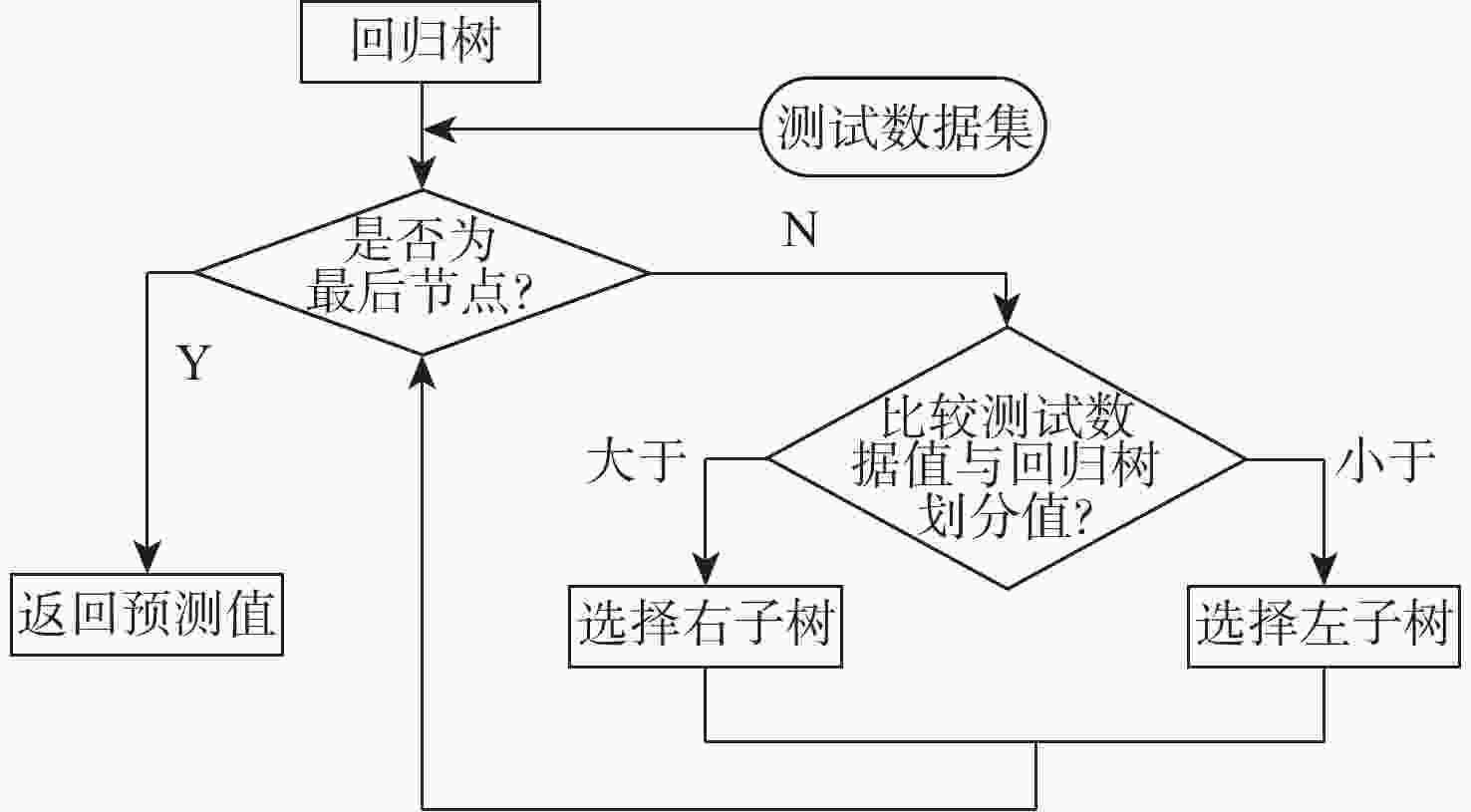
-
摘要:
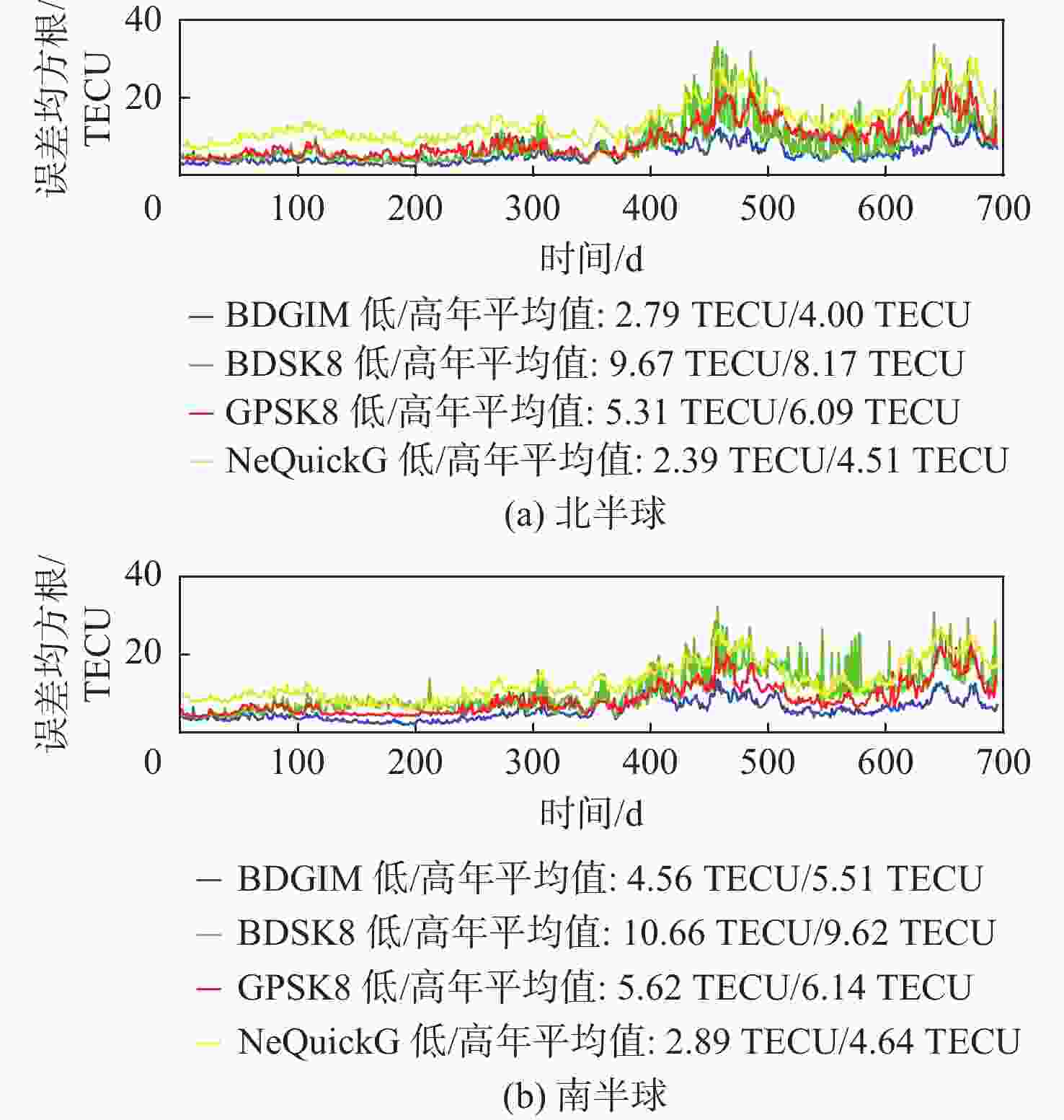
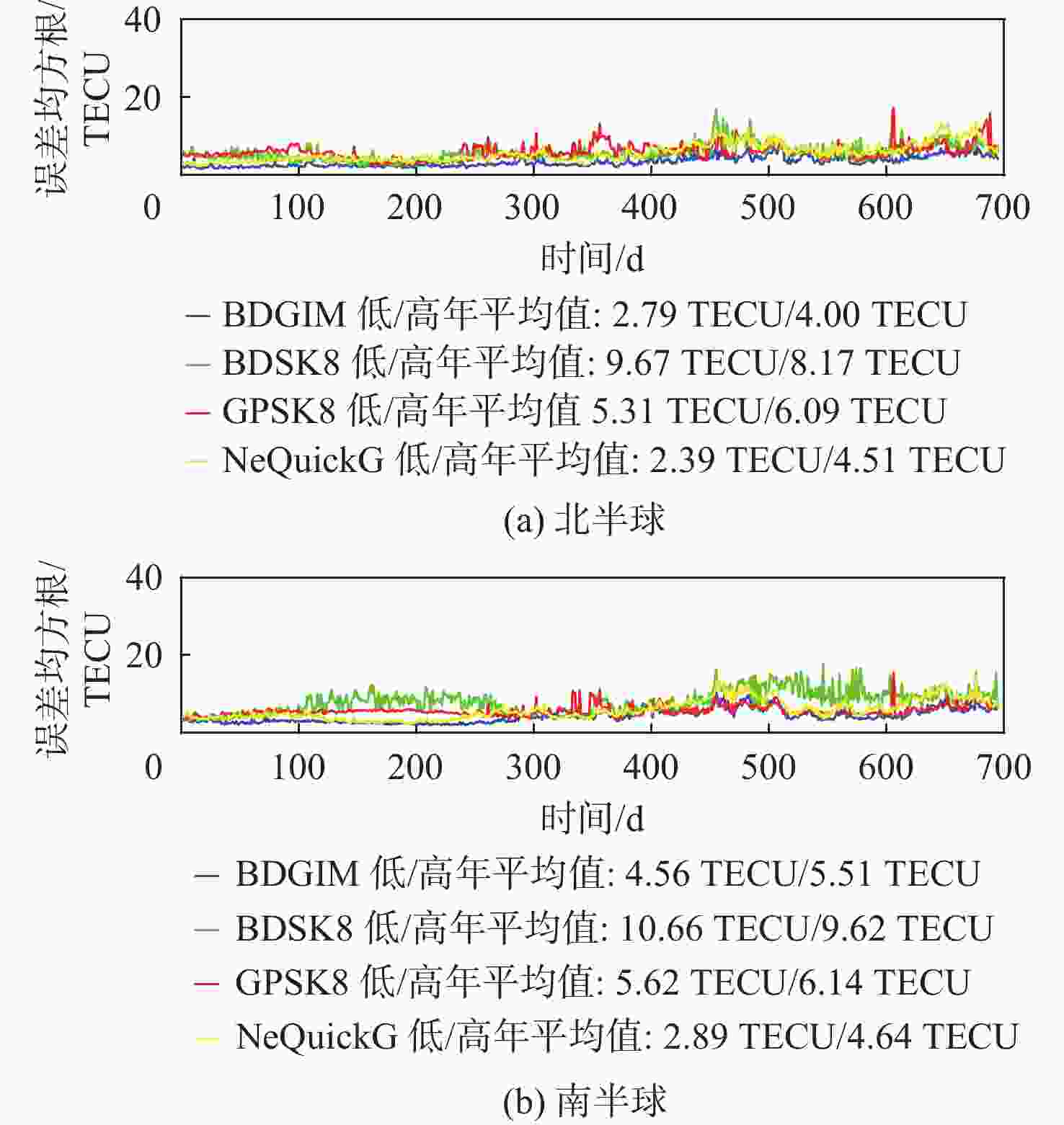
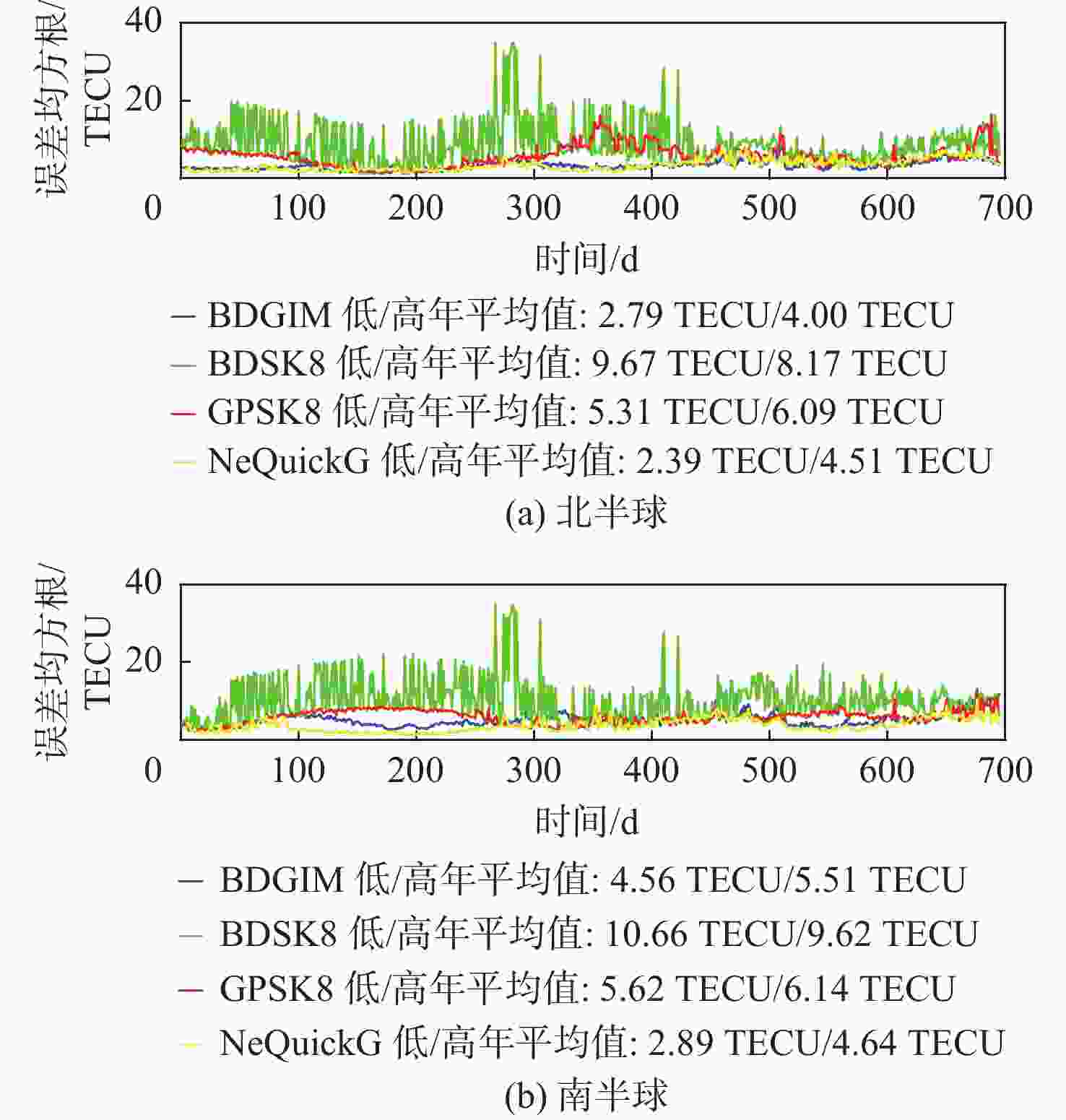
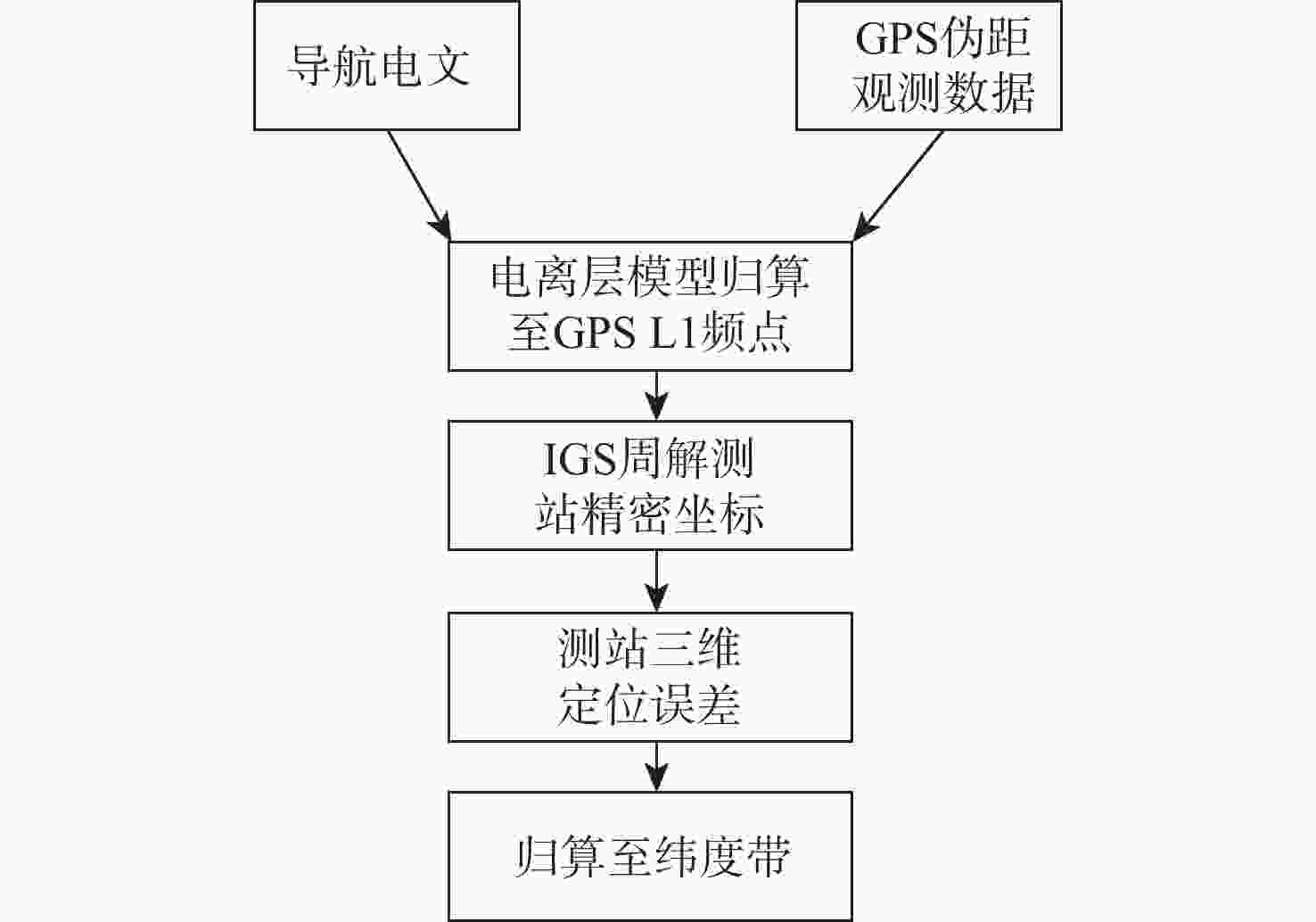
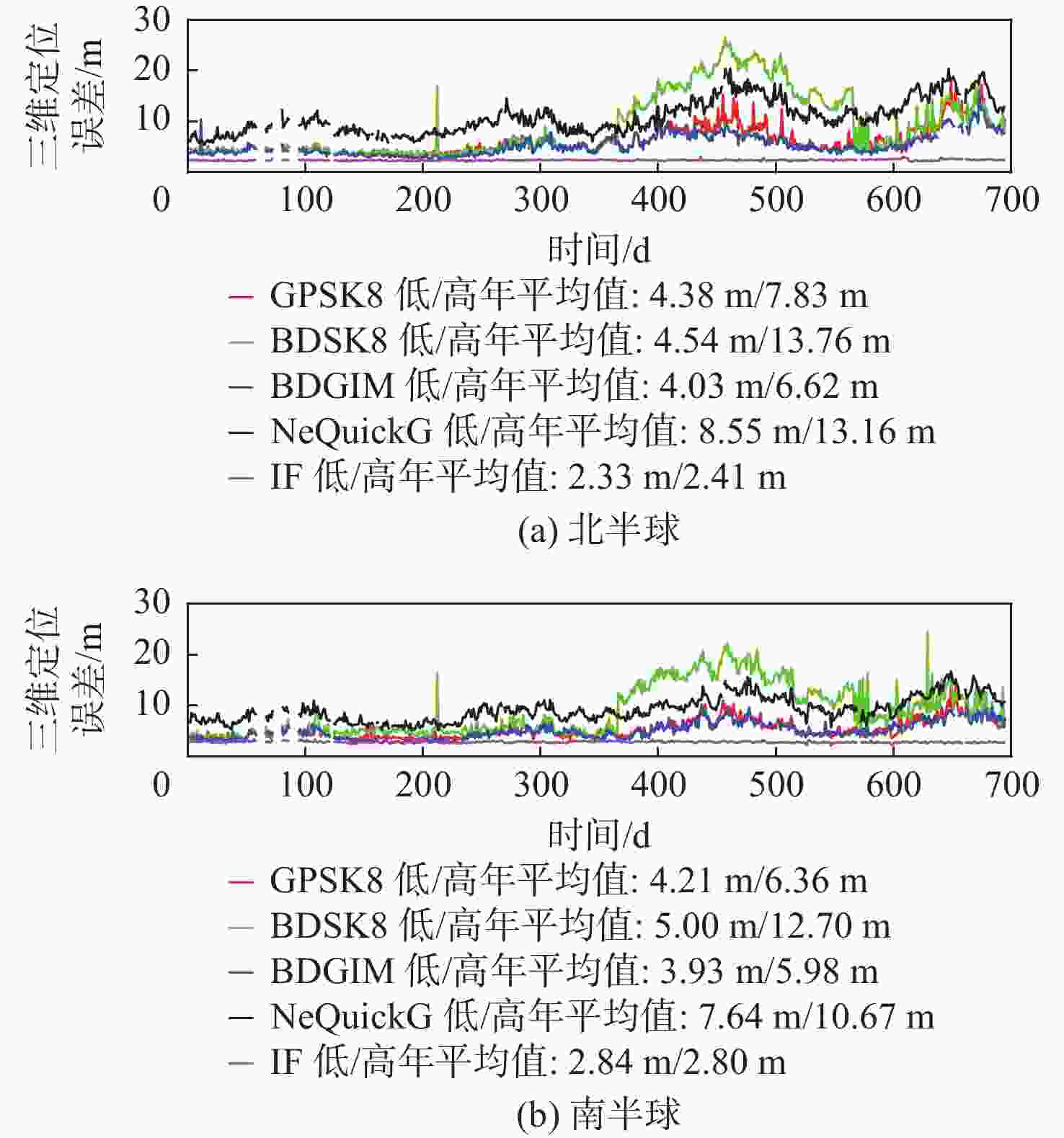
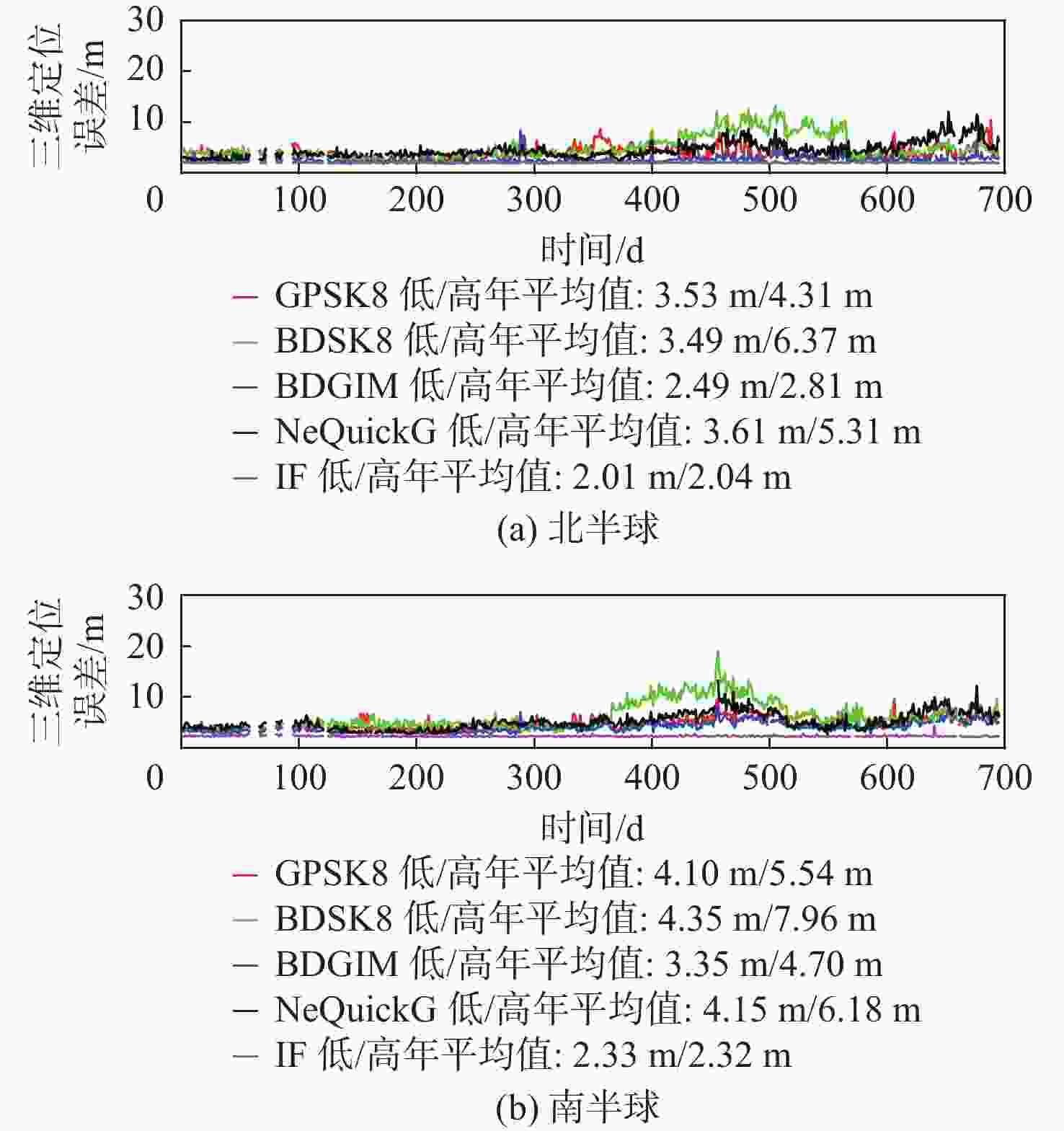
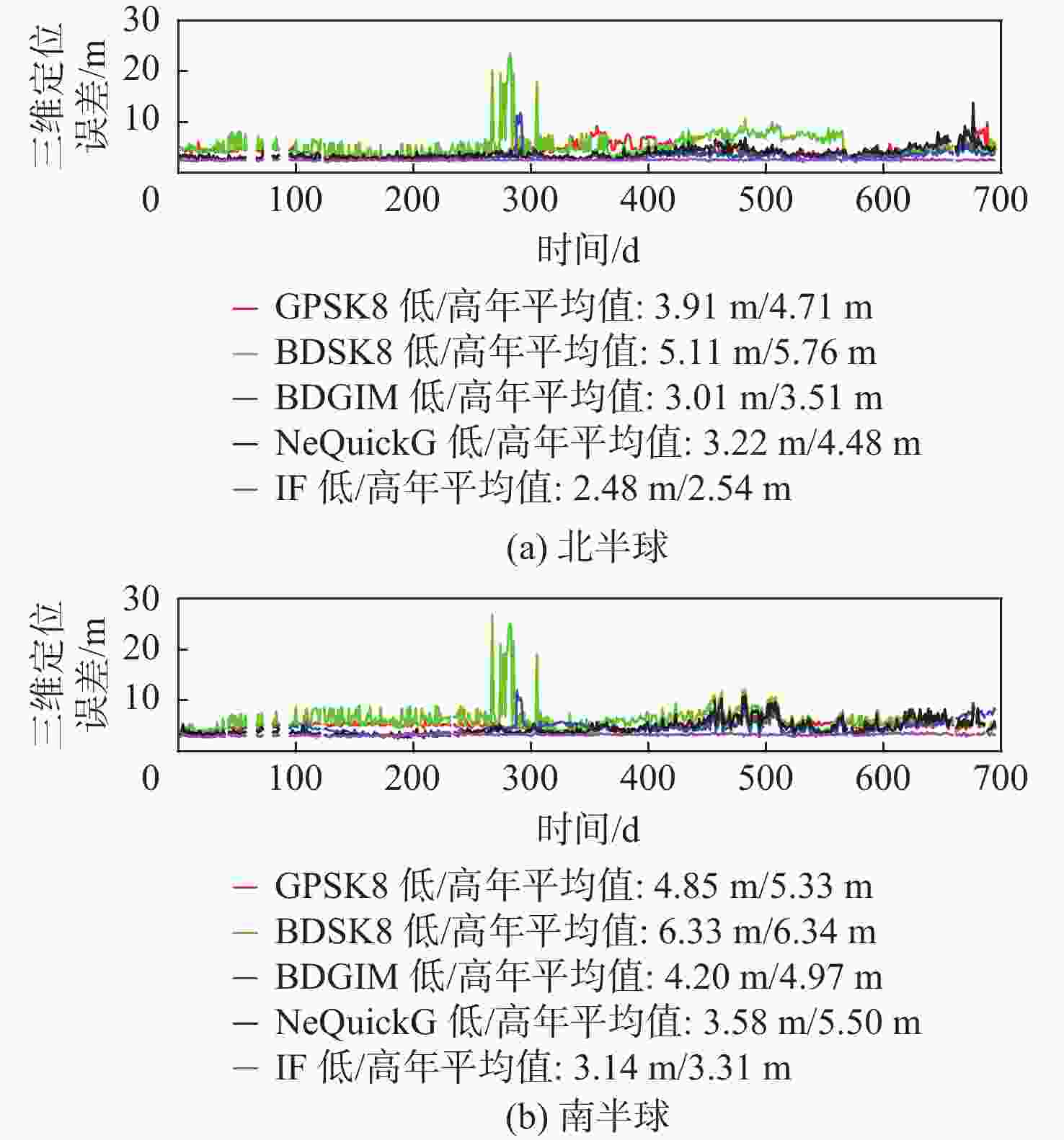
为评估现有全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)中广播电离层模型性能,利用国际GNSS服务(IGS)分析中心提供的事后全球电离层图(GIM)产品,对北斗系统、全球定位系统(GPS)、Galileo系统的广播电离层模型进行了电离层总电子含量(TEC)域及定位域的长期精度评估。发现在太阳活动爬坡过程中,北斗Klobuchar八参数模型(BDSK8)、GPS Klobuchar八参数模型(GPSK8)、北斗全球广播电离层模型(BDGIM)及NeQuickG 4种模型的精度均有一定程度的下降,在不同纬度带也表现出不同的特性。结果表明:BDGIM性能最优,在3个纬度带的误差均方根(RMS)均值分别上升至7.27、4.43、4.00 TECU,三维定位误差分别上升至6.62、2.81、3.51 m;BDSK8受太阳活动影响最大,RMS的放大系数可达4~5倍。利用Bagging回归树学习器对各广播电离层模型误差和空间物理参数进行了建模和预报,其中,BDGIM模型预测效果最优,3个纬度带的均方根误差(RMSE)分别为2.13、1.23、1.47 TECU,相对误差(RE)分别为18%、15%、14%;NeQuickG模型次之,RMSE分别为4.60、2.27、1.47 TECU,RE分别为17%、18%、21%;2种Klobuchar模型精度的预报效果不佳。
Abstract:To evaluate the performance of broadcast ionospheric models in existing global navigation satellite systems (GNSS), post-processed global ionospheric map (GIM) products provided by the International GNSS Service (IGS) Analysis Center are used. Long-term accuracy evaluations of ionospheric total electron content (TEC) and positioning domains are conducted for the BeiDou system, global positioning system (GPS), and Galileo broadcast ionospheric models. It is observed that during the solar activity ramp-up, the accuracy of all four models (BeiDou system Klobuchar 8-parameter model (BDSK8), GPS Klobuchar 8-parameter model (GPSK8), BeiDou global ionospheric model (BDGIM), NeQuickG) declines to varying extents, with distinct characteristics observed in different latitude bands. The results indicate that the BDGIM exhibits the best performance, with root mean square (RMS) increasing to 7.27, 4.43, and 4.00 TECU in the three latitude bands, and three-dimensional positioning errors increasing to 6.62, 2.81, and 3.51 meters, respectively. The BDSK8 is most influenced by solar activity, with an RMS amplification factor reaching up to 4 to 5 times. Finally, a Bagging regression tree learner is used to model and predict errors in various broadcast ionospheric models based on space physics parameters. The BDGIM model demonstrates the best predictive performance, with root mean square errors (RMSE) of 2.13, 1.23, and 1.47 TECU for the three latitude bands, and relative errors (RE) of 18%, 15%, and 14%, respectively. The NeQuickG model ranks second, with RMSE values of 4.60, 2.27, and 1.47 TECU, and RE of 17%, 18%, and 21%, respectively. The predictive accuracy of the two Klobuchar models is unsatisfactory.
-
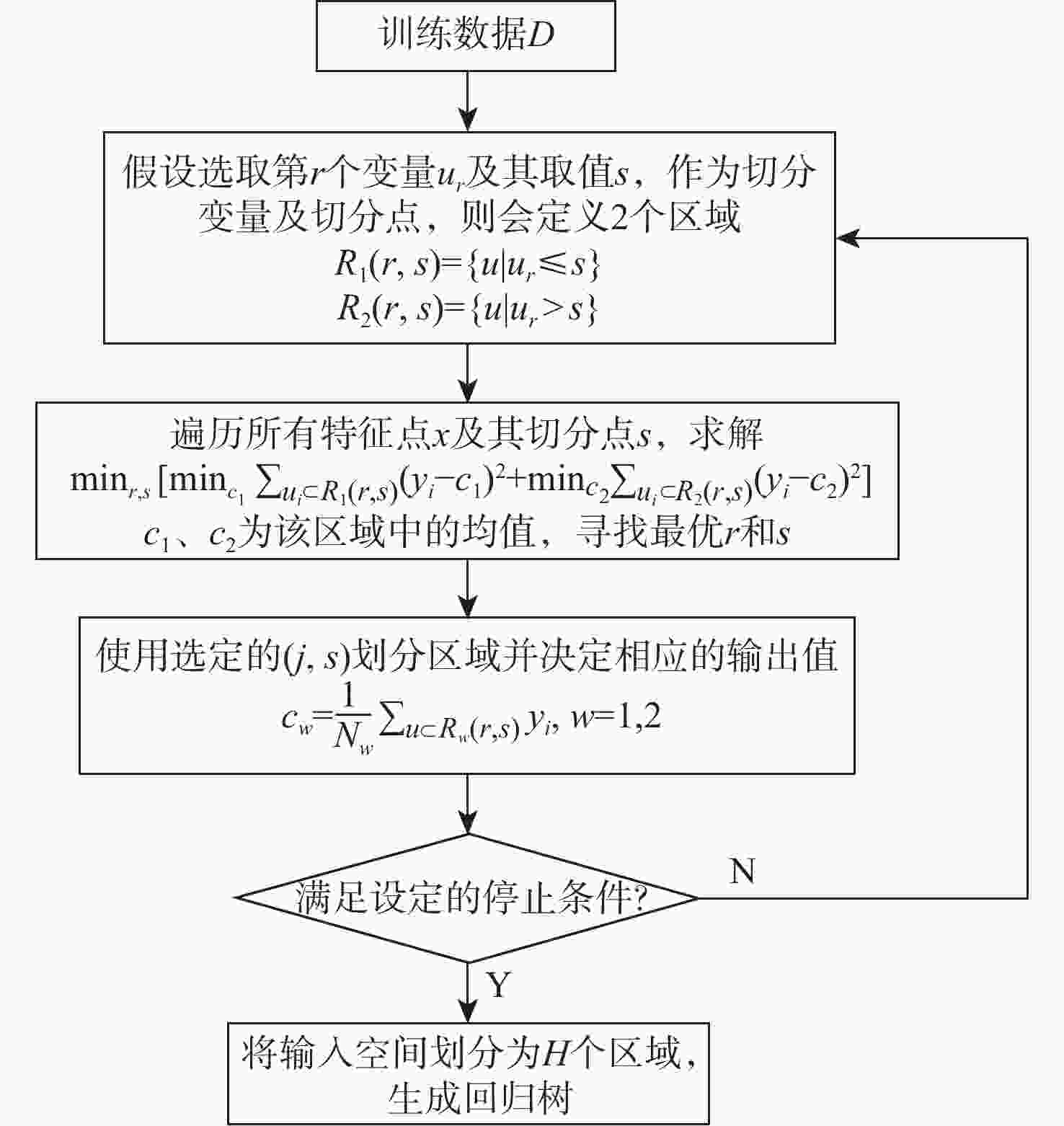
表 1 Bagging回归树对各广播电离层模型预报误差
Table 1. Forecast errors of Bagging regression tree for various broadcast ionospheric models
模型 纬度 RMSE RE/% BDSK8 低 5.20 36 中 1.43 15 高 3.23 26 GPSK8 低 6.20 46 中 3.90 31 高 5.30 42 NeQuickG 低 4.60 17 中 2.27 18 高 1.47 21 BDGIM 低 2.13 18 中 1.23 15 高 1.47 14 -
[1] 刘经南. 广域差分GPS原理和方法[M]. 北京: 测绘出版社, 1999.LIU J N. Principle and method of wide-area differential GPS[M]. Beijing: Sino Maps Press, 1999(in Chinese). [2] KLOBUCHAR J A. Ionospheric time-delay algorithm for single-frequency GPS users[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1987, AES-23(3): 325-331. [3] 王宁波. GNSS差分码偏差处理方法及全球广播电离层模型研究[J]. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(8): 1069. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20160387WANG N B. Study on GNSS differential code biases and global broadcast ionospheric models of GPS, Galileo and BDS[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(8): 1069(in Chinese). doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20160387 [4] 霍星亮. 基于GNSS的电离层形态监测与延迟模型研究[D]. 武汉: 中国科学院测量与地球物理研究所, 2008.HUO X L. Study on ionospheric morphology monitoring and delay model based on GNSS[D]. Whuhan: Institute of Geodesy and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2008(in Chinese). [5] 袁运斌, 霍星亮, 张宝成. 近年来我国GNSS电离层延迟精确建模及修正研究进展[J]. 测绘学报, 2017, 46(10): 1364-1378. doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170349YUAN Y B, HUO X L, ZHANG B C. Research progress of precise models and correction for GNSS ionospheric delay in China over recent years[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2017, 46(10): 1364-1378(in Chinese). doi: 10.11947/j.AGCS.2017.20170349 [6] 张强, 赵齐乐, 章红平, 等. 北斗卫星导航系统Klobuchar模型精度评估[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2014, 39(2): 142-146.ZHANG Q, ZHAO Q L, ZHANG H P, et al. Evaluation on the precision of Klobuchar model for BeiDou navigation satellite system[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2014, 39(2): 142-146(in Chinese). [7] 章红平. 基于地基GPS的中国区域电离层监测与延迟改正研究[D]. 上海: 中国科学院上海天文台, 2006.ZHANG H P. Study on ionospheric monitoring and delay correction in China area based on ground-based GPS[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2006(in Chinese). [8] ZHU Y X, TAN S S, ZHANG Q H, et al. Accuracy evaluation of the latest BDGIM for BDS-3 satellites[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2019, 64(6): 1217-1224. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2019.06.021 [9] WANG N B, LI Z S, YUAN Y B, et al. BeiDou global ionospheric delay correction model (BDGIM): performance analysis during different levels of solar conditions[J]. GPS Solutions, 2021, 25(3): 97. doi: 10.1007/s10291-021-01125-y [10] TIAN Y, LI S H, SHEN H, et al. Comparative analysis of BDGIM, NeQuick-G, and Klobuchar ionospheric broadcast models[J]. Astrophysics and Space Science, 2022, 367(8): 78. doi: 10.1007/s10509-022-04109-7 [11] 袁运斌, 李敏, 霍星亮, 等. 北斗三号全球导航卫星系统全球广播电离层延迟修正模型(BDGIM)应用性能评估[J]. 测绘学报, 2021, 50(4): 436-447.YUAN Y B, LI M, HUO X L, et al. Research on performance of BeiDou global broadcast ionospheric delay correction model (BDGIM) of BDS-3[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica, 2021, 50(4): 436-447(in Chinese). [12] 吴晓莉, 戴春丽, 刘利, 等. 地理与地磁坐标系下的K氏电离层延迟模型分析比较[C]//第一届中国卫星导航学术年会论文集(下). 北京: 中国卫星导航学术年会组委会, 2010: 288-293.WU X L, DAI C L, LIU L, et al. Analysis the difference between Klobuchar ionosphere model in geography and in geomagnetism reference frame[C]//Proceedings of the 1st China Satellite Navigation Conference (Part 2). Beijing: Organizing Committee of China Satellite Navigation Conference, 2010: 288-293(in Chinese). [13] LIU A, WANG N B, LI Z S, et al. Validation of CAS’s final global ionospheric maps during different geomagnetic activities from 2015 to 2017[J]. Results in Physics, 2018, 10: 481-486. doi: 10.1016/j.rinp.2018.06.057 [14] ZHANG Q, LIU X Z, LIU Z Y, et al. Performance evaluation of BDS-3 ionospheric delay correction models (BDSK and BDGIM): first year for full operational capability of global service[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2022, 70(3): 687-698. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2022.05.009 [15] YASYUKEVICH Y V, ZATOLOKIN D, PADOKHIN A, et al. Klobuchar, NeQuickG, BDGIM, GLONASS, IRI-2016, IRI-2012, IRI-plas, NeQuick2, and GEMTEC ionospheric models: a comparison in total electron content and positioning domains[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23(10): 4773. doi: 10.3390/s23104773 -






 下载:
下载: