-
摘要:
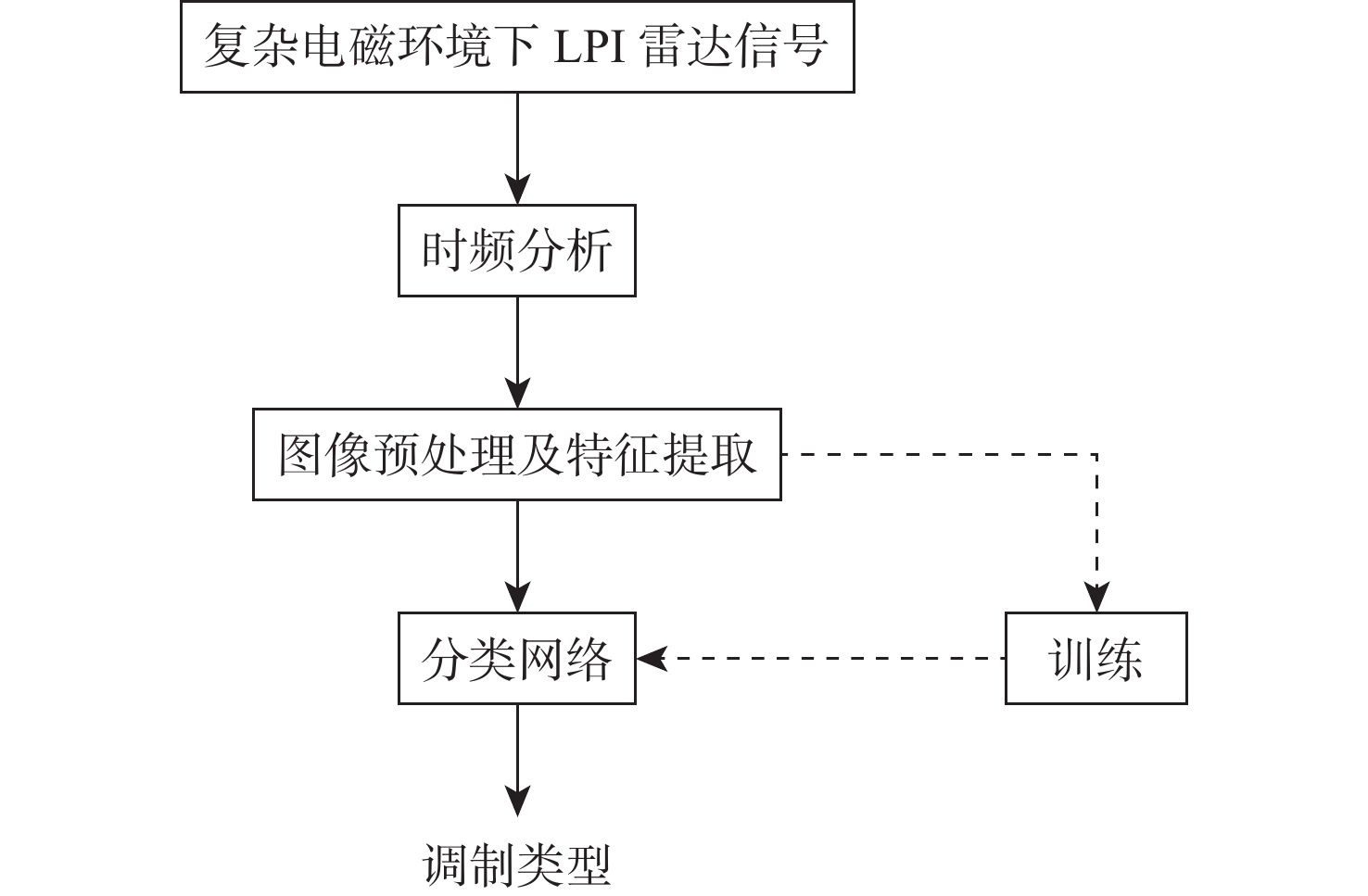
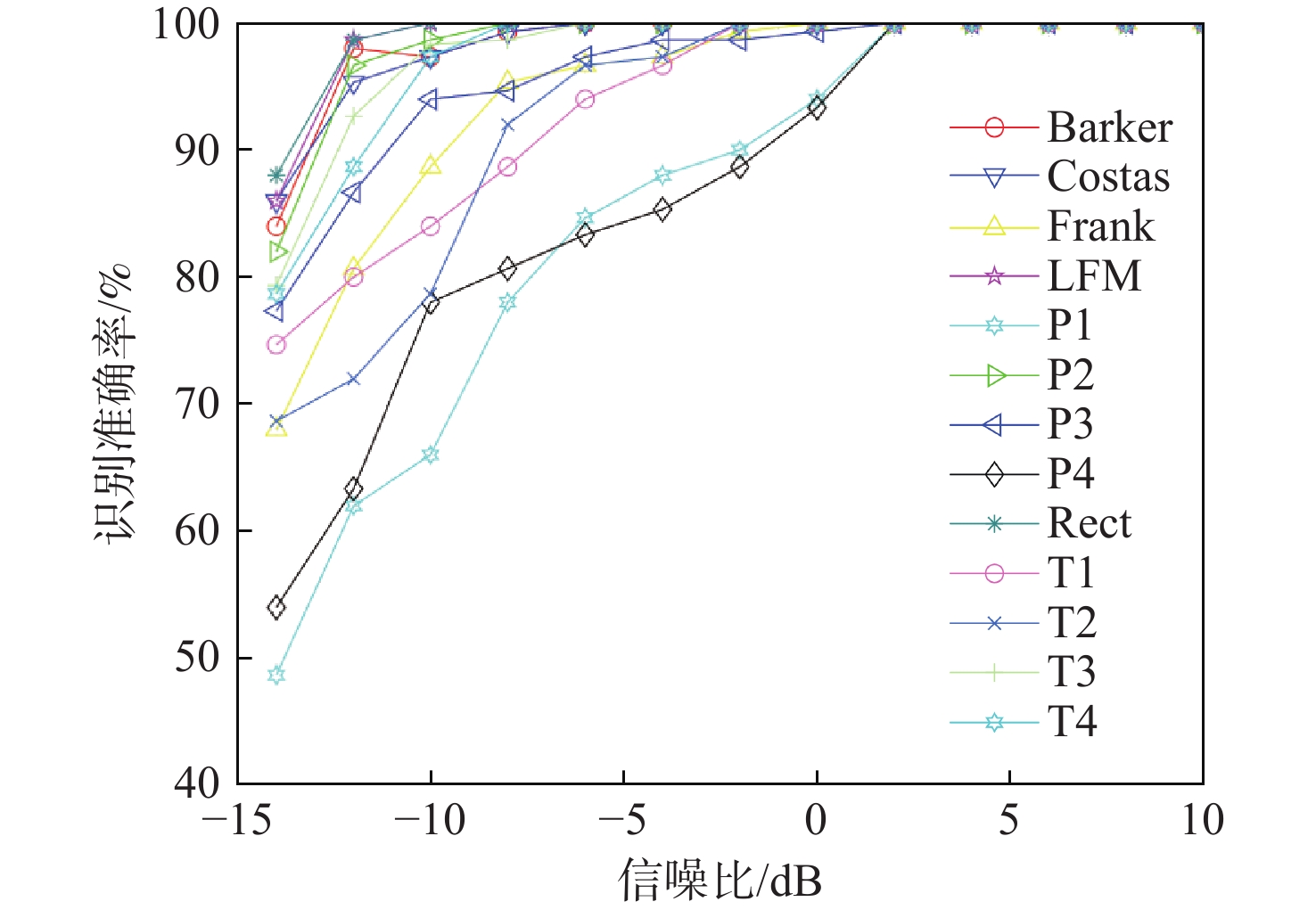
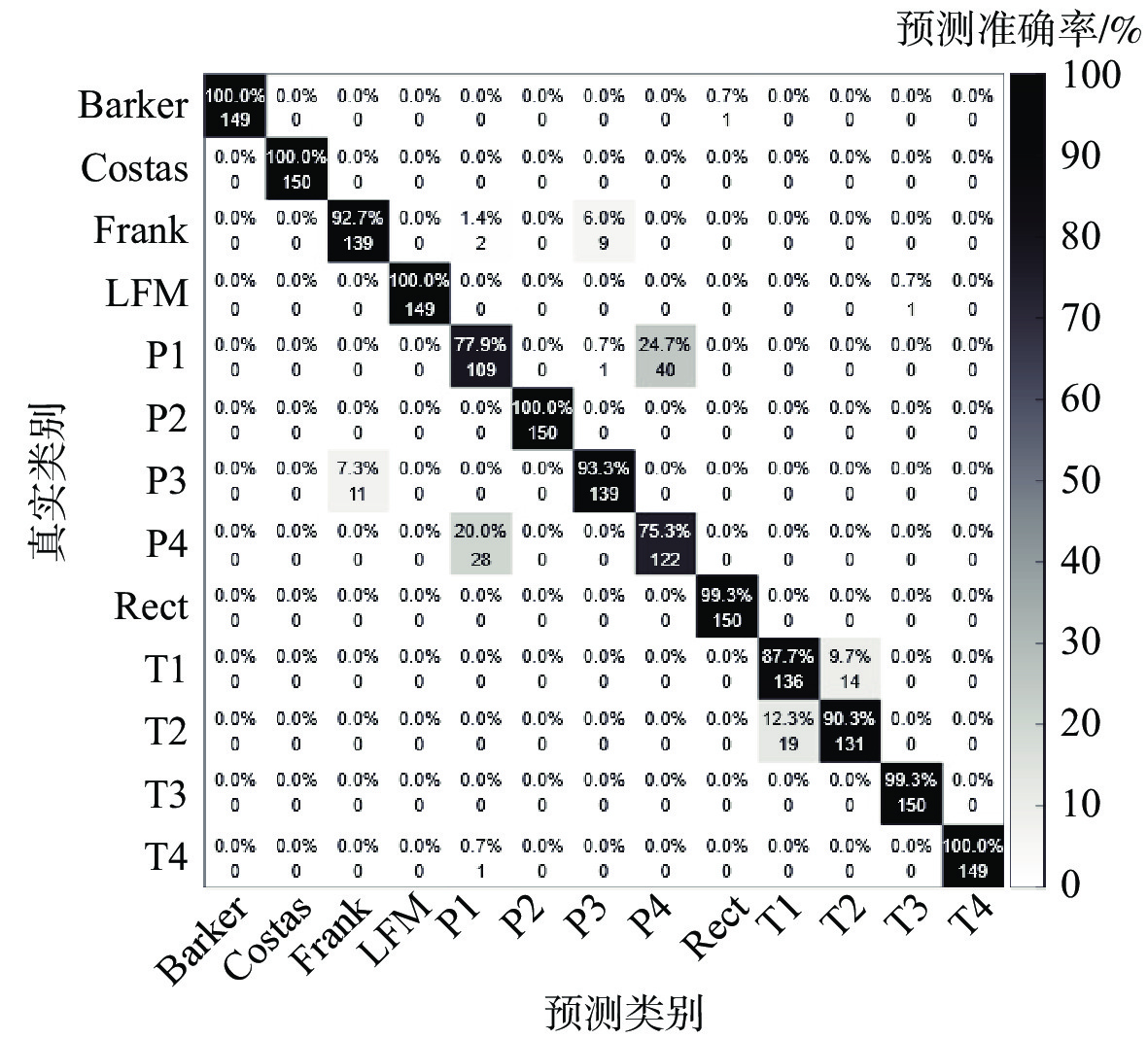
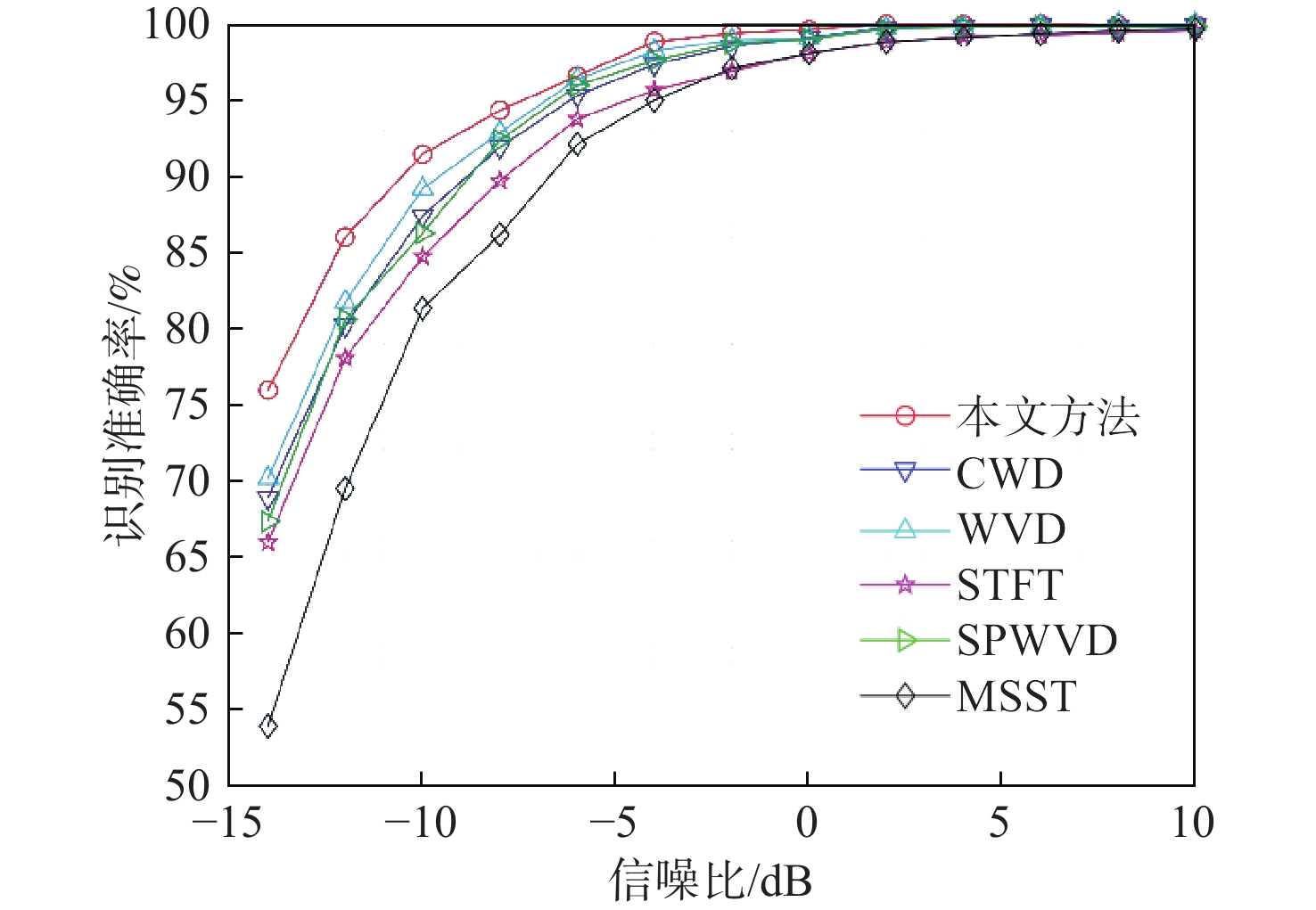
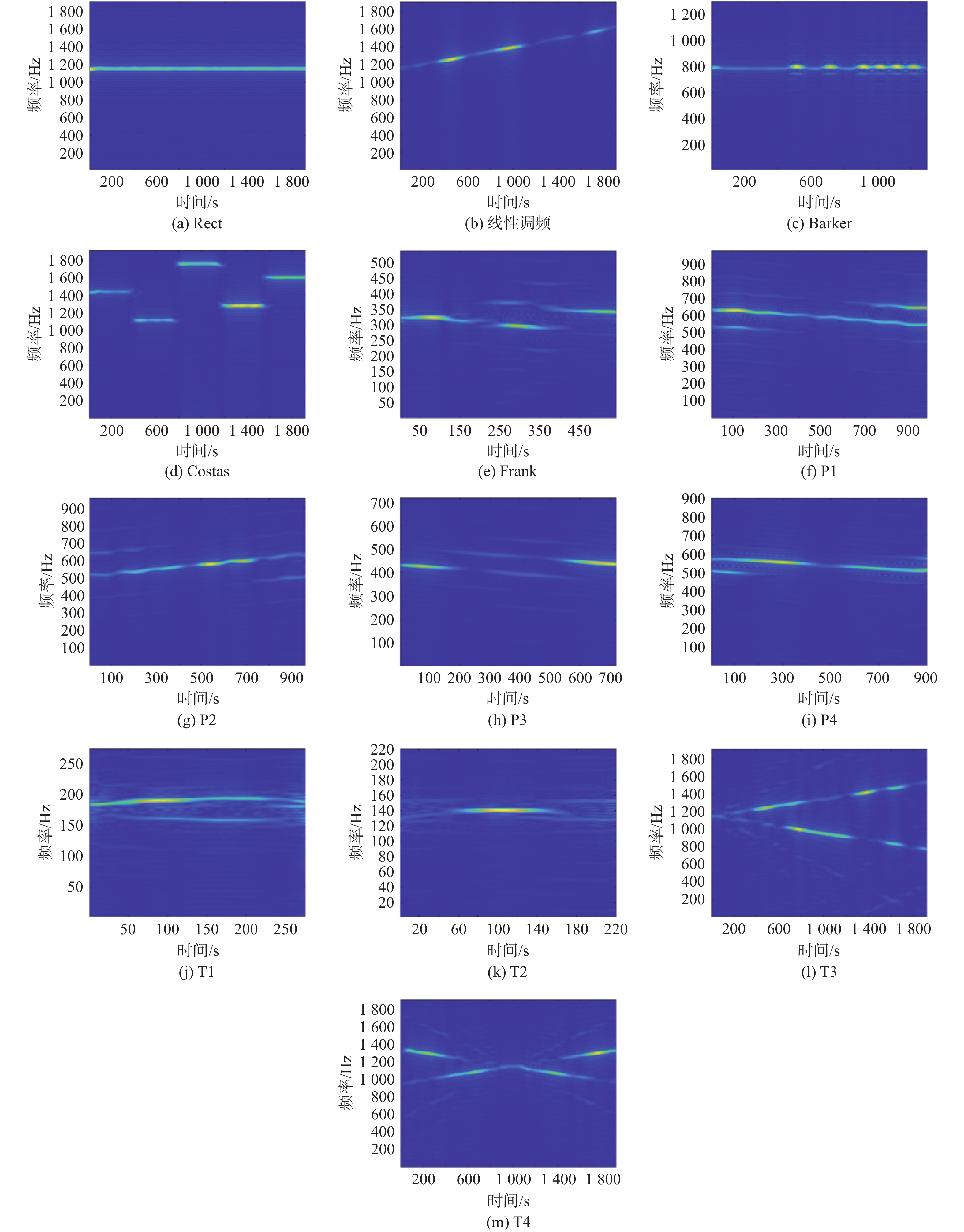
针对低截获概率(LPI)雷达信号在低信噪比(SNR)情况下识别效果不理想、网络模型复杂的问题,提出一种基于时频重排和多尺度残差网络的LPI雷达信号识别方法。该方法以魏格纳-维尔分布(WVD)为基础,通过时频重排算法提高信号的聚集性,得到信号的时频分布图像,输入到多尺度残差网络中完成信号的分类。通过构建多径莱斯衰落信道完成复杂电磁环境仿真,实验结果表明:所提方法在SNR为−8 dB时,对Costas、Frank、P1~P4等13类LPI雷达典型调制样式能达到94%的识别准确率,相比其他方法在低信噪比下具有更好的识别性能。
Abstract:In view of the problems of low probability of acquisition (LPI) radar signal recognition in low signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and complex network model, an LPI radar signal recognition method based on time-frequency reassignment and multi-scale residual network was proposed. The time-frequency reassignment approach is used to enhance the signal's aggregation based on the Wigner-Ville distribution (WVD). The resulting time-frequency distribution image is then fed into the multi-scale residual network to finish the signal's categorization. In addition, the complex electromagnetic environment simulation was completed by constructing a multi-path Rice-fading channel. According to the experimental results, when the SNR is −8 dB, the suggested approach can achieve 94% recognition accuracy for a total of 13 different types of typical LPI radar modulation patterns, including Costas, Frank, P1~P4, etc. Compared with other methods, it has better recognition performance at a low signal-to-noise ratio.
-
表 1 波形参数设置
Table 1. Waveform parameters setting
LPI信号调制样式 调制参数 取值范围 All 载频fc/Hz U(fs /6, fs/5) 线性调频 带宽B/Hz
采样个数NU(fs/20,fs/15)
[512,1024 ]Rect 采样个数N [512, 1024 ]Costas 跳频序列长度
基础频率fmin/Hz
采样个数N{3,4,5,6}
U(fs/32, fs/25)
[512,1024 ]Barker 码长L
相位子波数cpp{7,11,13}
[2,5]Frank 相位子波数cpp
频率步长M[3,5]
{6,7,8}P1,P2 相位子波数cpp
频率步长M[3,5]
{6,8}P3,P4 相位子波数cpp
子码数ns[3,5]
{36,64}T1,T2 相位状态数Np
相位波形段数Ng
采样个数N2
{4,5,6}
[512,1024 ]T3,T4 相位状态数Np
相位波形段数Ng
采样个数N
调制带宽B/Hz2
{4,5,6}
[512,1024 ]
U(fs/20,fs/15)表 2 信道参数设置
Table 2. Channel parameters setting
信道参数 取值范围 采样频率/Hz fs 多径衰减/ns U(1, 1000 )平均路径增益/dB U(−20,0) K-factor 4 最大多普勒频移/Hz U(10, 1000 )表 3 运行时间对比
Table 3. Comparison of running time
时频方法 时间/s 本文方法 0.269 3 CWD 0.307 2 WVD 0.039 2 STFT 0.064 6 SPWVD 0.264 1 MSST 0.199 3 -
[1] PACE P E. Detecting and classifying low probability of intercept radar[M]. 2nd ed. Boston: Artech House, 2009. [2] LIU Y J, XIAO P, WU H C, et al. LPI radar signal detection based on radial integration of Choi-Williams time-frequency image[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 26(5): 973-981. doi: 10.1109/JSEE.2015.00106 [3] XIAO Z L, YAN Z Y. Radar emitter identification based on novel time-frequency spectrum and convolutional neural network[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2021, 25(8): 2634-2638. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3084043 [4] QUAN D Y, TANG Z Y, WANG X F, et al. LPI radar signal recognition based on dual-channel CNN and feature fusion[J]. Symmetry, 2022, 14(3): 570. doi: 10.3390/sym14030570 [5] WANG X Z. Electronic radar signal recognition based on wavelet transform and convolution neural network[J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2022, 61(5): 3559-3569. doi: 10.1016/j.aej.2021.09.002 [6] CHEN K Y, ZHANG J Y, CHEN S, et al. Automatic modulation classification of radar signals utilizing X-net[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2022, 123: 103396. doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2022.103396 [7] YUAN S B, LI P, WU B, et al. Semi-supervised classification for intra-pulse modulation of radar emitter signals using convolutional neural network[J]. Remote Sensing, 2022, 14(9): 2059. doi: 10.3390/rs14092059 [8] ZHANG M, DIAO M, GAO L P, et al. Neural networks for radar waveform recognition[J]. Symmetry, 2017, 9(5): 75. doi: 10.3390/sym9050075 [9] WANG G, CHEN S, HUANG J, et al. Radar signal sorting and recognition based on transferred deep learning[J]. Computer Science and Application, 2019, 9(9): 1761-1778. doi: 10.12677/CSA.2019.99198 [10] BOASHASH B. Time frequency signal analysis and processing: a comprehensive reference[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2003. [11] 杨瑾, 郝新红, 陈齐乐. 基于多域特征的多雷达信号自动识别方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2024, 50(3): 931-939.YANG J, HAO X H, CHEN Q L. Automatic recognition method of multi-radar signals based on multi-domain features[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(3): 931-939(in Chinese). [12] AUGER F, FLANDRIN P. Improving the readability of time-frequency and time-scale representations by the reassignment method[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 1995, 43(5): 1068-1089. doi: 10.1109/78.382394 [13] WANG Y, WU X, LI W Z, et al. Analysis of micro-Doppler signatures of vibration targets using EMD and SPWVD[J]. Neurocomputing, 2016, 171: 48-56. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.06.005 [14] ATAIE R, EMRANI ZARANDI A A, SAFAEI MEHRABANI Y. An efficient inexact full adder cell design in CNFET technology with high-PSNR for image processing[J]. International Journal of Electronics, 2019, 106(6): 928-944. doi: 10.1080/00207217.2019.1576232 [15] 崔天舒, 崔凯, 黄永辉, 等. 卷积神经网络卫星信号自动调制识别算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(6): 986-994.CUI T S, CUI K, HUANG Y H, et al. Convolutional neural network based algorithm for automatic modulation recognition of satellite signals[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(6): 986-994(in Chinese). [16] 陈永, 陈锦, 陶美风. 多尺度特征和注意力融合的生成对抗壁画修复[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2023, 49(2): 254-264.CHEN Y, CHEN J, TAO M F. Mural inpainting with generative adversarial networks based on multi-scale feature and attention fusion[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2023, 49(2): 254-264(in Chinese). [17] GAO J P, LU Y, QI J W, et al. A radar signal recognition system based on non-negative matrix factorization network and improved artificial bee colony algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7: 117612-117626. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2936669 [18] KONG S H, KIM M, HOANG L M, et al. Automatic LPI radar waveform recognition using CNN[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6: 4207-4219. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2017.2788942 [19] HOANG L M, KIM M, KONG S H. Automatic recognition of general LPI radar waveform using SSD and supplementary classifier[J]. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 2019, 67(13): 3516-3530. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2918983 [20] 王功明, 陈世文, 黄洁, 等. 基于多重同步压缩变换的雷达辐射源分选识别[J]. 现代雷达, 2020, 42(3): 49-56.WANG G M, CHEN S W, HUANG J, et al. Radar emitter sorting and recognition based on multi-synchrosqueezing transform[J]. Modern Radar, 2020, 42(3): 49-56(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: