Dual-stream deep network for infrared gait recognition based on residual multi-scale fusion
-
摘要:
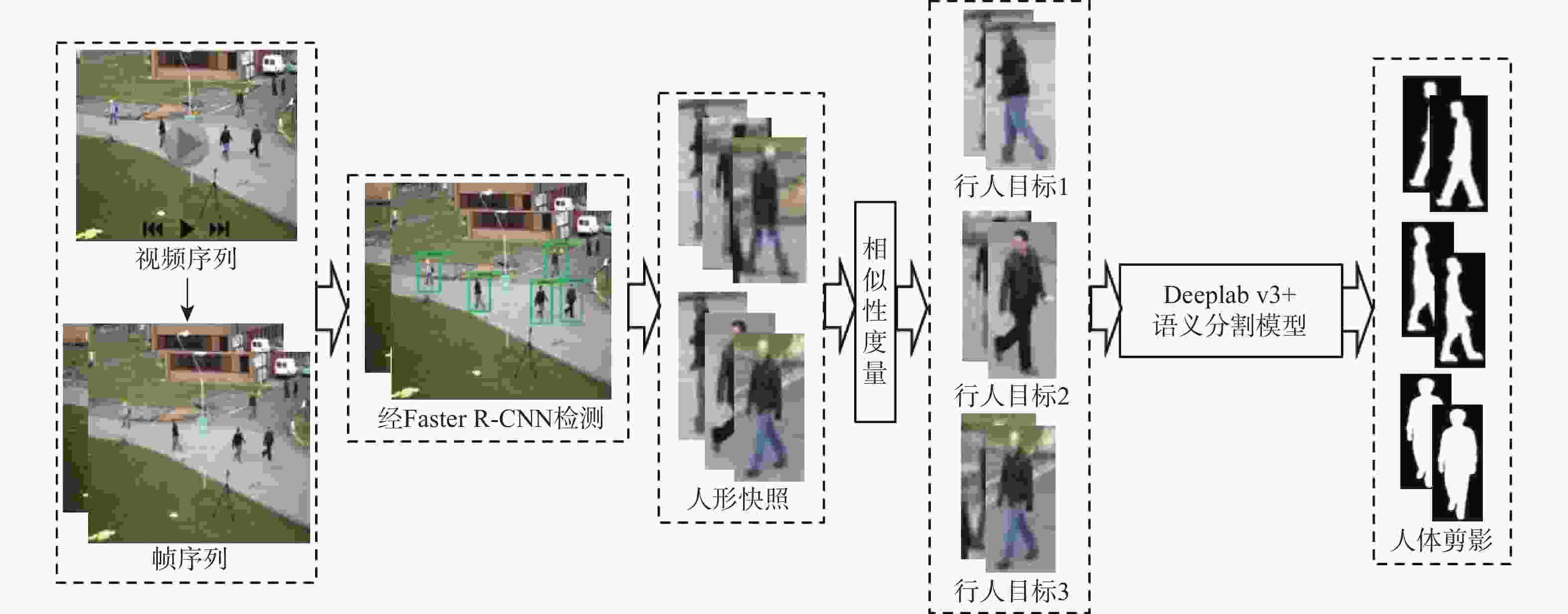
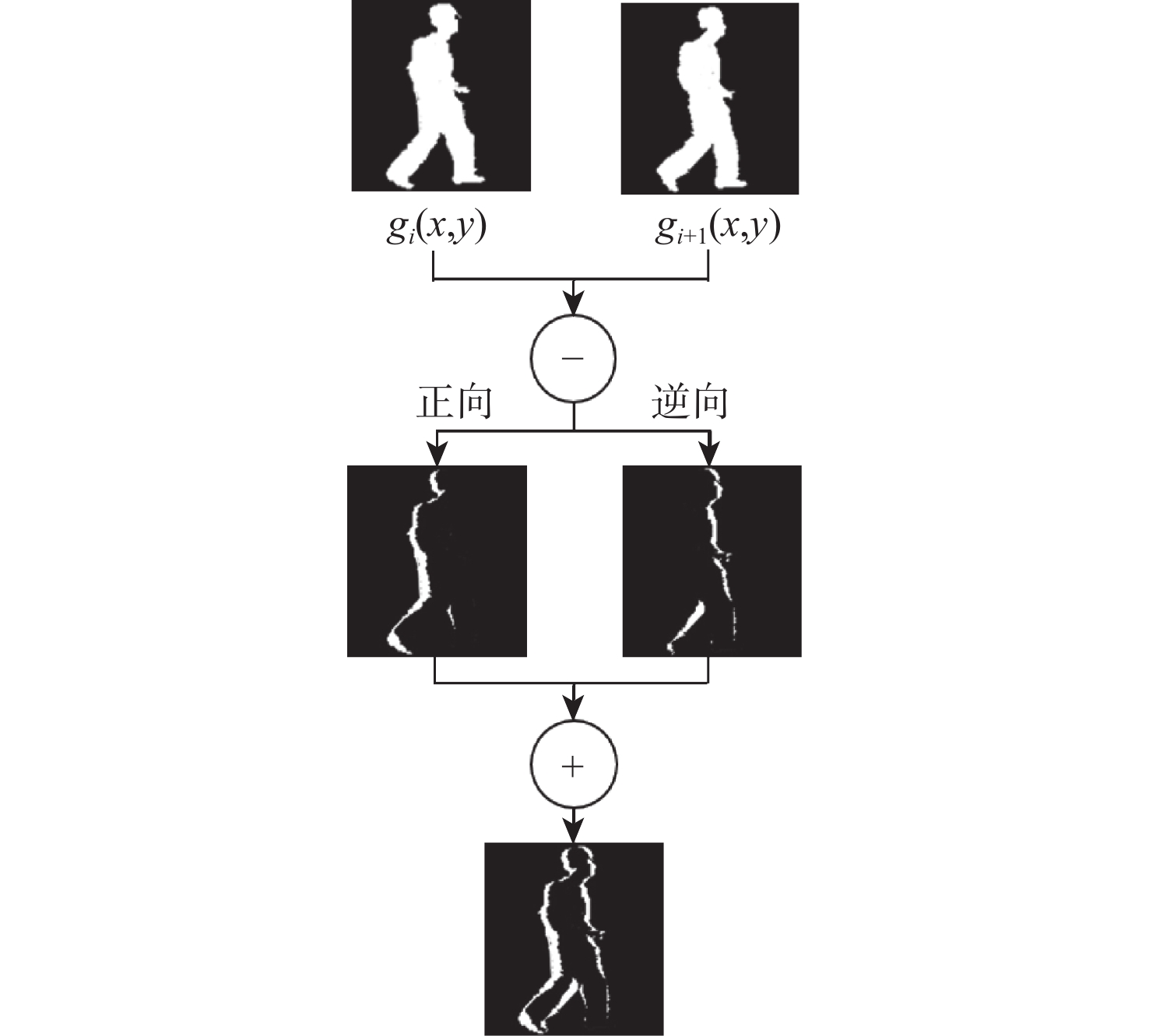
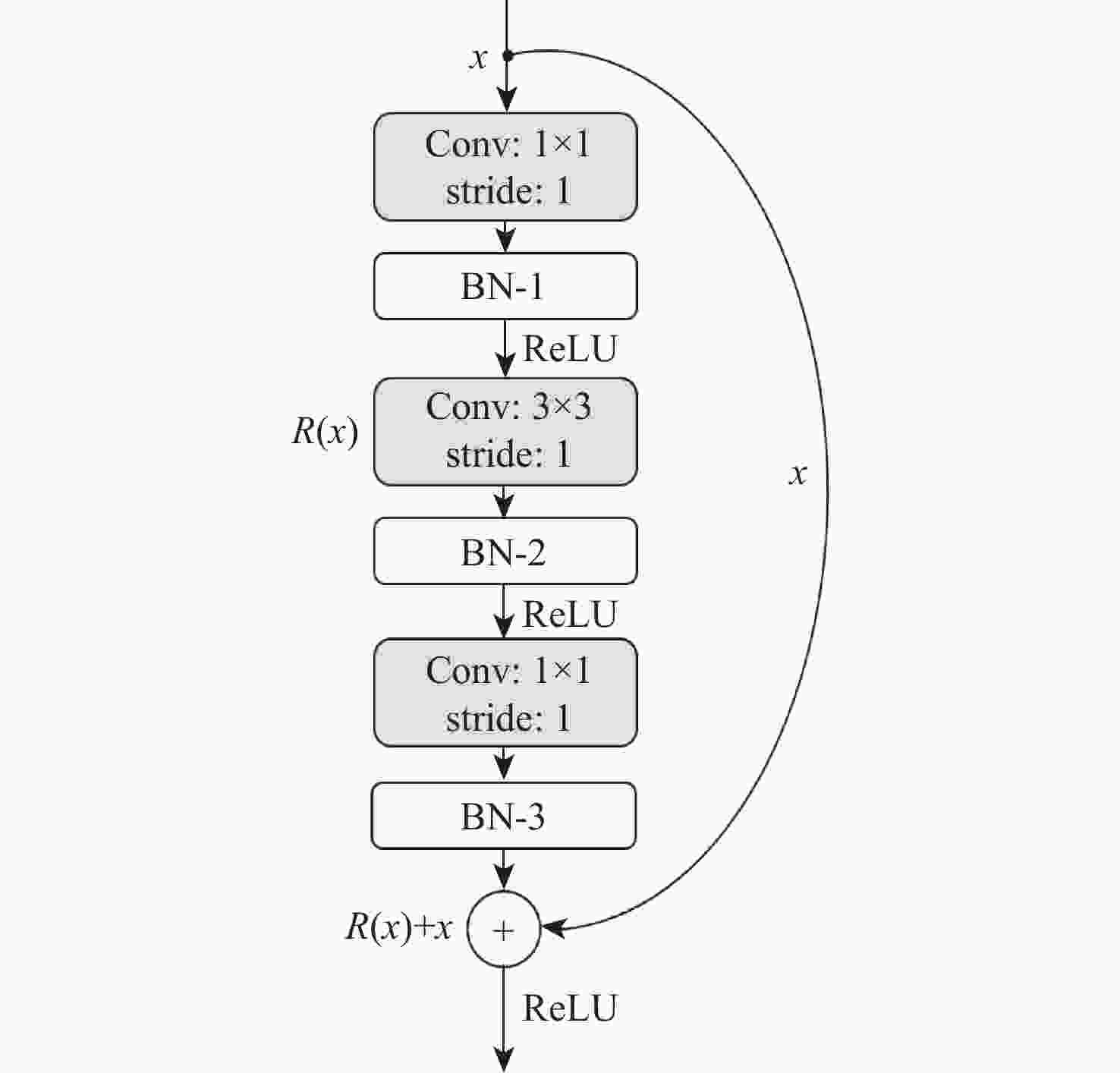
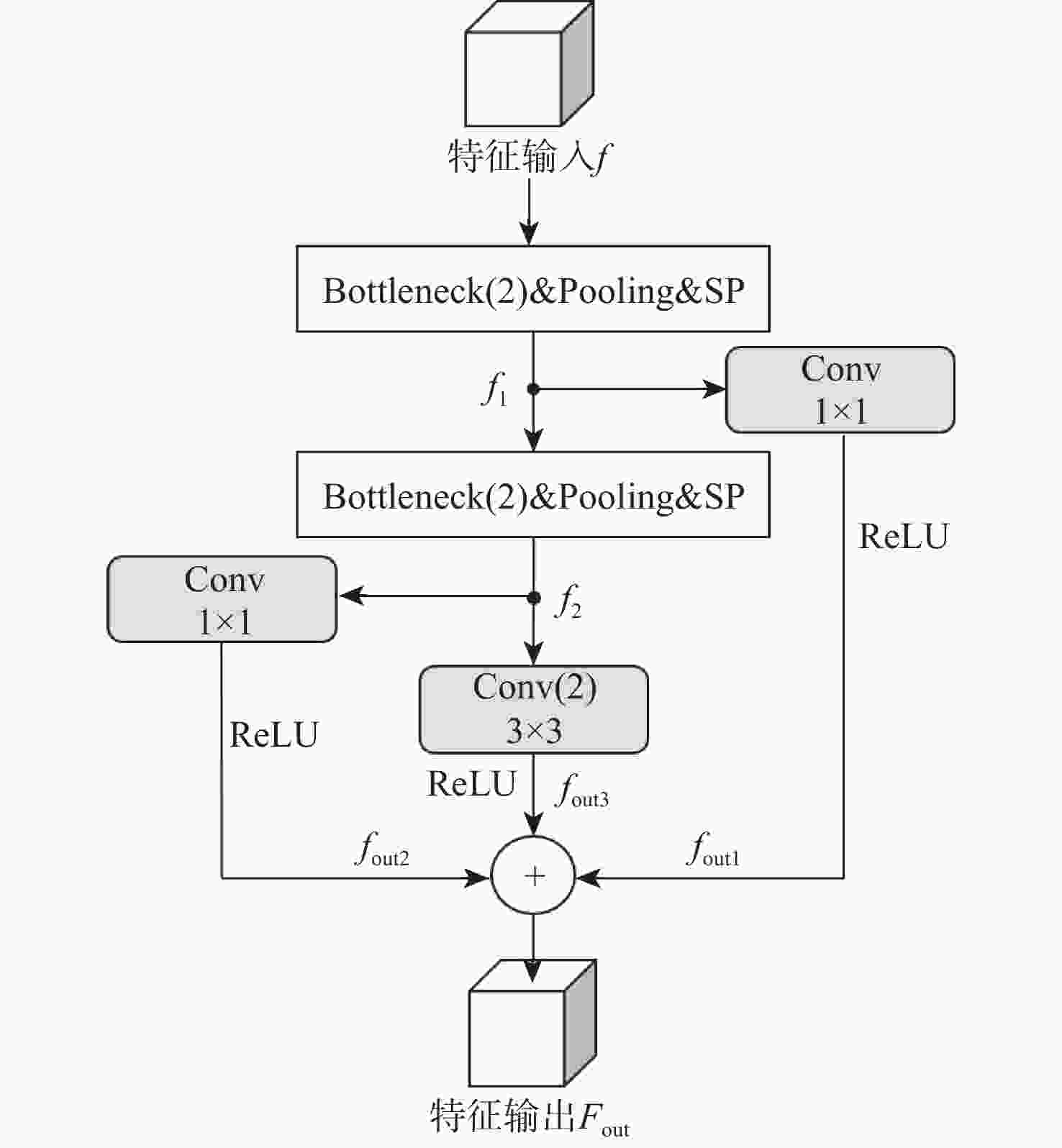
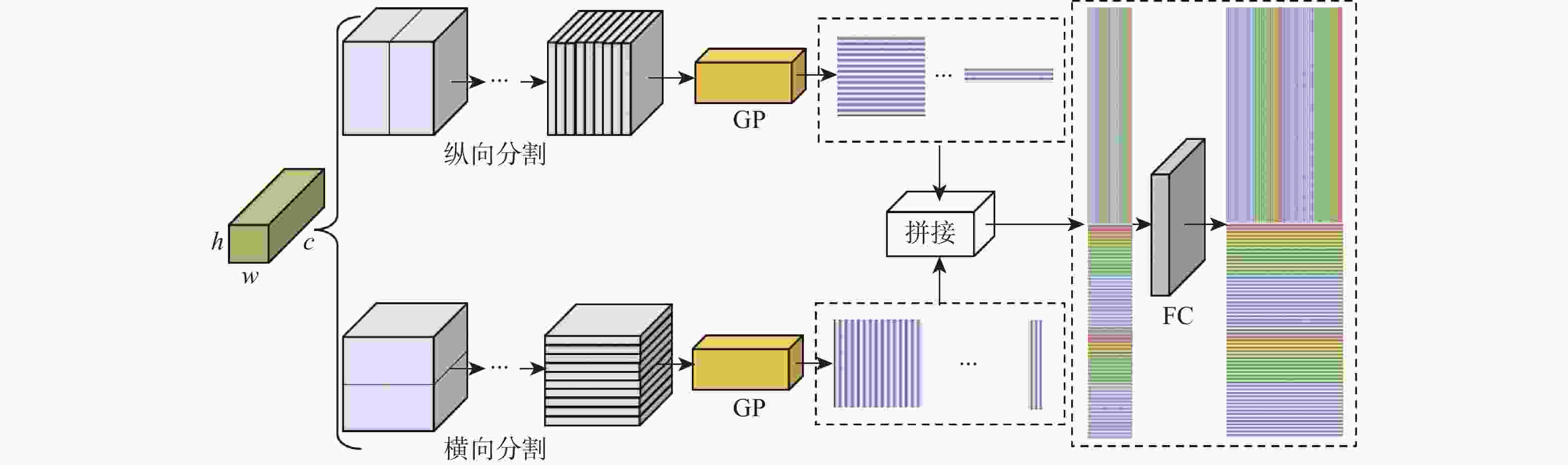
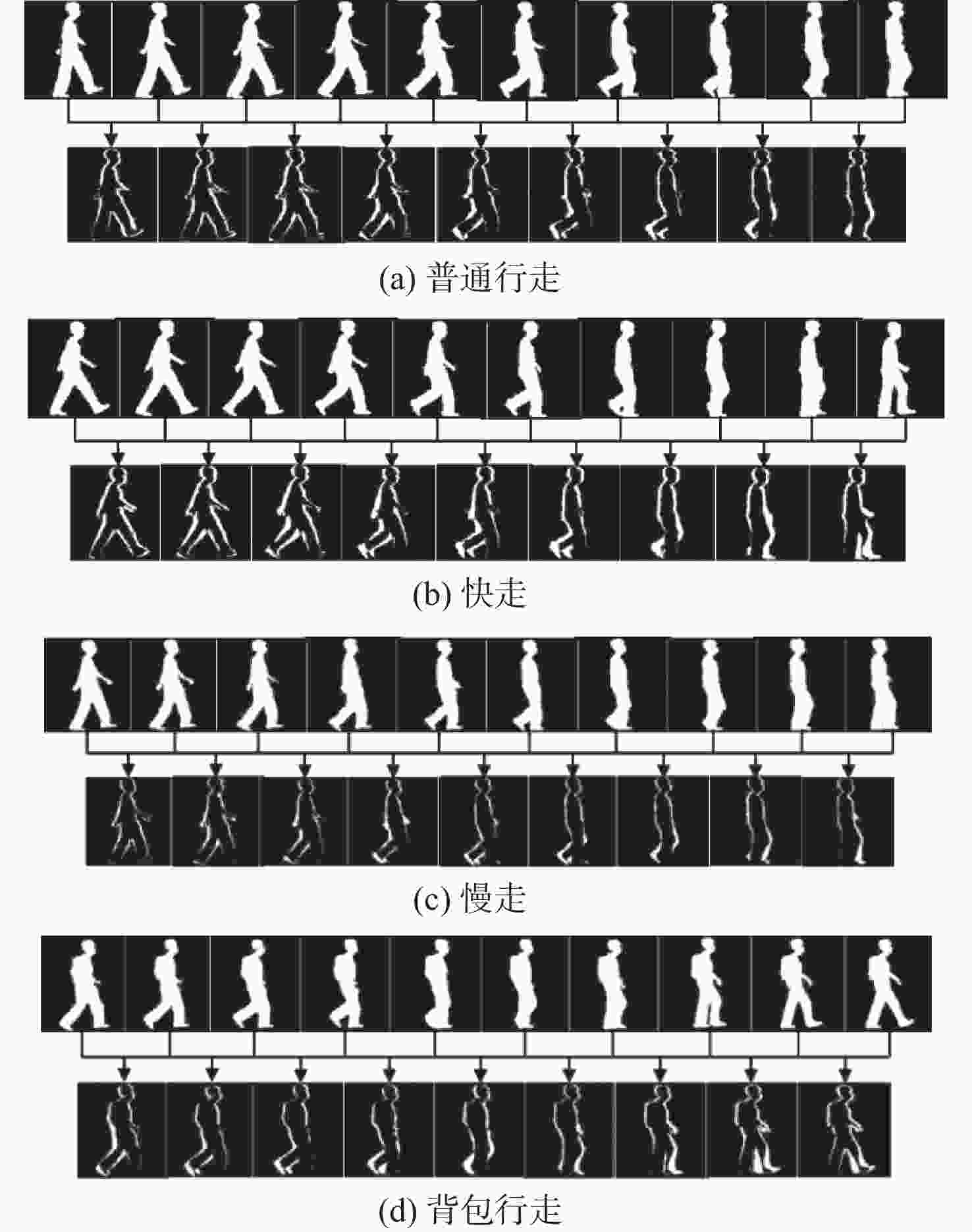
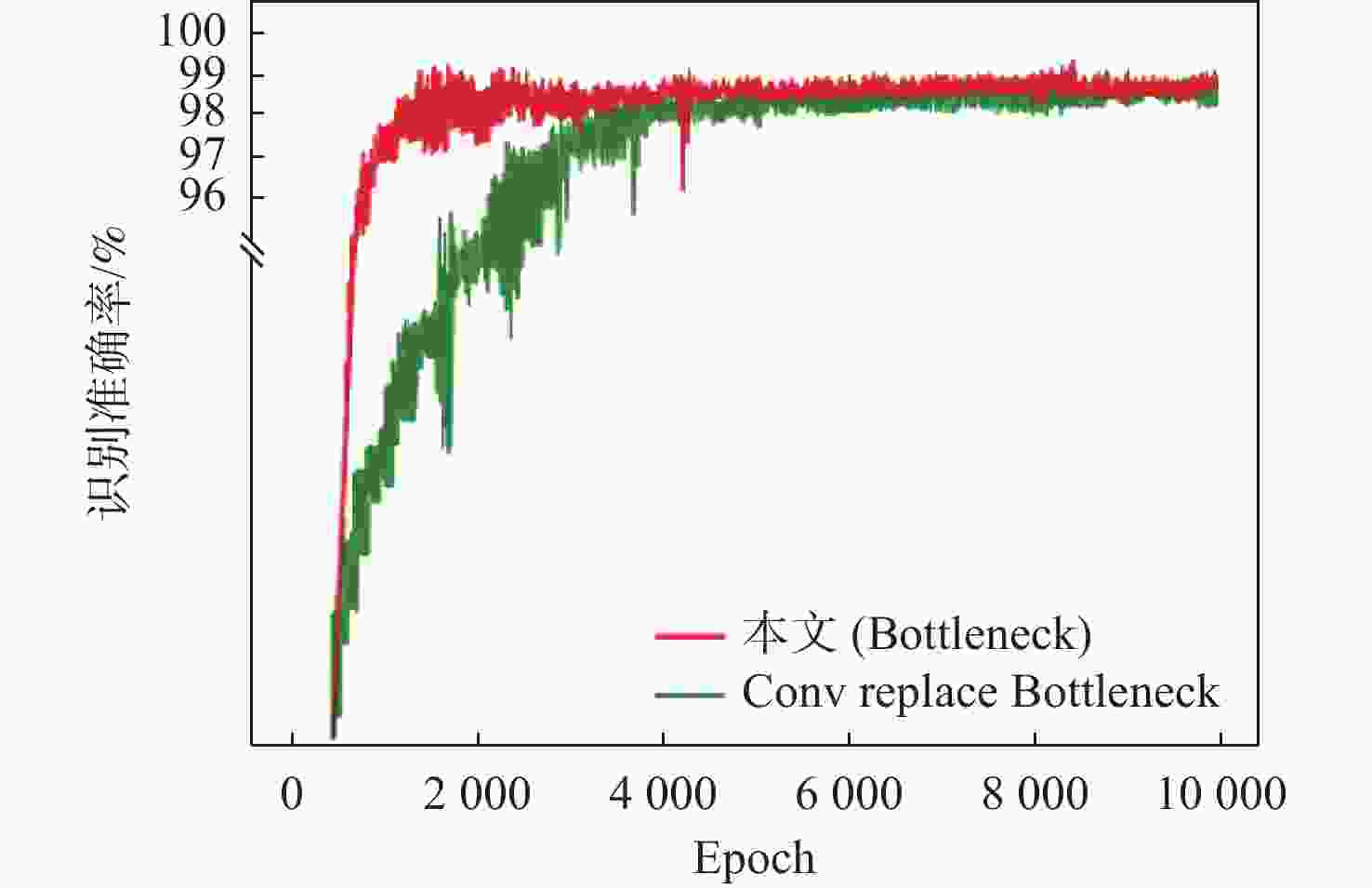
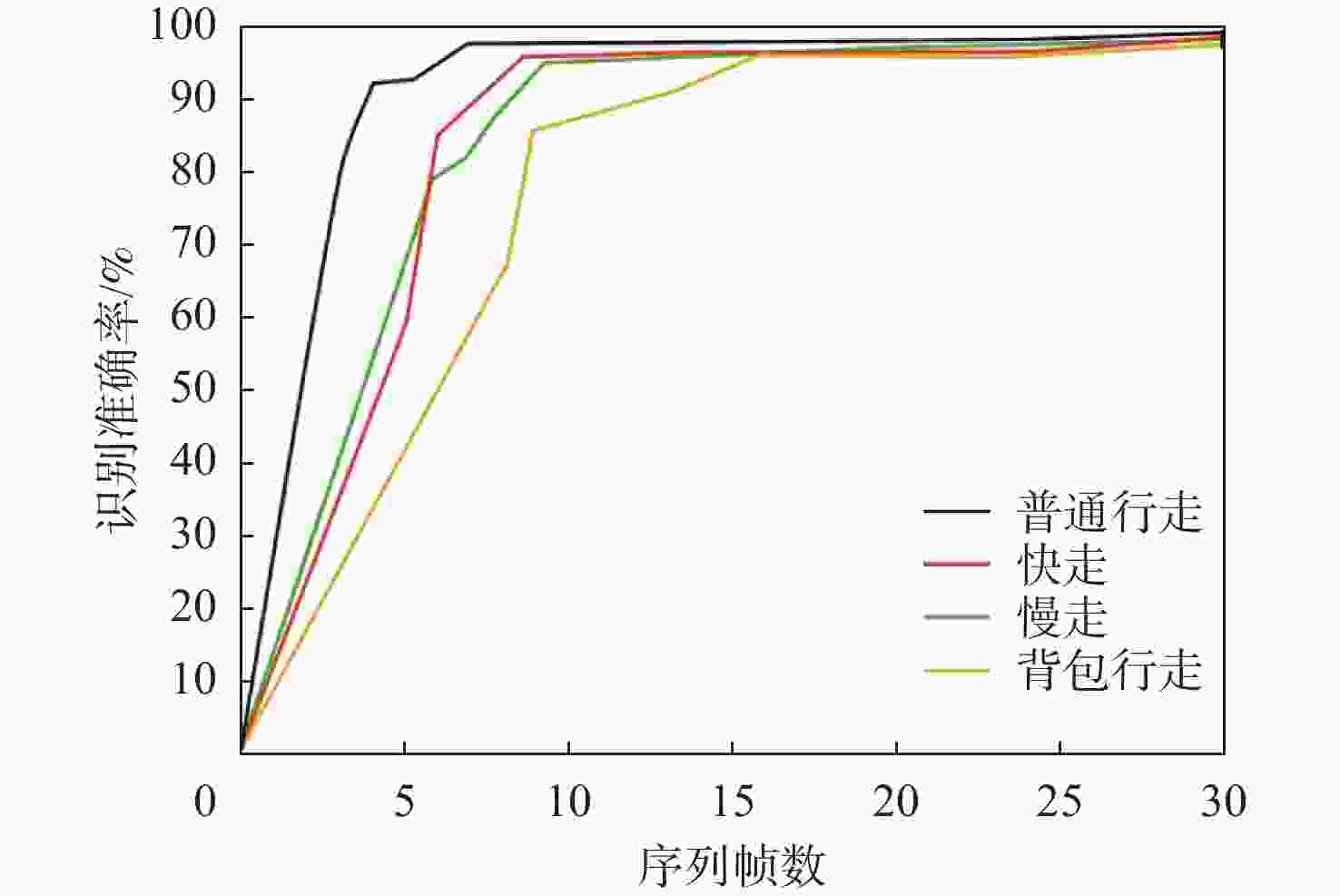
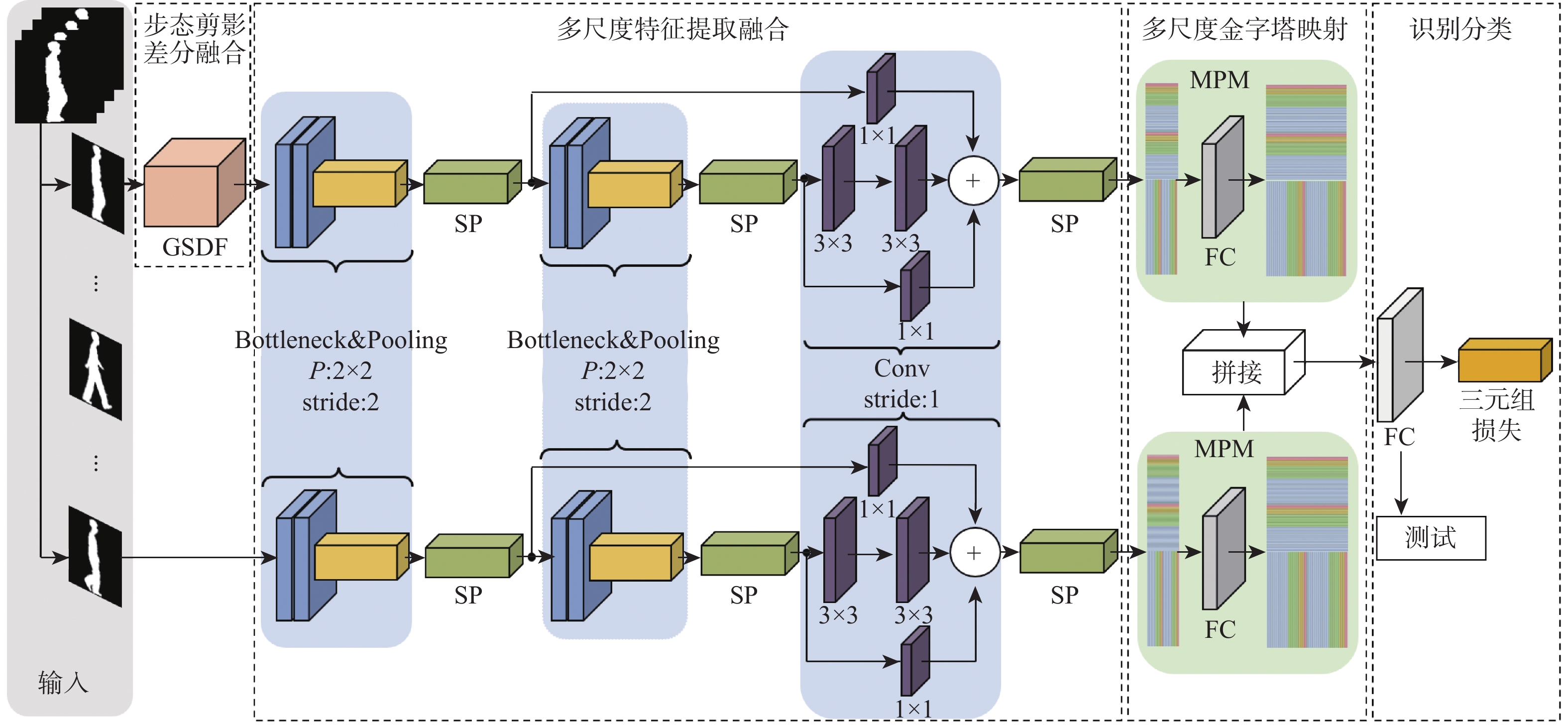
针对卷积神经网络在低质量红外图像的步态识别中不能充分捕捉和利用时空信息的问题,提出了一种基于剪影差分融合流和剪影流的残差多尺度融合的双流深度网络模型。在模型输入端采用Faster R-CNN和Deeplab v3+算法相结合的细粒度人体剪影分割策略来提取剪影,以减少噪点信息的影响,避免特征丢失;在模型上支流网络中引入步态剪影差分融合模块来获取相邻剪影帧之间的差异变化信息;在模型的特征提取部分使用残差单元和多尺度特征提取融合技术分别加深网络层次和提取不同粒度的时空信息;通过多尺度金字塔映射模块进一步增强模型对局部和全局特征的表征能力。由CASIA-C数据集上的4组不同行走条件对比实验数据可知,所提方法的平均步态识别率为98.85%,优于当前主流方法。
Abstract:A residual multi-scale dual-stream network model based on silhouette differential fusion flow and silhouette flow is proposed to address the challenge of convolutional neural networks being unable to fully capture and utilize spatiotemporal information in gait recognition of low-quality infrared images. Firstly, a fine-grained segmentation strategy combining Faster R-CNN and Deeplab v3+ algorithms is applied at the model’s input to extract silhouettes, thus reducing the impact of noise and preventing feature loss. Secondly, a gait silhouette differential fusion module is added to the branch network of the model to capture the differences and changes between adjacent silhouette frames. Then, residual units and multi-scale feature fusion techniques are employed in the feature extraction section of the model to deepen the network layers and extract spatiotemporal information at different granularities. Finally, the multi-scale pyramid mapping module is utilized to further enhance the model’s ability to represent both local and global features. Experimental results from four different walking conditions on the CASIA-C dataset show that the average gait recognition rate of the proposed method is 98.85%, outperforming current mainstream methods.
-
表 1 CASIA-C数据集上不同方法总的识别率比较
Table 1. Comparison of total recognition rates of different methods on CASIA-C dataset
% 表 2 不同方法在4组实验上的识别准确率比较
Table 2. Comparison of recognition accuracy races of different methods in 4 groups of experiments
表 3 横向对比实验结果
Table 3. Horizontal comparison experiment results
表 4 消融实验设置
Table 4. Ablation experiment settings
组号 模块A 模块B 模块C 模块D 模块E 1 √ √ √ √ 2 √ √ √ √ 3 √ √ √ √ 4 √ √ √ √ 5 √ √ √ √ 6 √ √ √ √ 7 √ √ √ √ √ 表 5 特征消融实验结果
Table 5. Feature ablation experiments results
组号 识别准确率/% 识别准确率
均值/%Test-A Test-B Test-C Test-D 1 92.11 88.84 85.47 79.20 86.41 2 89.28 81.97 80.66 71.00 80.73 3 98.99 98.30 98.11 97.16 98.14 4 96.10 95.64 94.00 90.59 94.08 5 96.05 94.22 94.13 87.40 92.95 6 95.87 94.01 93.93 86.25 92.52 7 99.87 98.61 99.13 97.78 98.85 -
[1] 魏鹏娜, 马鹏程, 张进华, 等. 基于双向长短时记忆神经网络的步态时空参数脑肌电解码方法[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2022, 56(9): 142-150. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb202209015WEI P N, MA P C, ZHANG J H, et al. EEG and SEMG decoding of gait spatiotemporal parameters based on bidirectional long short term memory neural network[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2022, 56(9): 142-150(in Chinese). doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb202209015 [2] 朱小鹏, 云利军, 张春节, 等. 基于深度学习的红外图像人体步态识别方法[J]. 计算机工程与设计, 2022, 43(3): 851-857.ZHU X P, YUN L J, ZHANG C J, et al. Gait recognition method based on deep learning in infrared image[J]. Computer Engineering and Design, 2022, 43(3): 851-857(in Chinese). [3] 段鹏松, 周志一, 王超, 等. WiNet: 一种适用于无线感知场景的步态识别模型[J]. 西安交通大学学报, 2020, 54(7): 187-195. doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb202007022DUAN P S, ZHOU Z Y, WANG C, et al. WiNet: a gait recognition model suitable for wireless sensing scene[J]. Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University, 2020, 54(7): 187-195(in Chinese). doi: 10.7652/xjtuxb202007022 [4] YU S Q, LIAO R J, AN W Z, et al. GaitGANv2: Invariant gait feature extraction using generative adversarial networks[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 87: 179-189. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.10.019 [5] XU Z P, LU W, ZHANG Q, et al. Gait recognition based on capsule network[J]. Journal of Visual Communication and Image Representation, 2019, 59: 159-167. [6] HAN J, BHANU B. Individual recognition using gait energy image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2006, 28(2): 316-322. [7] SOKOLOVA A, KONUSHIN A. View resistant gait recognition[C]//Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Video and Image Processing. New York: ACM, 2019: 7-12. [8] CASTRO F M, MARIN-JIMENEZ M J, GUIL N, et al. Evaluation of CNN architectures for gait recognition based on optical flow maps[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference of the Biometrics Special Interest Group. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1-5. [9] YU S Q, WANG Q, SHEN L L, et al. View invariant gait recognition using only one uniform model[C]//Proceedings of the 23rd International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 889-894. [10] WU Z F, HUANG Y Z, WANG L, et al. A comprehensive study on cross-view gait based human identification with deep CNNs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(2): 209-226. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2545669 [11] CHAO H Q, HE Y W, ZHANG J P, et al. GaitSet: regarding gait as a set for cross-view gait recognition[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 33(1): 8126-8133. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33018126 [12] LU Z, XU Y C, DAI Z X, et al. A gait recognition based on link model of infrared thermal imaging[C]//Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Control Science and Systems Engineering. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 165-168. [13] ZHU X P, YUN L J, CHENG F Y, et al. LFN: based on the convolutional neural network of gait recognition method[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2020, 1650(3): 032075. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1650/3/032075 [14] 梅建华, 云利军, 朱小鹏. 基于长短期记忆网络的红外人体步态识别方法研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2022, 59(8): 0811005.MEI J H, YUN L J, ZHU X P. Infrared human gait recognition method based on long and short term memory network[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(8): 0811005(in Chinese). [15] 杨彦辰, 云利军, 梅建华, 等. 基于改进ViT的红外人体图像步态识别方法研究[J]. 应用光学, 2023, 44(1): 71-78. doi: 10.5768/JAO202344.0102002YANG Y C, YUN L J, MEI J H, et al. Gait recognition method of infrared human body images based on improved ViT[J]. Journal of Applied Optics, 2023, 44(1): 71-78(in Chinese). doi: 10.5768/JAO202344.0102002 [16] 胡少晖, 王修晖, 刘砚秋. 基于多支路残差深度网络的跨视角步态识别方法[J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 2021, 34(5): 455-462.HU S H, WANG X H, LIU Y Q. Cross-view gait recognition method based on multi-branch residual deep network[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2021, 34(5): 455-462(in Chinese). [17] 张家波, 李杰, 甘海洋. 结合双流网络和金字塔映射的步态识别[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2022, 39(6): 1911-1915.ZHANG J B, LI J, GAN H Y. Gait recognition combined with two-stream network and pyramid mapping[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2022, 39(6): 1911-1915(in Chinese). [18] REN S Q, HE K M, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [19] CHEN L C, ZHU Y K, PAPANDREOU G, et al. Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 833-851. [20] 肖祖安. 视频监控中的步态特征提取系统研究与开发[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2019.XIAO Z A. Research and development of gait feature extraction system in video surveillance[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [21] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [22] DOLLÁR P, APPEL R, BELONGIE S, et al. Fast feature pyramids for object detection[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2014, 36(8): 1532-1545. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2014.2300479 [23] FU Y, WEI Y C, ZHOU Y Q, et al. Horizontal pyramid matching for person re-identification[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 33(1): 8295-8302. doi: 10.1609/aaai.v33i01.33018295 [24] TAN D L, HUANG K Q, YU S Q, et al. Efficient night gait recognition based on template matching[C]//Proceedings of the18th International Conference on Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2006: 1000-1003. -







 下载:
下载: