Fault diagnosis method for EMA based on multi-source signal fusion with GRU and improved attention mechanism
-
摘要:
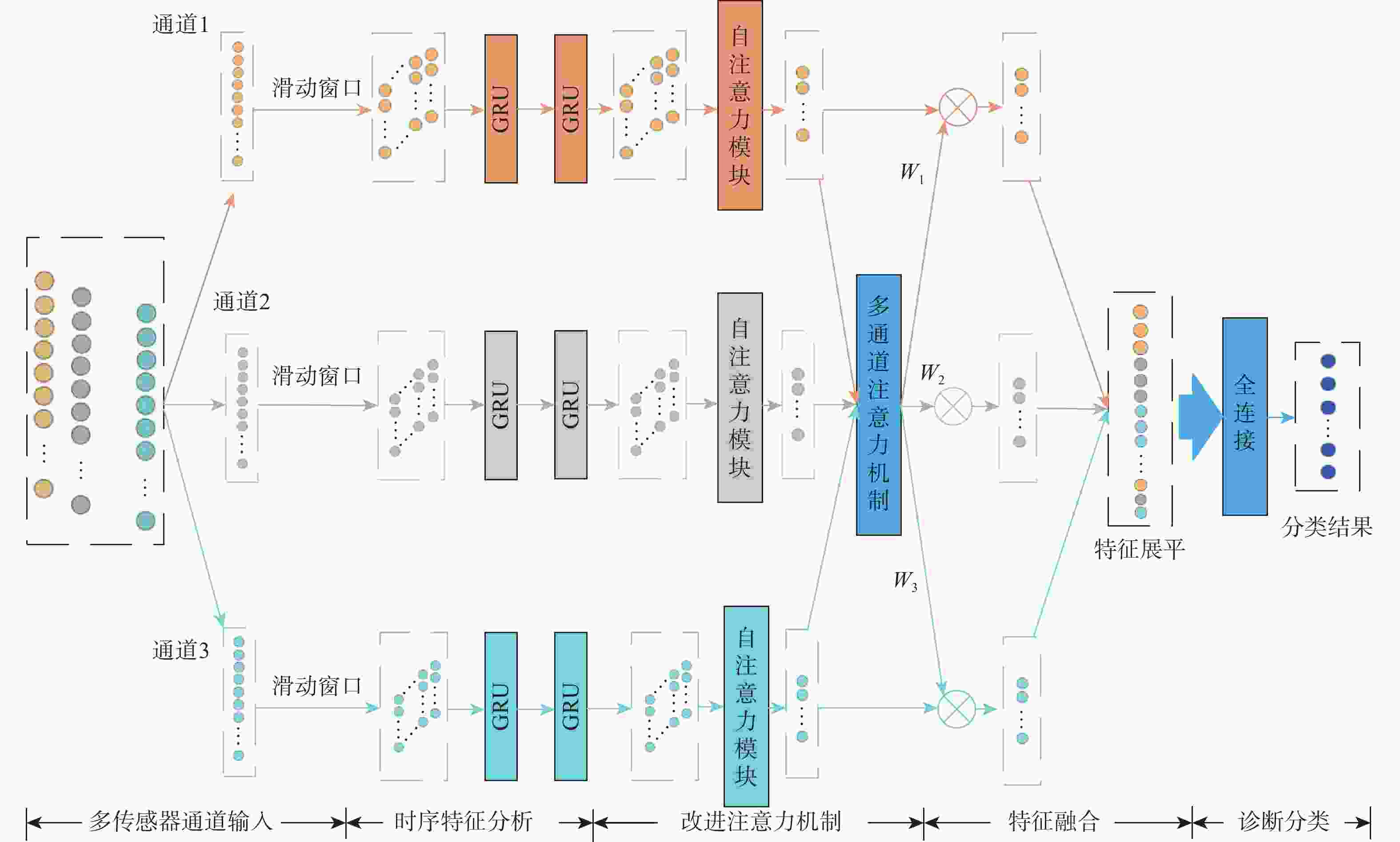
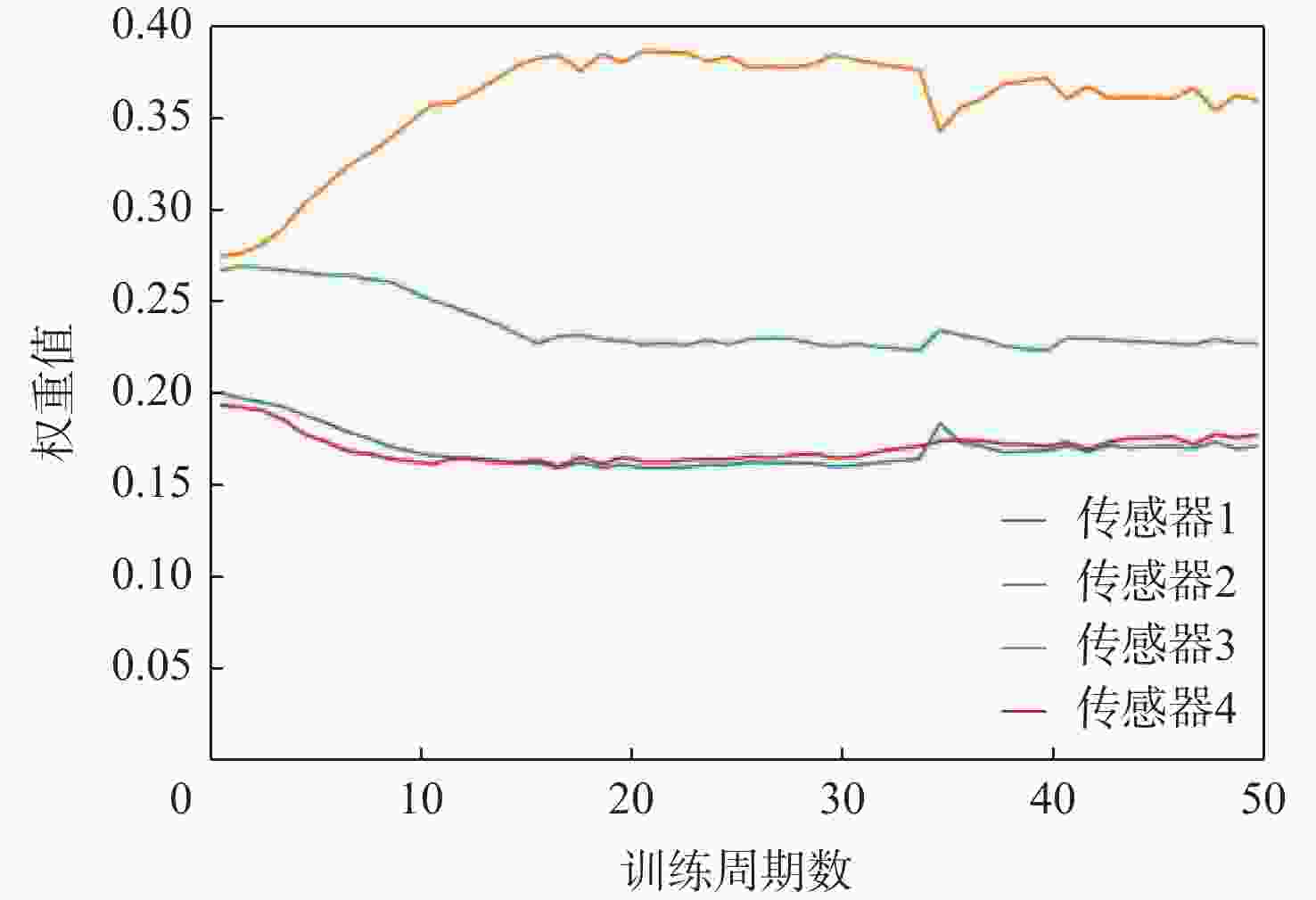
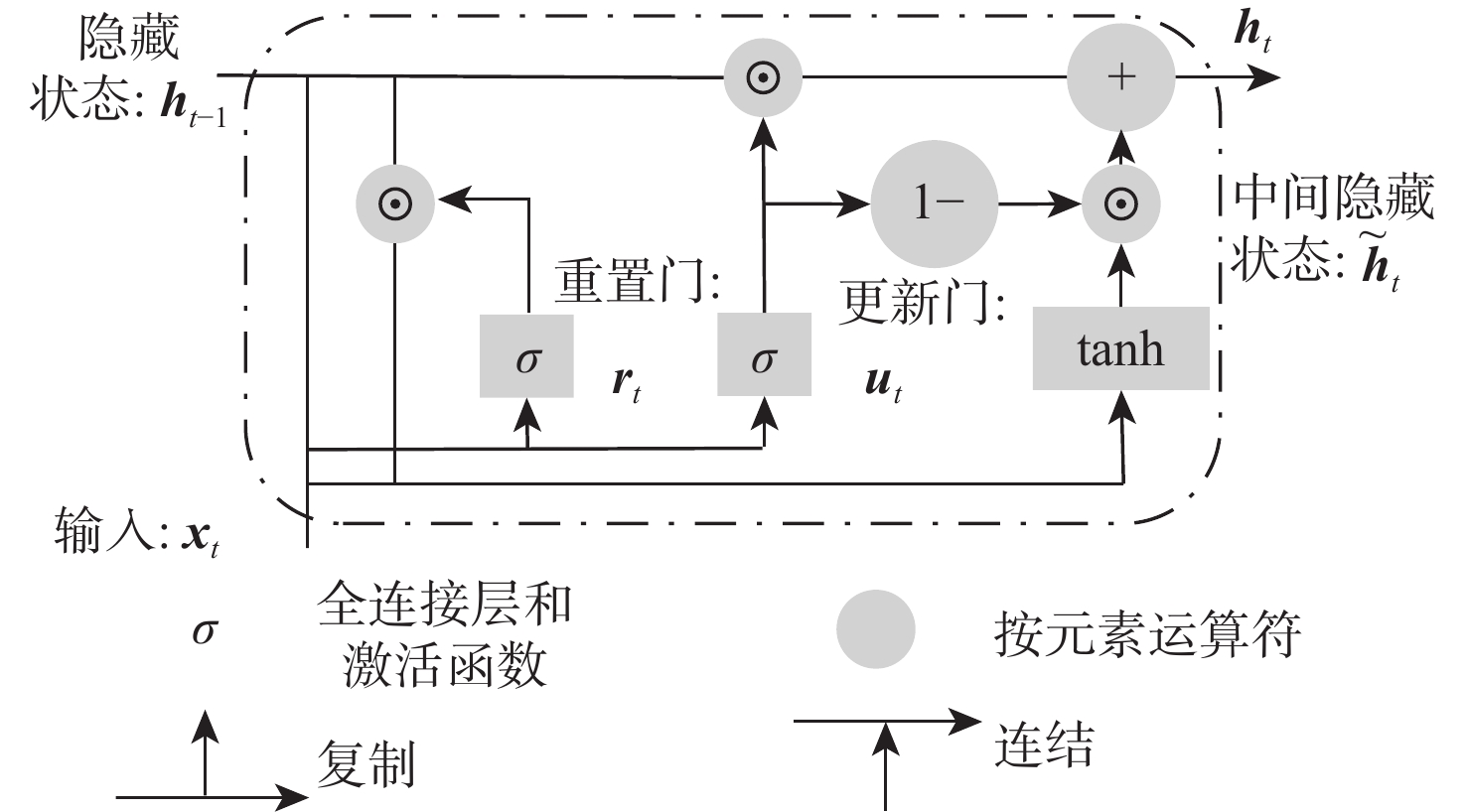
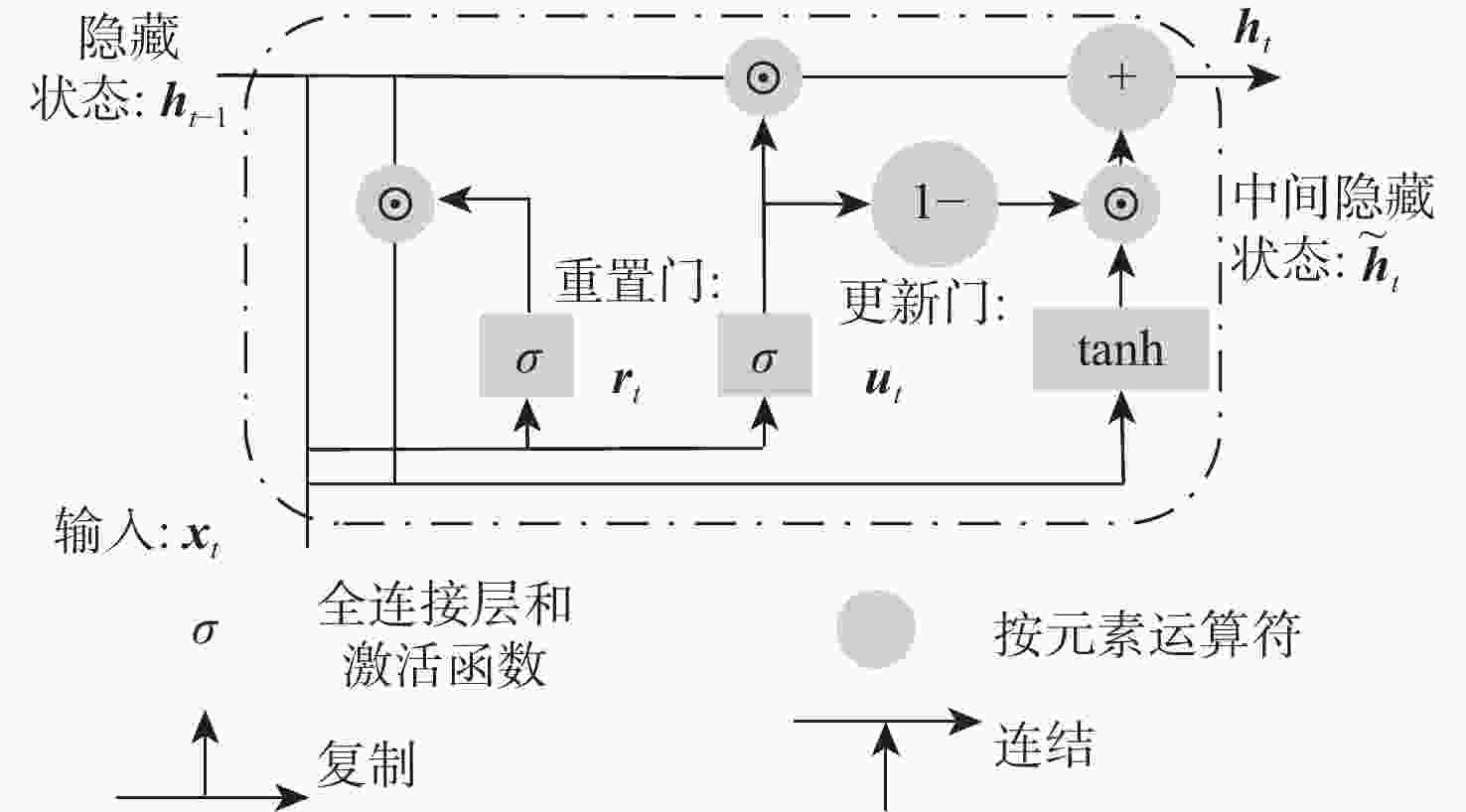
针对传统基于机器学习和深度学习的机电伺服系统(EMA)故障诊断方法存在时序特征丢失、故障信息丢失的问题,提出一种基于门控循环单元(GRU)和改进注意力机制的多信息融合的EMA故障诊断方法。将采集的不同传感器信号分为不同通道,通过GRU提取每个通道信号的时序特征,再引入自注意力机制进一步分辨信号不同时间点之间的重要关系,进一步引入多通道注意力机制自适应融合不同通道的特征,通过分类器实现故障诊断。基于测试试验台数据集的试验结果表明:所提方法与单传感器的模型相比,诊断准确率提升10%;与不引入注意力机制的模型相比,诊断准确率提升5.2%;与经典的机器学习、深度学习和近两年基于深度学习的改进算法相比,所提方法的诊断准确率在98.5%以上,诊断效果最优。
Abstract:Addressing the issues of insufficient time-series features and incomplete fault information in fault diagnosis methods for electromechanical actuators (EMAs) based on traditional machine learning and deep learning, a fault diagnosis method for EMAs based on multi-source signal fusion with gated recurrent unit (GRU) and an improved attention mechanism is proposed. First, the collected signals from different sensors are divided into separate channels, and the time-series features of each channel’s signal are extracted using GRU. The self-attention mechanism is then introduced to further distinguish the important relationships between different time points of the signal. A multi-channel attention mechanism is employed to adaptively fuse the features from different channels. Finally, fault diagnosis is achieved through the classifier. Experimental results based on the test rig dataset show that the diagnostic accuracy improves by 10% compared to the single-sensor model and by 5.2% compared to the model without the attention mechanism. Compared to classical machine learning, deep learning and recent improvements in deep learning-based algorithms from the past two years, the diagnostic accuracy of the proposed model exceeds 98.5%, demonstrating optimal diagnostic performance.
-
表 1 EMA数据集
Table 1. EMA dataset
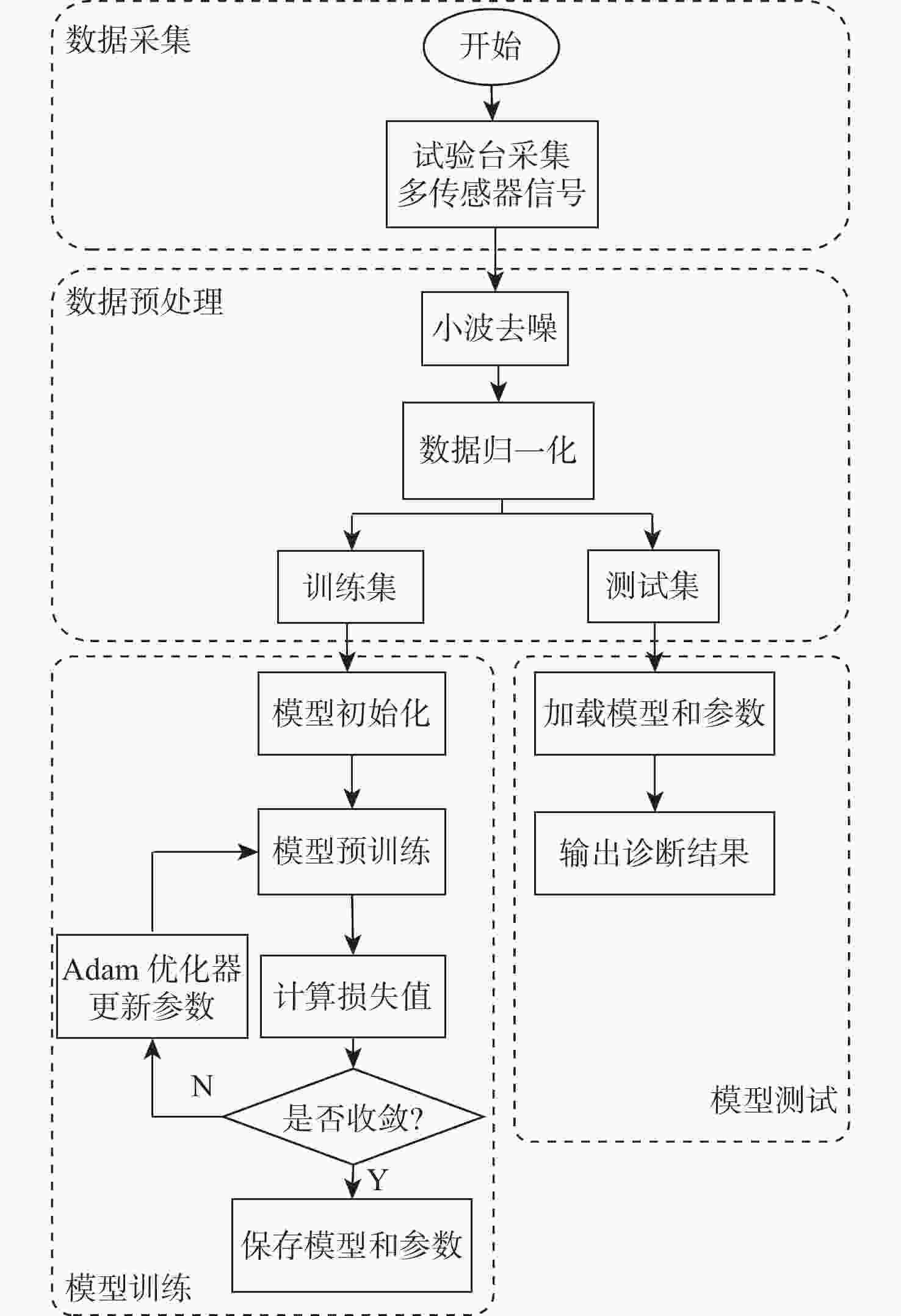
故障类型 故障程度/% 类别 正常 0 0 塑性变形 10 A1 20 A2 30 A3 40 A4 50 A5 60 A6 磨损 10 B1 20 B2 30 B3 40 B4 50 B5 60 B6 表 2 本文模型的结构参数
Table 2. Structure parameters of the proposed model
网络层 关键参数 输入形状/
像素输出形状/
像素GRU 层数大小为2
输入特征维度为16
隐层状态维度为64
Dropout 0.264×64×16 64×64×64 MHSA 输入特征维度为64
注意力头数为4
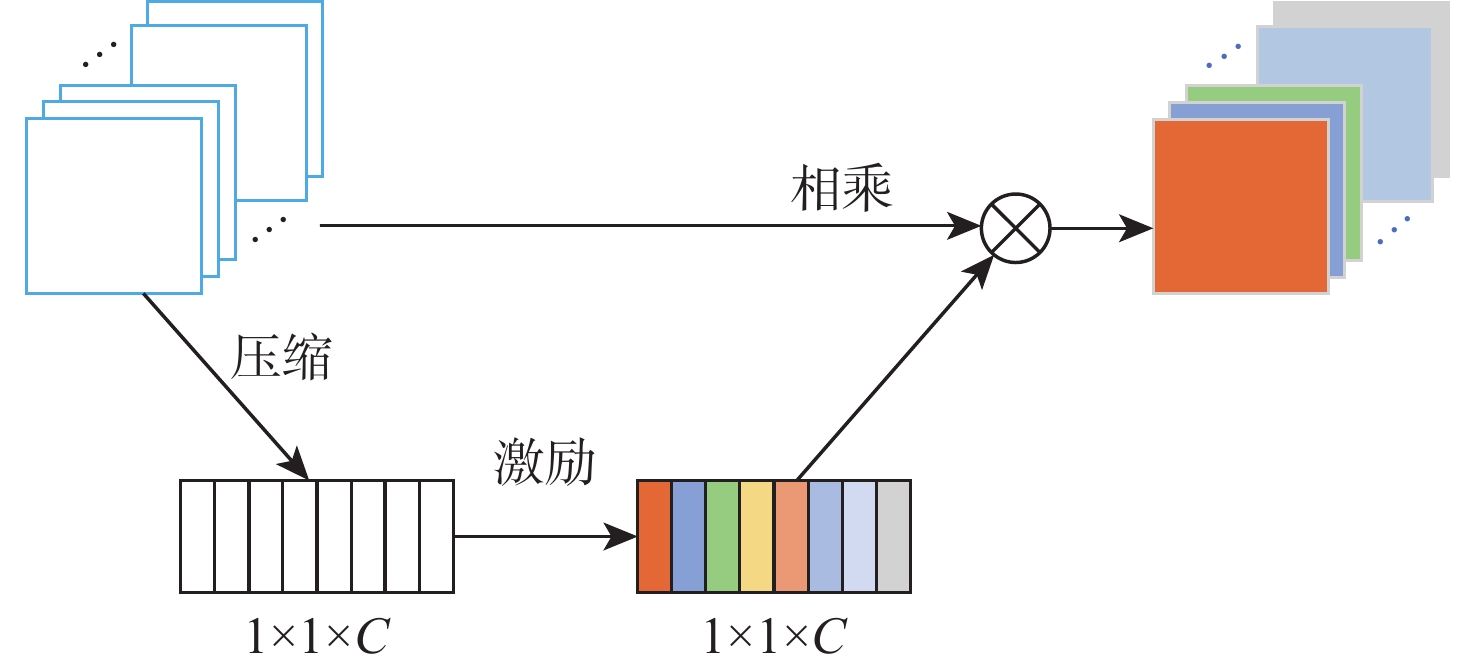
Dropout 0.264×64×64 64×64 SE多通道注意力机制 输入通道为4
缩减比例为0.264×4×64 64×4×64 展平层 64×4×64 64×256 Relu层 64×256 64×256 Dropout层 64×256 64×256 全连接层 64×256 64×13 表 3 GRU的层数对准确率和训练时间的影响
Table 3. Effect of number of GRU on accuracy and training time
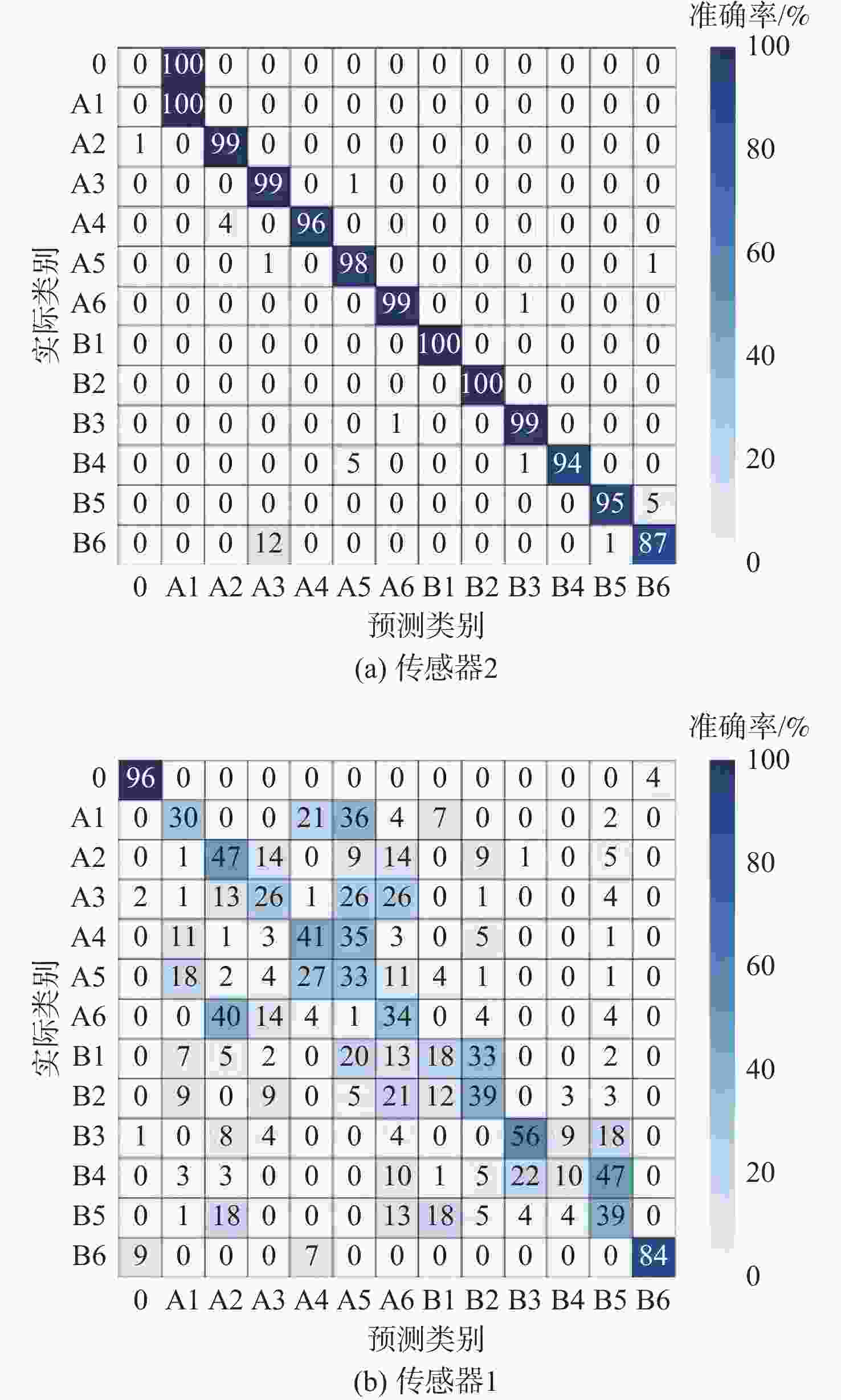
层数 准确率/% 训练时间/s 1 96.18 64.44 2 98.53 74.81 3 99.12 95.35 4 98.53 112.30 表 4 不同传感器的诊断效果
Table 4. Diagnosis performance of different sensors
传感器 Accuracy/% Precision/% Recall/% F1/% 传感器1
(负载扭矩)42.84 44.76 42.84 42.62 传感器2
(温度)88.53 84.44 88.53 85.70 传感器3
(纵向振动)86.57 86.72 86.57 86.58 传感器4
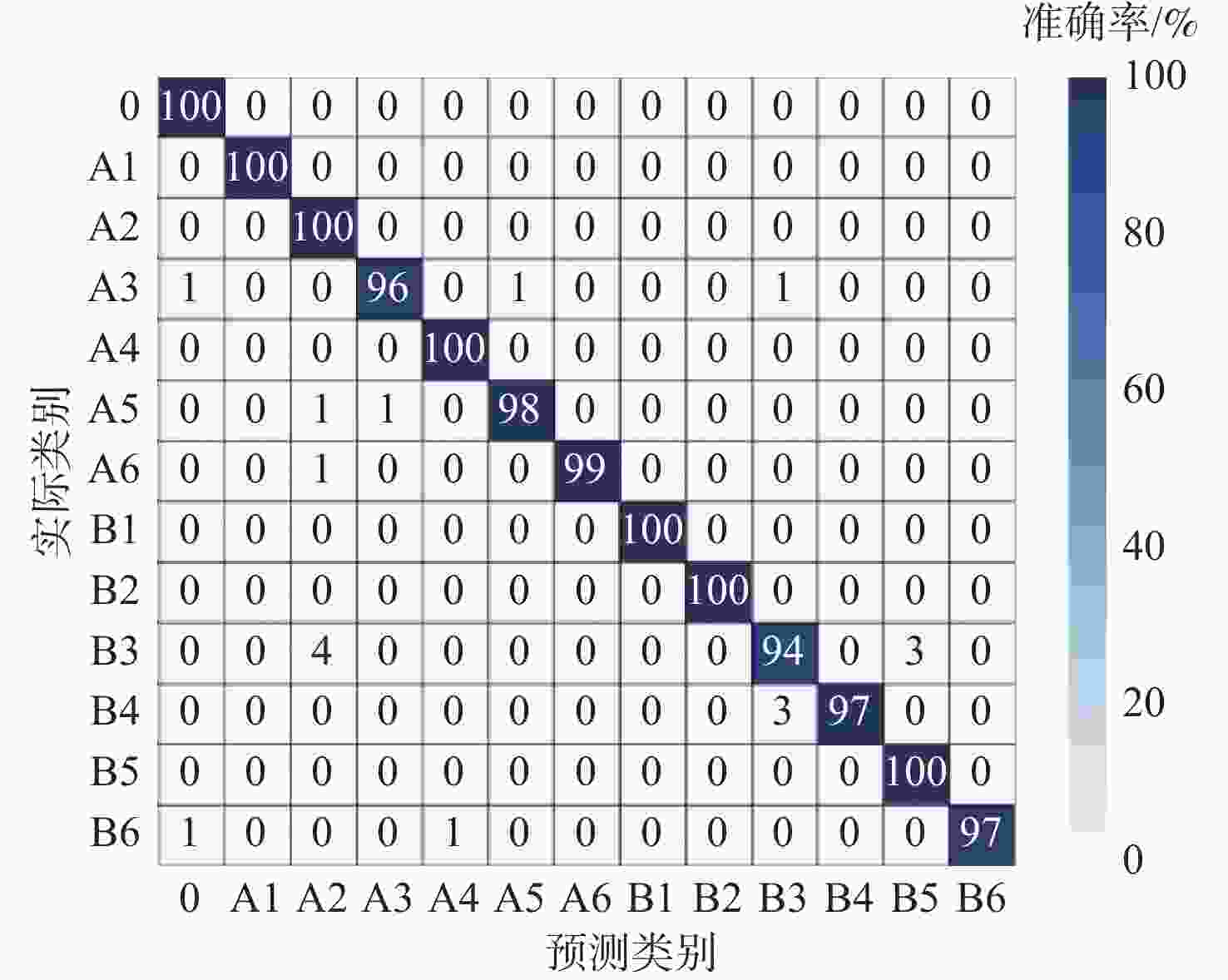
(横向振动)80.10 81.93 80.10 80.28 多传感器 98.53 98.53 98.52 98.53 表 5 不同模型的诊断效果
Table 5. Diagnosis performance of different models
模型 Accuracy/% Precision/% Recall/% F1/% KNN[22] 67.85 68.52 67.85 67.58 SVM[23] 80.27 82.48 80.27 80.55 SSAE[24] 87.15 87.87 87.15 86.99 1D-CNN-LSTM[25] 89.71 90.44 89.71 89.71 GRU-DAE[14] 96.57 97.24 96.57 96.52 NA-GRU 93.33 93.61 93.33 93.35 MHSA-GRU 97.35 97.67 97.35 97.34 本文模型 98.53 98.53 98.52 98.53 -
[1] MAZZOLENI M, RITO G D, PREVIDI F. Electro-mechanical actuators for the more electric aircraft[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2021. [2] 刘俊志. 飞机机电系统故障诊断方法研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2023.LIU J Z. Research on fault diagnosis methods for aircraft electromechanical systems[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2023(in Chinese). [3] ASAD B, VAIMANN T, BELAHCEN A, et al. Broken rotor bar fault diagnostic of inverter fed induction motor using FFT, Hilbert and park’s vector approach[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Electrical Machines. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 2352-2358. [4] WANG J, DU G F, ZHU Z K, et al. Fault diagnosis of rotating machines based on the EMD manifold[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2020, 135: 106-443. [5] 雷亚国, 贾峰, 孔德同, 等. 大数据下机械智能故障诊断的机遇与挑战[J]. 机械工程学报, 2018, 54(5): 94-104. doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.05.094LEI Y G, JIA F, KONG D T, et al. Opportunities and challenges of machinery intelligent fault diagnosis in big data era[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 54(5): 94-104(in Chinese). doi: 10.3901/JME.2018.05.094 [6] OTTER D W, MEDINA J R, KALITA J K. A survey of the usages of deep learning for natural language processing[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(2): 604-624. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.2979670 [7] HUANG R Y, LIAO Y X, ZHANG S H, et al. Deep decoupling convolutional neural network for intelligent compound fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 7: 1848-1858. [8] WANG J Y, ZHANG Y J, LUO C, et al. Deep learning domain adaptation for electro-mechanical actuator fault diagnosis under variable driving waveforms[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2022, 22(11): 10783-10793. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2022.3168875 [9] SONG Y T, DU J H, LI S X, et al. Multi-scale feature fusion convolutional neural networks for fault diagnosis of electromechanical actuator[J]. Applied Sciences, 2023, 13(15): 8689. doi: 10.3390/app13158689 [10] LINDEMANN B, MASCHLER B, SAHLAB N, et al. A survey on anomaly detection for technical systems using LSTM networks[J]. Computers in Industry, 2021, 131: 103498. doi: 10.1016/j.compind.2021.103498 [11] YANG S D, YU X Y, ZHOU Y. LSTM and GRU neural network performance comparison study: taking yelp review dataset as an example[C]//Proceedings of the International Workshop on Electronic Communication and Artificial Intelligence. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 98-101. [12] ENCALADA-DÁVILA Á, MOYÓN L, TUTIVÉN C, et al. Early fault detection in the main bearing of wind turbines based on gated recurrent unit (GRU) neural networks and SCADA data[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2022, 27(6): 5583-5593. doi: 10.1109/TMECH.2022.3185675 [13] 张立鹏, 毕凤荣, 程建刚, 等. 基于注意力BiGRU的机械故障诊断方法研究[J]. 振动与冲击, 2021, 40(5): 113-118.ZHANG L P, BI F R, CHENG J G, et al. Mechanical fault diagnosis method based on attention BiGRU[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2021, 40(5): 113-118(in Chinese). [14] LI D L, WEI X Y, WEI Z, et al. A fault diagnosis method of rolling bearing based on GRU convolution denoising auto-encoder[C]//Proceedings of the Advances in Mechanism, Machine Science and Engineering. Berlin: Springer, 2023: 2009-2022. [15] QIAN G S, LIU J Q. Fault diagnosis based on gated recurrent unit network with attention mechanism and transfer learning under few samples in nuclear power plants[J]. Progress in Nuclear Energy, 2023, 155: 104502. doi: 10.1016/j.pnucene.2022.104502 [16] YANG J, GUO Y Q, ZHAO W L. An intelligent fault diagnosis method for an electromechanical actuator based on sparse feature and long short-term network[J]. Measurement Science and Technology, 2021, 32(9): 095102. doi: 10.1088/1361-6501/abfbab [17] 许同乐. 旋转机械故障信号处理与诊断方法[M]. 北京: 高等教育出版社, 2020.XU T L. Methods for signal processing and fault diagnosis of rotating machinery[M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press, 2020(in Chinese). [18] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, NIKI P, et al. Attention is all you need[EB/OL]. (2023-08-02)[2023-09-10]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1706.03762. [19] 祁宣豪, 智敏. 图像处理中注意力机制综述[J]. 计算机科学与探索, 2024, 18(2): 345-362. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2305057QI X H, ZHI M. Review of attention mechanisms in image processing[J]. Journal of Frontiers of Computer Science and Technology, 2024, 18(2): 345-362(in Chinese). doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1673-9418.2305057 [20] KUMAR A, VEERUBHOTLA A S, NARAPAREDDY V T, et al. Aspect term extraction for opinion mining using a hierarchical self-attention network[J]. Neurocomputing, 2021, 465: 195-204. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2021.08.133 [21] HU J, SHEN L, SUN G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 7132-7141. [22] HAN T, ZHANG L W, YIN Z J, et al. Rolling bearing fault diagnosis with combined convolutional neural networks and support vector machine[J]. Measurement, 2021, 177: 109022. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2021.109022 [23] MEDINA R, MACANCELA J C, LUCERO P, et al. Gear and bearing fault classification under different load and speed by using Poincaré plot features and SVM[J]. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2022, 33(4): 1031-1055. doi: 10.1007/s10845-020-01712-9 [24] CHEN Z Y, LI W H. Multisensor feature fusion for bearing fault diagnosis using sparse autoencoder and deep belief network[J]. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2017, 66(7): 1693-1702. doi: 10.1109/TIM.2017.2669947 [25] ALSUMAIDAEE Y A M, YAW C T, KOH S P, et al. Detection of corona faults in switchgear by using 1D-CNN, LSTM, and 1D-CNN-LSTM methods[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(6): 3108. doi: 10.3390/s23063108 -






 下载:
下载: