Model predictive current control of asynchronous motor in rolling mill based on sliding mode theory
-
摘要:
小型热连轧机异步传动电机具有生产效率高、操作简单等特点,但由于其经常处于高温、高压、粉尘等恶劣的工作环境中,对控制器的抗干扰性要求较高。针对小型热连轧机异步传动电机,结合滑模控制理论和模型预测控制,运用自适应滑模控制器(ASMC)作为转速外环控制器,且运用全阶滑模磁链观测器(SMRFO)观测并计算转子磁链,设计控制系统。仿真结果表明:该系统能够有效地控制小型热连轧机异步传动电机,相较于传统的模型预测电流控制系统,其响应速度和精度得到显著提升;当电机负载转矩突变时,该系统能够快速重新追踪给定速度,进一步提升抗干扰能力。
Abstract:The asynchronous drive motor of small-scale hot-rolling mills has the characteristics of high production efficiency and straightforward operation. However, due to its often harsh working environment with high temperature, high pressure, and dust, the performance requirements for the controller are higher. To use an adaptive sliding mode controller (ASMC) as the outer speed control loop and to calculate and observe the rotor flux via a full-order sliding mode flux observer (SMRFO), this article focuses on the asynchronous drive motor of small-scale hot-rolling mills. Sliding mode control theory and model predictive control are combined in this design process. According to simulation studies, this system may considerably increase response speed and accuracy over conventional model predictive current control systems while also efficiently controlling the asynchronous drive motor of small-scale hot-rolling mills. The system's capacity to promptly retrace the specified speed in the event of abrupt variations in the motor load torque enhances its anti-interference performance.
-
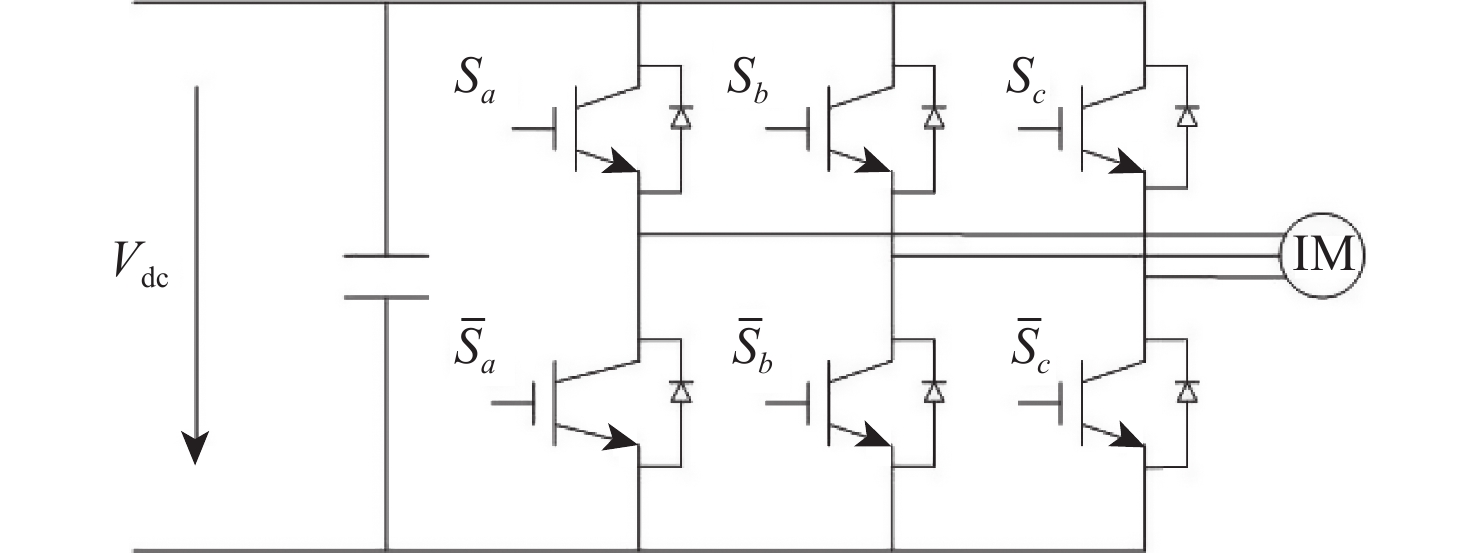
表 1 开关状态和电压矢量对应
Table 1. Switch state and voltage vector correspondence table
电压 SaSbSc |us|=usα+jusβ u0 000 0 u1 001 23Vdc u2 010 13Vdc+j√33Vdc u3 011 −13Vdc+j√33Vdc u4 100 −23Vdc u5 101 −13Vdc−j√33Vdc u6 110 13Vdc−j√33Vdc u7 111 0 表 2 热连轧机异步传动电机参数
Table 2. Parameters of asynchronous drive motor for hot rolling mill
参数 数值 参数 数值 功率/kW 12 定子电阻/Ω 1.2 额定电压/V 380 转子电阻/Ω 1 额定频率/Hz 50 定子电感/H 0.175 转动惯量/(kg·m2) 0.062 转子电感/H 0.175 极对数 1 互感/H 0.17 -
[1] 韩东颖, 时培明, 赵东伟. 板带轧机机电传动系统参激非线性扭振鲁棒控制研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2016, 35(12): 1-6.HAN D Y, SHI P M, ZHAO D W. Study on robust control for parametric excitation nonlinear torsional vibration of a strip-rolling mill’s mechanical and electrical drive system[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2016, 35(12): 1-6(in Chinese). [2] 王晓明. 轧机主传动交流调速系统的发展及应用[J]. 山东冶金, 2019, 41(1): 79-80.WANG X M. Development and application of alternating current governor system of mill main drive[J]. Shandong Metallurgy, 2019, 41(1): 79-80(in Chinese). [3] GOUWS R. Efficiency analysis of an induction motor with direct torque and flux control at a hot rolling mill[C]//Proceedings of the 8th Conference on the Industrial and Commercial Use of Energy. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 64-68. [4] 张希扬. 基于无差拍控制的异步电机模型预测转矩控制研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019.ZHANG X Y. Research of model predictive torque control for asynchronous motor based on dead-beat control[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019(in Chinese). [5] 刘涛, 方毅芳, 吴达远. 基于负载转矩观测器的热连轧电机模型预测控制[J]. 制造技术与机床, 2023(3): 121-129.LIU T, FANG Y F, WU D Y. Model predictive torque control of hot strip mill motor based on load torque observer[J]. Manufacturing Technology & Machine Tool, 2023(3): 121-129(in Chinese). [6] 宁博文, 周凤星, 卢少武. 基于高阶滑模速度控制器的异步电机模型预测转矩控制[J]. 控制与决策, 2021, 36(4): 953-958.NING B W, ZHOU F X, LU S W. A model predictive torque control for induction motor based on high order sliding mode speed controller[J]. Control and Decision, 2021, 36(4): 953-958(in Chinese). [7] 丁鲜花. 永磁同步电动机减小电流静差的低复杂度三矢量模型预测电流控制[D]. 西安: 西安理工大学, 2019.DING X H. Three-vector based low-complexity model predic-tive current control with reduced steady-state current error for permanent magnet synchronous motor[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [8] 滕青芳, 靳宇星, 李姝湲. 基于全局快速终端滑模转速调节器的PMSM驱动系统模型预测电流控制[J]. 信息与控制, 2017, 46(6): 691-697.TENG Q F, JIN Y X, LI S Y. Model predictive current control for PMSM drive system based on global fast terminal sliding mode speed regulator[J]. Information and Control, 2017, 46(6): 691-697(in Chinese). [9] 侯利民, 王怀震, 李勇, 等. 带扰动补偿的离散滑模SPMSM模型预测电流控制[J]. 信息与控制, 2017, 46(2): 186-191.HOU L M, WANG H Z, LI Y, et al. Model predictive current control for SPMSM using discrete sliding-mode control based on disturbance compensation[J]. Information and Control, 2017, 46(2): 186-191(in Chinese). [10] SAEED S, ZHAO W X, WANG H N, et al. Fault-tolerant deadbeat model predictive current control for a five-phase PMSM with improved SVPWM[J]. Chinese Journal of Electrical Engineering, 2021, 7(3): 111-123. doi: 10.23919/CJEE.2021.000030 [11] ZHANG Y Q, YIN Z G, LI W, et al. Adaptive sliding-mode-based speed control in finite control set model predictive torque control for induction motors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2021, 36(7): 8076-8087. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2020.3042181 [12] NIU F, CHEN X, HUANG S P, et al. Model predictive current control with adaptive-adjusting timescales for PMSMs[J]. CES Transactions on Electrical Machines and Systems, 2021, 5(2): 108-117. doi: 10.30941/CESTEMS.2021.00014 [13] SUN Z, DENG Y T, WANG J L, et al. Finite control set model-free predictive current control of PMSM with two voltage vectors based on ultralocal model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Electronics, 2023, 38(1): 776-788. doi: 10.1109/TPEL.2022.3198990 [14] 张亚林. 异步电机模型预测电流控制技术研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2012.ZHANG Y L. Research on model predictive current control of inverter supplied induction machine[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2012(in Chinese). [15] 窦智峰, 晋玉祥, 金楠, 等. 高效电压源逆变器双矢量模型预测电流控制[J]. 电机与控制学报, 2020, 24(6): 153-162.DOU Z F, JIN Y X, JIN N, et al. Two-vector-based mode predictive current control for voltage source inverter with high efficiency[J]. Electric Machines and Control, 2020, 24(6): 153-162(in Chinese). [16] YIN Z G, LI L T, GAO F T, et al. Robust current predicted control of permanent magnet synchronous motors based on novel sliding model observer[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 4th International Electrical and Energy Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 1-6. [17] LIN C K, YU J T, FU L C, et al. Model-based predictive current control for four-switch three-phase inverter-fed IPMSM with an adaptive backstepping complementary PI sliding-mode position controller[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2012: 1042-1047. [18] SUN X D, LI T, ZHU Z, et al. Speed sensorless model predictive current control based on finite position set for PMSHM drives[J]. IEEE Transactions on Transportation Electrification, 2021, 7(4): 2743-2752. doi: 10.1109/TTE.2021.3081436 [19] TENG Q F, LUO W D. Model predictive current control for PMSM driven by three-level inverter based on fractional sliding mode speed observer[J]. Journal of Measurement Science and Instrumentation, 2020, 11(4): 358-364. -







 下载:
下载:










