Finite-time path tracking control of unmanned vehicles based on multi-dimensional Taylor network
-
摘要:
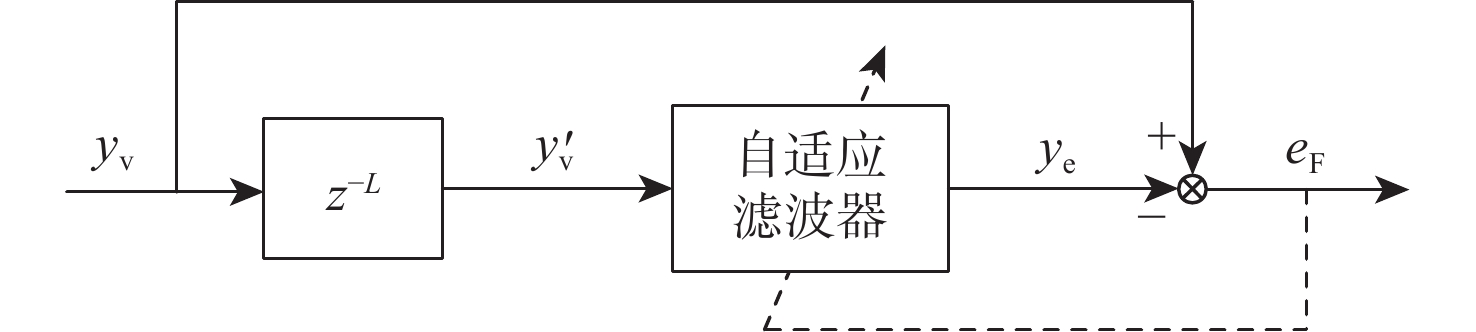
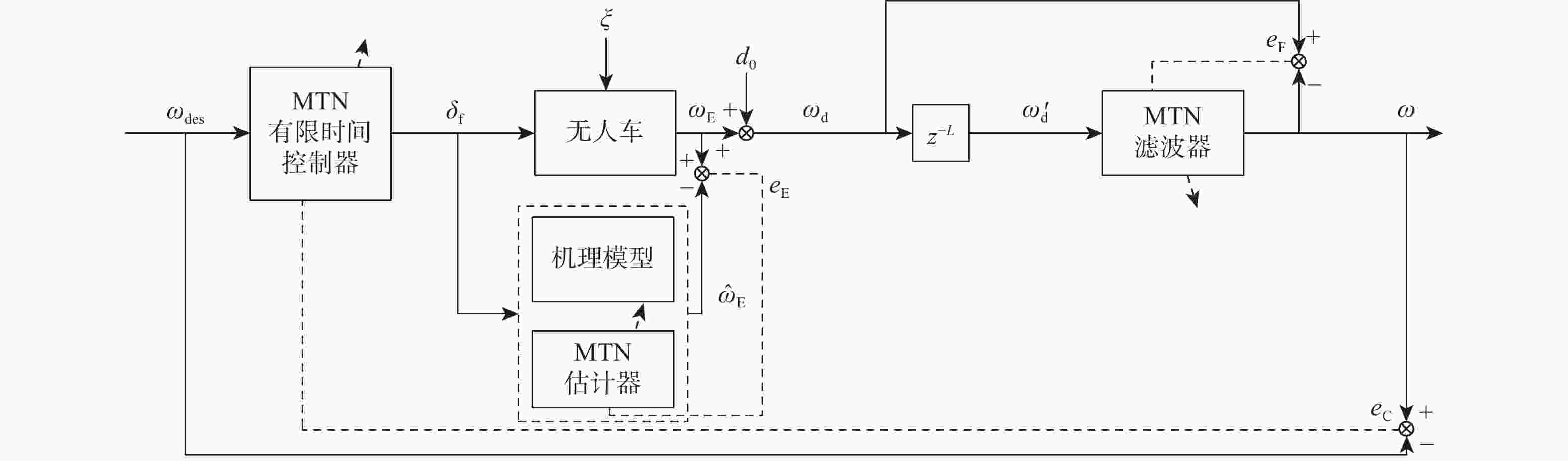
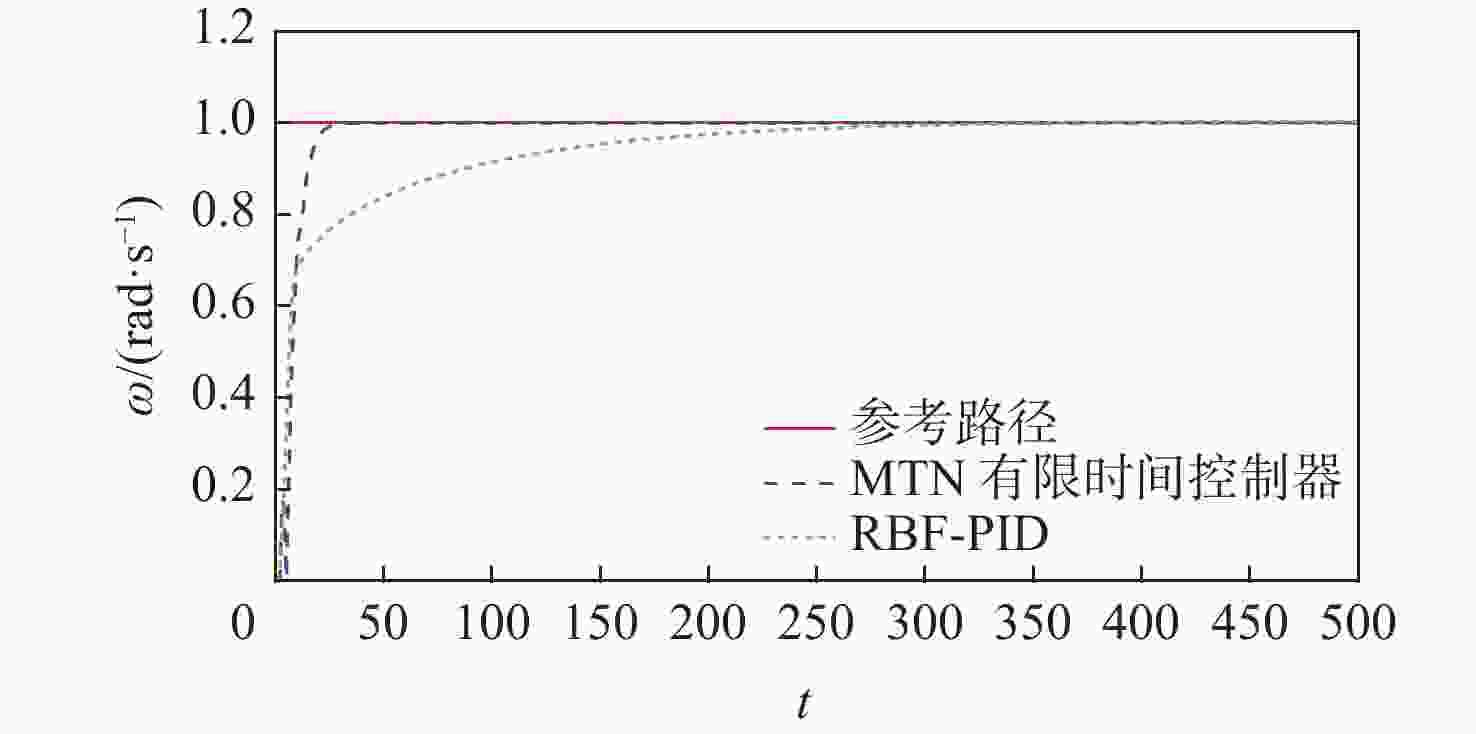
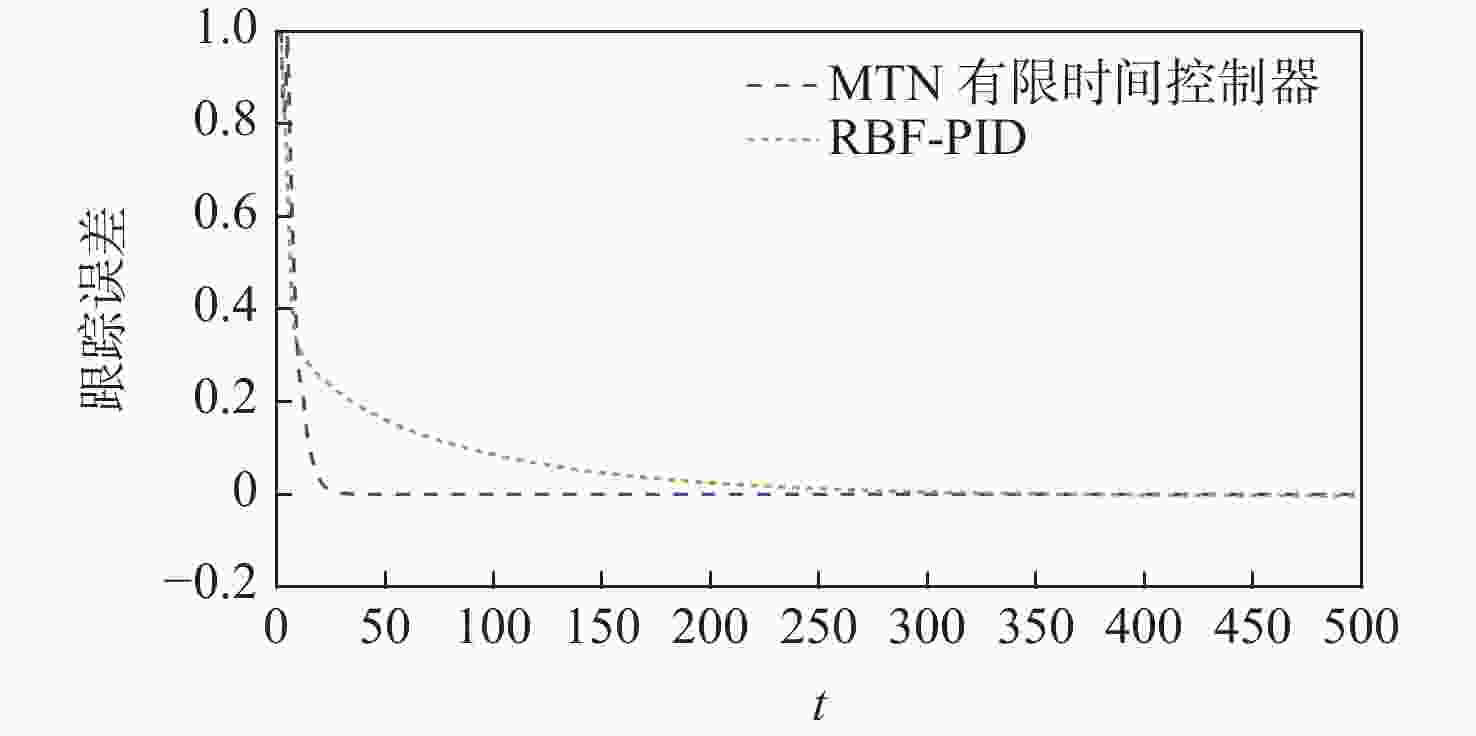
针对含有模型不确定和测量噪声条件下的无人车路径跟踪控制问题,提出基于多维泰勒网(MTN)的有限时间路径跟踪控制方案。利用MTN模型刻画无人车模型的不确定性,改进的反向传递(BP)算法作为其学习算法;设计自适应MTN滤波器来滤除测量噪声,MTN作为滤波器,最小均方(LMS)算法作为其学习算法;设计MTN有限时间控制器对无人车进行精确路径跟踪控制,其可以快速准确跟踪参考路径;根据有限时间控制理论,给出了收敛性证明。通过无人车仿真实验验证了所提方法的有效性。
Abstract:In this paper, a finite-time tracking control scheme based on the multi-dimensional Taylor network (MTN) is proposed for path tracking control of unmanned vehicles with model uncertainty and measurement noise. First, the MTN model is used to characterize the uncertainties of the unmanned vehicle model, and the improved back propagation (BP) algorithm is adopted as its learning algorithm. Second, an adaptive MTN filter is designed to suppress the measurement noise. MTN serves as the filter, and the least mean square (LMS) algorithm is employed as its learning algorithm. Then, the MTN finite-time controller is designed for precise path tracking control of the unmanned vehicle, which can track the reference trajectory quickly and accurately. Based on finite-time control theory, the convergence of the system is proved. Finally, unmanned vehicle simulation experiments are conducted to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method.
-
表 1 复杂度分析
Table 1. Complexity analysis
模型 结构 加法数 乘法数 MTNE 4-15-1 14 25 MTNF 4-15-1 14 25 -
[1] CHEN G, CHEN S, LANGARI R, et al. Driver-behavior-based adaptive steering robust nonlinear control of unmanned driving robotic vehicle with modeling uncertainties and disturbance observer[J]. IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology, 2019, 68(8): 8183-8190. doi: 10.1109/TVT.2019.2922452 [2] VICENTE B A H, TRODDEN P A, ANDERSON S R. Fast tube model predictive control for driverless cars using linear data-driven models[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2023, 31(3): 1395-1410. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2022.3224089 [3] 李雷, 贾新春, 贾祝融, 等. 带测量噪声干扰的无人驾驶汽车路径跟踪控制[J]. 山西大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 33(3): 384-387.LI L, JIA X C, JIA Z R, et al. Path tracking control for autonomous vehicle with measurement noise[J]. Journal of Shanxi University (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 33(3): 384-387(in Chinese). [4] AMER N H, ZAMZURI H, HUDHA K, et al. Modelling and control strategies in path tracking control for autonomous ground vehicles: a review of state of the art and challenges[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2017, 86(2): 225-254. [5] WU Y L, LI S M, ZHANG Q J, et al. Route planning and tracking control of an intelligent automatic unmanned transportation system based on dynamic nonlinear model predictive control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(9): 16576-16589. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2022.3141214 [6] GU Z, YIN T T, DING Z T. Path tracking control of autonomous vehicles subject to deception attacks via a learning-based event-triggered mechanism[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32(12): 5644-5653. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2021.3056764 [7] AGUIAR A P, HESPANHA J P. Trajectory-tracking and path-following of underactuated autonomous vehicles with parametric modeling uncertainty[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2007, 52(8): 1362-1379. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2007.902731 [8] AN D D, LIU J, ZHANG M, et al. Uncertainty modeling and runtime verification for autonomous vehicles driving control: a machine learning-based approach[J]. Journal of Systems and Software, 2020, 167: 110617. doi: 10.1016/j.jss.2020.110617 [9] 张守武, 李擎, 王恒, 等. 非匹配不确定性影响下的无人车路径跟踪控制[J]. 控制与决策, 2022, 37(1): 160-166.ZHANG S W, LI Q, WANG H, et al. Path following control for autonomous vehicles with mismatched uncertainties[J]. Control and Decision, 2022, 37(1): 160-166(in Chinese). [10] KELIRIS C, POLYCARPOU M M, PARISINI T. An integrated learning and filtering approach for fault diagnosis of a class of nonlinear dynamical systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 28(4): 988-1004. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2015.2504418 [11] 张超. 具有噪声干扰的非线性时变系统多维泰勒网优化控制[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2018.ZHANG C. Optimal control of multi-dimensional Taylor network for nonlinear time-varying systems with noise interference[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2018(in Chinese). [12] 李晨龙. 非线性时滞定常系统多维泰勒网辨识与预测控制[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2020.LI C L. Multi-dimensional Taylor network identification and predictive control for nonlinear time-delay time-invariant systems[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2020(in Chinese). [13] SCHWARTING W, ALONSO-MORA J, PAULL L, et al. Safe nonlinear trajectory generation for parallel autonomy with a dynamic vehicle model[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2018, 19(9): 2994-3008. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2017.2771351 [14] LI R M, ZHANG L W, HAN L, et al. Multiple vehicle formation control based on robust adaptive control algorithm[J]. IEEE Intelligent Transportation Systems Magazine, 2017, 9(2): 41-51. doi: 10.1109/MITS.2017.2666581 [15] YAN Y, DU H P, WANG Y F, et al. Multi-objective asymmetric sliding mode control of connected autonomous vehicles[J]. IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2022, 23(9): 16342-16357. doi: 10.1109/TITS.2022.3149985 [16] AWAD N, LASHEEN A, ELNAGGAR M, et al. Model predictive control with fuzzy logic switching for path tracking of autonomous vehicles[J]. ISA Transactions, 2022, 129: 193-205. doi: 10.1016/j.isatra.2021.12.022 [17] FANG P J, CAI Y F, CHEN L, et al. A high-performance neural network vehicle dynamics model for trajectory tracking control[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part D: Journal of Automobile Engineering, 2023, 237(7): 1695-1709. doi: 10.1177/09544070221095660 [18] KABZAN J, HEWING L, LINIGER A, et al. Learning-based model predictive control for autonomous racing[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2019, 4(4): 3363-3370. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2019.2926677 [19] SUN K K, QIU J B, KARIMI H R, et al. A novel finite-time control for nonstrict feedback saturated nonlinear systems with tracking error constraint[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics: Systems, 2021, 51(6): 3968-3979. [20] REN C C, PARK J H, HE S P. Positiveness and finite-time control of dual-switching Poisson jump networked control systems with time-varying delays and packet drops[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2022, 9(2): 575-587. doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2022.3165075 [21] 李晨龙, 严洪森. 基于多维泰勒网的多入多出非线性时滞系统辨识[J]. 计算机应用研究, 2022, 39(8): 2432-2437.LI C L, YAN H S. Identification of MIMO nonlinear time-delay system using multi-dimensional Taylor network[J]. Application Research of Computers, 2022, 39(8): 2432-2437(in Chinese). [22] 李晨龙, 严洪森. 基于多维泰勒网的超前d步预测模型研究[J]. 控制与决策, 2021, 36(2): 345-354.LI C L, YAN H S. d-step-ahead predictive model based on multi-dimensional Taylor network[J]. Control and Decision, 2021, 36(2): 345-354(in Chinese). [23] YAN H S, ZHANG J J, SUN Q M. MTN optimal control of SISO nonlinear time-varying discrete-time systems for tracking by output feedback[J]. Intelligent Automation and Soft Computing, 2018, 3: 487-507. [24] YAN H S, DUAN Z Y. Tube-based model predictive control using multidimensional Taylor network for nonlinear time-delay systems[J]. IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2021, 66(5): 2099-2114. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2020.3005674 [25] KLAMBAUER G. Mathematical analysis[M]. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc, 1975. [26] 闫振争, 庄继晖, 程晓鸣, 等. 自抗扰算法在无人车路径跟踪控制中的应用[J]. 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学), 2021, 35(3): 61-70.YAN Z Z, ZHUANG J H, CHENG X M, et al. Active disturbance rejection algorithm applied to path tracking in autonomous vehicles[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science), 2021, 35(3): 61-70(in Chinese). [27] DONMEZ B, NEHME C, CUMMINGS M L. Modeling workload impact in multiple unmanned vehicle supervisory control[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part A: Systems and Humans, 2010, 40(6): 1180-1190. doi: 10.1109/TSMCA.2010.2046731 [28] SUN S L. Multi-sensor information fusion white noise filter weighted by scalars based on Kalman predictor[J]. Automatica, 2004, 40(8): 1447-1453. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2004.03.012 [29] ZWEIRI Y H, WHIDBORNE J F, SENEVIRATNE L D. A three-term backpropagation algorithm[J]. Neurocomputing, 2003, 50: 305-318. doi: 10.1016/S0925-2312(02)00569-6 [30] ZWEIRI Y H, SENEVIRATNE L D, ALTHOEFER K. Stability analysis of a three-term backpropagation algorithm[J]. Neural Networks, 2005, 18(10): 1341-1347. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2005.04.007 [31] PEARLMUTTER B A. Gradient descent: second-order momentum and saturating error[C]//Proceedings of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems. [S. l. ]: NIPS, 1992: 887-894. [32] SHU T X, CHEN J H, BHARGAVA V K, et al. An energy-efficient dual prediction scheme using LMS filter and LSTM in wireless sensor networks for environment monitoring[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6(4): 6736-6747. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2911295 [33] BHAT S P, BERNSTEIN D S. Finite-time stability of continuous autonomous systems[J]. SIAM Journal on Control and Optimization, 2000, 38(3): 751-766. doi: 10.1137/S0363012997321358 [34] 丁锋. 系统辨识算法的复杂性、收敛性及计算效率研究[J]. 控制与决策, 2016, 31(10): 1729-1741.DING F. Complexity, convergence and computational efficiency for system identification algorithms[J]. Control and Decision, 2016, 31(10): 1729-1741(in Chinese). [35] GOLUB G H, VAN LOAN C F. Matrix computations[M]. Baltimore: JHU Press, 2012. -







 下载:
下载: