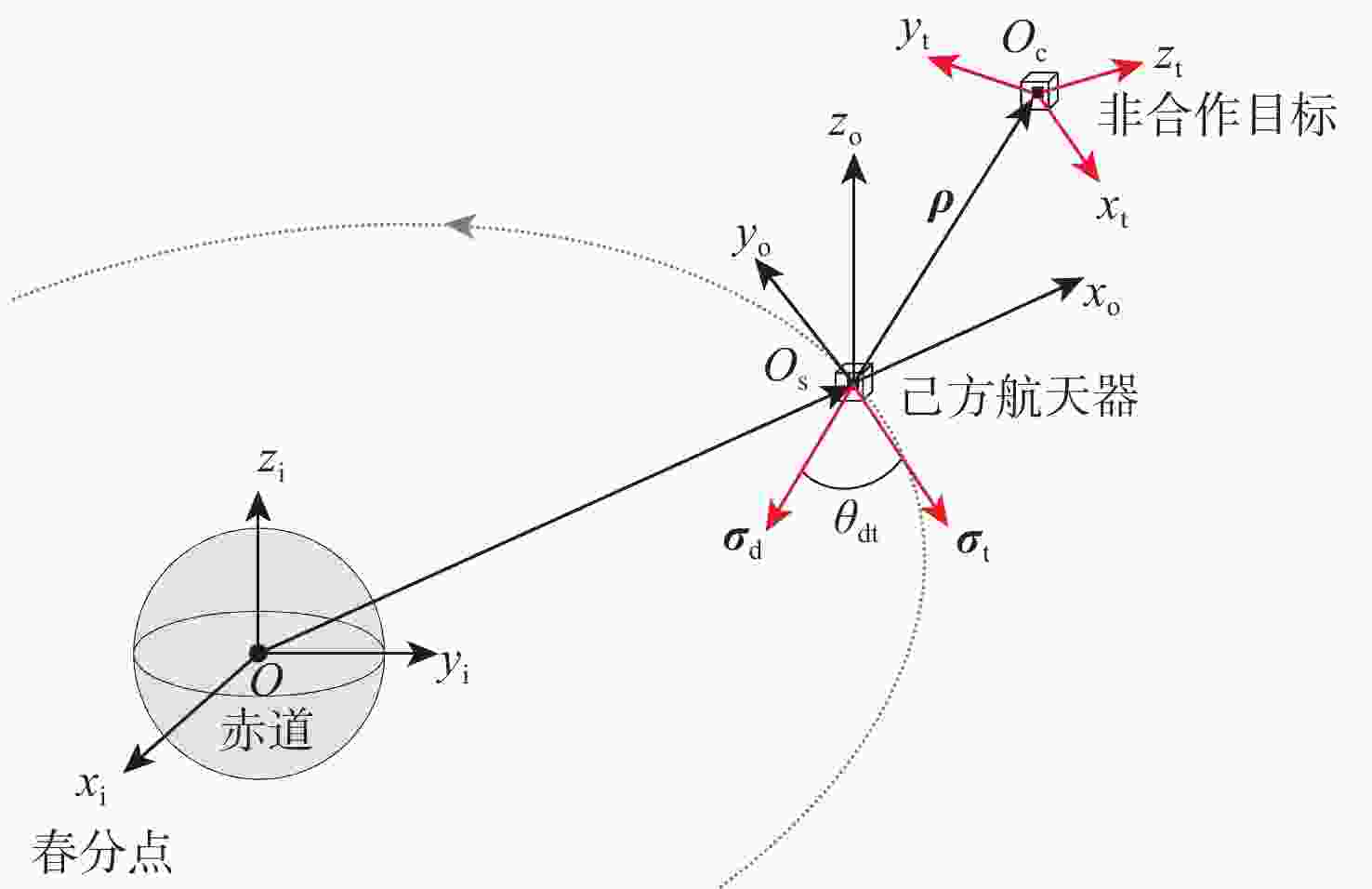
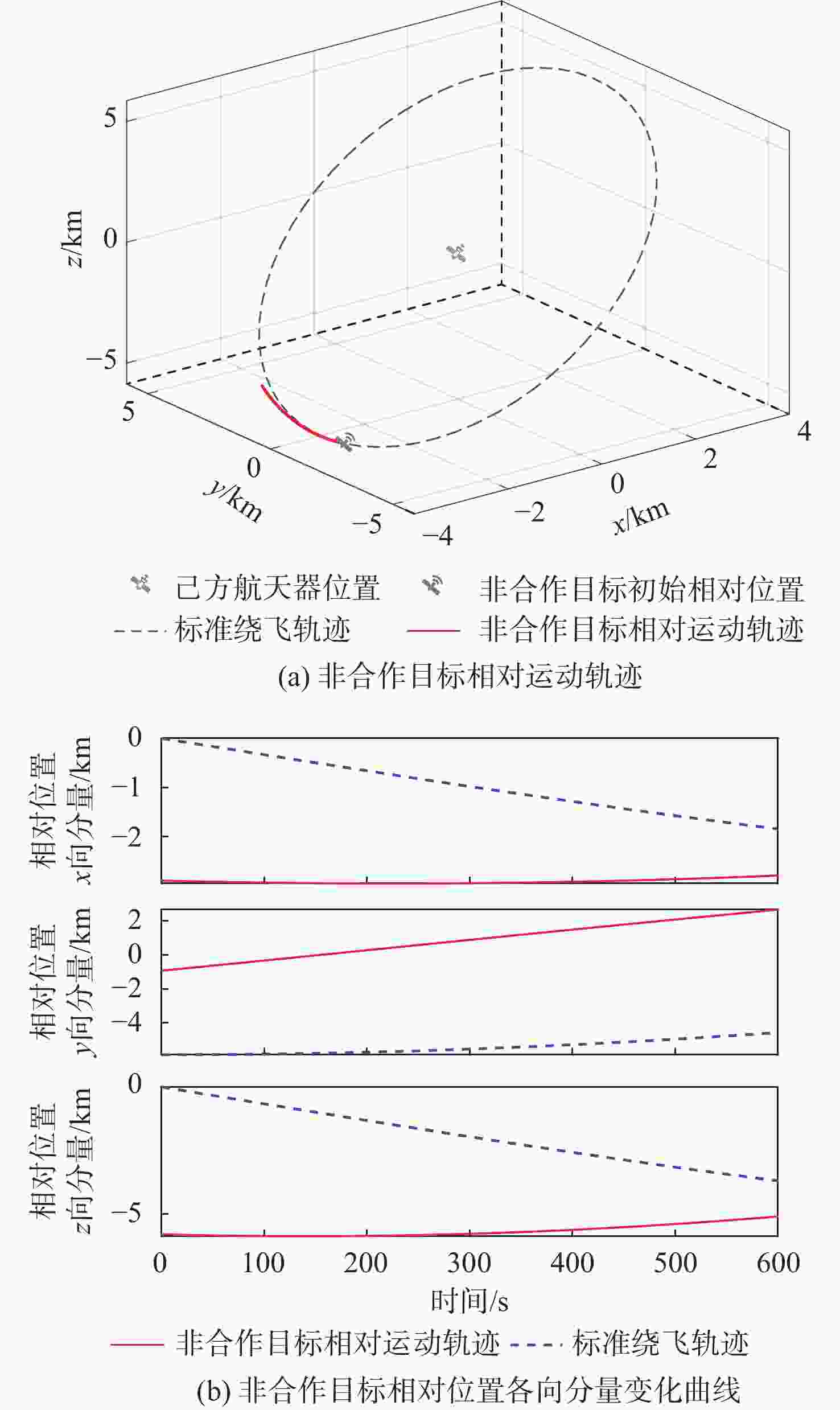
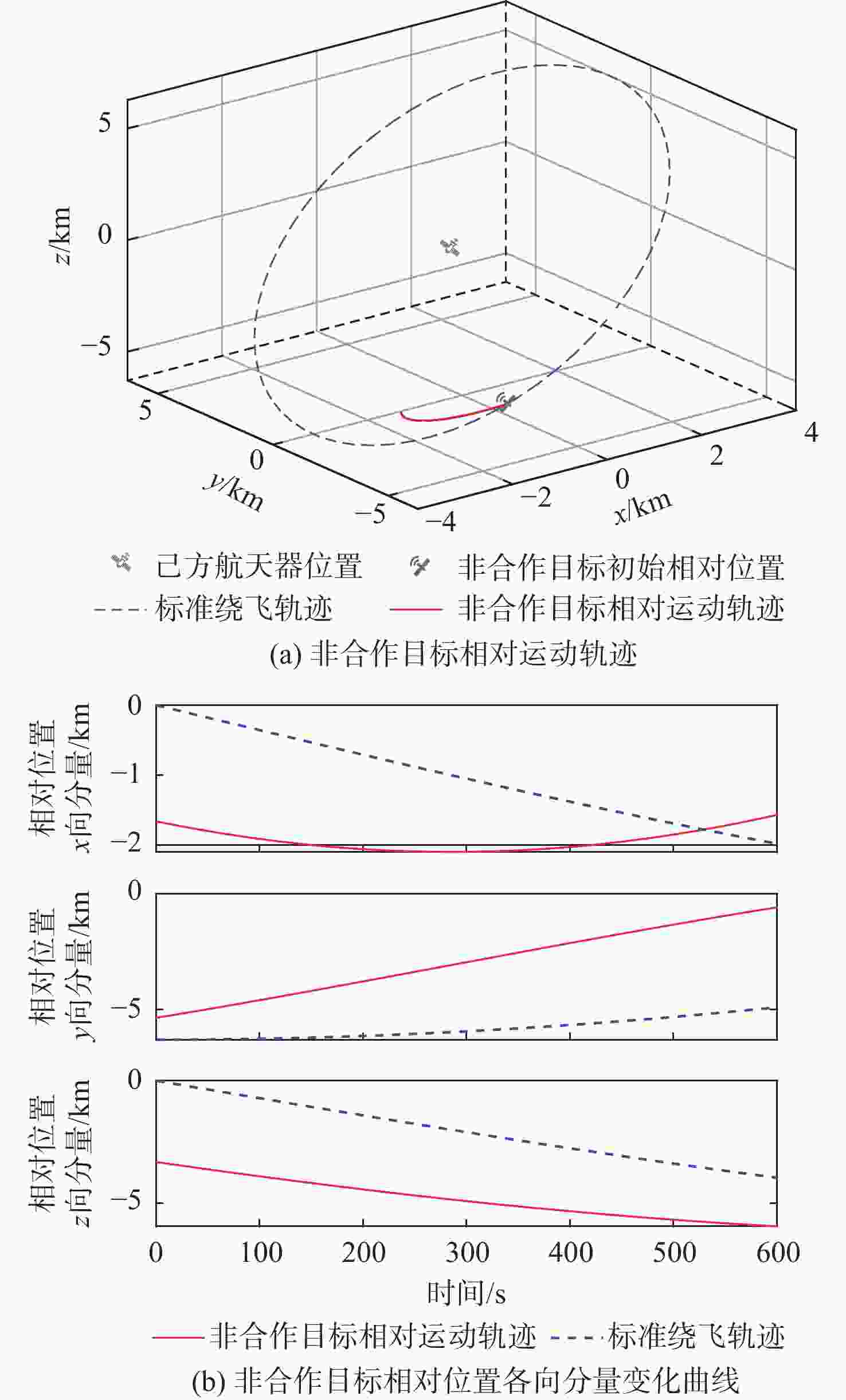
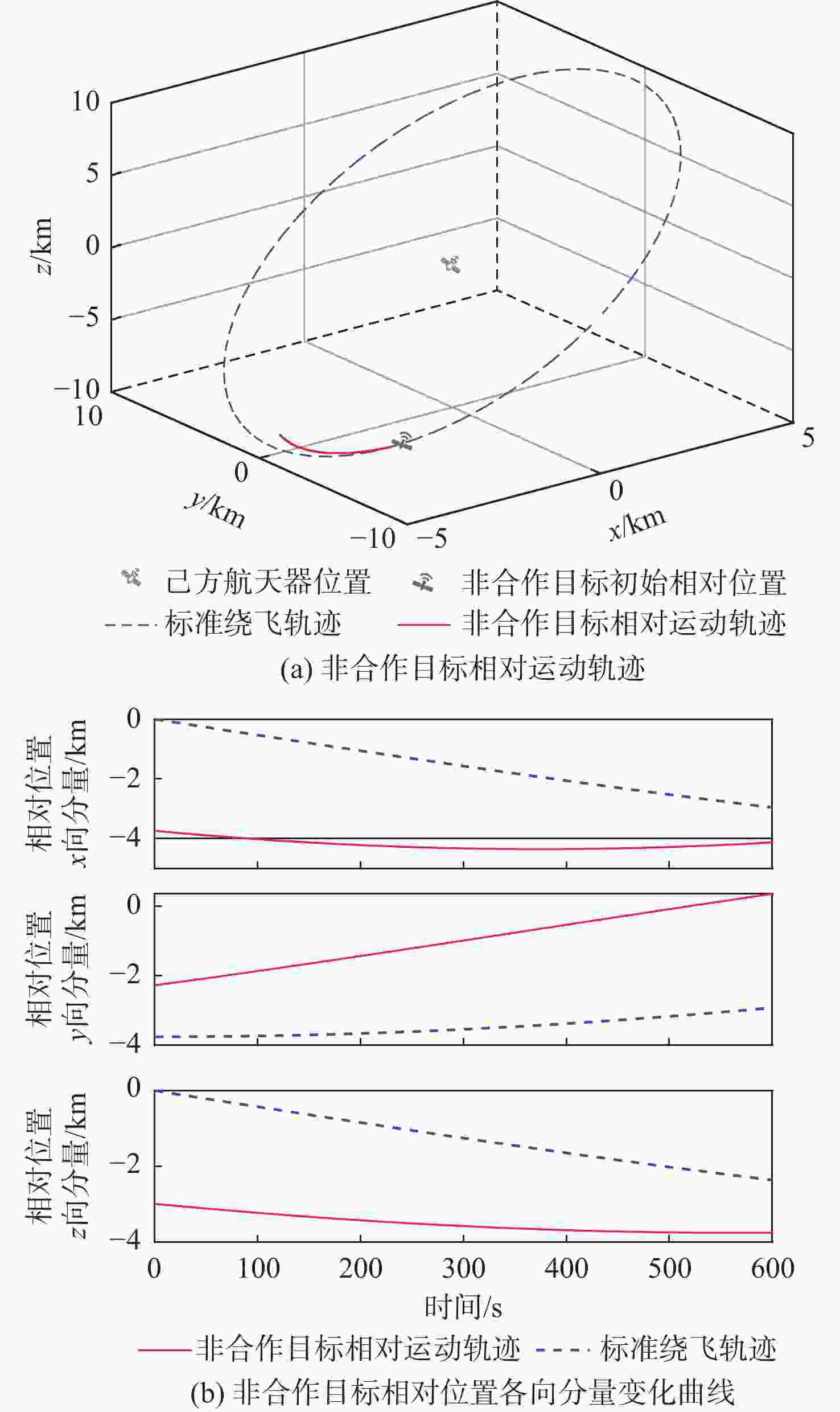
Intention recognition method for space non-cooperative targets based on fuzzy reasoning
-
摘要:
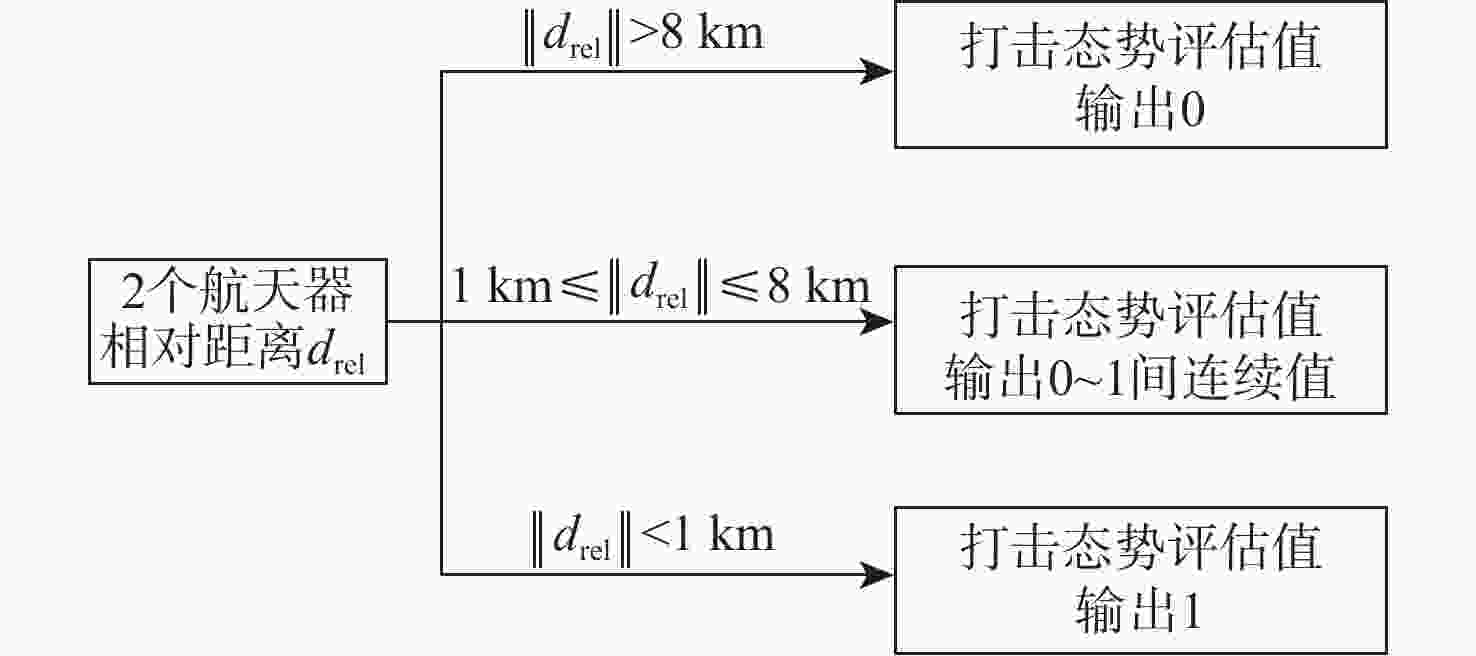
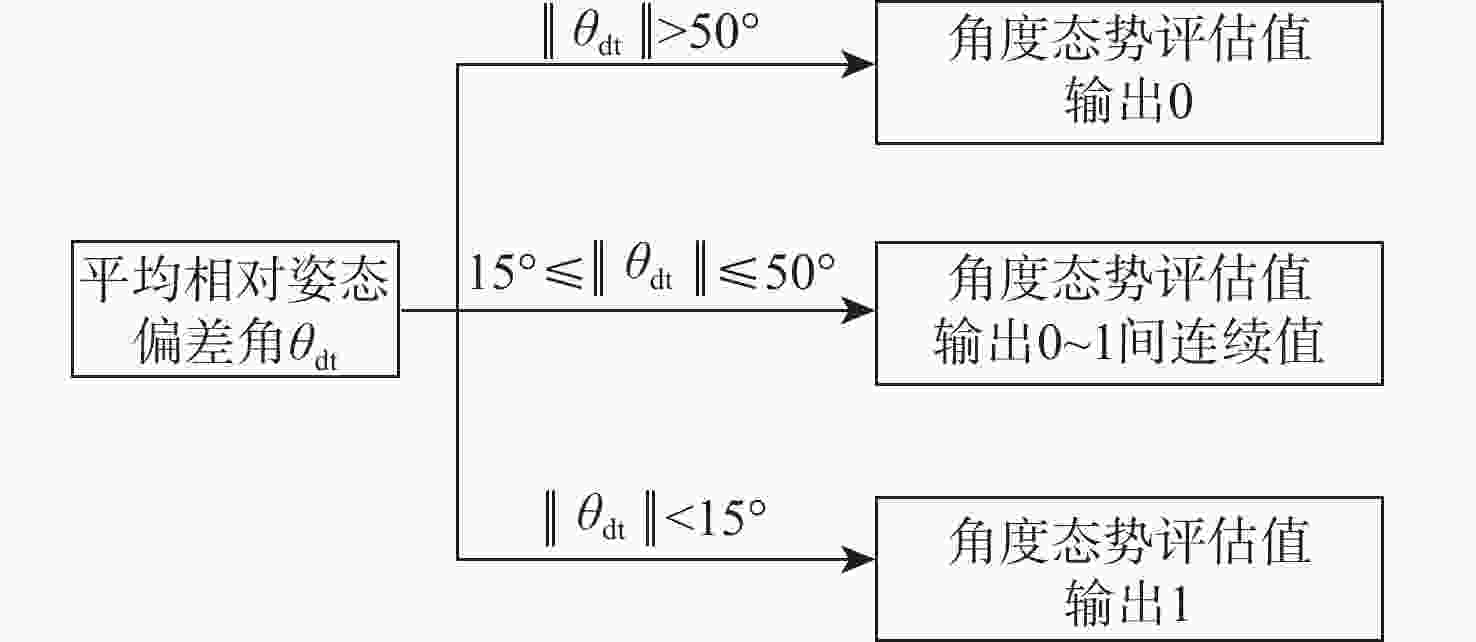
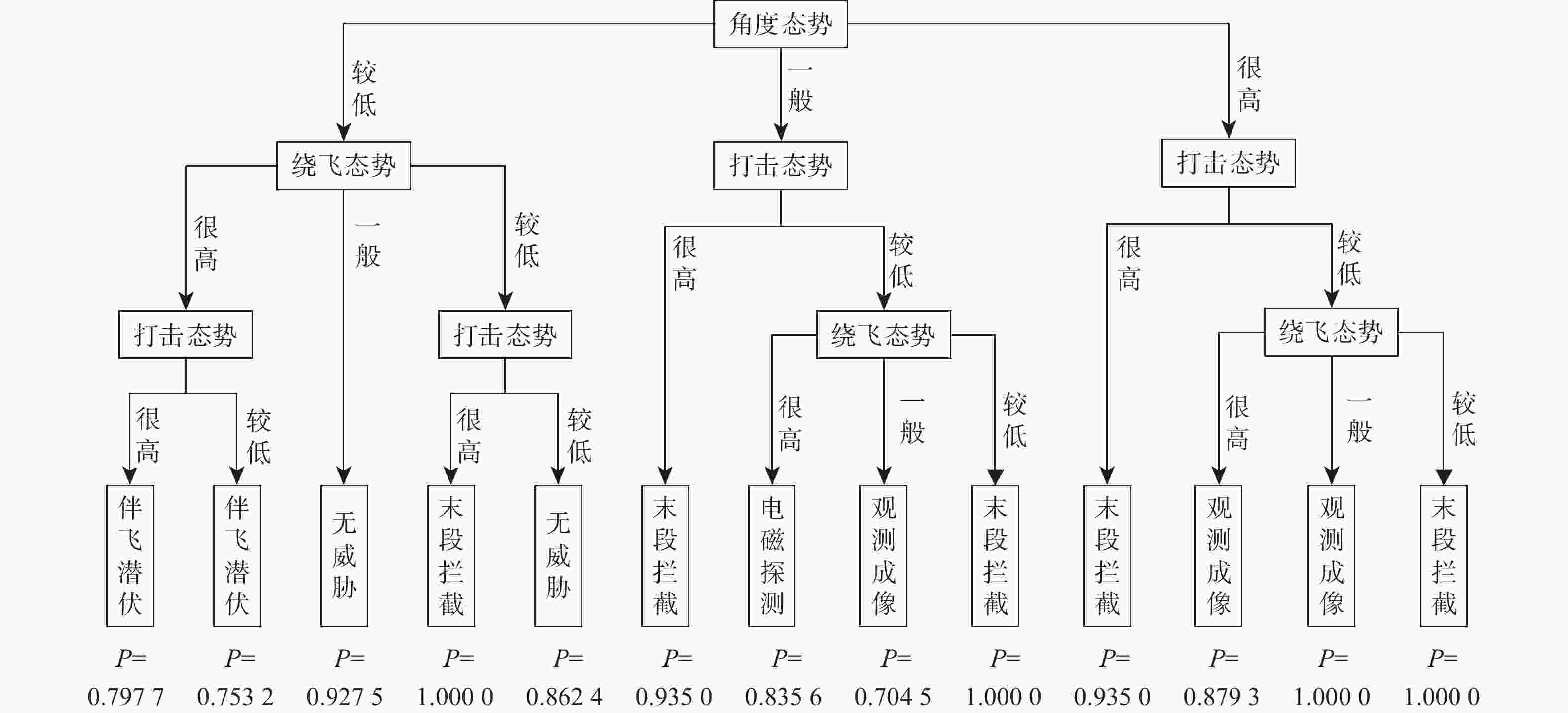
针对空间中无先验信息的非合作目标意图难以判别的问题,提出一种基于模糊推理的意图识别方法,实现对目标意图的可溯源识别。以绕飞、打击和角度3种度量作为态势评估指标,综合利用非合作目标典型抵近行为的特征信息和领域专家知识构建意图识别数据集。通过聚类分析和隶属度划分对目标意图的特征数据进行模糊化处理,采用模糊决策树算法建立意图识别模型,实现对目标意图的可溯源准确识别。用数值方法进行仿真验证,验证了所提方法的有效性,且识别准确率优于比较方法。
Abstract:Aiming at the problem of recognizing the intention of space non-cooperative targets without prior information, an intention recognition method based on fuzzy reasoning is proposed to enable traceable identification of target intentions. The three indicators “flying around”, “strike”, and “angle” are used as situation assessment metrics. An intention recognition dataset is constructed by integrating characteristic information of typical close-approach behaviors of space non-cooperative targets with domain expert knowledge. The intention-related feature data is fuzzified through cluster analysis and membership function assignment. A fuzzy decision tree algorithm is then employed to build the intention recognition model, enabling accurate and traceable identification. Finally, numerical simulations are conducted to validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, demonstrating superior recognition accuracy compared to the baseline algorithm.
-
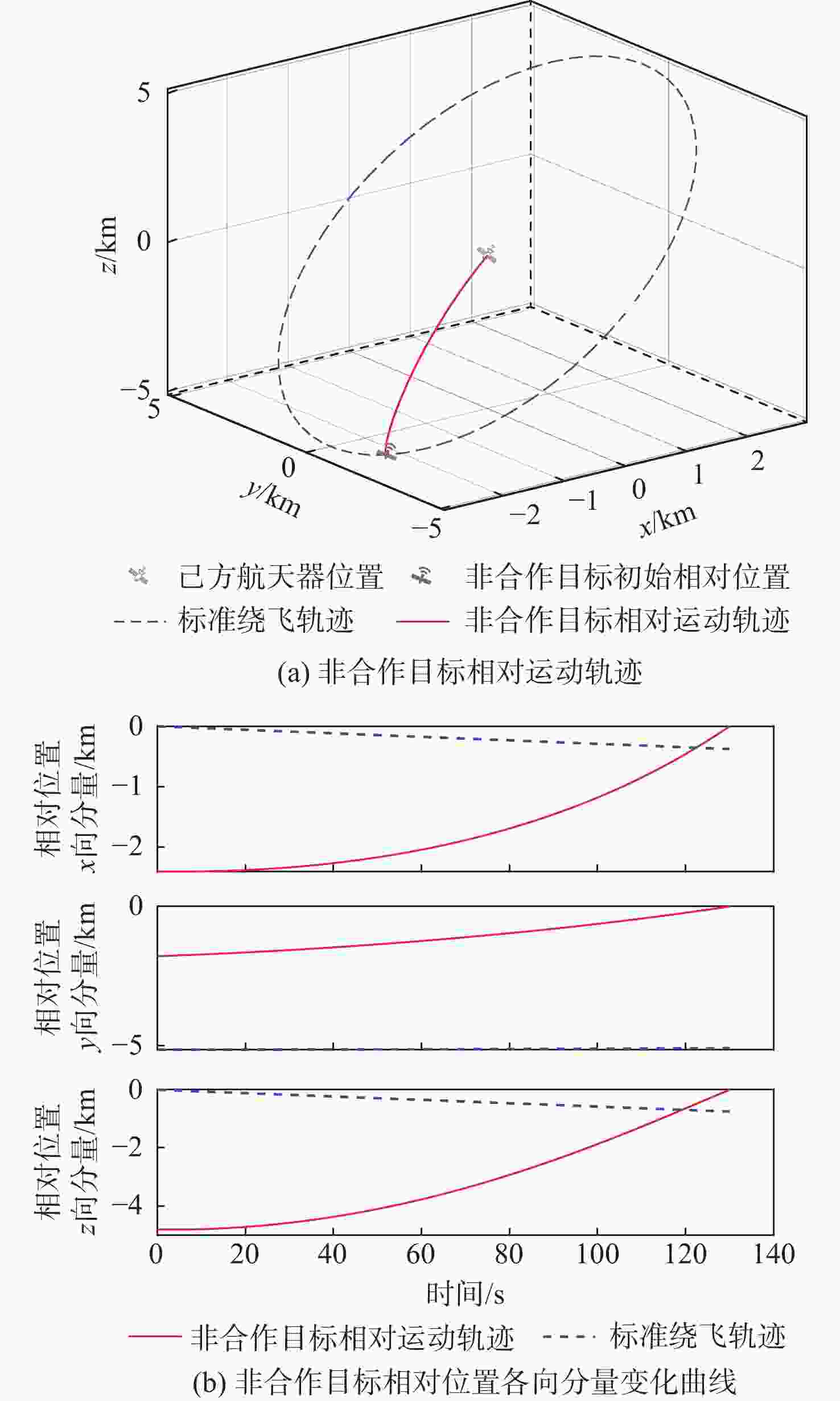
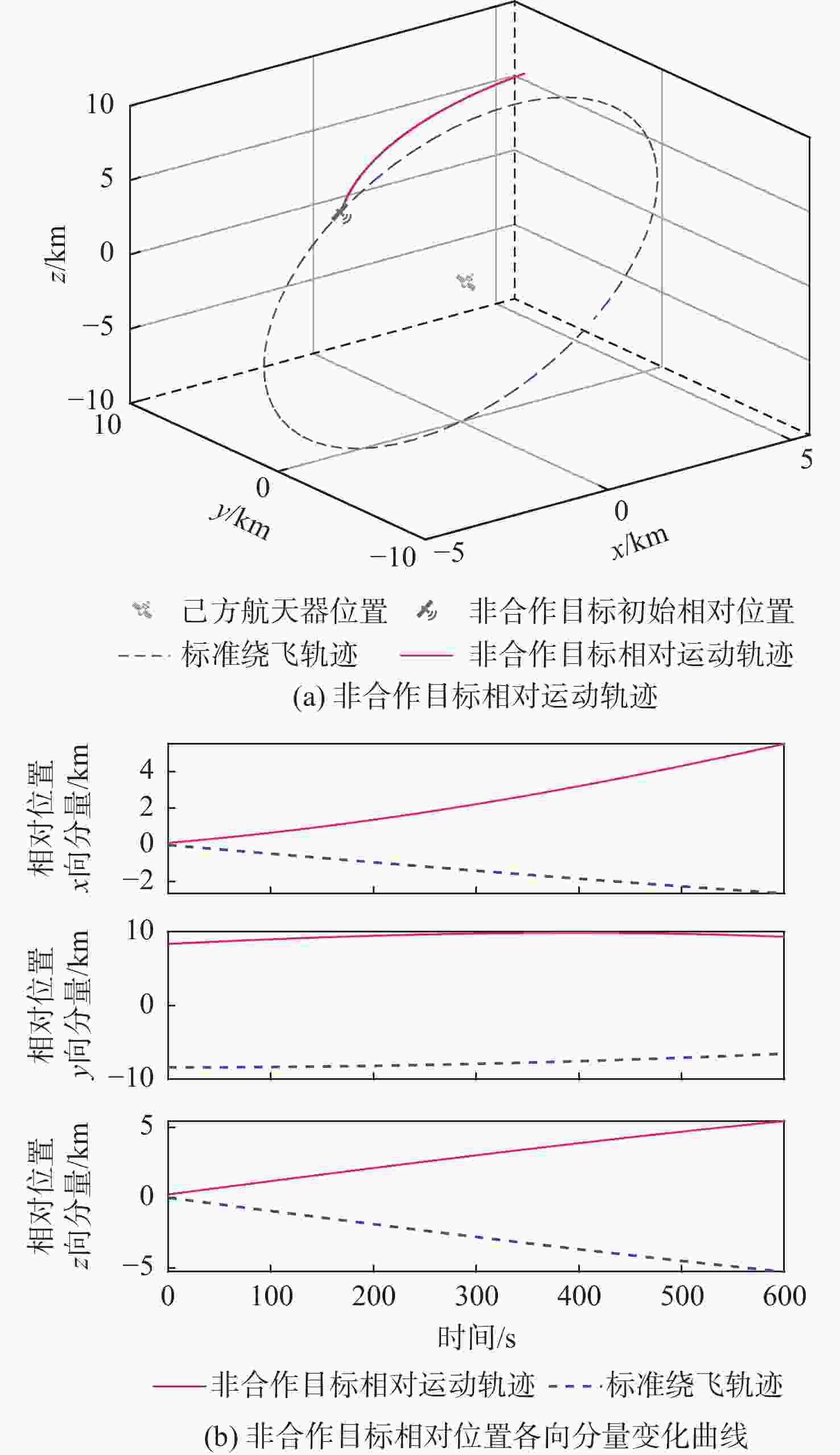
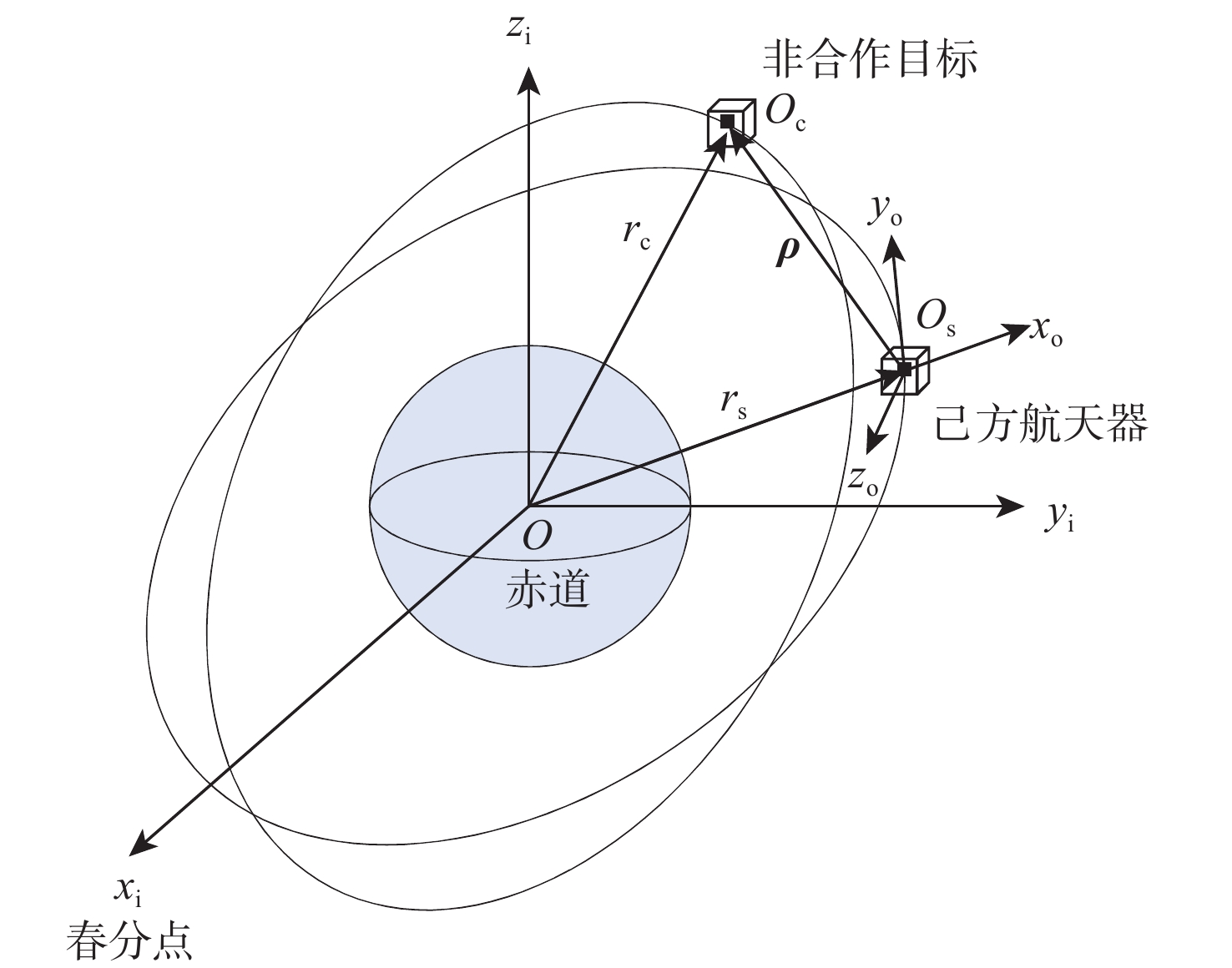
表 1 己方航天器初始轨道根数
Table 1. Initial orbit elements of our spacecraft
初始轨道根数 数值 半长轴/km 6771.00 偏心率 0 轨道倾角/(°) 41.47 升交点赤经/(°) 58.01 近地点幅角/(°) 196.64 真近点角/(°) 176.64 表 2 意图识别训练集
Table 2. Intention recognition training set
意图标签 数量 电磁探测 30 观测成像 30 伴飞潜伏 30 末段拦截 30 无威胁 30 表 3 各态势属性聚类中心点
Table 3. Clustering centers of situation attributes
态势属性 聚类中心点 名称 数值 绕飞态势 FA1 0.0262 FA2 0.2272 FA3 0.8882 角度态势 AG1 0.1182 AG2 0.6291 AG3 0.9636 打击态势 HT1 0.0226 HT2 0.8521 表 4 不同算法的意图识别性能比较
Table 4. Performance comparison of intention recognition among different algorithms
算法 决策树节点数 规则数 识别准确率/% KMFDT 21 13 93.33 ID3[21] 12 8 89.33 -
[1] ANSELMO L, PARDINI C. Analysis of the consequences in low Earth orbit of the collision between Cosmos 2251 and Iridium 33[C]//Proceedings of the 21st International Symposium on Space Flight Dynamics. Paris: Centre National D’études Spatiales, 2009: 294. [2] 刘付成, 叶立军. 基于多星编队的GEO目标巡视策略[J]. 空间控制技术与应用, 2022, 48(3): 29-38.LIU F C, YE L J. Patrol strategy of the GEO targets based on muti-satellite formation[J]. Aerospace Control and Application, 2022, 48(3): 29-38(in Chinese). [3] 袁利, 姜甜甜. 航天器威胁规避智能自主控制技术研究综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2023, 49(2): 229-245.YUAN L, JIANG T T. Review on intelligent autonomous control for spacecraft confronting orbital threats[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2023, 49(2): 229-245(in Chinese). [4] ZHENG L H, LU Y, ZHANG J D, et al. Research on formation-based time-series dynamic threat assessment method[C]//Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Autonomous Unmanned Systems. Berlin: Springer, 2023: 1220-1232. [5] 柴慧敏, 张勇, 李欣粤, 等. 基于深度学习的空中目标威胁评估方法[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2022, 34(7): 1459-1467.CHAI H M, ZHANG Y, LI X Y, et al. Aerial target threat assessment method based on deep learning[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2022, 34(7): 1459-1467(in Chinese). [6] 周立新, 李智. 基于DBN的空间战场目标威胁评估[J]. 装备指挥技术学院学报, 2011, 22(5): 68-73.ZHOU L X, LI Z. Threat assessment for space battlefield targets based on dynamic Bayesian network[J]. Journal of the Academy of Equipment Command & Technology, 2011, 22(5): 68-73(in Chinese). [7] LI J X, YUAN L, ZHANG C, et al. Fuzzy dynamic Bayesian network based threat assessment model for space targets[C]//Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 1176-1181. [8] 伍之前, 李登峰. 基于推理和多属性决策的空中目标攻击意图判断模型[J]. 电光与控制, 2010, 17(5): 10-13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2010.05.003WU Z Q, LI D F. A model for aerial target attacking intention judgment based on reasoning and multi-attribute decision making[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2010, 17(5): 10-13(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-637X.2010.05.003 [9] JIN Q, GOU X T, JIN W D, et al. Intention recognition of aerial targets based on Bayesian optimization algorithm[C]//Proceedings of the 2nd IEEE International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Engineering. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 356-359. [10] 夏曦. 基于模板匹配的目标意图识别方法研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科学技术大学, 2006: 42-60.XIA X. The study of target intent assessment method based on the template-matching[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2006: 42-60(in Chinese). [11] GONG B C, LI S, SHI J J, et al. Rotation based analytic range-only initial relative orbit solution for natural periodic motion[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2021, 178: 584-594. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2020.09.050 [12] 周军, 刘莹莹. 航天器姿态与轨道控制原理[M]. 西安: 西北工业大学出版社, 2016: 77-78.ZHOU J, LIU Y Y. Principle of spacecraft attitude and orbit control[M]. Xi’an: Northwestern Polytechnical University Press, 2016: 77-78(in Chinese). [13] 符俊, 蔡洪, 张士峰, 等. 航天器远程最优拦截方法研究[J]. 固体火箭技术, 2011, 34(6): 682-686. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2793.2011.06.003FU J, CAI H, ZHANG S F, et al. Research on spacecraft long-range optimal interception[J]. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology, 2011, 34(6): 682-686(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2793.2011.06.003 [14] BRYSON A E, HO Y C. Applied optimal control: optimization, estimation, and control[M]. Washington, D.C.: Hemisphere Pub. Corp., 1975: 47-51. [15] VEDANTAM M, AKELLA M R, GRANT M J. Multi-stage stabilized continuation for indirect optimal control of hypersonic trajectories[C]//Proceedings of the AIAA Scitech 2020 Forum. Reston: AIAA, 2020: 0472. [16] YOON S W, PETUKHOV V. Minimum-fuel low-thrust trajectories to the moon[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2023, 210: 102-116. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2023.05.006 [17] 赵育善, 师鹏. 航天器飞行动力学建模理论与方法[M]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 2012: 13-14.ZHAO Y S, SHI P. Theory and method of spacecraft flight dynamics modeling[M]. Beijing: Beihang University Press, 2012: 13-14(in Chinese). [18] YAO Y, XIE R Q, HE F H. Flyaround orbit design for autonomous rendezvous based on relative orbit elements[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2010, 33(5): 1687-1692. doi: 10.2514/1.48494 [19] YUAN Y, SHAW M J. Induction of fuzzy decision trees[J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 1995, 69(2): 125-139. doi: 10.1016/0165-0114(94)00229-Z [20] 杨俊闯, 赵超. K-Means聚类算法研究综述[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2019, 55(23): 7-14. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1908-0347YANG J C, ZHAO C. Survey on K-Means clustering algorithm[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2019, 55(23): 7-14(in Chinese). doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1908-0347 [21] OGHENEOVO E E, NLERUM P A. Iterative dichotomizer 3 (ID3) decision tree: a machine learning algorithm for data classification and predictive analysis[J]. International Journal of Advanced Engineering Research and Science, 2020, 7(4): 514-521. doi: 10.22161/ijaers.74.60 -







 下载:
下载: