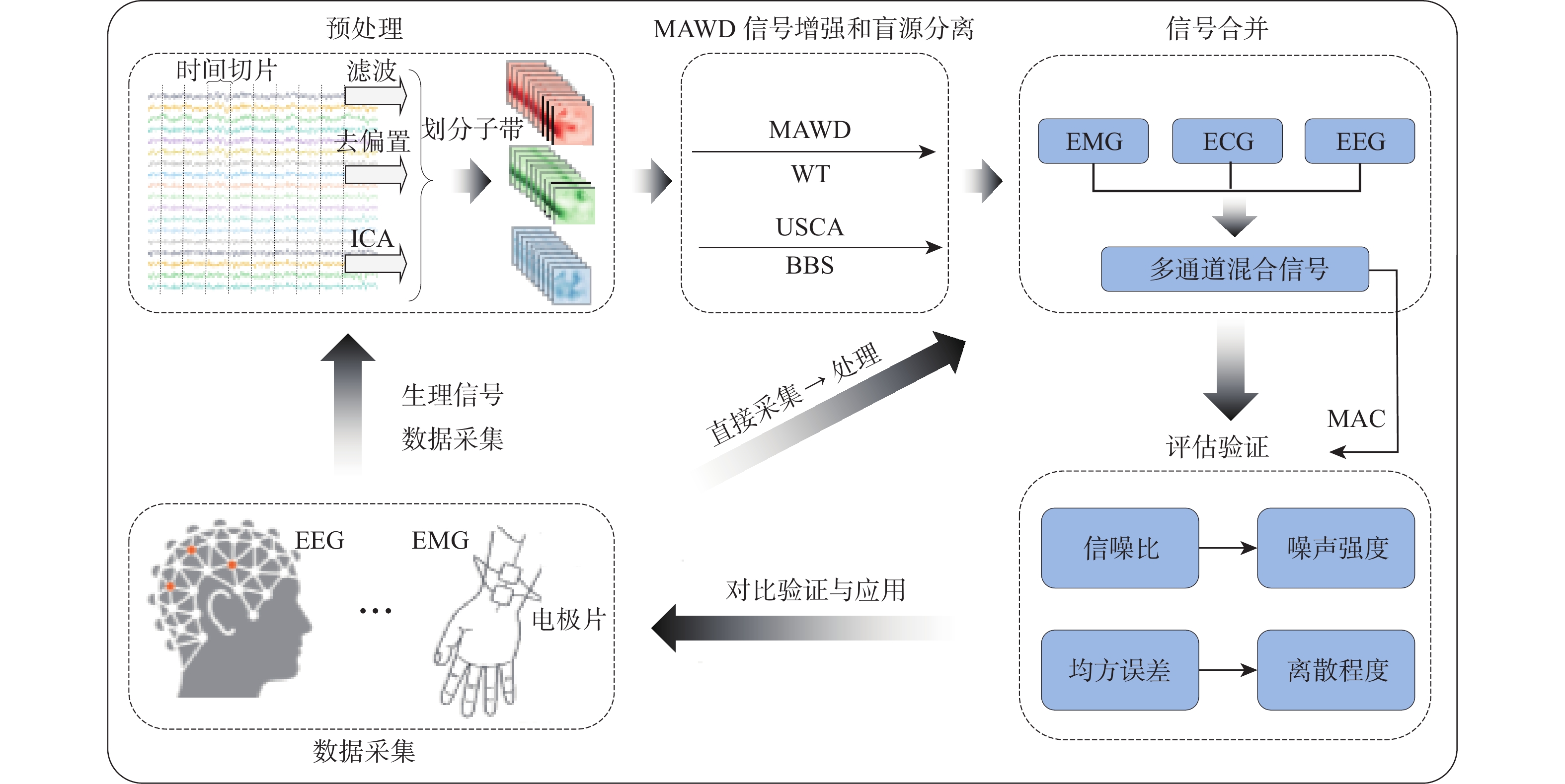
为提高生理信号的质量和可靠性,将盲源分离和小波阈值方法进行耦合研究,提出了多谱自适应小波信号增强方法并与改进的盲源分离方法相结合进行降噪处理。为评估所提方法的有效性,使用小波变换中软阈值、硬阈值、自适应阈值3种方法计算信噪比(SNR)和均方根误差(RMSE)。结果表明:所提方法在软阈值下具有较强的适用性,增强后的信号软阈值相比硬阈值,SNR提升约44.2%,RMSE下降约28.8%,处理时间减少约1.4%。软阈值相比自适应阈值,SNR提升约706%,RMSE下降约16.7%,处理时间减少约3.0%。为对比软阈值下各参数差异,使用软阈值对原始信号、加噪信号和增强信号进行对比分析及归一化处理。结果显示增强后的信号具有较好的SNR、较低的RMSE和较短的处理时间,软阈值下增强后的信号与原始信号相比,SNR提升约0.12%,RMSE下降约2.5%,处理时间减少约3.9%,进一步验证了所提方法的有效性,并提高了信号质量。
Abstract:In order to improve the quality and reliability of physiological signals, blind source separation and wavelet threshold methods were coupled to propose a multi-spectrum adaptive wavelet signal enhancement method, which was combined with an improved blind source separation method for denoising. To evaluate the effectiveness of the proposed method, the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and root mean square error (RMSE) indicators were calculated by using three wavelet transform methods: soft threshold, hard threshold, and adaptive threshold. The results show that the proposed method has strong applicability under the soft threshold, and compared with that under a hard threshold, the enhanced signal under a soft threshold has an SNR improvement of about 44.2%, RMSE reduction of about 28.8%, and a time reduction of about 1.4%. Compared with the adaptive threshold, SNR is improved by about 706%; RMSE is reduced by about 16.7%, and time is reduced by about 3.0%. The original, noisy, and enhanced signals are analyzed and normalized by using a soft threshold to compare the differences in various parameters under a soft threshold. The results show that the enhanced signal has a better SNR, lower RMSE, and shorter processing time. Compared with the original signal under the soft threshold, SNR is improved by about 0.12%; RMSE is reduced by about 2.5%, and time is reduced by about 3.9%, which further verifies the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm and improves the signal quality.
-
表 1 原始信号、加噪信号、增强信号参数对比
Table 1. Comparison of parameters of original, noisy, and enhanced signals
指标 SNR提升/μV RMSE下降/μV 处理时间/s 原始信号 加噪信号 增强信号 原始信号 加噪信号 增强信号 原始信号 加噪信号 增强信号 软阈值 8.17 8.16 8.15 0.05 0.05 0.05 3.81 3.72 3.67 硬阈值 5.65 5.63 5.61 0.066 0.07 0.07 3.83 3.74 3.65 自适应阈值 1.08 1.06 1.01 0.12 0.12 0.12 3.82 3.73 3.69 表 2 盲源分离前后参数对比
Table 2. Comparison of parameters before and after blind source separation
指标 SNR提升/μV RMSE下降/μV 处理时间/s 分离前 分离后 分离前 分离后 分离前 分离后 软阈值 7.90 7.96 10.76 7.65 4.18 4.04 硬阈值 5.43 5.51 14.30 10.15 4.25 4.12 自适应阈值 0.15 0.17 26.26 18.74 4.16 1.14 -
[1] SHU L, XIE J Y, YANG M Y, et al. A review of emotion recognition using physiological signals[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(7): 2074. doi: 10.3390/s18072074 [2] LAL B, GRAVINA R, SPAGNOLO F, et al. Compressed sensing approach for physiological signals: a review[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23(6): 5513-5534. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3243390 [3] ZHU J J, WEI Y X, FENG Y F, et al. Physiological signals-based emotion recognition via high-order correlation learning[J]. ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications, 2019, 15(3s): 1-18. [4] BELOUCHRANI A, ABED-MERAIM K, CARDOSO J F, et al. A blind source separation technique using second-order statistics[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1997, 45(2): 434-444. doi: 10.1109/78.554307 [5] FU Z Z, ZHANG B N, HE X R, et al. Emotion recognition based on multi-modal physiological signals and transfer learning[J]. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 2022, 16: 1000716. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.1000716 [6] GOLDHACKER M, KECK P, IGEL A, et al. A multi-variate blind source separation algorithm[J]. Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine, 2017, 151: 91-99. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2017.08.019 [7] CHEN X, WANG Z J, MCKEOWN M. Joint blind source separation for neurophysiological data analysis: Multiset and multimodal methods[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2016, 33(3): 86-107. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2016.2521870 [8] XIONG F, CHEN D Y. CEEMDAN-IMFx-PCA-CICA: an improved single-channel blind source separation in multimedia environment for motion artifact reduction in ambulatory ECG[J]. Complex & Intelligent Systems, 2023, 9(3): 2555-2569. [9] VON LÜHMANN A, BOUKOUVALAS Z, MÜLLER K R, et al. A new blind source separation framework for signal analysis and artifact rejection in functional Near-Infrared Spectroscopy[J]. NeuroImage, 2019, 200: 72-88. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.06.021 [10] ROY V, SHUKLA S. Designing efficient blind source separation methods for EEG motion artifact removal based on statistical evaluation[J]. Wireless Personal Communications, 2019, 108(3): 1311-1327. doi: 10.1007/s11277-019-06470-3 [11] SAUER J, STREPPEL M, PETERSEN E, et al. Blind source separation of inspiration and expiration in respiratory sEMG signals[J]. Physiological Measurement, 2022, 43(7): 075007. doi: 10.1088/1361-6579/ac799c [12] ROUSSEL J, RAVIER P, HARITOPOULOS M, et al. Decomposition of multi-channel intramuscular EMG signals by cyclostationary-based blind source separation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering, 2017, 25(11): 2035-2045. doi: 10.1109/TNSRE.2017.2700890 [13] NEGRO F, MUCELI S, CASTRONOVO A M, et al. Multi-channel intramuscular and surface EMG decomposition by convolutive blind source separation[J]. Journal of Neural Engineering, 2016, 13(2): 026027. doi: 10.1088/1741-2560/13/2/026027 [14] WEDEKIND D, KLEYKO D, OSIPOV E, et al. Robust methods for automated selection of cardiac signals after blind source separation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 65(10): 2248-2258. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2017.2788701 [15] WAN P W, HAO B J, LI Z, et al. Time differences of arrival estimation of mixed interference signals using blind source separation based on wireless sensor networks[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2016, 10(8): 924-929. doi: 10.1049/iet-spr.2016.0002 [16] DONOHO D L, JOHNSTONE I M. Adapting to unknown smoothness via wavelet shrinkage[J]. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 1995, 90(432): 1200-1224. doi: 10.1080/01621459.1995.10476626 [17] DAUBECHIES I. Orthonormal bases of compactly supported wavelets[J]. Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics, 1988, 41(7): 909-996. doi: 10.1002/cpa.3160410705 [18] ZHAO H M, ZUO S Y, HOU M, et al. A novel adaptive signal processing method based on enhanced empirical wavelet transform technology[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(10): 3323. doi: 10.3390/s18103323 [19] JUTTEN C, HERAULT J. Blind separation of sources, part I: an adaptive algorithm based on neuromimetic architecture[J]. Signal Processing, 1991, 24(1): 1-10. doi: 10.1016/0165-1684(91)90079-X [20] XIE Y, ZOU T, YANG J, et al. SA-UCBSS: sparsity-based adaptive underdetermined convolutive blind source separation[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2024, 212: 112224. [21] LI Q, YANG J H, CHEN X, et al. The decomposition of surface EMG signals based on blind source separation of convolved mixtures[J]. Conference Proceedings, 2005, 2005: 5912-5915. [22] HU J, GUO T, HAN C. Stochastic linearized generalized alternating direction method of multipliers: expected convergence rates and large deviation properties[J]. Mathematical Structures in Computer Science, 2023, 66(3): 1-18. [23] YAN X T, BOUDRIAS M H, MITSIS G D. Removal of transcranial alternating current stimulation EEG artifacts using blind source separation and wavelets[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2022, 69(10): 3183-3192. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2022.3162490 [24] ORTIZ-ECHEVERRI C J, SALAZAR-COLORES S, RODRÍGUEZ-RESÉNDIZ J, et al. A new approach for motor imagery classification based on sorted blind source separation, continuous wavelet transform, and convolutional neural network[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(20): 4541. doi: 10.3390/s19204541 [25] LI X, ZHENG Y, ZHANG J, et al. Finite SNR diversity-multiplexing trade-off in hybrid ABCom/RCom-assisted NOMA networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing, 2024, 23(10): 9108-9119. doi: 10.1109/TMC.2024.3357753 [26] HASSAN N, RAMLI D A. Sparse component analysis (SCA) based on adaptive time: frequency thresholding for underdetermined blind source separation (UBSS)[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(4): 2060. doi: 10.3390/s23042060 [27] CASTAÑO USUGA F A, GISSEL C, HERNÁNDEZ A M. Motion artifact reduction in electrocardiogram signals through a redundant denoising independent component analysis method for wearable health care monitoring systems: algorithm development and validation[J]. JMIR Medical Informatics, 2022, 10(11): e40826. doi: 10.2196/40826 [28] METSOMAA J, SARVAS J, ILMONIEMI R J. Blind source separation of event-related EEG/MEG[J]. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering, 2017, 64(9): 2054-2064. doi: 10.1109/TBME.2016.2616389 [29] CHEN Y, CHENG Y N, LIU H L. Application of improved wavelet adaptive threshold de-noising algorithm in FBG demodulation[J]. Optik, 2017, 132: 243-248. doi: 10.1016/j.ijleo.2016.12.052 [30] MA S, ZHANG H J, MIAO Z Y. Blind source separation for the analysis sparse model[J]. Neural Computing and Applications, 2021, 33(14): 8543-8553. doi: 10.1007/s00521-020-05606-y [31] XU X W, LIANG Y, HE P, et al. Adaptive motion artifact reduction based on empirical wavelet transform and wavelet thresholding for the non-contact ECG monitoring systems[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19(13): 2916. doi: 10.3390/s19132916 -







 下载:
下载: