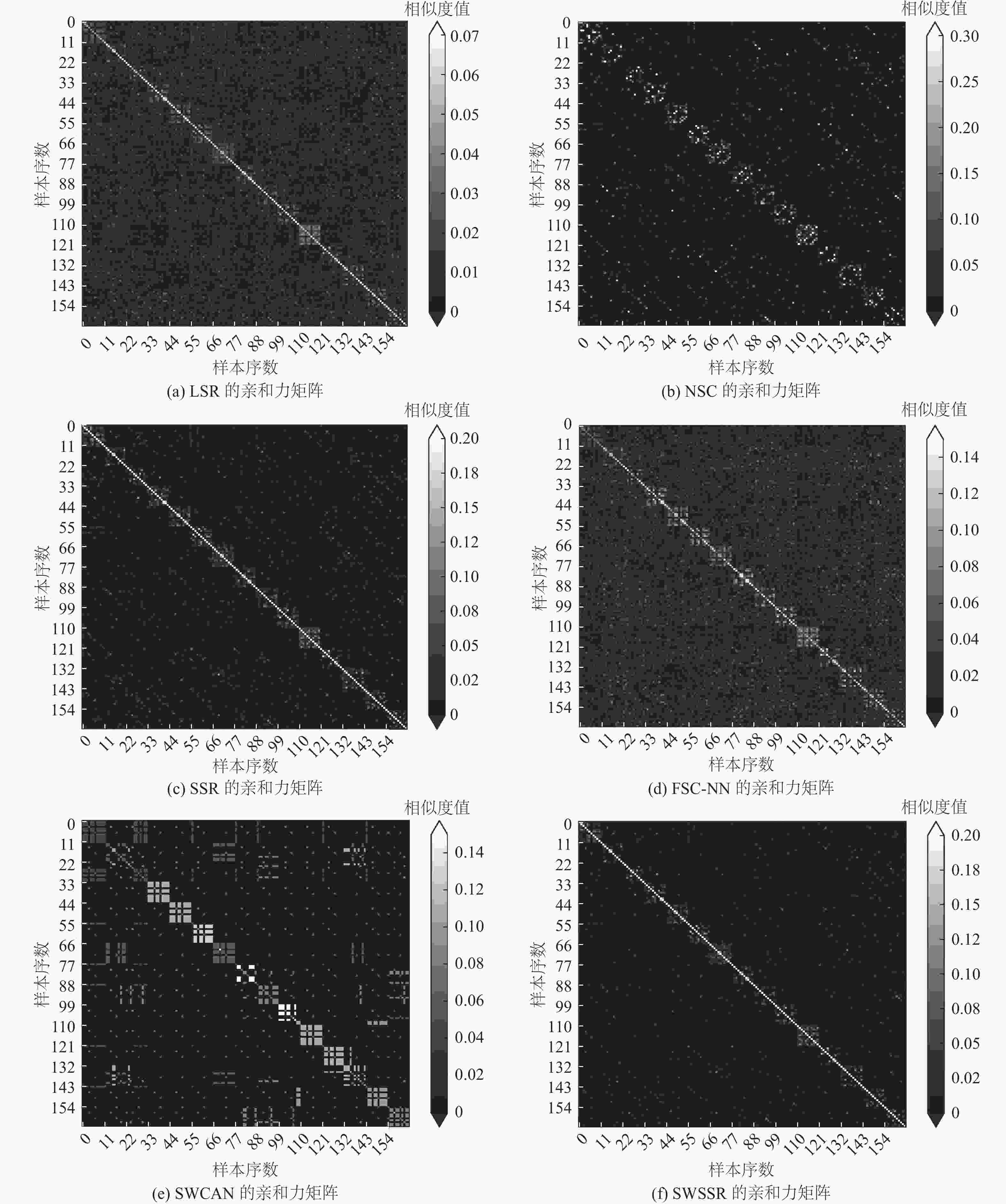
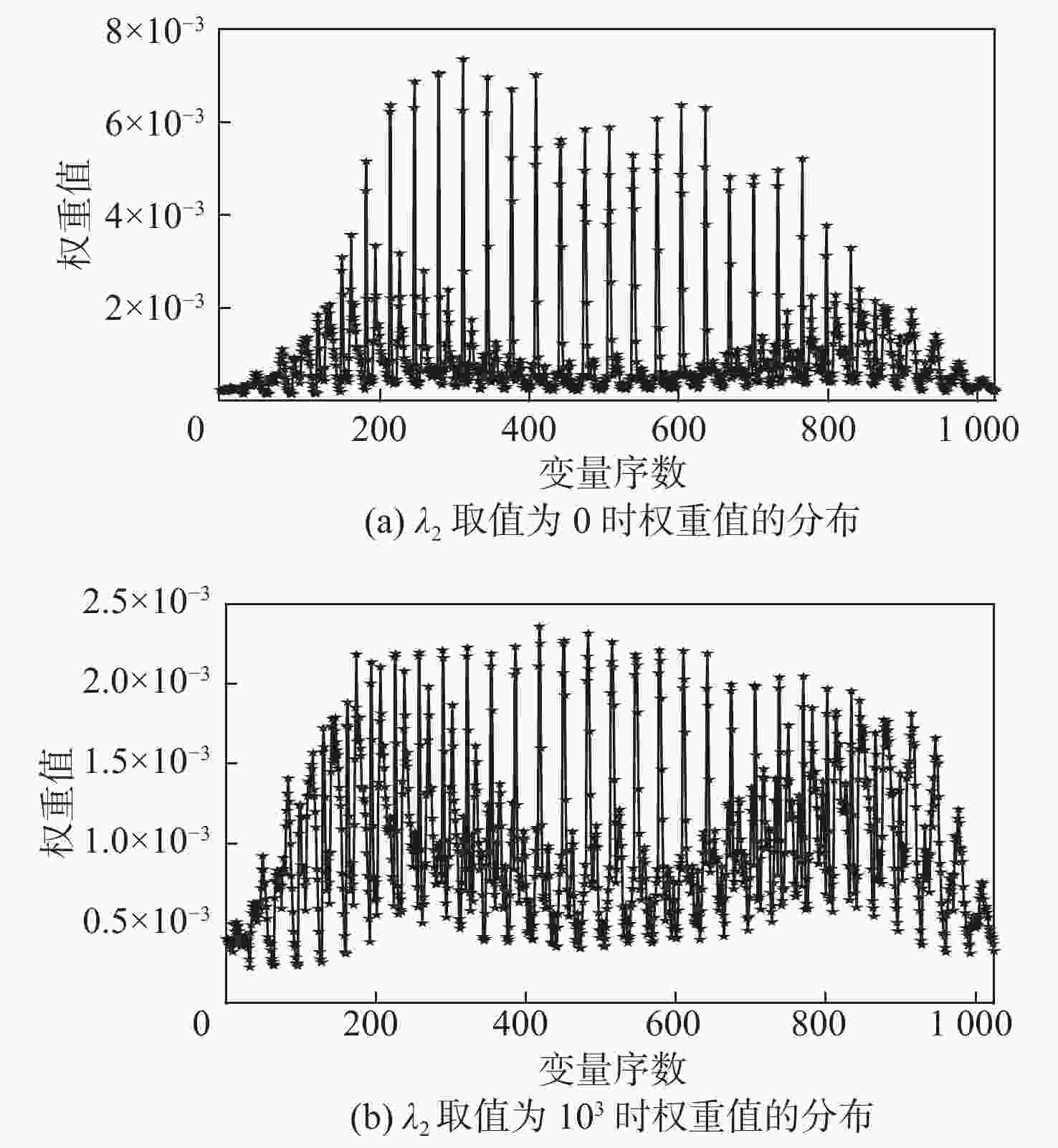
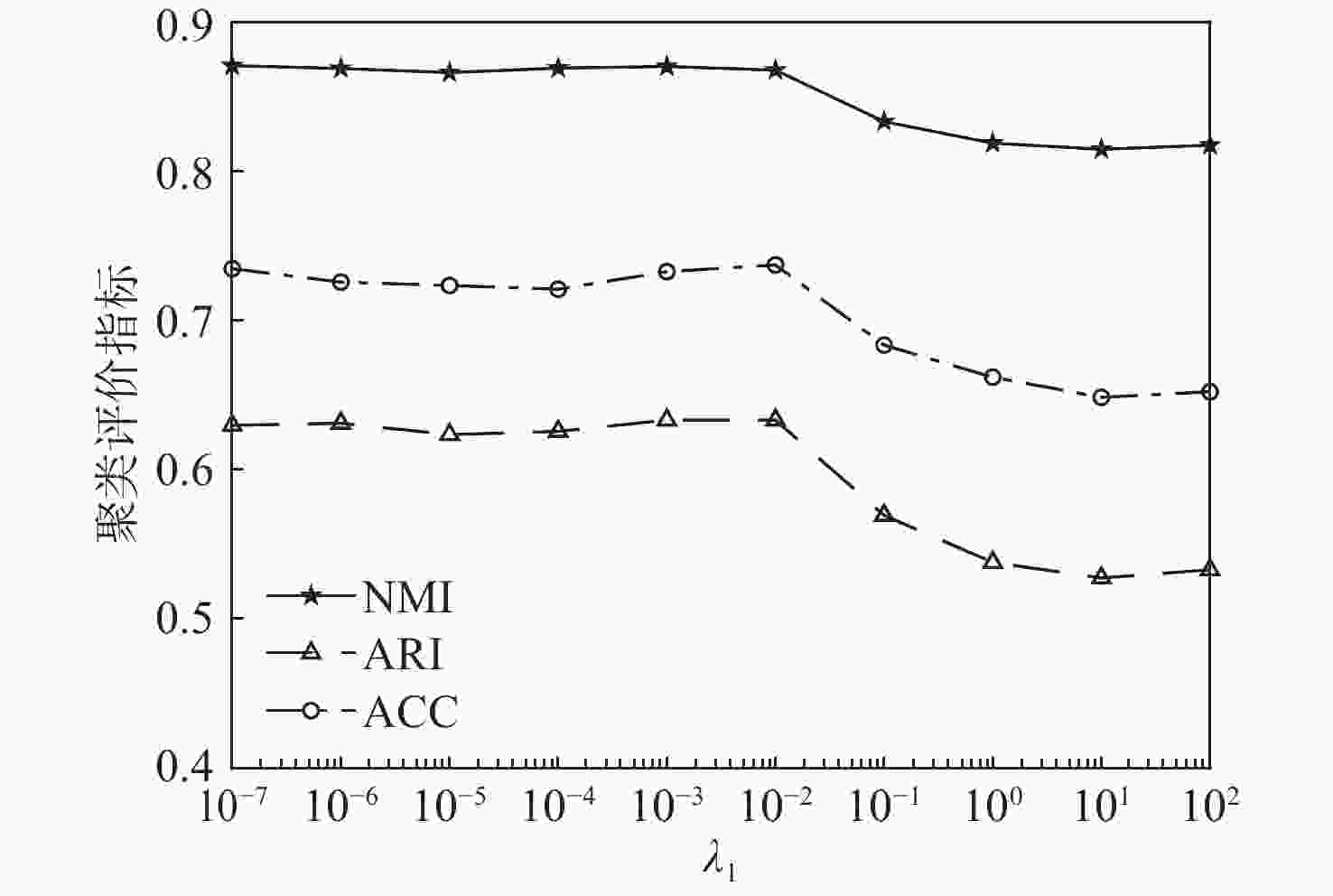
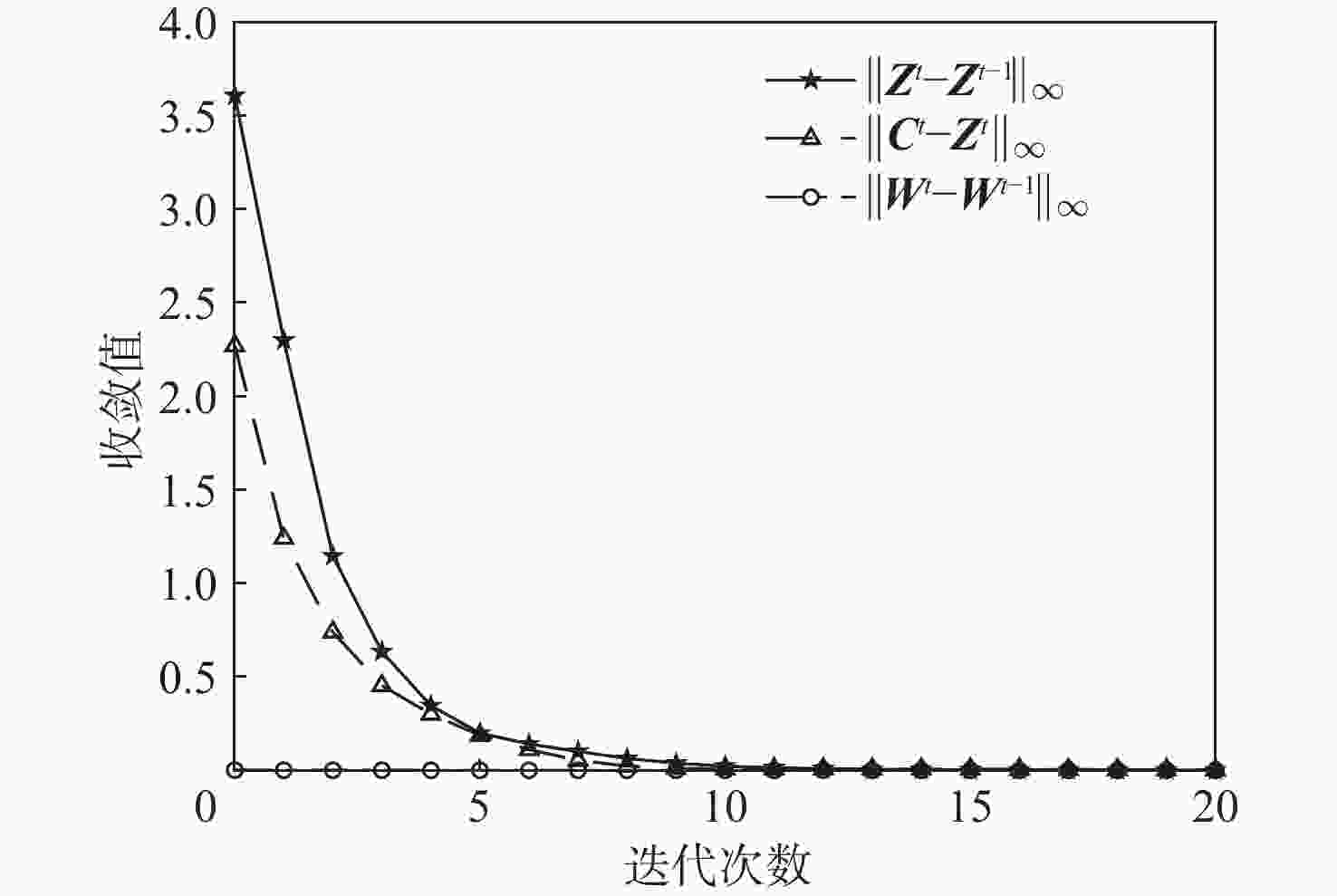
-
摘要:
子空间聚类可将高维数据划分到不同的低维子空间中,具有广泛的应用场景,但已有的大部分子空间聚类算法通常假定不同变量在聚类过程中的作用是相同的,这在实际应用中可能并不适用。基于此,提出一种自加权的缩放单形表示子空间聚类算法,根据不同变量的重要程度为每个变量学习相应的权重,并通过自表示方法对加权后的数据进行重构。利用缩放单形表示得到更加可靠的系数矩阵,同时引入关于权重的正则化项来调节变量权重稀疏度。将上述过程纳入统一的模型框架中,使用增广拉格朗日乘子法进行优化求解,进一步实施谱聚类算法完成聚类任务。在真实数据集上的实验结果表明:与已有聚类算法相比,所提算法具有较好的聚类性能。
Abstract:Subspace clustering can assign high-dimensional data to different low-dimensional subspaces, which has extensive applications. The majority of subspace clustering techniques usually make the assumption that each variable in high-dimensional data has an equal impact on the clustering process. However, this assumption is not suitable for practical applications. To address the above issue, this paper proposes a self-weighted scaled simplex representation subspace clustering method. The self-expressive method is used to reconstruct the weighted data after each variable has been given an appropriate weight based on differences in relevance. In addition, a sparsity regularization term is utilized to control the sparsity of weights. Simultaneously, the scaled simplex representation is introduced to obtain a more reliable coefficient matrix. The enhanced Lagrangian multipliers approach is used to optimize all of these phases and combine them into a single framework. Experimental results on real-world datasets demonstrate that the proposed algorithm has better clustering performance than existing clustering methods.
-
表 1 各算法在ORL数据集上的聚类性能比较
Table 1. Comparison of clustering performance of different algorithms on ORL dataset
算法 NMI ARI ACC K-means[26] 0.711±0.021 0.309±0.037 0.489±0.042 LSR[14] 0.838±0.014 0.580±0.036 0.701±0.029 SSR[17] 0.844±0.008 0.596±0.021 0.711±0.021 NSC[27] 0.847±0.005 0.601±0.012 0.715±0.022 FSC-LD[20] 0.839±0.011 0.583±0.028 0.690±0.030 FSC-NN[20] 0.852±0.011 0.610±0.022 0.718±0.020 SWCAN[21] 0.850 0.542 0.680 本文算法 0.871±0.008 0.634±0.014 0.737±0.013 表 2 各算法在Yale数据集上的聚类性能比较
Table 2. Comparison of Clustering performance of different algorithms on Yale dataset
算法 NMI ARI ACC K-means[26] 0.533±0.026 0.275±0.034 0.494±0.048 LSR[14] 0.552±0.010 0.290±0.012 0.528±0.011 SSR[17] 0.633±0.012 0.409±0.017 0.636±0.018 NSC[27] 0.635±0.014 0.413±0.012 0.649±0.011 FSC-LD[20] 0.561±0.023 0.323±0.030 0.539±0.025 FSC-NN[20] 0.576±0.023 0.350±0.030 0.575±0.031 SWCAN[21] 0.591 0.324 0.539 本文算法 0.647±0.005 0.432±0.006 0.659±0.004 表 3 各算法在COIL20数据集上的聚类性能比较
Table 3. Comparison of Clustering performance of different algorithms on COIL20 dataset
算法 NMI ARI ACC K-means[26] 0.710±0.022 0.467±0.050 0.508±0.037 LSR[14] 0.732±0.013 0.543±0.022 0.631±0.020 SSR[17] 0.954 0.868 0.885 NSC[27] 0.946 0.863 0.894 FSC-LD[20] 0.759±0.006 0.586±0.008 0.671±0.006 FSC-NN[20] 0.762±0.008 0.583±0.017 0.658±0.025 SWCAN[21] 0.954 0.824 0.849 本文算法 0.938 0.873 0.910 -
[1] LIAO M M, GU X D. Face recognition approach by subspace extended sparse representation and discriminative feature learning[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 373: 35-49. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2019.09.025 [2] ZHU W B, WANG C Y, TSENG K L, et al. Local-adaptive face recognition via graph-based meta-clustering and regularized adaptation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2022: 20269-20278. [3] 张熳, 徐兆瑞, 沈项军. 一种傅里叶域海量数据高速谱聚类方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2022, 48(8): 1445-1454.ZHANG M, XU Z R, SHEN X J. A high-speed spectral clustering method in Fourier domain for massive data[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2022, 48(8): 1445-1454(in Chinese). [4] 唐厂, 王俊. 基于近邻子空间划分的高光谱影像波段选择方法[J]. 天津大学学报(自然科学与工程技术版), 2022, 55(3): 255-262.TANG C, WANG J. A hyperspectral band selection method via adjacent subspace partition[J]. Journal of Tianjin University(Science and Technology), 2022, 55(3): 255-262(in Chinese). [5] QU W T, XIU X C, CHEN H Y, et al. A survey on high-dimensional subspace clustering[J]. Mathematics, 2023, 11(2): 436. doi: 10.3390/math11020436 [6] CAI Y M, ZHANG Z J, CAI Z H, et al. Graph convolutional subspace clustering: a robust subspace clustering framework for hyperspectral image[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 59(5): 4191-4202. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2020.3018135 [7] TSAKIRIS M C, VIDAL R. Algebraic clustering of affine subspaces[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(2): 482-489. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2678477 [8] RODRIGUES É O, TOROK L, LIATSIS P, et al. K-MS: a novel clustering algorithm based on morphological reconstruction[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2017, 66: 392-403. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.12.027 [9] ADLER A, ELAD M, HEL-OR Y. Probabilistic subspace clustering via sparse representations[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20(1): 63-66. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2012.2229705 [10] WANG L B, WANG Y L, DENG H, et al. Attention reweighted sparse subspace clustering[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2023, 139: 109438. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2023.109438 [11] 胡慧旗, 张维强, 徐晨. 判别性增强的稀疏子空间聚类[J]. 计算机工程, 2023, 49(2): 98-104.HU H Q, ZHANG W Q, XU C. Discriminant enhanced sparse subspace clustering[J]. Computer Engineering, 2023, 49(2): 98-104(in Chinese). [12] ELHAMIFAR E, VIDAL R. Sparse subspace clustering: algorithm, theory, and applications[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 35(11): 2765-2781. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2013.57 [13] LIU G C, LIN Z C, YAN S C, et al. Robust recovery of subspace structures by low-rank representation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2012, 35(1): 171-184. [14] LU C Y, MIN H, ZHAO Z Q, et al. Robust and efficient subspace segmentation via least squares regression[C]//Proceedings of the 12th European Conference on Computer Vision. Berlin: Springer, 2012: 347-360. [15] 罗申星, 于腾腾, 刘新为, 等. 一种稀疏流形低秩表示的子空间聚类方法[J]. 河北工业大学学报, 2023, 52(2): 16-27.LUO S X, YU T T, LIU X W, et al. A subspace clustering method based on sparse manifold and low-rank representation[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Technology, 2023, 52(2): 16-27(in Chinese). [16] 卢桂馥, 汤荣, 姚亮. 双重结构的最小二乘回归子空间聚类算法[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学), 2022, 58(6): 1050-1058.LU G F, TANG R, YAO L. Double structure least squares regression subspace clustering[J]. Journal of Nanjing University(Natural Science), 2022, 58(6): 1050-1058(in Chinese). [17] XU J, YU M Y, SHAO L, et al. Scaled simplex representation for subspace clustering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 2021, 51(3): 1493-1505. doi: 10.1109/TCYB.2019.2943691 [18] 简彩仁, 翁谦, 夏靖波. 系数增强最小二乘回归子空间聚类法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2022, 58(20): 73-78.JIAN C R, WENG Q, XIA J B. Coefficient enhanced least square regression subspace clustering method[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2022, 58(20): 73-78(in Chinese). [19] TANG C, ZHENG X, ZHANG W, et al. Unsupervised feature selection via multiple graph fusion and feature weight learning[J]. Science China Information Science, 2023, 66(5): 152101. doi: 10.1007/s11432-022-3579-1 [20] PENG C, KANG Z, YANG M, et al. Feature selection embedded subspace clustering[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(7): 1018-1022. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2573159 [21] NIE F P, WU D Y, WANG R, et al. Self-weighted clustering with adaptive neighbors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2020, 31(9): 3428-3441. doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2019.2944565 [22] KANG Z, PENG C, CHENG Q. Twin learning for similarity and clustering: a unified kernel approach[J]. Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2017, 31(1): 1705.00678. [23] DUCHI J, SHALEV-SHWARTZ S, SINGER Y, et al. Efficient projections onto the l1-ball for learning in high dimensions[C]//Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Machine Learning- ICML '08. New York: ACM, 2008: 272-279. [24] GHOSH J, ACHARYA A. Cluster ensembles[J]. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery, 2011, 1(4): 305-315. doi: 10.1002/widm.32 [25] HUBERT L, ARABIE P. Comparing partitions[J]. Journal of Classification, 1985, 2: 193-218. doi: 10.1007/BF01908075 [26] HARTIGAN J A, WONG M A. Algorithm AS 136: a K-means clustering algorithm[J]. Applied Statistics, 1979, 28(1): 100-108. doi: 10.2307/2346830 [27] JIA H J, ZHU D X, HUANG L X, et al. Global and local structure preserving nonnegative subspace clustering[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2023, 138: 109388. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2023.109388 [28] ZHOU E J, FAN H Q, CAO Z M, et al. Extensive facial landmark localization with coarse-to-fine convolutional network cascade[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 386-391. [29] BURGOS-ARTIZZU X P, PERONA P, DOLLÁR P. Robust face landmark estimation under occlusion[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2013: 1513-1520. -







 下载:
下载: