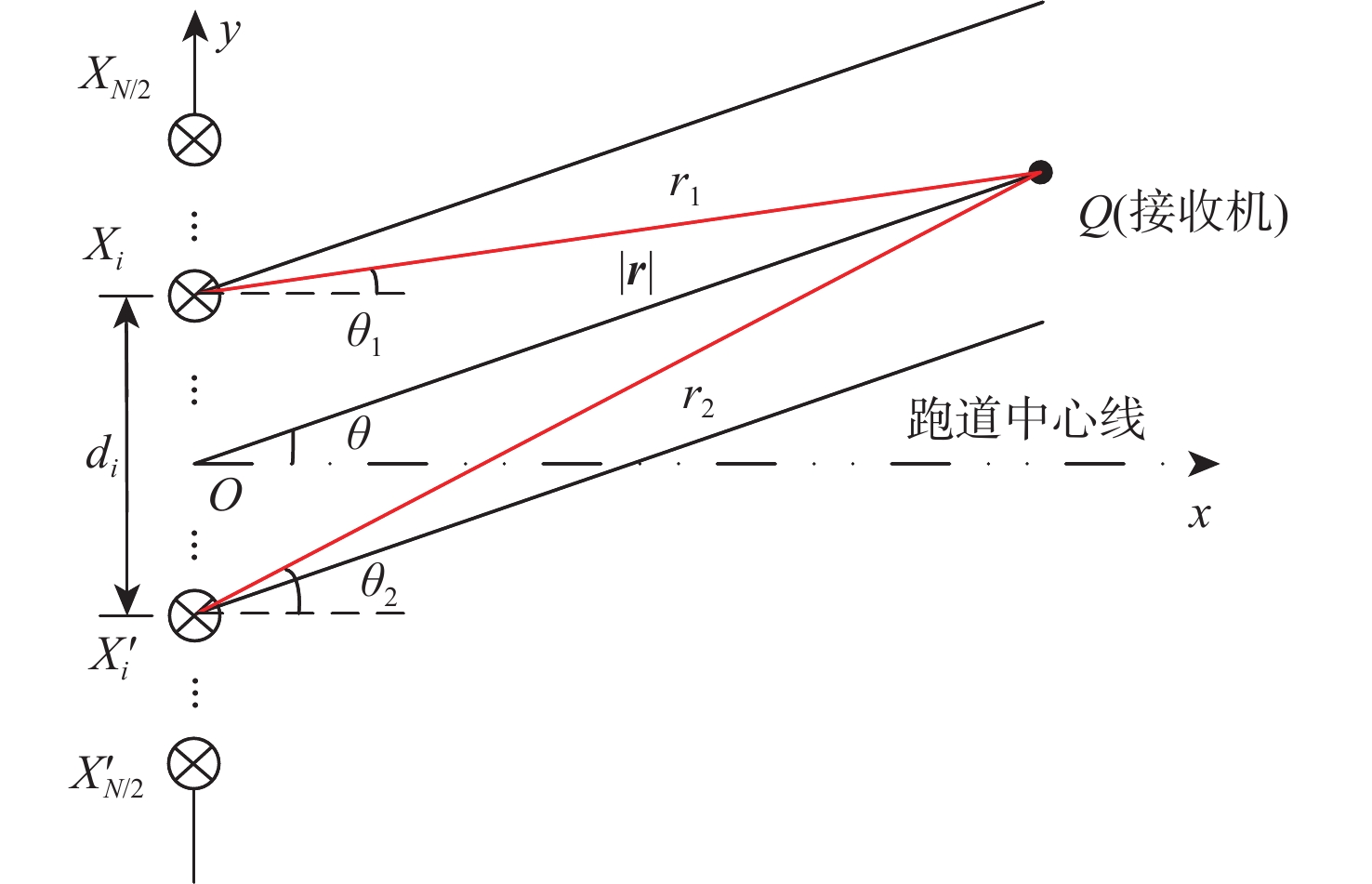
-
摘要:
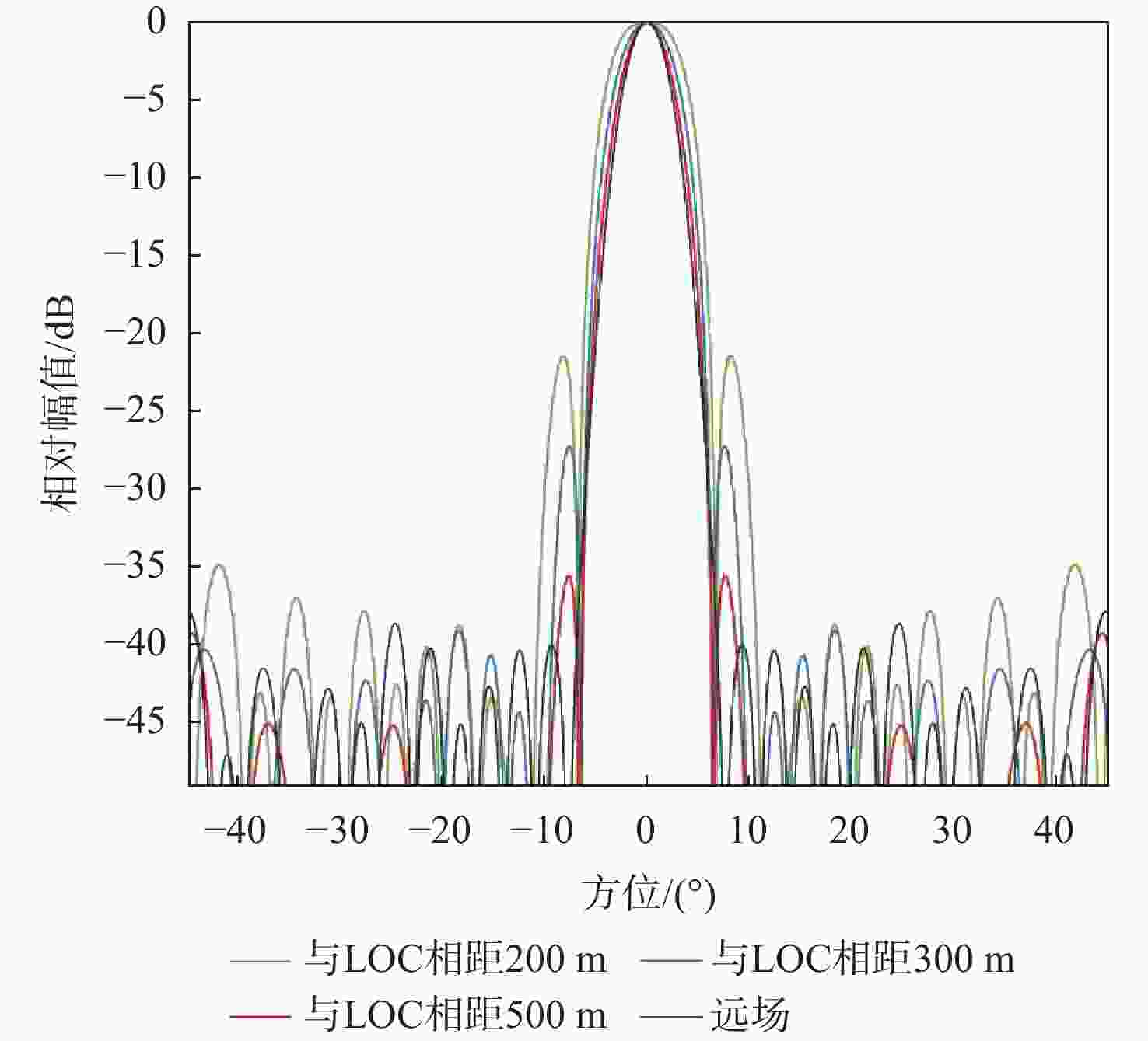
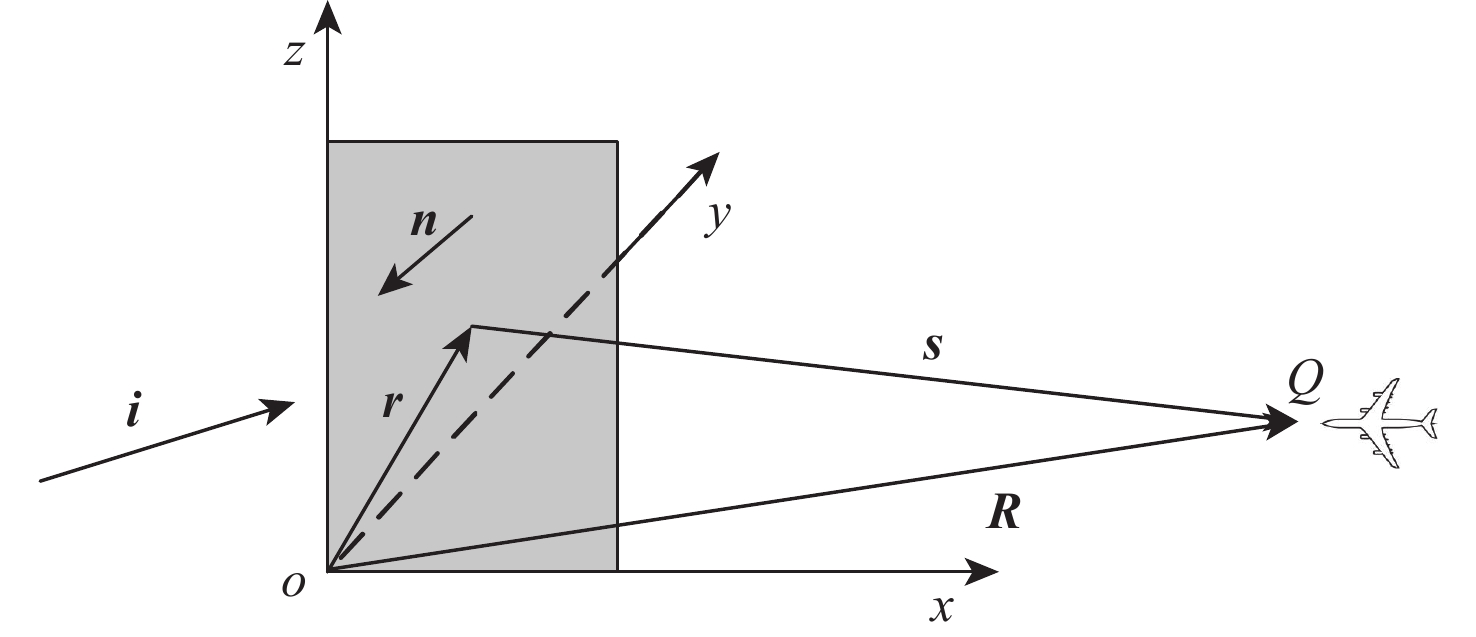
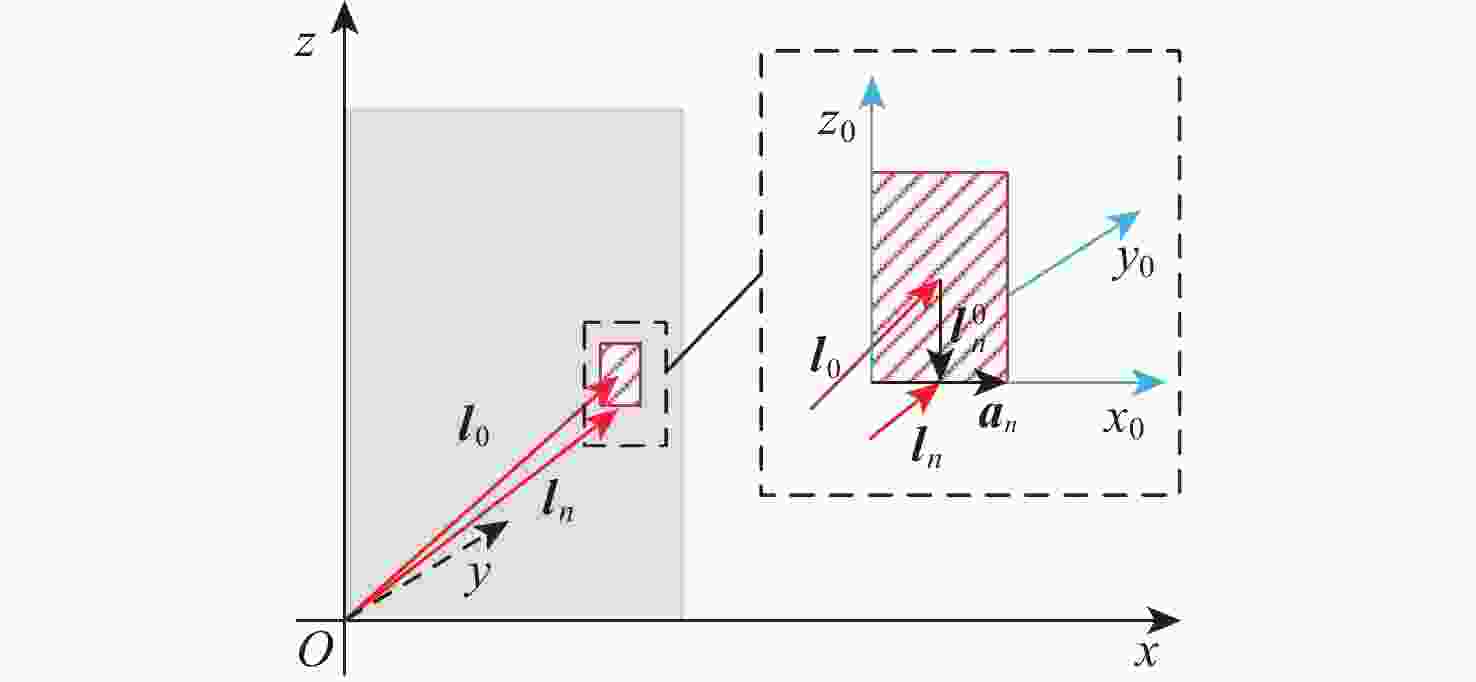
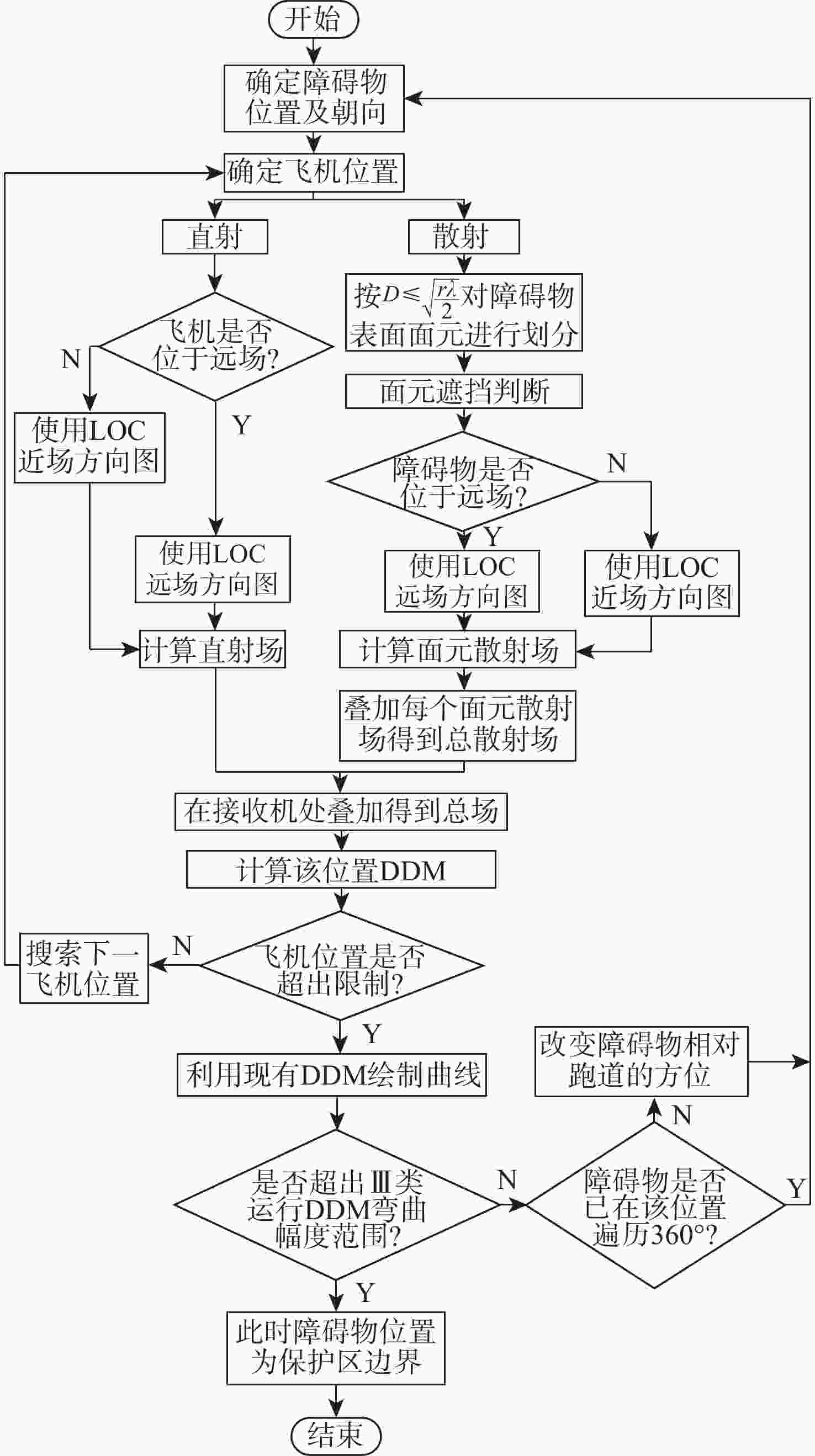
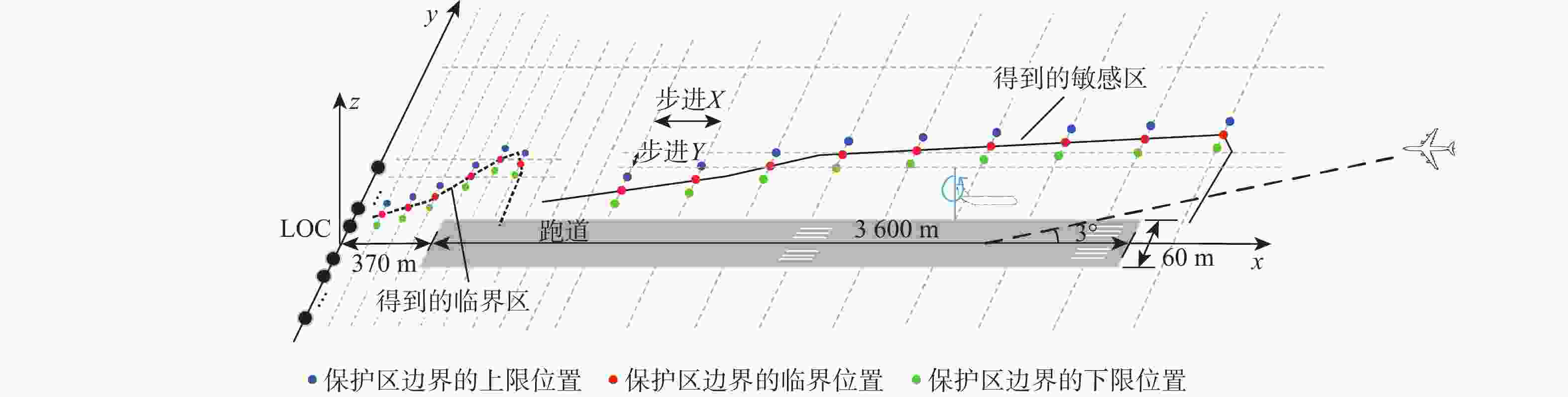
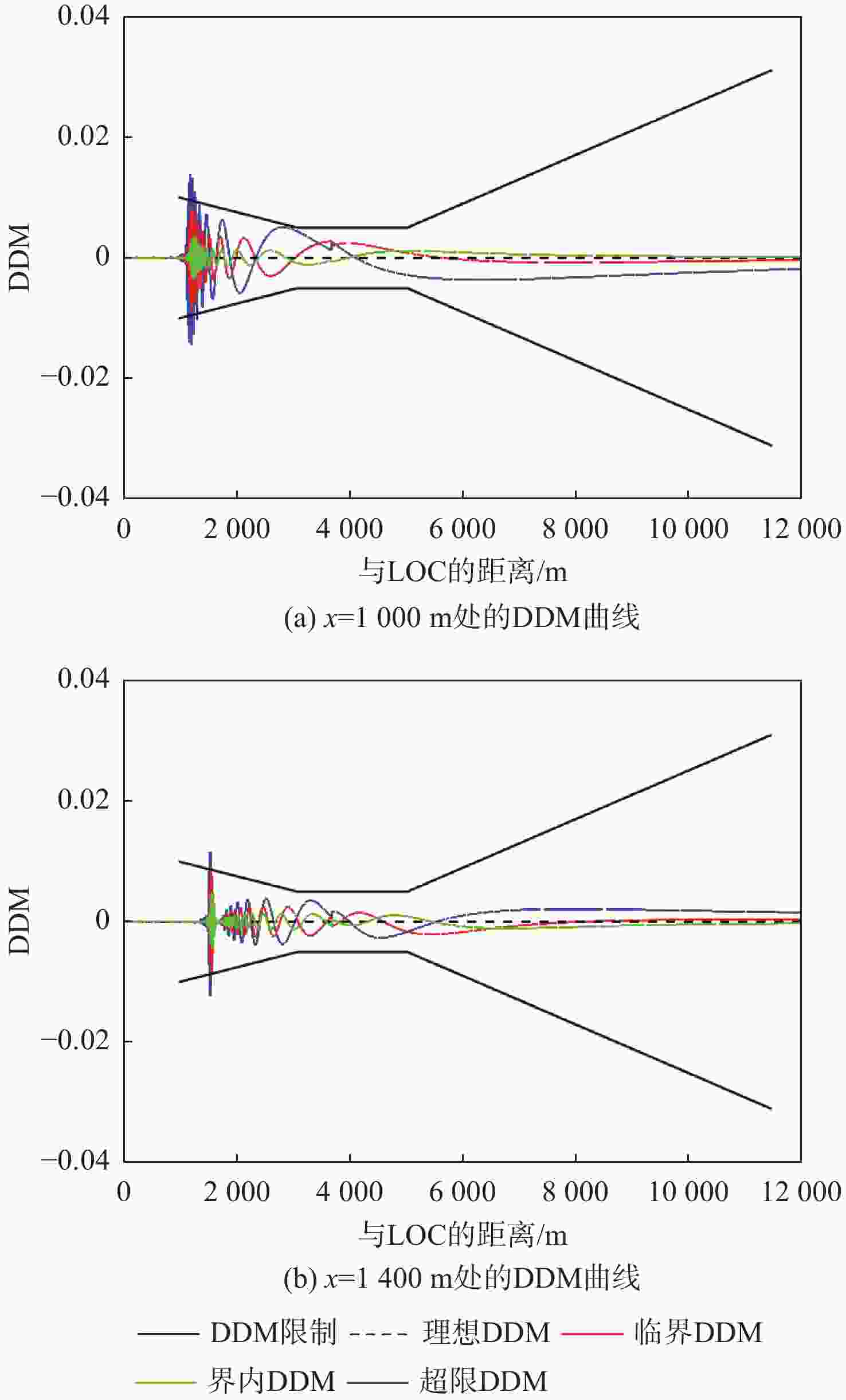
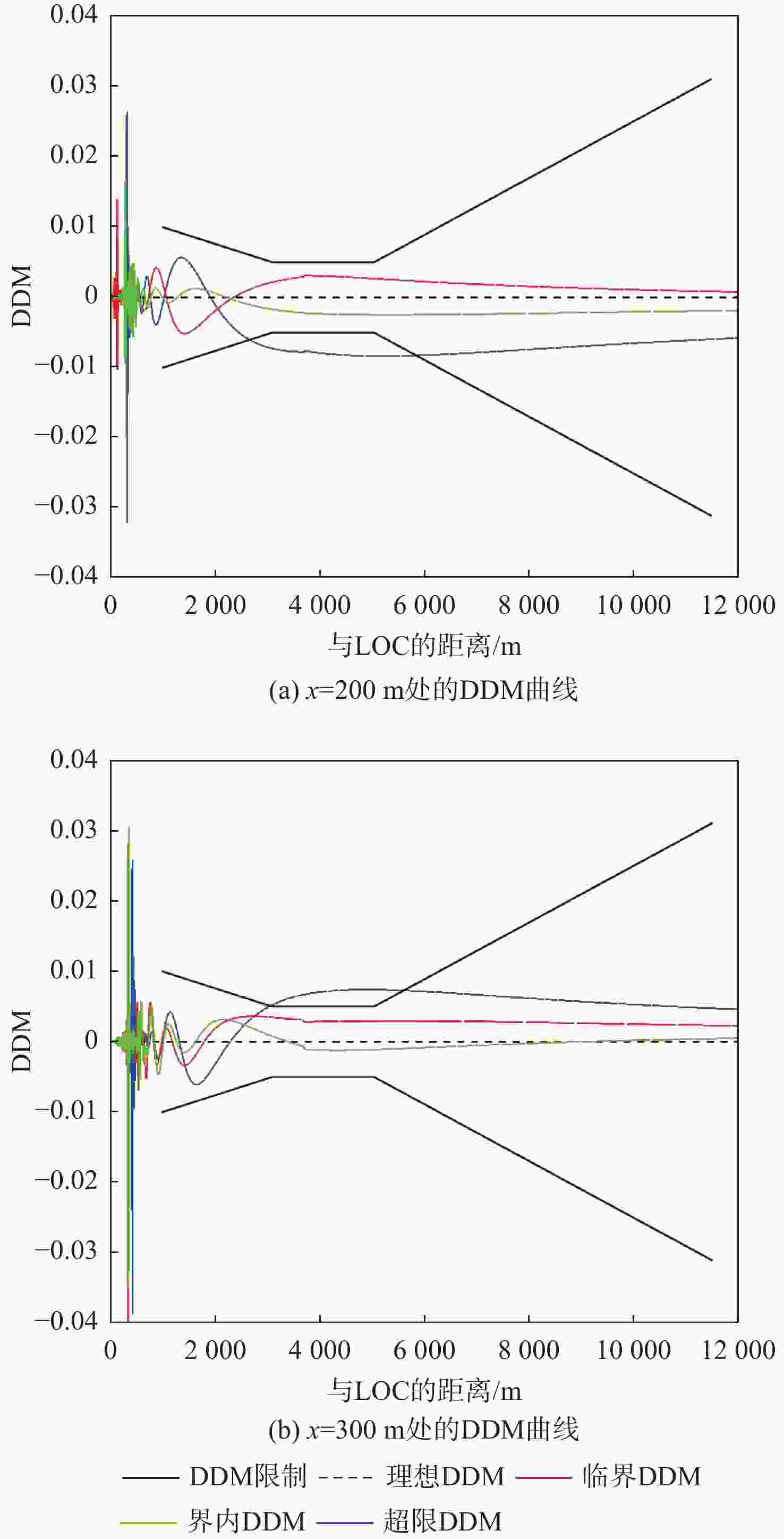
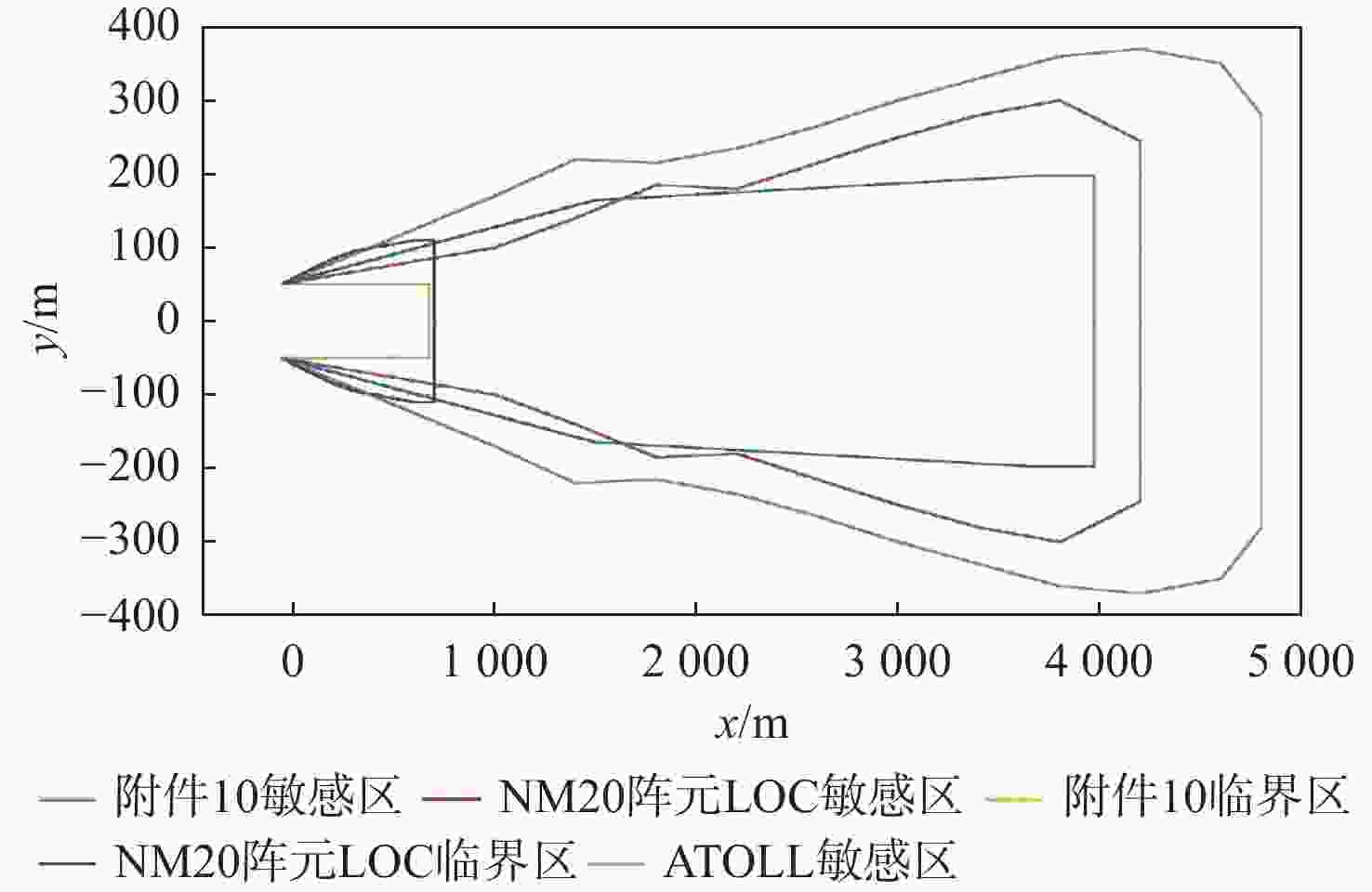
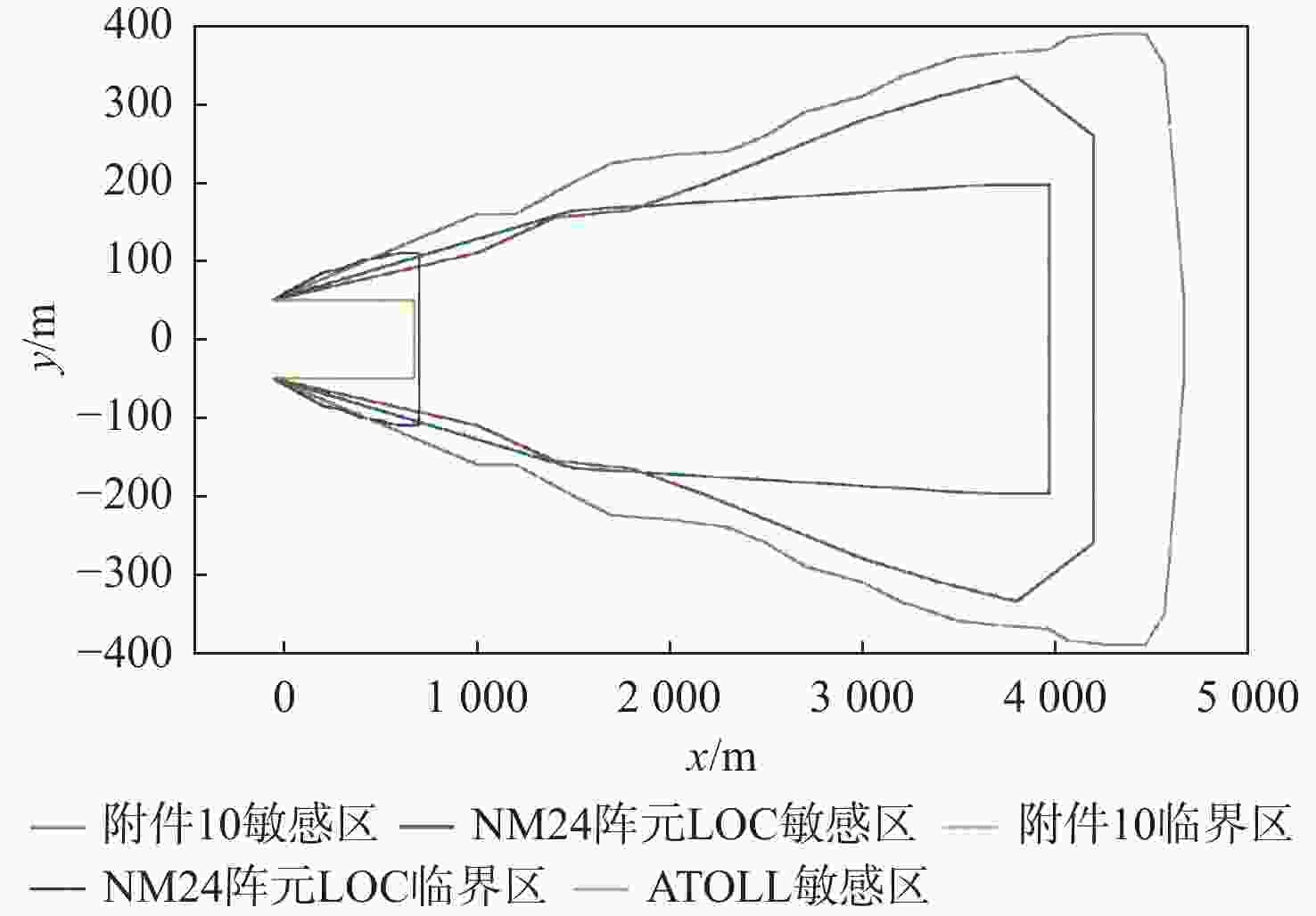
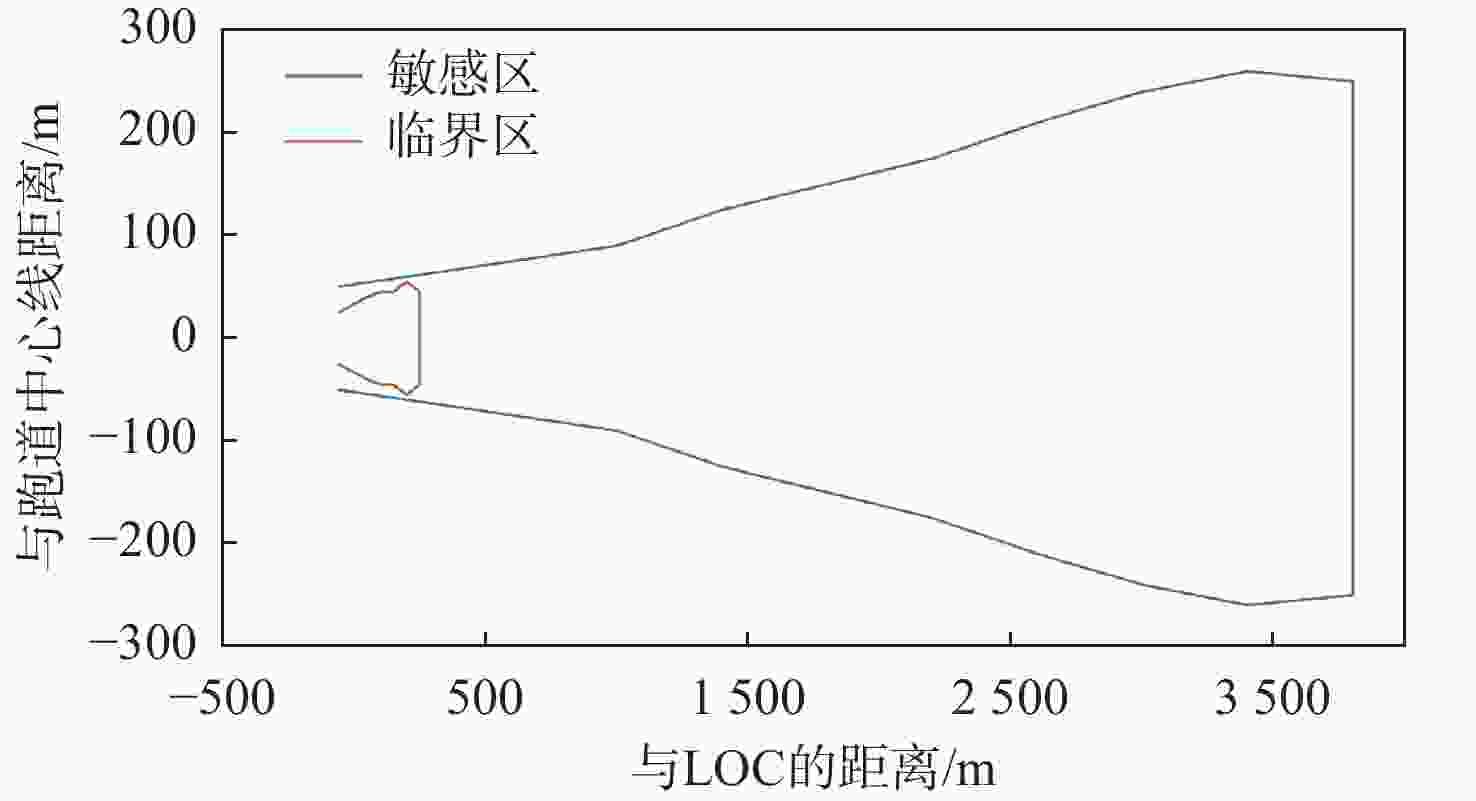
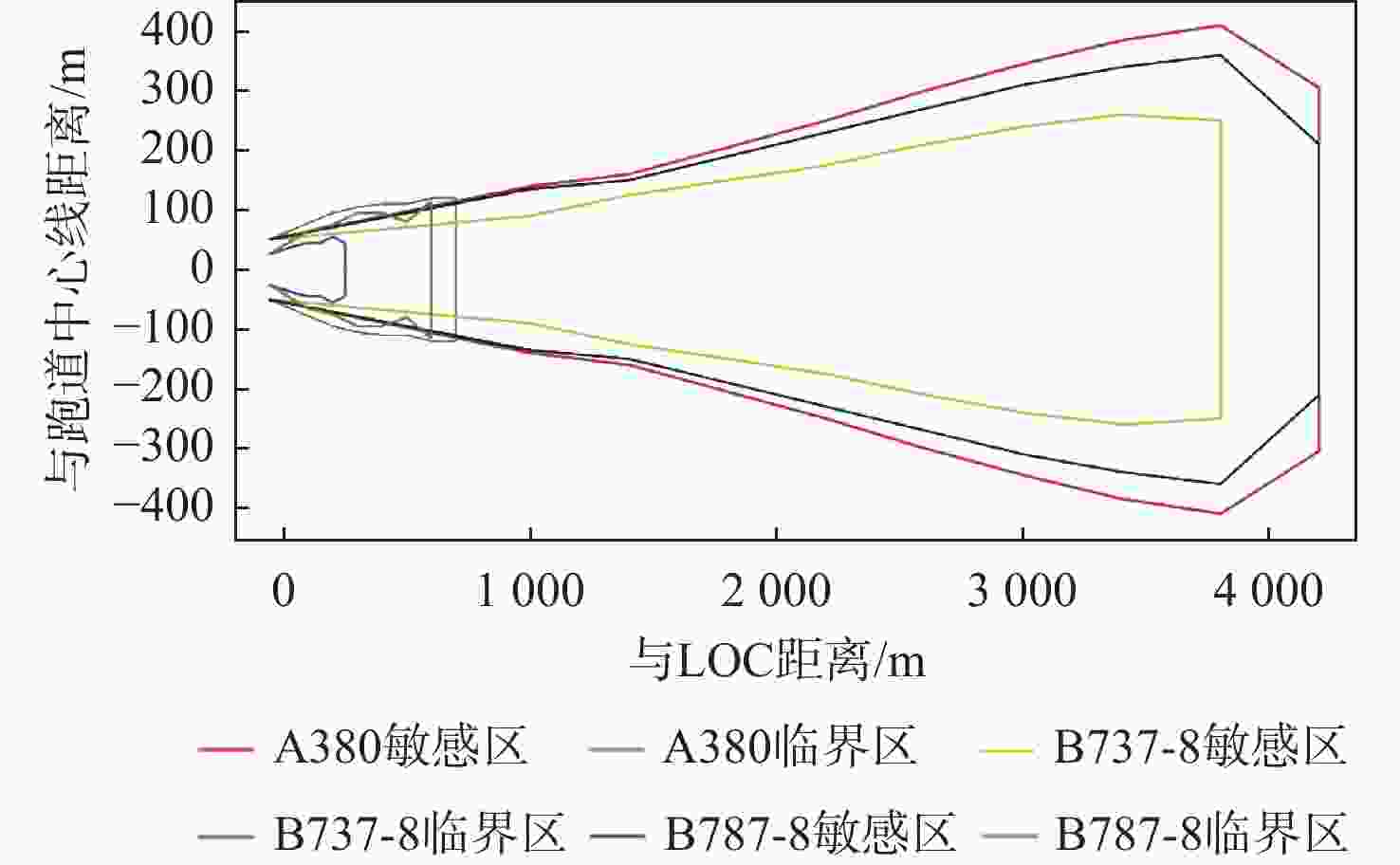
仪表着陆系统(ILS)保护区是保证飞机安全着陆的重要屏障。针对ILS中航向信标(LOC)保护区划设理论依据研究不足的问题,依据《国际民用航空公约》附件10的要求,利用物理光学(PO)法系统研究了LOC保护区的划设。对LOC辐射远场和近场进行划分,并推导求解LOC近场方向图,避免障碍物处于近场时仍使用远场条件计算带来的误差;结合跑道周围停止等待飞机的垂直表面特征进行面元划分,使用物理光学法计算这些飞机作为障碍物在不同位置及转向时造成的电磁散射场,根据其对进近着陆飞机接收信号调制度差(DDM)的影响程度划设LOC保护区;分别使用20阵元与24阵元LOC,以A380、B737-8与B787-8为障碍物进行LOC保护区划设仿真实验。实验结果与《国际民用航空公约》附件10规定的保护区具有较大接近度,敏感区差距最大处相差约100 m,临界区差距最大处相差约50 m;与专业软件ATOLL的仿真结果相比,保护区的走势基本相同。实验结果证明了所提思想方法、理论建模及技术处理的正确性,可以为LOC保护区划设提供重要理论依据。
Abstract:The instrument landing system (ILS) protection area is an important barrier to ensure the safe landing of aircraft. In view of the insufficiency in the theoretical study on the delineation of the protection area of the localizer (LOC) in the ILS, the LOC protection area is systematically studied for the first time using the physical optics (PO) method, in accordance with the requirements of the Annex 10 of the Convention on International Civil Aviation. First, the LOC radiation field is divided into far-field and near-field regions, and the LOC near-field radiation pattern is derived and solved to avoid errors caused by applying far-field conditions when obstacles are actually in the near-field. Then, based on the vertical surface characteristics of aircraft waiting around the runway, the surfaces are discretized into small facets. The electromagnetic scattering field caused by these aircraft, considered as obstacles in different positions and orientations, is calculated using the PO method. The LOC protection area is delineated according to the impact of these scattering fields on the difference in depth modulation (DDM) of the signal received by approaching aircraft. Finally, simulation experiments are conducted using 20-element and 24-element LOC arrays, with the A380, B737-8, and B787-8 serving as the obstacles. The simulation results show high consistency with the protection area requirements specified in Annex 10 of the Convention on International Civil Aviation, with the maximum deviation in the sensitive area being about 100 m and in the critical area about 50 m. Compared with simulations performed using the professional software ATOLL, the overall trend of the protection area is basically the same. The experimental results validate the correctness of the proposed conceptual approach, theoretical modeling, and technical processing, and can provide an important theoretical basis for LOC protection area delineation.
-
Key words:
- localizer /
- near field /
- protection area /
- physical optics method /
- electromagnetic scattering
-
表 1 实验设置
Table 1. Experimental setup
LOC型号 障碍物设置 临界区 敏感区 NM 20阵元LOC A380机身和尾翼 A380尾翼 NM 24阵元LOC A380机身和尾翼 A380尾翼 NM 20阵元LOC B737-8机身和尾翼 B737-8尾翼 NM 20阵元LOC B787-8机身和尾翼 B787-8尾翼 表 2 不同障碍物的近似尺寸
Table 2. Approximate dimensions of different obstacles
飞机
型号尾翼近似尺寸/m 机身近似尺寸/m 长 高 离地高度 长 高 离地高度 A380 8.5 14 10 72.5 8.5 1.5 B737-8 3 8.5 4 39.5 2.7 1.3 B787-8 6.7 9 8 56.7 6 2 表 3 NM 20阵元LOC保护区边界坐标
Table 3. Boundary coordinates of NM 20-element LOC protection area
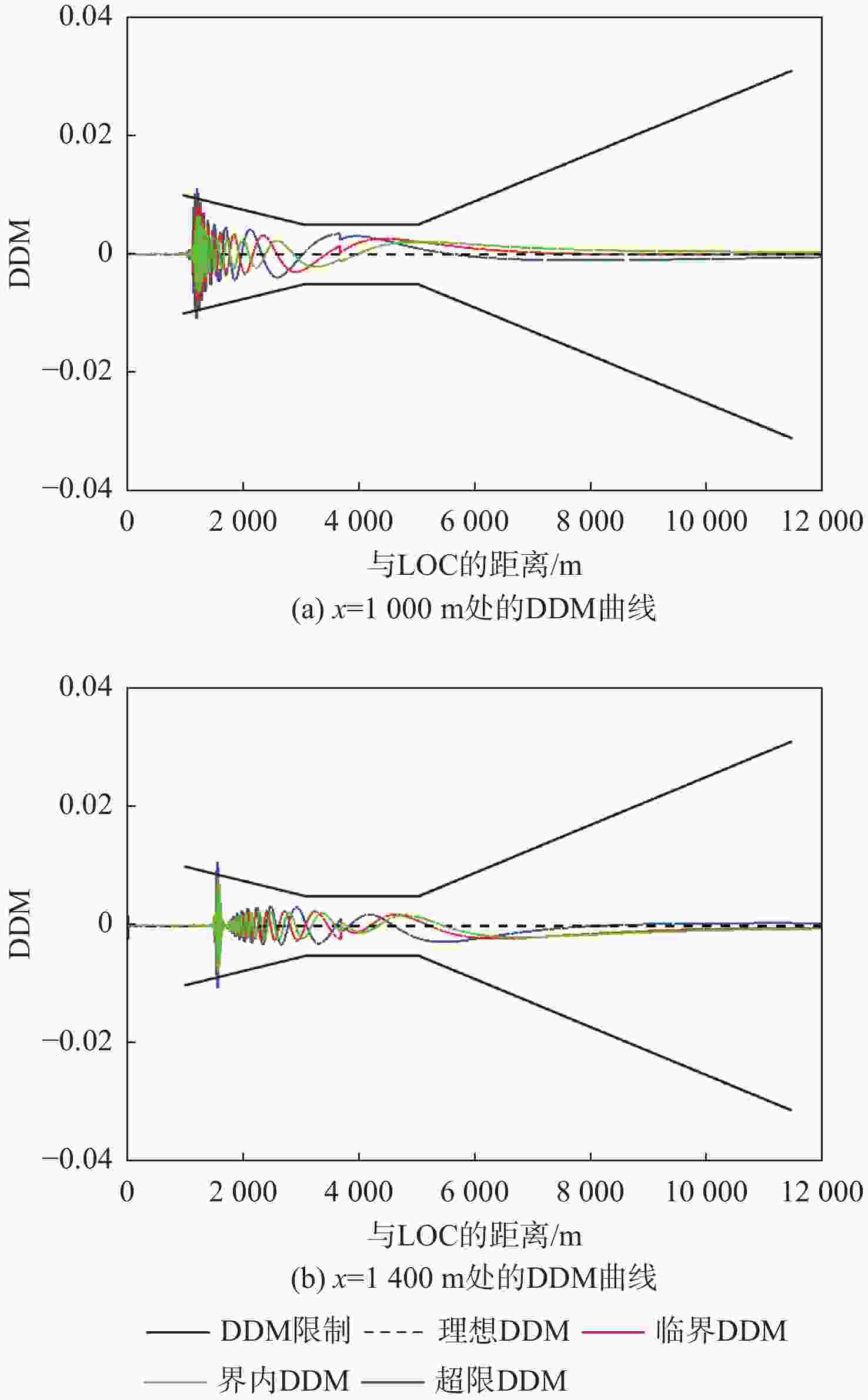
保护区 x/m y/m 敏感区 1000 100 1400 140 1800 185 2200 180 2600 215 3000 250 3400 280 3800 300 4200 245 临界区 200 85 300 95 400 100 500 105 600 110 700 110 表 4 NM 24阵元LOC保护区边界坐标
Table 4. Boundary coordinates of NM 24-element LOC protection area
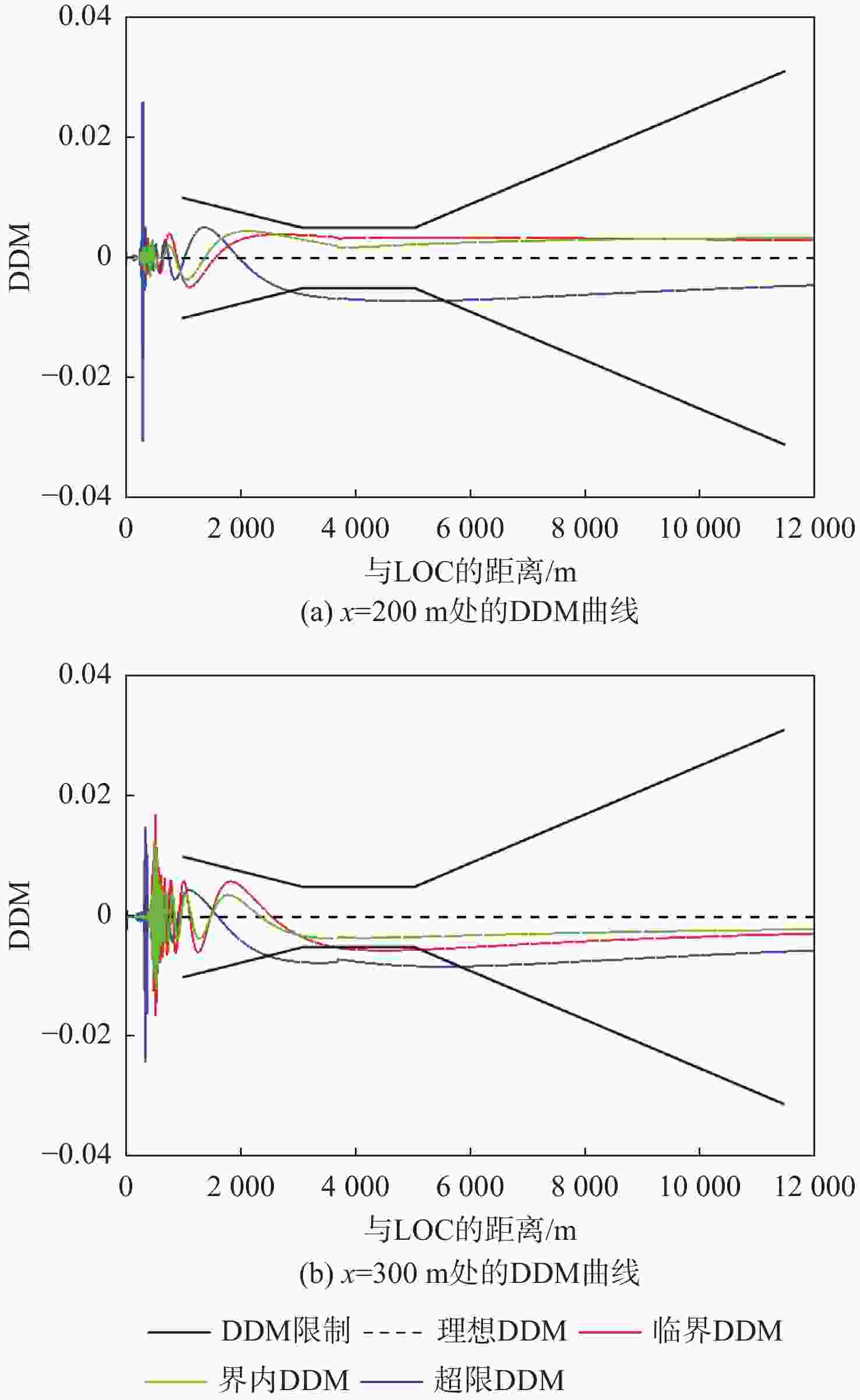
保护区 x/m y/m 敏感区 1000 110 1400 155 1800 165 2200 200 2600 240 3000 280 3400 310 3800 335 4200 260 临界区 200 85 300 90 400 100 500 105 600 110 700 110 表 5 B737-8为障碍物时NM 20阵元LOC保护区边界坐标
Table 5. Boundary coordinates of NM 20-element LOC protection area with B737-8 as obstacle
保护区 x/m y/m 敏感区 1000 90 1400 125 1800 150 2200 175 2600 205 3000 235 3400 255 3800 245 临界区 50 40 100 45 150 45 200 55 250 45 表 6 B787-8为障碍物时NM 20阵元LOC保护区边界坐标
Table 6. Boundary coordinates of NM 20-element LOC protection area with B787-8 as obstacle
保护区 x/m y/m 敏感区 1000 135 1400 150 1800 190 2200 230 2600 270 3000 310 3400 340 3800 260 4200 210 临界区 100 65 200 75 300 95 400 95 500 80 600 115 -
[1] 鲁合德, 张强. 高铁弓网电弧对飞机进近着陆的电磁干扰影响[J]. 航空学报, 2020, 41(10): 324036.LU H D, ZHANG Q. EMI effect of pantograph catenary arc of high-speed railway on aircraft approach landing[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2020, 41(10): 324036(in Chinese). [2] 倪育德, 张振楠, 刘瑞华, 等. GBAS与ILS联合导航系统数据融合方法与验证[J]. 信号处理, 2022, 38(11): 2385-2399.NI Y D, ZHANG Z N, LIU R H, et al. Data fusion method of GBAS and ILS joint navigation system[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(11): 2385-2399(in Chinese). [3] 倪育德, 卢丹, 王颖, 等. 导航原理与系统[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2015: 238-241.NI Y D, LU D, WANG Y, et al. Navigation principles and systems[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2015: 238-241(in Chinese). [4] 倪育德, 于颖丽, 刘瑞华. 保护区内地形对ILS下滑信标辐射场的影响[J]. 信号处理, 2022, 38(9): 1892-1902.NI Y D, YU Y L, LIU R H. Influence of terrain in protected area on radiation field of glide slope of ILS[J]. Journal of Signal Processing, 2022, 38(9): 1892-1902(in Chinese). [5] International Civil Aviation Organization. Aeronautical telecommunications. Annex 10 to the convention on international civil aviation. Volume Ⅰ(6th edition)[S]. Montreal: International Civil Aviation Organization, 2006. [6] International Civil Aviation Organization. Aeronautical telecommunications. Annex 10 to the convention on international civil aviation. Volume Ⅰ(7th edition)[S]. Montreal: International Civil Aviation Organization, 2018. [7] Department of Transportation Federal Aviation Administration. Siting criteria for instrument landing systems: FAA ORDER 6750.16E[S]. Washington, D. C. : Federal Aviation Administration, 2014. [8] 中国民用航空局. 民用航空通信导航监视台(站)设置场地规范 第1部分: 导航: MH/T 4003.1—2021[S]. 北京: 中国民用航空局, 2021.Civil Aviation Administration of China. Specification for aeronautical communication navigation and surveillance station siting criteria-Part 1: navigation: MH/T 4003.1—2021[S]. Beijing: Civil Aviation Administration of China, 2021(in Chinese). [9] 刘勇, 吴德伟, 王永胜. 仪表着陆系统辐射场型的场地影响分析[J]. 无线电通信技术, 2004, 30(2): 31-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2004.02.012LIU Y, WU D W, WANG Y S. Site impact analysis of radiation pattern of instrument landing system[J]. Radio Communications Technology, 2004, 30(2): 31-33(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2004.02.012 [10] 李紫丹. 基于回波模型多径效应对航向信标系统的影响研究[J]. 信息通信, 2015, 28(3): 18.LI Z D. Research on the influence of multipath effect on heading beacon system based on echo model[J]. Information & Communications, 2015, 28(3): 18(in Chinese). [11] THAIN A, ESTIENNE J P, PERES G, et al. Comparisons of different approaches for ILS simulation[C]//Proceedings of the 4th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 1-5. [12] THAIN A, ESTIENNE J P, ROBERT J, et al. A solution for ILS disturbance due to a building[C]//Proceedings of the 6th European Conference on Antennas and Propagation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2012: 2392-2395. [13] 朱峰, 翁文雯, 谢雨轩, 等. 多径效应对航向信标系统电磁环境影响分析[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41(12): 2703-2709.ZHU F, WENG W W, XIE Y X, et al. Analysis of influence of multipath effect on electromagnetic environment of localizer[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(12): 2703-2709(in Chinese). [14] 陈超, 黄裕文. 仪表着陆系统下滑信号结构分析与改善[J]. 现代雷达, 2020, 42(7): 17-22.CHEN C, HUANG Y W. Analysis and improvement of glide signal structure of instrument landing system[J]. Modern Radar, 2020, 42(7): 17-22(in Chinese). [15] WANG Q Q, SHEN Z Y, CHENG X M, et al. A fast ILS electromagnetic covering analysis method for new obstacles impact at expanded airport[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/AIAA 38th Digital Avionics Systems Conference. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2019: 1-5. [16] 费钟阳, 蒋相闻, 招启军. 基于动态RCS特征相似的直升机靶机旋翼设计[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(7): 125465.FEI Z Y, JIANG X W, ZHAO Q J. Design of helicopter target rotor based on similar dynamic RCS characteristics[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(7): 125465(in Chinese). [17] REDLICH R W, GORMAN J T. Disturbance of ILS localizer signals by reflections from large hangers[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1969, AES-5(6): 1001-1002. [18] SHIH S L. LS localizer multipath analysis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1971, AES-7(1): 54-60. [19] HONDA J, YOKOYAMA H, TAJIMA H, et al. Influences of 3D aircraft model to ILS localizer[C]//Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Complex, Intelligent, and Software Intensive Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 180-185. [20] HONDA J. Influences of scattered field caused by buildings to ILS localizer in Airport[C]//Proceedings of the International Symposium on Antennas and Propagation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-4. [21] 赵修斌, 戴传金, 许进, 等. 进近着陆系统多径效应仿真设计与实现[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2006, 18(11): 3316-3319. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-731X.2006.11.078ZHAO X B, DAI C J, XU J, et al. Design of simulations for multipath effect of the approaching landing system and implementation[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2006, 18(11): 3316-3319(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-731X.2006.11.078 [22] 吴华新, 赵修斌, 陈校平, 等. PO分米波着陆系统多径环境分析和仿真[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2011, 36(8): 103-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2011.08.026WU H X, ZHAO X B, CHEN X P, et al. Analysis and simulation of multi-path environment for decimeter wave instrument landing system based on physical optics[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2011, 36(8): 103-106(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2011.08.026 [23] 吴华新, 赵修斌, 戴传金. 基于PO的进近着陆系统信道环境分析和仿真预测[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2012, 24(2): 414-418.WU H X, ZHAO X B, DAI C J. Analysis and simulation prediction on approach landing system channel environment based on physical optics[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2012, 24(2): 414-418(in Chinese). [24] GONG F X, GUO F Y, MA Y Q. Analysis of electromagnetic interference on localizer beam using in parallel runway[C]//Proceedings of the 4th IEEE International Symposium on Microwave, Antenna, Propagation and EMC Technologies for Wireless Communications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 562-565. [25] 倪育德, 于颖丽, 刘瑞华, 等. 大型障碍物影响下航向信标敏感区的划设[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 45(2): 360-372.NI Y D, YU Y L, LIU R H, et al. Setting the sensitive area of localizer under the influence of large obstacles[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(2): 360-372(in Chinese). [26] 赵京城, 娄长玉, 李家碧, 等. 一种方形腔体的目标散射特性及测量方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(12): 2415-2424.ZHAO J C, LOU C Y, LI J B, et al. Scattering characteristics and measurement method of a square cavity[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(12): 2415-2424(in Chinese). [27] HUO J C, XU L, SHI X W, et al. An accelerated PO for EM scattering from electrically large targets[J]. IEEE Antennas and Wireless Propagation Letters, 2021, 20(12): 2300-2304. doi: 10.1109/LAWP.2021.3108786 [28] 郭霄, 杨青真, 文振华, 等. 吸波材料脱落对球面收敛喷管电磁散射特性的影响[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(6): 224466.GUO X, YANG Q Z, WEN Z H, et al. Influence of RAM abscission on electromagnetic scattering characterisitic of cavity[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(6): 224466(in Chinese). [29] 苏东林, 崔朔, 白江飞, 等. 复杂电磁环境辐射-散射耦合场快速预估方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(9): 1553-1560.SU D L, CUI S, BAI J F, et al. Fast prediction method for radiated and scattered coupled fields in complex electromagnetic environment[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(9): 1553-1560(in Chinese). [30] XIAO D H, GUO L X, LIU W, et al. Efficient RCS prediction of the conducting target based on physics-inspired machine learning and experimental design[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propagation, 2021, 69(4): 2274-2289. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2020.3027594 [31] 秦远田, 孙汗青, 岳鑫. 微小卫星隐身构型设计及优化分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(11): 2102-2110.QIN Y T, SUN H Q, YUE X. Stealthy configuration design and optimization analysis of microsatellite[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(11): 2102-2110(in Chinese). [32] 中国民用航空总局. 航空无线电导航设备 第1部分: 仪表着陆系统(ILS)技术要求: MH/T 4006.1—1998[S]. 北京: 中国民用航空总局, 1998.General Administration of Civil Aviation of China. Aeronautical radio navigation aids. Part 1: technical requirements for instrument landing system (ILS): MH/T 4006.1—1998[S]. Beijing: General Administration of Civil Aviation of China, 1998(in Chinese). -






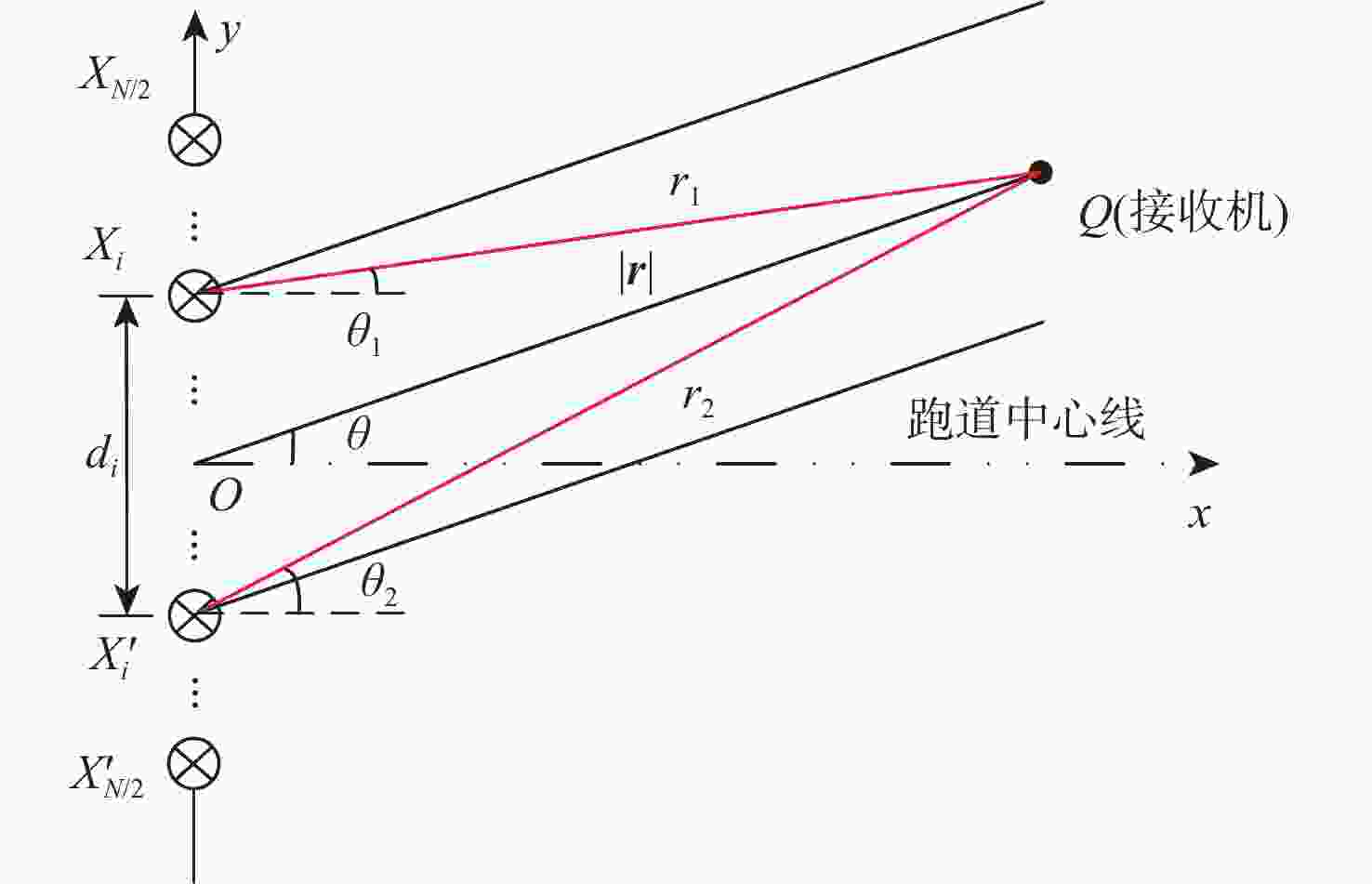
 下载:
下载: