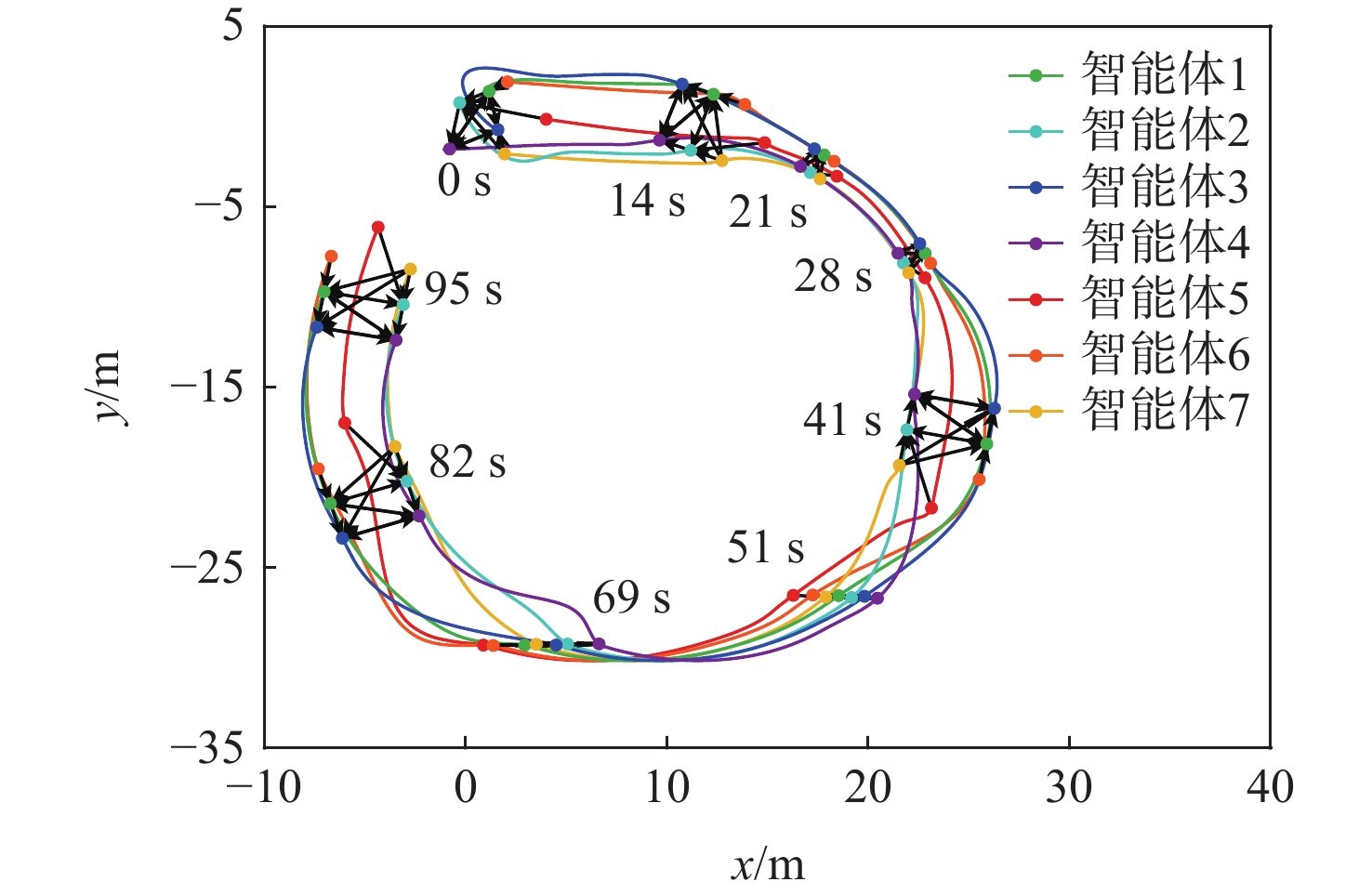
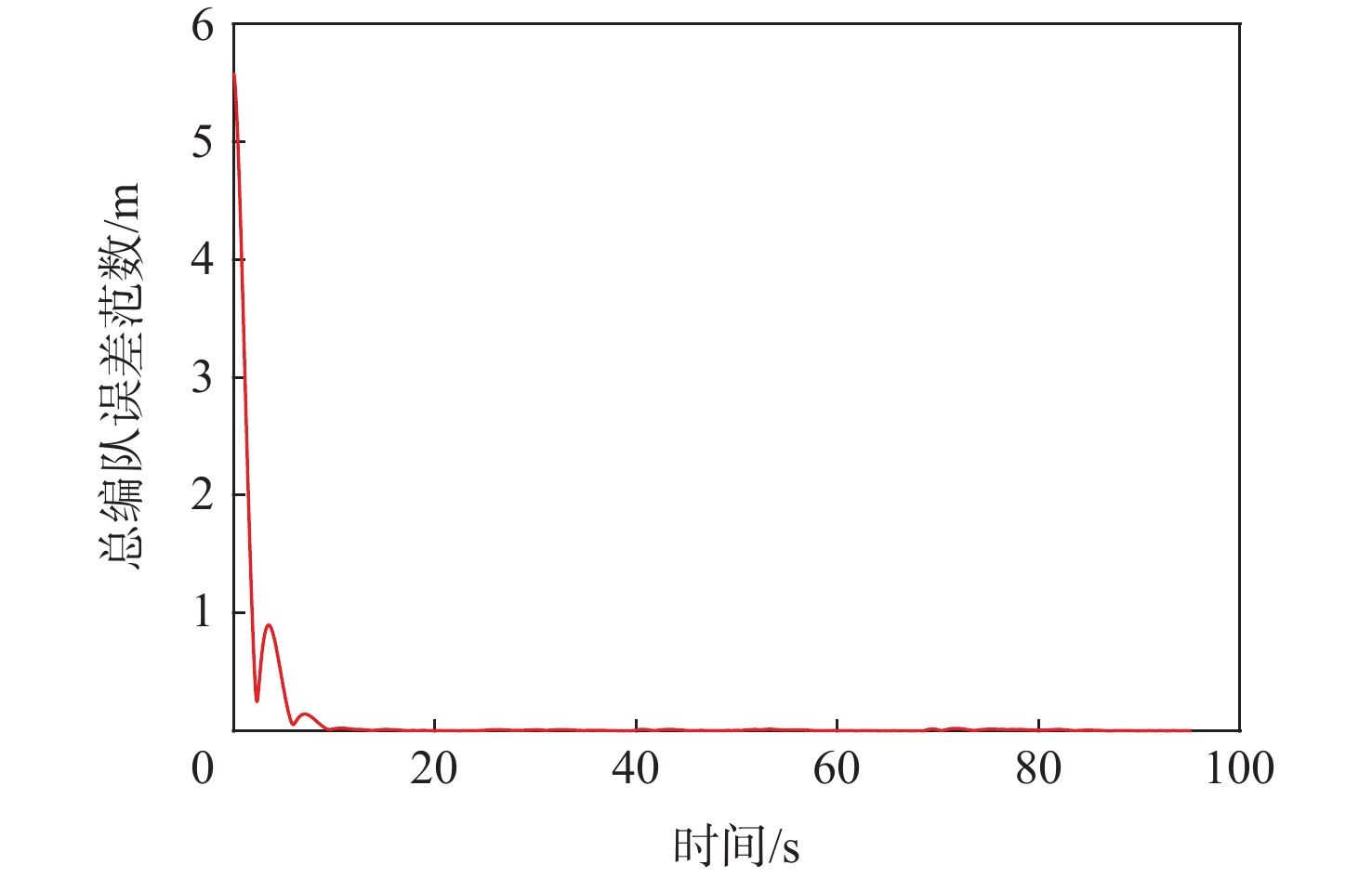
Directed interactive topology optimization design for multi-agent affine formation maneuver control
-
摘要:
研究了多智能体仿射编队机动控制的有向交互拓扑优化设计问题。考虑信息交互成本、信息传播能耗等优化指标,建立了包含拓扑结构构造和权重配置的仿射编队机动有向拓扑优化模型;针对仿射编队机动拓扑结构构造,提出了有向
k 根图的检测方法,实现了有向信息交互拓扑的d +1根约束求解,并设计了一种改进NSGA-II的拓扑结构构造优化算法,以二维空间中7个智能体的编队为例进行仿真验证,结果表明:改进NSGA-II的拓扑结构构造优化算法具有更好的优化效果,能够有效地为仿射编队机动控制提供多种可行的有向交互拓扑,并且所生成的交互拓扑能够满足有向d +1根图的要求。Abstract:This paper investigated the directed interactive topology optimization design problem for multi-agent affine formation maneuver control. Firstly, by considering the optimization indexes such as information interaction cost and energy consumption during information spreading, a directed topology optimization model for affine formation maneuver was established, including topology structure construction and weight allocation. Secondly, in view of the topological structure construction for affine formation maneuver, a directed
k -rooted graph detection method was proposed, which could realize the solution ofd + 1-rooted constraint for directed information interaction topology. Then, an improved NSGA-II-based topology structure construction optimization algorithm was designed. Finally, a formation of seven agents in two-dimensional space was taken as an example for simulation verification. The results show that the improved NSGA-II-based topology structure construction optimization algorithm has better optimization effects. It can effectively provide a variety of feasible directed interactive topologies for affine formation maneuver control, and the generated interactive topology can meet the requirements of a directedd + 1-rooted graph. -
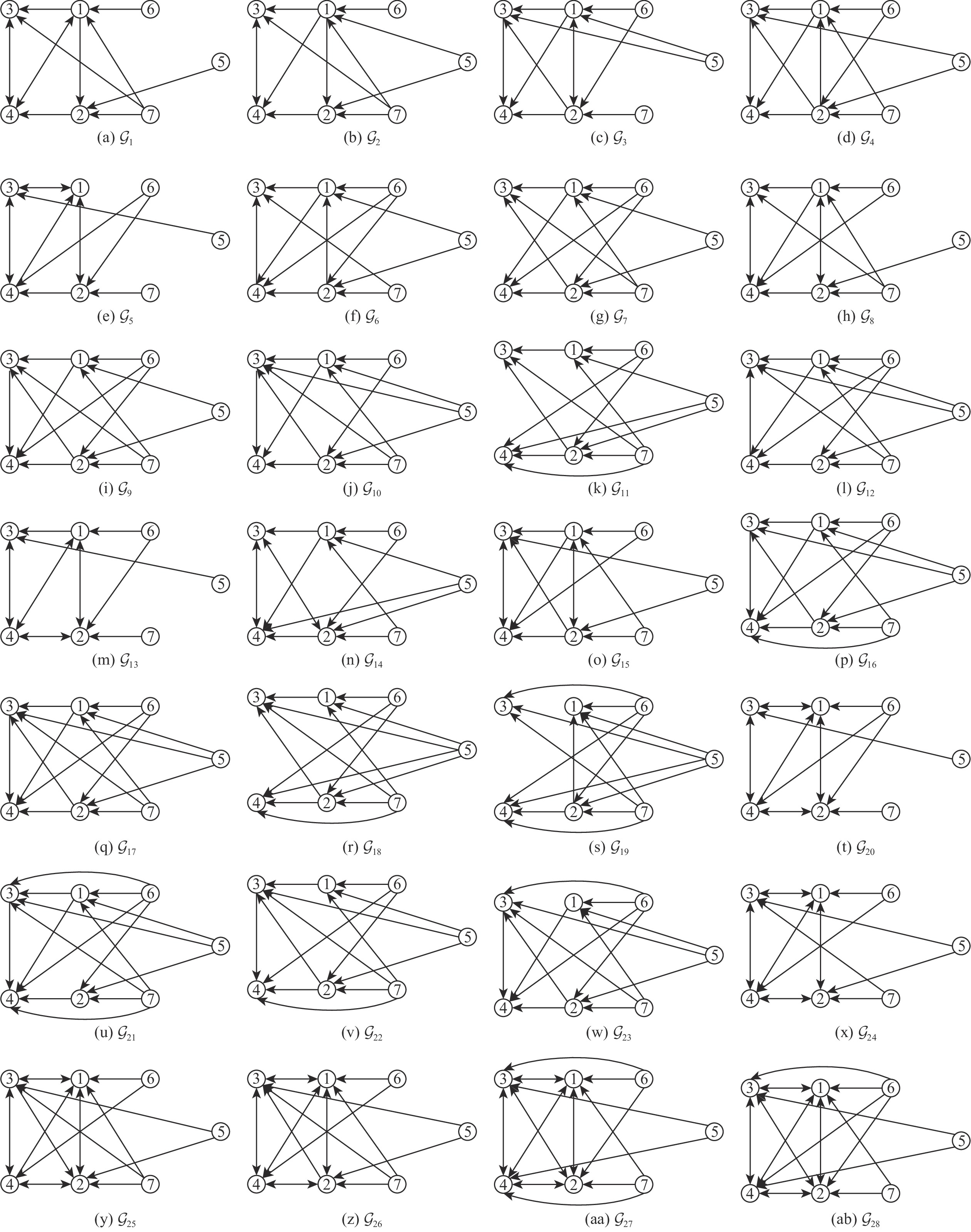
表 1 拓扑结构构造结果
Table 1. Topology structure construction results
拓扑编号 f1 f2 f3 f4 G1 12 43.55 6.00 1.25 G2 12 43.55 4.83 1.50 G3 12 44.21 4.00 1.25 G4 12 44.69 3.50 1.50 G5 12 44.93 4.00 1.00 G6 12 45.20 2.50 1.75 G7 12 46.15 2.00 2.00. G8 13 48.73 3.33 1.50 G9 13 50.15 1.83 2.00 G10 13 50.81 1.67 2.00 G11 13 52.00 1.00 2.50 G12 13 52.00 1.50 2.25 G13 14 47.74 3.50 1.00 G14 14 53.63 2.33 1.75 G15 14 53.87 2.50 1.50 G16 14 54.81 1.33 2.25 G17 14 56.47 1.17 2.25 G18 14 58.32 0.50 2.75 G19 14 59.85 0.00 3.00 G20 15 53.40 3.00 1.25 G21 15 60.00 0.33 2.75 G22 15 60.47 0.83 2.50 G23 15 62.47 0.67 2.50 G24 16 59.05 2.00 1.50 G25 18 68.00 1.83 1.75 G26 18 68.00 1.83 1.75 G27 20 75.48 1.33 2.00 G28 20 77.14 1.00 2.00 表 2 算法评估指标结果
Table 2. Algorithm evaluation indicator results
算法 NPS
平均值NPSMF
平均值IGDX IGDF 暴力
搜索平均值 方差 平均值 方差 imNSGA-II 2.15 0.05 3.1857 4.9742 3.7809 423.7237 37 本文 23.16 0.58 2.3401 3.4508 1.3760 5.8359 15 -
[1] DONG X W, HU G Q. Time-varying formation control for general linear multi-agent systems with switching directed topologies[J]. Automatica, 2016, 73: 47-55. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2016.06.024 [2] LIN Z Y, DING W, YAN G F, et al. Leader–follower formation via complex Laplacian[J]. Automatica, 2013, 49(6): 1900-1906. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2013.02.055 [3] LIN Z Y, WANG L L, CHEN Z Y, et al. Necessary and sufficient graphical conditions for affine formation control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2015, 61(10): 2877-2891. [4] HAN Z M, WANG L L, LIN Z Y, et al. Formation control with size scaling via a complex Laplacian-based approach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2016, 46(10): 2348-2359. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2015.2477107 [5] FANG X, LI X L, XIE L H. Distributed formation maneuver control of multiagent systems over directed graphs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(8): 8201-8212. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2020.3044581 [6] ZHAO S Y. Affine formation maneuver control of multiagent systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2018, 63(12): 4140-4155. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2018.2798805 [7] XU Y, ZHAO S Y, LUO D L, et al. Affine formation maneuver control of high-order multi-agent systems over directed networks[J]. Automatica, 2020, 118: 109004. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2020.109004 [8] XU Y, LUO D L, YOU Y C, et al. Affine transformation based formation maneuvering for discrete-time directed networked systems[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2020, 63(1): 73-85. doi: 10.1007/s11431-018-9456-0 [9] CHEN L M, MEI J, LI C J, et al. Distributed leader–follower affine formation maneuver control for high-order multiagent systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2020, 65(11): 4941-4948. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2020.2986684 [10] XU Y, LUO D L, LI D Y, et al. Affine formation control for heterogeneous multi-agent systems with directed interaction networks[J]. Neurocomputing, 2019, 330: 104-115. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2018.11.023 [11] XU Y, LUO D L, LI D Y, et al. Target-enclosing affine formation control of two-layer networked spacecraft with collision avoidance[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2019, 32(12): 2679-2693. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2019.04.016 [12] XU Y, LI D Y, LUO D L, et al. Affine formation maneuver tracking control of multiple second-order agents with time-varying delays[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2019, 62(4): 665-676. doi: 10.1007/s11431-018-9328-2 [13] LUO Z X, ZHANG P Y, DING X J, et al. Adaptive affine formation maneuver control of second-order multi-agent systems with disturbances[C]// 2020 16th International Conference on Control, Automation, Robotics and Vision (ICARCV). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1071-1076. [14] CHANG Z Z, WANG J J, LI Z K. Fully distributed event-triggered affine formation maneuver control over directed graphs[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2022, 55(3): 178-183. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2022.05.031 [15] YANG Q K, CAO M, FANG H, et al. Constructing universally rigid tensegrity frameworks with application in multiagent formation control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2018, 64(1): 381-388. [16] XIAO F, YANG Q K, ZHAO X Y, et al. A framework for optimized topology design and leader selection in affine formation control[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2022, 7(4): 8627-8634. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2022.3188883 [17] YANG J Y, XIAO F, CHEN T W. Formation tracking of nonholonomic systems on the special euclidean group under fixed and switching topologies: an affine formation strategy[J]. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 2021, 59(4): 2850-2874. doi: 10.1137/20M1328130 [18] MONDAL S, TSOURDOS A. Optimal topology for consensus using genetic algorithm[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 404: 41-49. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2020.04.107 [19] 崔亚妮, 任佳, 杜文才, 等. 多无人船通信网络拓扑优化控制算法[J]. 控制理论与应用, 2016, 33(12): 1639-1649.CUI Y N, REN J, DU W C, et al. Network topology optimization control algorithm for multiple unmanned surface vehicle[J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2016, 33(12): 1639-1649(in Chinese). [20] 谷晓燕, 陈亮, 邓香平. 无人机编队信息交互拓扑多目标优化[J]. 电光与控制, 2022, 29(9): 27-31,52.GU X Y, CHEN L, DENG X P. Multi-objective optimization of UAV formation information interaction topology[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2022, 29(9): 27-31,52(in Chinese). [21] 邦詹森 J, 古廷 G Z. 有向图的理论、算法及其应用[M]. 姚兵, 张忠辅, 译. 北京: 科学出版社, 2009.BANG-JENSEN J, GUTIN G Z. Digraphs theory, algorithms and applications[M]. YAO B, ZHANG Z F translated. Beijing: Science Press, 2009(in Chinese). [22] HONG H, KIM B J, CHOI M Y, et al. Factors that predict better synchronizability on complex networks[J]. Physical Review E, Statistical, Nonlinear, and Soft Matter Physics, 2004, 69(6 Pt 2): 067105. [23] 岳彩通, 梁静, 瞿博阳, 等. 多模态多目标优化综述[J]. 控制与决策, 2021, 36(11): 2577-2588.YUE C T, LIANG J, QU B Y, et al. A survey on multimodal multiobjective optimization[J]. Control and Decision, 2021, 36(11): 2577-2588(in Chinese). [24] DEB K, PRATAP A, AGARWAL S, et al. A fast and elitist multiobjective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(2): 182-197. doi: 10.1109/4235.996017 [25] DEB K, JAIN H. An evolutionary many-objective optimization algorithm using reference-point-based nondominated sorting approach, part I: solving problems with box constraints[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2013, 18(4): 577-601. [26] DENG W, ZHANG X X, ZHOU Y Q, et al. An enhanced fast non-dominated solution sorting genetic algorithm for multi-objective problems[J]. Information Sciences, 2022, 585: 441-453. doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2021.11.052 [27] ZHOU A M, ZHANG Q F, JIN Y C. Approximating the set of Pareto-optimal solutions in both the decision and objective spaces by an estimation of distribution algorithm[J]. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary Computation, 2009, 13(5): 1167-1189. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2009.2021467 -







 下载:
下载: