-
摘要:
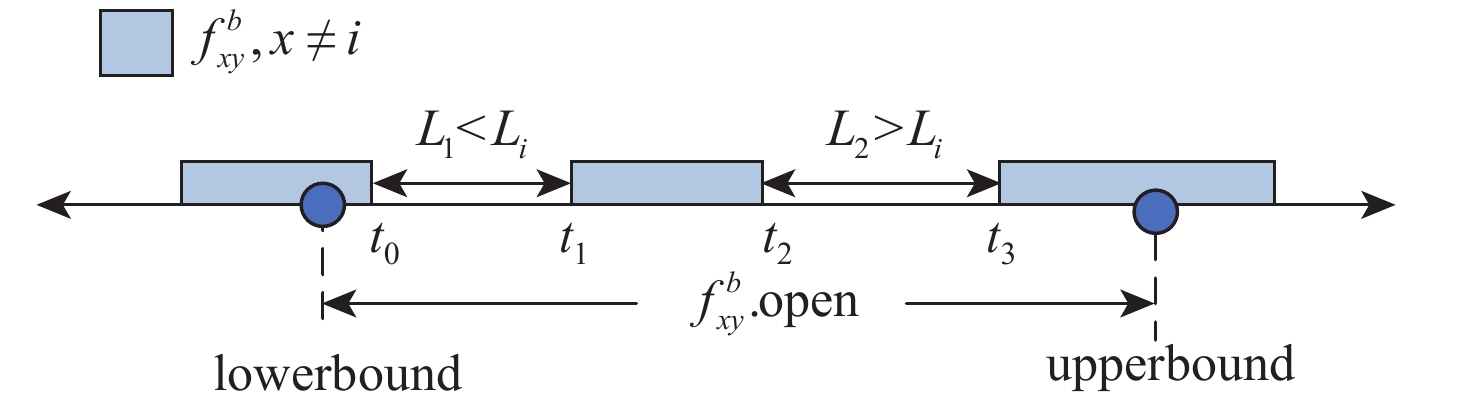
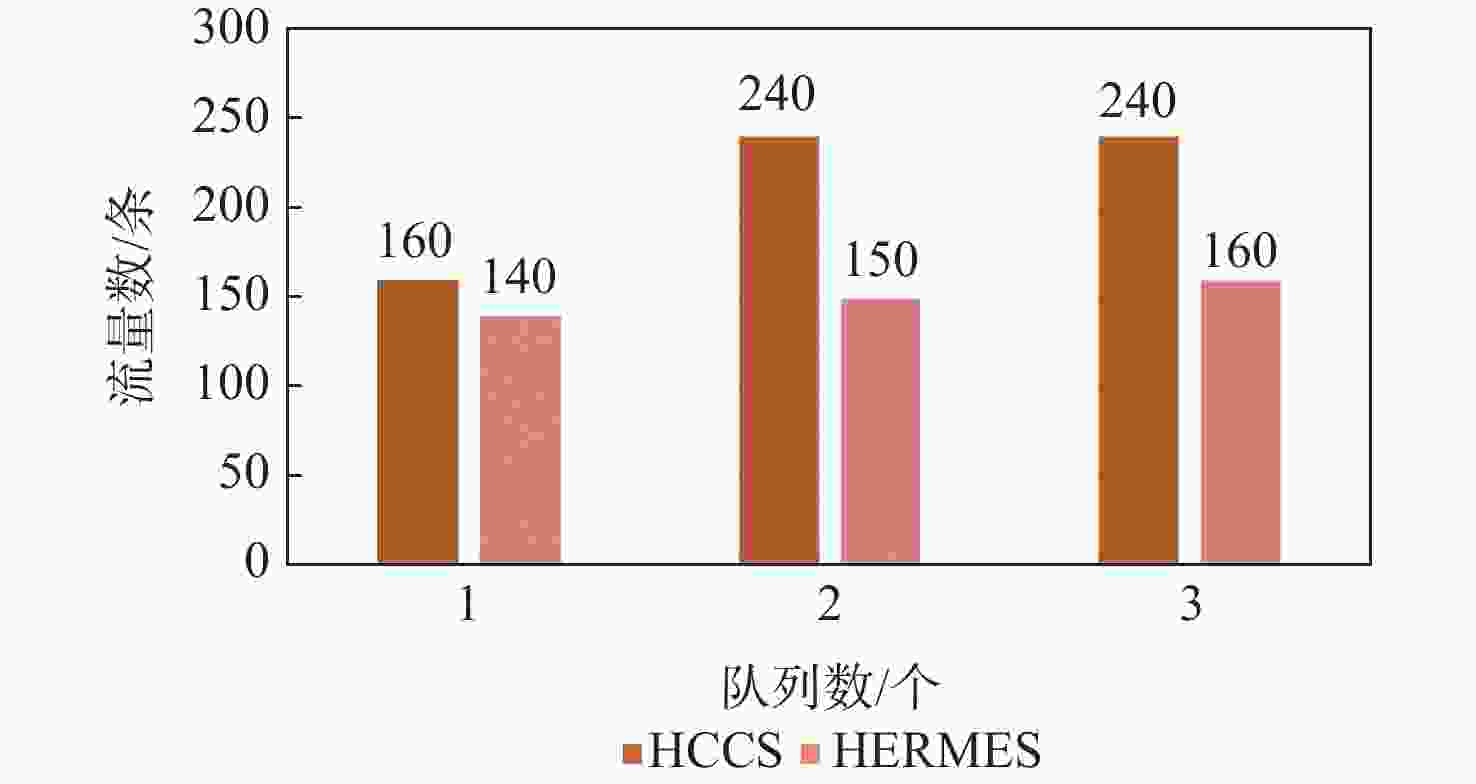
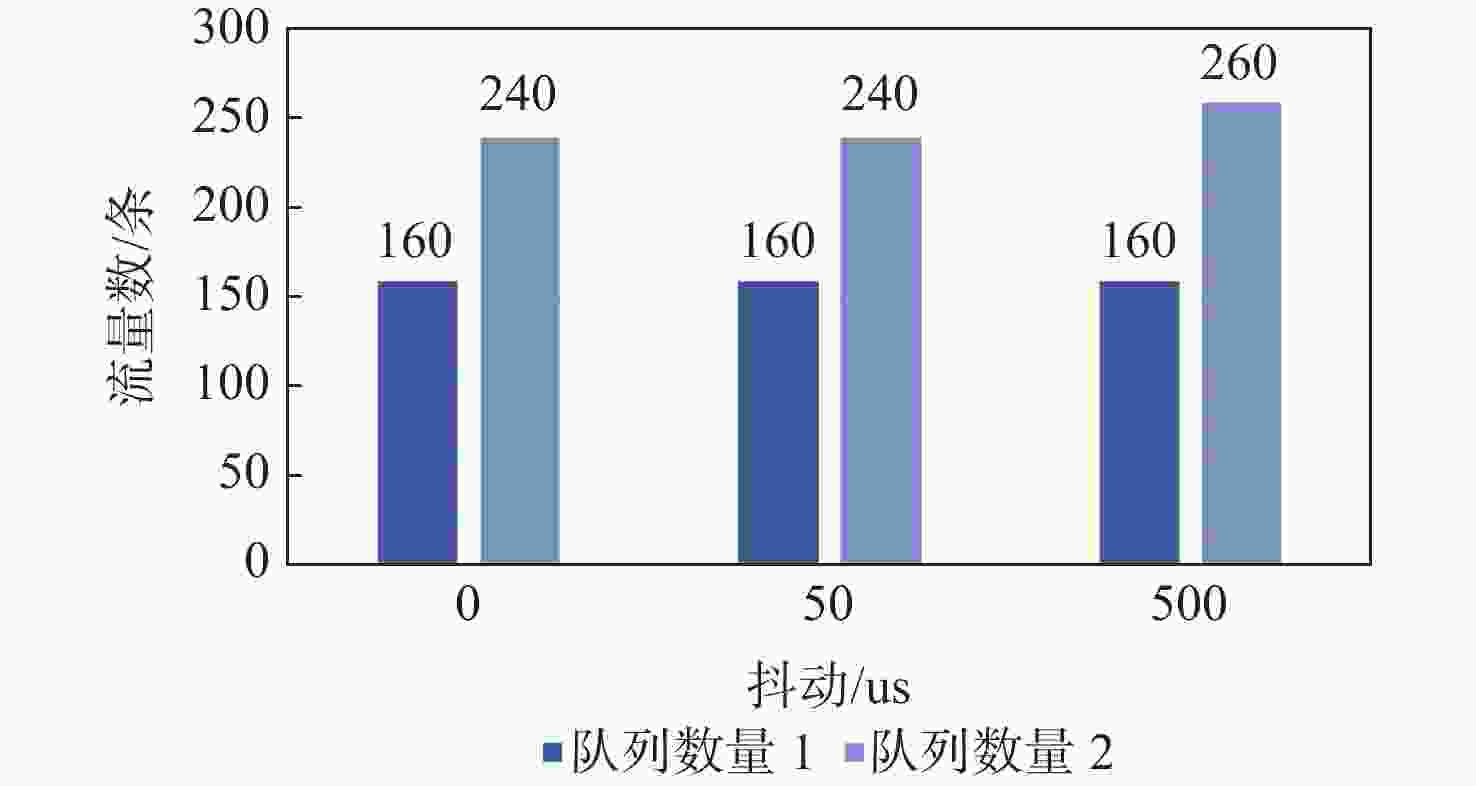
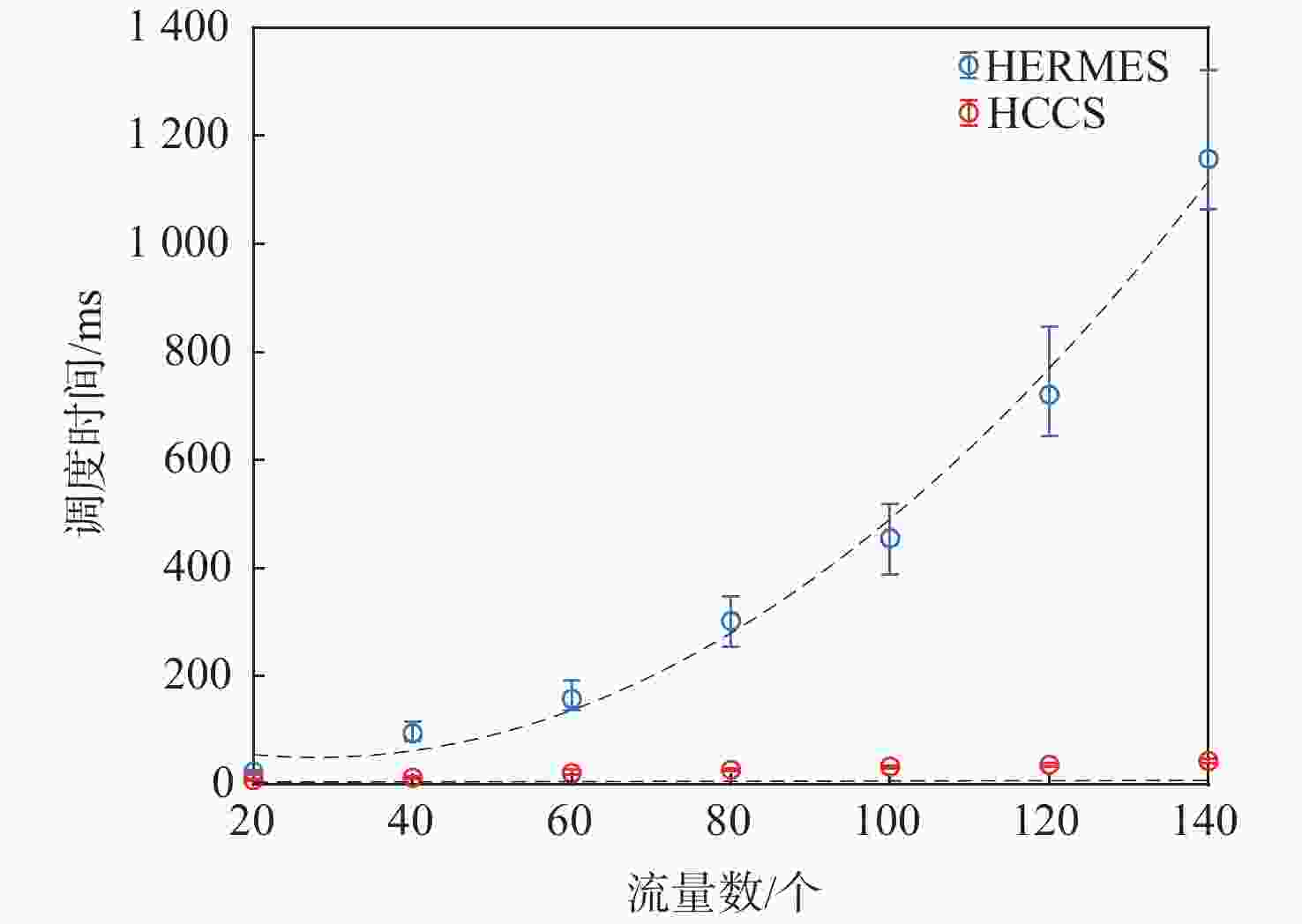
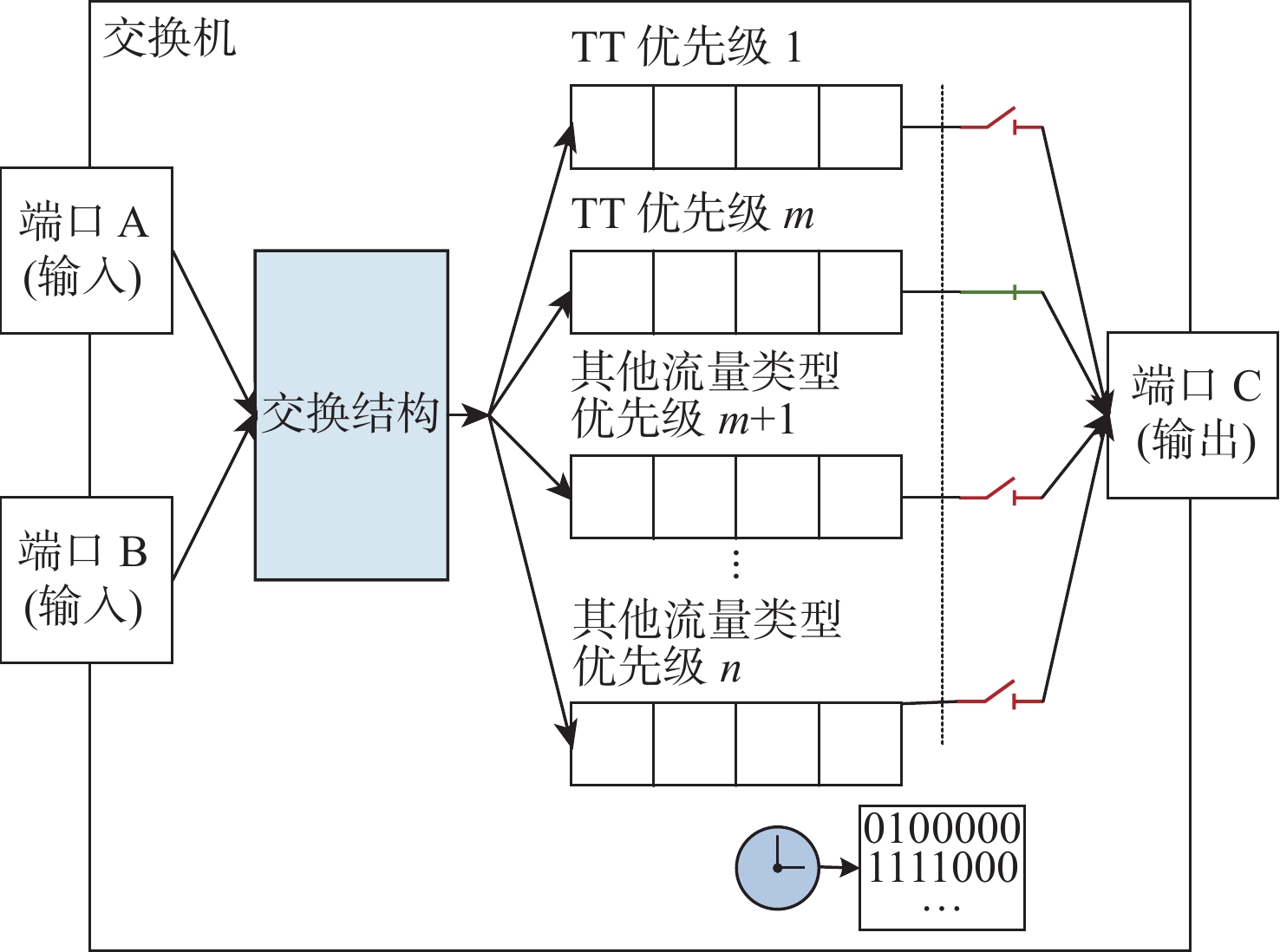
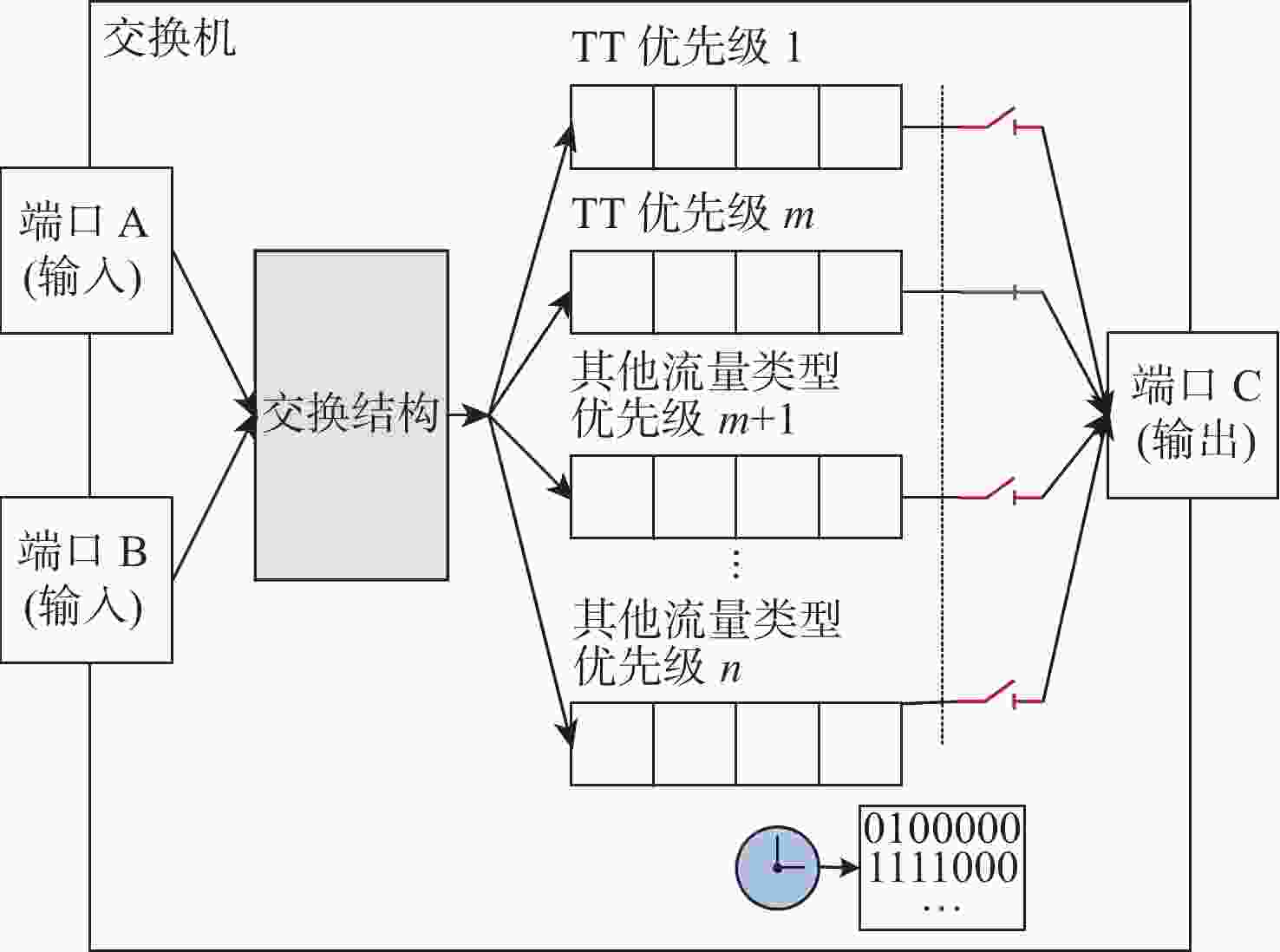
针对时间敏感网络(TSN)的时间触发流通信,提出了一种启发式约束转化调度方法(HCCS)。该方法依据路径和单流时序约束确定端口优先序,使流实例在高优先序端口的转发时间不受低优先序端口影响;对于经过相同端口的流实例,再考虑所属流的优先级和超周期内释放的先后关系,形成流实例的调度次序;依次将流实例的约束转化为可调度时间区间,在区间内启发式搜索足够长度的空时隙,确定相应端口中的门控转发时间。每次转化仅需考虑单个流实例的约束,且转化所得的时间区间限定了搜索范围,大幅度提高了约束求解效率;并且,约束转化使HCCS方法既可以设置单队列也可以设置多队列,既适用于零抖动也适用于抖动在一定范围内的调度。与已有的HERMES算法进行仿真对比,发现HCCS能使更大比例的流获得可调度性,且在不同的流量规模下计算速度提升3~25倍。
Abstract:In this paper, a heuristic constraint conversion scheduling method (HCCS) is presented for time-triggered flows in time-sensitive networks (TSNs). The HCCS method establishes a port scheduling order based on path and per-flow temporal constraints, ensuring that the transmission time of flow instances through high-priority ports is unaffected by low-priority ports. For flow instances passing through the same port, their scheduling order is determined by the flow priorities and their release times within the hyper-period. The constraints of flow instances are then converted into schedulable time intervals, within which heuristic searches are conducted to identify a time slot of sufficient length to determine the gate-controlled forwarding times of the corresponding ports. Each conversion addresses the constraints of individual flow instances, so the resulting time intervals confine the search space, significantly improving constraint-solving efficiency. Moreover, constraint conversion allows the HCCS method to be applied to both single-queue and multi-queue configurations, making it suitable for both zero-jitter and jitter-limited scheduling scenarios. Comparative simulations with the existing heuristic multi-queue scheduler (HERMES) algorithm show that HCCS increases the proportion of schedulable flows and achieves a computation speedup of approximately 3 to 25 times over HERMES, depending on the traffic scale.
-
Key words:
- time-sensitive network /
- time-triggered /
- scheduling /
- heuristic method /
- constraint programming
-
-
[1] KOPETZ H, GRUNSTEIDL G. TTP - A time-triggered protocol for fault-tolerant real-time systems[C]//Proceedings of the FTCS-23 The Twenty-Third International Symposium on Fault-Tolerant Computing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2002: 524-533. [2] CRACIUNAS S S, SERNA OLIVER R , STEINER W. Demo abstract: slate XNS: an online management tool for deterministic TSN Networks[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Real-Time and Embedded Technology and Applications Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 103-104. [3] LARRANAGA A, LUCAS-ESTAN M C, MARTINEZ I, et al. Analysis of 5G-TSN integration to support industry 4.0[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 25th IEEE International Conference on Emerging Technologies and Factory Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1111-1114. [4] ALI SYED A A, AYAZ S, LEINMULLER T, et al. Fault-tolerant dynamic scheduling and routing for TSN based in-vehicle networks[C]//Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE Vehicular Networking Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2021: 72-75. [5] IEEE. IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks-timing and synchronization for time-sensitive applications in bridged local area networks-corrigendum 2: technical and editorial corrections: IEEE Std 802.1AS-2011/Cor 2-2015[S]. Piscataway: IEEE, 2016: 1-13. [6] IEEE. IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks-virtual bridged local area networks amendment 12: forwarding and queuing enhancements for time-sensitive streams: 802.1Qav-2009[S]. Piscataway: IEEE, 2010: 1-72. [7] IEEE. IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks-virtual bridged local area networks amendment 14: stream reservation protocol: 802.1Qat-2010[S]. IEEE, 2010: 1-119. [8] IEEE. IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks-bridges and bridged networks-amendment 25: enhancements for scheduled traffic: 802.1Qbv[S]. Piscataway: IEEE, 2015: 1-57. [9] IEEE. IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks-bridges and bridged networks-amendment 26: frame preemption: 802.1Qbu-2016[S]. Piscataway: IEEE, 2016: 1-52. [10] IEEE. IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks-bridges and bridged networks-amendment 28: per-stream filtering and policing: 802.1Qci-2017[S]. Piscataway: IEEE, 2017: 1-65. [11] IEEE. IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks-frame replication and elimination for reliability: 802.1CB[S]. Piscataway: IEEE, 2017: 1-102. [12] IEEE. IEEE standard for local and metropolitan area networks-bridges and bridged networks-amendment 31: stream reservation protocol enhancements and performance improvements: 802.1Qcc-2018[S]. Piscataway: IEEE, 2018: 1-208. [13] LO BELLO L, STEINER W. A perspective on IEEE time-sensitive networking for industrial communication and automation systems[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2019, 107(6): 1094-1120. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2019.2905334 [14] SCHWEISSGUTH E, DANIELIS P, TIMMERMANN D, et al. ILP-based joint routing and scheduling for time-triggered networks[C]//Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Real-Time Networks and Systems. New York: Association for Computing Machinery, 2017: 8-17. [15] FALK J, DÜRR F, ROTHERMEL K. Exploring practical limitations of joint routing and scheduling for TSN with ILP[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE 24th International Conference on Embedded and Real-Time Computing Systems and Applications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 136-146. [16] SCHWEISSGUTH E, TIMMERMANN D, PARZYJEGLA H, et al. ILP-based routing and scheduling of multicast realtime traffic in time-sensitive networks[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 26th International Conference on Embedded and Real-Time Computing Systems and Applications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1-11. [17] CRACIUNAS S S, OLIVER R S, CHMELÍK M, et al. Scheduling real-time communication in IEEE 802.1 Qbv time sensitive networks[C]//Proceedings of the 24th International Conference on Real-Time Networks and Systems. New York: Association for Computing Machinery, 2016: 183-192. [18] SERNA OLIVER R, CRACIUNAS S S, STEINER W. IEEE 802.1 Qbv gate control list synthesis using array theory encoding[C]//Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Real-Time and Embedded Technology and Applications Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2018: 13-24. [19] RAAGAARD M L, POP P, GUTIERREZ M, et al. Runtime reconfiguration of time-sensitive networking (TSN) schedules for fog computing[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Fog World Congress (FWC). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1-6. [20] ANSAH F, ABID M A, DE MEER H. Schedulability analysis and GCL computation for time-sensitive networks[C]//Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 17th International Conference on Industrial Informatics. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019, 1: 926-932. [21] REUSCH N, ZHAO L, CRACIUNAS S S, et al. Window-based schedule synthesis for industrial IEEE 802.1 Qbv TSN networks[C]//Proceedings of the 2020 16th IEEE International Conference on Factory Communication Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2020: 1-4. [22] KIM H J, CHOI M H, KIM M H, et al. Development of an Ethernet-based heuristic time-sensitive networking scheduling algorithm for real-time in-vehicle data transmission[J]. Electronics, 2021, 10(2): 157. doi: 10.3390/electronics10020157 [23] BUJOSA D, ASHJAEI M, PAPADOPOULOS A V, et al. HERMES: heuristic multi-queue scheduler for TSN time-triggered traffic with zero reception jitter capabilities[C]//Proceedings of the 30th International Conference on Real-Time Networks and Systems. Paris: Association for Computing Machinery, 2022: 70-80. [24] LEE D J. Incremental routing and scheduling using multipath and nonzero jitter bound for IEEE 802.1 Qbv time aware shaper[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11: 25035-25049. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3255416 [25] CRACIUNAS S S, OLIVER R S. Combined task-and network-level scheduling for distributed time-triggered systems[J]. Real-Time Systems, 2016, 52(2): 161-200. doi: 10.1007/s11241-015-9244-x -






 下载:
下载: