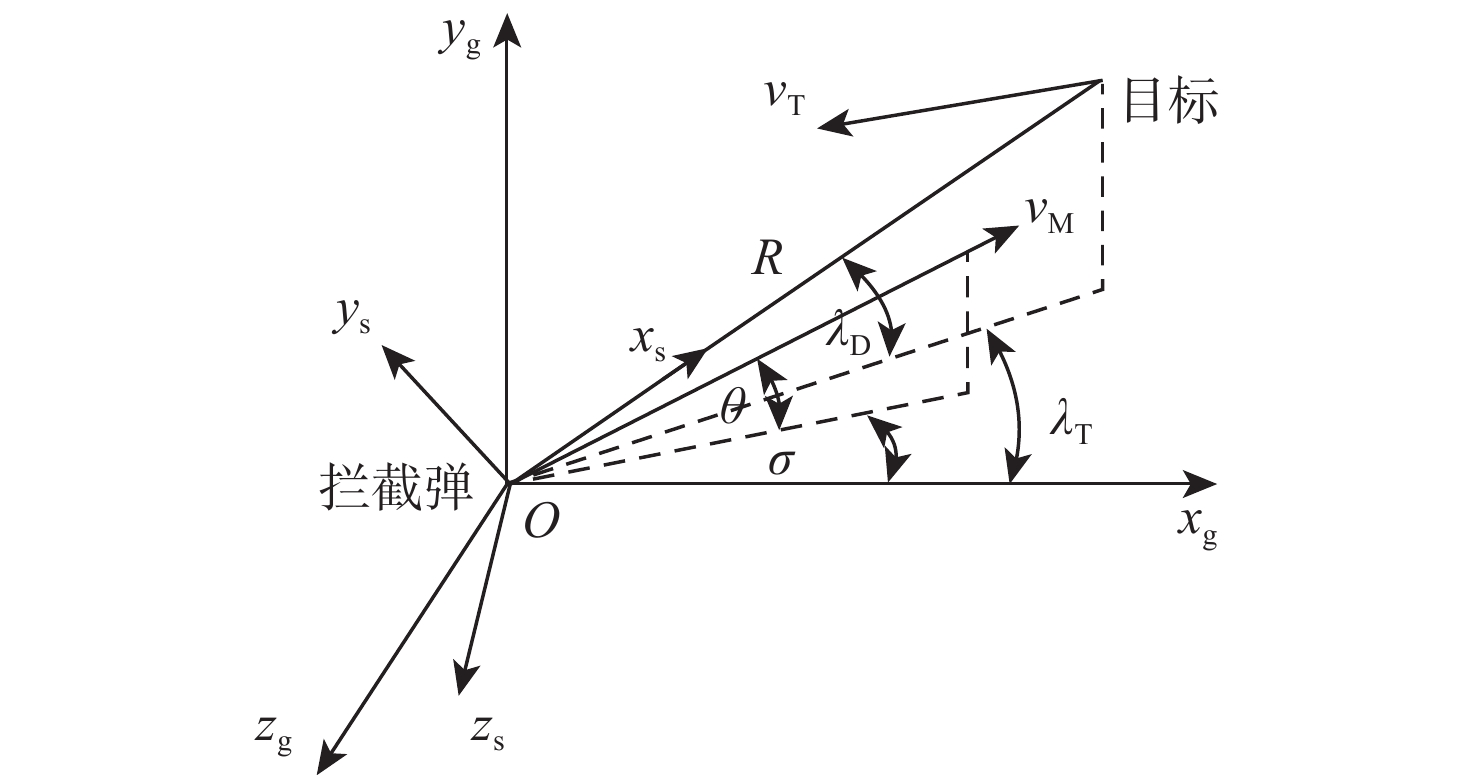
Deep reinforcement learning intelligent guidance for intercepting high maneuvering targets
-
摘要:
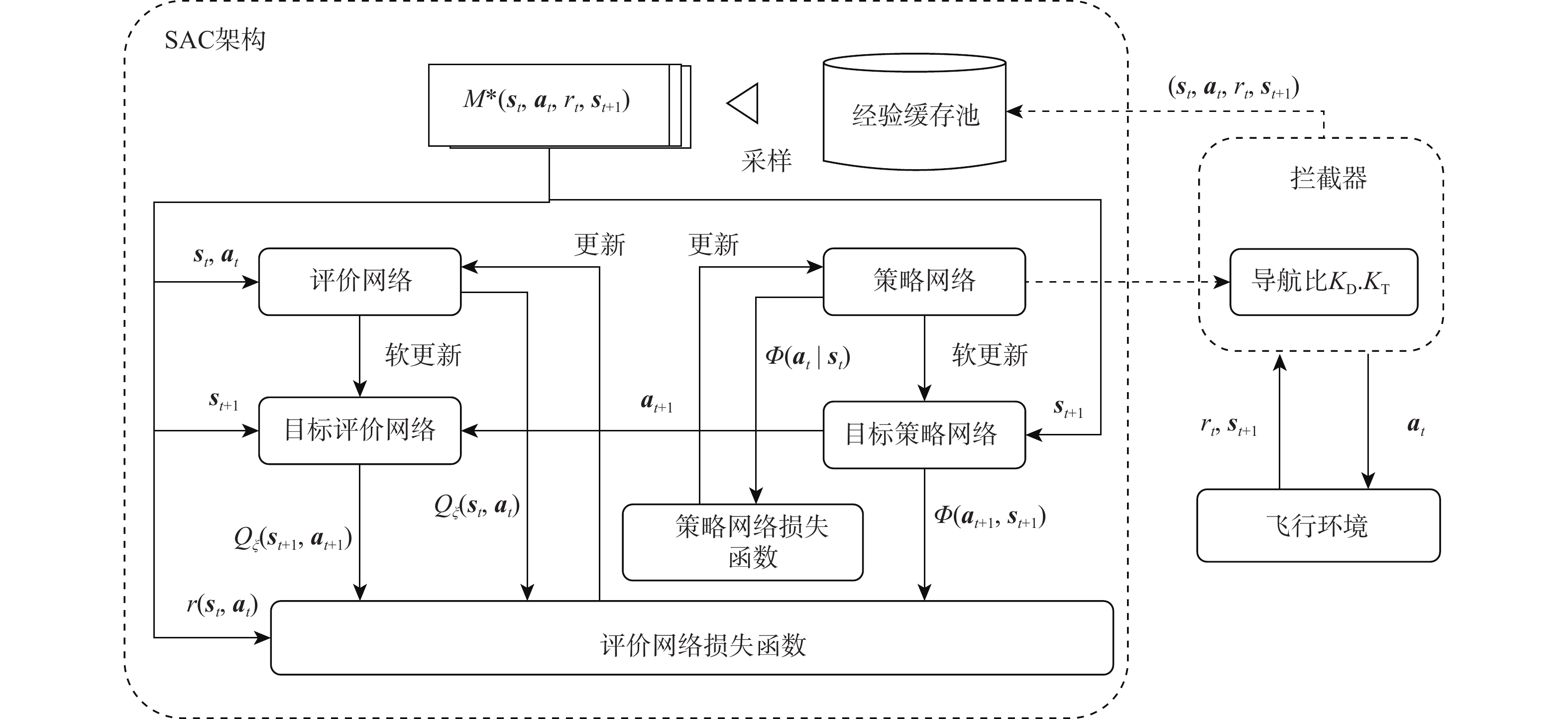
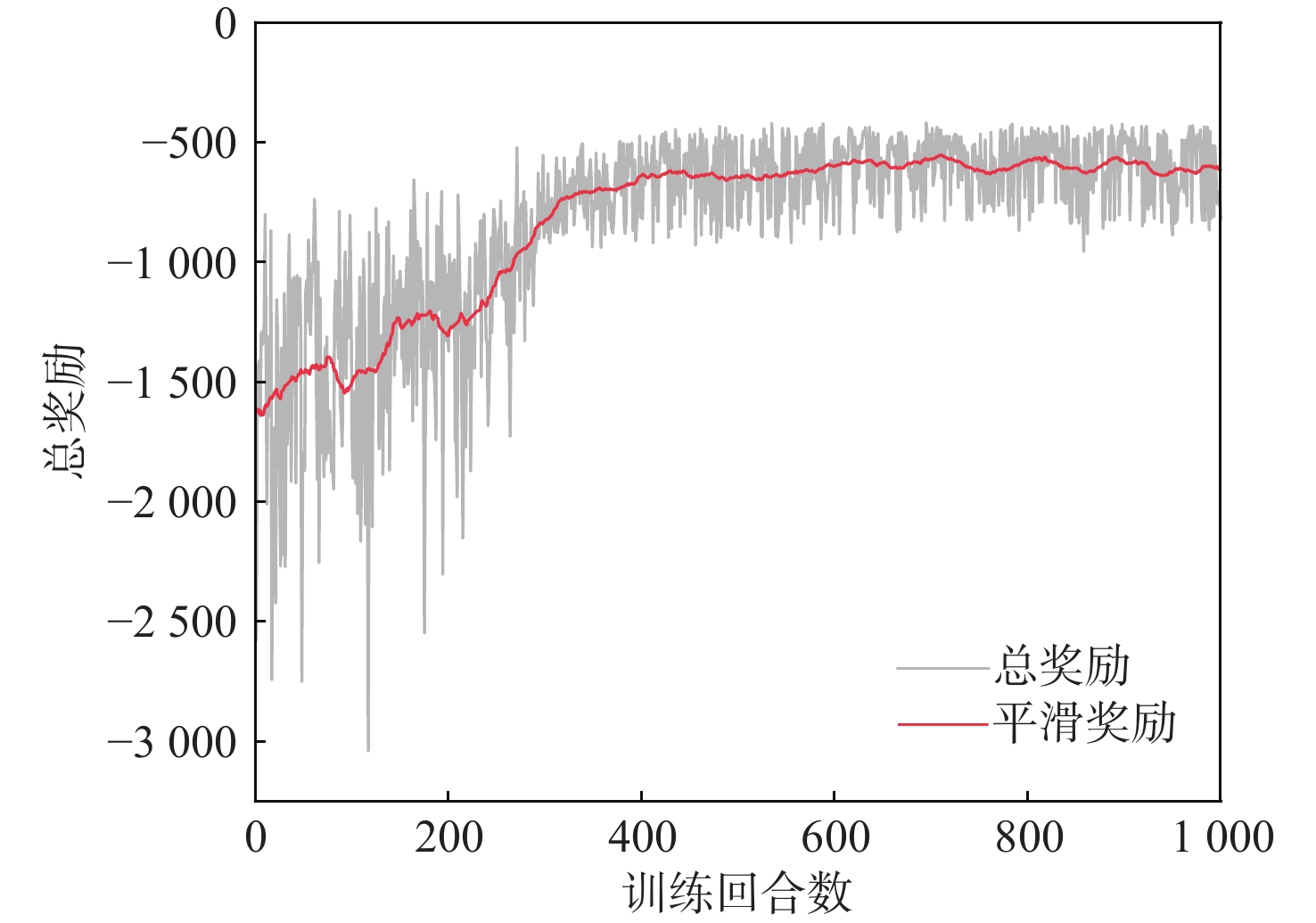
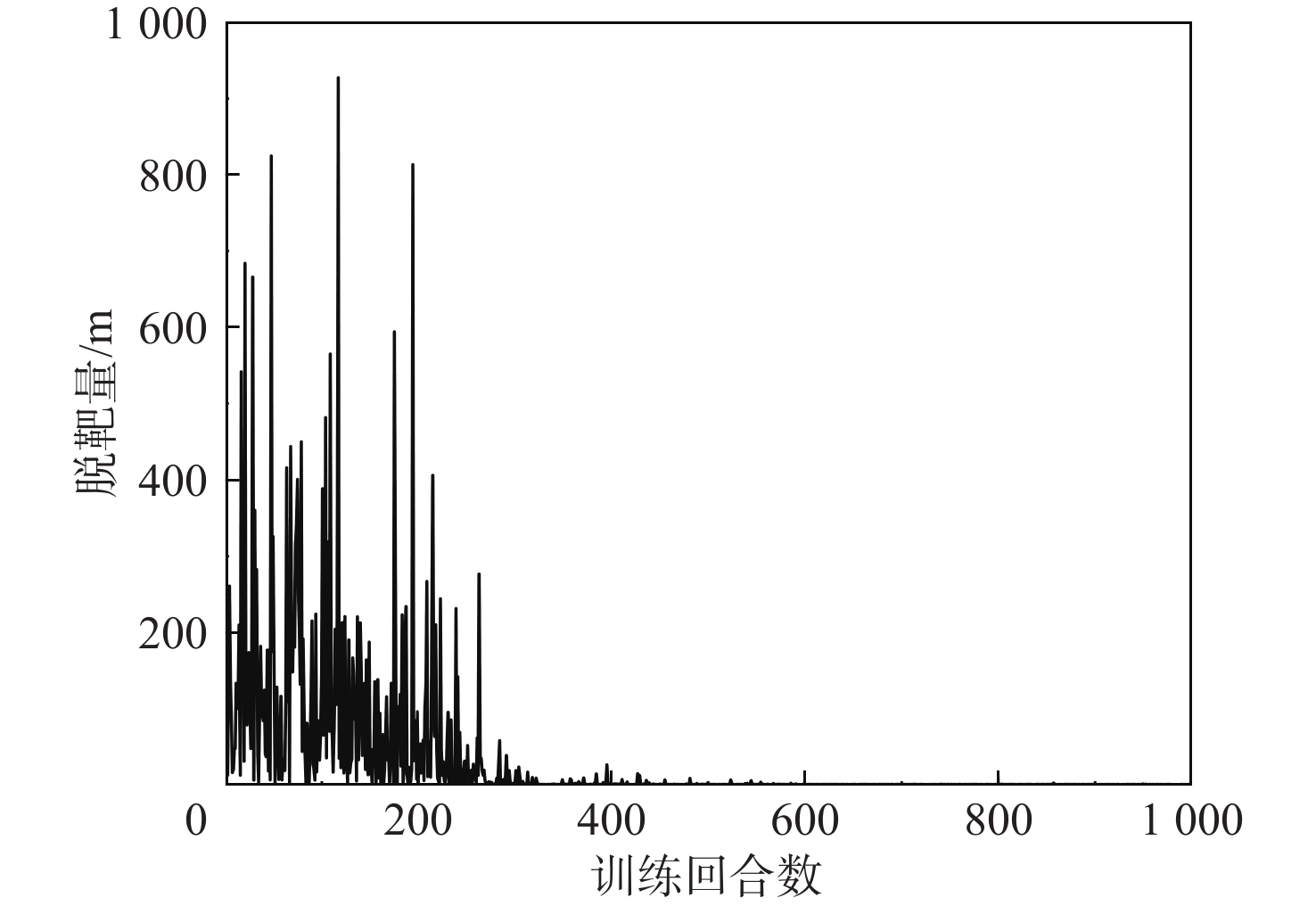
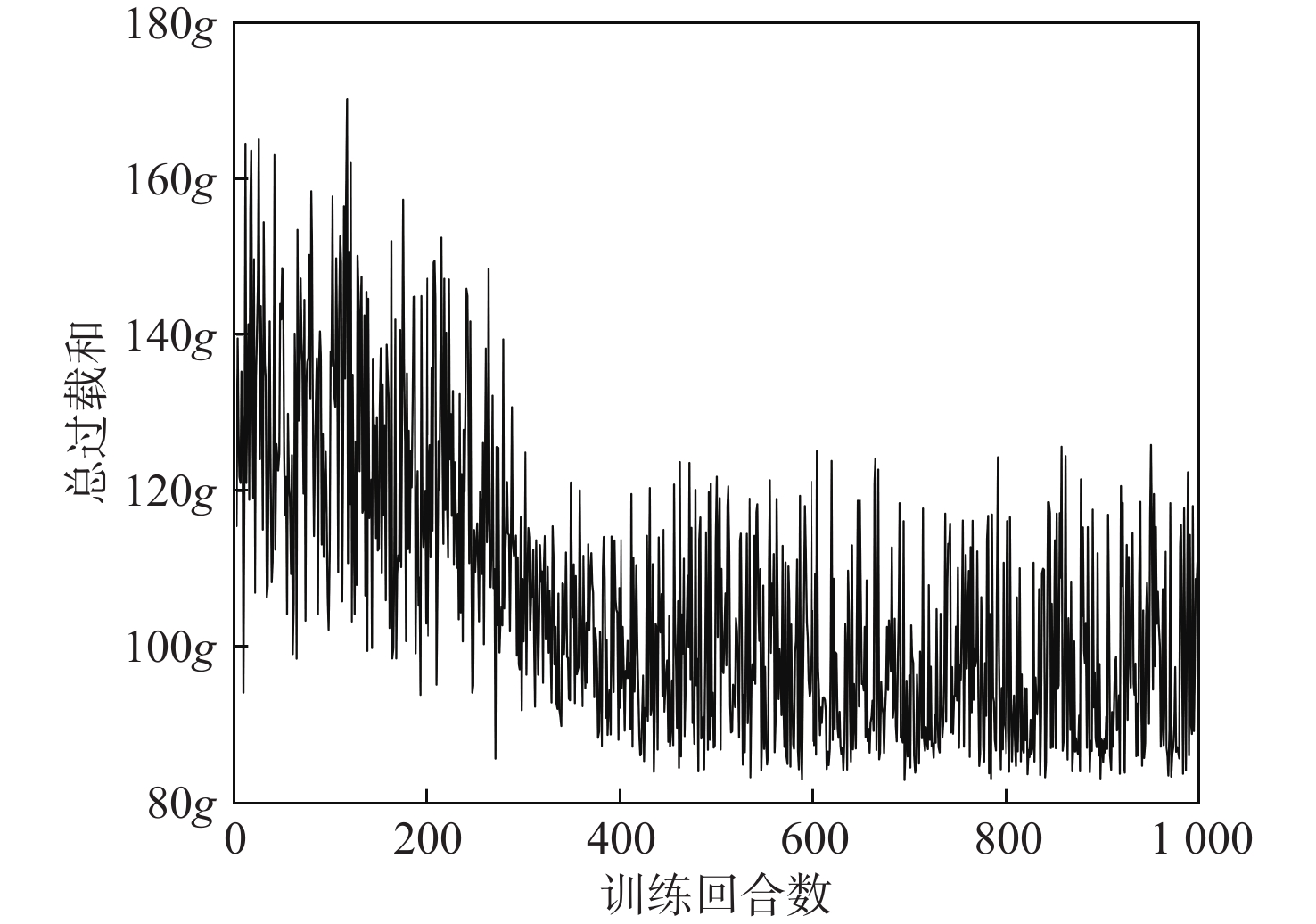
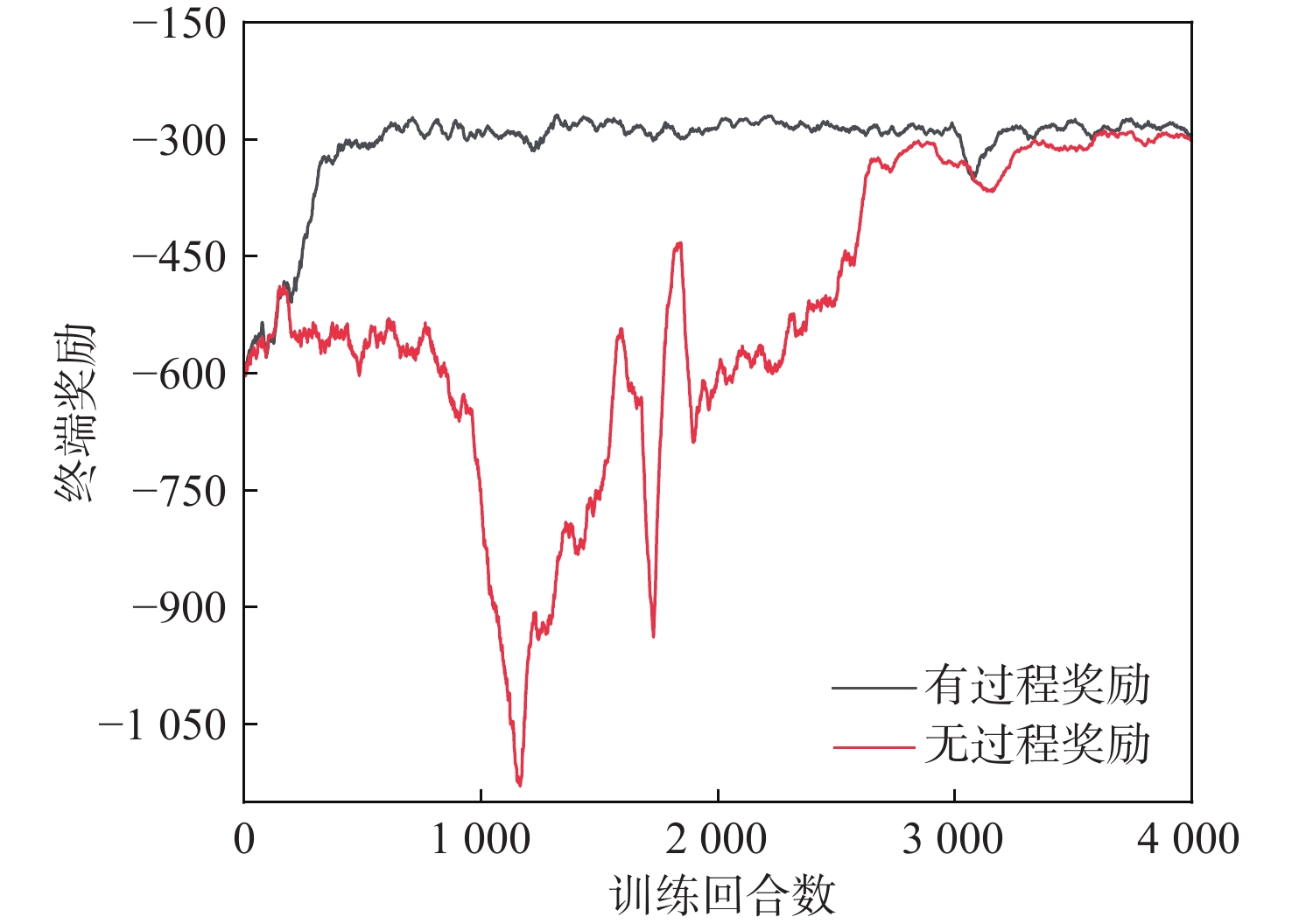
针对固定系数比例导引律在拦截高机动目标时脱靶量与能量损耗过大的问题,提出一种基于深度强化学习智能调参的自适应比例导引律。建立基于实时飞行状态的状态空间和包含横向、纵向导航比的动作空间,以及综合不同状态的奖励函数模型;在奖励函数的模型设计中,引入预测-校正方法,以提高动作评估的准确性;利用柔性演员-评论(SAC)算法,根据拦截器和目标的相对运动状态,训练获得综合考虑脱靶量和能量损耗的网络参数与制导参数决策系统。仿真结果表明:相较于传统比例导引律,所提制导策略可在保证低脱靶量的同时显著降低能量损耗,并且对未训练场景具有良好的适应性。
Abstract:An adaptive proportional navigation law with intelligent parameter adjustment by deep reinforcement learning is presented to address the issue of excessive miss distances and energy loss in the interception of moving targets using fixed coefficient proportional navigation law. First, a state space based on real-time flight states, an action space containing lateral and vertical gains, and a reward function model integrating different states is established. Meanwhile, a prediction-correction method is introduced to improve the accuracy of action evaluation in the model design of the reward function. Secondly, the soft actor-critic (SAC) algorithm is employed to train a network parameter and guidance parameter decision system that takes into account the miss distances and energy loss according to the relative motion states of the interceptor and the target. In comparison to traditional proportional navigation guidance, the simulation results demonstrate that the guidance technique has strong adaptability and can greatly minimize energy loss while retaining low miss distances.
-
表 1 奖励函数中的权重
Table 1. Weights in the reward function
−0.1 −0.5 −1 −4 100 表 2 策略网络和评价网络结构
Table 2. Architecture of the policy and critic networks
网络层 节关数 策略网络 评价网络 输入层 7 9 隐藏层1 256 256 隐藏层 2 256 256 隐藏层3 256 256 输出层 4 1 表 3 超参数设置
Table 3. Hyperparameters setting
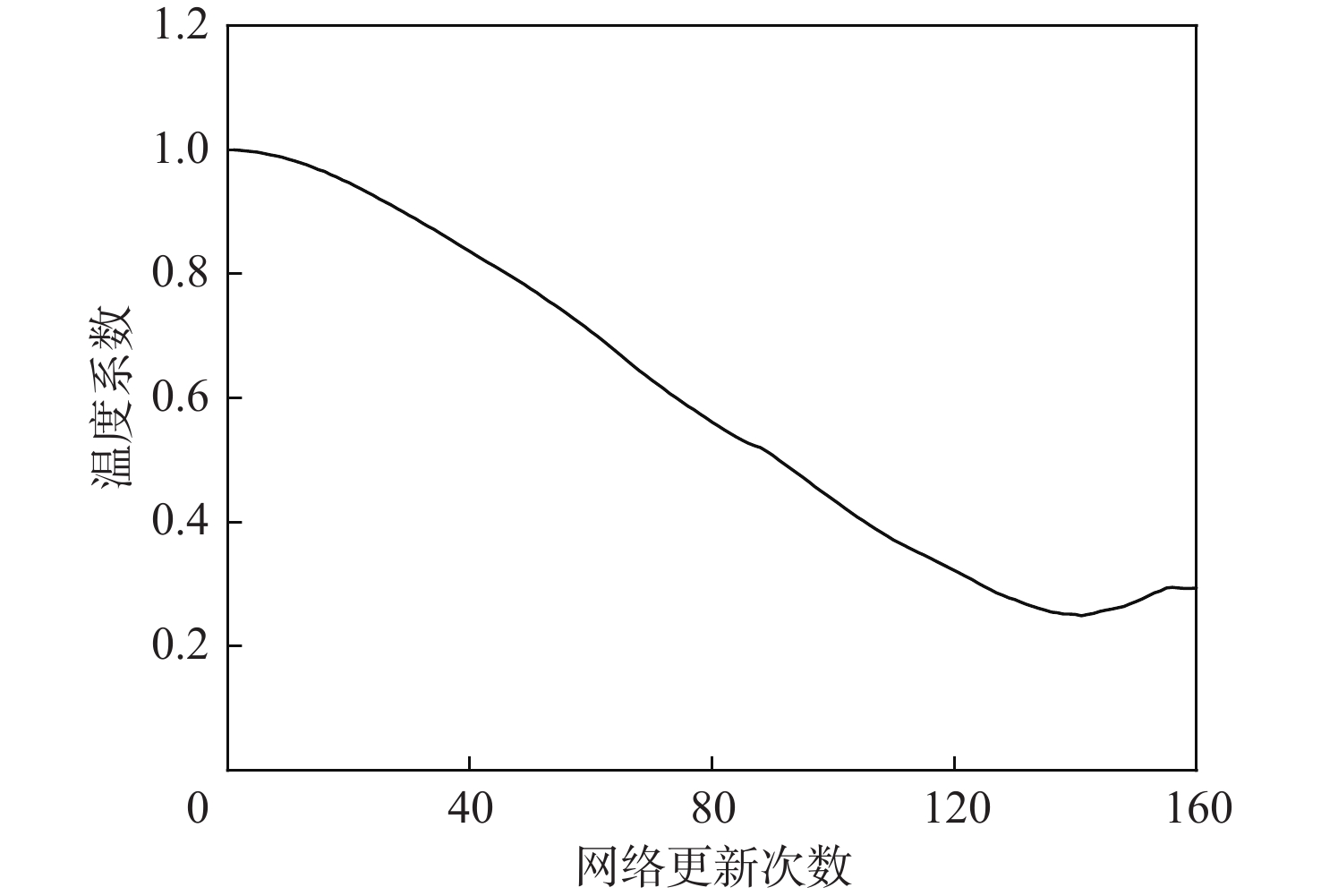
超参数 数值 经验缓存池大小 5000 采样经验大小 128 折扣率 0.98 学习率 0.0005 期望熵 −5 温度系数 1 平滑常数 0.005 网络更新频率 60 表 4 不同制导律下的终端参数
Table 4. Terminal parameters with different guidance laws
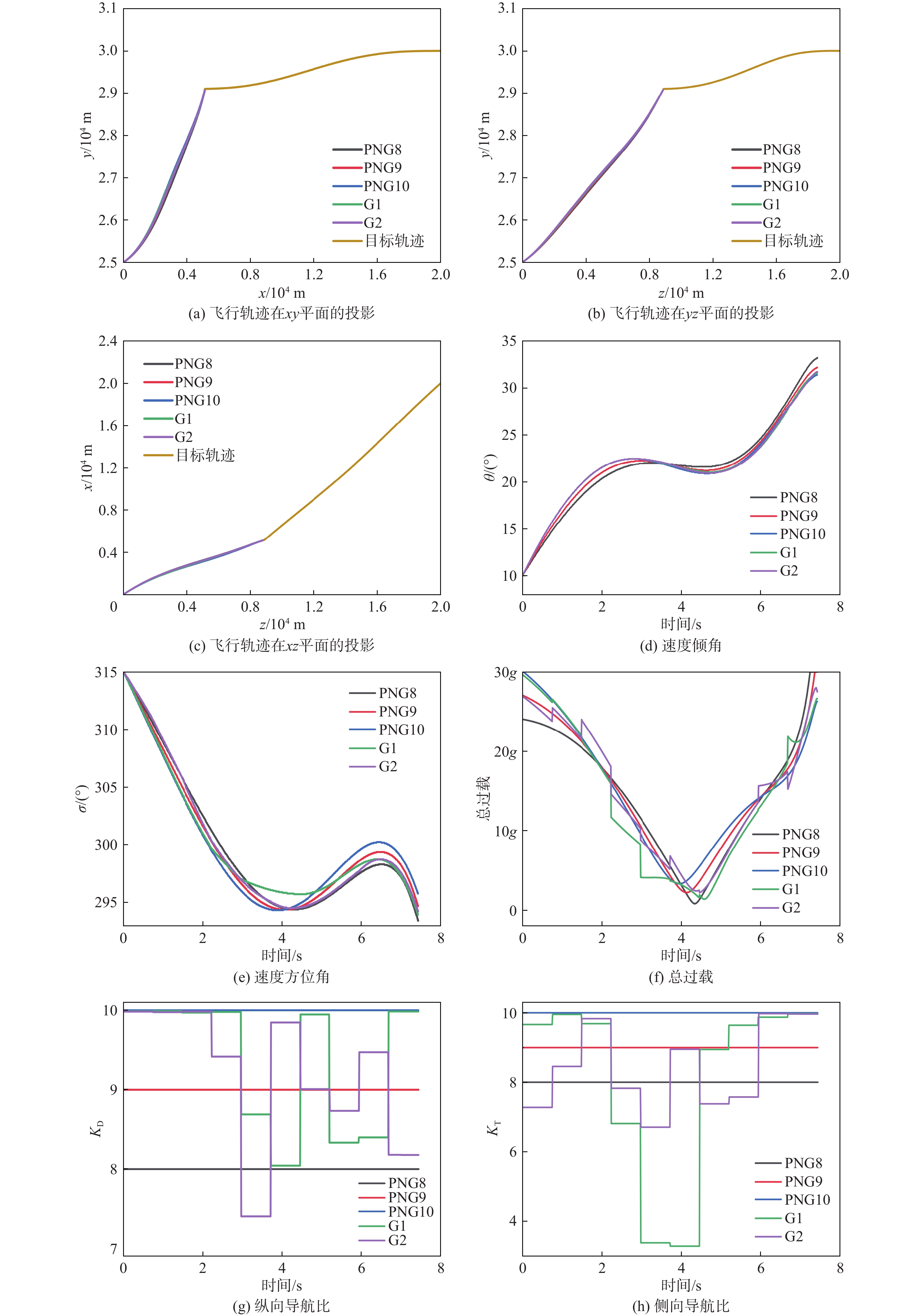
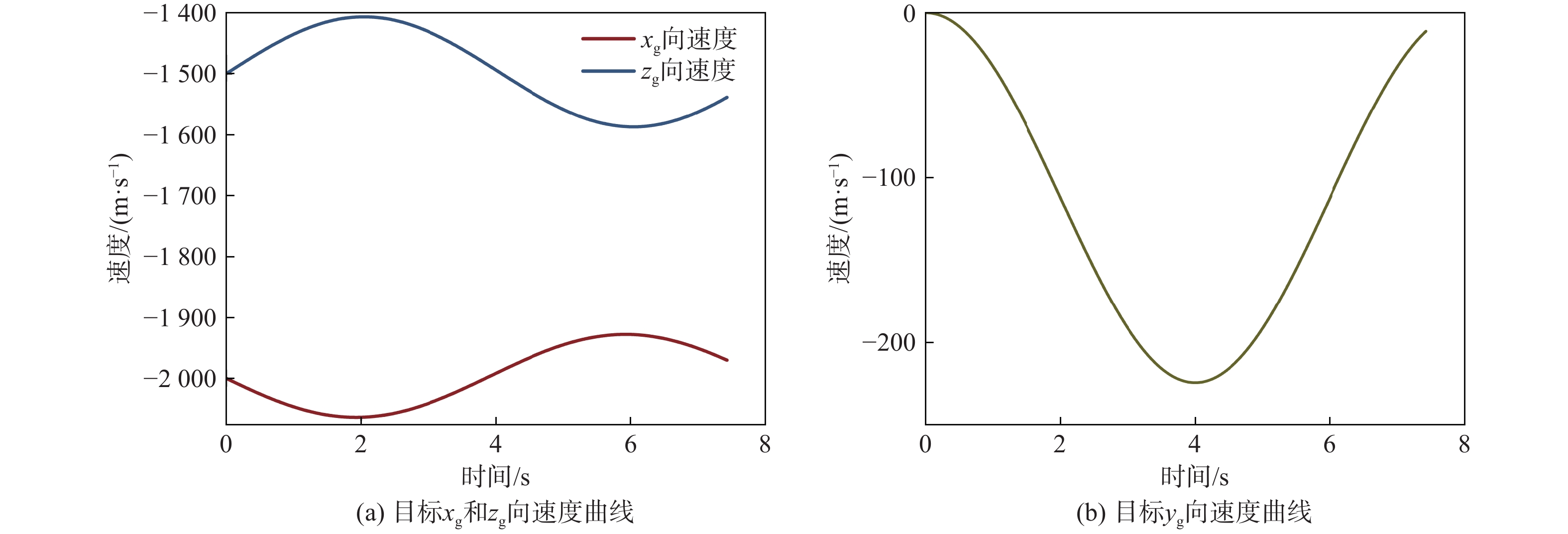
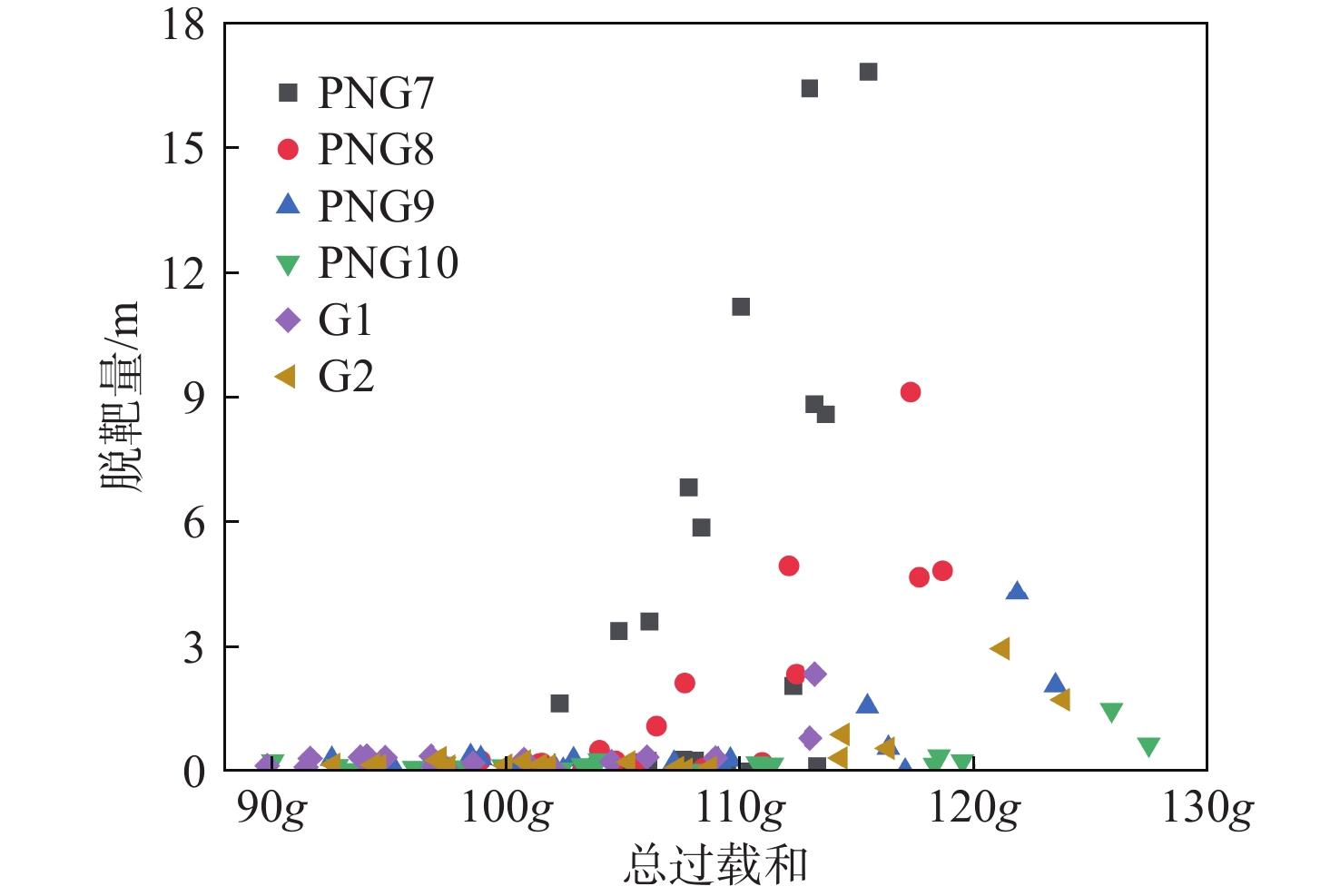
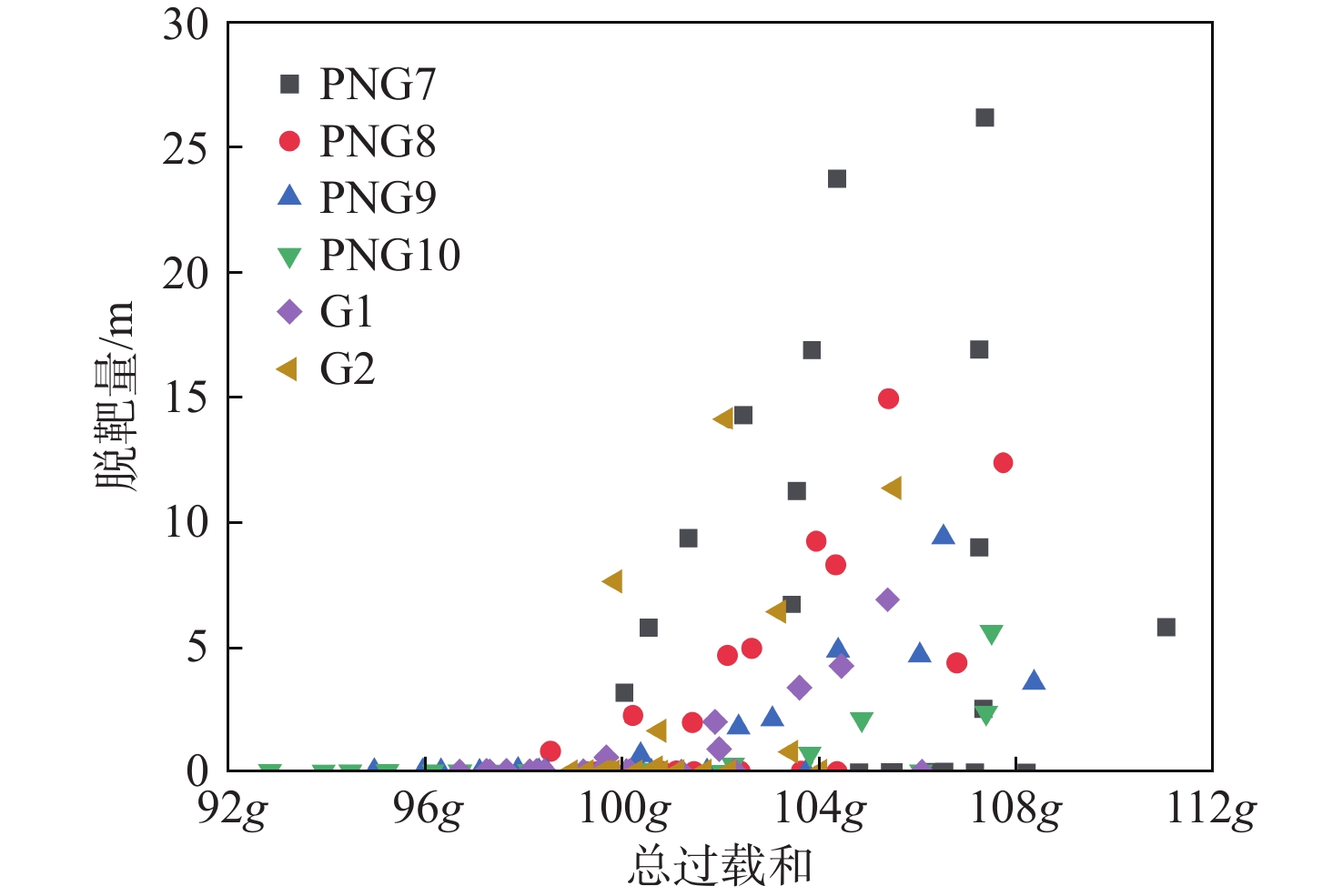
制导律 飞行时间/s 脱靶量/m 总过载和 PNG7 7.439 2.974 107.217 g PNG8 7.435 0.780 108.323 g PNG9 7.432 0.263 110.543 g PNG10 7.430 0.113 112.474 g G1 7.430 0.220 103.326 g G2 7.432 0.248 109.267 g 表 5 未训练场景下蒙特卡罗结果统计
Table 5. Monte Carlo results statistics in untrained scenarios
制导律 脱靶量均值/m 脱靶量方差/m2 总过载和均值 PNG7 1.793 2.504 105.983 g PNG8 0.380 0.116 104.811 g PNG9 0.192 0.012 105.242 g PNG10 0.187 0.012 106.297 g G1 0.189 0.012 98.532 g G2 0.188 0.018 104.906 g -
[1] 纪毅, 王伟, 张宏岩, 等. 面向高机动目标拦截任务的空空导弹制导方法综述[J]. 航空兵器, 2022, 29(6): 15-25. doi: 10.12132/ISSN.1673-5048.2022.0119JI Y, WANG W, ZHANG H Y, et al. A survey on guidance method of air-to-air missiles facing high maneuvering targets[J]. Aero Weaponry, 2022, 29(6): 15-25(in Chinese). doi: 10.12132/ISSN.1673-5048.2022.0119 [2] JEON I S, KARPENKO M, LEE J I. Connections between proportional navigation and terminal velocity maximization guidance[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2020, 43(2): 383-388. doi: 10.2514/1.G004672 [3] ZHANG B L, ZHOU D. Optimal predictive sliding-mode guidance law for intercepting near-space hypersonic maneuvering target[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2022, 35(4): 320-331. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2021.05.021 [4] LI C D, WANG J, HE S M, et al. Collision-geometry-based generalized optimal impact angle guidance for various missile and target motions[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2020, 106: 106204. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.106204 [5] YE D, SHI M M, SUN Z W. Satellite proximate interception vector guidance based on differential games[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2018, 31(6): 1352-1361. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2018.03.012 [6] 郭建国, 胡冠杰, 郭宗易, 等. 天线罩误差下基于ADP的机动目标拦截制导策略[J]. 宇航学报, 2022, 43(7): 911-920. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2022.07.007GUO J G, HU G J, GUO Z Y, et al. ADP-based guidance strategy for maneuvering target interception under radome errors[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2022, 43(7): 911-920(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2022.07.007 [7] 白志会, 黎克波, 苏文山, 等. 现实真比例导引拦截任意机动目标捕获区域[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(8): 323947.BAI Z H, LI K B, SU W S, et al. Capture region of RTPN guidance law against arbitrarily maneuvering targets[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(8): 323947(in Chinese). [8] 王荣刚, 唐硕. 拦截高速运动目标广义相对偏置比例制导律[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2019, 37(4): 682-690. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2019.04.006WANG R G, TANG S. Intercepting higher-speed targets using generalized relative biased proportional navigation[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2019, 37(4): 682-690(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2019.04.006 [9] LI K B, SHIN H S, TSOURDOS A, et al. Capturability of 3D PPN against lower-speed maneuvering target for homing phase[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56(1): 711-722. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2019.2938601 [10] SHIN H S, LI K B. An improvement in three-dimensional pure proportional navigation guidance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2021, 57(5): 3004-3014. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2021.3067656 [11] 张秦浩, 敖百强, 张秦雪. Q-learning强化学习制导律[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2020, 42(2): 414-419. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.02.21ZHANG Q H, AO B Q, ZHANG Q X. Reinforcement learning guidance law of Q-learning[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(2): 414-419(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.02.21 [12] 李庆波, 李芳, 董瑞星, 等. 利用强化学习开展比例导引律的导航比设计[J]. 兵工学报, 2022, 43(12): 3040-3047. doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2021.0631LI Q B, LI F, DONG R X, et al. Navigation ratio design of proportional navigation law using reinforcement learning[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2022, 43(12): 3040-3047(in Chinese). doi: 10.12382/bgxb.2021.0631 [13] 邱潇颀, 高长生, 荆武兴. 拦截大气层内机动目标的深度强化学习制导律[J]. 宇航学报, 2022, 43(5): 685-695. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2022.05.013QIU X Q, GAO C S, JING W X. Deep reinforcement learning guidance law for intercepting endo-atmospheric maneuvering targets[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2022, 43(5): 685-695(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2022.05.013 [14] CHEN W X, GAO C S, JING W X. Proximal policy optimization guidance algorithm for intercepting near-space maneuvering targets[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2023, 132: 108031. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2022.108031 [15] HE S M, SHIN H S, TSOURDOS A. Computational missile guidance: a deep reinforcement learning approach[J]. Journal of Aerospace Information Systems, 2021, 18(8): 571-582. doi: 10.2514/1.I010970 [16] GAUDET B, FURFARO R, LINARES R. Reinforcement learning for angle-only intercept guidance of maneuvering targets[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2020, 99: 105746. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2020.105746 [17] HAARNOJA T, ZHOU A, ABBEEL P, et al. Soft actor-critic: off-policy maximum entropy deep reinforcement learning with a stochastic actor[C]//Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning. Stockholm: PMLR, 2018, 80: 1861-1870. [18] HAARNOJA T, ZHOU A, HARTIKAINEN K, et al. Soft actor-critic algorithms and applications[EB/OL]. (2019-01-29)[2023-06-01]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1812.05905v2. -







 下载:
下载: