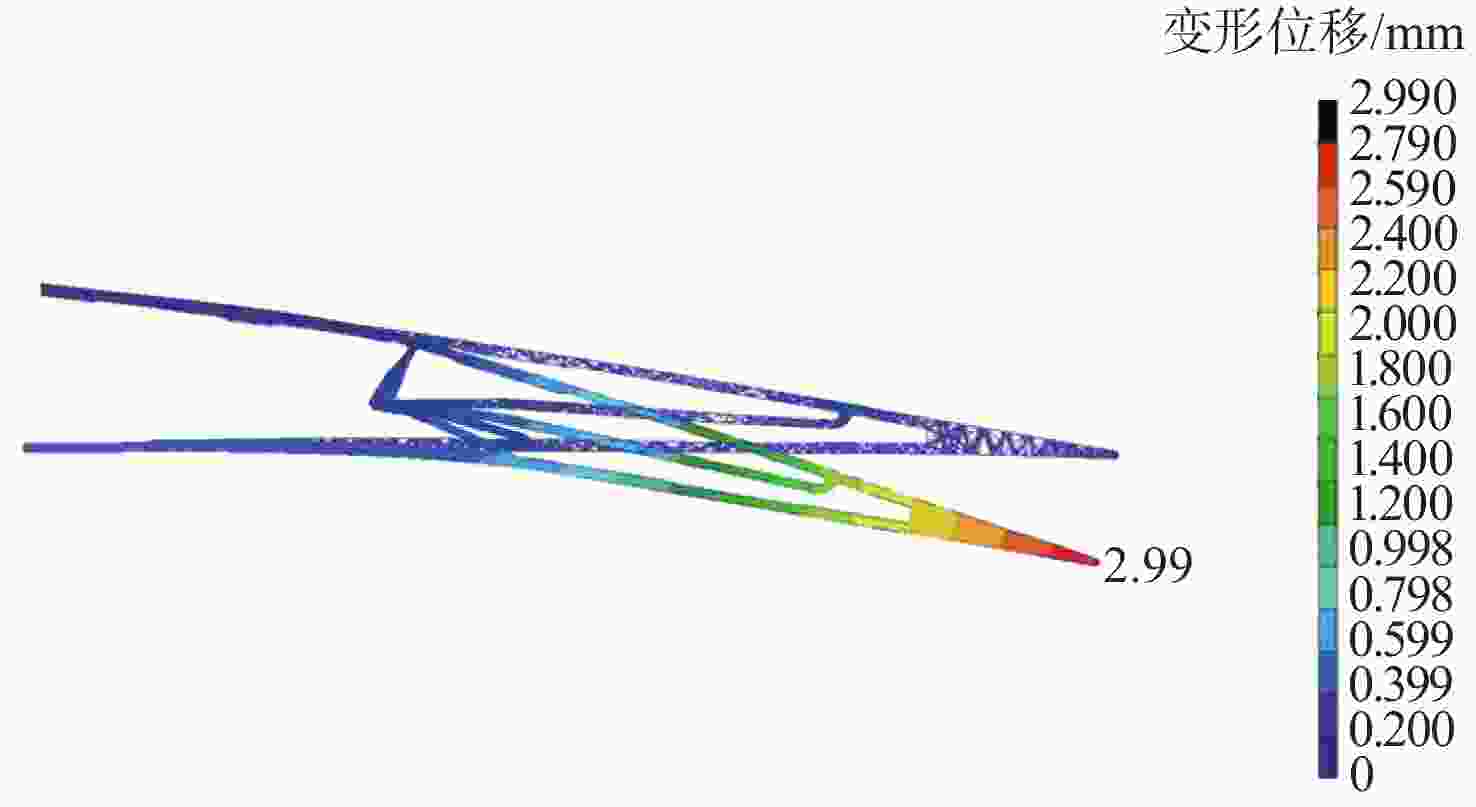
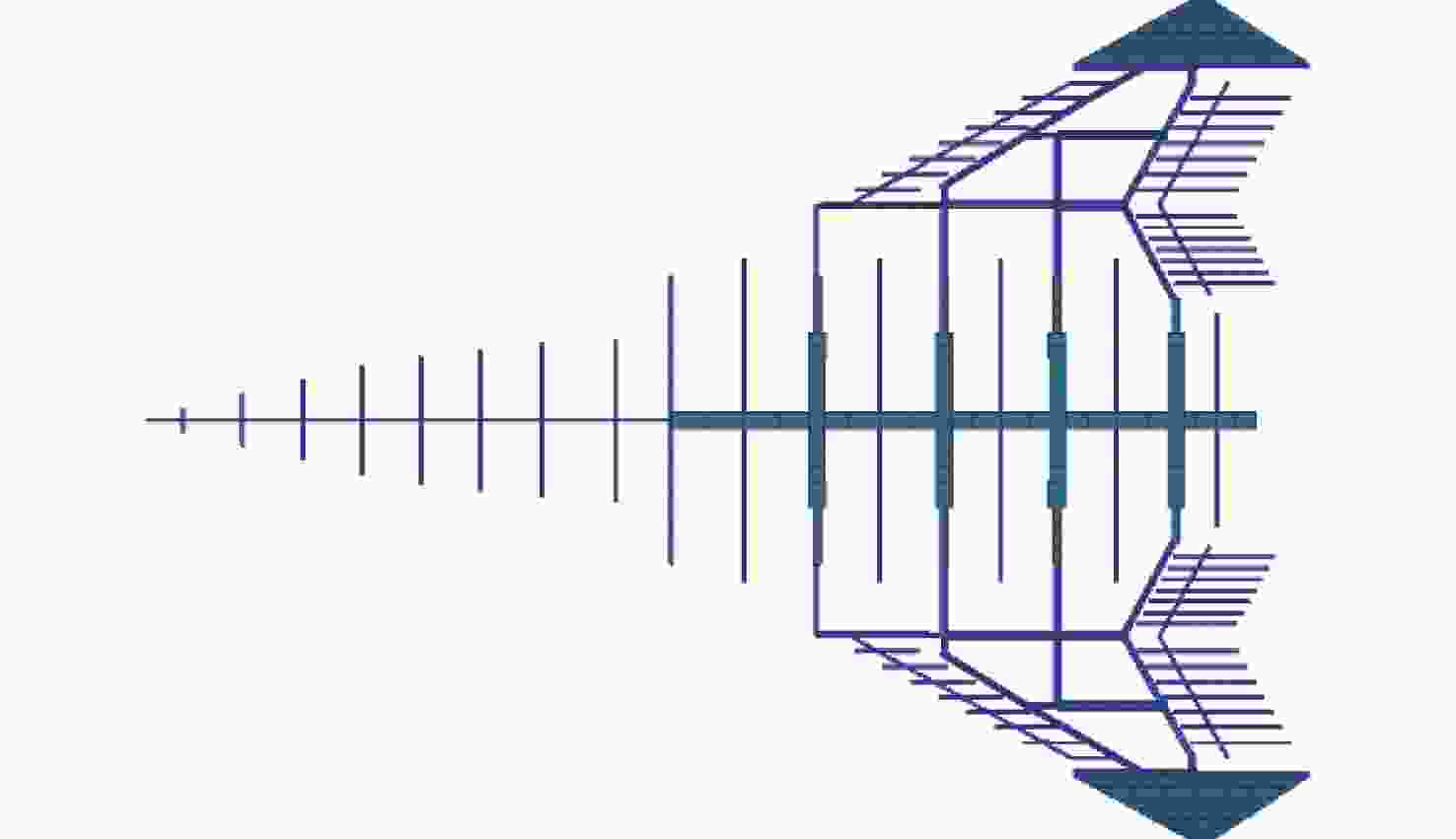
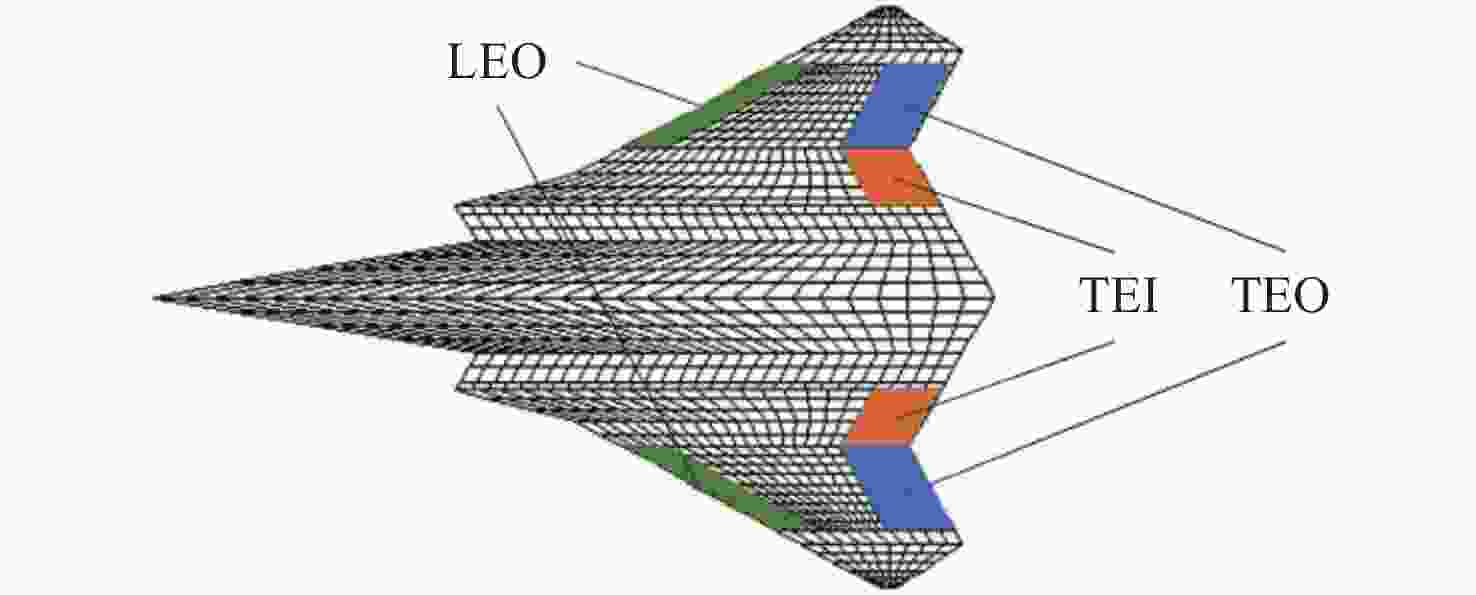
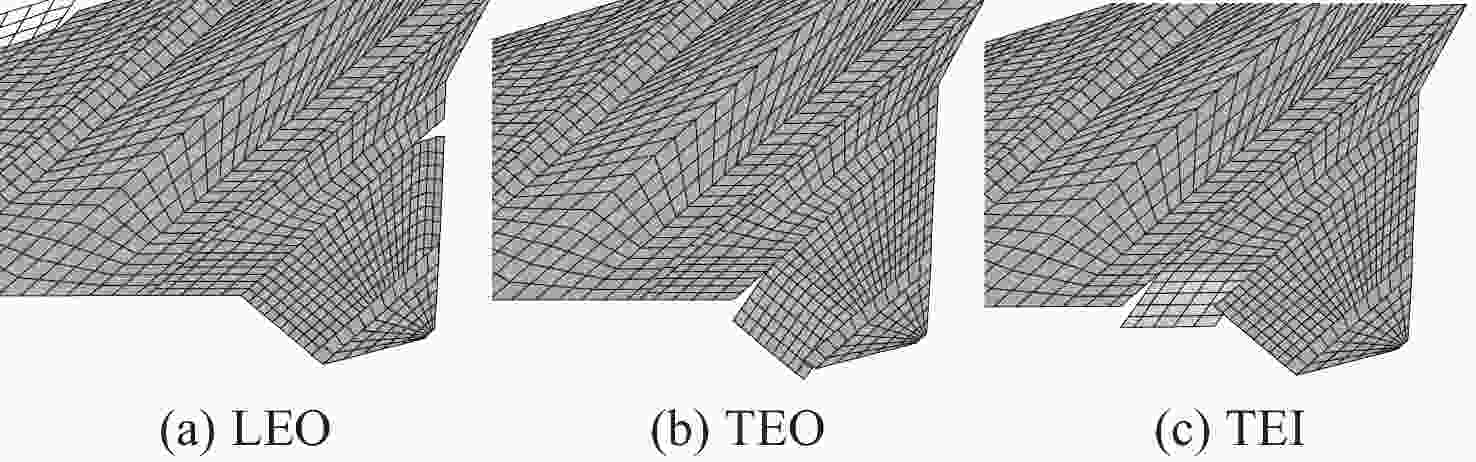
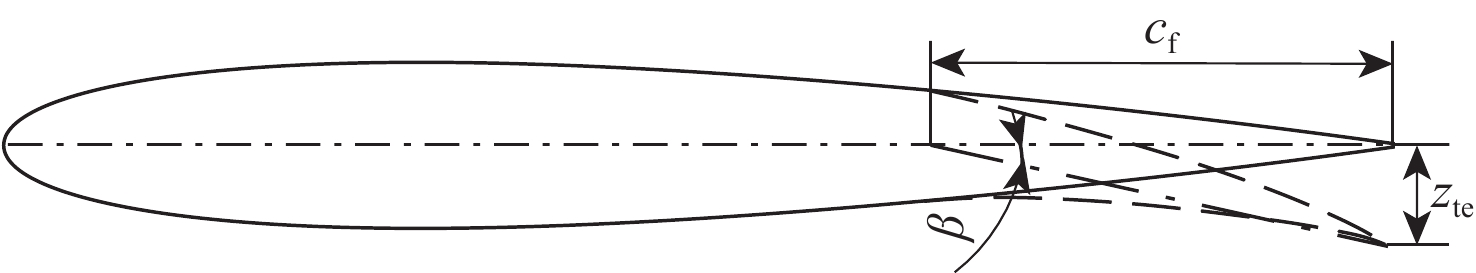
-
摘要:
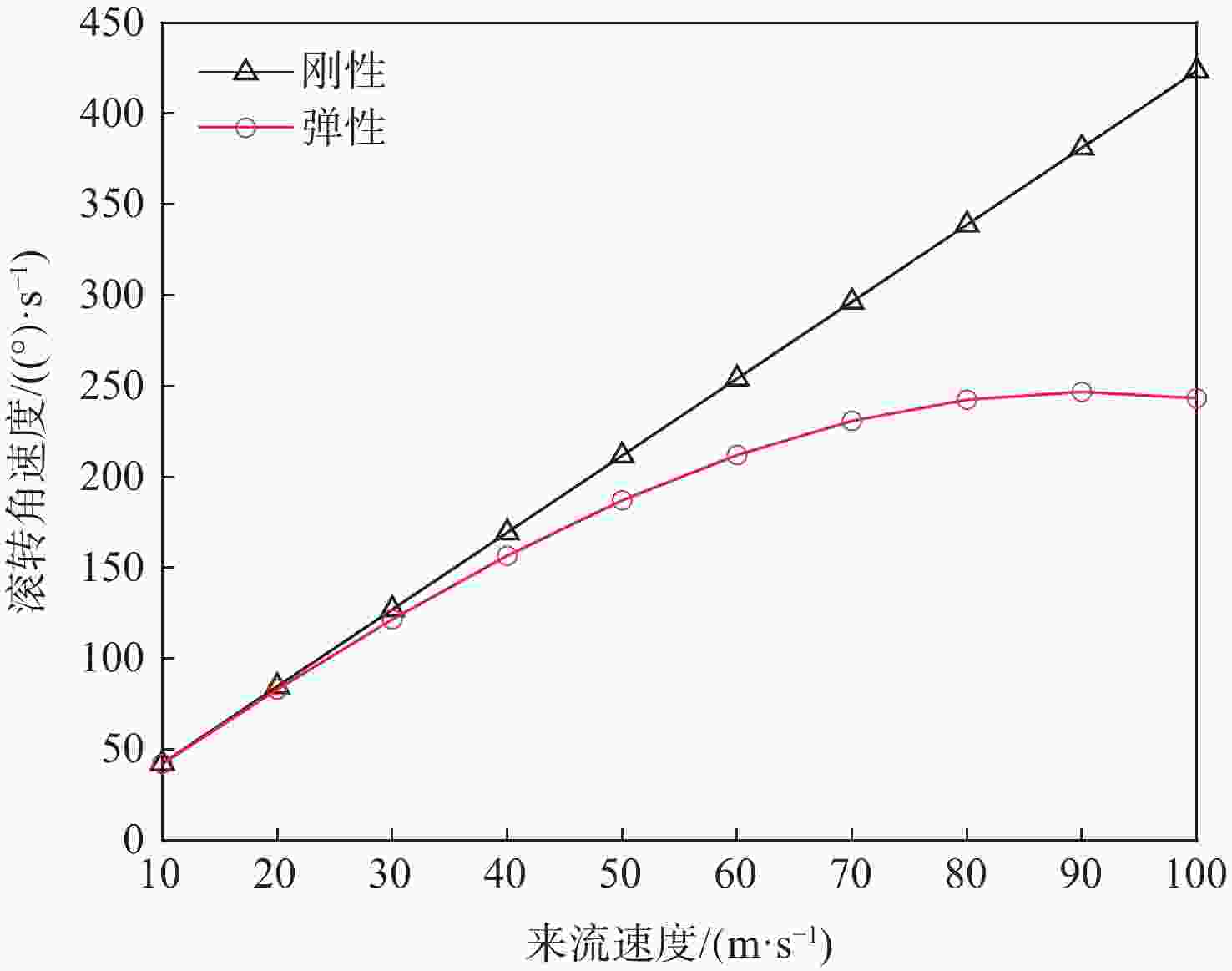
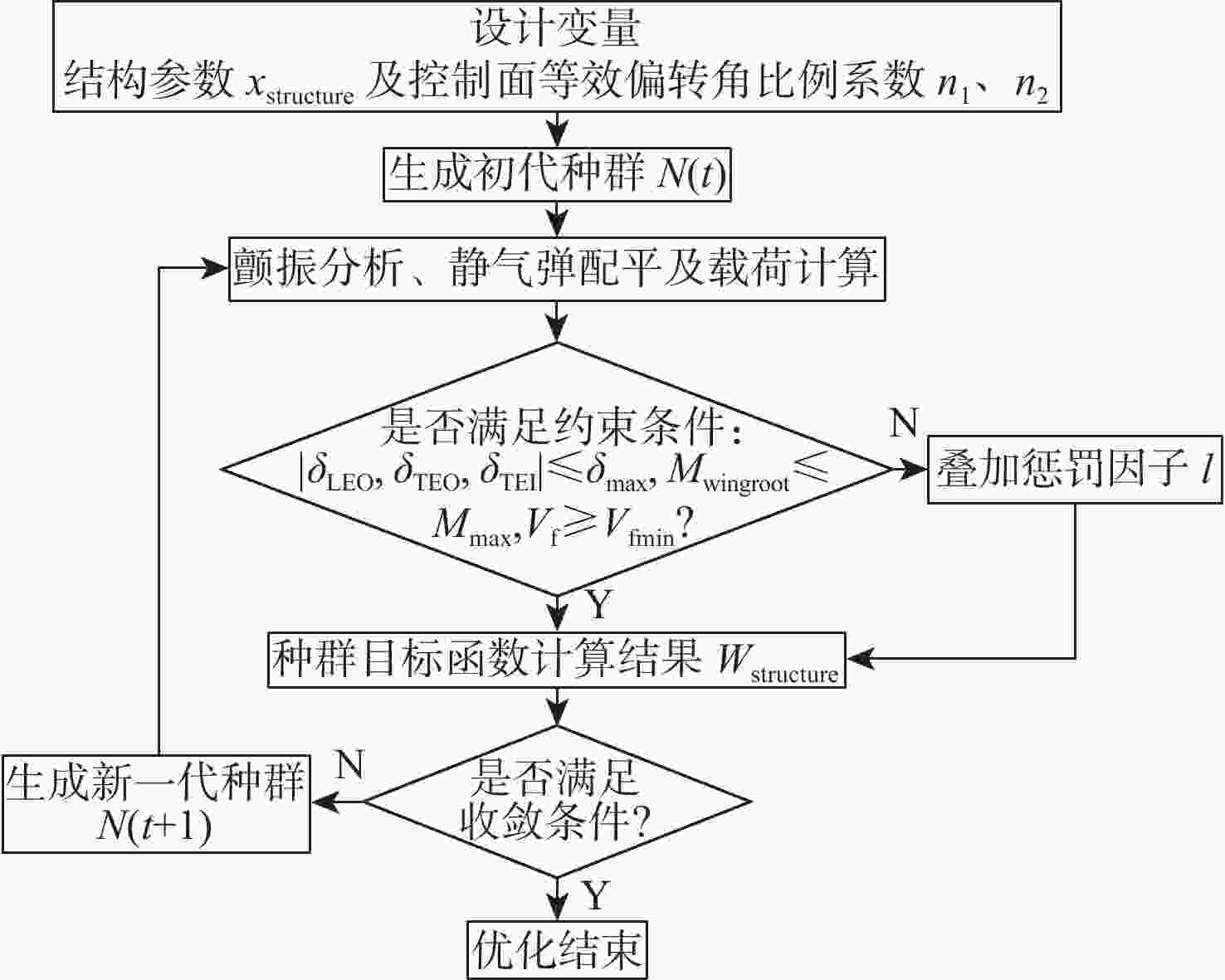
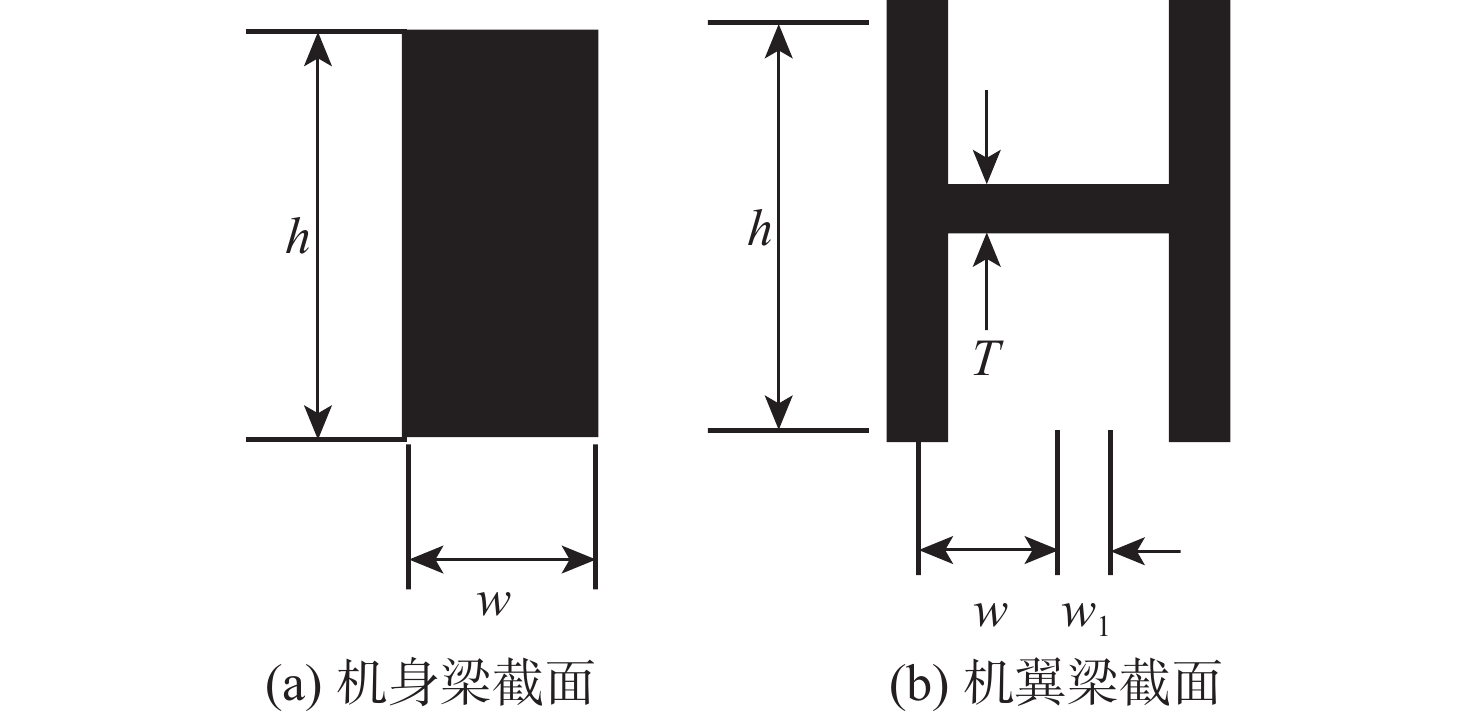
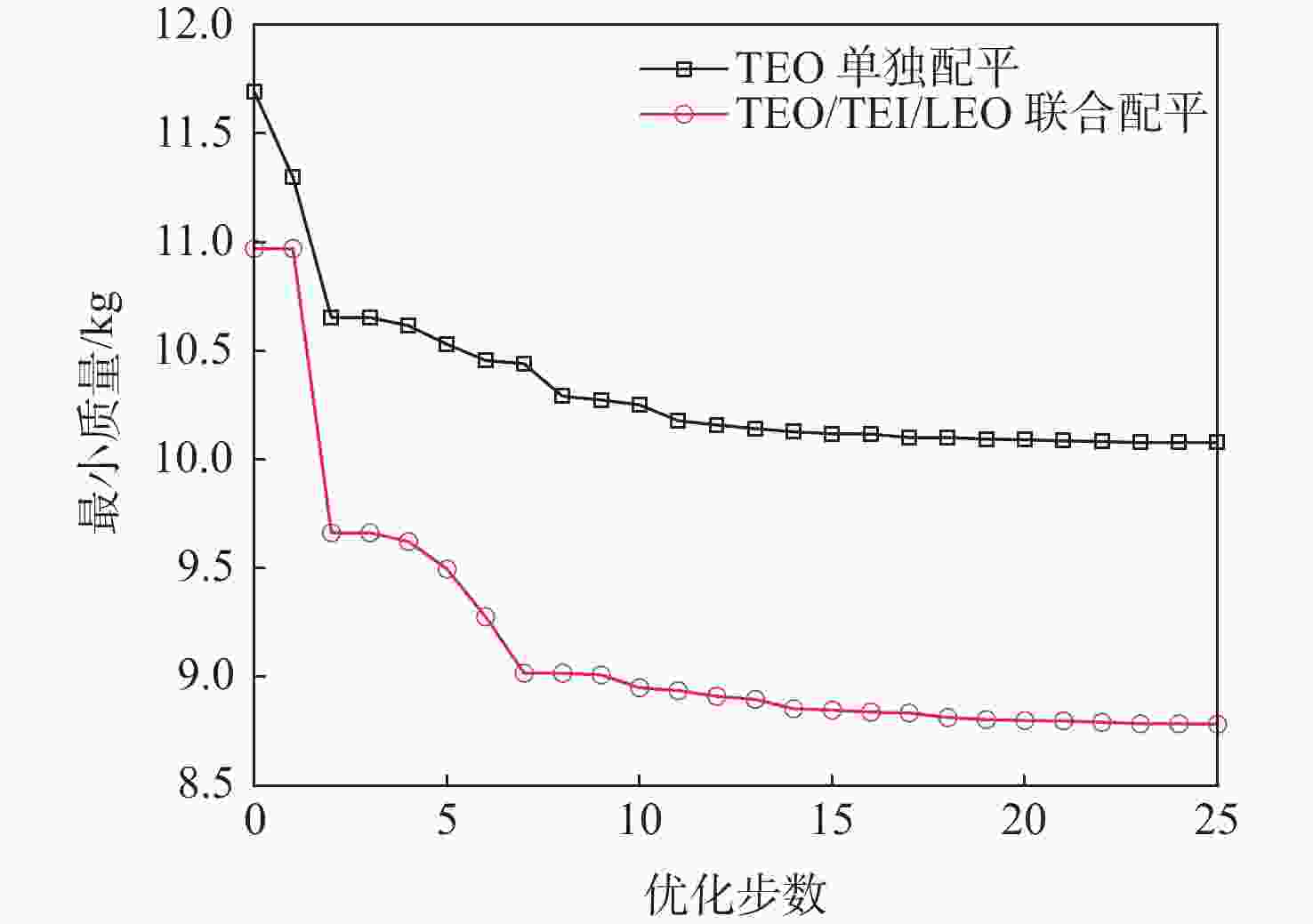
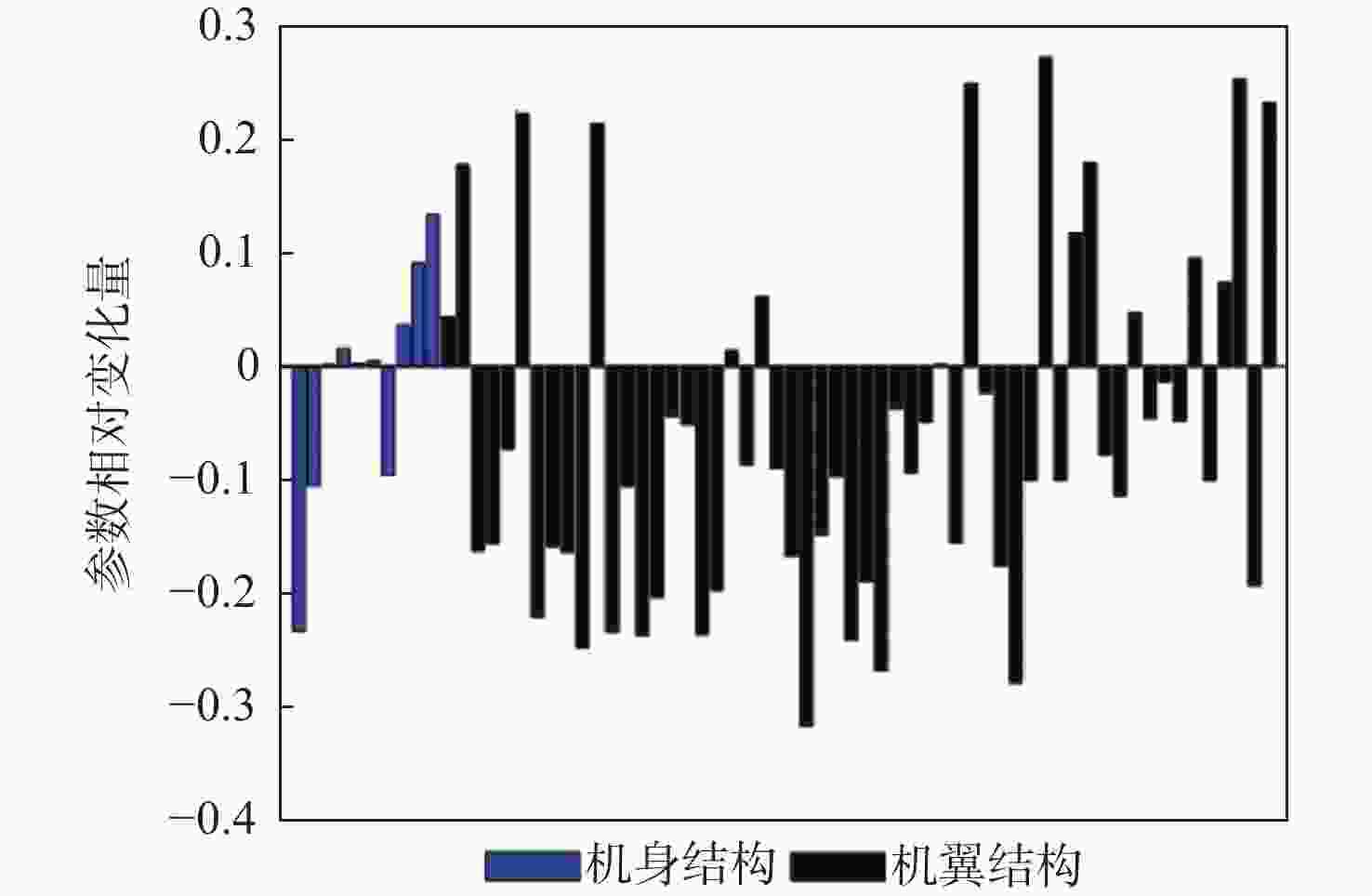
针对连续变弯度机翼,采用主动气动弹性机翼(AAW)技术,发展基于遗传算法的机翼结构综合优化设计方法。以结构质量最小化为目标,变弯度前/后缘等效偏转角、翼根弯矩和颤振速度为约束条件,在稳态滚转机动状态下对基于多个连续变弯度结构配平的小展弦比飞机缩比模型进行优化设计,并与传统单变弯度结构配平的设计方法进行对比。结果表明:变弯度前/后缘较传统舵面可提高34.71%的操纵效率,且采用多段变弯度前/后缘联合变形的AAW技术可充分利用机翼结构的柔性,从而有效降低机翼机动载荷,结构质量可减轻12.9%。
Abstract:An integrated optimization design methodology is developed for variable camber wing using active aeroelastic wing (AAW) technology, based on a genetic optimization algorithm. The optimization design for low aspect ratio aircraft’s scale model’s trim using multiple variable camber wings is conducted in a steady rolling maneuver. The goal is to reduce the structural mass while taking into account the limitations of the wing root’s moment, flutter speed, and the equivalent deflection angle of the morphing leading and trailing edges. A comparison between the new method and the conventional design method with single variable camber is also presented. The results showed that morphing the leading and trailing edges could increase control efficiency by 34.71% when compared to the traditional control surface. By coordinating the morphing of multiple leading and trailing edges, the AAW technology could fully utilize the flexibility of the wing structure to effectively reduce maneuver load and the wing’s structural mass by 12.9%.
-
Key words:
- wing /
- variable camber /
- active aeroelastic /
- optimization design /
- genetic algorithm /
- maneuver load
-
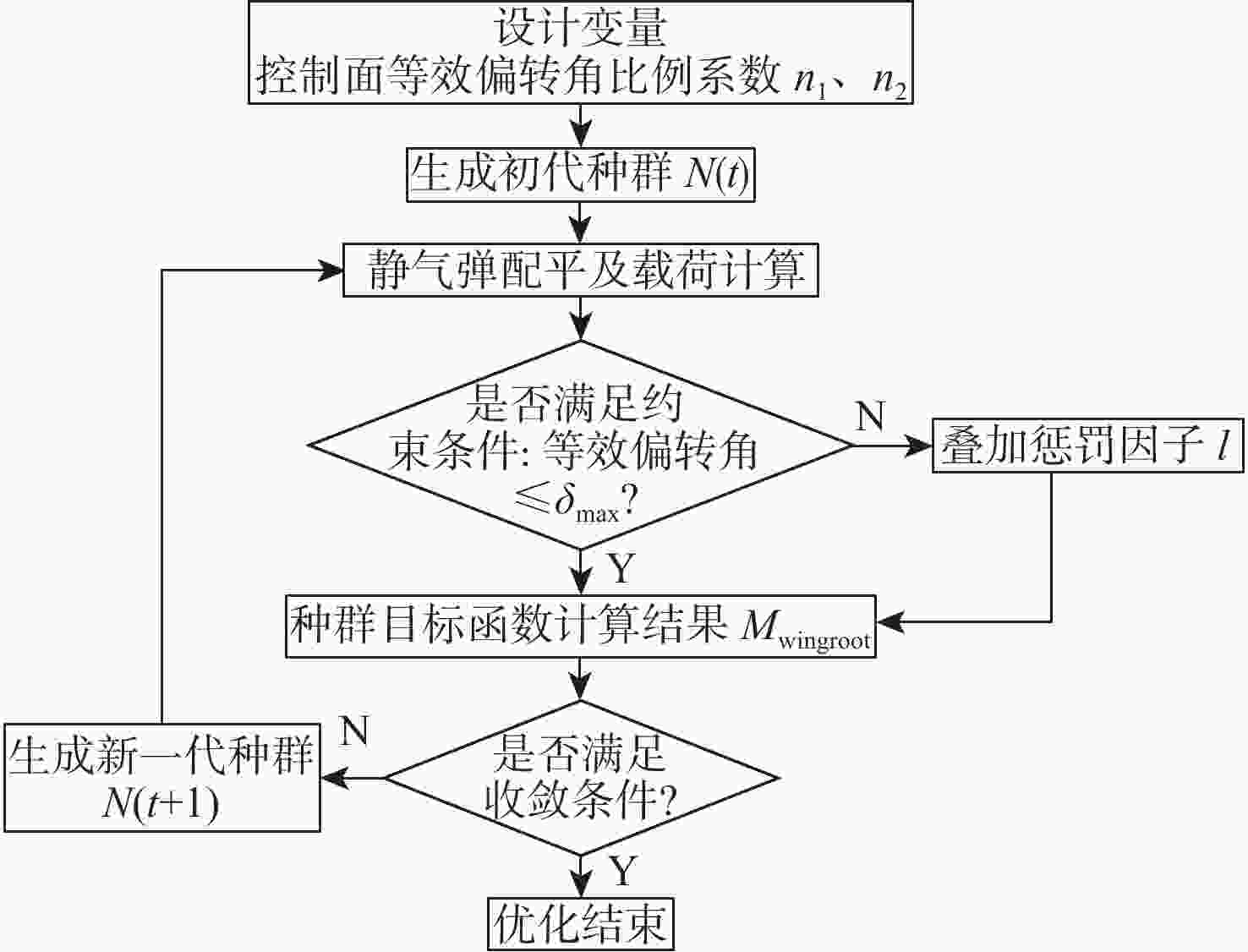
表 1 优化变量取值范围
Table 1. Optimization variables range
变量 最小值 最大值 n1 −10 10 n2 −10 10 δLEO/(°) −10 10 δTEO/(°) −10 10 δTEI/(°) −10 10 表 2 约束变量取值范围
Table 2. Constrained variables range
取值范围 Mwingroot/(N·m) n1 n2 δLEO/(°) δTEO/(°) δTEI/(°) Vf/(m·s−1) 最小值 −10 −10 −10 −10 −10 −10 255 最大值 10 10 10 10 10 10 10 表 3 优化结果
Table 3. Optimization outcome
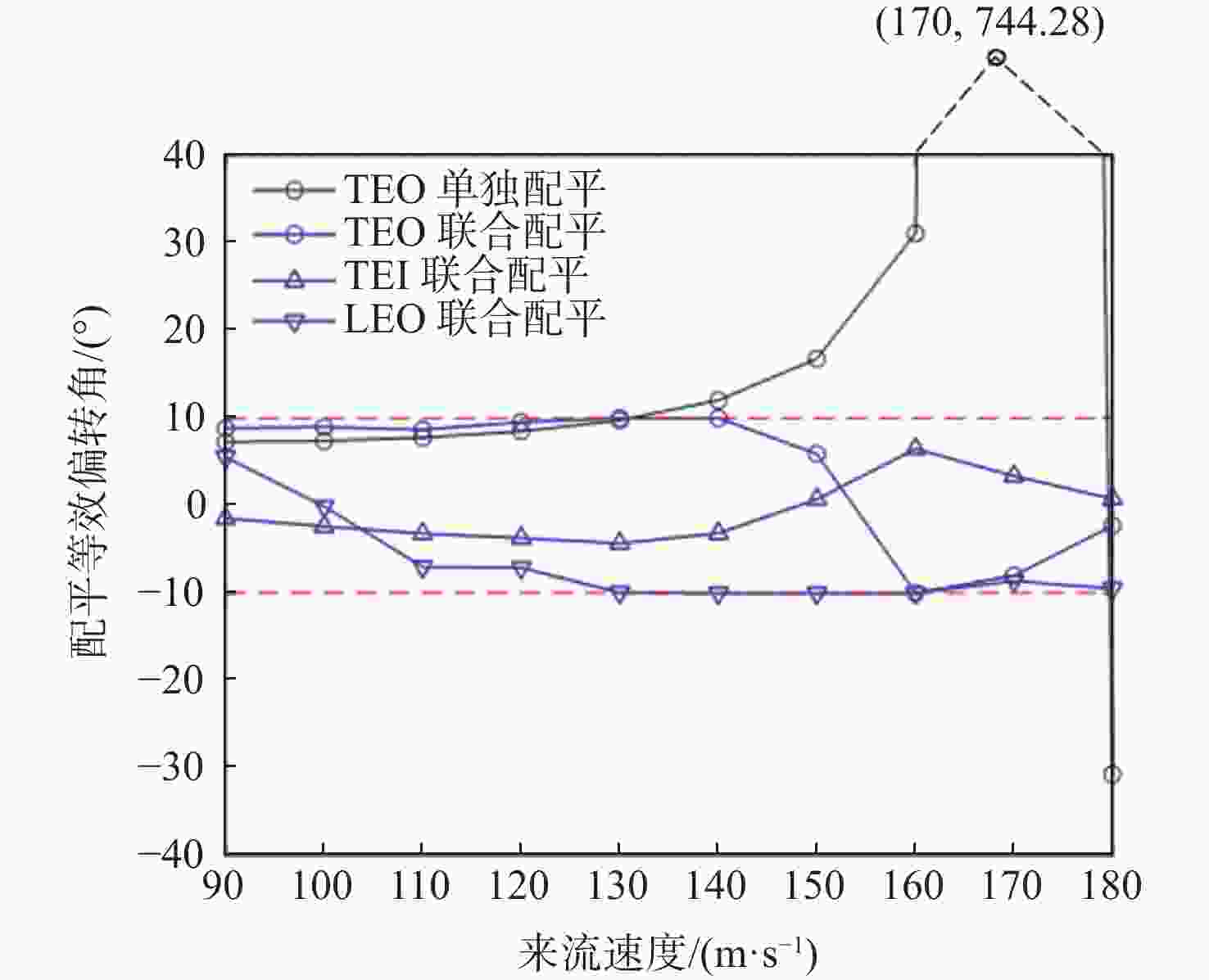
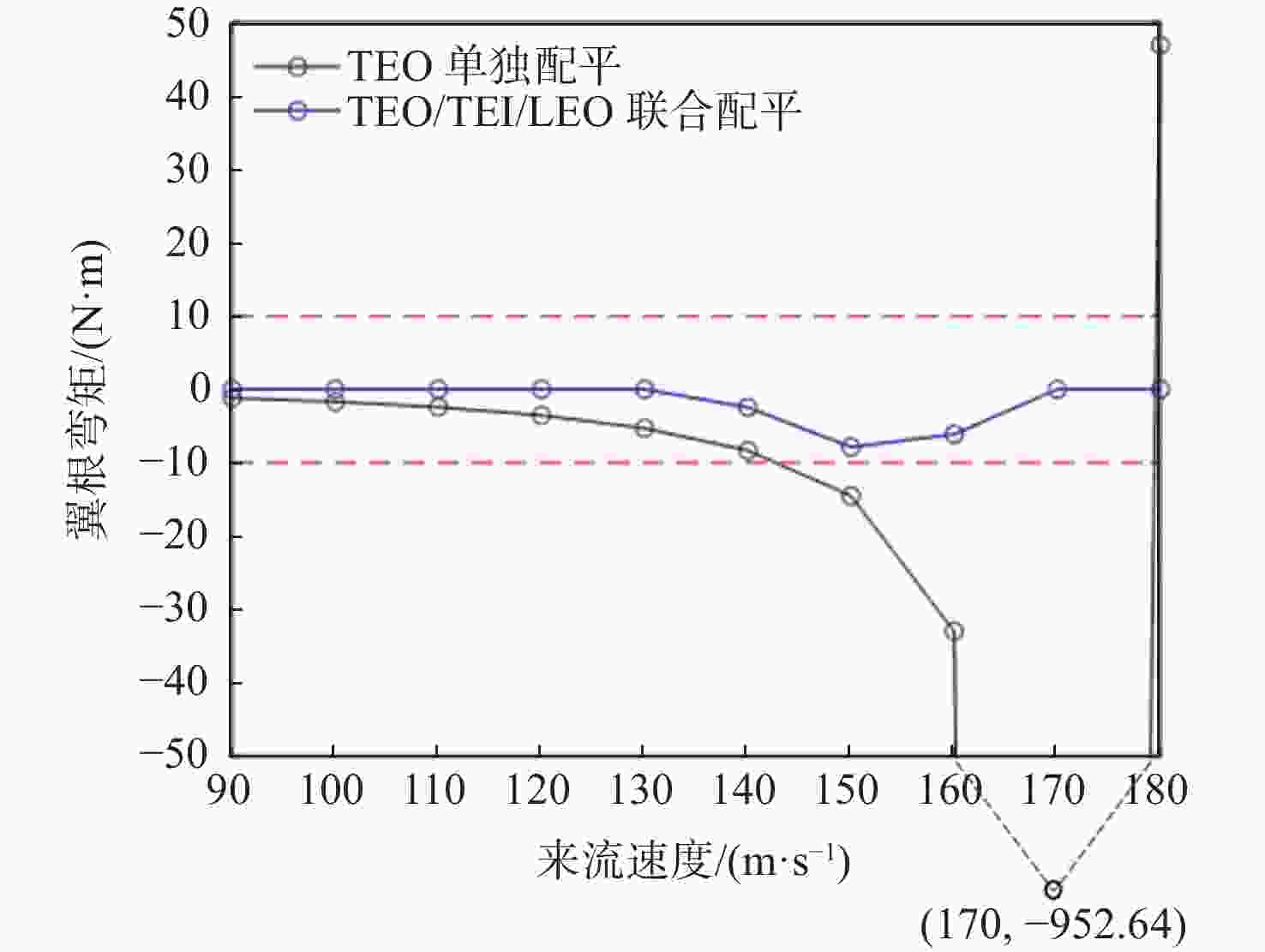
配平方案 δLEO/(°) δTEO/(°) δTEI/(°) Mwingroot/(N·m) TEO单独配平 0 −9.98 0 −9.3 TEO/TEI/LEO联合配平 −8.5 −0.9 3.2 −8.5 -
[1] 杨超, 陈桂彬, 邹丛青. 主动气动弹性机翼技术分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 1999, 25(2): 171-175.YANG C, CHEN G B, ZOU C Q. Analysis of active aeroelastic wing technology[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 1999, 25(2): 171-175(in Chinese). [2] DAS S, VENKATRAMAN K, PADMANABHAN M A. A study of the active aeroelastic wing concept for a delta wing aircraft[C]//Proceedings of the AIAA Scitech 2021 Forum. Reston: AIAA, 2021: 0730. [3] PENDLETON E, GRIFFIN K, KEHOE M, et al. A flight research program for active aeroelastic wing technology[C]//Proceedings of the 37th Structure, Structural Dynamics and Materials Conference. Reston: AIAA, 1996: 1574. [4] BOEHM B, FLICK P, SANDERS B, et al. Static aeroelastic response predictions of the active aeroelastic wing (AAW) flight research vehicle[C]//Proceedings of the 19th AIAA Applied Aerodynamics Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2001: 1372. [5] 杨超, 肖志鹏, 万志强. 主动气动弹性机翼多控制面配平综合优化设计[J]. 工程力学, 2011, 28(12): 244-249.YANG C, XIAO Z P, WAN Z Q. Integrated optimization design of multiple-control-surface trim for active aeroelastic wing[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2011, 28(12): 244-249(in Chinese). [6] LIU H J, GAO X M, WANG X. Parametric active aeroelastic control of a morphing wing using the receptance method[J]. Journal of Fluids and Structures, 2020, 98: 103098. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluidstructs.2020.103098 [7] ZHANG S, WANG Z J. Dynamic distributed morphing control of an aeroelastic wing for a small drone[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2019, 56(6): 2324-2341. doi: 10.2514/1.C035182 [8] CHANZY Q, KEANE A J. Analysis and experimental validation of morphing UAV wings[J]. The Aeronautical Journal, 2018, 122(1249): 390-408. doi: 10.1017/aer.2017.130 [9] WANG X R, MKHOYAN T, MKHOYAN I, et al. Seamless active morphing wing simultaneous gust and maneuver load alleviation[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2021, 44(9): 1649-1662. doi: 10.2514/1.G005870 [10] 杨永健, 宋晨, 张桢锴, 等. 变弯度后缘与常规舵面机翼的颤振主动抑制对比[J]. 航空工程进展, 2023, 14(3): 41-49.YANG Y J, SONG C, ZHANG Z K, et al. Comparison of morphing trailing edges and conventional control surfaces for active flutter suppression[J]. Advances in Aeronautical Science and Engineering, 2023, 14(3): 41-49(in Chinese). [11] 杨永健. 后缘连续变弯度机翼的阵风减缓研究[D]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学, 2023.YANG Y J. Gust alleviation research for the wing with continuous variable-camber trailing edge[D]. Beijing: Beihang University, 2023(in Chinese). [12] 张育鸣, 戴玉婷, 尉濡恺, 等. 变弯度柔性后缘机翼动响应减缓试验[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2024, 50(10): 3239-3249.ZHANG Y M, DAI Y T, WEI R K, et al. Experiment on dynamic response alleviation of a wing with variable-camber flexible trailing edge[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(10): 3239-3249(in Chinese). [13] RODDEN W P, JOHNSON E H. MSC. NASTRAN aeroelastic analysis user’s guide V68[M]. Los Angeles: The MacNeal-Schwendler Corporation, 1994: 35-65. [14] 雷朝辉, 杨超, 宋晨, 等. 连续变弯度后缘飞机的滚转机动载荷减缓[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2024, 50(10): 3172-3182.LEI C H, YANG C, SONG C, et al. Rolling maneuver load alleviation of aircraft with continuously variable-camber trailing edge[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2024, 50(10): 3172-3182(in Chinese). [15] FORSTER E, SANDERS B, EASTEP F. Modelling and sensitivity analysis of a variable geometry trailing edge control surface[C]//Proceedings of the 44th AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2003: 1807. [16] 张桢锴, 贾思嘉, 宋晨, 等. 柔性变弯度后缘机翼的风洞试验模型优化设计[J]. 航空学报, 2022, 43(3): 226071.ZHANG Z K, JIA S J, SONG C, et al. Optimum design of wind tunnel test model for compliant morphing trailing edge[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2022, 43(3): 226071(in Chinese). [17] 杨超, 吴志刚, 万志强, 等. 飞行器气动弹性原理[M]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 2011: 70-80.YANG C, WU Z G, WAN Z Q, et al. Aeroelasticity principle of aircraft[M]. Beijing: Beihang University Press, 2011: 70-80(in Chinese). [18] 万志强, 杨超. 飞行器飞行载荷分析与气动弹性优化[M]. 北京: 航空工业出版社, 2021: 193-200.WAN Z Q, YANG C. Flight load analysis and aeroelastic optimization of aircraft[M]. Beijing: Aviation Industry Press, 2021: 193-200(in Chinese). -






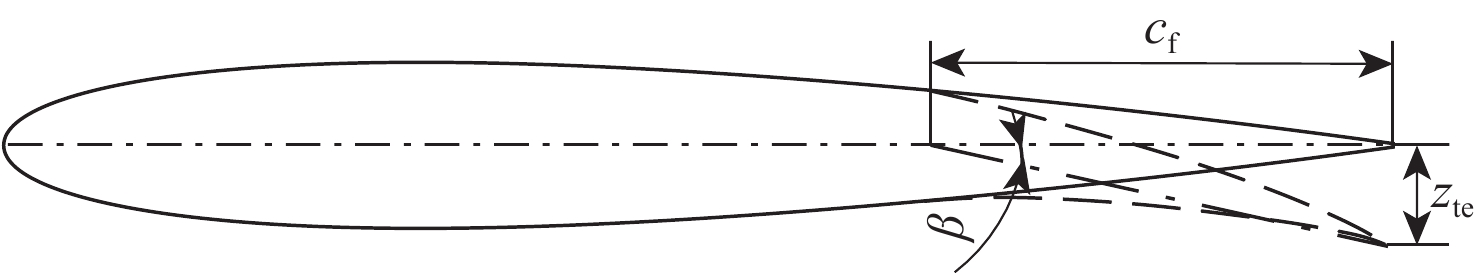
 下载:
下载: