Stability control of vehicles powered by non-pneumatic wheels based on robust optimal sliding mode
-
摘要:
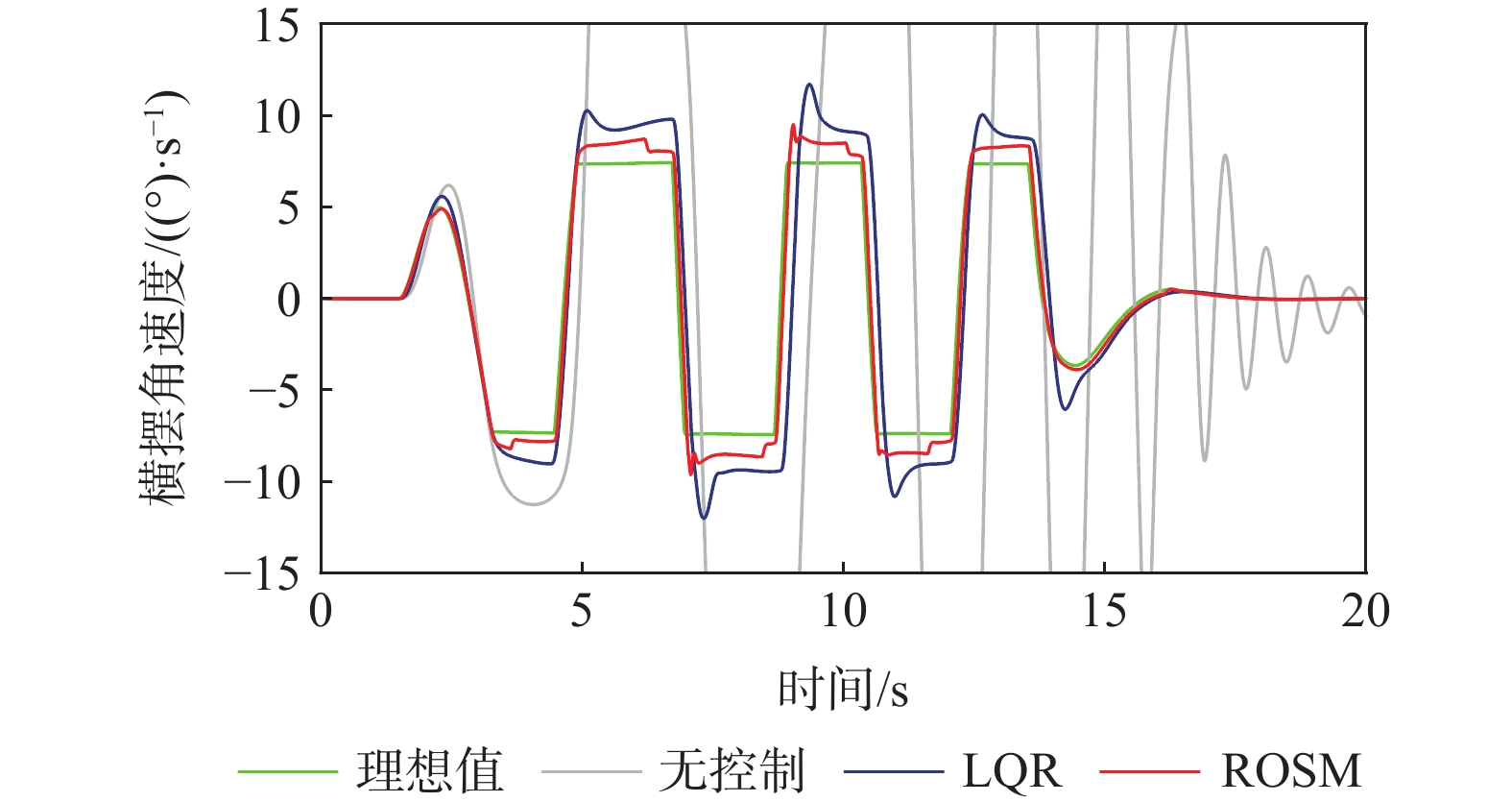
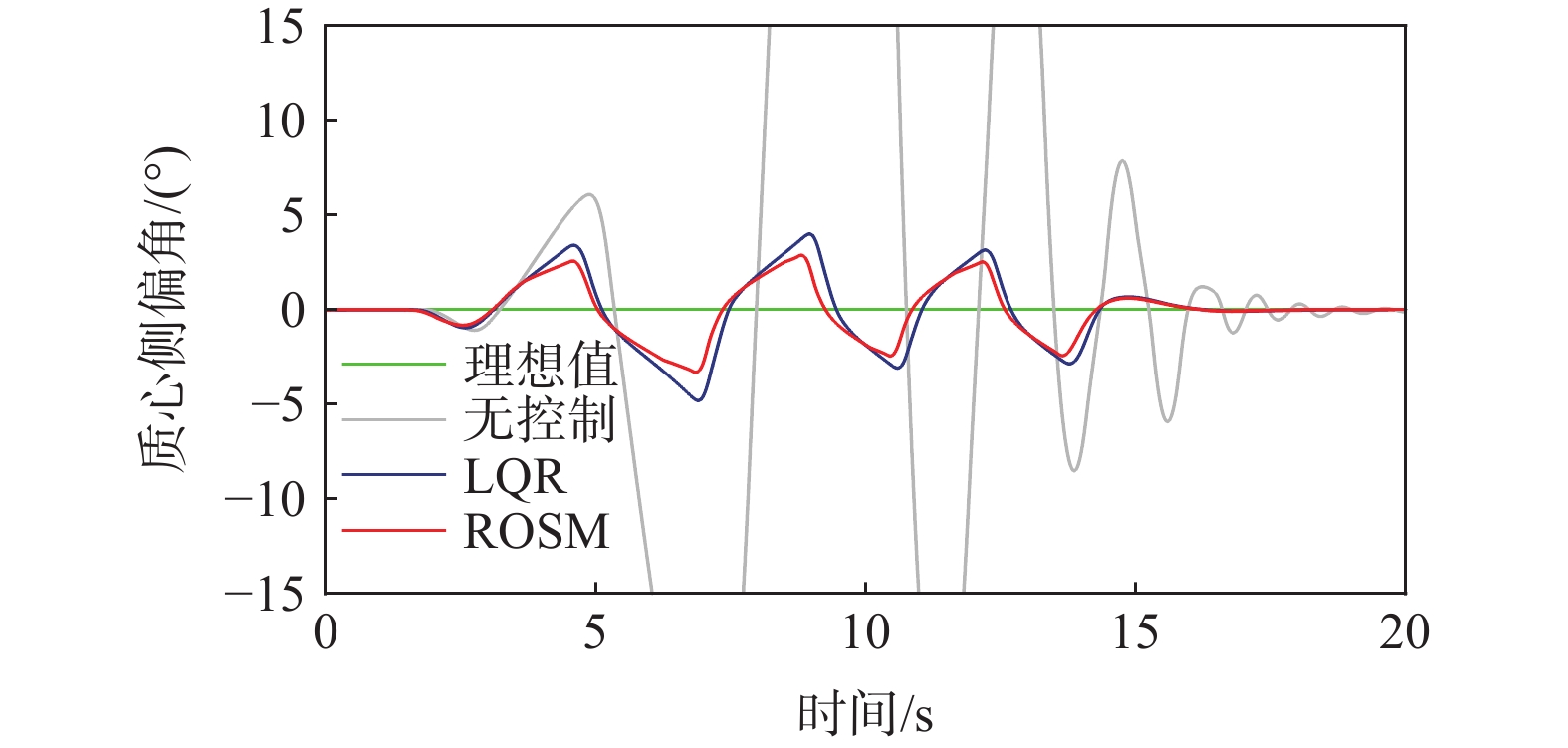
机械弹性电动轮是一种新式非充气轮胎,具有防爆、防胎刺等优点,文章中基于匹配该电动轮的分布式汽车,提出了一种鲁棒最优滑模(ROSM)控制策略,以便提高车辆转向时的横摆稳定性。针对线性二自由度模型,为实现最优控制采用线性二自由度调节器(LQR),输出初始的附加横摆力矩;考虑到实际行驶中车辆状态是复杂的非线性系统,建立包含不确定参数的车辆动力学模型,并在初始最优控制量的基础上设计一种鲁棒积分滑模控制器,该控制器对不确定参数与外部干扰具有良好的鲁棒性,且仍能实现最优控制;通过MATLAB/Simulink和Carsim联合仿真,对控制方法进行仿真验证,结果表明:双移线工况中,ROSM控制下横摆角速度的平均绝对误差(MAE)、均方根误差(RMSE)与LQR控制相比分别下降了63.83%、65.33%;蛇形工况中,其分别降低了58.38%、60.02%。
Abstract:Mechanical elastic electric wheel is a new type of non-pneumatic tire, which has the advantages of explosion-proof, anti-puncture, etc. In this paper, based on the distributed vehicle matching with the electric wheel, a robust optimal sliding mode (ROSM) control strategy is proposed to improve the yaw stability of the vehicle. Firstly, the initial additional yaw moment is calculated using a linear 2-DOF regulator (LQR) control rule for the linear 2-DOF model. Secondly, considering the complex nonlinearity of the actual vehicle system, a vehicle dynamics model with uncertain parameters is established. And a robust integral sliding mode controller is designed on the basis of the initial optimal control law. The improved controller has good robustness to uncertain parameters and external disturbances, which could still achieve optimal control effectiveness. Finally, the control scheme is verified by co-simulations of MATLAB/Simulink and Carsim. The findings demonstrate that, in the simulation of double lane change, the mean absolute error (MAE) and root mean square error (RMSE) of the yaw rate under ROSM control are decreased by 63.83% and 65.33%, respectively, in comparison to LQR control. As for the serpentine condition, they respectively decreased by 58.38% and 60.02%.
-
Key words:
- non-pneumatic wheels /
- direct yaw moment /
- LQR /
- robust optimal control /
- sliding mode control
-
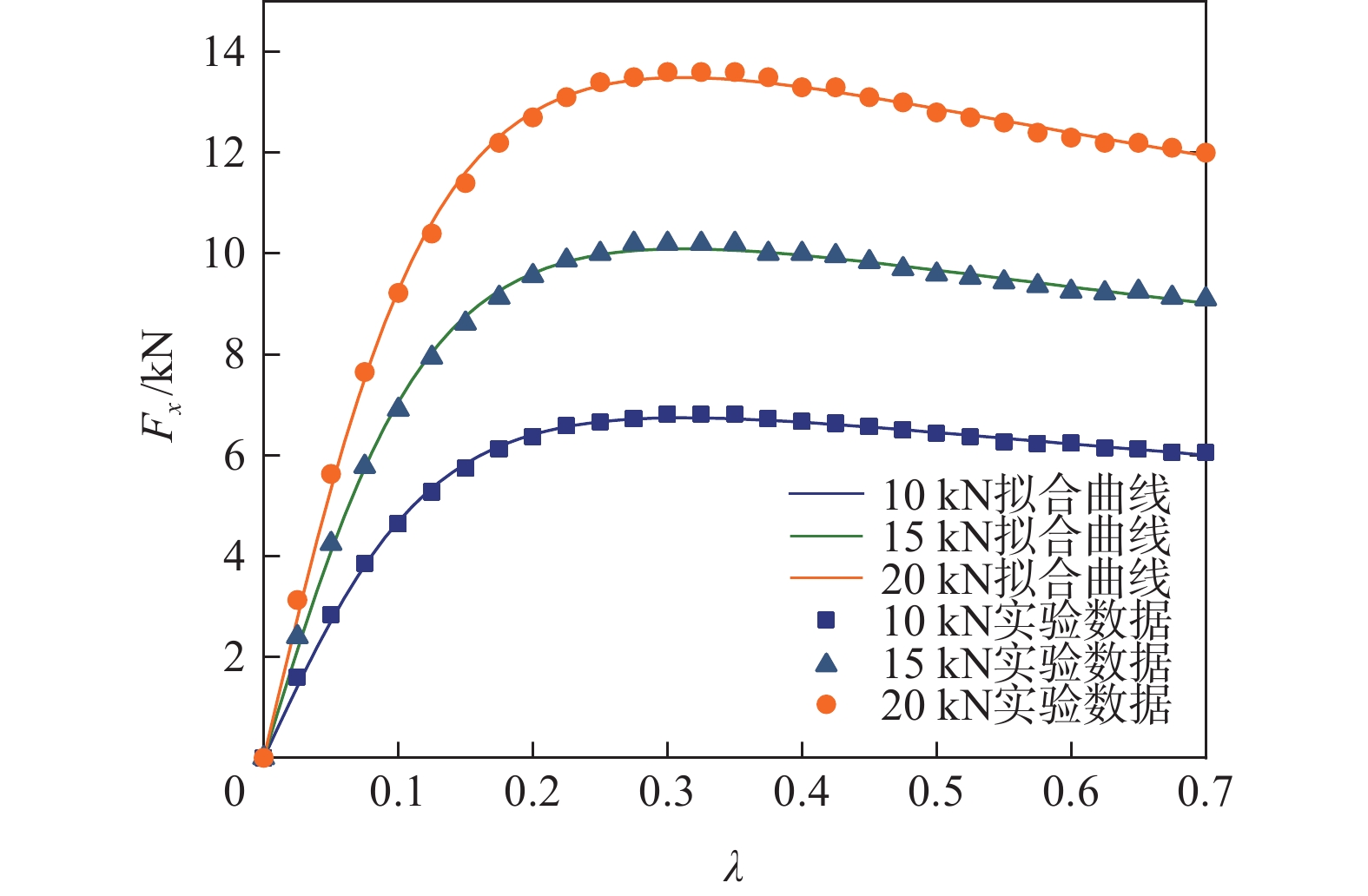
表 1 MEEW参数拟合结果
Table 1. Parameter fitting results
Fz/kN Bx Cx Dx Ex By Cy Dy Ey 10 4.9477 1.7216 6795.14 0.4541 0.1364 1.2682 8150 − 0.0988 15 3.9323 2.1252 10103.66 0.8742 0.1271 1.2682 12200 − 0.0952 20 4.8070 1.7390 13495.56 0.4411 0.1116 1.2682 16310 − 0.0914 表 2 车辆参数
Table 2. Vehicle parameters
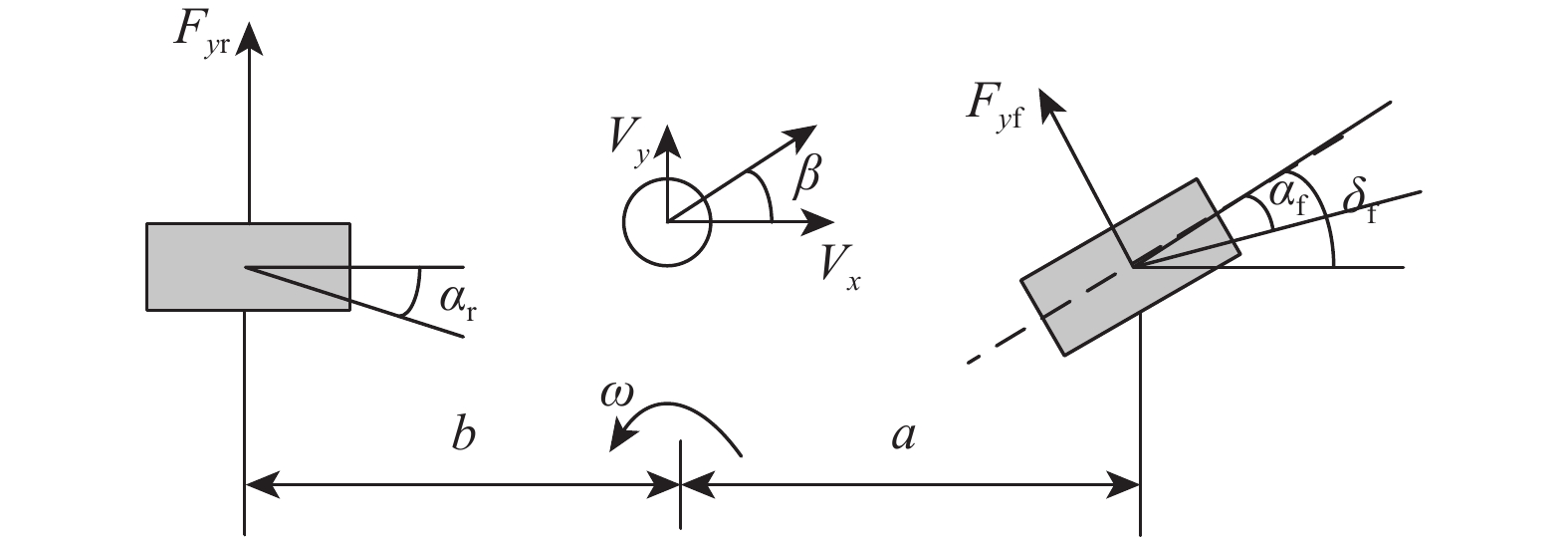
参数 数值 车辆质量 m/kg 1610 转动惯量 Iz/(kg·m2 ) 2059.2 质心到前轴距离 a/m 1.05 质心到后轴距离 b/m 1.61 轮距 d/m 1.565 轮胎滚动半径 R/m 0.35 前轮等效刚度 kf /(N·rad−1 ) − 87002 后轮等效刚度 kr /(N·rad−1 ) − 79240 表 3 评估指标对比
Table 3. Comparison of evaluation indicators
工况 ωδMAE ωδRSME βδMAE βδRSME 双移线LQR 1.0161 1.8285 1.0270 1.7139 双移线ROSM 0.3675 0.6339 0.7070 1.1663 蛇形LQR 1.4944 2.2791 1.2446 1.7863 蛇形ROSM 0.6220 0.9111 0.9732 1.3679 -
[1] 赵又群. 非充气机械弹性安全车轮理论与方法[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2020: 12-28.ZHAO Y Q. Theory and method for non-pneumatic mechanical elastic safety wheel[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2020: 12-28 (in Chinese). [2] DENG Y J, ZHAO Y Q, XU H, et al. Finite element modeling of interaction between non-pneumatic mechanical elastic wheel and soil[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2019, 233(13): 3293-3304. doi: 10.1177/0954407018821555 [3] 张陈曦, 赵又群, 冯世林, 等. 伪刚体-柔体耦合的新式免充气轮胎刚度分析[J]. 中国机械工程, 2021, 32(9): 1051-1060,1072.ZHANG C X, ZHAO Y Q, FENG S L, et al. Stiffness analysis of new type non-pneumatic tires based on pseudo-rigid-flexible body coupling model[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 32(9): 1051-1060,1072(in Chinese). [4] 张晨, 赵又群, 郑鑫, 等. 随机载荷下机械弹性车轮的热力耦合耐久性研究[J]. 中国机械工程, 2021, 32(14): 1669-1676.ZHANG C, ZHAO Y Q, ZHENG X, et al. Study on thermal coupling durability of mechanical elastic wheels under random loads[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2021, 32(14): 1669-1676(in Chinese). [5] WANG Q G, ZHUANG Y, WEI J N, et al. A driver model–based direct yaw moment controller for in-wheel motor electric vehicles[J]. Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 11(9): 1687814019877319. [6] GAN L. Study on yaw moment control for electric vehicle with four-wheel in-wheel motor based on fuzzy PI control[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2015, 7: 103-107. [7] ASIABAR A N, KAZEMI R. A direct yaw moment controller for a four in-wheel motor drive electric vehicle using adaptive sliding mode control[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part K: Journal of Multi-body Dynamics, 2019, 233(3): 549-567. doi: 10.1177/1464419318807700 [8] 段敏, 孙小松, 张博涵. 基于模型预测控制与离散线性二次型调节器的智能车横纵解耦跟踪控制[J]. 汽车技术, 2022(8): 38-46.DUAN M, SUN X S, ZHANG B H. Horizontal and vertical decoupling tracking control based on MPC and DLQR[J]. Automobile Technology, 2022(8): 38-46(in Chinese). [9] LIU D Y, HUANG S, WU S, et al. Direct yaw-moment control of electric vehicle with in-wheel motor drive system[J]. International Journal of Automotive Technology, 2020, 21(4): 1013-1028. doi: 10.1007/s12239-020-0096-6 [10] 林棻, 蔡亦璋, 赵又群, 等. 匹配机械弹性车轮的分布式驱动电动汽车稳定性控制[J]. 机械工程学报, 2022, 58(8): 236-243. doi: 10.3901/JME.2022.08.236LIN F, CAI Y Z, ZHAO Y Q, et al. Lateral stability control of distributed drive electric vehicle with mechanical elastic wheel[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2022, 58(8): 236-243(in Chinese). doi: 10.3901/JME.2022.08.236 [11] ZHU J J, WANG Z P, ZHANG L, et al. Braking/steering coordination control for in-wheel motor drive electric vehicles based on nonlinear model predictive control[J]. Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2019, 142: 103586. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2019.103586 [12] YAN Z P, WANG M, XU J. Robust adaptive sliding mode control of underactuated autonomous underwater vehicles with uncertain dynamics[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2019, 173: 802-809. [13] RANGEL M A G, MANZANILLA A, SUAREZ A E Z, et al. Adaptive non-singular terminal sliding mode control for an unmanned underwater vehicle: real-time experiments[J]. International Journal of Control, Automation and Systems, 2020, 18(3): 615-628. doi: 10.1007/s12555-019-0674-4 [14] NORSAHPERI N M H, DANAPALASINGAM K A. An improved optimal integral sliding mode control for uncertain robotic manipulators with reduced tracking error, chattering, and energy consumption[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2020, 142: 106747. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2020.106747 [15] XU T, ZHAO Y Q, DENG H F, et al. Integrated optimal control of distributed in-wheel motor drive electric vehicle in consideration of the stability and economy[J]. Energy, 2023, 282: 128990. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2023.128990 [16] 丛森森, 高峰, 许述财. 基于动态稳定域的车辆横纵向稳定性协同控制[J]. 汽车工程, 2022, 44(6): 900-908.CONG S S, GAO F, XU S C. Cooperative control of vehicle lateral and longitudinal stability based on dynamic stability region[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2022, 44(6): 900-908(in Chinese). [17] 梁宝钰, 汪怡平, 刘珣, 等. 基于滑模理论的高速车辆侧风稳定性控制研究[J]. 汽车工程, 2022, 44(1): 123-130.LIANG B Y, WANG Y P, LIU X, et al. Study on crosswind stability control of high-speed vehicle based on sliding mode theory[J]. Automotive Engineering, 2022, 44(1): 123-130(in Chinese). [18] 陈特, 徐兴, 蔡英凤, 等. 基于状态估计的无人车前轮转角与横摆稳定协调控制[J]. 北京理工大学学报, 2021, 41(10): 1050-1057.CHEN T, XU X, CAI Y F, et al. Coordinated control of front-wheel steering angle and yaw stability for unmanned ground vehicle based on state estimation[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2021, 41(10): 1050-1057(in Chinese). [19] BAI R, WANG H B. Robust optimal control for the vehicle suspension system with uncertainties[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2022, 52(9): 9263-9273. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2021.3052816 [20] DENG H F, ZHAO Y Q, FENG S L, et al. Torque vectoring algorithm based on mechanical elastic electric wheels with consideration of the stability and economy[J]. Energy, 2021, 219: 119643. doi: 10.1016/j.energy.2020.119643 [21] PACEJKA H. Tire and vehicle dynamics[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2005: 27-29. [22] 龙文, 刘豪. 车辆稳定性控制系统LQR算法设计[J]. 汽车实用技术, 2021, 46(23): 76-79,110.LONG W, LIU H. Design of vehicle system dynamics control algorithm based on LQR method[J]. Automobile Applied Technology, 2021, 46(23): 76-79,110(in Chinese). [23] 郑鑫, 赵又群, 王秋伟, 等. 匹配机械弹性车轮的电子稳定控制器参数分析[J]. 中国机械工程, 2020, 31(23): 2883-2890.ZHENG X, ZHAO Y Q, WANG Q W, et al. Parameter analysis of electronic stability controller matching mechanical elastic wheels[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 31(23): 2883-2890(in Chinese). [24] ALI MASOOD CHEEMA M, FLETCHER J E, FARSHADNIA M, et al. Sliding mode based combined speed and direct thrust force control of linear permanent magnet synchronous motors with first-order plus integral sliding condition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2018, 34(3): 2526-2538. [25] 王文伟, 赵一凡, 张伟, 等. 多轴轮边驱动铰接客车的横摆稳定性控制策略[J]. 机械工程学报, 2020, 56(14): 161-172. doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.14.161WANG W W, ZHAO Y F, ZHANG W, et al. Yaw stability control strategy of multi-wheel independent electric articulated bus[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 56(14): 161-172(in Chinese). doi: 10.3901/JME.2020.14.161 -







 下载:
下载: